Unit 2: Biological Bases of Behavior Overview
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Psychology
AP Psychology
Unit 2: Biological Bases of Behavior
Biological Bases of Behavior
psychology
Chapter 2
Techniques to Learn About Structure and Function
Paul broca
Broca
Broca’s area
expressive aphasia
Carl Wernicke
Lesions
Roger Sperry
Michael Gazzaniga
Computerized axial tomography
magnetic resonance imaging
Measuring Brain Function
Positron emission tomography
Functional MRI
magnetic source image
Organization of Your Nervous System
Central nervous system
Peripheral nervous system
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic stimulation
Parasympathetic stimulation
Spinal cord
old mammalian brain
AP PSYCHOLOGY
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
Dopamine
influences mood, movement, attention, and learning
motivates people to seek out pleasurable activities like food, sex, or drugs. It's also associated with positive feelings of euphoria and pleasure, and helps with learning by acting as a reward.
Serotonin
sexual activity, concentration and attention, moods, and emotions.
Albinism
a lack of pigment and quivering eyes.
It also makes it difficult to perceive depth with both eyes.
Paul Broca
________ (1861) performed an autopsy on the brain of a patient, nicknamed Tan, who had lost the capacity to speak, although his mouth and his vocal cords werent damaged and he could still understand language.
Insomnia
inability to fall asleep and /or stay asleep.
Psychological dependence
emotional and mental withdrawal symptoms that occur after a person stops using a substance or engaging in a behavior for a long time.
These symptoms include anxiety, depression, and anhedonia.
Electroencephalograms
(EEGs) a painless, non-invasive procedure that records the brain's electrical activity. During an EEG, electrodes are attached to the scalp to detect the brain's electrical signals, which are amplified and recorded.
different states, such as sleeping and dreaming.
Positron emission tomography
(PET) a visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task
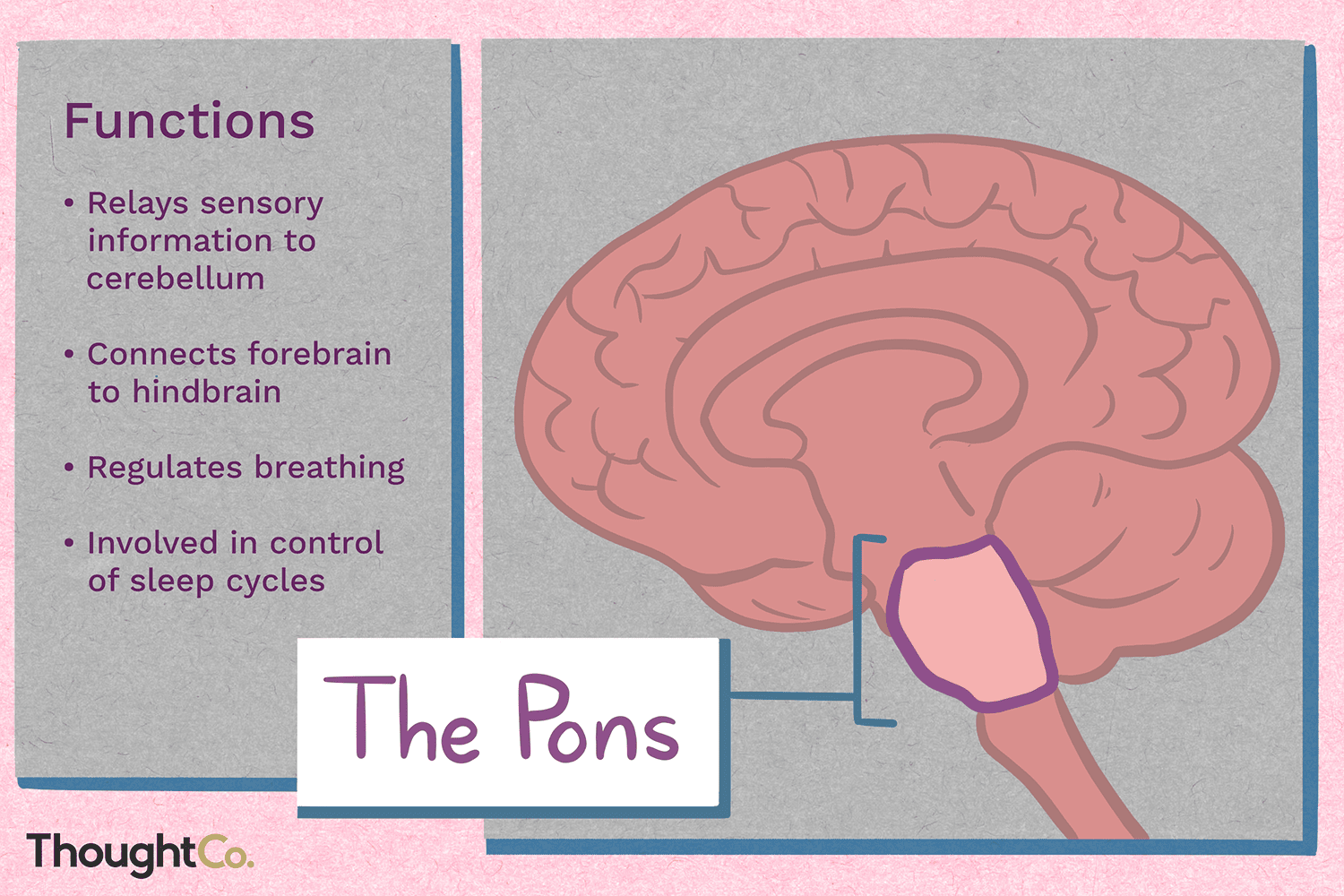
Pons
connects the brain to the spinal cord
regulates several functions including hearing, equilibrium, taste, and facial sensations and movements.
Cyton/cell body
main part of the neuron containing the nucleus where the information is processed
Glutamate
main excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system
Nonconscious
body processes controlled by your mind that we are not aware of.
Psychoactive drugs
substances that cause changes in the normal activities of the central nervous system.
producing a wide range of effects from mild relaxation or increased alertness to vivid hallucinations.
Glial cells
support and protect neurons in the central nervous system
"glue of the nervous system"
Functional MRI
(fMRI) brain at work at higher resolution than the PET scanner.
Circadian rhythm
our internal clock, controlling our temperature and wakefulness in 24-hour cycles
natural, internal process that regulates the sleep- wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours.
Tay Sachs syndrome
produces progressive loss of nervous function and death in a baby.
Freud
tried to analyze dreams to uncover the unconscious desires (many of them sexual) and fears disguised in dreams.
Stimulants
activate motivational centers and reduce activity in inhibitory centers of the central nervous system
increasing activity of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine neurotransmitter systems.
Unconsciousness
loss of responsiveness to the environment, resulting from disease, trauma, or anesthesia.
Cerebral cortex center
higher- order processes such as thinking, planning, judgment; receives and processes sensory information and directs movement.
endocrine system
consists of glands that secrete chemical messengers called hormones into your blood.
Hypothalamus
autonomic nervous system by producing and releasing hormones
"control center" of the brain
regulate sleep-wake cycles, respiration, and other autonomic responses.
Gamma aminobutyric acid
(GABA) inhibits firing of neurons.
Lucid dreaming
the ability to be aware of and direct ones dreams, has been used to help people make recurrent nightmares less frightening.
Hypnosis
altered state of consciousness characterized by deep relaxation and heightened suggestibility.
dissociation theory
hypnotized individuals experience two or more streams of consciousness cut off from each other.
Antagonists
block a receptor site, inhibiting the effect of the neurotransmitter or agonist.
******an antagonist as a bouncer at a club, preventing certain party-goers (neurotransmitters) from entering the receptor sites. ****
Tolerance
decreasing responsivity to a drug.
Endocrine
glands include the pineal gland, hypothalamus, and pituitary gland in your brain; the thyroid and parathyroids in your neck; the adrenal glands atop your kidneys; pancreas near your stomach; and either testes or ovaries.
Withdrawal symptoms
intense craving for the drug and effects opposite to those the drug usually induces.
Heritability
proportion of variation among individuals in a population that is due to genetic causes.
Agonists
may mimic a neurotransmitter and bind to its receptor site to produce the effect of the neurotransmitter.
****stimulating agents****
Reflex
A simple, automatic response to a sensory stimulus, such as the knee-jerk response.
Narcotics
(pain reducers) that work by depressing the central nervous system.
Preconscious
level of consciousness that is outside of awareness but contains feelings and memories that you can easily bring into conscious awareness.
Depressants
psychoactive drugs that reduce the activity of the central nervous system and induce relaxation.
Central nervous system
brain and your spinal cord
Somatic nervous system
has motor neurons that stimulate skeletal (voluntary) muscle
Autonomic nervous system
has motor neurons that stimulate smooth (involuntary) and heart muscle
Plasticity
brain's ability to reorganize itself after an accident or tragedy, or to modify itself in response to experience or change.
Pineal Gland
secretes melatonin; contributes to circadian rhythm
Pituitary Gland
secretes growth hormone & oxytocin promotes pair bonding and trust
Thyroid Gland
affects metabolism
Parathyroids
maintain calcium ion level in blood necessary for normal functioning of neurons
Adrenal Glands
trigger fight or flight
release epinephrine and norepinephrine
Pancreas
regulates blood sugar levels and release insulin
Ovaries and Testes
gonads in females and males, respectively, that produce hormones necessary for reproduction and development of secondary sex characteristics
Tolerance
decreasing responsivity to a drug
epigenetics
environment influences how genes are expressed w/o the change in DNA
somatic NS
charge of voluntary movements of skeletal muscles
automatic NS
control automatic functions of internal organs (heart beating)
sympathetic NS
in charge of arousal
parasympathetic NS
remains up to a calm and natural state
sensory/afferent neurons
carry incoming sensory info into brain & spinal cord
motor/efferent neurons
impulses away from the brain or spinal cord to the peripheral nervous system, initiating an action.
dendrites
recieve info & transfers it to the cell body
axon
passes messages to its terminal branches
myelin sheath
layer of tissues that causes axon & speeds up neural impulse
terminal branches
pass chemical messages to other cells & parts of the body
what must occur for messages to continue to travel down axons
action potential
action potential
short-term change in the polarization of a nerve cell
inhibitory
pushes neurons “brakes” - block responses
excitatory
pushes neurons “accelerator” - encites response
dopamine influences…
movement, learning, attention, emotion
serotonin affects
mood, hunger, sleep, arousal
norepinephrine helps control…
alertness and arousal
GABA major
inhibitory neurotransmitter
glutamate major
excitatory neurotransmitter (memory)
endorphins diminish
the perception of pain & act as a natural sedatiue
acetylcholine enables
muscle action, learning, and memory
dopamine malfunction
oversupply = schizophrenia
undersupply = parkinson’s disease
serotonin malfunction
undersupply = depression
norepinephrine malfunction
undersupply = depress mood
GABA malfunction
undersupply = seizures, insomnia
glutamate malfunction
oversupply = over stimulates in brain = migraines and seizures
endorphins
undersupply = depression, anxiety, moodiness
depressants
reduce or slow neural activity and body functions
stimulates
excite neural activity and speed up body functions
hallucinogens
disory perceptions & sensory images w/o any sensory input
thalamus
receives sensory input
cerebellum
processes sensory input
ex. coordinated mov, balance, & nonverbal learning
pons
coordination of mov
medulla
heart rate and breathing
reticular formation
consciousness
amygdala
linked w/emotion
hypothalamus
maintaining homeostasis & reward system
hippocampus
explicis memory
cerebral cortex
control & processing center
frontal cortex
speaking, planning, judgment
parietal lobes
sensory input for touch & body position
somatosensory cortex
registers touch & movement
occipital lobe
visual input
temporal lobe
auditory input
association areas
higher mental functioning : learning, remembering, thinking, speaking
corpus callosum
communication between hemispheres
“split brain”
both hemispheres operate independently
dual processing
info processed on the unconscious track
left hemi
right hand, spoken langauge, written language, logical thoughts
right hemi
artistic, visual,left, emotional thoughts