Language, Thinking, and Reasoning in Psychology
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
Language
Communication using symbols and structured rules.
Phonemes
Basic sound units in spoken language.
Morphemes
Smallest meaning units in a language.
Syntax
Rules for constructing sentences in a language.
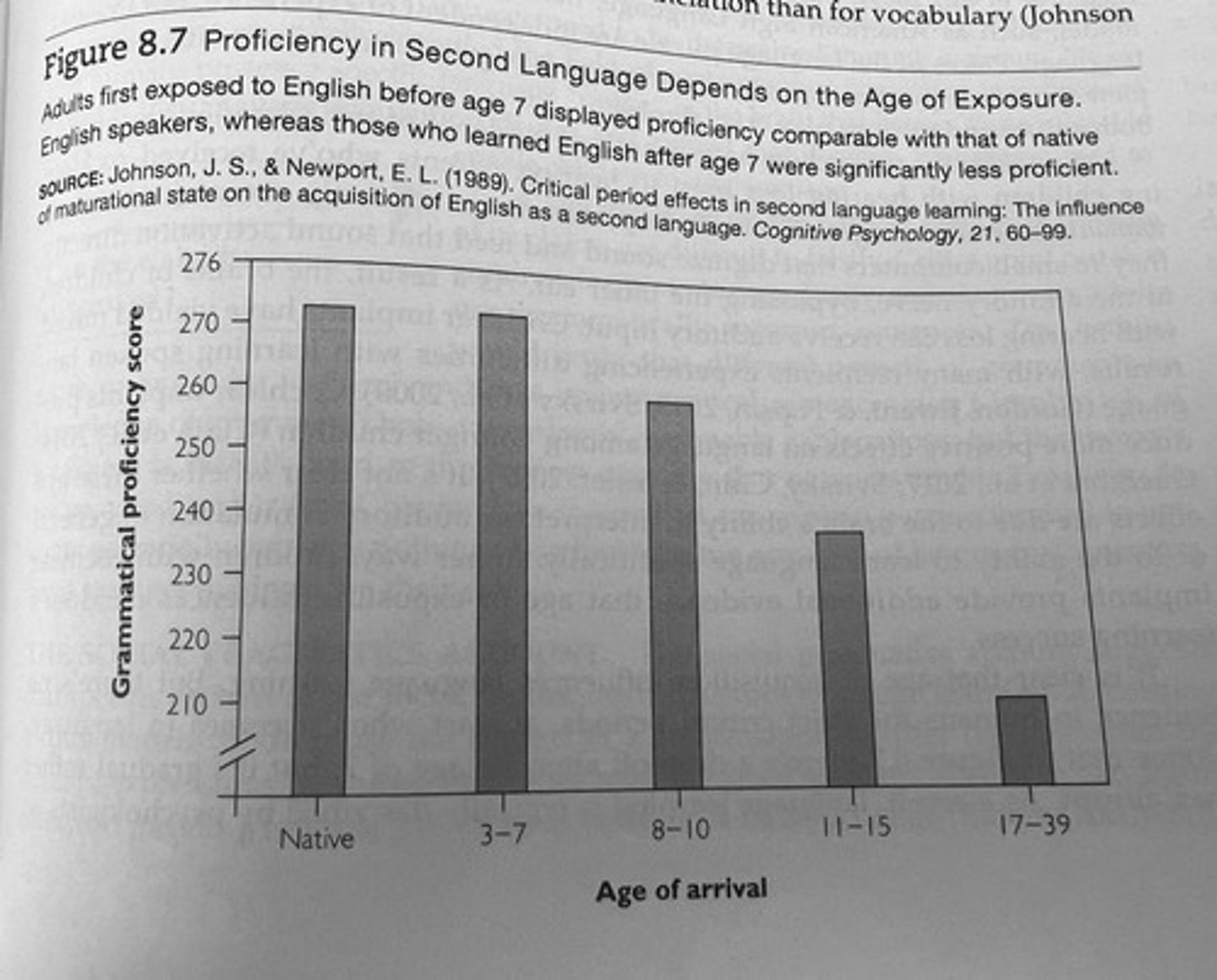
Critical period
Optimal time for language acquisition early in life.
Bilingualism
Learning two languages enhances cognitive abilities.
Babbling
Early vocalization stage from 3 months to 1 year.
Telegraphic speech
Two-word phrases expressing simple ideas.
Overgeneralization
Applying grammar rules incorrectly, e.g., 'runned'.
Nativist theory
Innate ability for language acquisition exists at birth.
Interactionist theory
Language develops through interaction and environmental exposure.
Language acquisition device
Innate mechanism for learning language, proposed by Chomsky.
Reinforcement
Positive feedback for correct language usage.
Language deprivation
Lack of exposure impairs language development.
Cross-linguistic differences
Variations in phoneme usage across languages.
Phoneme pruning
Loss of unused phoneme recognition over time.
Cultural language patterns
Language development influenced by cultural context.
Language development stages
Sequential milestones in children's language learning.
Genie Wylie
Case study highlighting critical period for language.
Nonverbal gestures
Communication through body language and expressions.
Language understanding
Cognitive processing of linguistic information.
Language and thought
Language shapes our understanding of the world.
Guugu Yimithirr
Indigenous language from Far North Queensland.

Cardinal directions
Directions based on north, east, south, west.
Linguistic relativity
Language influences thought and perception.
Sapir-Whorf Hypothesis
Language shapes our understanding of the world.
Egocentric perspective
Self-centered viewpoint in language and thought.
Geocentric perspective
World-centered viewpoint using cardinal directions.
Cognitive economy
Efficient use of cognitive resources in thinking.
Prototypes
Most typical example of a concept.
Top-down processes
Using existing knowledge to interpret new information.
Algorithm
Rule guaranteeing a solution for well-defined problems.
Heuristic
General problem-solving shortcut or rule of thumb.
Cognitive biases
Systematic errors in thinking and judgment.
Representativeness heuristic
Judgments based on similarity to stereotypes.
Base rate fallacy
Ignoring statistical base rates in judgments.
Availability heuristic
Estimating frequency based on ease of recall.
Cognitive misers
Tendency to minimize cognitive effort in thinking.
Mental sets
Fixed patterns of thinking that hinder problem-solving.
Functional fixedness
Inability to see alternative uses for an object.
Decision-making process
Steps taken to solve problems or make choices.
Time perception
How language influences our understanding of time.
Stereotyping
Oversimplified beliefs about a group of people.
Cognitive processing
Mental activities involved in understanding and reasoning.
Anchoring
Using an initial piece of information to influence decisions.
Heuristic
Mental shortcuts for quick decision-making.
Framing
Presentation of information affecting decision outcomes.
Accuracy-effort trade off
Balancing precision with the effort required.
Hindsight bias
Overestimating prediction ability after an event occurs.
Confirmation bias
Favoring information that supports existing beliefs.
Tunnel vision
Focusing narrowly on evidence supporting a viewpoint.
Functional fixedness
Inability to see alternate uses for an object.
Mental sets
Sticking to one problem-solving strategy.
Monday Morning Quarterback
Critiquing decisions after outcomes are known.
Englich & Mussweiler (2001)
Study on judges' sentencing influenced by anchors.
Guy Paul Morin
Wrongfully convicted due to heuristic biases.
Loss-framed messages
Communications emphasizing potential losses.
Gain-framed messages
Communications emphasizing potential gains.
COVID-19 & Framing
Framing effects on public anxiety and behavior.
Stereotypes
Oversimplified beliefs about groups influencing judgments.
Racialization of crime
Media portrayal linking race and criminality.
Circumstantial evidence
Indirect evidence used to infer conclusions.
Amanda Knox
Wrongfully convicted based on circumstantial evidence.
Emotional toll
Psychological impact of loss-framed communications.
Judicial bias
Judges' decisions influenced by external recommendations.
Crown prosecutor
Legal representative recommending sentences in court.
Memory
Process of encoding, storing, and retrieving information.
Mistaken Identity
Memory errors leading to incorrect recall of events.
Three-Stage Model
Memory consists of sensory, short-term, and long-term stages.
Sensory Memory
Brief storage of sensory information, lasts milliseconds.
Iconic Memory
Visual sensory memory lasting less than 1 second.
Echoic Memory
Auditory sensory memory lasting 2-3 seconds.
Short-Term Memory
Limited capacity memory lasting up to 30 seconds.
Magic Number 7
Short-term memory capacity is 7 ± 2 items.
Chunking
Organizing information into smaller, meaningful groups.
Rehearsal
Repeating information to transfer it to long-term memory.
Maintenance Rehearsal
Repetition of stimuli in the same form.
Elaborative Rehearsal
Linking information meaningfully for better retention.
Working Memory
Active manipulation of information for reasoning tasks.
Central Executive Processor
Component of working memory for decision-making.
Long-Term Memory
Continuous storage of information, potentially lifelong.
Anterograde Amnesia
Inability to form new memories after an event.
Retrograde Amnesia
Loss of memories formed before an event.
Primacy Effect
Better recall of first presented stimuli.
Recency Effect
Better recall of most recently presented stimuli.
Case Study: Henry Molaison
Patient with hippocampus removal, suffered memory loss.
Explicit vs. Implicit Memory
Explicit: conscious recall; Implicit: skills and habits.
Implicit Memory
Memory without conscious recollection of experiences.
Explicit Memory
Conscious recollection of facts and events.
Semantic Memory
General knowledge about the world.
Episodic Memory
Recollection of personal life events.
Non-declarative Memory
Memory not requiring conscious thought.
Procedural Memory
Memory for skills and actions.
Priming
Activation of existing information to aid recall.
Hippocampus
Brain region crucial for memory consolidation.
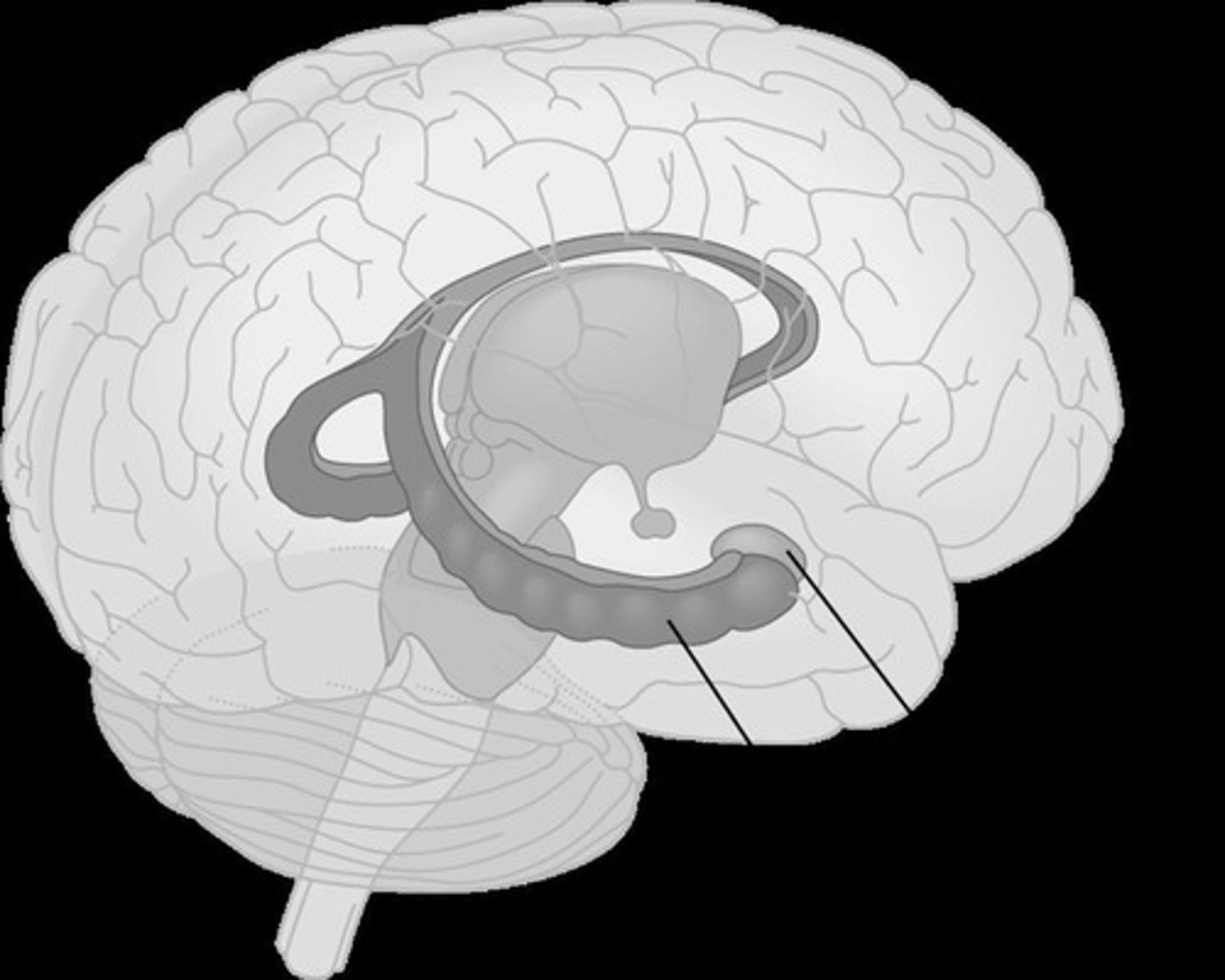
Amygdala
Brain area involved in emotional memory.
Long-term Potentiation
Strengthening of synapses based on recent patterns.
Encoding Failures
Inability to store information due to lack of attention.
Self-reference Effect
Better memory for information relating to oneself.
Stress Effects
Stress can impair memory accuracy and recall.