Unit 2 - Laryngeal stuff
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
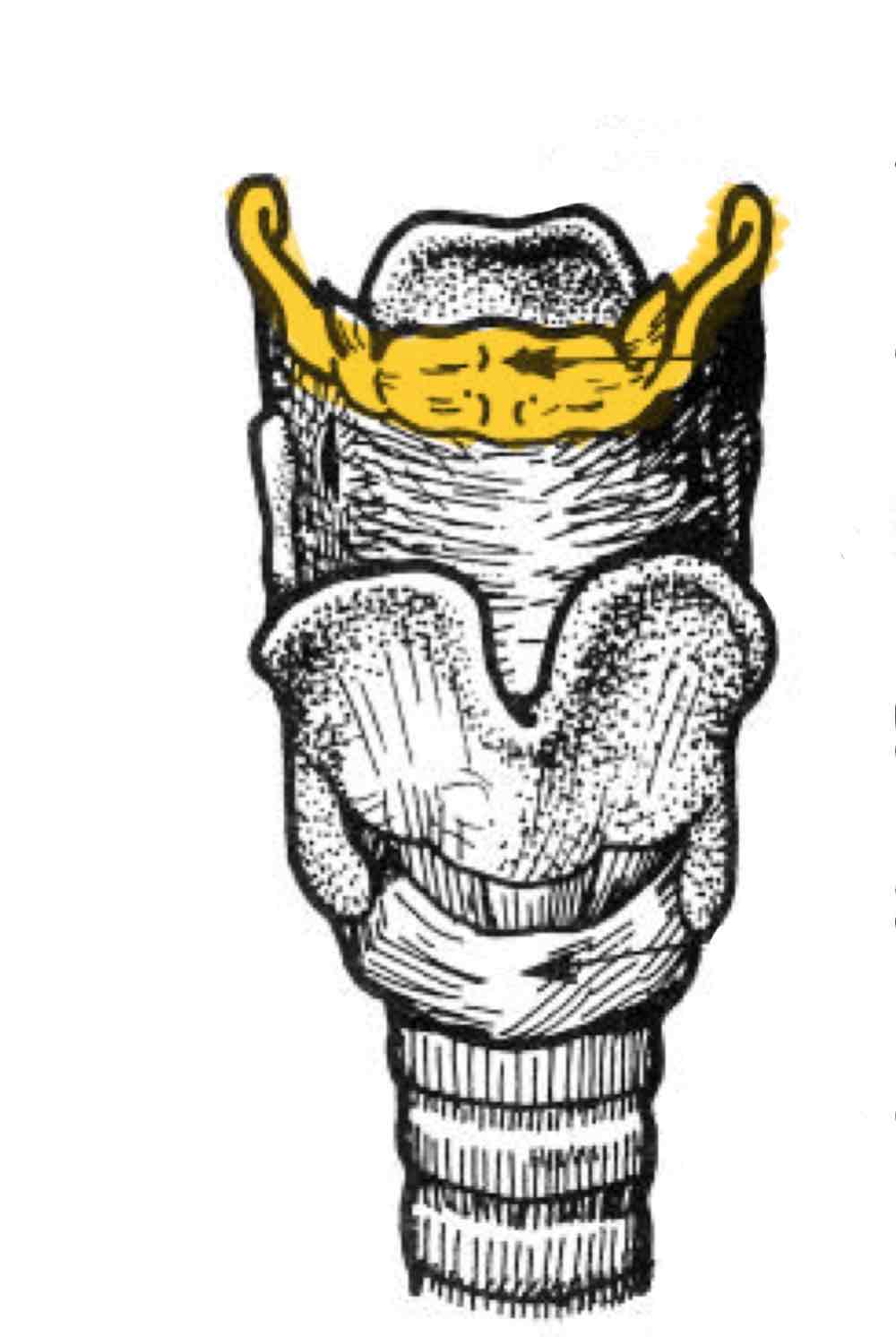
Hyoid bone
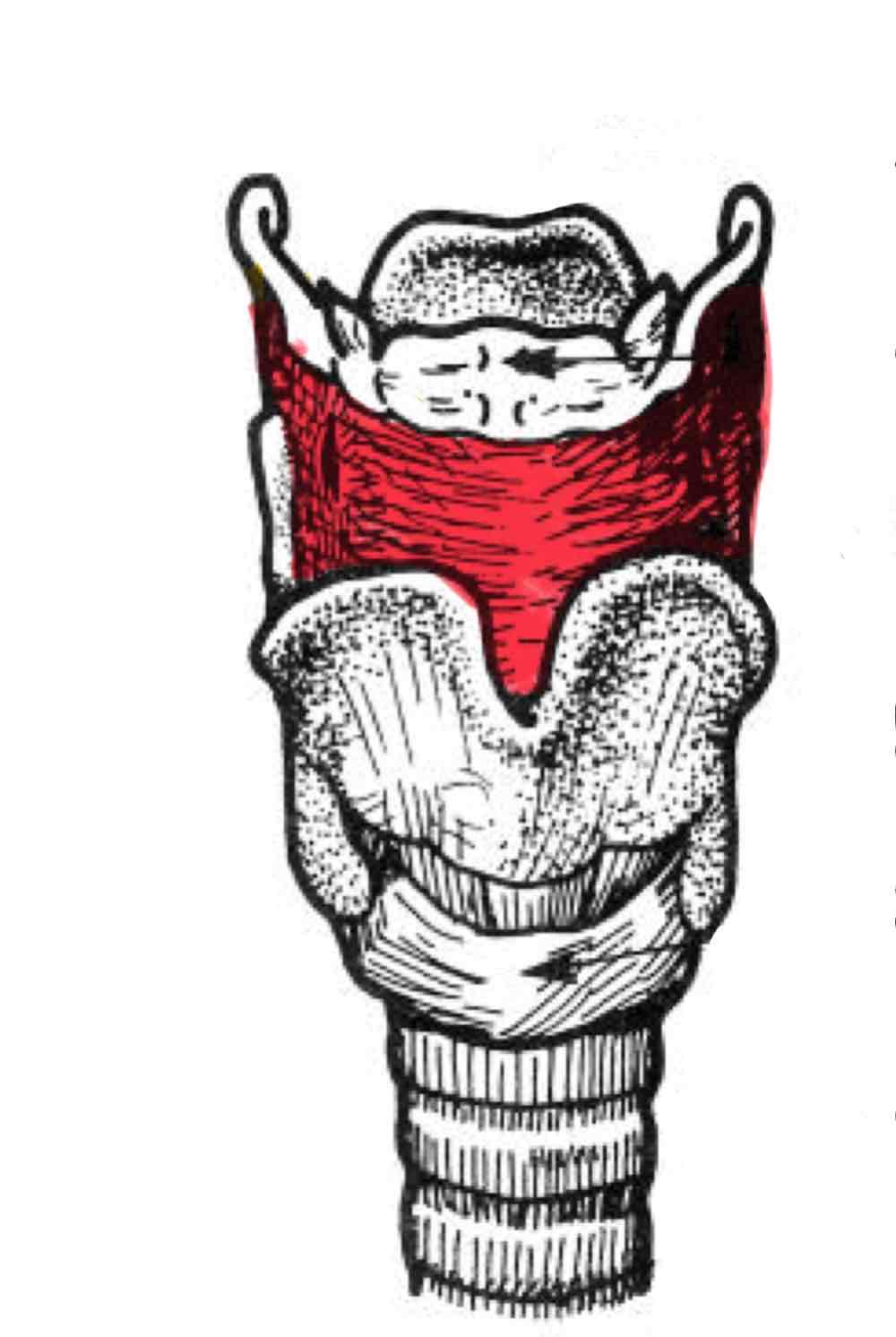
Thyro-hyoid lamina
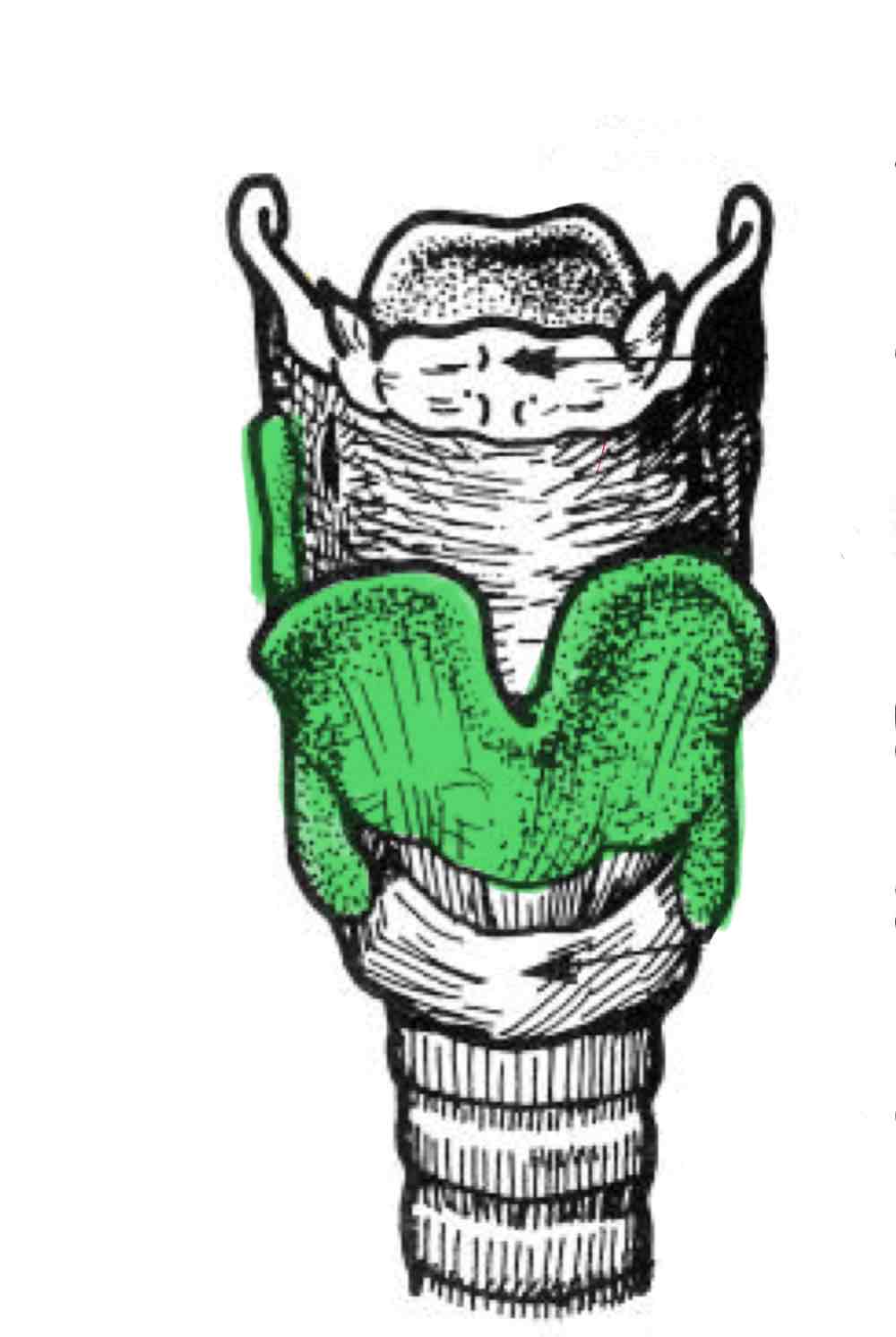
Thyroid cartilage
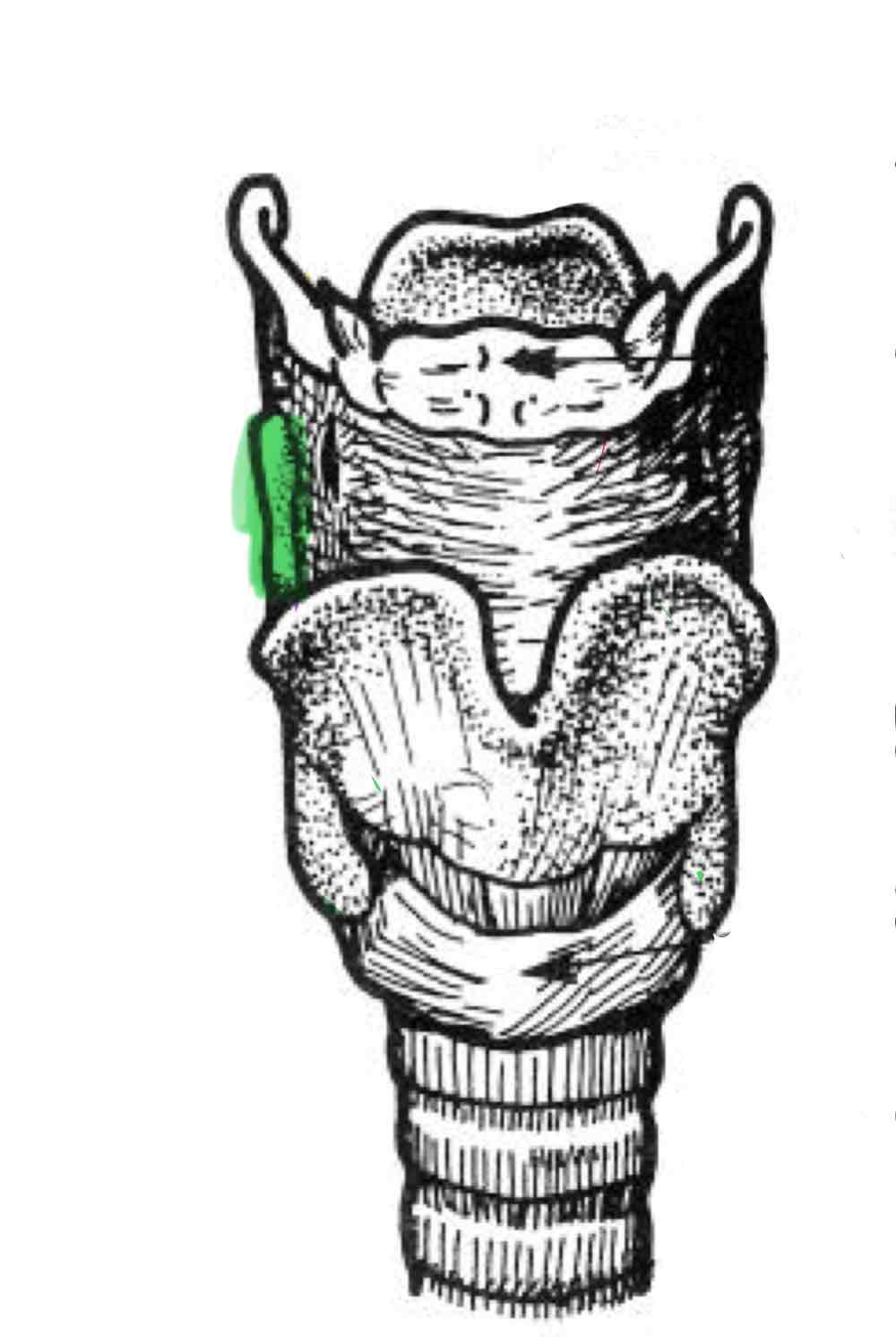
Superior Cornu
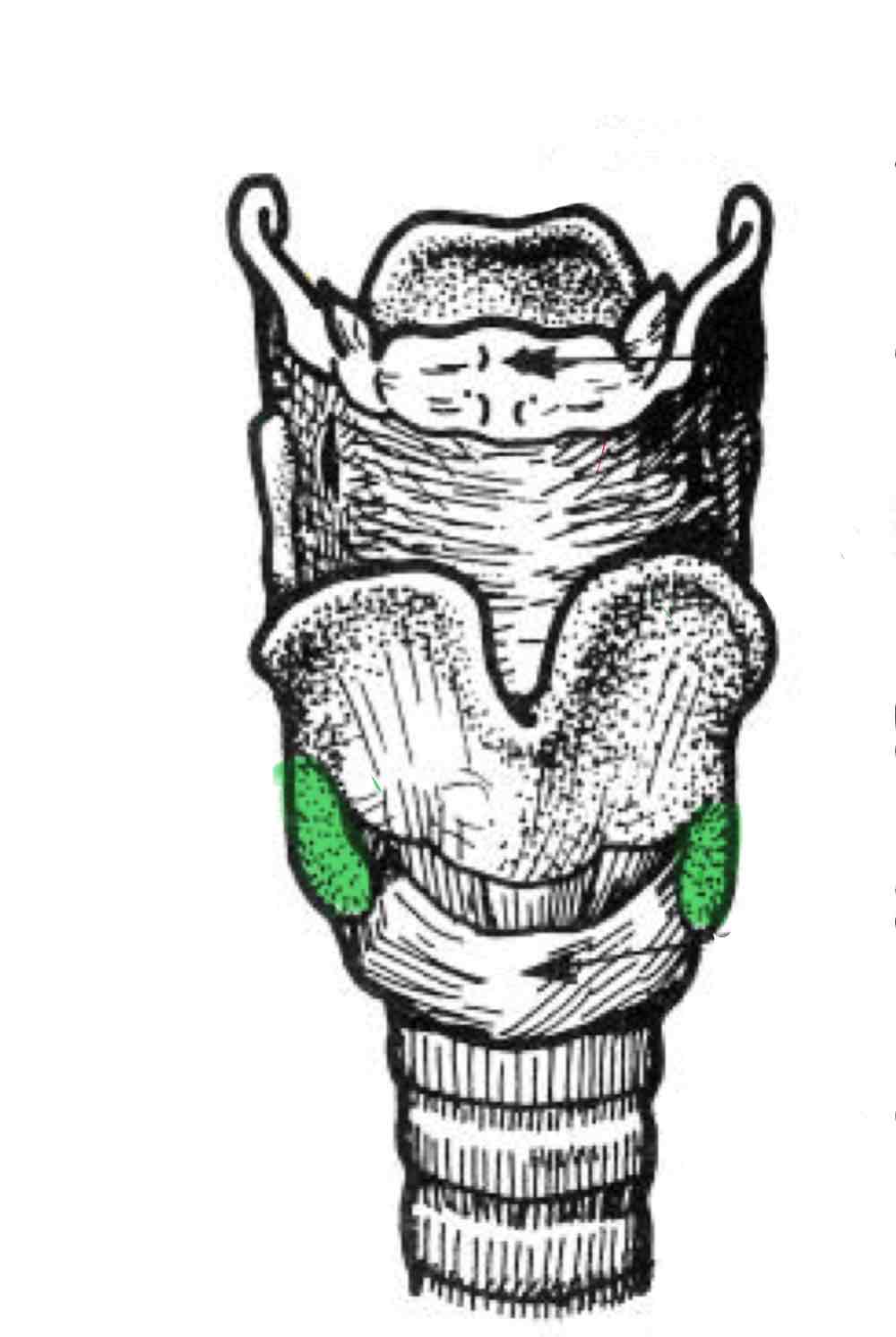
Inferior Cornu
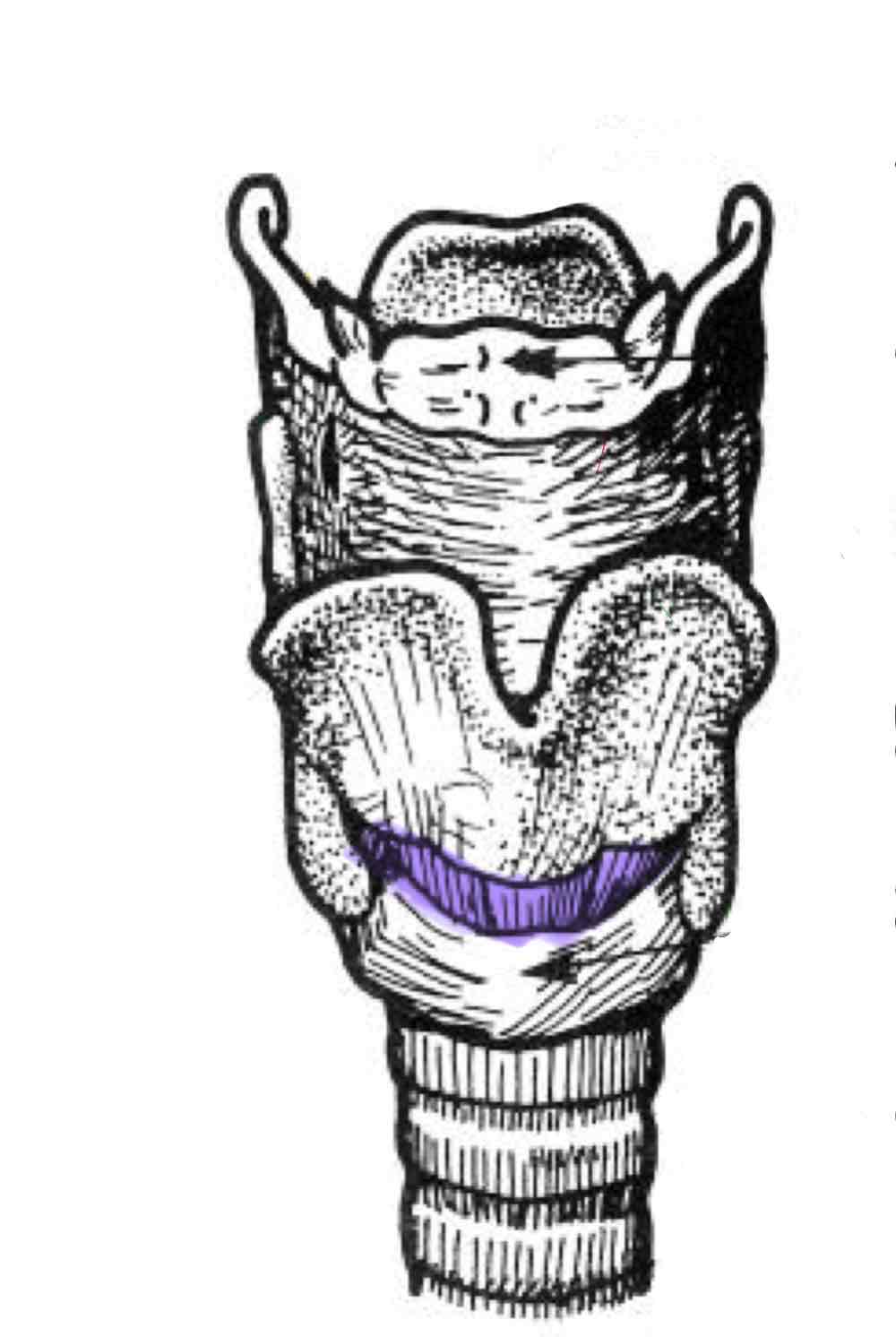
Crico-thyroid ligament
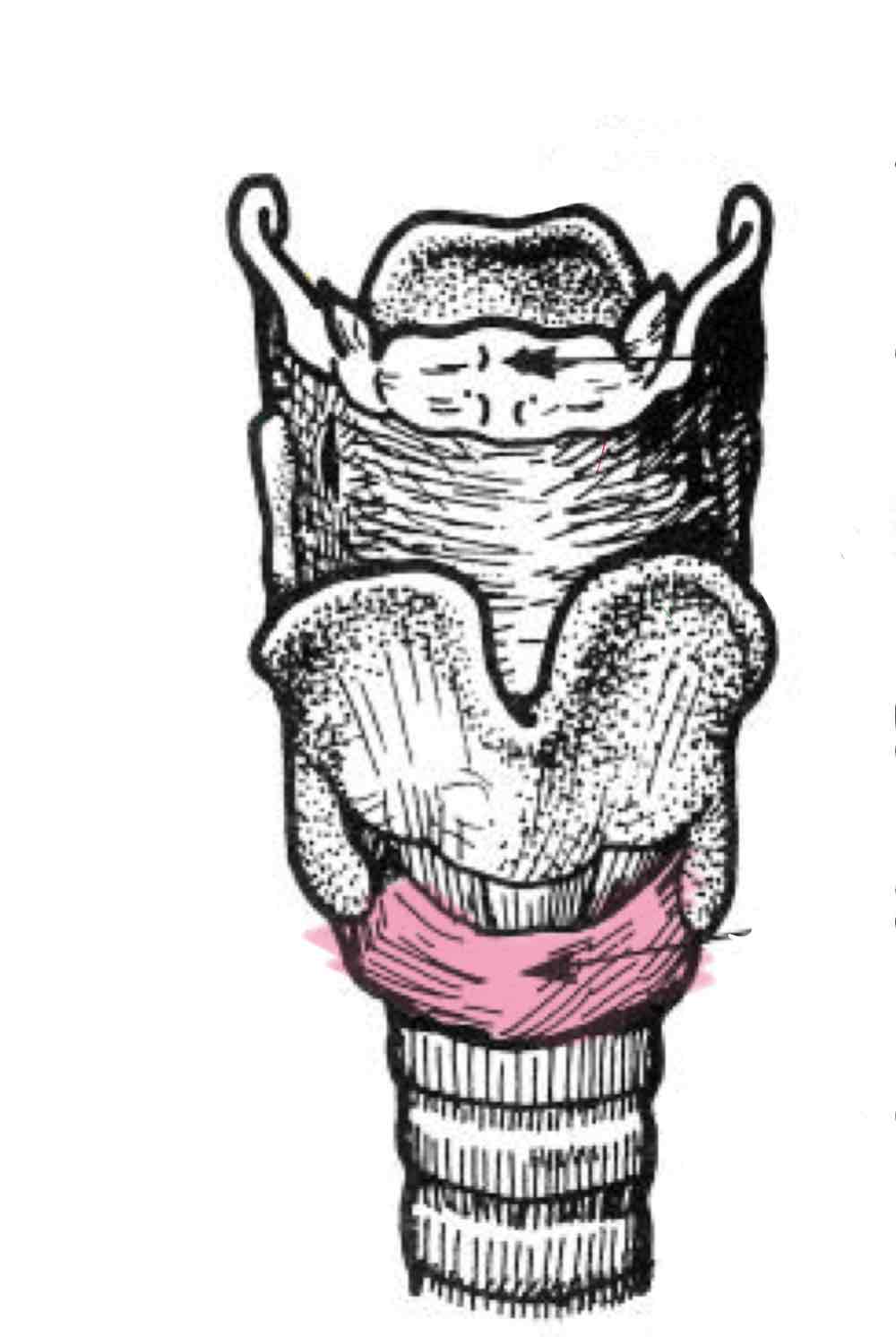
Cricoid cartilage
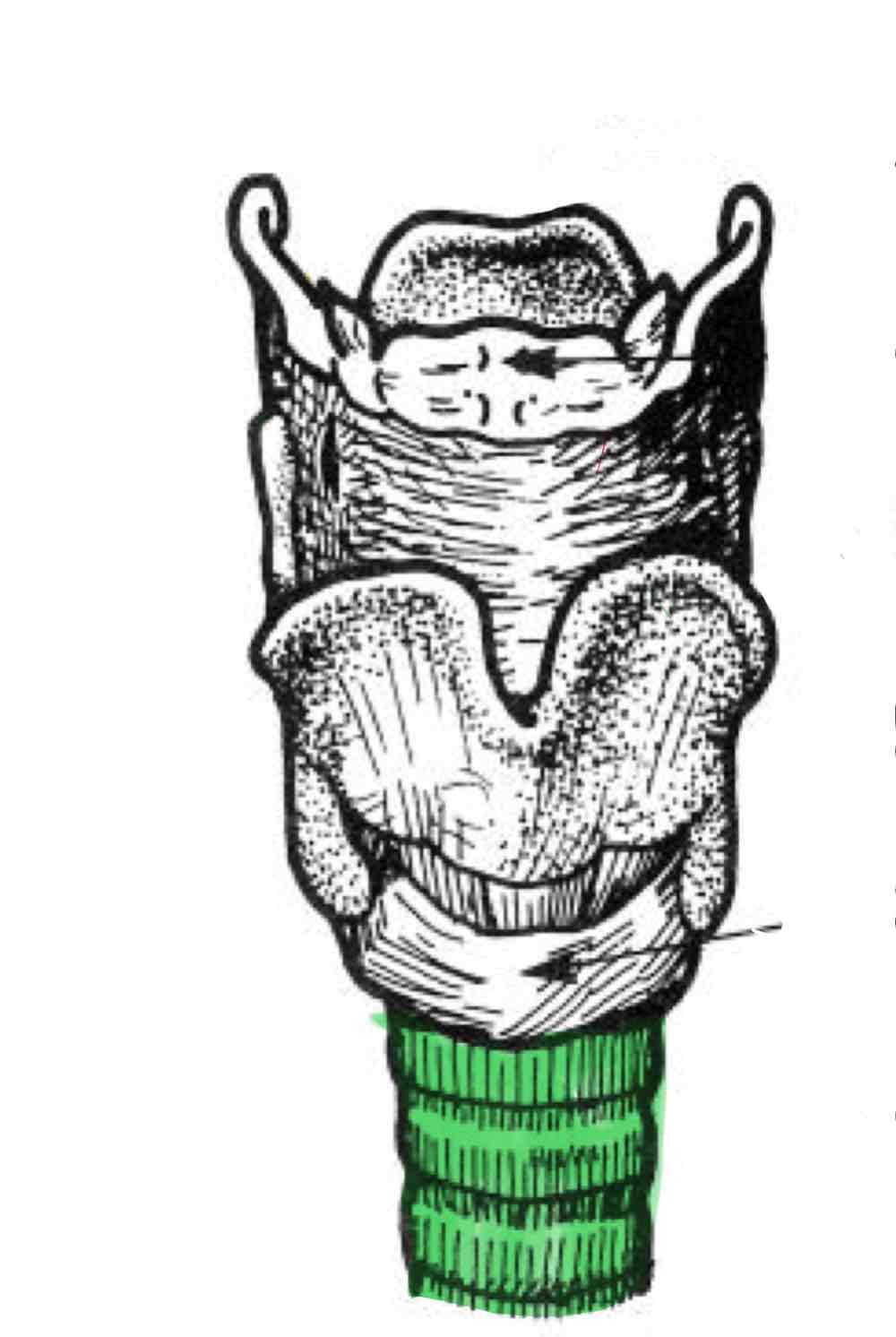
Trachea
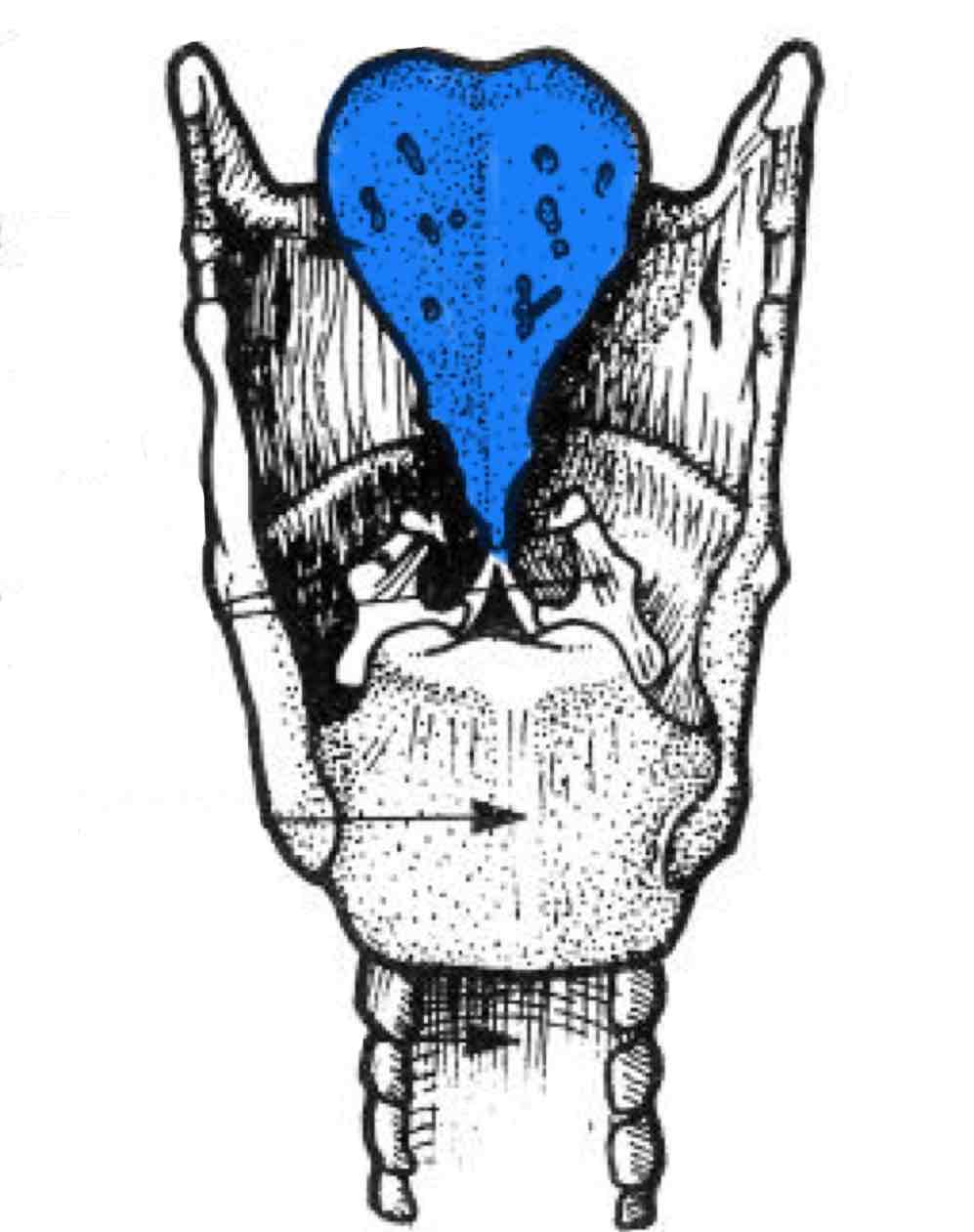
Epiglottis
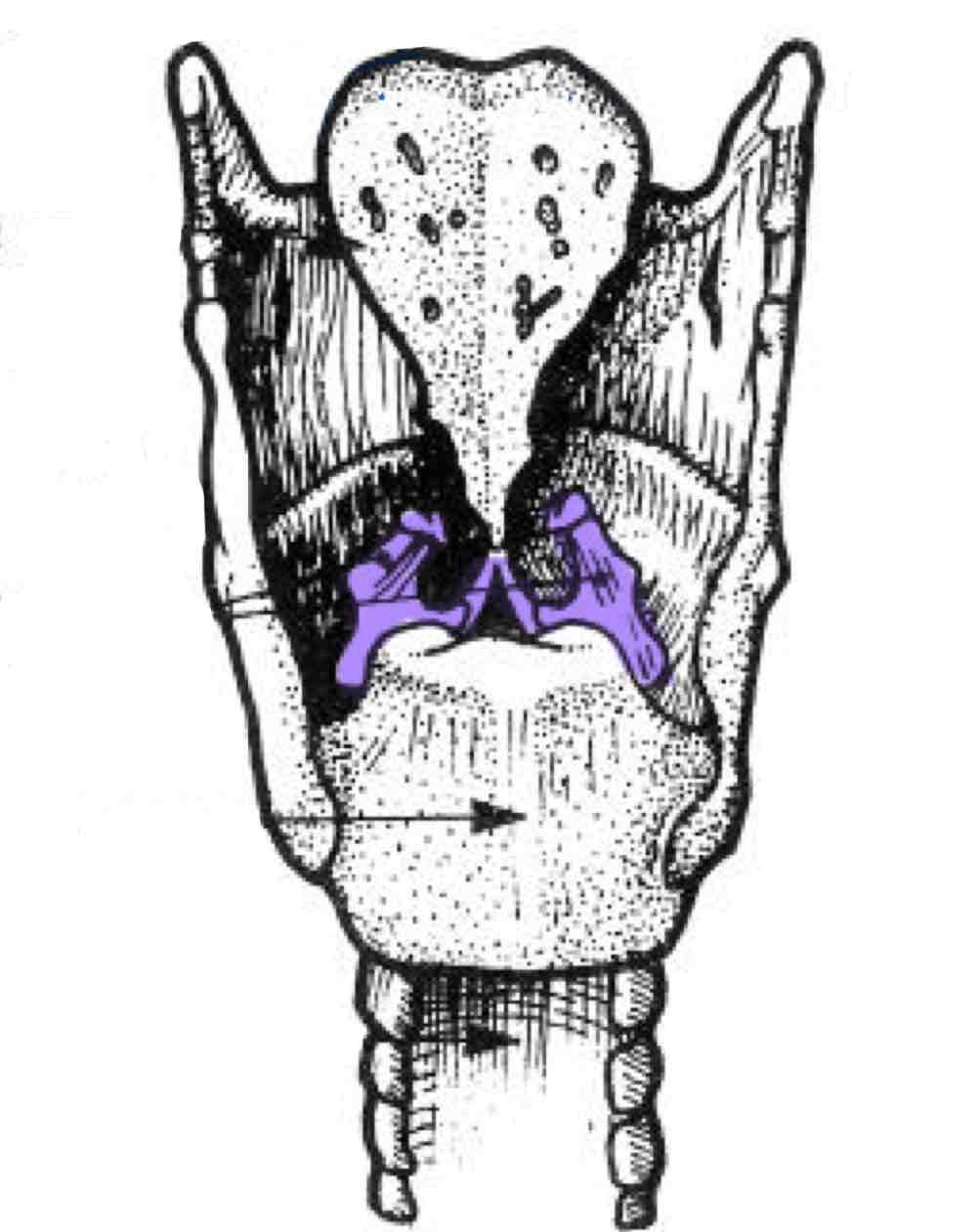
Arytenoid cartilages
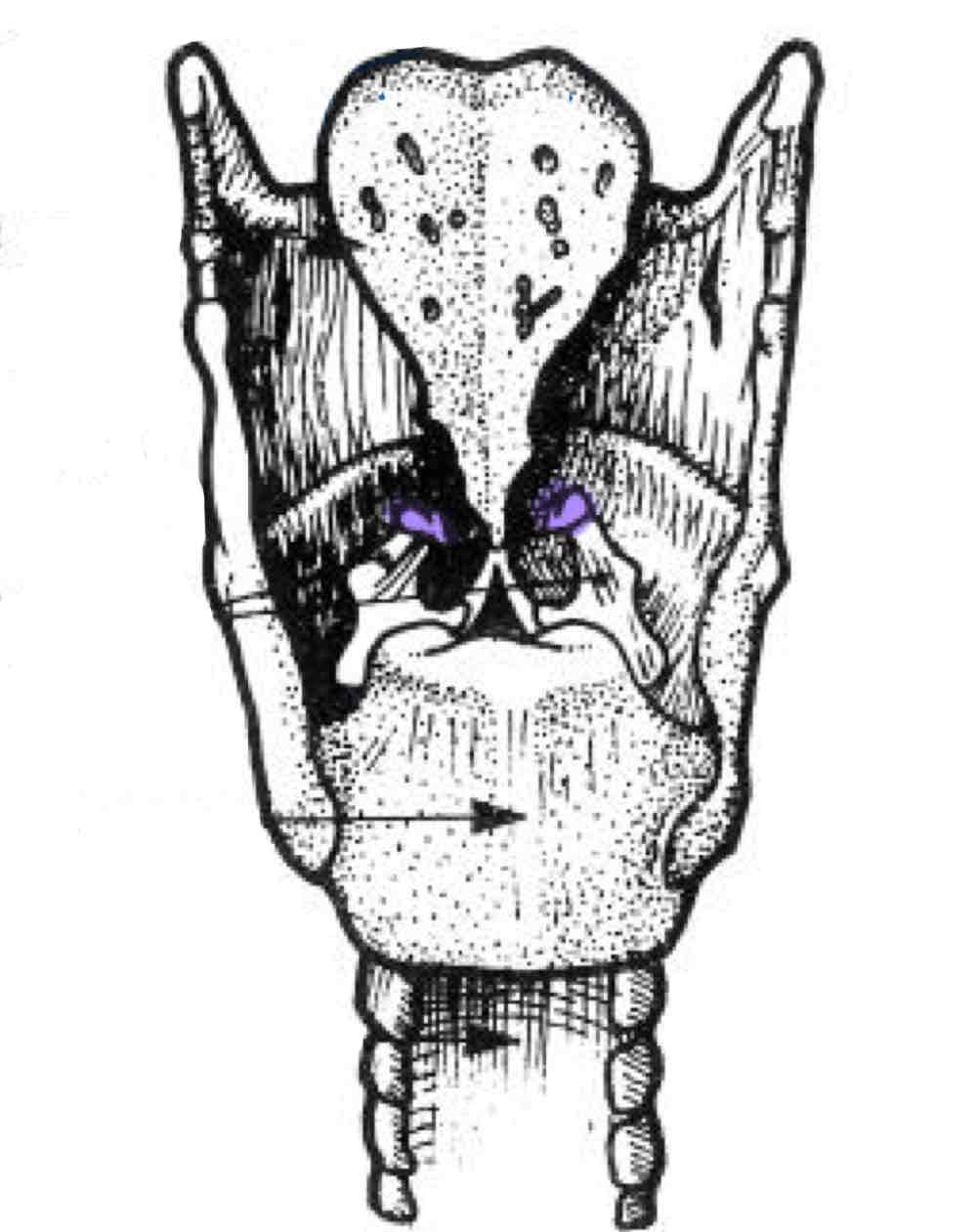
Corniculate cartilages
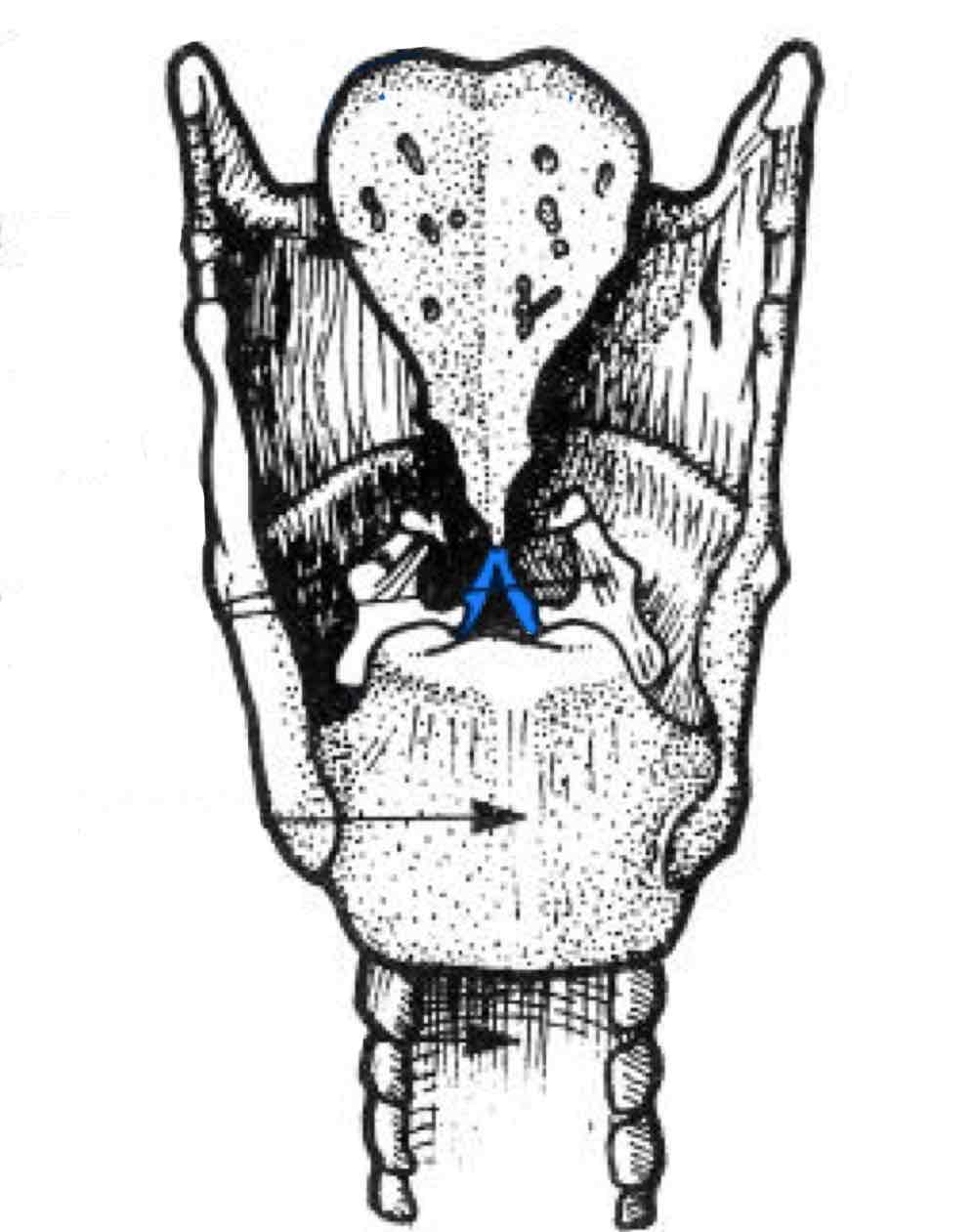
Vocal ligament
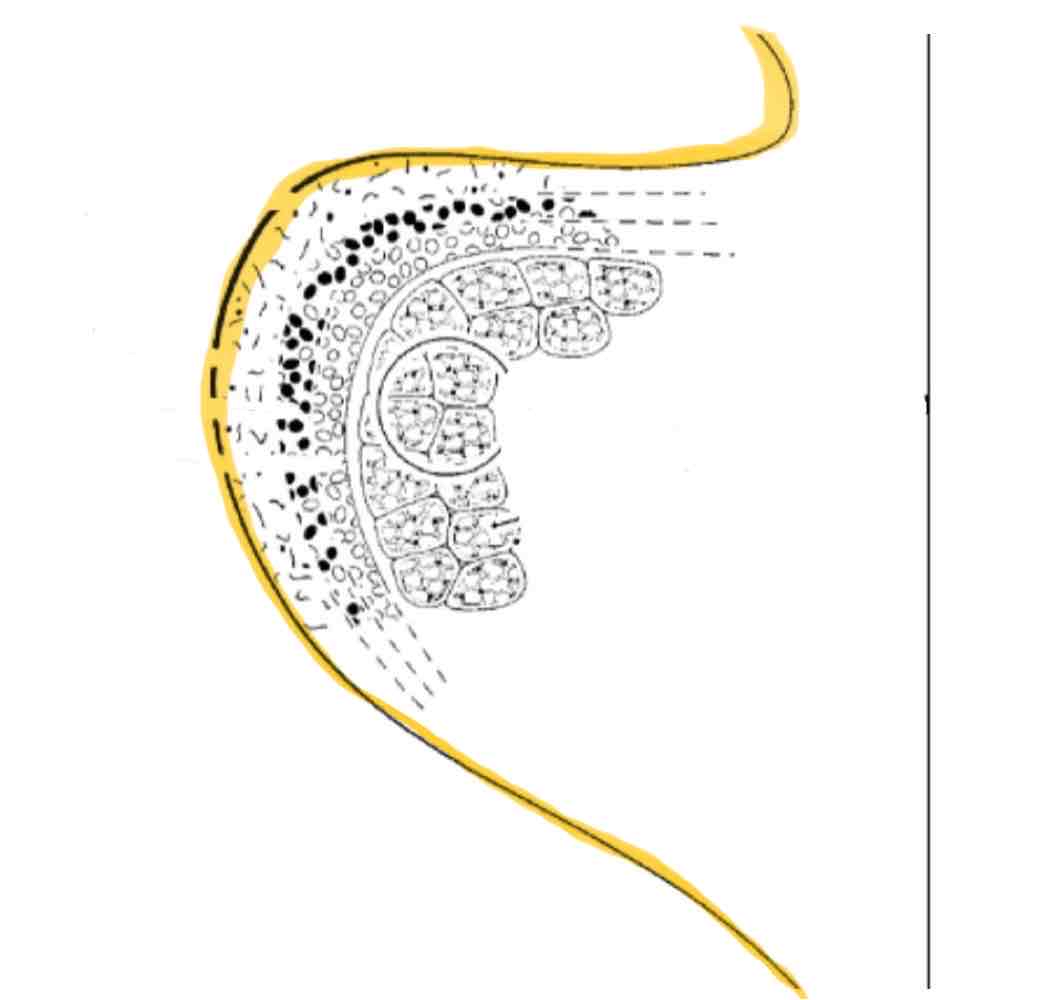
Epithelium
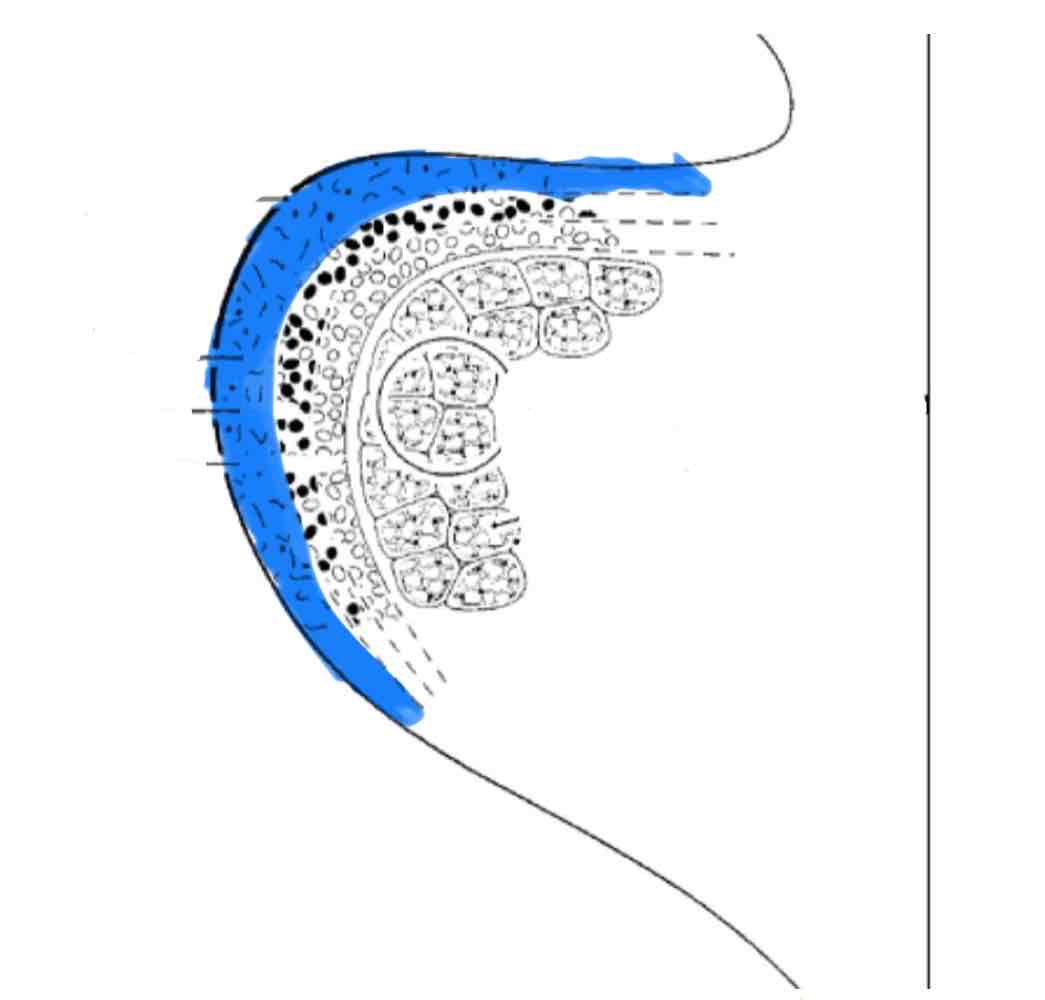
Lamina Propria - superficial layer
What is the Appoggio Technique?
Singing on the gesture of inhalation
What is the muscle in the vocal folds? Describe its theoretical division.
Thyroarytenoid muscle
Divides in two parts:
Vocalis or Thyrovocalis: medial tensing (pitch control)
Thyromuscularis: quick shortening
What is the first stage of Titze’s breath cycle?
Inspiration: abdominal muscles and internal intercostals release - external intercostals contract - diaphragm contracts
What is the second stage of Titze’s breath cycle?
Expiration, first phase: rib cage and lung tissue want to return to the point of equilibrium (elastic recoil) aka (relaxation pressure). (The pressure from recoil is sufficient to start the airflow; With a deep breath, the pressure from the recoil will be greater than desired, and the air pressure needs to be restrained somewhat by continued contraction of the diaphragm and/or activation of external intercostals. This is known as the Appoggio technique)
What is the third stage of Titze’s breath cycle?
Expiration, second phase: continues until no more elastic recoil - internal intercostals activate.
What is the fourth stage of Titze’s breath cycle?
Expiration, third phase: The abdominal muscles kick in.
Describe the Hyoid Bone
Horseshoe shaped with the opening at the back
Only free floating bone in the body
Kept in position (loosely) by muscle/ligaments- loosely jointed to superior cornu
Positioned above the thyroid cartilage
Define Intrinsic Musculature
Interconnects cartilages of the Larynx
Define Extrensic Musculature
connects larynx to other surrounding structures, e.g. sternum, hyoid bone, styloid process, ect.
Which muscle is the main pitch control and responsible for stretching and thinning the folds?
The cricothyroid muscle
How long are AMAB vocal folds?
17-25mm (¾ -1 inch)
How long are AFAB vocal folds?
12.5-17.5 mm (½ - ¾ inch)
Which muscle is the main adductor of the vocal folds? Which part of the vocal folds does it adduct?
Lateral cricoarytenoids– adducts folds from anterior commissure to the vocal process.
What is Boyle’s Law?
Within a soft-walled enclosure, at a constant temperature, pressure and volume are inversely related.
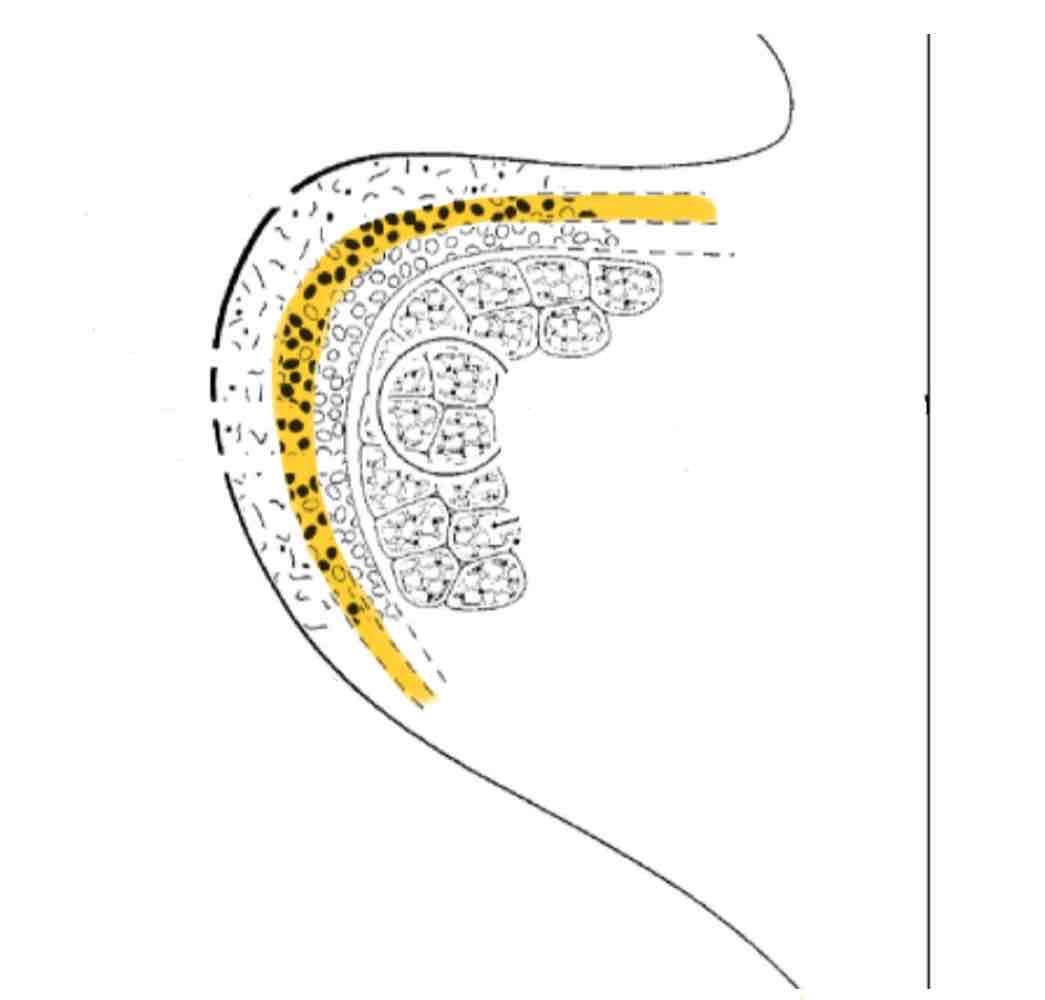
Lamina propria - intermediate layer
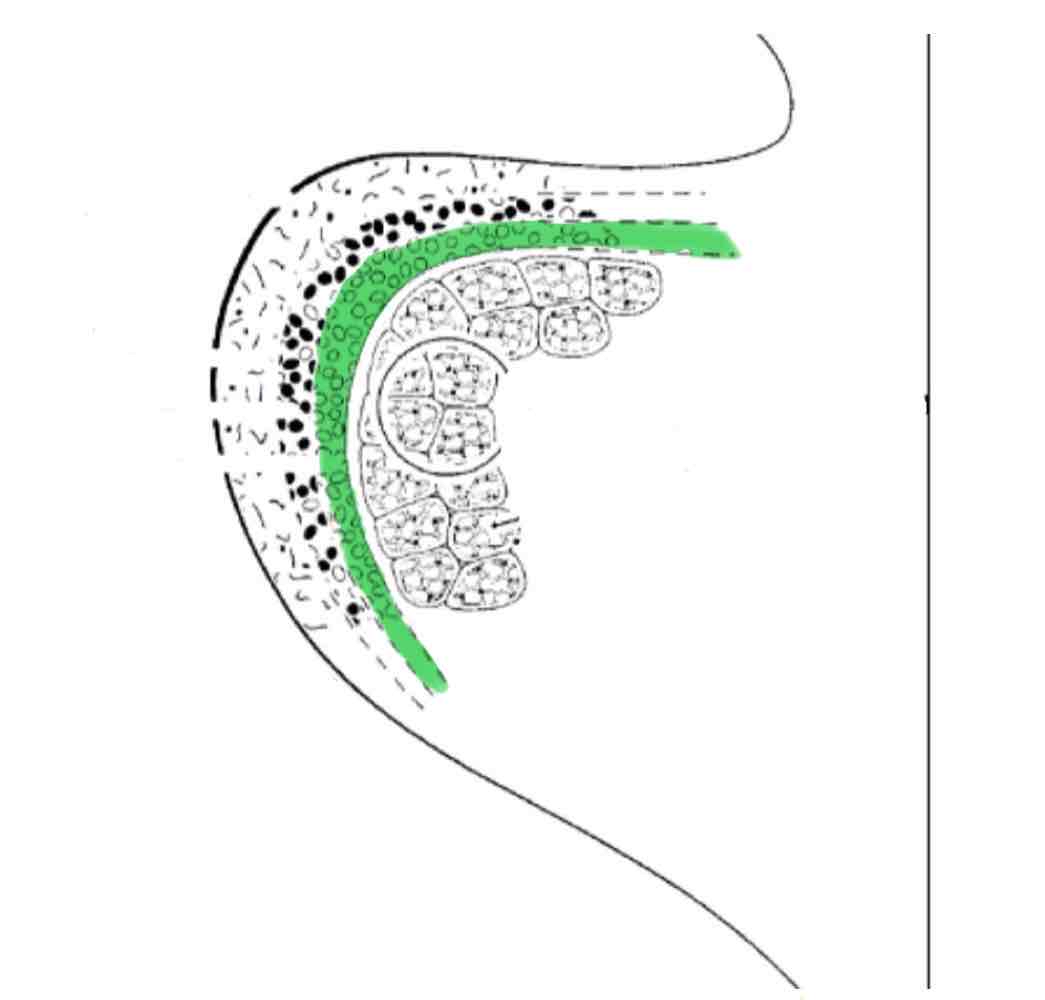
Lamina Propria - deep layer
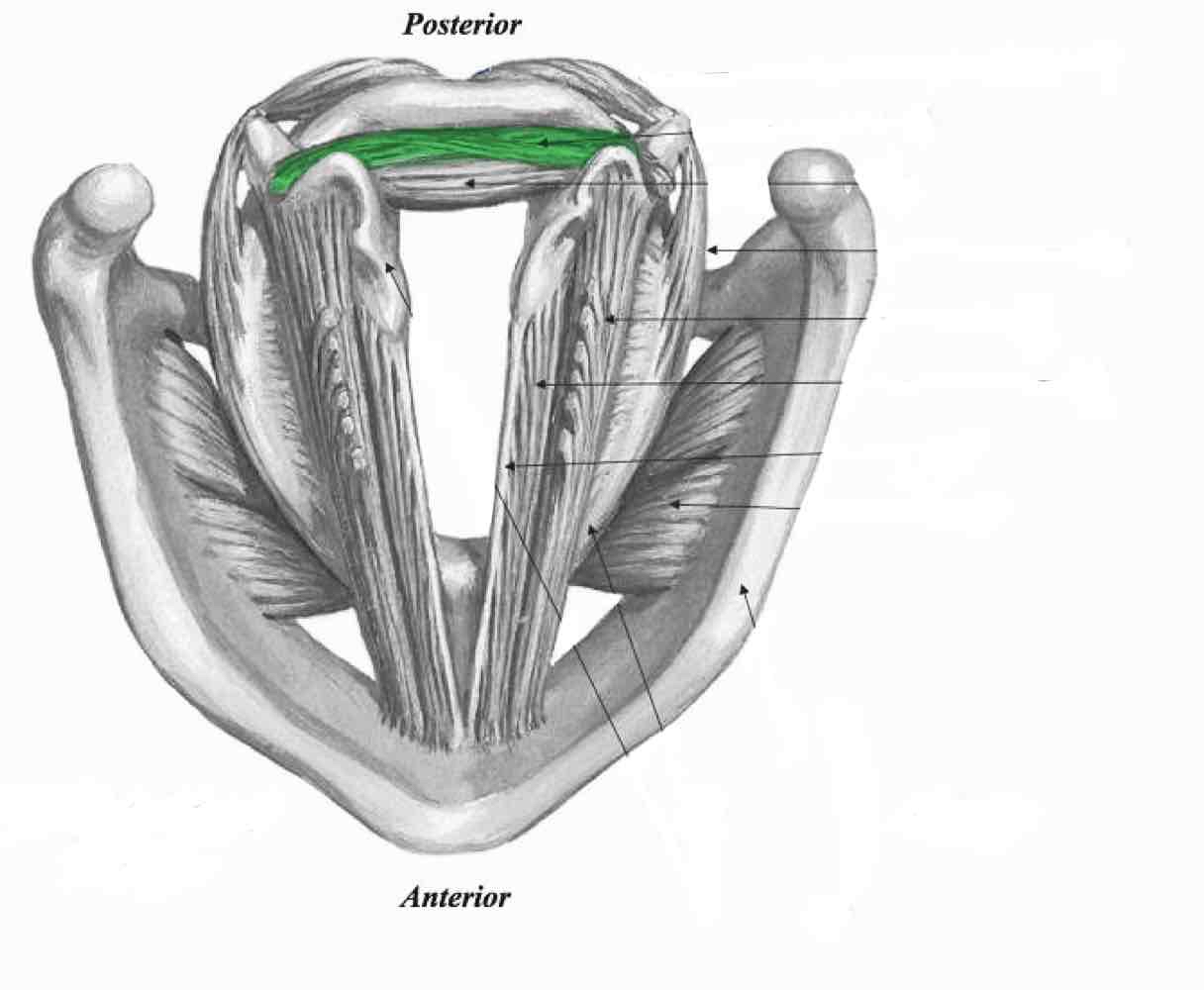
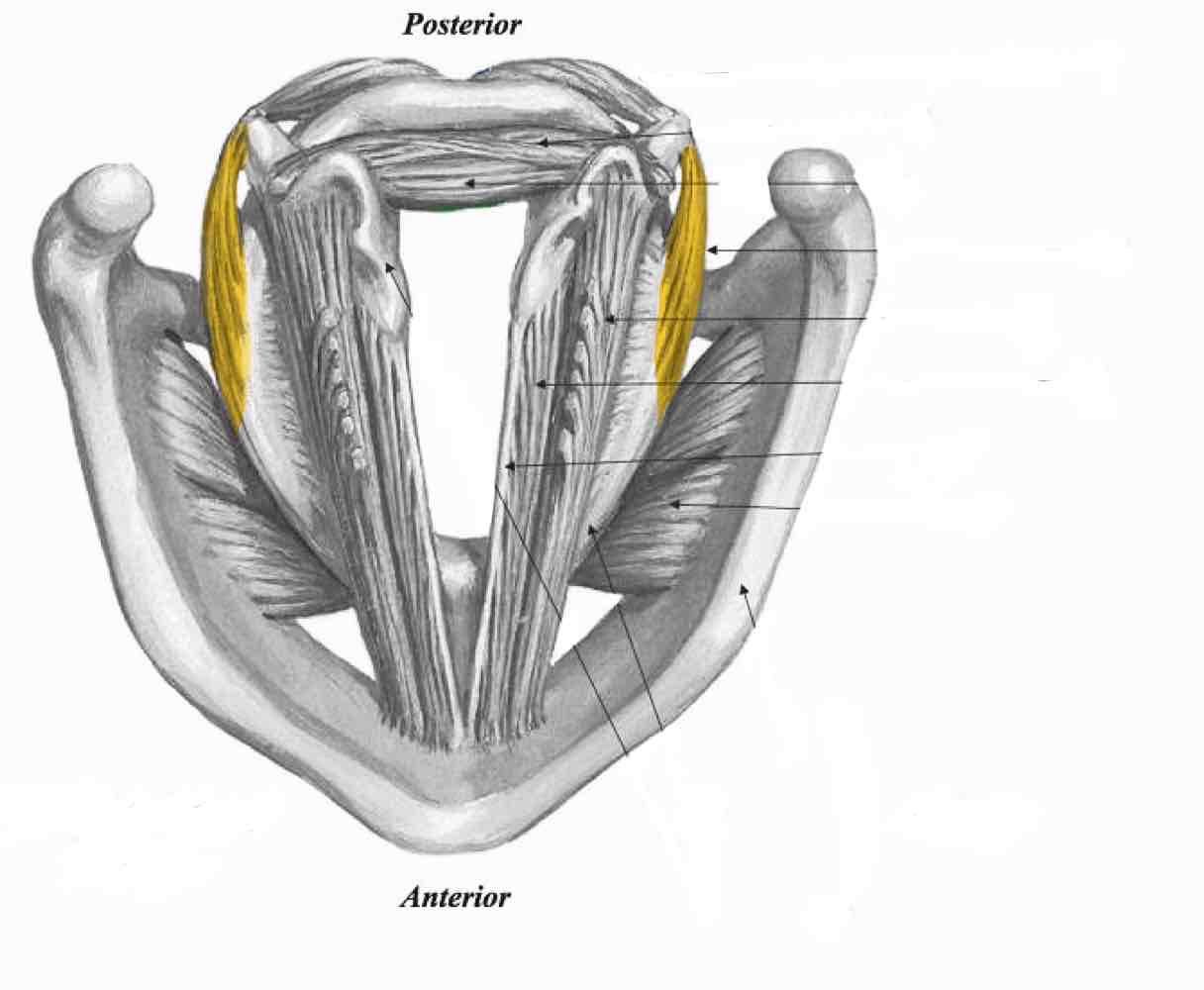
Thyroarytenoid muscle
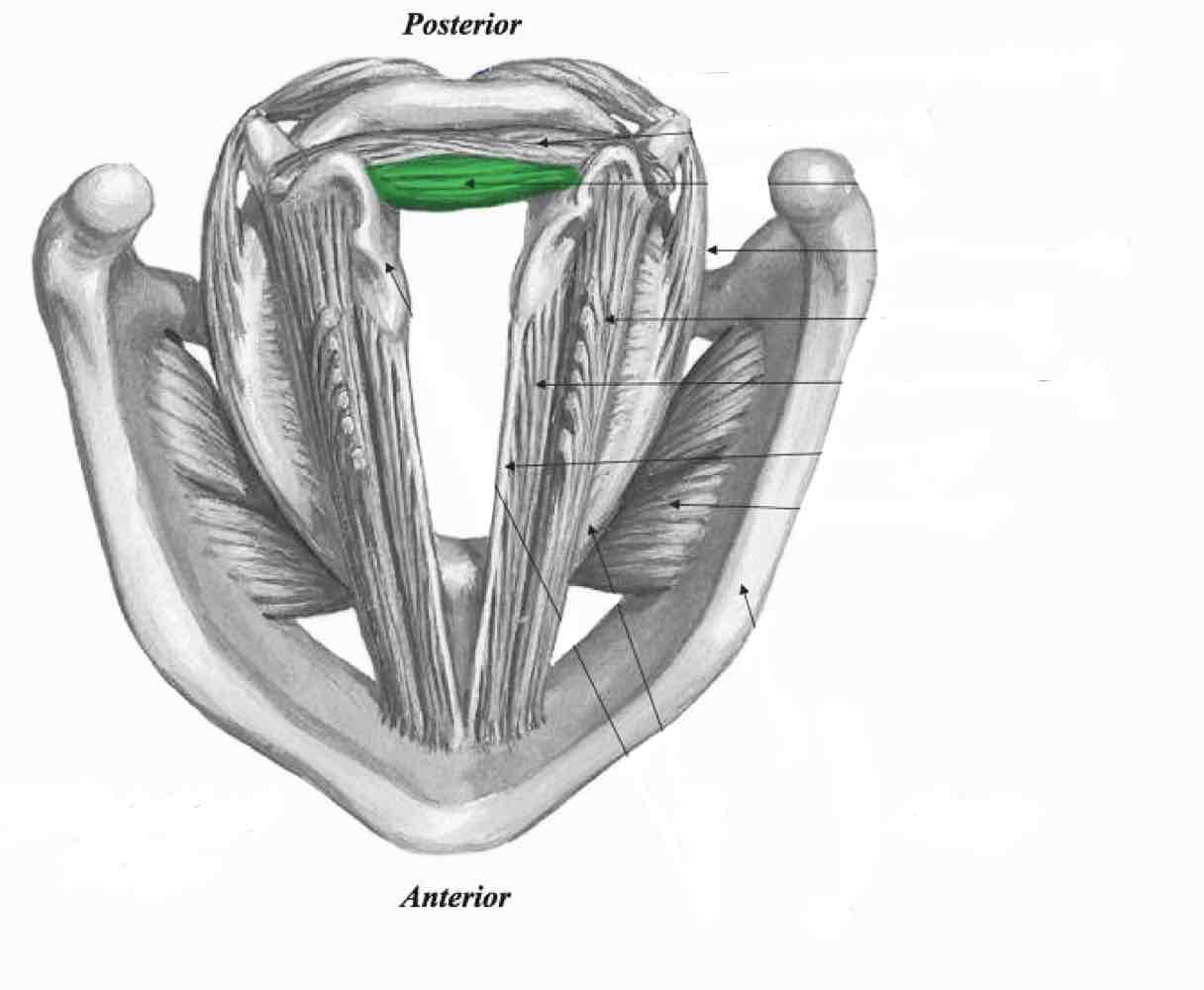
Posterior Cricoarytenoid
Oblique interarytenoids
transverse interarytenoids
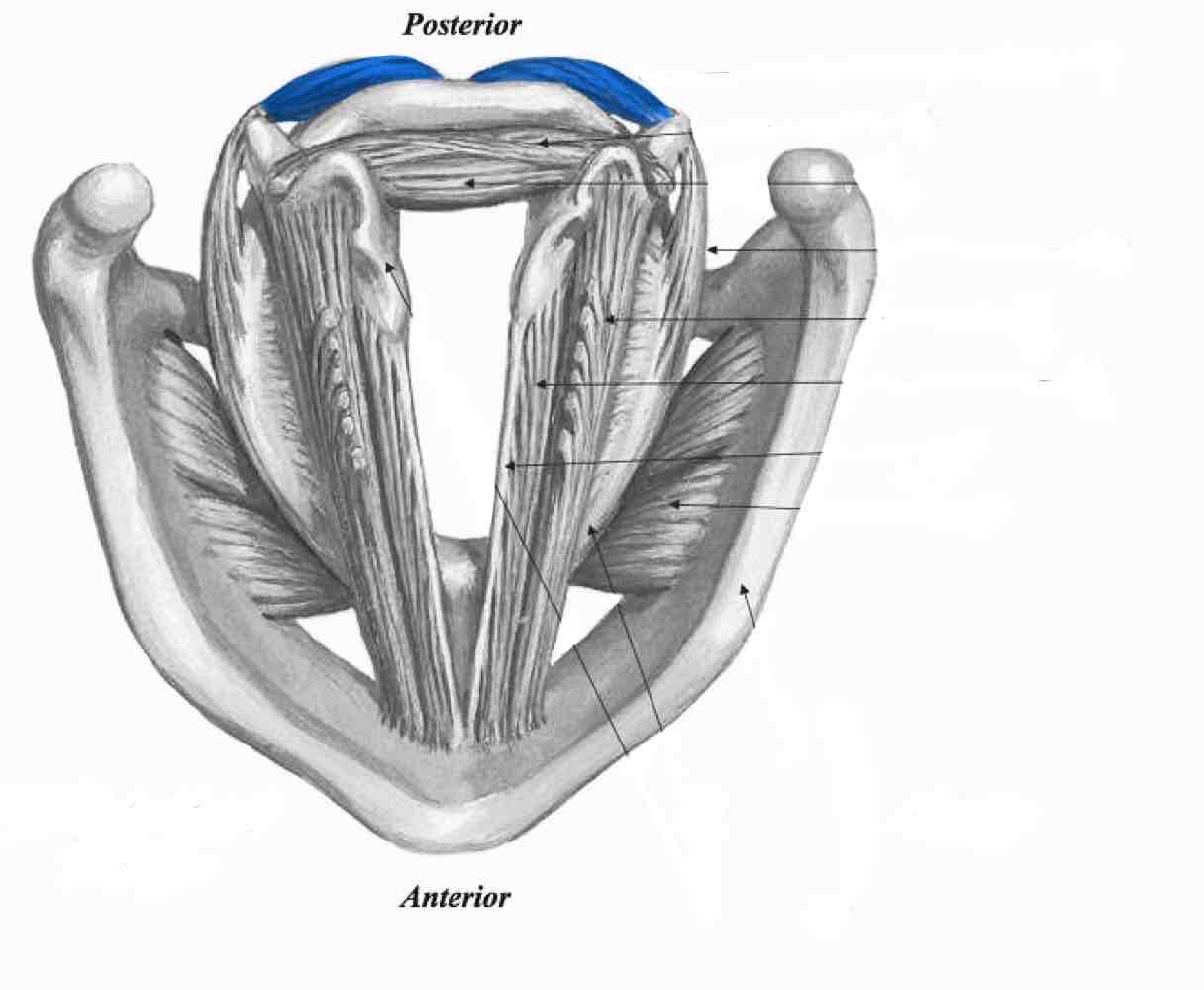
Lateral cricoarytenoid
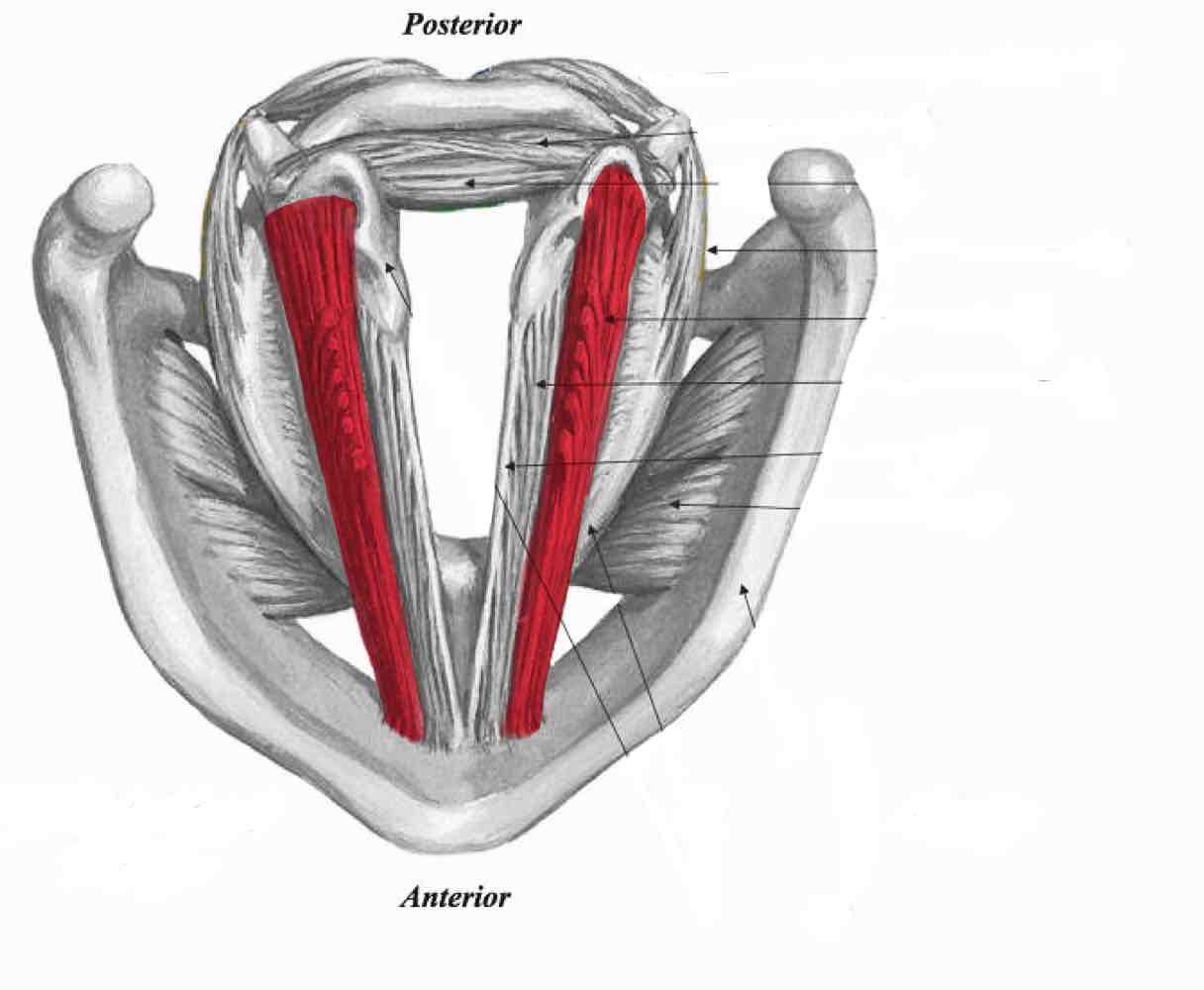
Thyroarytenoid (thyromuscularis)
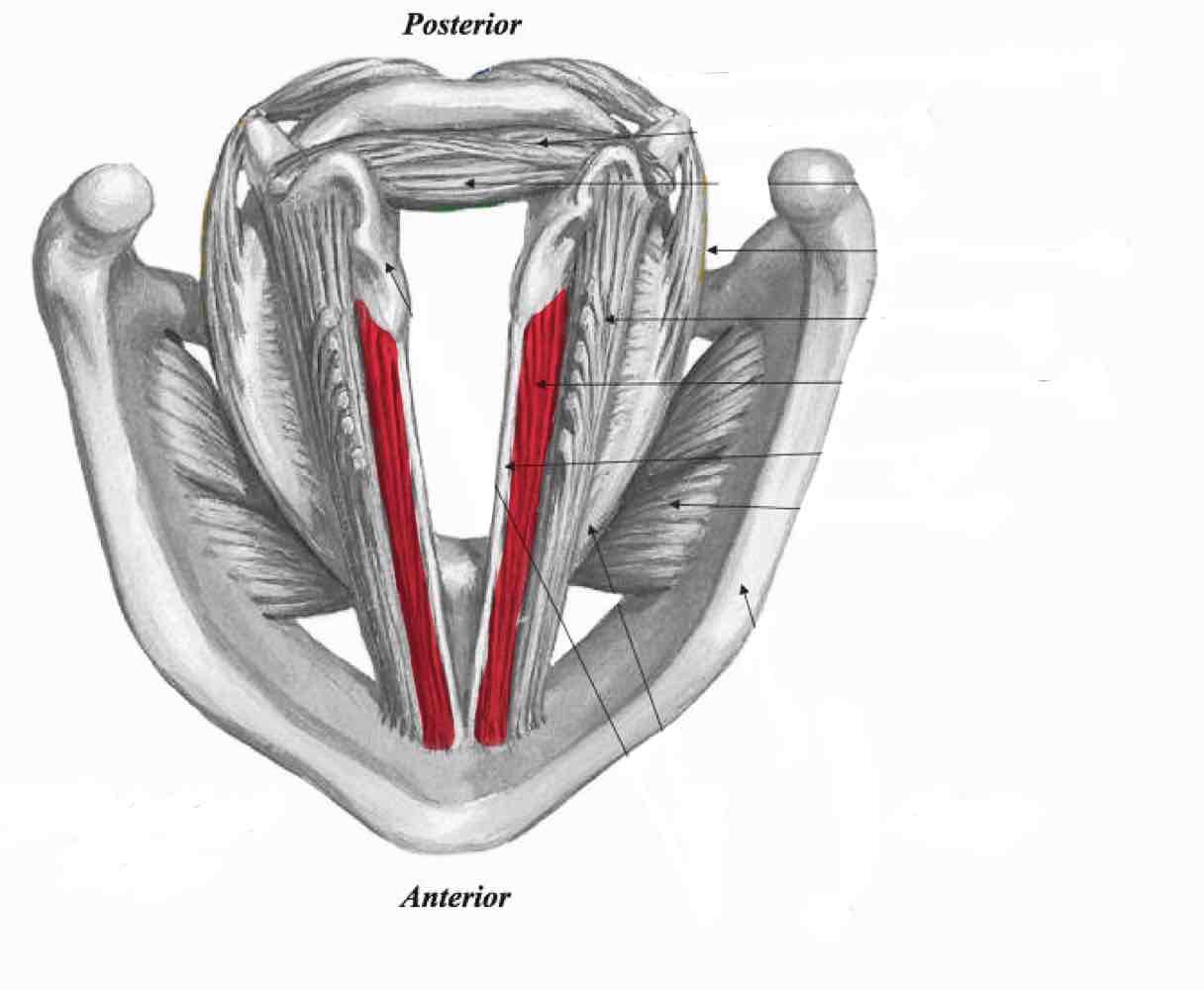
Thyroarytenoid (thyrovocalis)
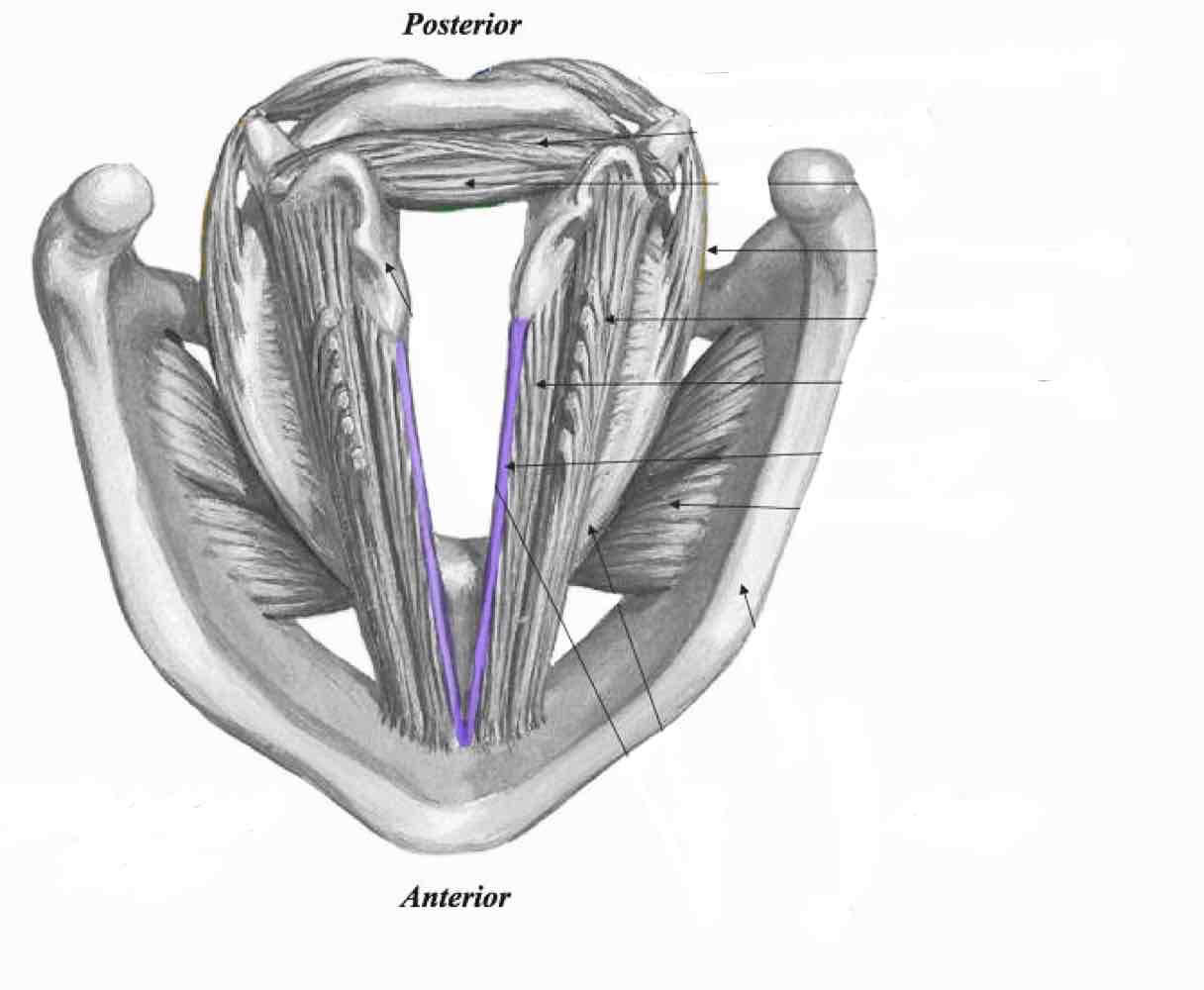
Vocal ligament
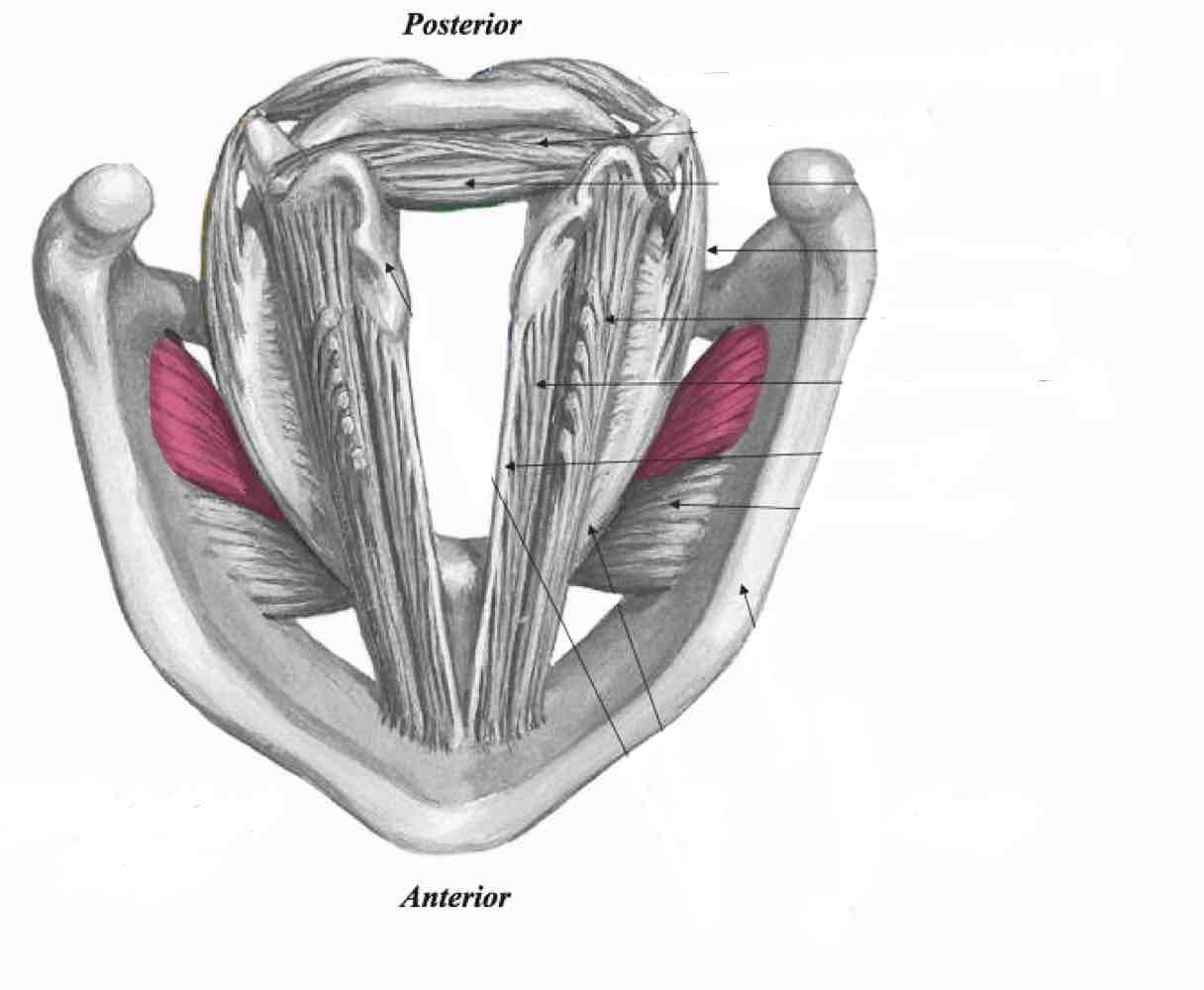
Cricothyroid (pars oblique)
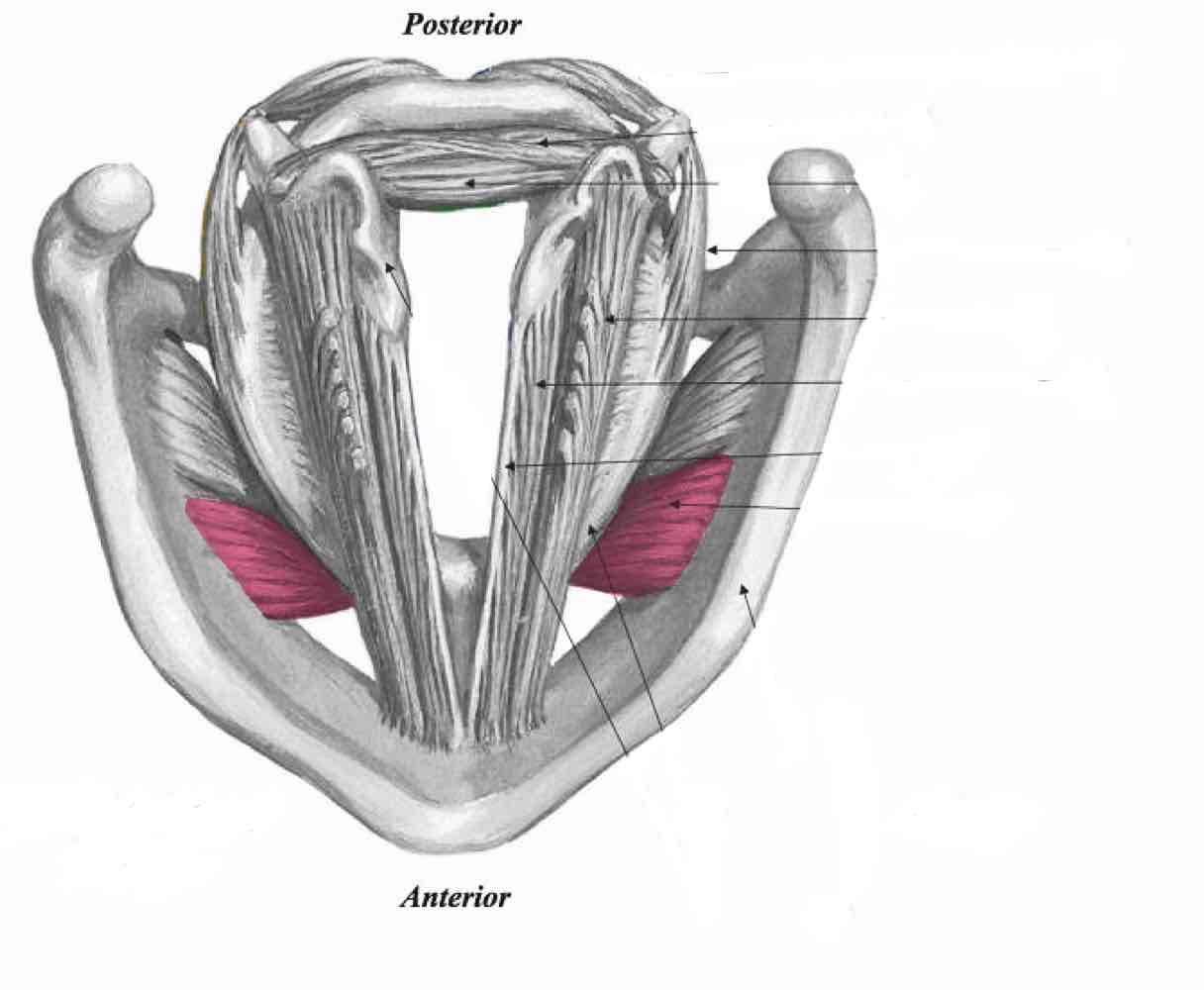
Cricothyroid. (Pars recta)
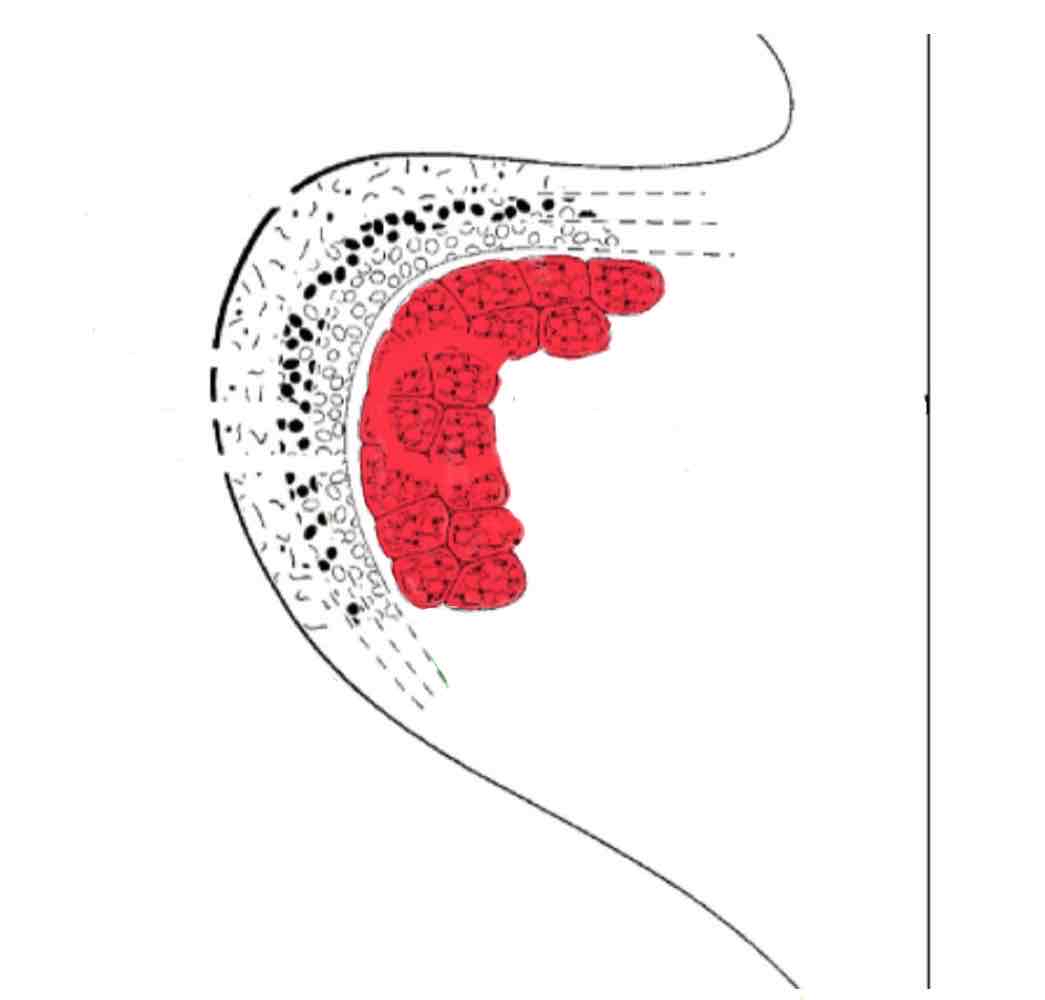
Name the 5 layers of the vocal folds and include any descriptions
Epithelium- layered scale-like (stratified squamous)
Lamina Propria (3 layers):
Superficial layer- mostly elastin (flexible) fibers
Intermediate layer- some elastin and collagen (rigid) fibers
Deep layer- mostly collagen fibers
Thyroarytenoid muscle
What is the glottis?
The space between the vocal folds