Section 5:Cell Chemistry
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:43 PM on 4/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
1
New cards
Element
substances that cannot be broken down or transformed chemically into other substances
2
New cards
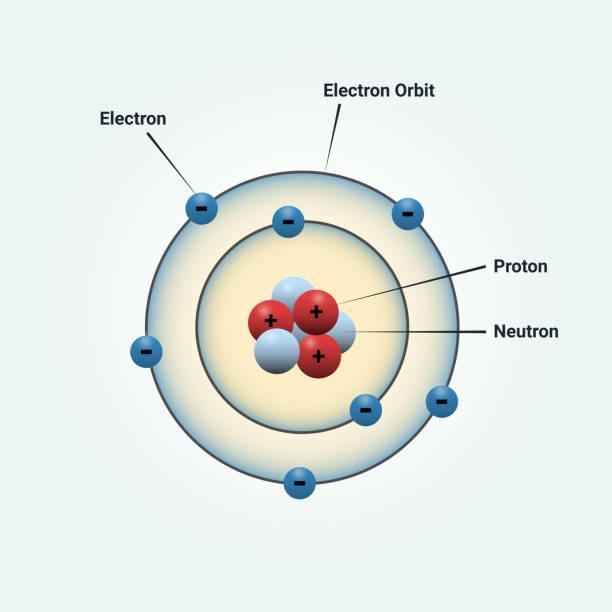
Atom
the smallest component of an element that retains all of the chemical properties of that element.
3
New cards
Proton
is a positively charged particle that resides in the *nucleus* (the core of the atom) of an atom and has a mass of 1 and a charge of +1.
4
New cards
Neutron
resides in the nucleus of an atom. They have a mass of 1 and no charge
5
New cards
Electron
is a negatively charged particle that travels in the space around the nucleus
6
New cards
Atomic Number
of an element is equal to the number of protons that element contains.
7
New cards
Isotope
Different forms of the same element that have the same number of protons, but a different number of neutrons
8
New cards
Electron Shells
an electron shell may be thought of as an orbit followed by electrons around an atom's nucleus
9
New cards
Chemical Bond
interactions between two or more of the same or different elements that result in the formation of molecules
10
New cards
Ionic Bond
a chemical bond that forms between ions of opposite charges. Formed by
* by the complete transfer of some electrons from one atom to another.
* by the complete transfer of some electrons from one atom to another.
11
New cards
Covalent Bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms.
12
New cards
Electronegtitvity
symbolized as χ, is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons when forming a chemical bond
13
New cards
Non-Polar Covalent Bond
form between two atoms of the same element or between different elements that share the electrons equally.
14
New cards
Polar Covalent Bond
the electrons shared by the atoms spend more time closer to one nucleus than to the other nucleus.
15
New cards
Ion
When an atom does not contain equal numbers of protons and electrons
16
New cards
Hydrogen Bond
a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group, and another electronegative atom bearing a lone pair of electrons—the hydrogen bond acceptor.
17
New cards
Cohesion
the attraction of molecules for other molecules of the same kind
18
New cards
Adhesion
the attraction between water molecules and other molecules.
19
New cards
Surface Tension
the capacity of a substance to withstand rupture when placed under tension or stress.
20
New cards
Solvent
substance capable of dissolving another substance.
21
New cards
Acid
ubstances that provide hydrogen ions (H+) and lower pH
22
New cards
Buffer
readily absorb excess H+ or OH–, keeping the pH of the body carefully maintained in the aforementioned narrow range.
23
New cards
provide hydroxide ions (OH–) and raise pH
24
New cards
Hydrophilic
When a substance readily forms hydrogen bonds with water, it can dissolve in water
25
New cards
Hydrophobic
Hydrogen bonds are not readily formed with nonpolar substances like oils and fats.These nonpolar compounds are (“water-fearing”) and will not dissolve in water.
26
New cards
Macromolecules
The large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules
27
New cards
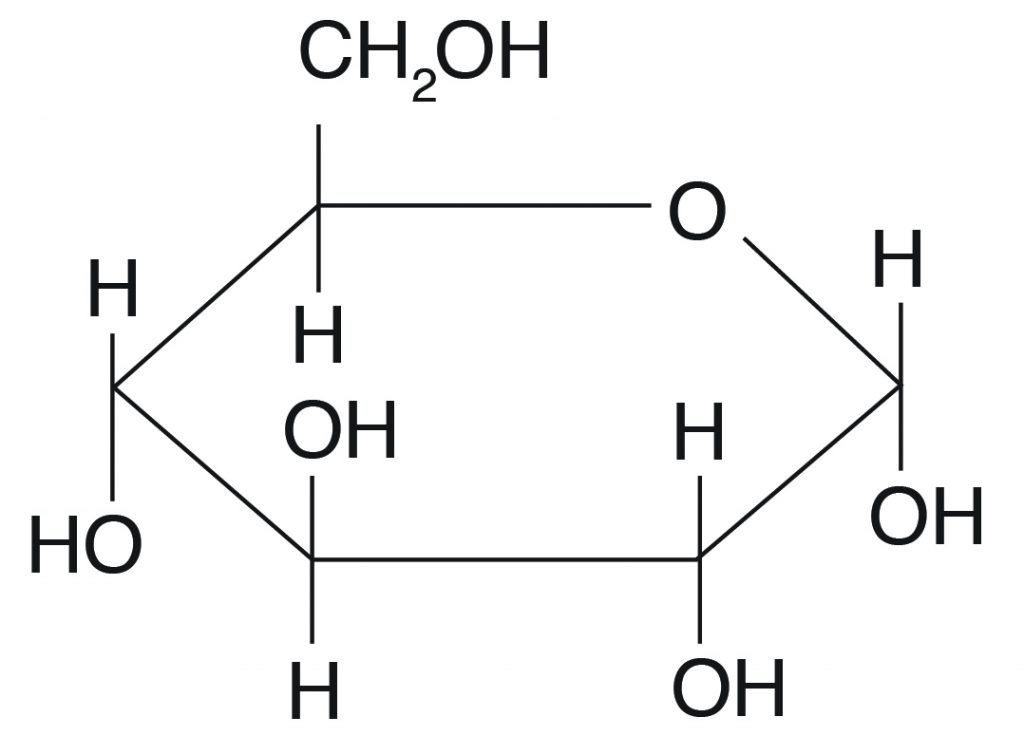
Carbohydrates
any of a large group of organic compounds that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose, containing hydrogen and oxygen in the same ratio as water (2:1) and used as structural materials and for energy storage within living tissues.
28
New cards
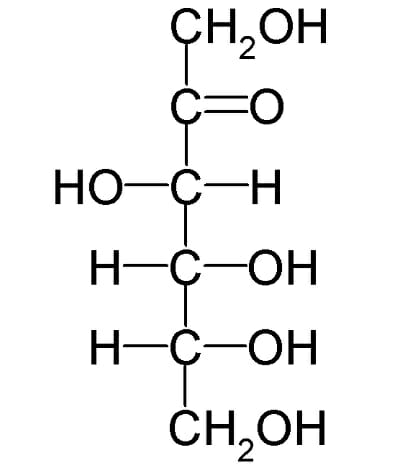
Monosaccharide
also called simple sugars, are the simplest forms of sugar and the most basic units from which all carbohydrates are built. They are usually colorless, water-soluble, and crystalline solids
29
New cards
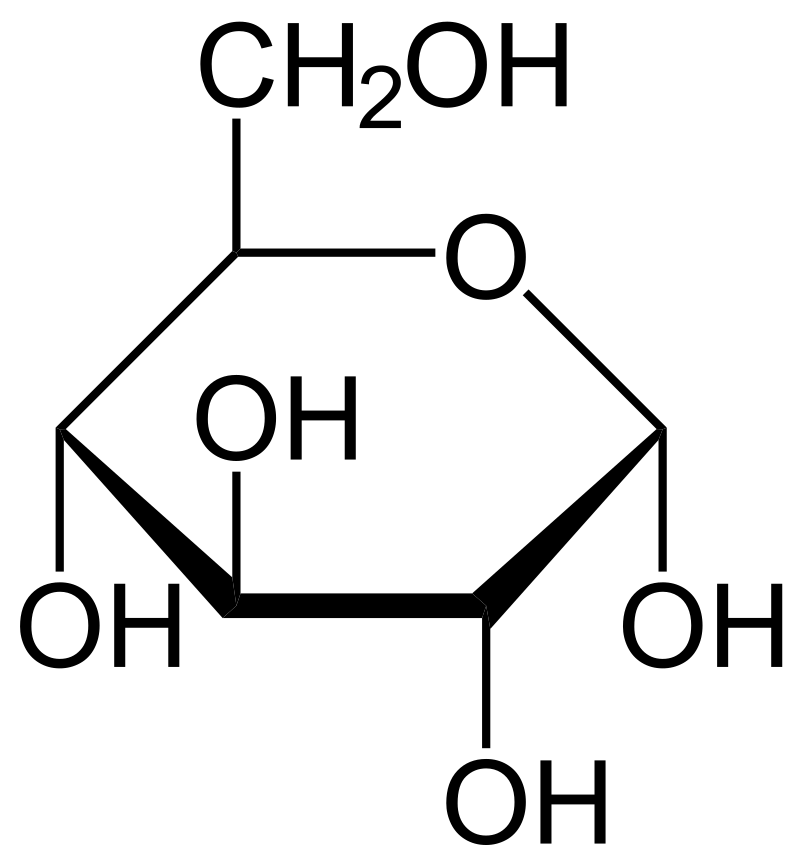
Glucose
a simple sugar which is an important energy source in living organisms and is a component of many
30
New cards
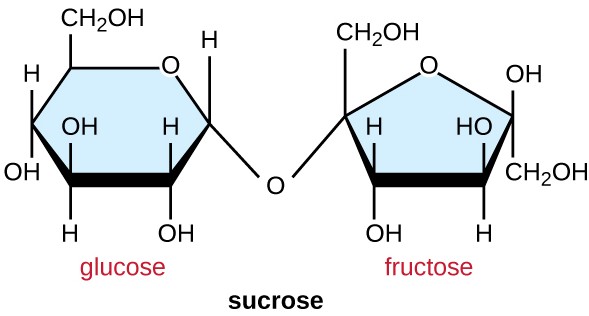
Disaccharide
any of a class of sugars whose molecules contain two monosaccharide residues.
* Surcrose
* lactose
* maltose
* Surcrose
* lactose
* maltose
31
New cards
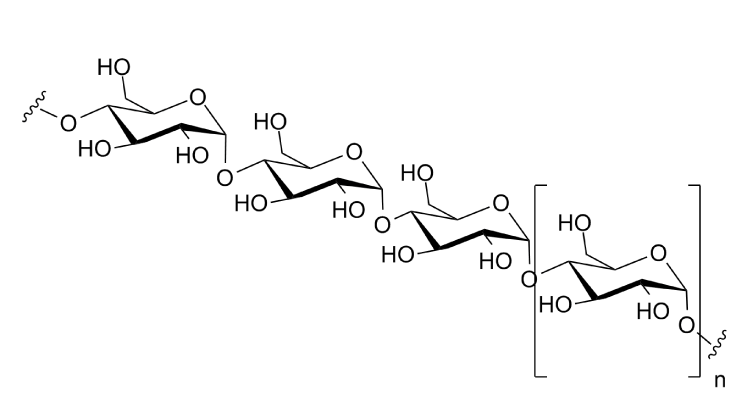
Polysaccharide
a carbohydrate (e.g. starch, cellulose, or glycogen) whose molecules consist of a number of sugar molecules bonded together.
32
New cards
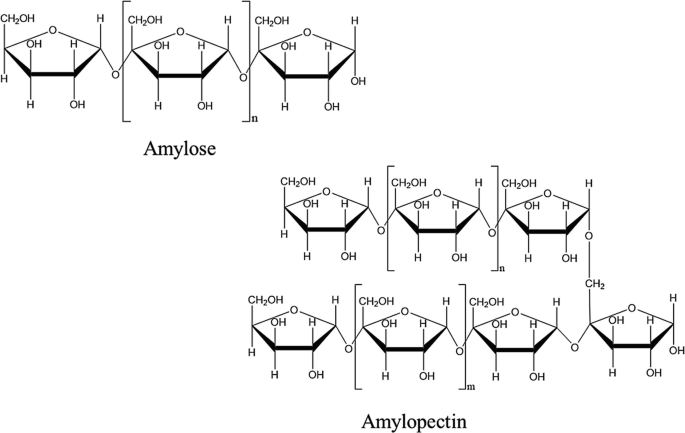
Starch
or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by α--D glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage
33
New cards
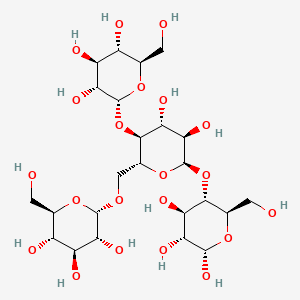
Glycogen
a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. It is the main storage form of glucose in the human body
34
New cards
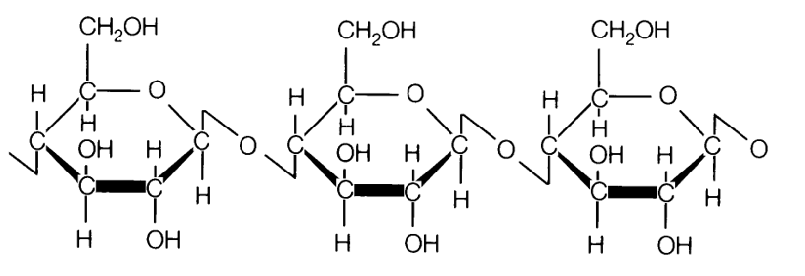
Celluslose
is an organic compound with the formula ₙ, a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β linked D-glucose units
35
New cards
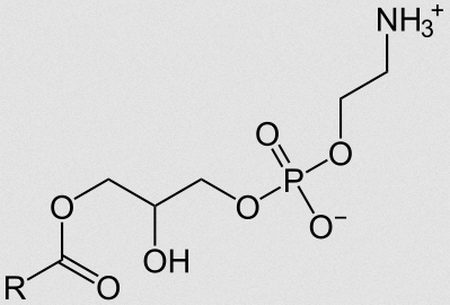
Lipids
are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins, monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others
36
New cards
Fats
any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
37
New cards
Phospholipid
are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue.
38
New cards
Steroid
have a ring structure. Although they do not resemble other lipids, they are grouped with them because they are also hydrophobic.
39
New cards
Saturated Fatty Acid
are saturated with hydrogen; in other words, the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon skeleton is maximized.
40
New cards
Unsaturated Fatty Acid
are a component of the phospholipids in cell membranes and help maintain membrane fluidity but not all of these can be synthesized in the bod
41
New cards
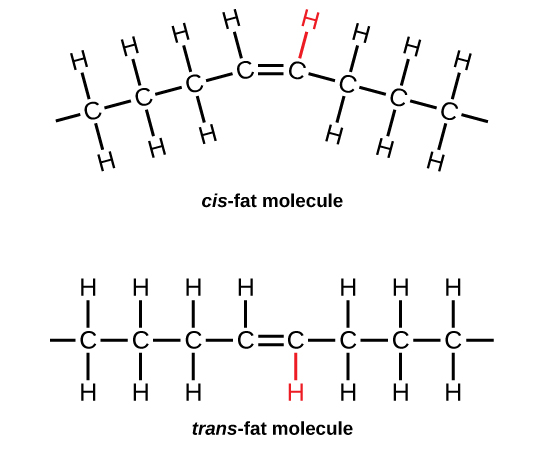
Trans Fatty Acid
orientation of the double bonds affects the chemical properties of the fat.s a type of unsaturated fat that occurs in foods. Trace concentrations of trans fats occur naturally, but large amounts are found in some processed food
42
New cards
Protein
a biological macromolecule composed of one or more chains of amino acids
43
New cards
Amino Acid
a monomer of a protein
44
New cards
Polypetide
a long chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds
45
New cards
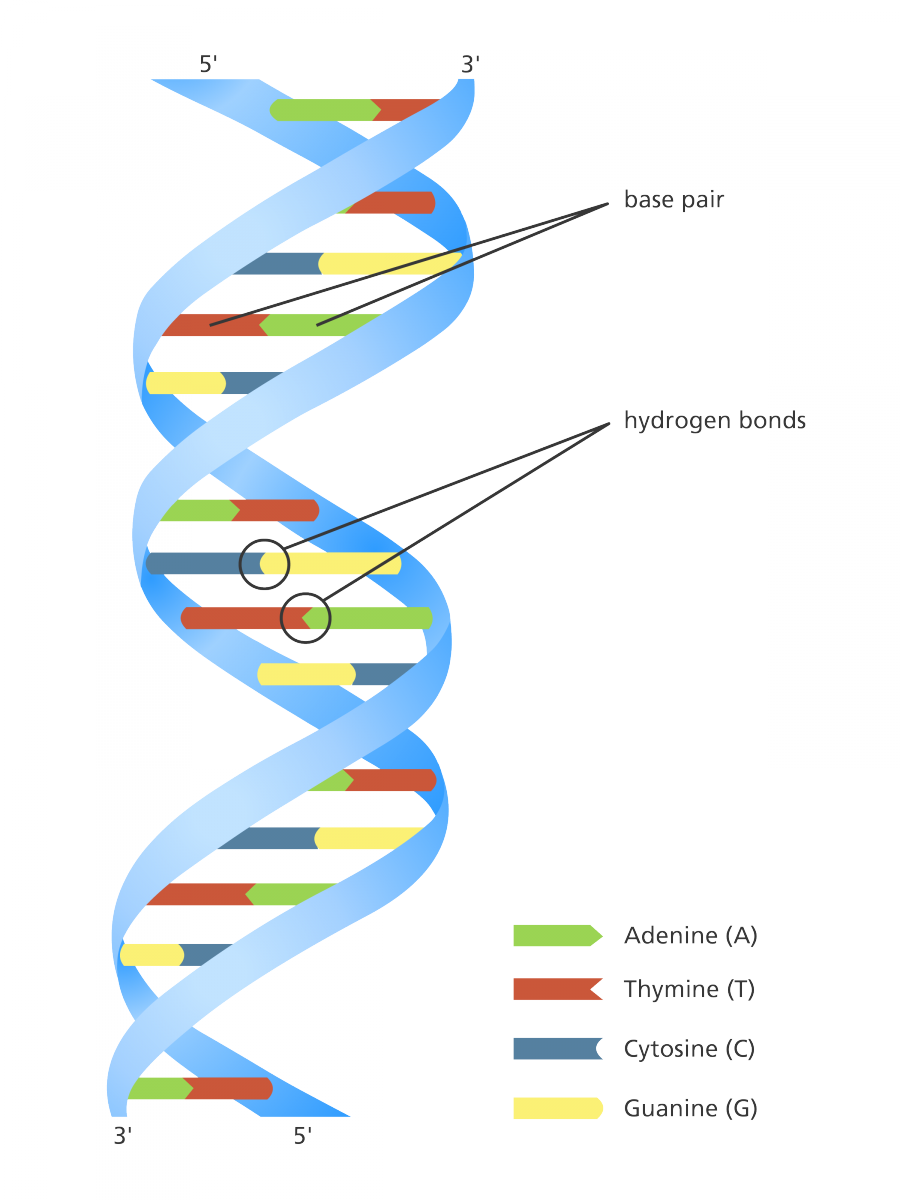
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
a double-stranded polymer of nucleotides that carries the hereditary information of the cell
46
New cards
ribonucleic acid(RNA)
a single-stranded polymer of nucleotides that is involved in protein synthesis
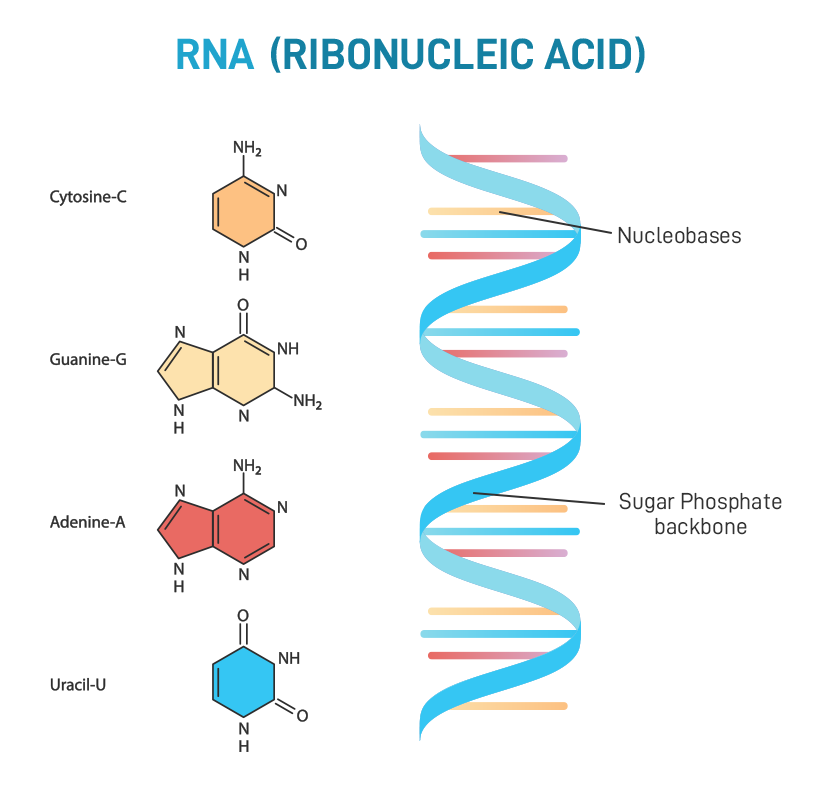
47
New cards
Nucleotide
a monomer of nucleic acids; contains a pentose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
48
New cards
Radioactive Isotope
an isotope that spontaneously emits particles or energy to form a more stable element.Used in
* Carbon dating
* Carbon dating