Flashcards para kay babycakes
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
I love you baby mwa!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Transduction
The study of how sound is generated and measured by loudspeakers, microphones, sonar projectors, hydrophones, ultrasonic transducers and sensors.
Ultrasonic
The study of high frequency sound which is beyond the range of human hearing.
Lin-lun
The minister of the Yellow Emperor Huangundi who was commissioned to establish a standard pitch for music.
Huan-zhong pipe
Produced by Lin-un, wherein he cut a bamboo stem between the nodes to make his fundamental note.
Fohi
A Chinese philosopher who attempted to establish a relationship between the pitch of a sound and the five elements: earth, water, air, fire, and wind
Pythagoras of Samos
He discovered that musical notes could be translated into mathematical equations.
Aristotle
On Acoustics, the first monograph on the subject is attributed to him.
Aristotle
Referred to the nature of sound in ‘De Anima’ and ‘De Audilibus’
Theophrastus of Eresos
Who clarified the relationship between sound velocity and frequency.
Chrysippus
One of the earliest acousticians.
Vitruvius
He discussed the Classical Theater in his De Architectura and in Chapter five of his Ten Books of Architecture. He also used the spread of circular waves on water’s surface as an example and explained that true sound waves travel in three-dimensional word not as circles but as outwardly spreading spherical waves.
Quintilianus
Demonstrated with small straw segments the resonance of a string in air.
Boethius
A Roman scholar and statesman; translator and commentator on Greek writings and logic such as those of Plato, Aristotle, and Nichomachus.
Leonardo da Vinci
He knew that “there cannot be any sound when there is no movement or percussion of the air.”
Leonardo da Vinci
His observations led him to correlate the waves generated by a stone cast into the water with the propagation of sound waves as similar phenomena.
Galileo Galilei
He introduced the concept of frequency during the 16th century.
Marin Mersenne
Who is often referred to as the “Father of acoustics“?
Pierre Gassendi
A contemporary of Galileo and Mersenne who argued for a ray theory whereby sound is attributed to a stream of atoms in motion and the frequency is the number of atoms emitted per unit time.
Robert Boyle
Performed a classic experiment in 1660 by placing a ticking watch in a partially evacuated glass chamber.
Bell-jar experiment
level of sound produced by a ringing bell within the jar decreases as the air is pumped out – indicates a need for a medium for the transmission of sound.
Joseph Sauveur
He introduced ‘acoustics’ as the term to define the science of sound.
Sir Isaac Newton
Made statement on the analogy between sound and color.
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz
Cotemporary of Newton in the field of theoretical physics and applied mechanics.
Brook Taylor
An English mathematician and the first to provide a formula for frequency expressed in terms of length, tension and mass of a stretched string.
Reverend William Derham
He arranged guns to be fired from various church towers up to twelve miles away.
Joseph-Louis Lagrange
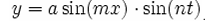
Pierre-Simon, marquis de Laplace
Corrected Newton’s derivation of the expression for the velocity of sound.
Félix Savart
He developed the Savart wheel which produces sound at specific graduated frequencies using rotating disks.
Michael Faraday
Was an English chemist and physicist who contributed to the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry.
George Gabriel Stokes
He worked on the effects of fluid viscosity on sound propagation.
Rene Theophile Hyacinthe Laennerc
Who invented the stethoscope?
Microphone
What device was coined by Wheatstone to denote a sensitive sound receiver in the accounts of sound experiments on the vibration of surfaces.
Lord Rayleigh
Produced the two-volume Theory of Sound: an authoritative reference document on the theoretical foundations of acoustics.
James P. Joules
Introduced ultrasonics with his discovery of the magnetostrictive effect – the alteration of the dimensions of a magnetic material under the influence of magnetic field.
Wallace Clement Ware Sabine
He discovered that excessive reverberations tend to mask the lecturer’s words.
Harvey Flectcher
Led the Bell Telephone Laboratories in describing and quantifying the concepts of loudness and masking and regarded as “the father of psychoacoustics”.