Body wall
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What are the 3 body cavities?
Thoracic
Abdominal
Pelvic
What are the five components of the abdominal cavity boundaries?
Diaphragm
Sternum
Caudal ribs
Lumbar vertebrae and fascia
Pelvis
Lumbodorsal fascia
deep fascia of the trunk
there are superficial and deep layers
Linea Alba
Ventral midline seam where tendonous sheets meet.
What do the abdominal muscles contain?
Viscera
How many abdominal muscles make up the lateral wall?
3
What do the abdominal muscles look like?
thin, sheet-like muscles
fibres run in different directions
Where do the abdominal muscles originate and insert?
Originate: lumbar vertebrae and fascia, caudal ribs, pelvis
Insert: ventral midline via tendonous sheets
Aponeurosis
Sheet of white tissue that takes the place of tendons in flat muscles to allow for a wider area of attachment
External abdominal oblique
most superficial
fibres run dorso-cranially to ventro-caudally
inserts on linea alba
Internal abdominal oblique
middle layer
fibres run dorso-caudally to ventro-cranially
inserts on linea alba
transversus abdominis
deep layer
fibres run dorso-laterally to ventro-medially
inserts on linea alba
rectus abdominis
ventral mid-line
runs in cranio-caudal direction
rib 1 and adjacent sternum to prepubic tendon
inserts on linea alba
what are the 2 peritoneal membranes?
parietal
visceral
Parietal peritoneum
lines the abdominal cavity
visceral peritoneum
covers the abdominal organs
peritoneal membrane properties
formed from lateral plate mesoderm
single cell thick serous membranes
produce peritoneal fluid - lubricates movement
potential space between 2 membranes is peritoneal cavity
What are the 2 roles of abdominal muscles?
static - supportive
dynamic - movement (respiratory, sneezing, coughing, vomiting, micturition, defecation, parturition, spinal flexion - rectus abdominis)
Heave-line
Line formed in an equine abdominal wall following chronic expiratory effort
What are the structures passing through the femoral canal?
psoas major
femoral a & v
femoral nerve
What are the structures passing through the inguinal canal in both sexes?
genitofemoral nerve
external pudendal artery and vein
caudal superficial epigastric artery and vein
What are the structures passing through the inguinal canal in a male only?
spermatic cord
cremaster muscle
What are the structures passing through the inguinal canal in a female only?
vaginal process
What is the clinical relevance of the inguinal canal?
Site of potential weakness in the muscle layers (especially in males)
breach results in an inguinal hernia
usually herniation of fat/gut
testicles can become lodged here during normal descent and must be surgically removed
What structure separates the abdominal and thoracic cavities?
diaphragm
Why do the muscle fibres run in different directions?
Makes the abdomen stronger
What is the origin and insertion of the thoracolumbar fascia?
Origin: Spinous processes of thoracic and lumbar vertebrae
Insertion: Fascia opposite the linea alba and caudal attachment to the ilium
What is the origin and insertion of the external abdominal oblique?
Origin: Middle of 4th to 12th rib and thoracolumbar fascia
Insertion: Linea alba and prepubic tendon
What is the action of the external abdominal oblique?
Supports the abdominal wall
What is the origin and insertion of the internal abdominal oblique?
Origin: Lumbar thoracolumbar fascia caudal to the last rib and the tuber coxae
Insertion: 12th and 13th rib and linear alba
What is the action of the internal abdominal oblique muscle?
Supports the abdominal wall
What is the origin and insertion of the transverse abdominis muscle?
Origin: 8th - 9th costal cartilage (last ribs), all lumbar transverse processes and tuber coxae
Insertion: linea alba
From and to where does the Linea alba run?
From xiphoid cartilage to cranial end of pelvic symphysis via prepubic tendon
What is the origin and insertion of rectus abdominis?
Origin: Cranial sternum and first costal cartilage
Insertion: Pecten ossis pubis
What is the action of the rectus abdominis?
Support and compression of abdominal viscera
Helps with expiration, urination, defecation, parturition etc.
Falciform ligament
Vertebral attachment of the liver
runs down to the umbilicus
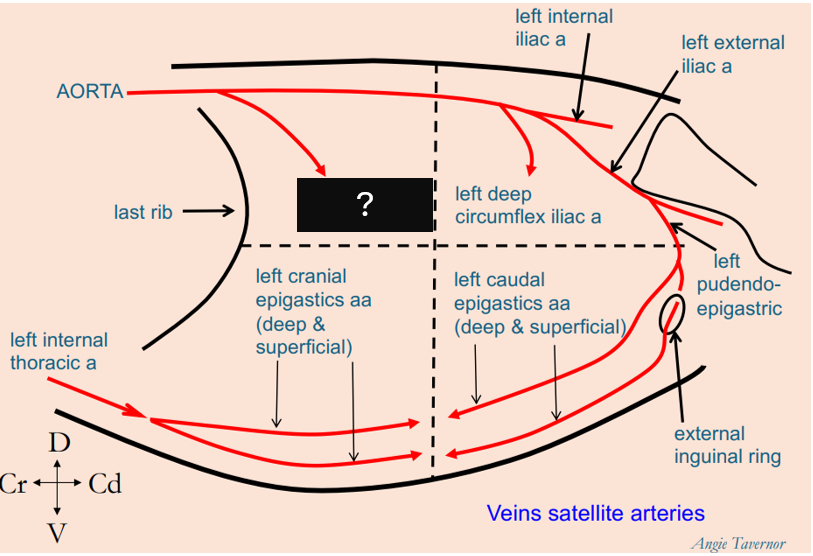
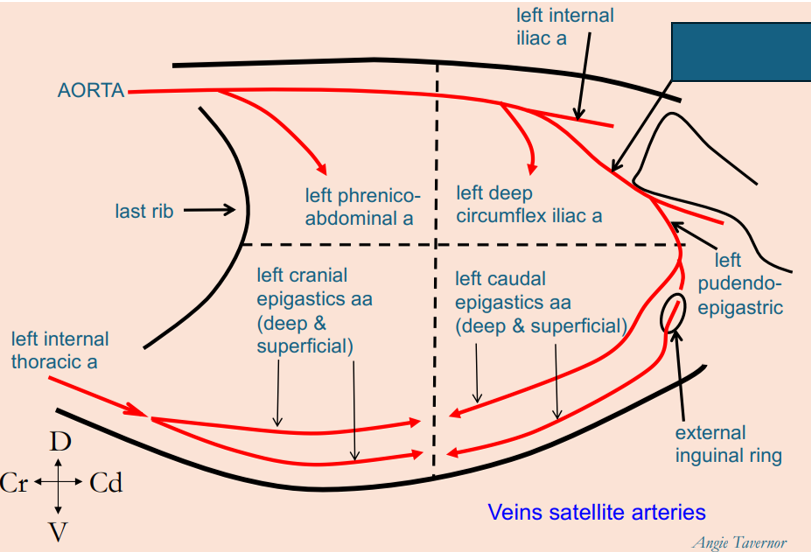
What artery penetrates the craniodorsal abdominal quadrant?
left phrenico-abdominal artery
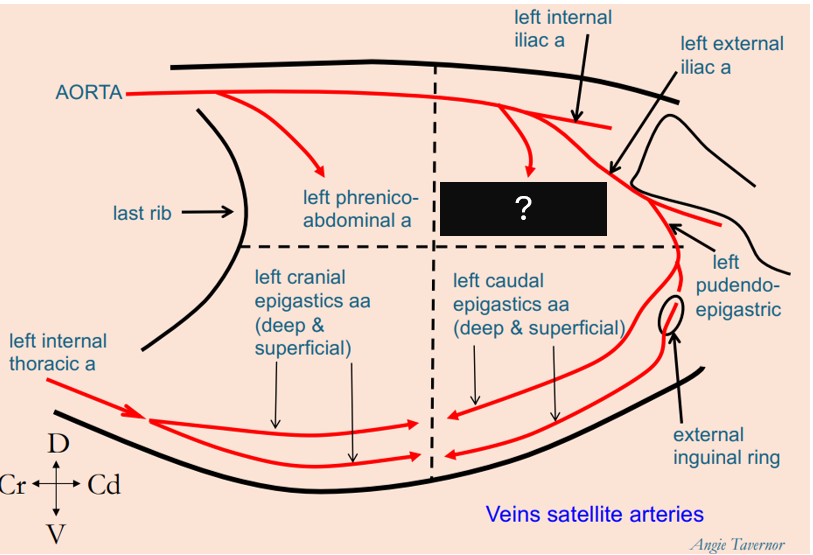
What artery penetrates the caudodorsal abdominal quadrant?
left deep circumflex iliac artery
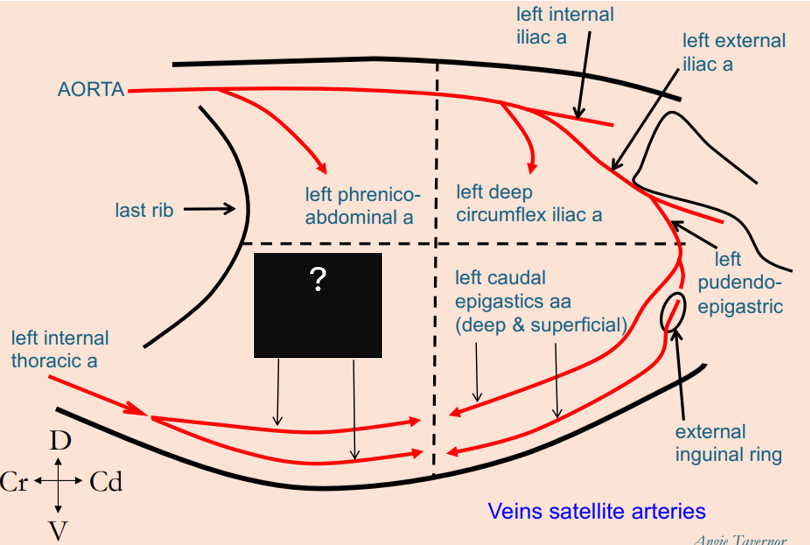
What arteries penetrate the cranioventral abdominal quadrant?
deep and superficial left cranial epigastric arteries

What arteries penetrate the caudoventral abdominal quadrant?
deep and superficial left caudal epigastric arteries
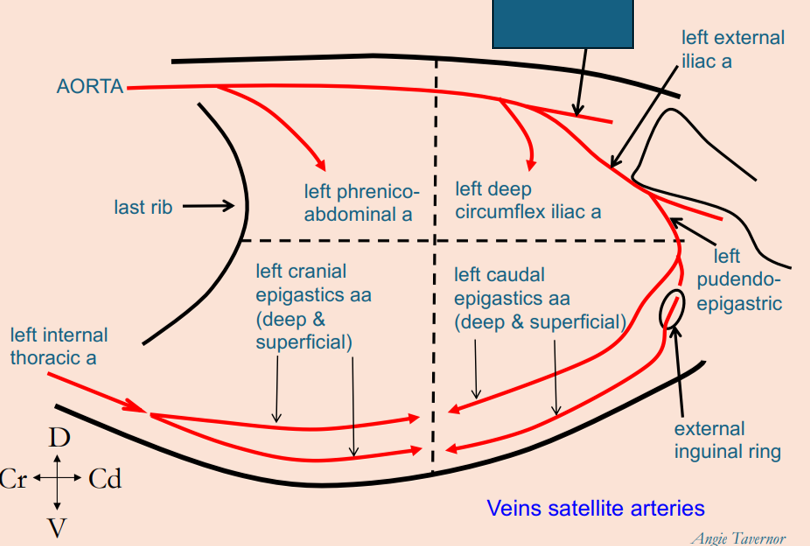
What artery is this?
left internal iliac artery
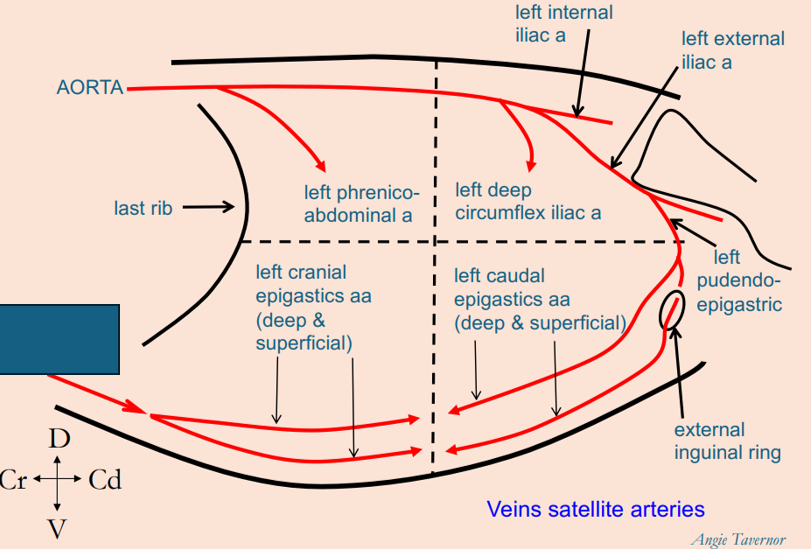
What artery is this?
left external iliac artery
What artery is this?
left internal thoracic artery
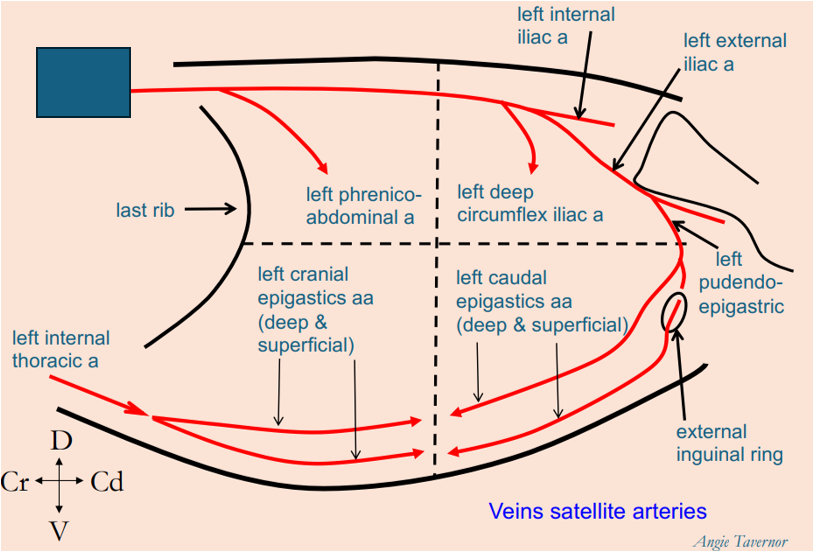
What artery is this?
Aorta
What 3 structures lie within the femoral sheath?
Femoral artery
Femoral vein
Saphenous nerve
Where is the femoral canal located?
Slit like space between the femoral vein and pectineus muscle
Function of the femoral canal
allow femoral vein to expand during increased venous return
contains mainly loose connective tissue and lymphatics - no major vessels
Inguinal ligament
Thick fibrous band formed by aponeurosis of the caudal edge of external abdominal obliques