Chapter 15: The Cardiovascular System: Blood
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
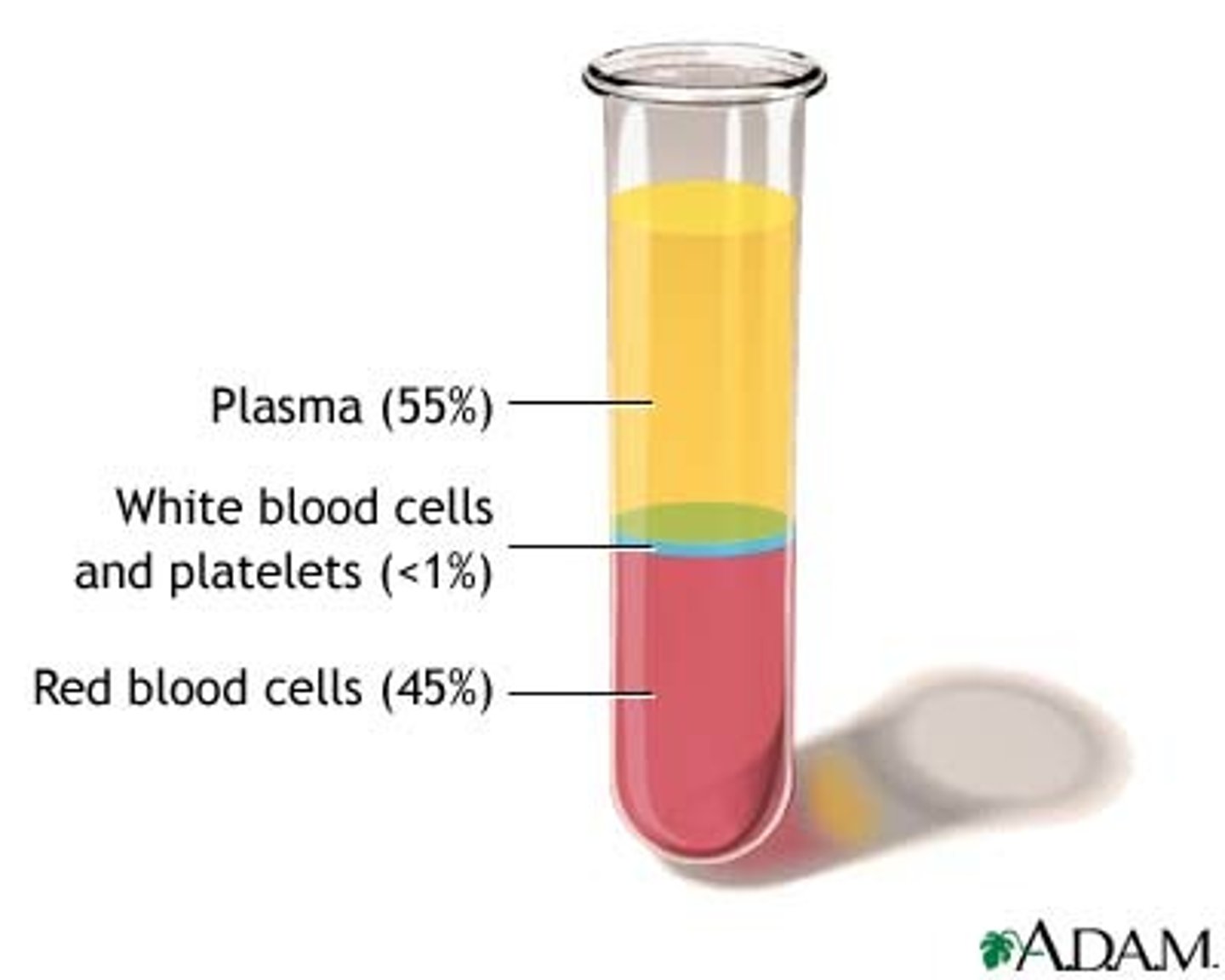
plasma
liquid portion of blood
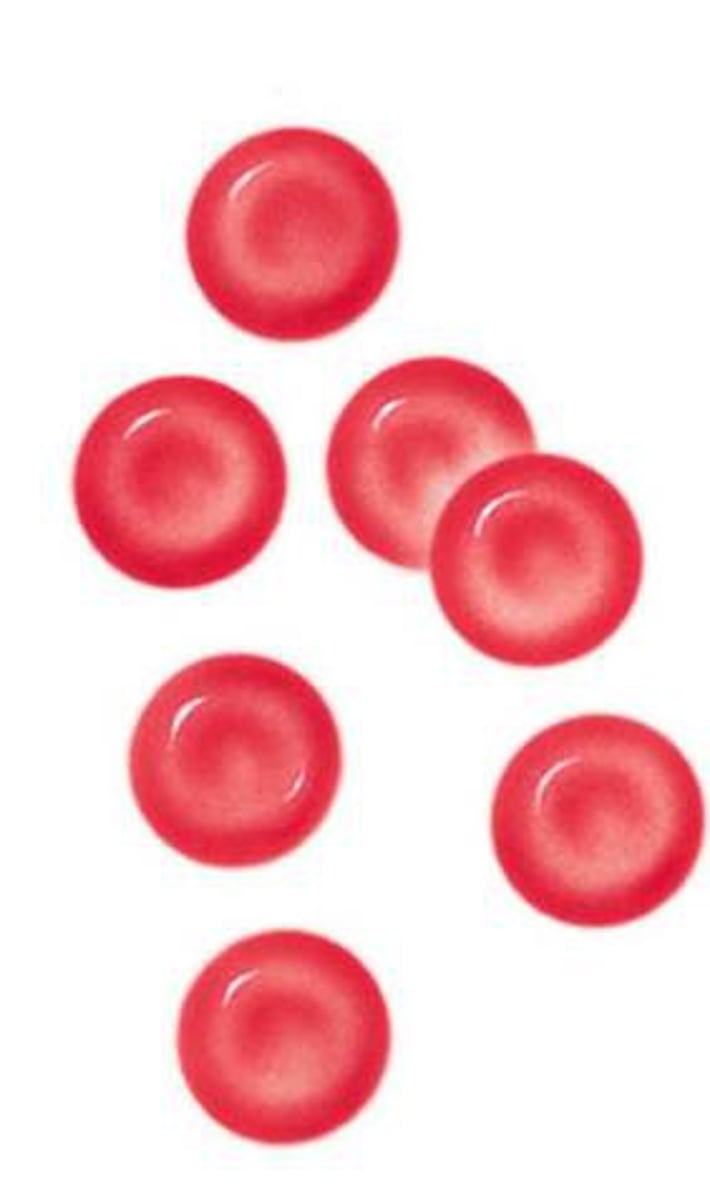
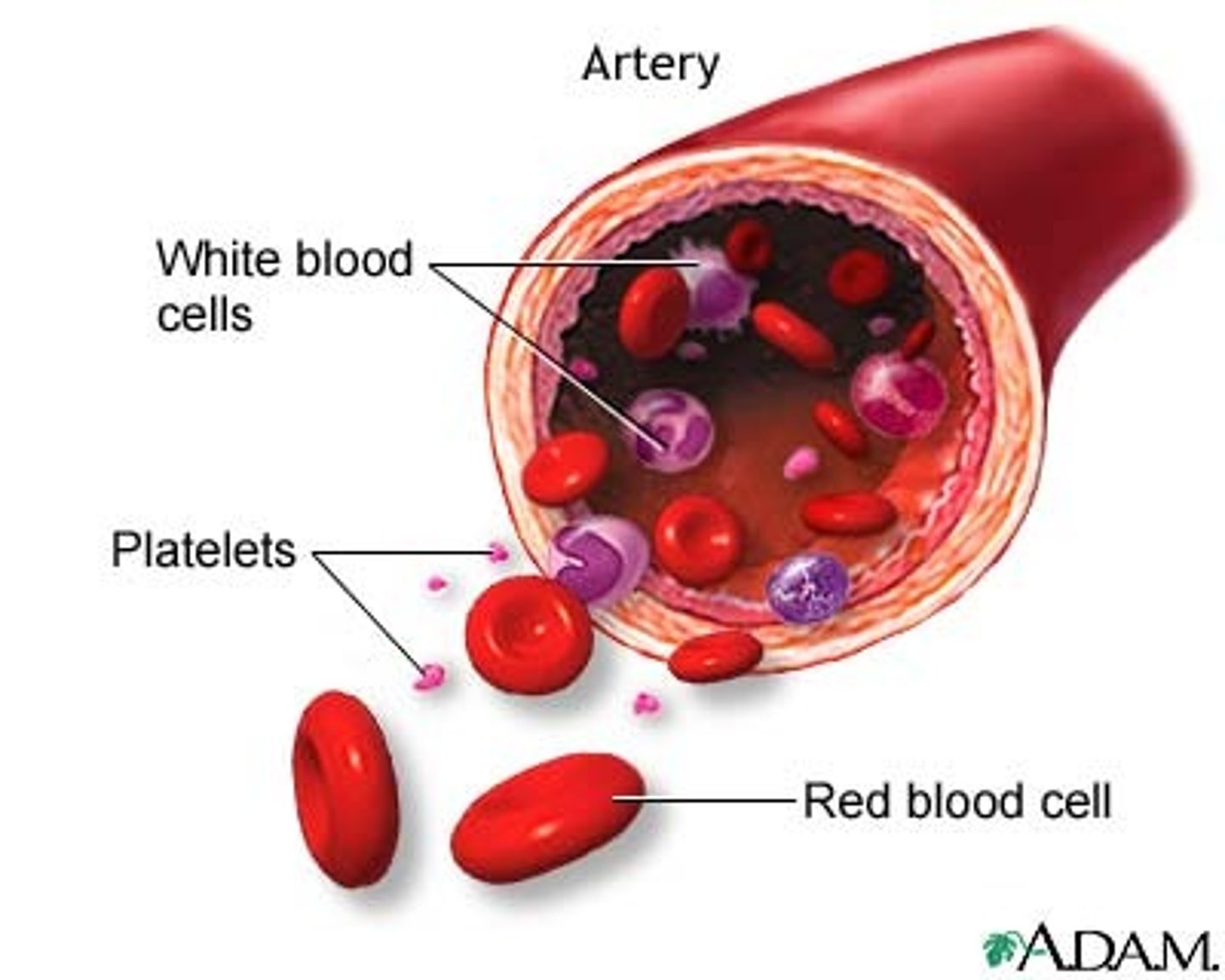
erythrocytes
red blood cells
leukocytes
white blood cells
platelets
a small colorless disk-shaped cell fragment without a nucleus, found in large numbers in blood and involved in clotting
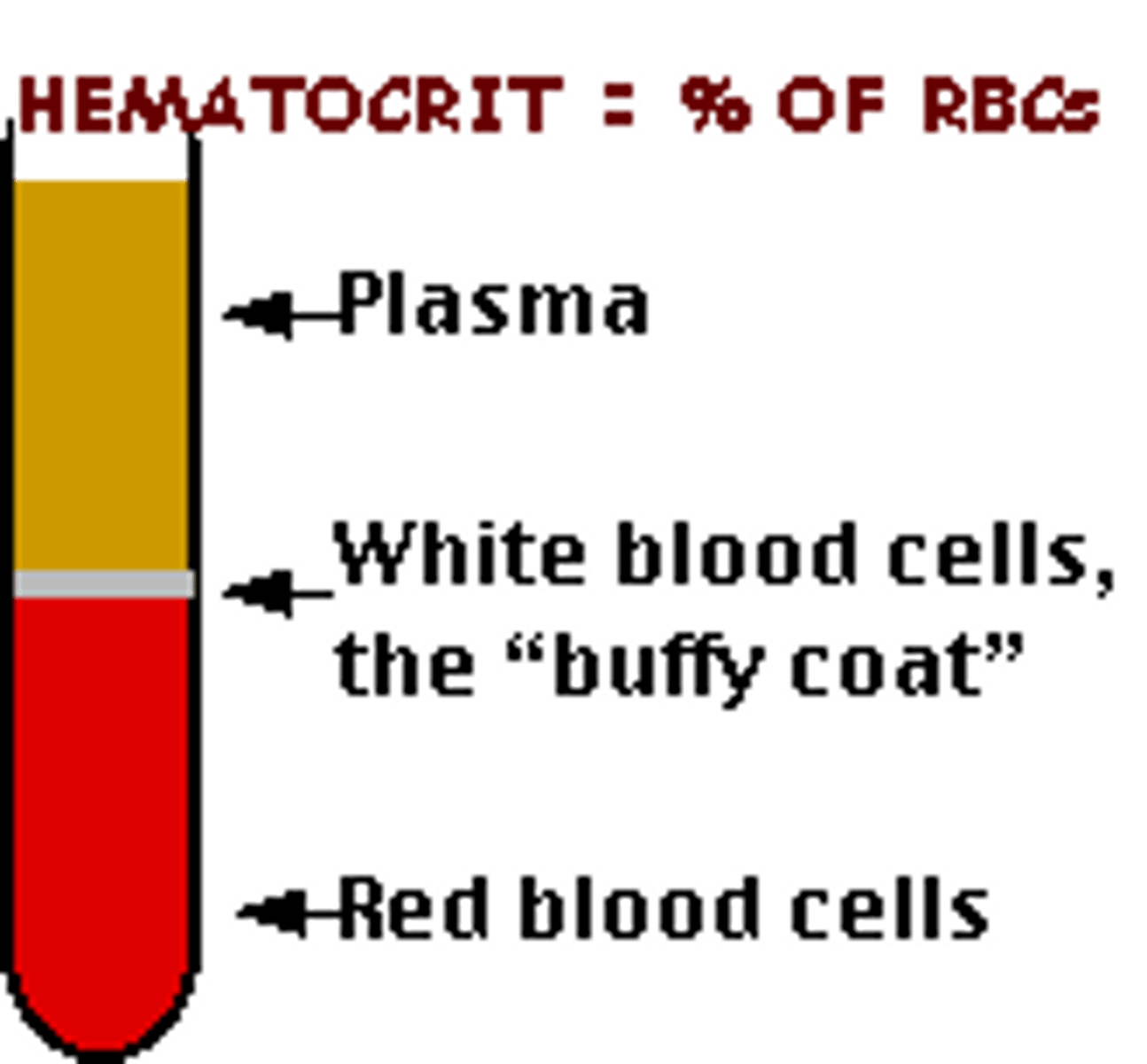
hematocrit (Hct) or packed cell volume (PCV)
percentage of erythrocytes in a volume of blood
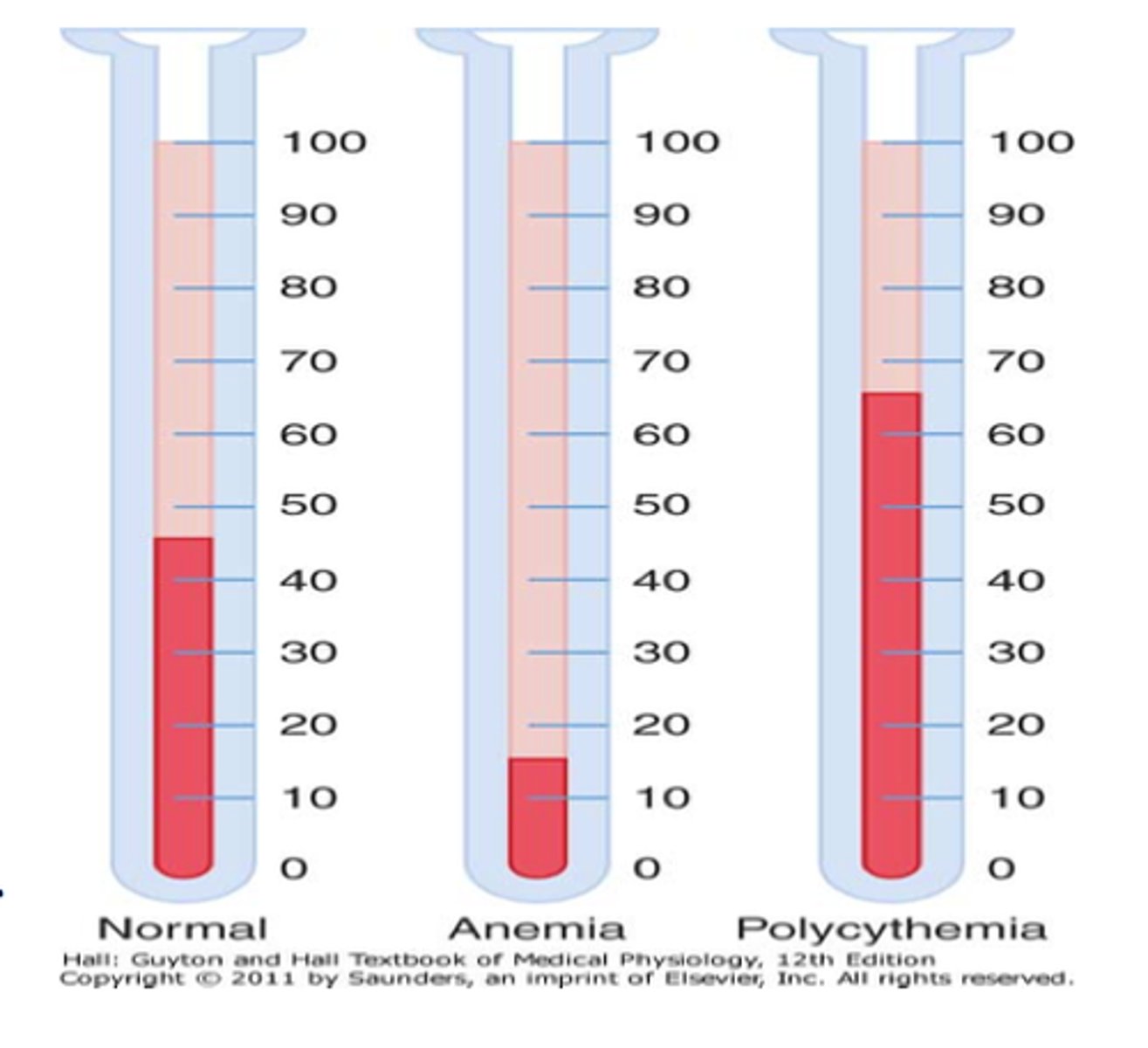
anemia
lack of a normal number of red blood cells
polycythemia
A disorder characterized by an abnormal increase in the number of red blood cells in the blood
blood osmotic pressure
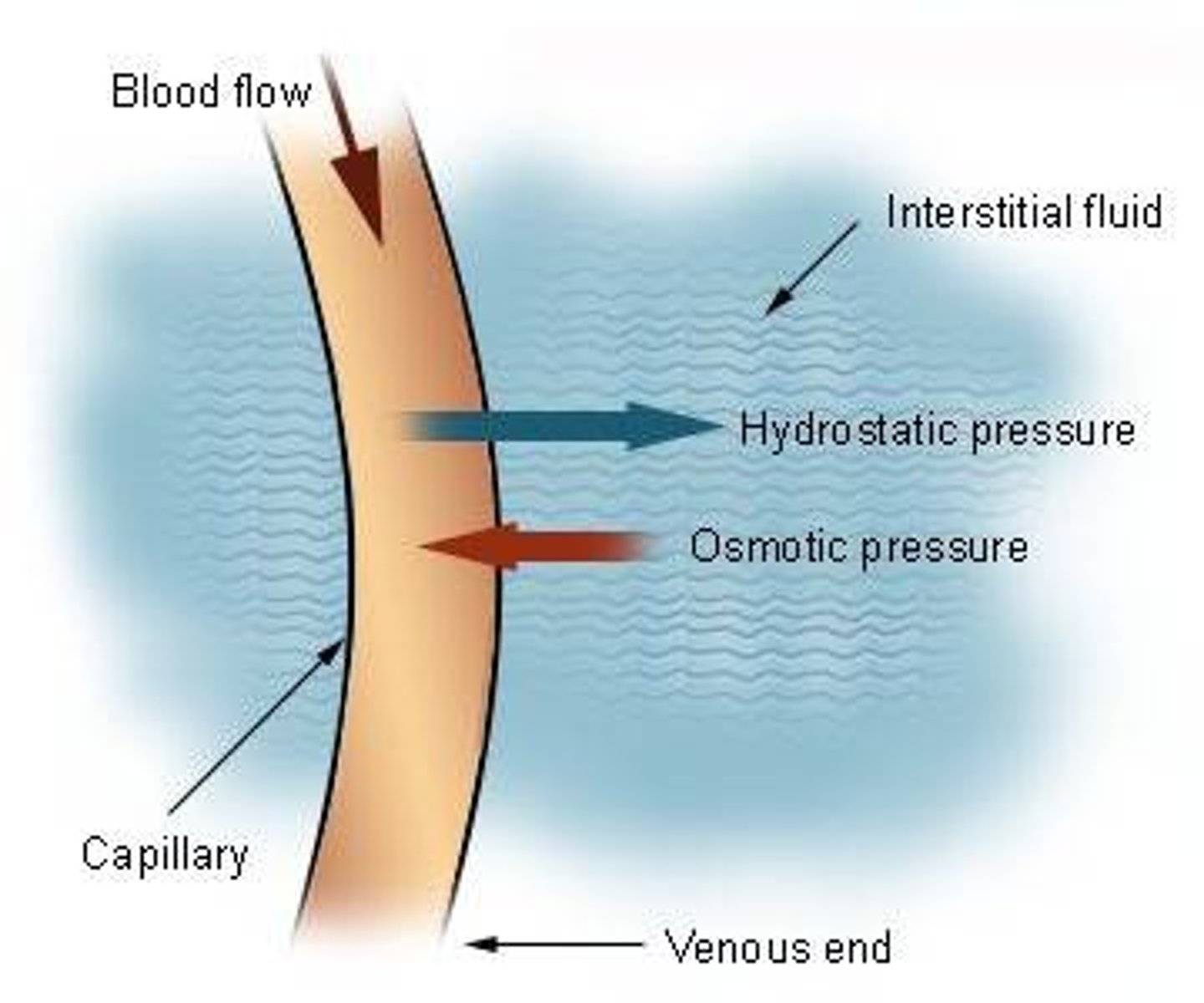
a force caused by the colloidal suspension of large proteins in plasma. This pressure pulls fluid from interstitial spaces into the capillary bed. High blood osmotic pressure will cause water to be taken out of the cells, into the interstitial fluid, and then into the blood plasma.
blood viscosity
The thickness and stickiness of the blood due to formed elements and plasma proteins.
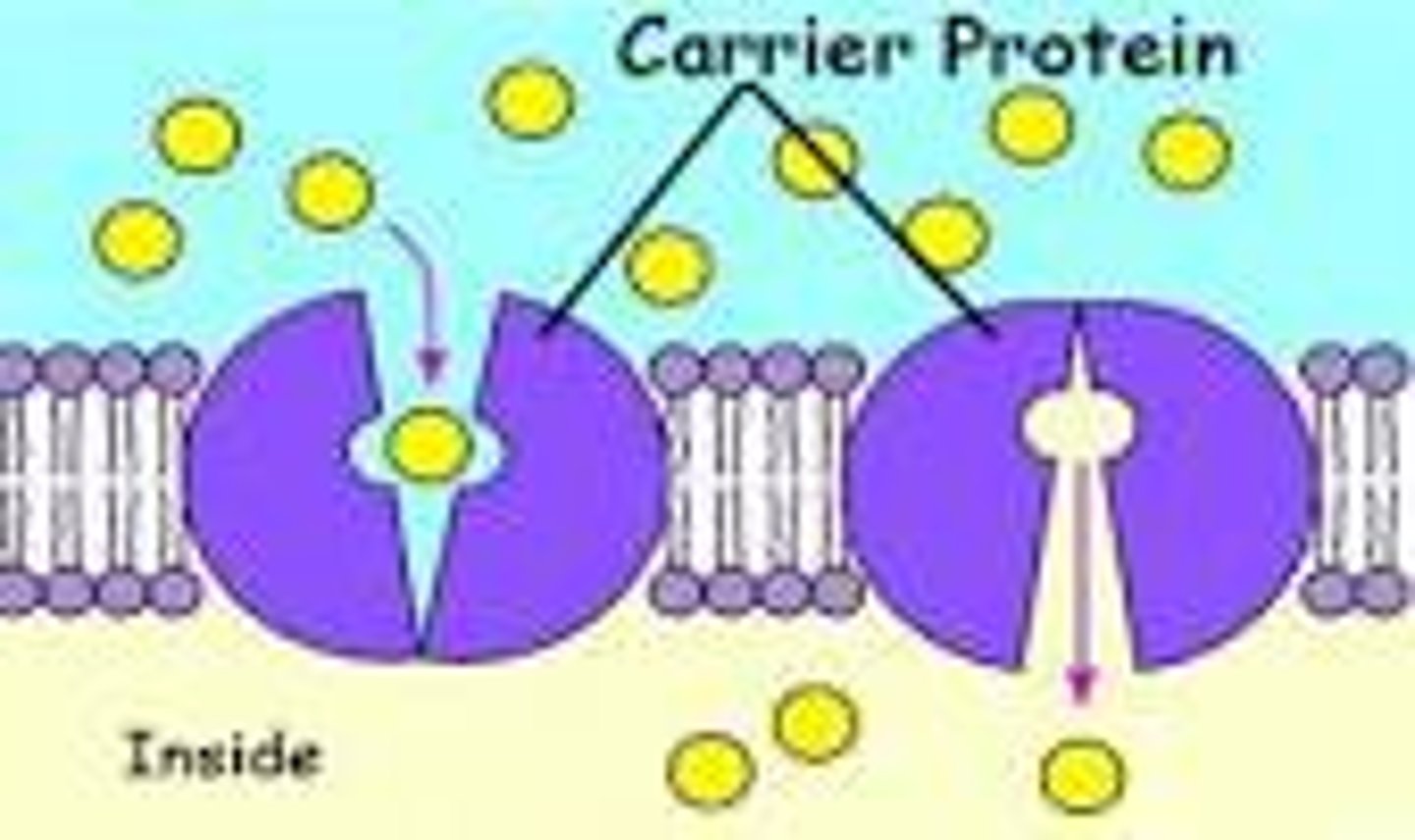
carrier proteins
a protein that transports substances across a cell membrane
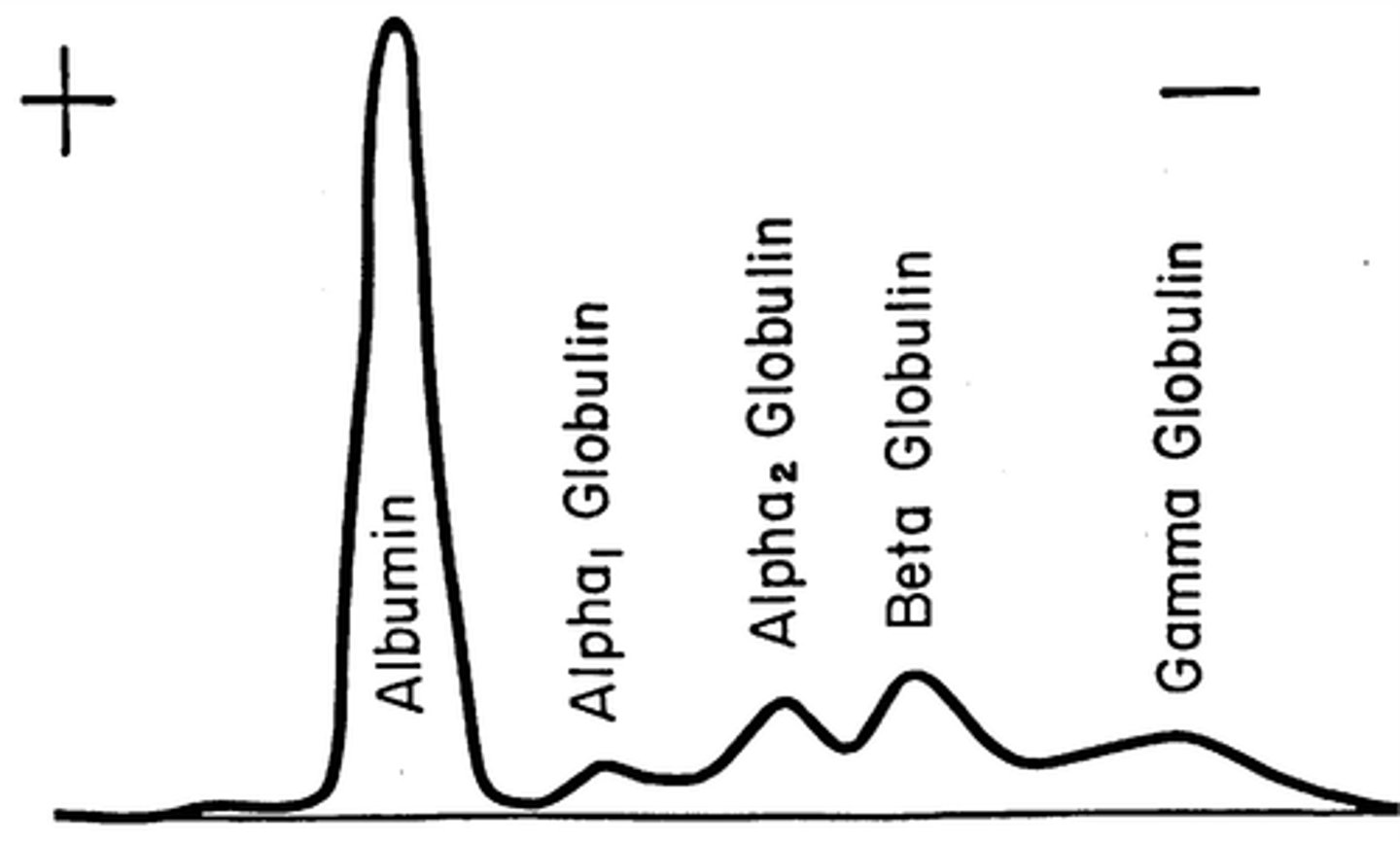
albumins
Transport fatty acids and steroids, help regulate osmotic pressure of the blood.

globulins
alpha, beta, gamma
fibrinogen
plasma protein that is converted to fibrin in the clotting process
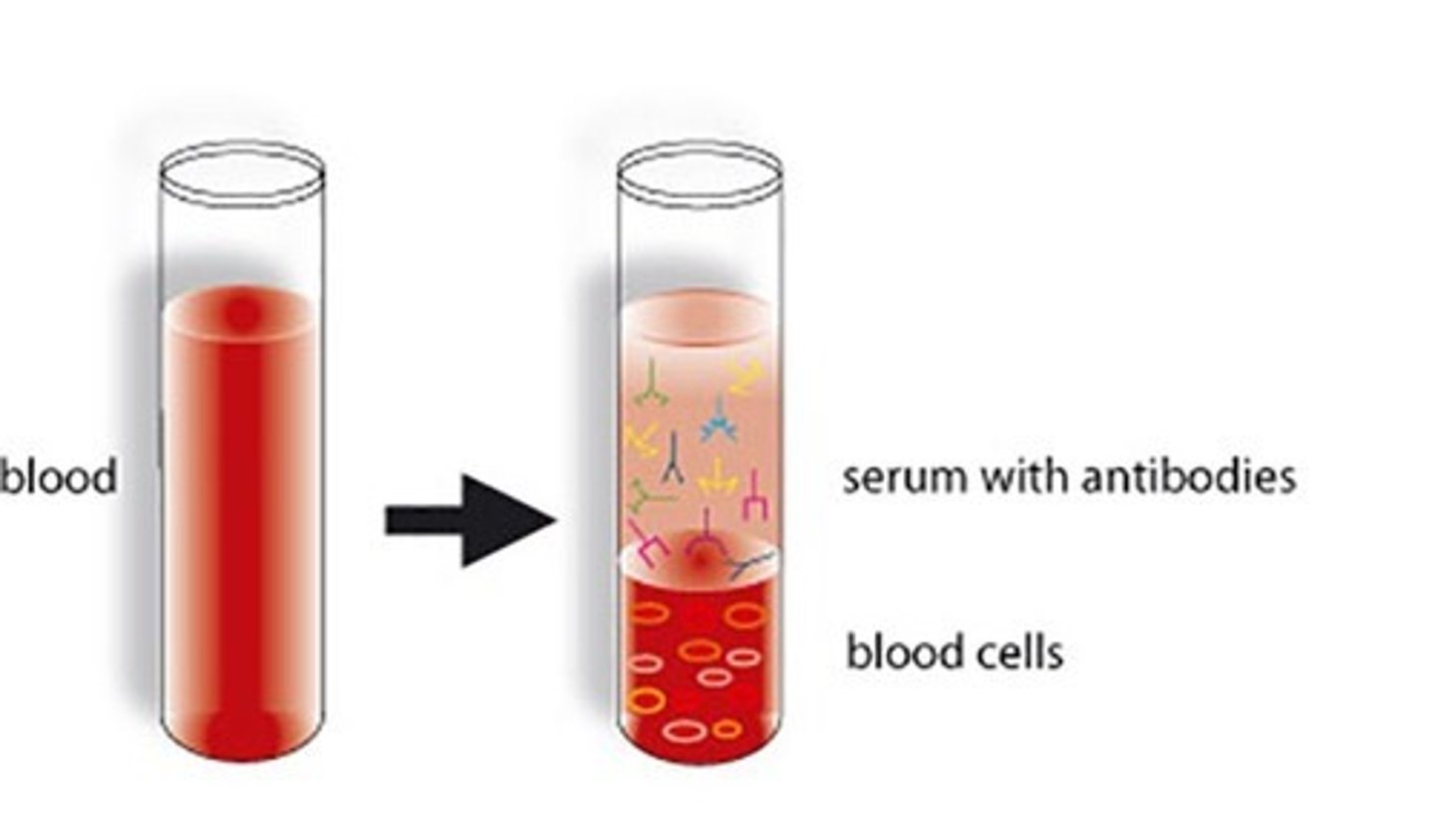
serum
plasma without clotting factors
biconcave disk
shape of red blood cell
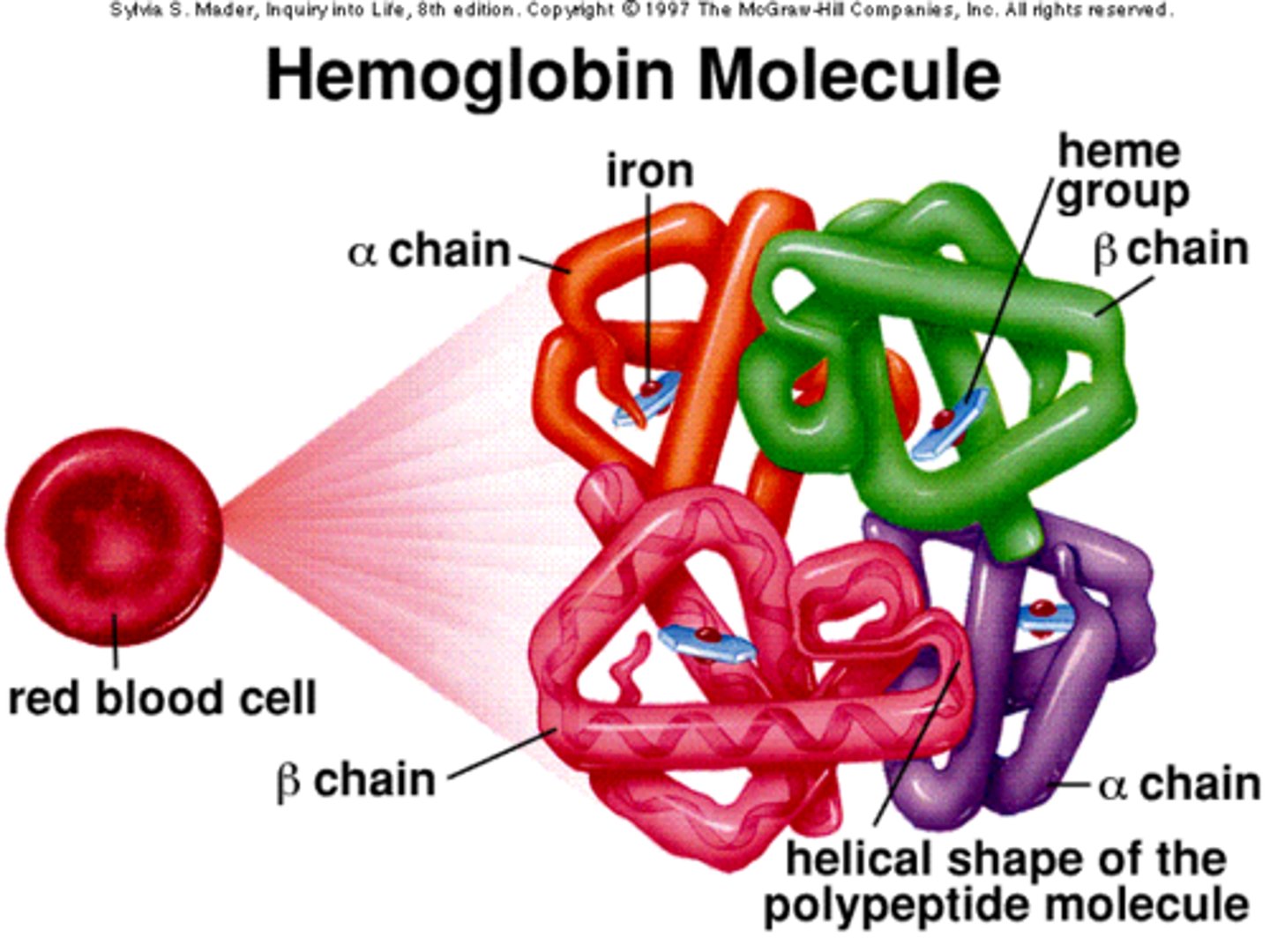
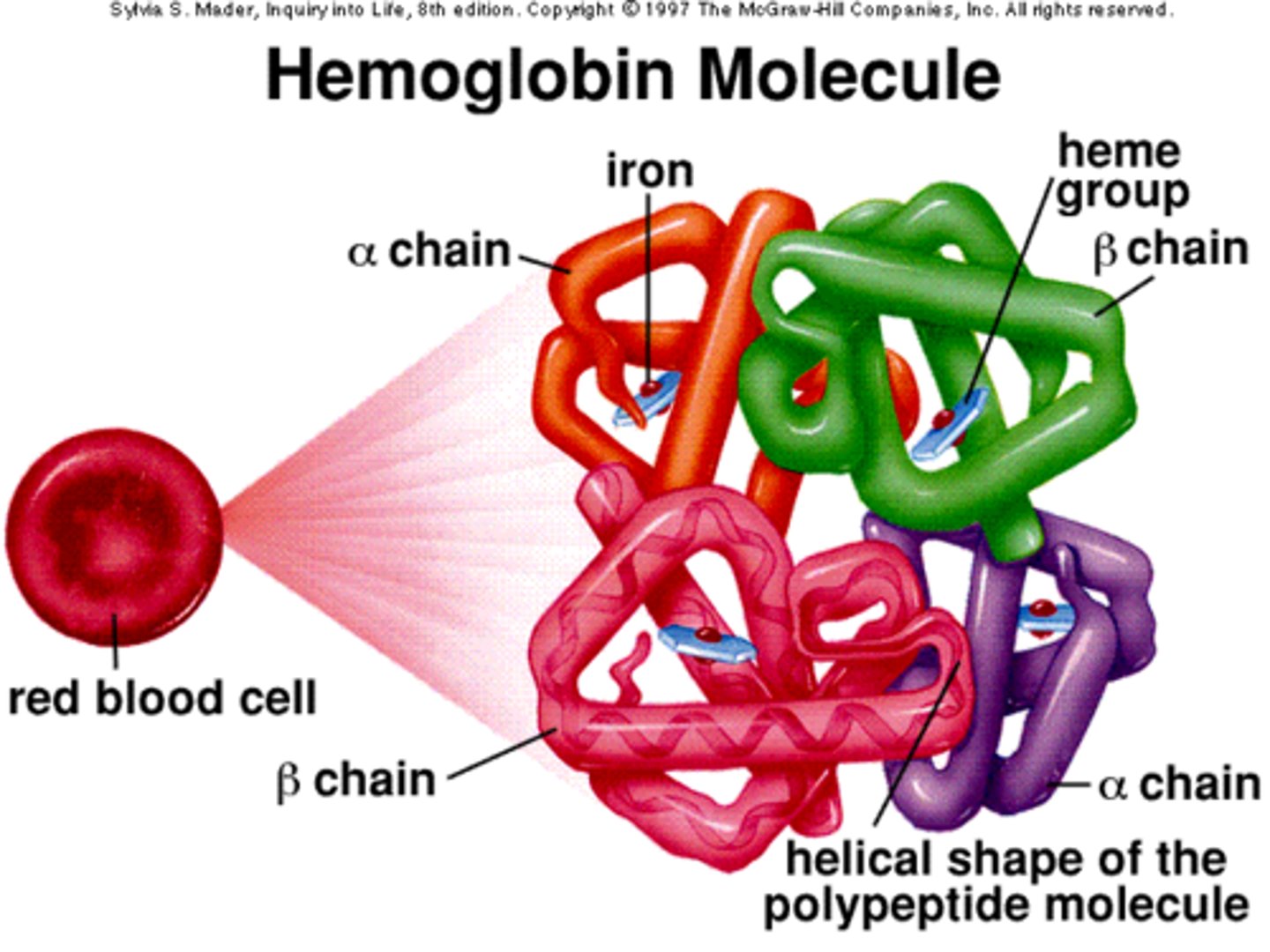
hemoglobin
Oxygen carrying pigment in red blood cells
carbonic anhydrase
enzyme that catalyzes the reaction between carbon dioxide and water to form carbonic acid
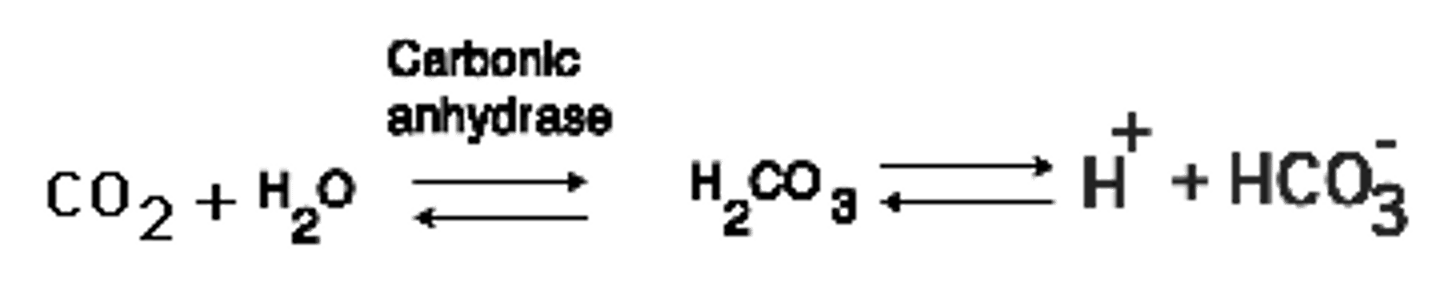
central pallor
the central pale area of an RBC that represents the thinnest part of the biconcave disc
heme group
iron-containing structures on hemoglobin, the sites of oxygen binding
erythropoiesis
production of red blood cells
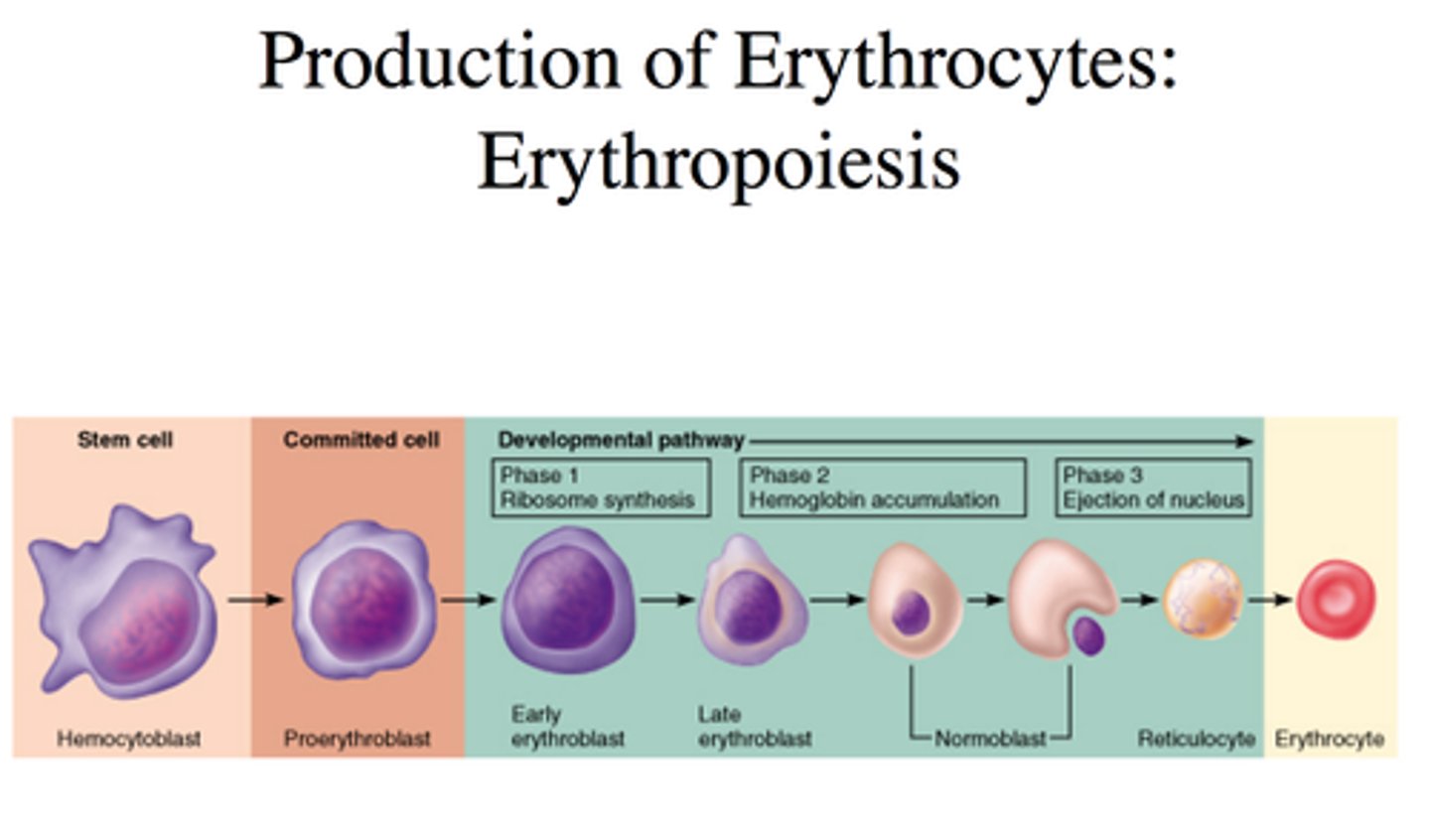
hematopoietic stem cells
bone marrow
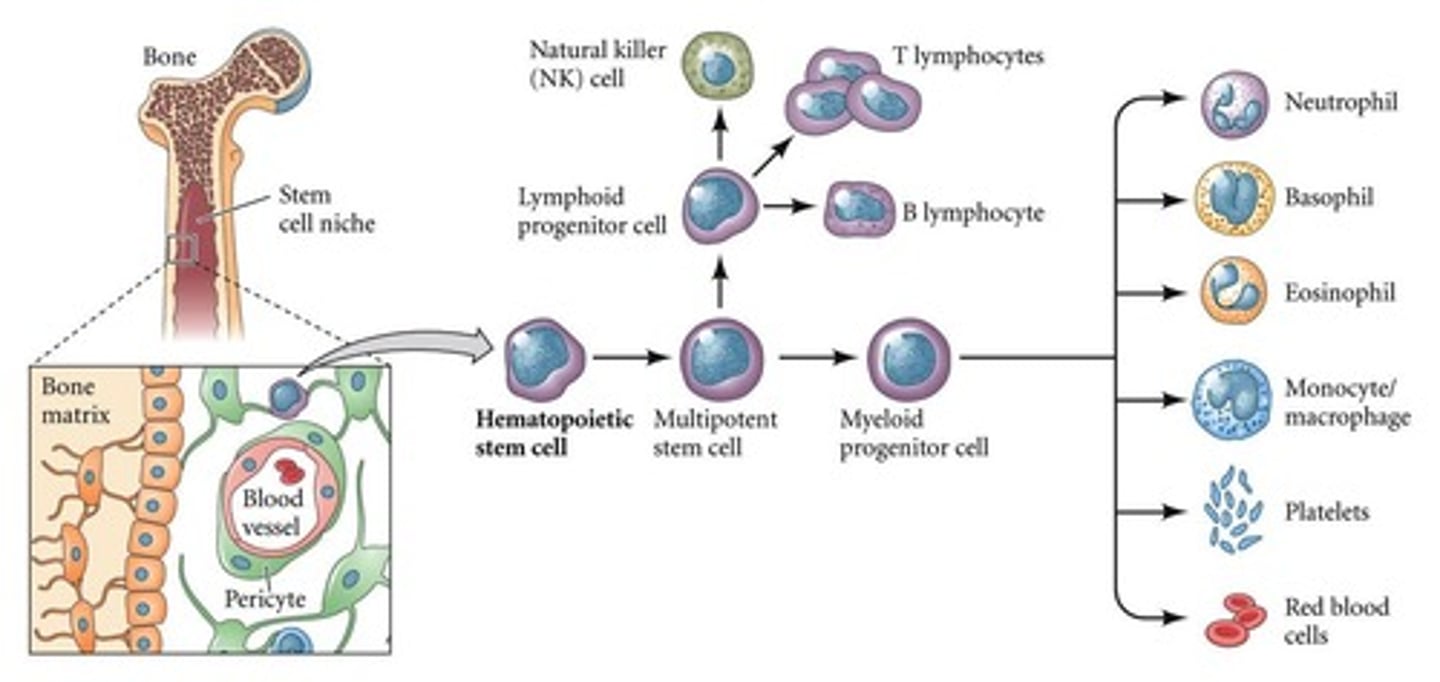
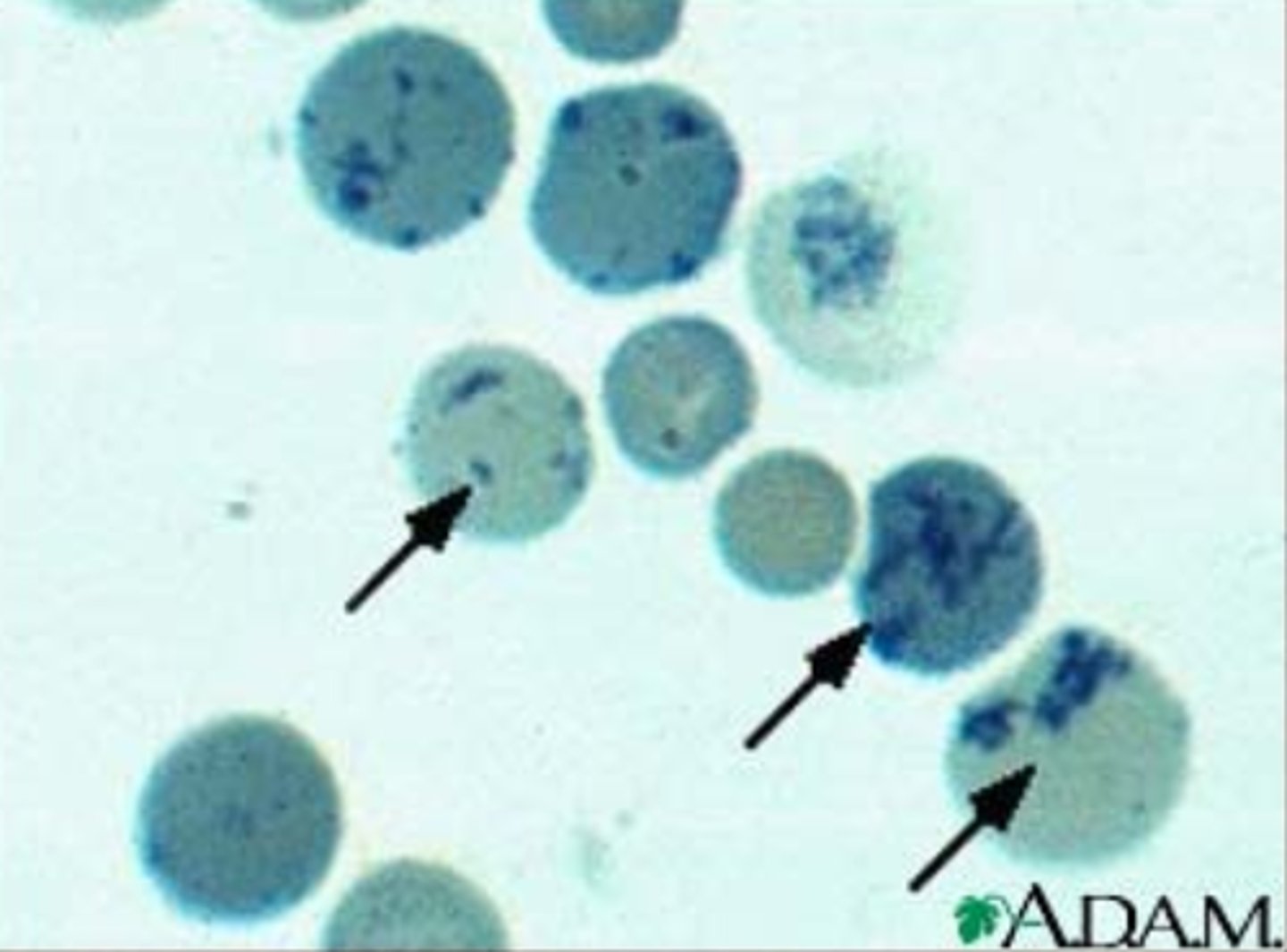
reticulocytes
immature red blood cells
Vitamin B12
Cyanocobalamin
folic acid
A nutrient in the vitamin B complex that the body needs in small amounts to function and stay healthy. Folic acid helps to make red blood cells
hemolysis
destruction of red blood cells
bilirubin
pigment released by the liver in bile
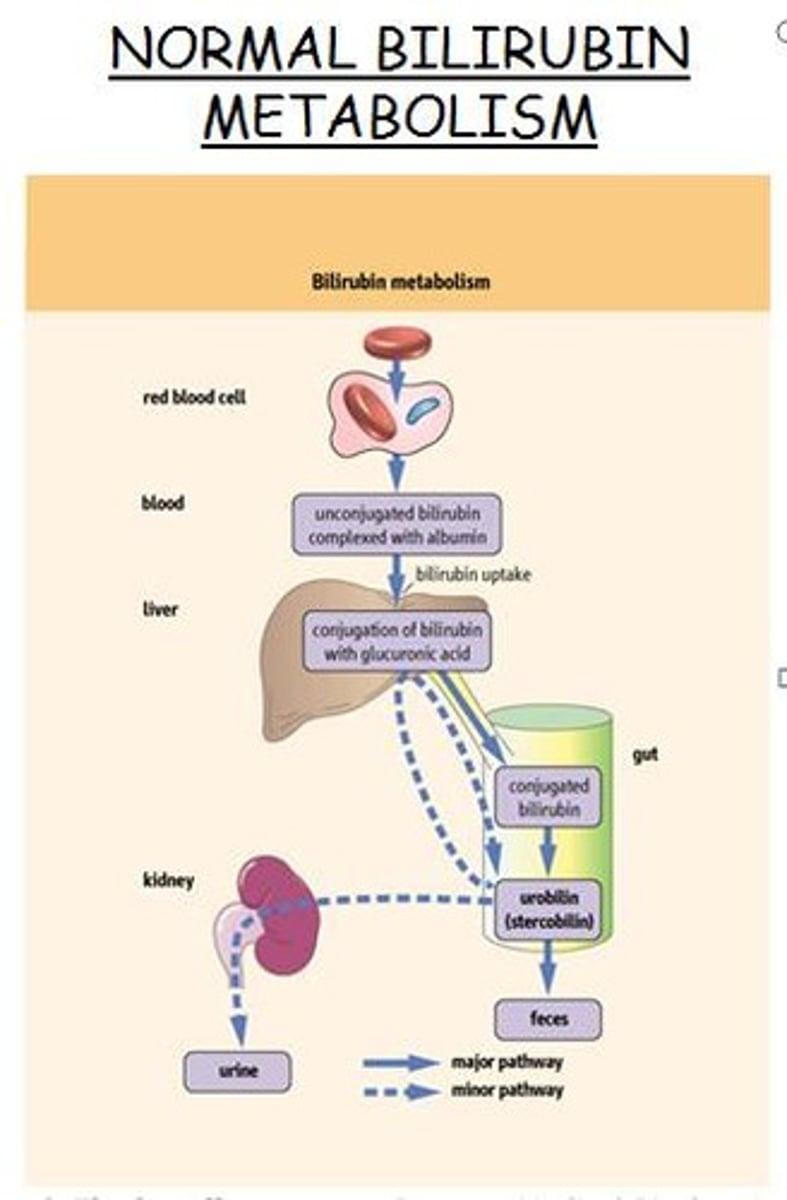
bile
A substance produced by the liver that breaks up fat particles.
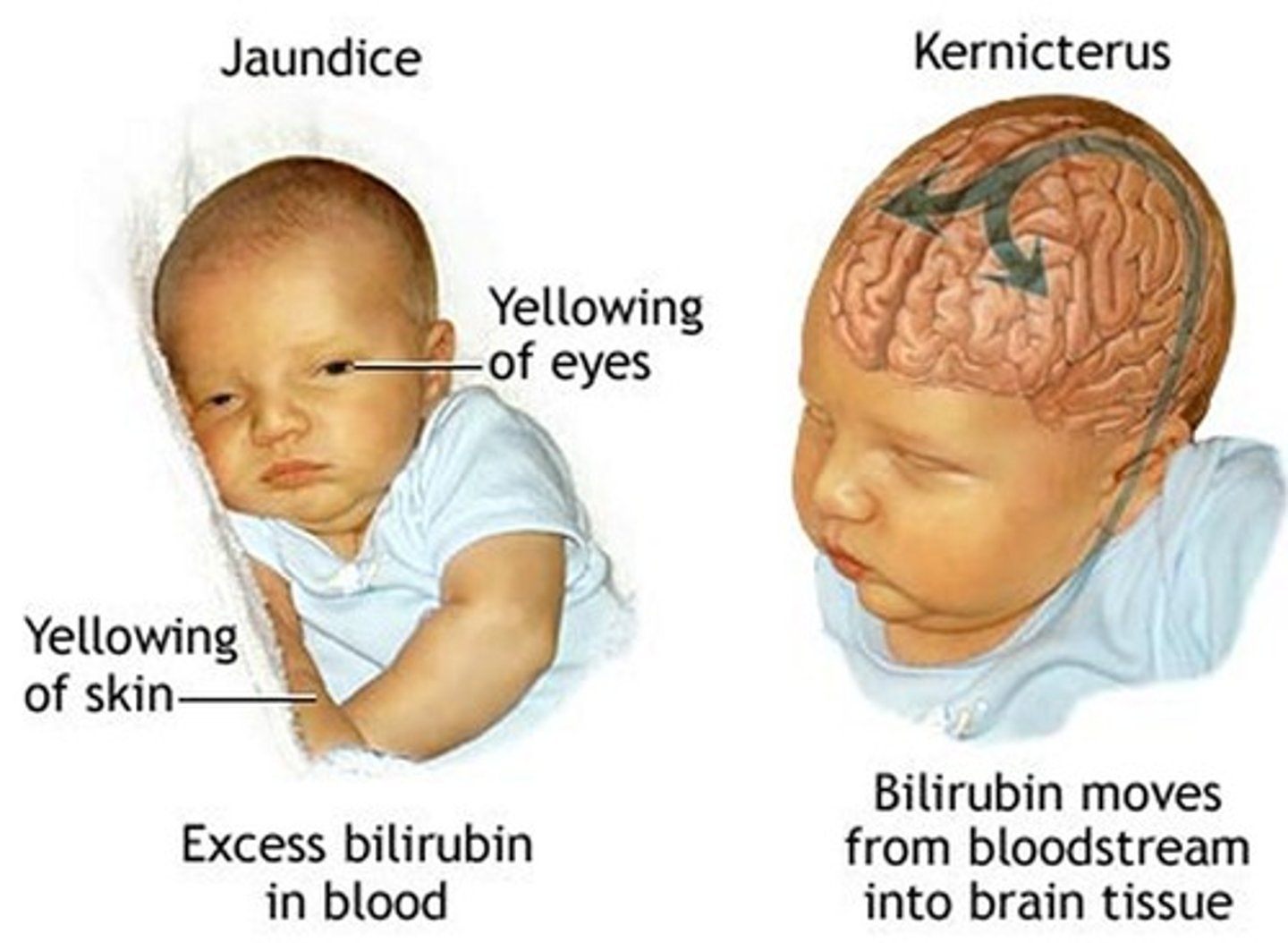
jaundice (icterus)
yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes caused by an accumulation of bile pigment (bilirubin) in the blood
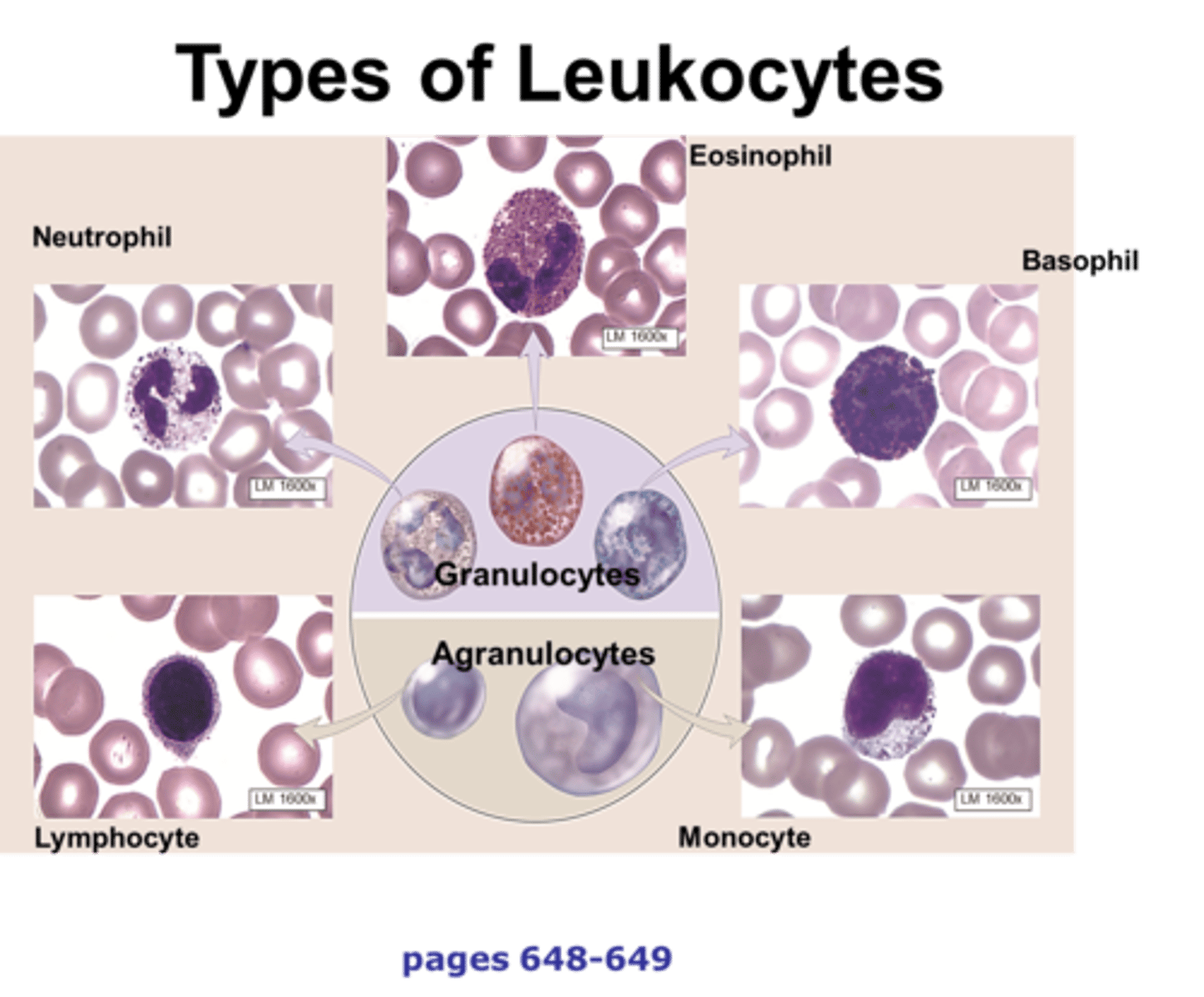
granulocytes
A group of leukocytes containing granules in their cytoplasm; neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils.
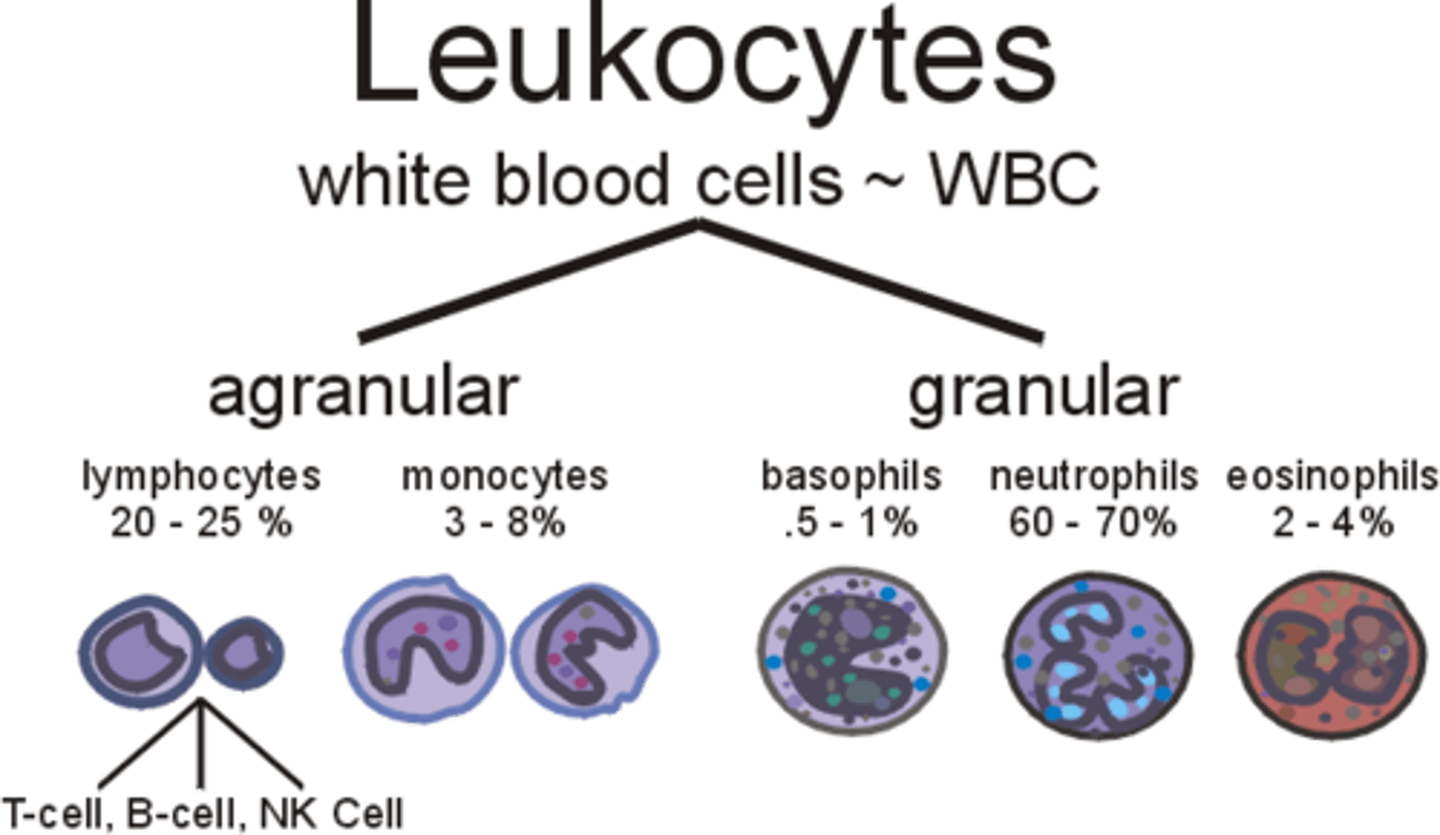
agranulocytes
A group of leukocytes without granules in their nuclei; lymphocytes, monocytes.
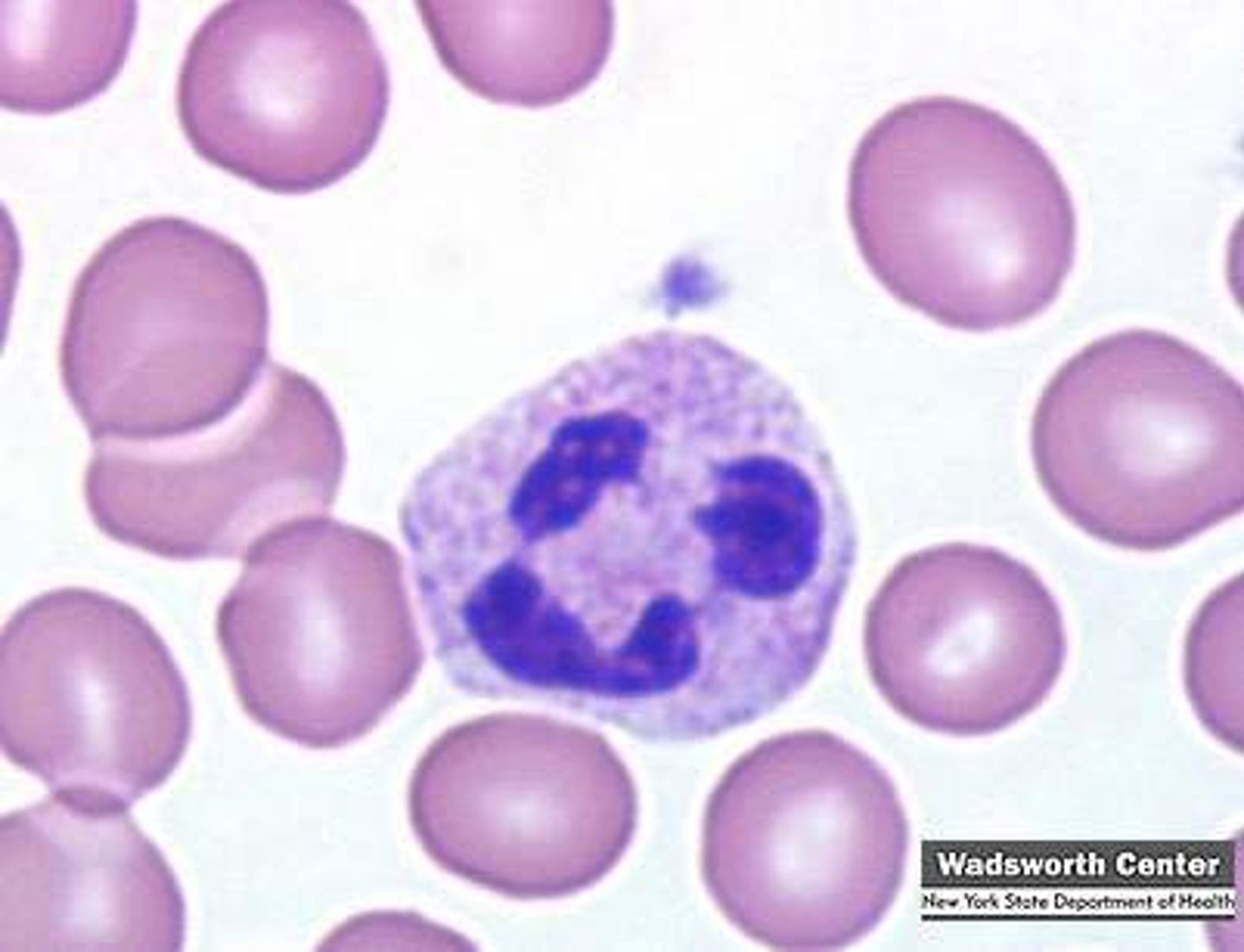
neutrophils
A type of white blood cell that engulfs invading microbes and contributes to the nonspecific defenses of the body against disease.
phagocytes
A type of white blood cell that ingests invading microbes

eosinophils
a white blood cell containing granules that are readily stained by eosin.
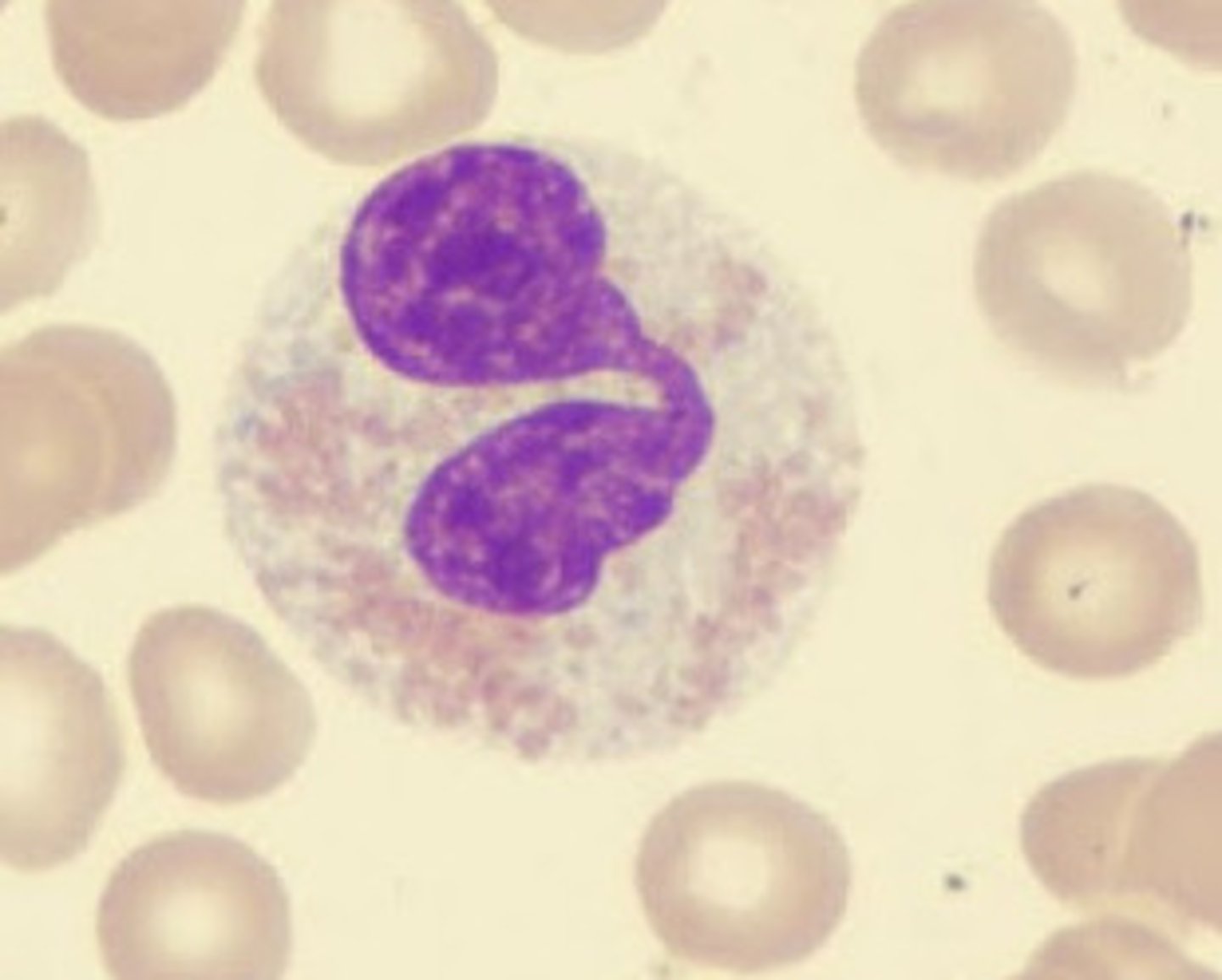
basophils
A circulating leukocyte that produces histamine.
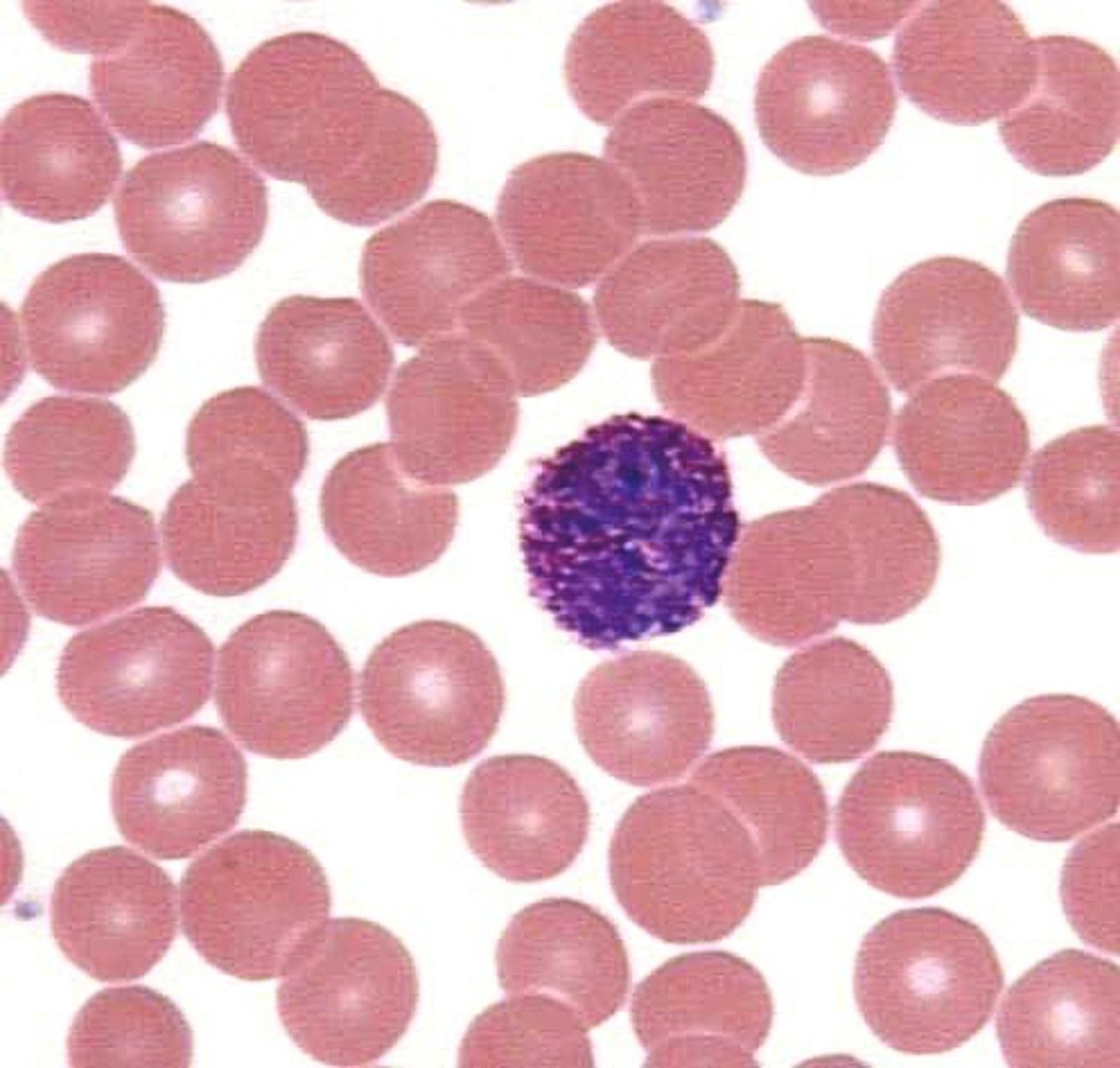
monocytes
An agranular leukocyte that is able to migrate into tissues and transform into a macrophage.
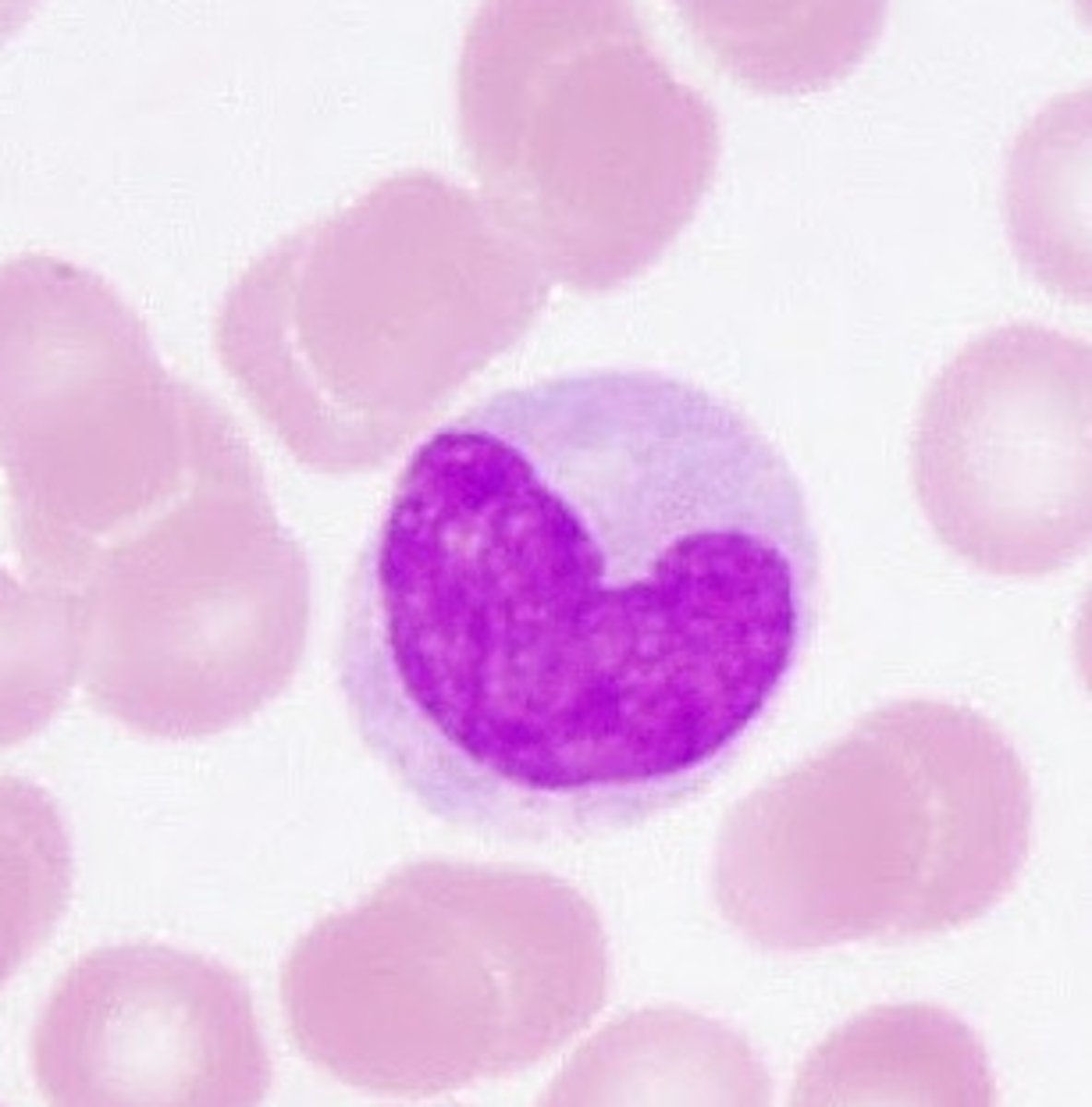
macrophages
Amoeboid cells that roam connective tissue and engulf foreign particles and debris of dead cells.
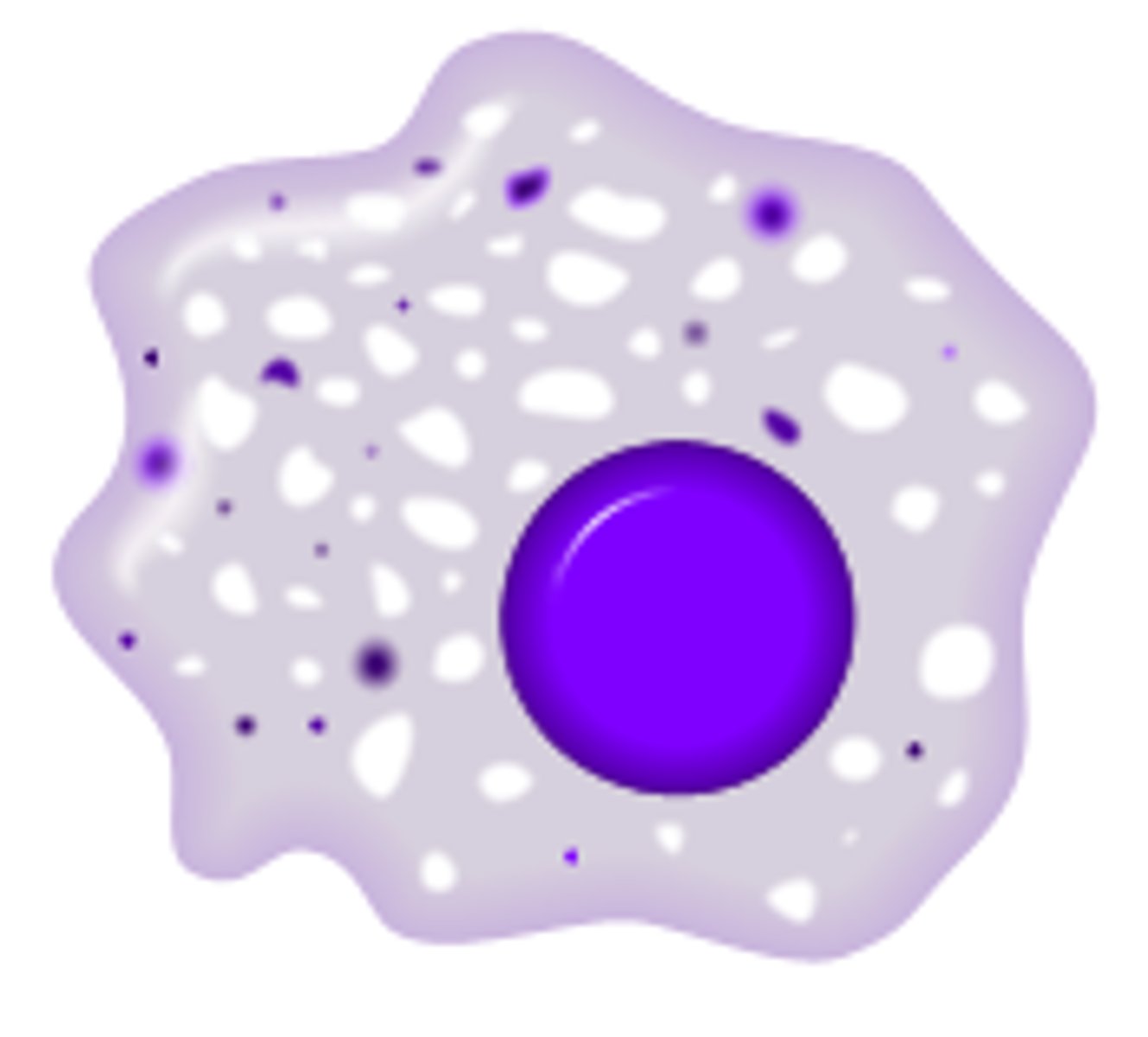
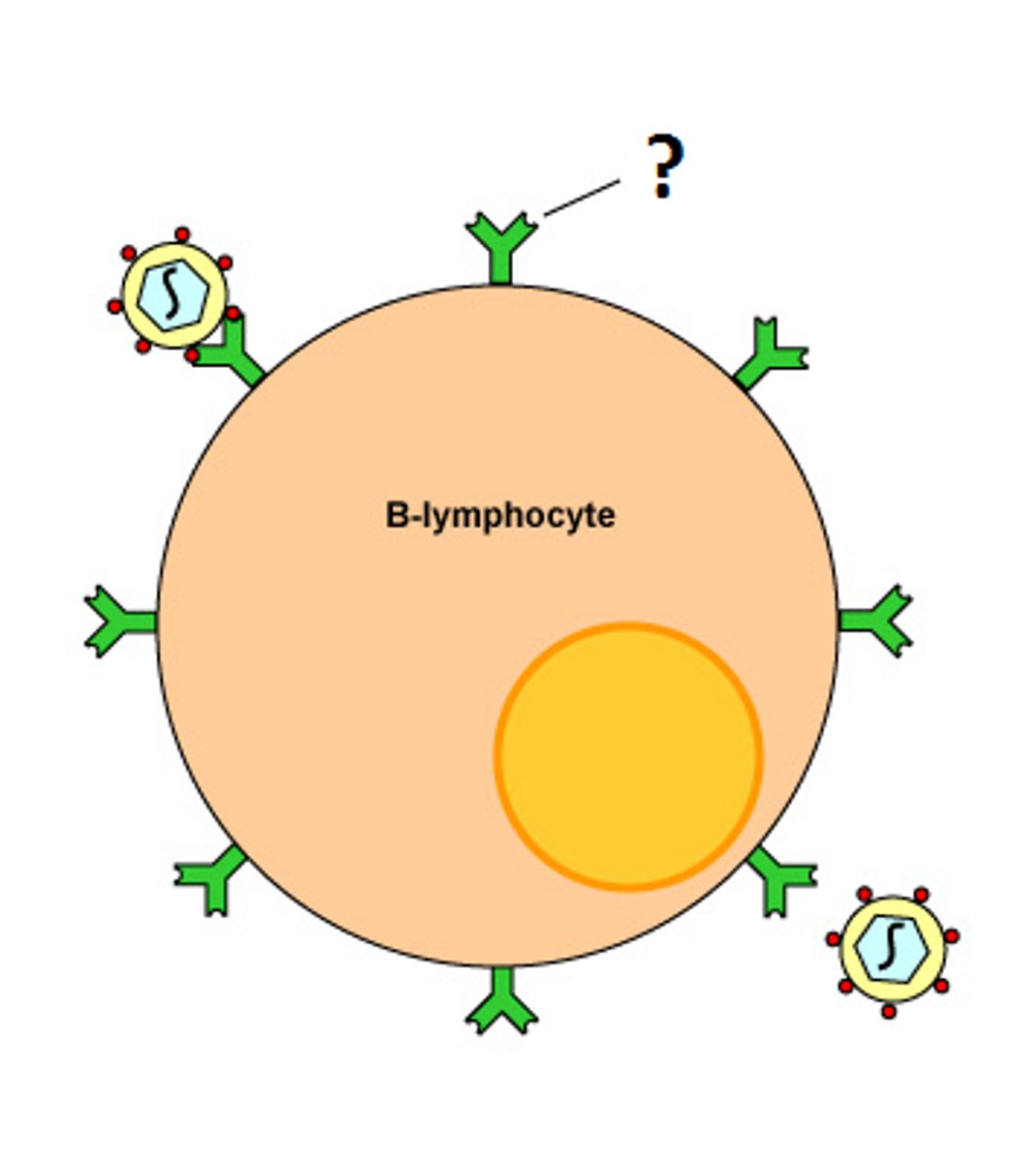
B lymphocytes
form in the bone marrow and release antibodies that fight bacterial infections
T lymphocytes
form in the thymus and other lymphatic tissue and attack cancer cells, viruses, and foreign substances
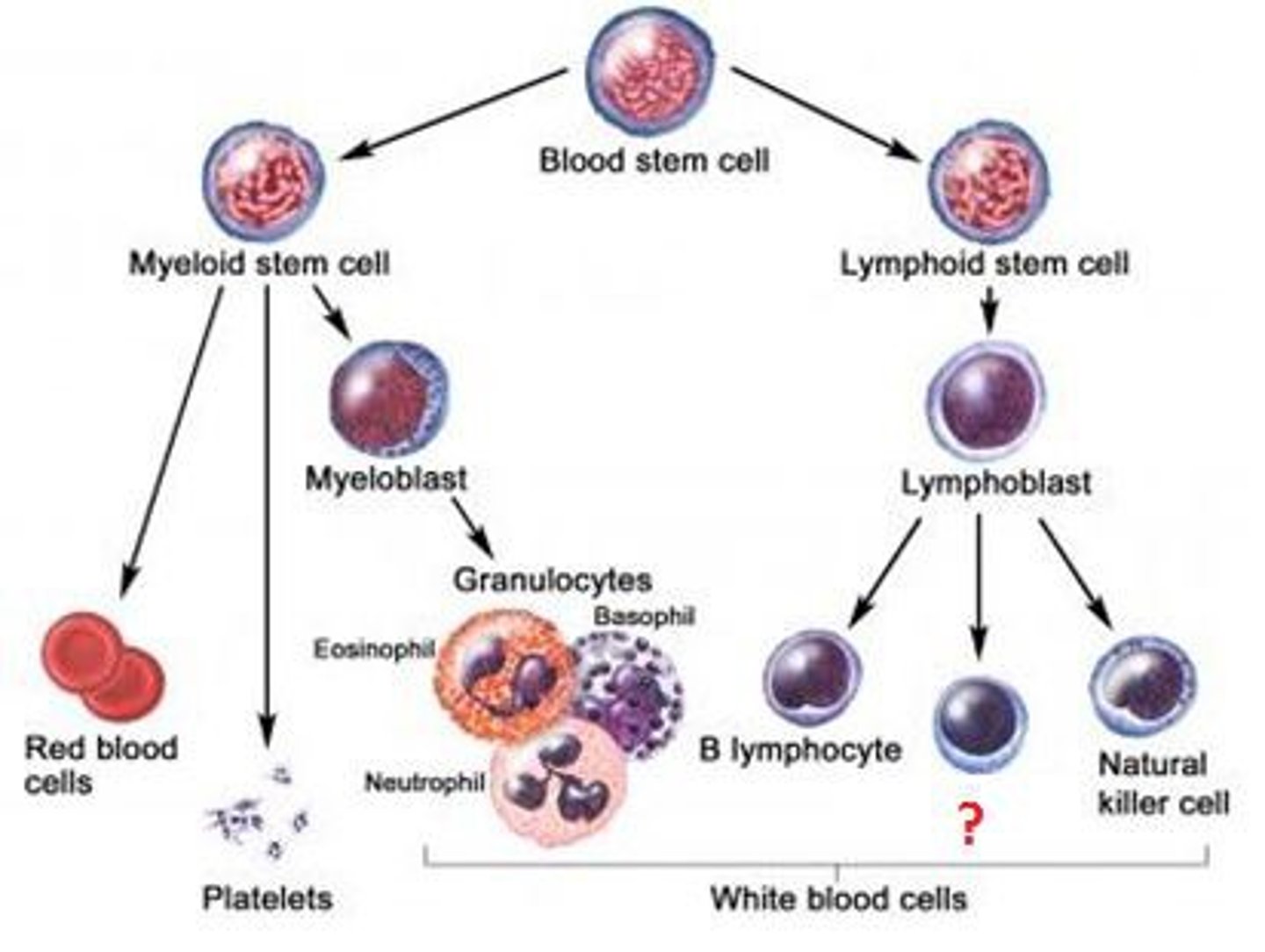
natural killer cells
A type of white blood cell that can kill tumor cells and virus-infected cells; an important component of innate immunity.
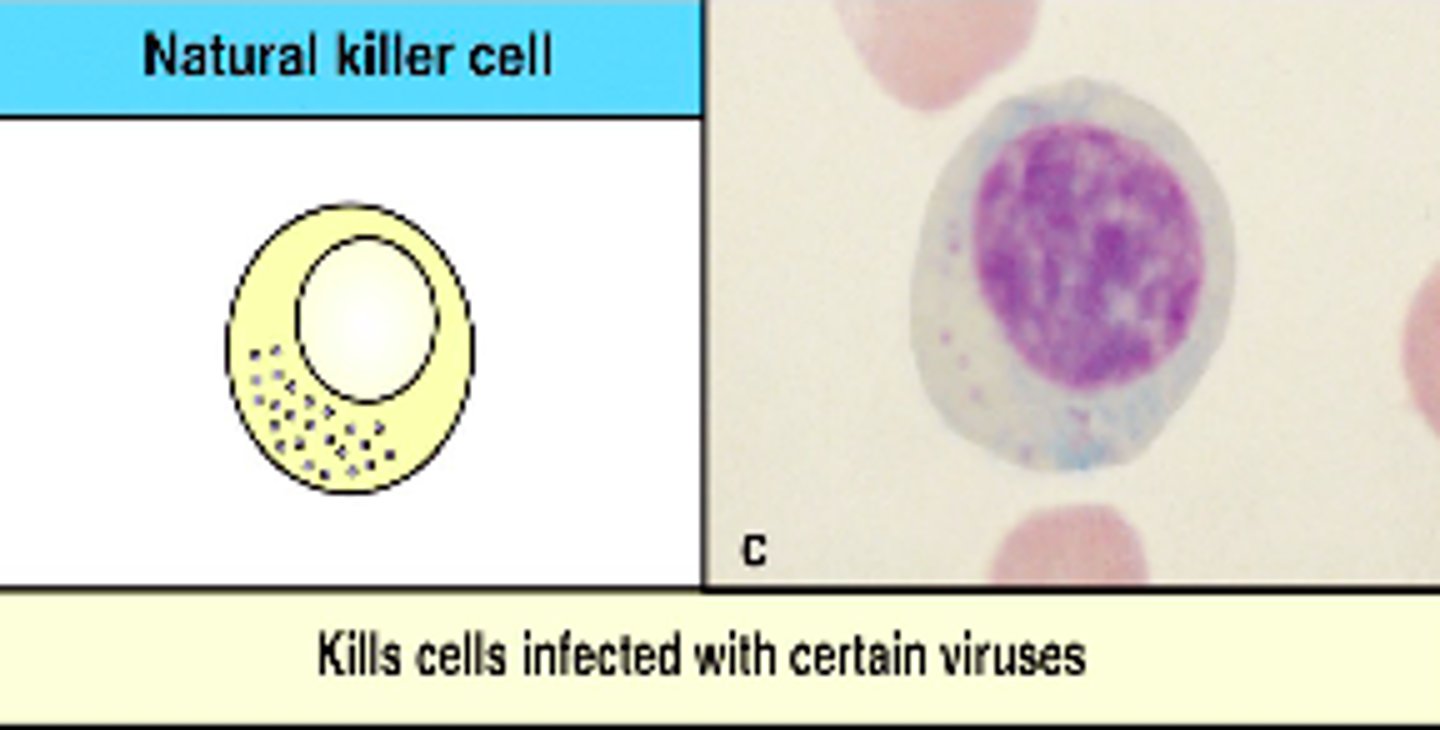
thrombocytes
another name for platelets
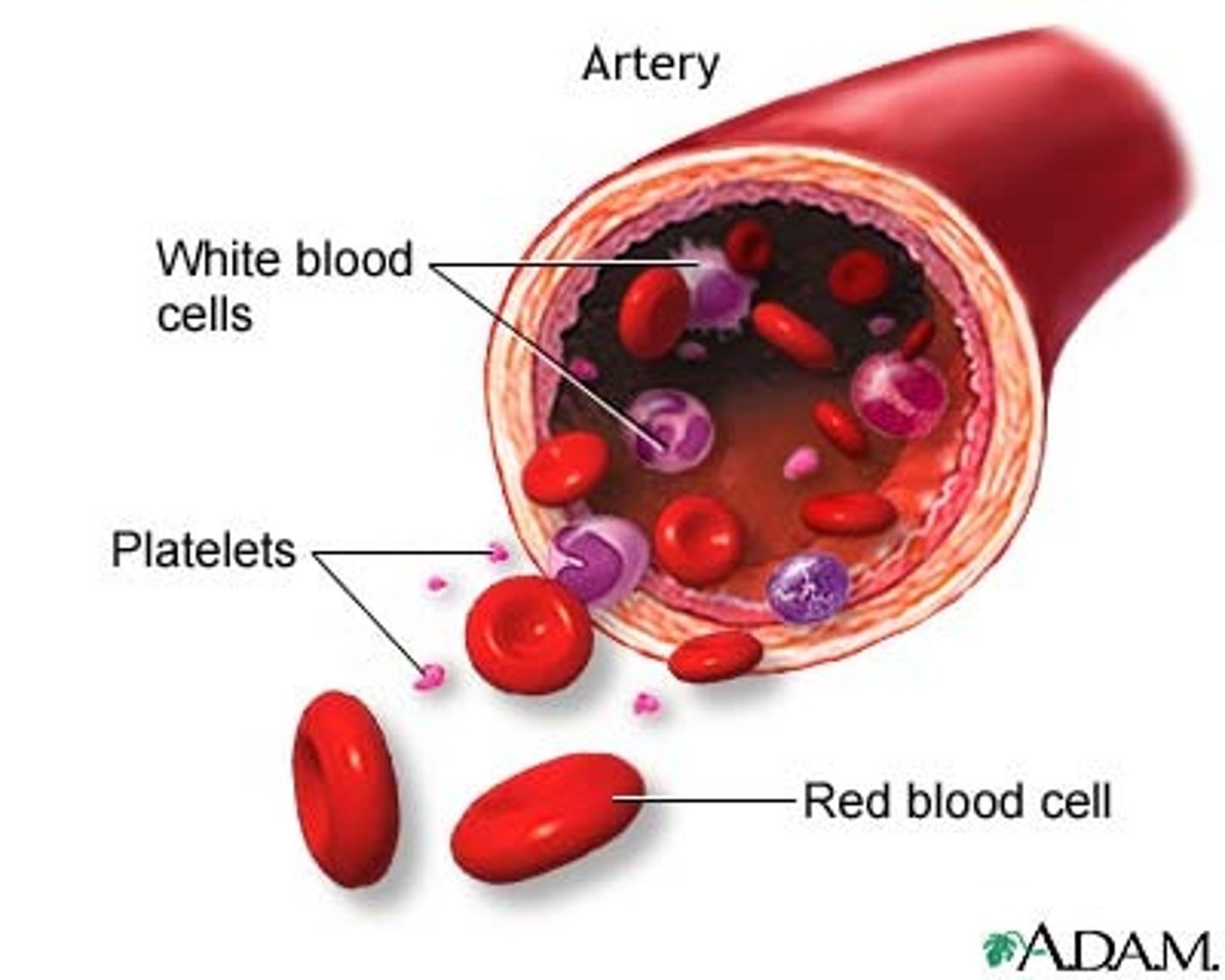
red bone marrow
produces red and white blood cells and platelets
hemostasis
the stopping of a flow of blood.
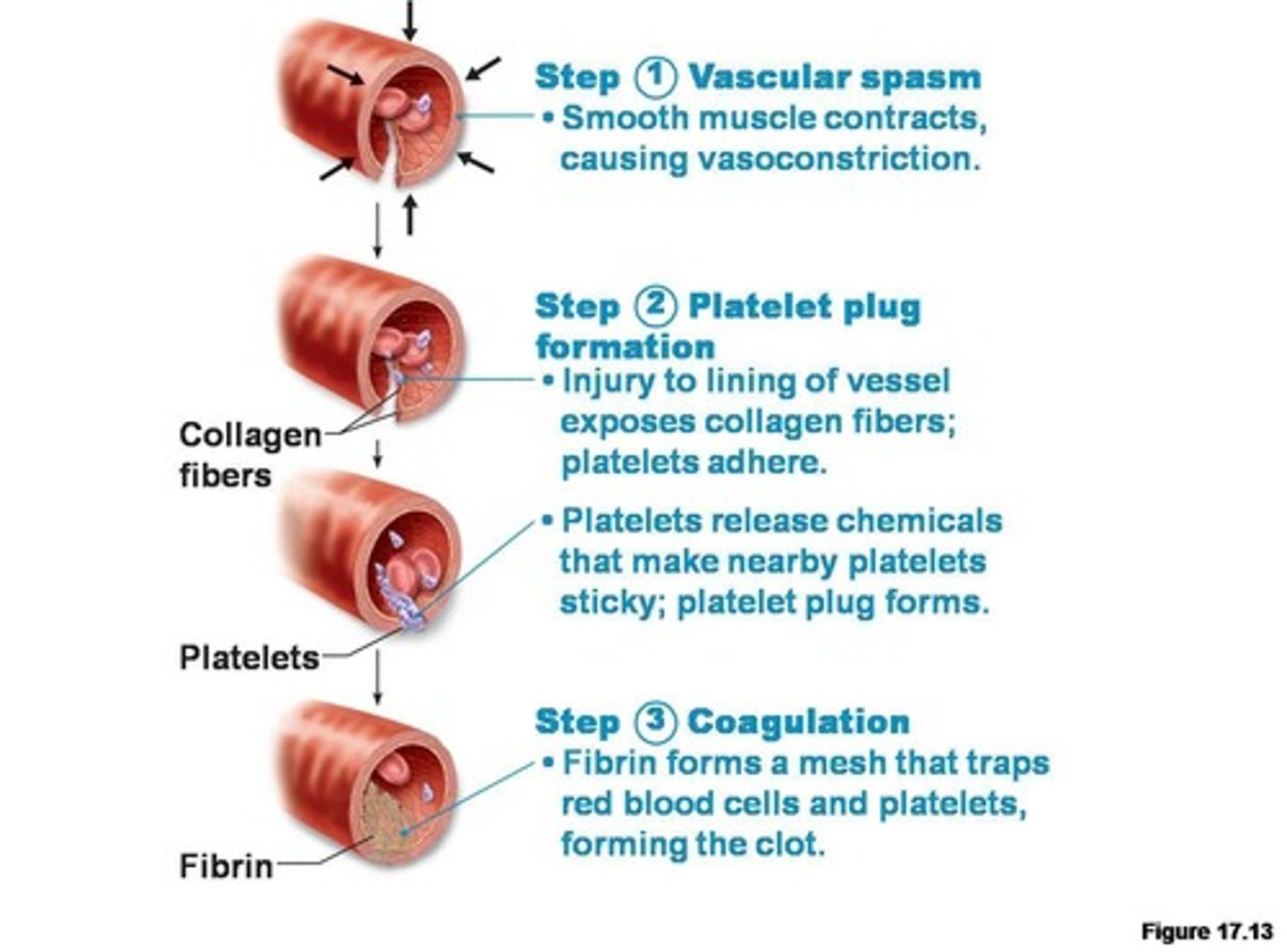
vascular spasm
immediate response to blood vessel injury; results in constriction
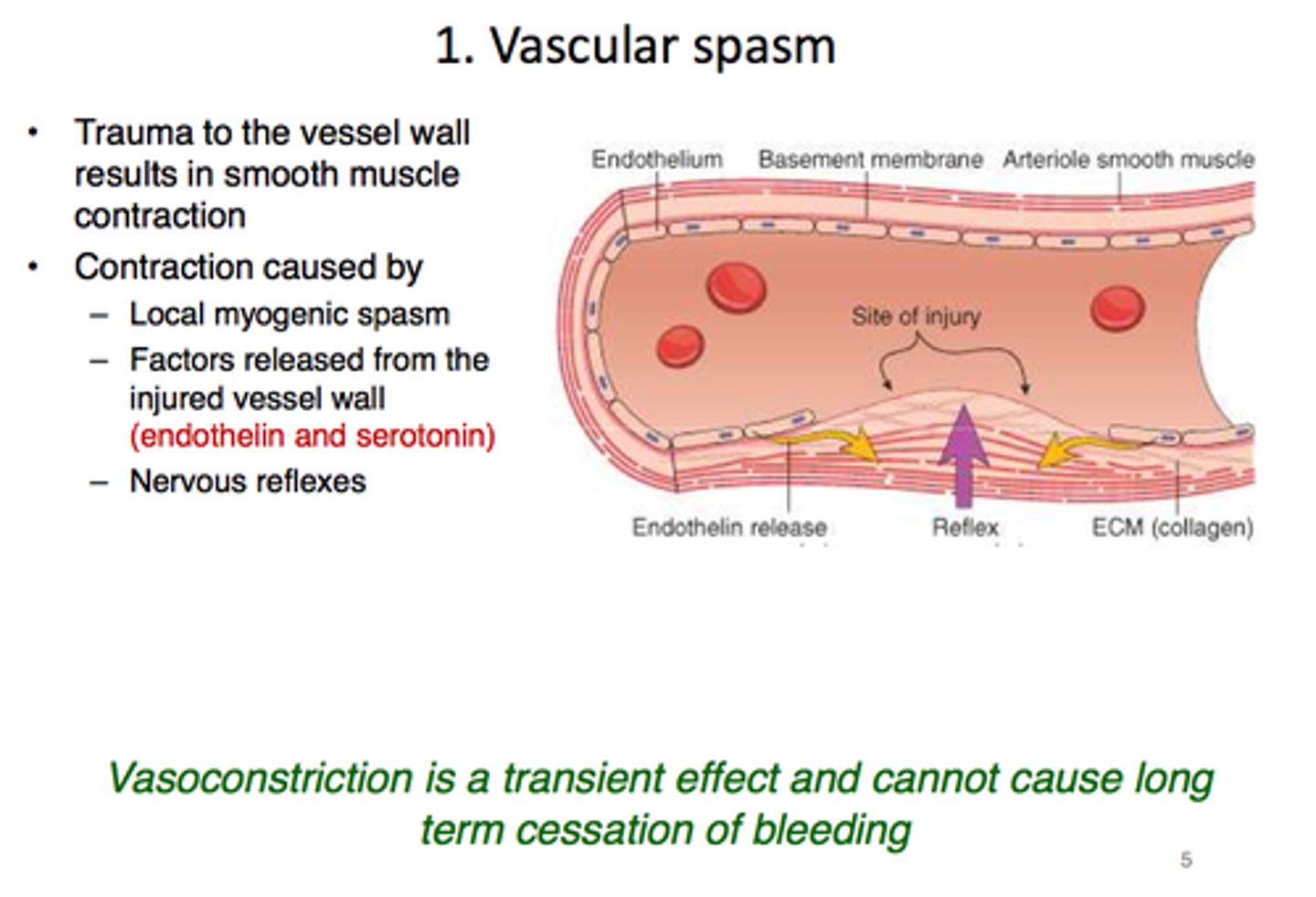
vasoconstriction
narrowing of blood vessels
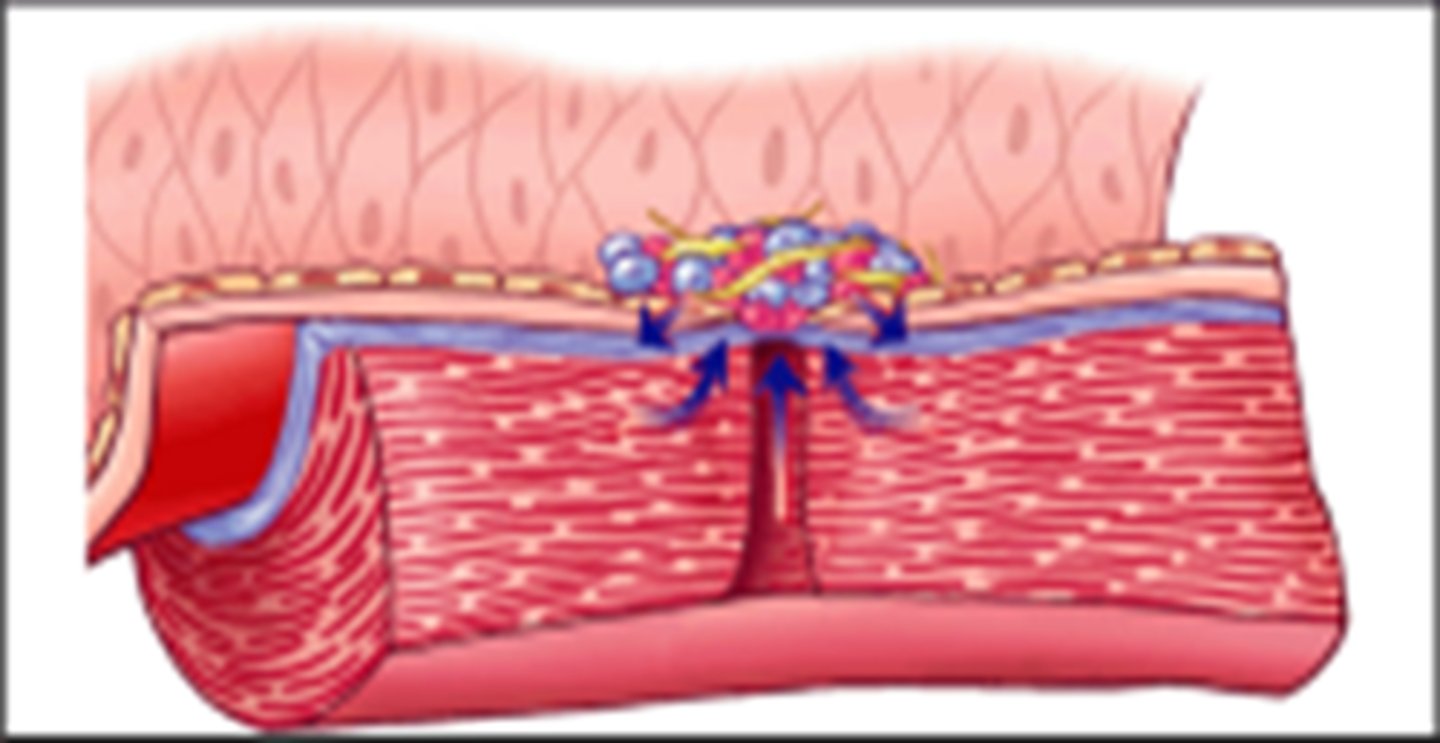
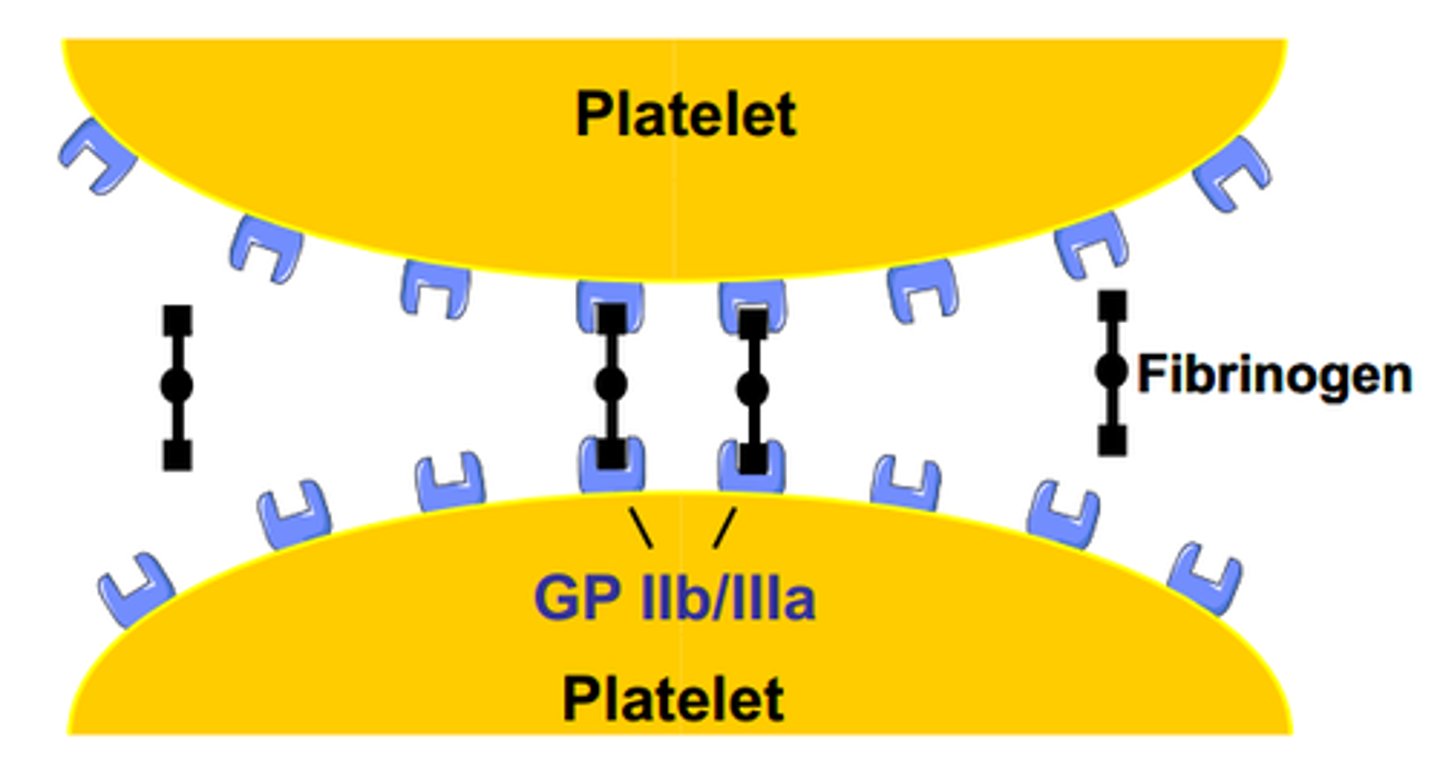
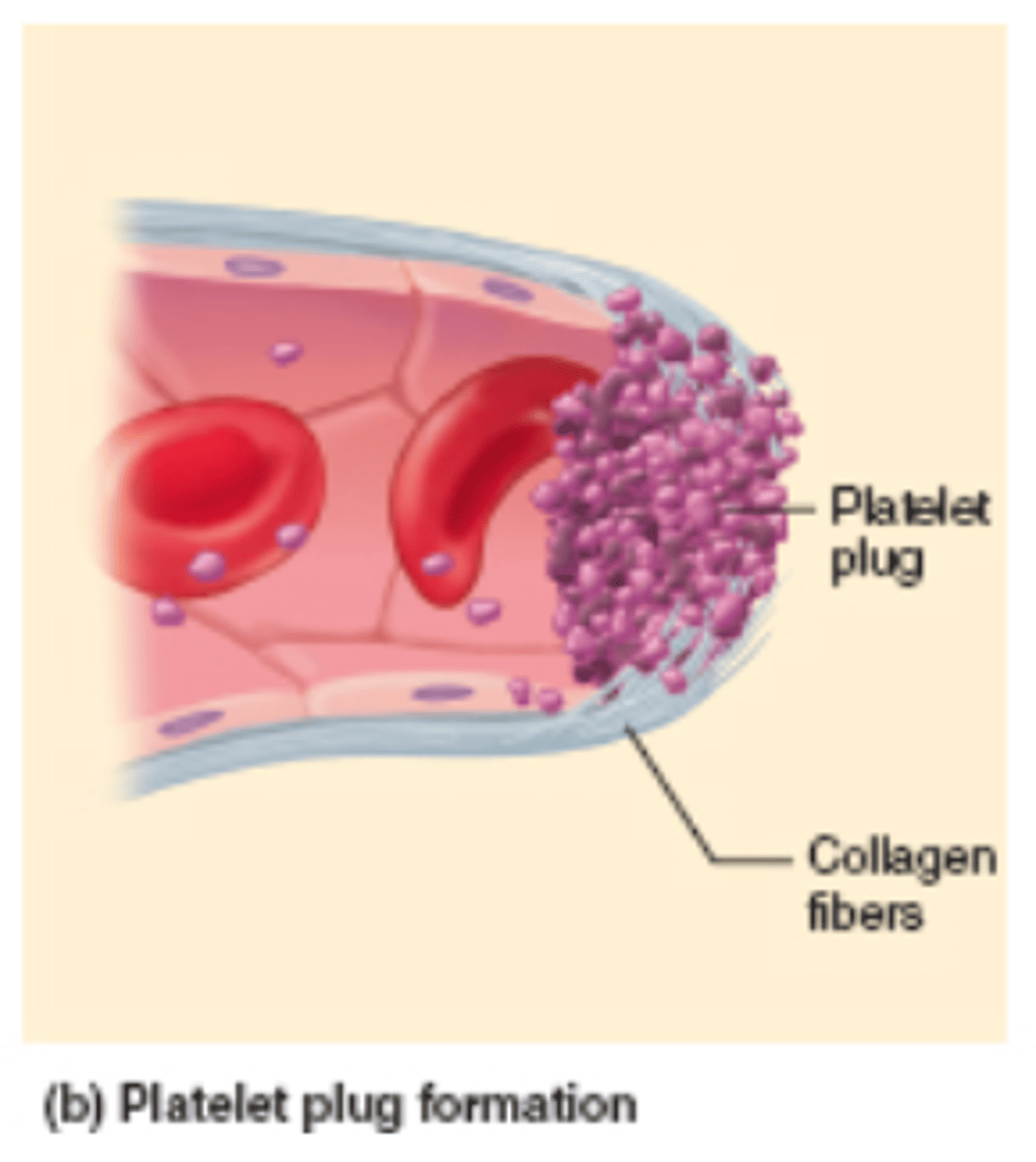
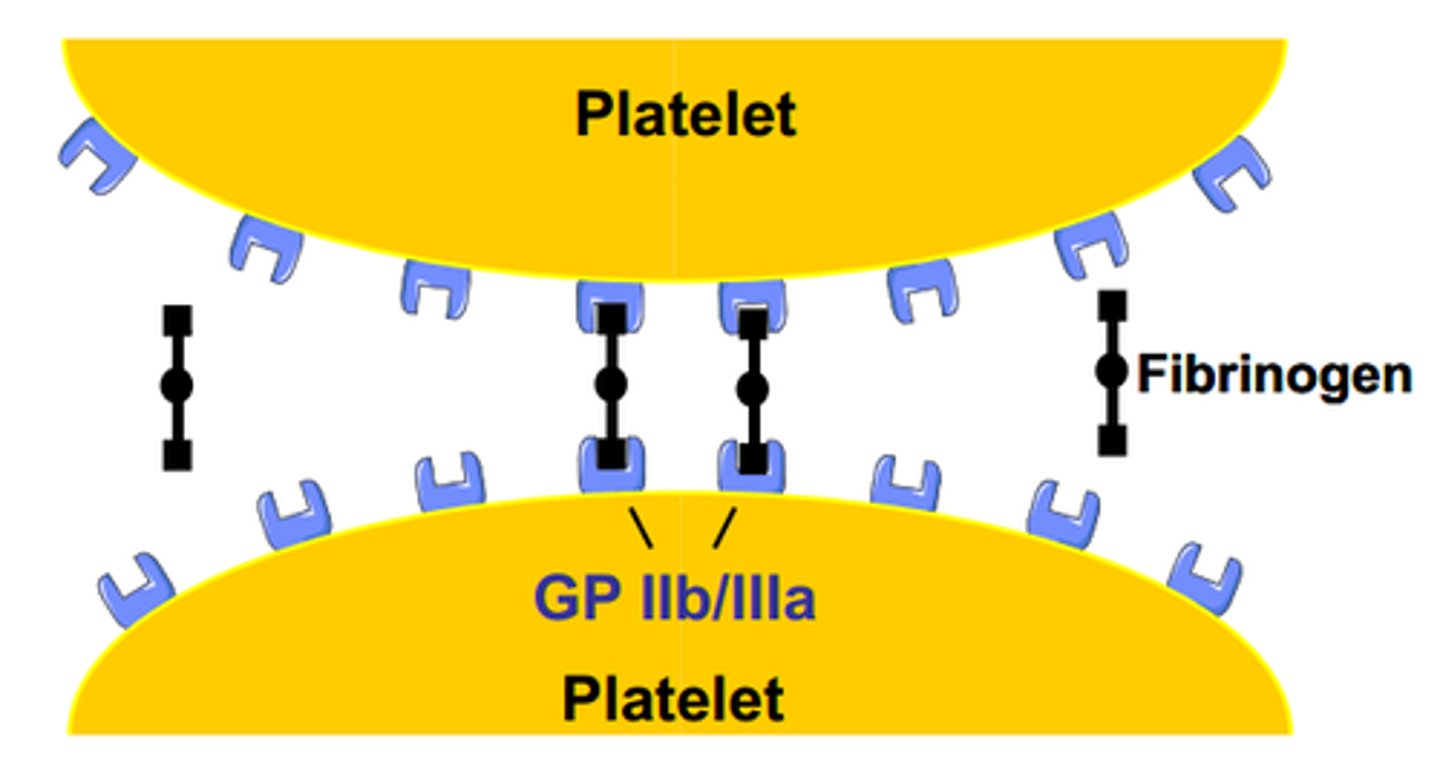
platelet plug
a collection of platelets at the site of a damaged blood vessel that helps slow or stop blood loss
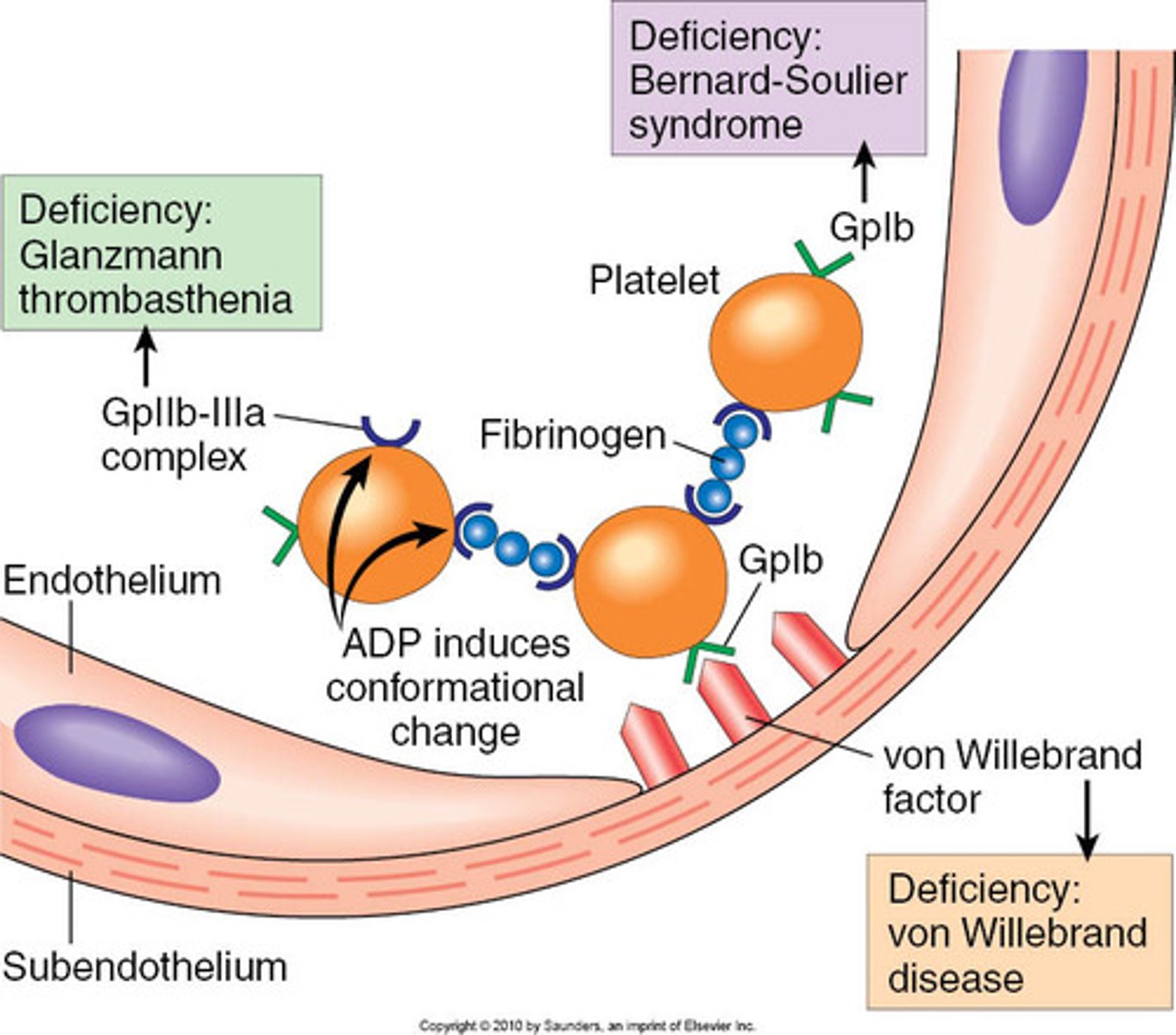
platelet adhesion
the attachment of platelets to exposed surfaces
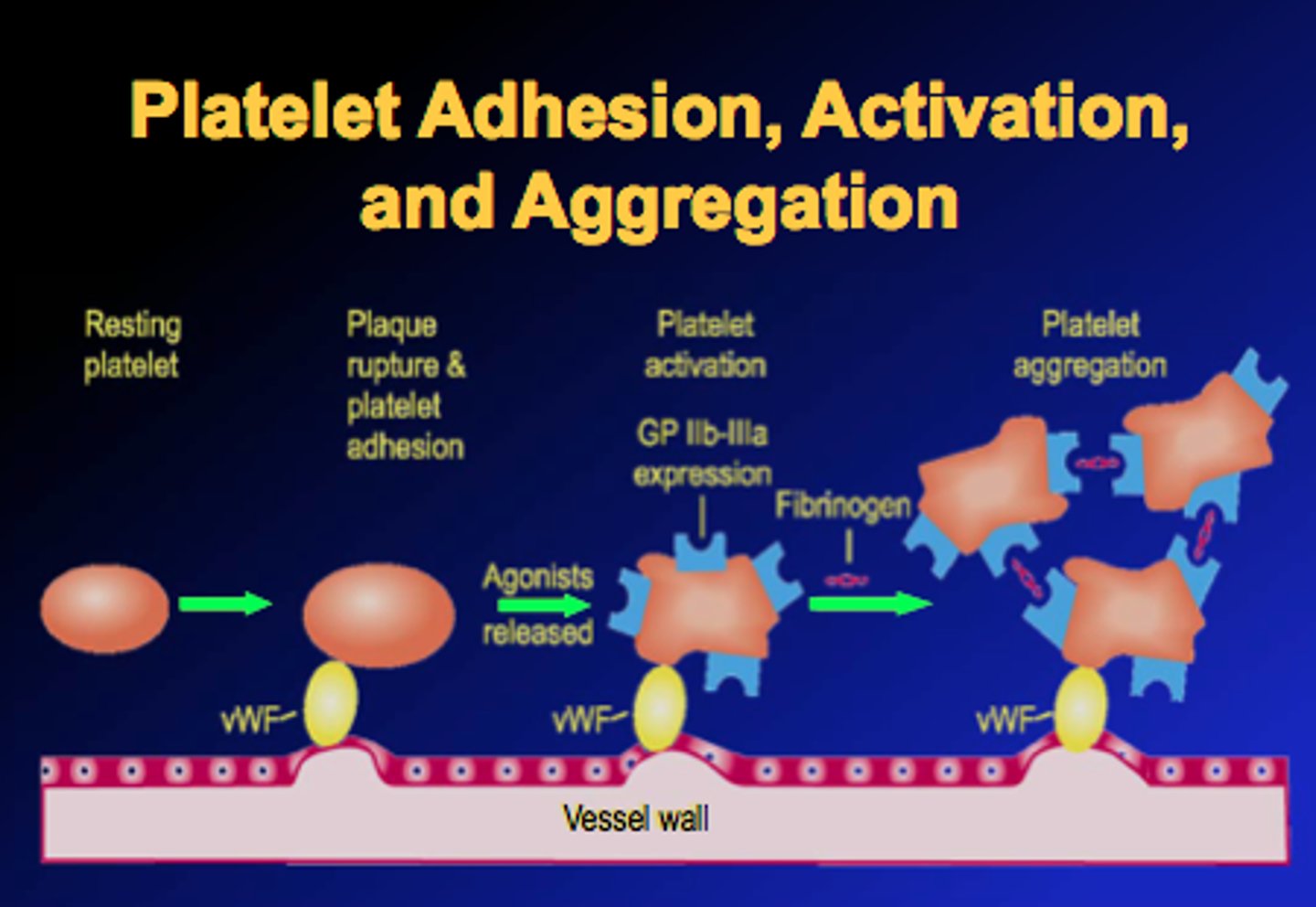
platelet aggregation
property of platelets to adhere to an injured surface and then attract other platelets, which clump together or aggregate at the area, plugging up an injury to the vascular system
von Willebrand factor
activates clotting
epinephrine
adrenaline
serotonin
A neurotransmitter that affects hunger, sleep, arousal, and mood.
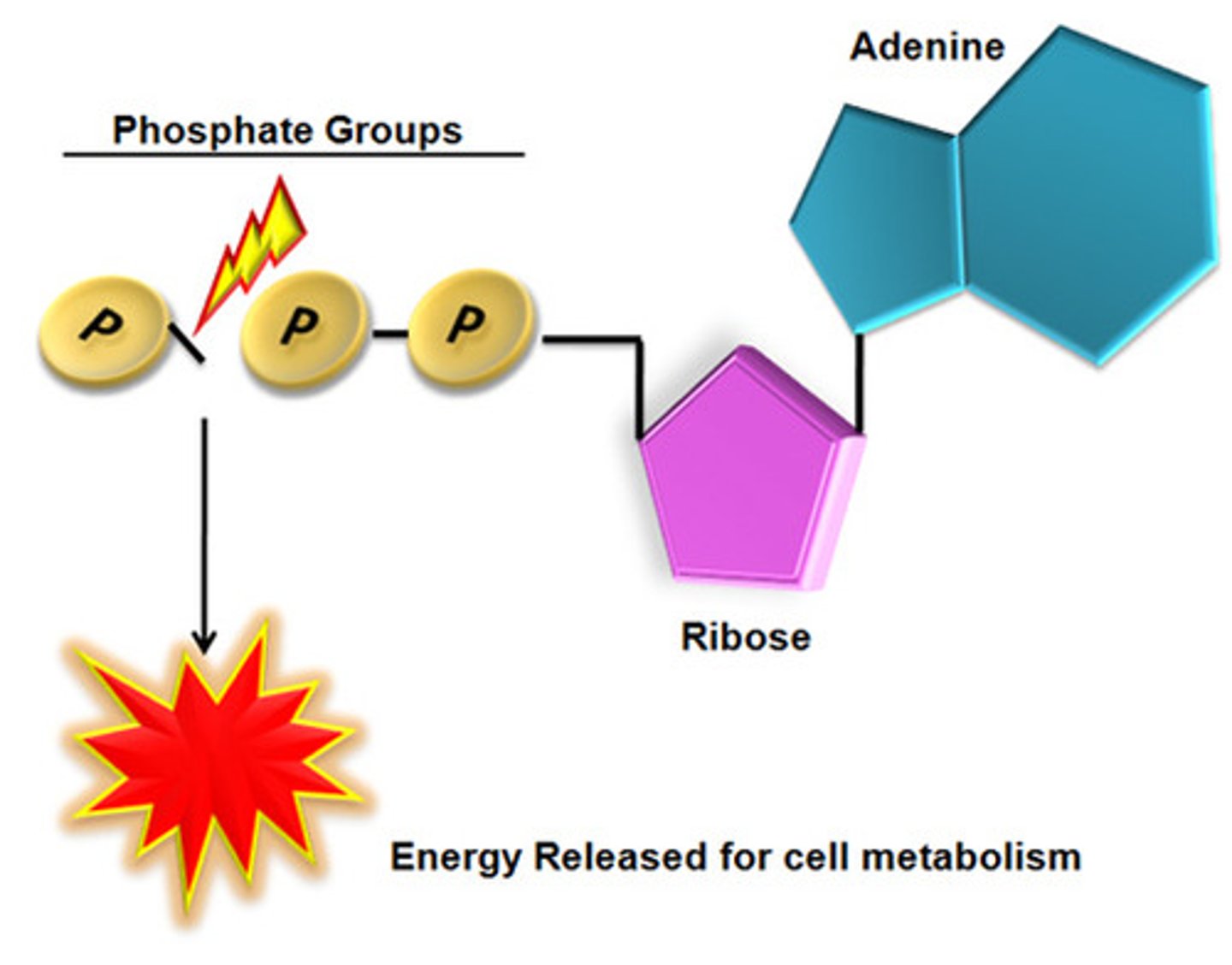
ADP (adenosine diphosphate)
the molecule that is produced when ATP is split to yield energy
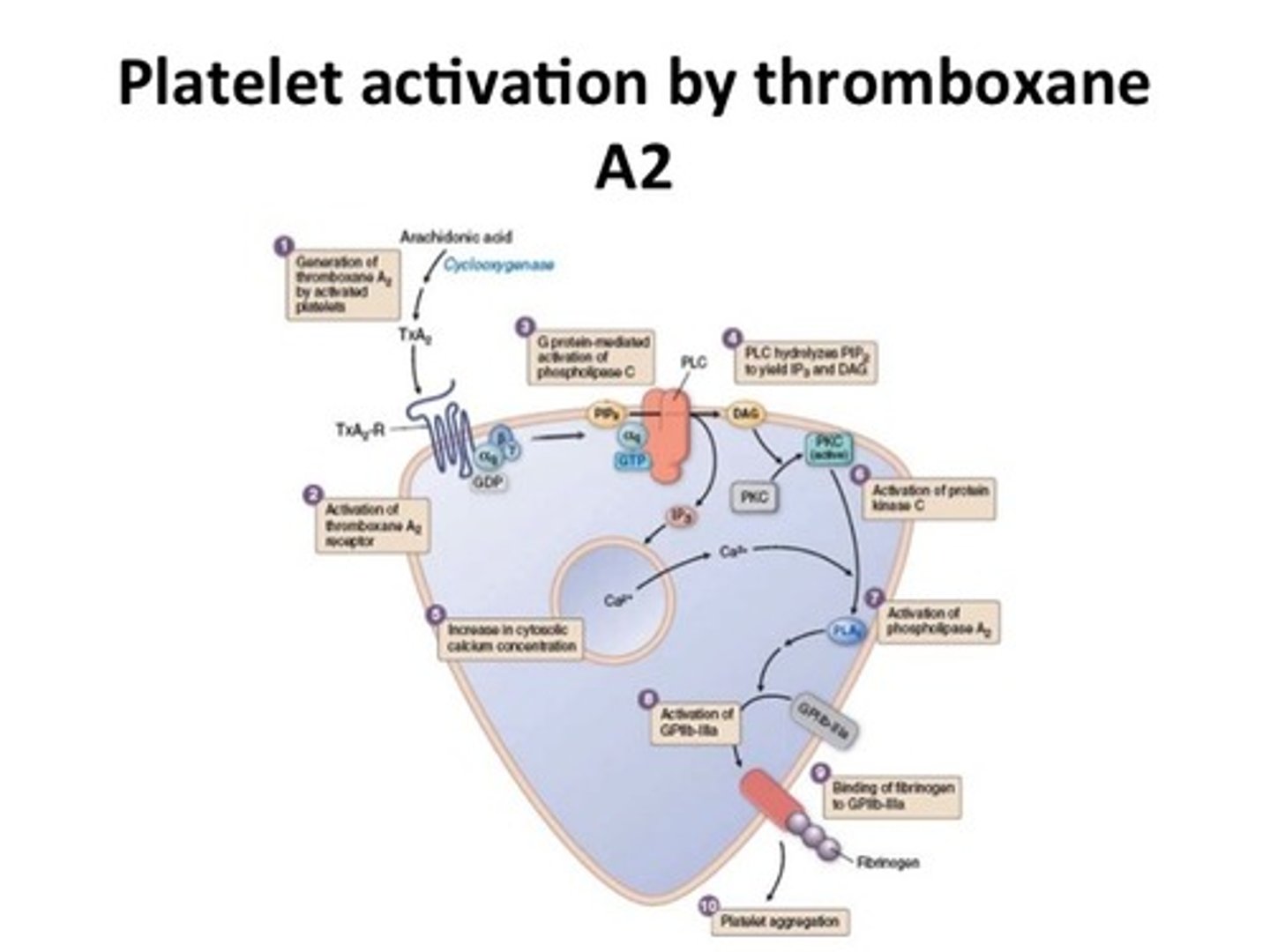
Thromboxane A2
it stimulates activation of new platelets as well as increases platelet aggregation, produced by platelets
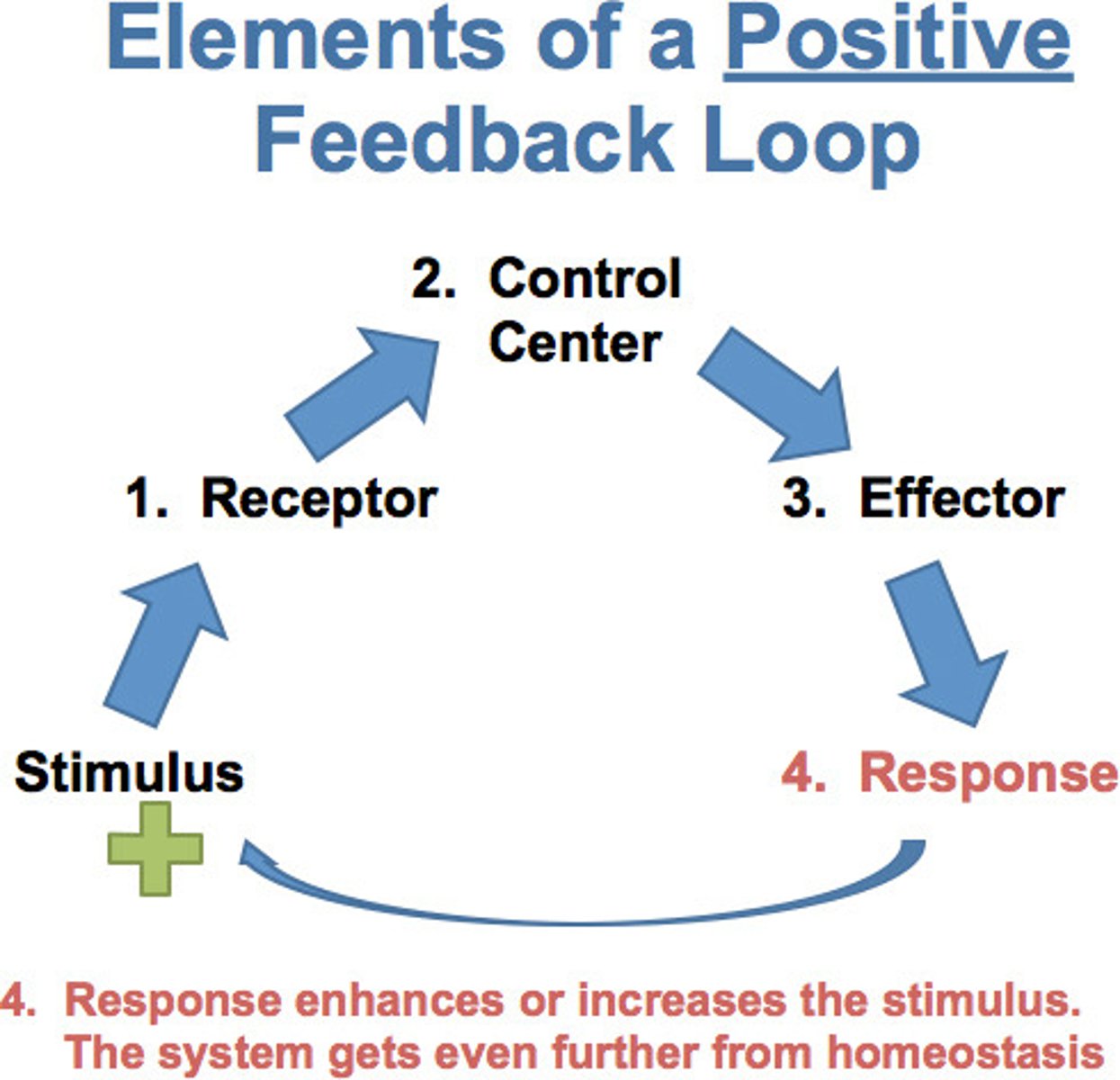
positive feedback
A physiological control mechanism in which a change in some variable triggers mechanisms that amplify the change.
prostacyclin
inhibits blood clotting and vasoconstriction
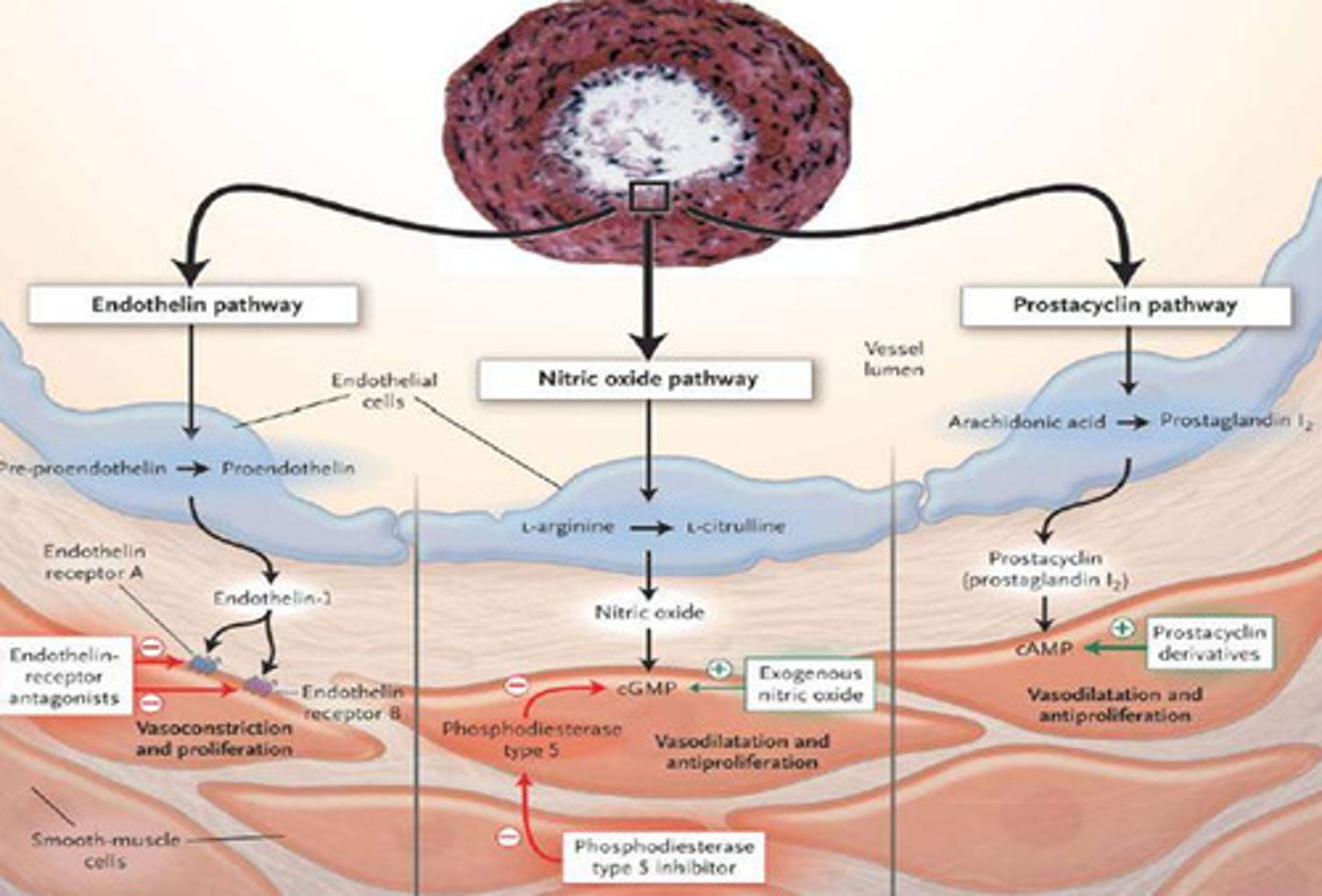
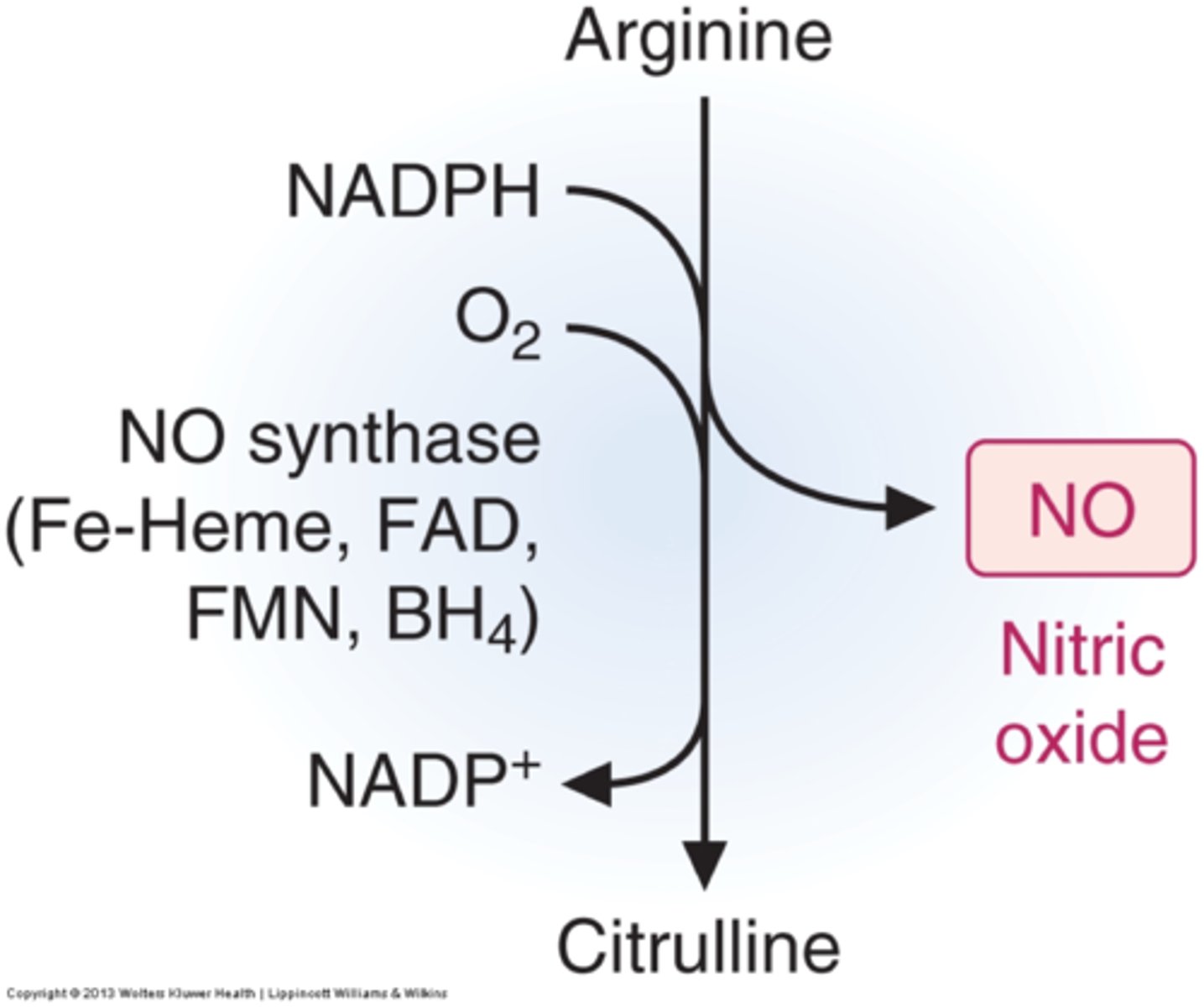
nitric oxide
a gas released by the endothelial cells to promote blood flow
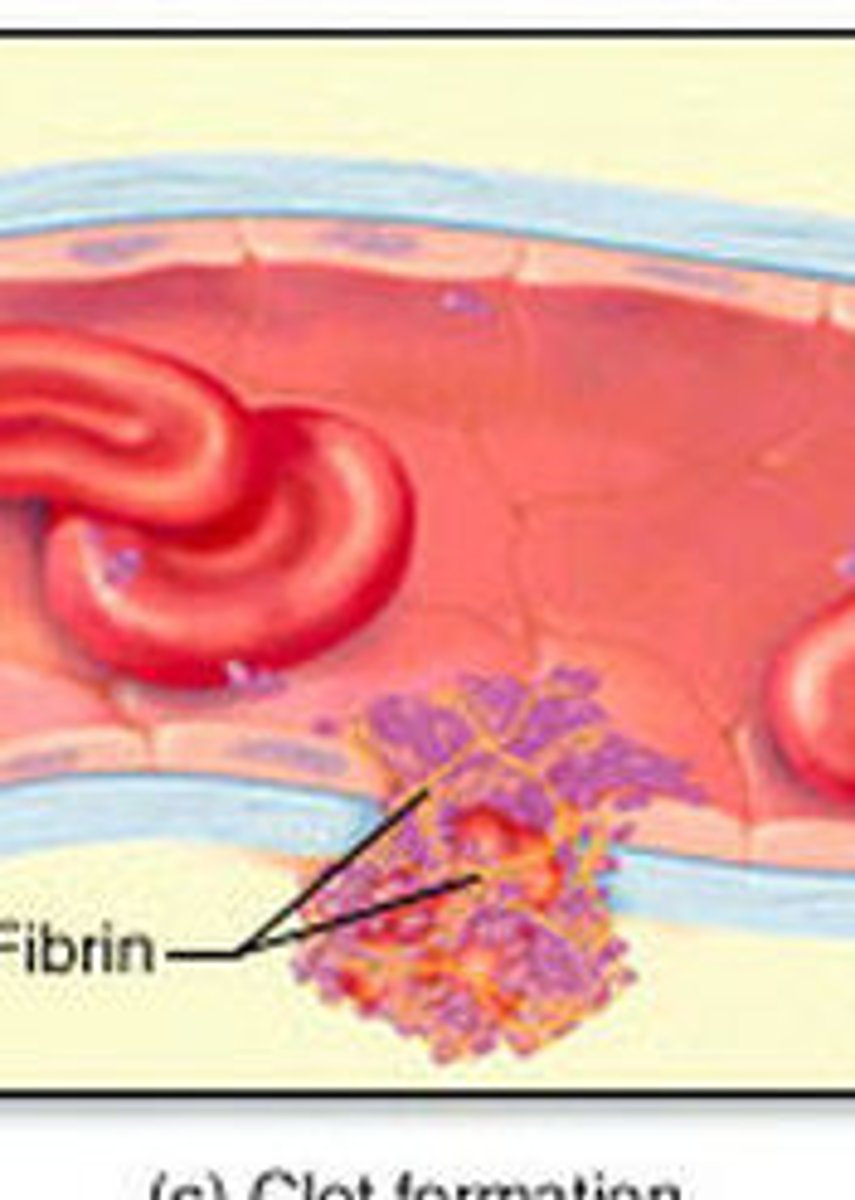
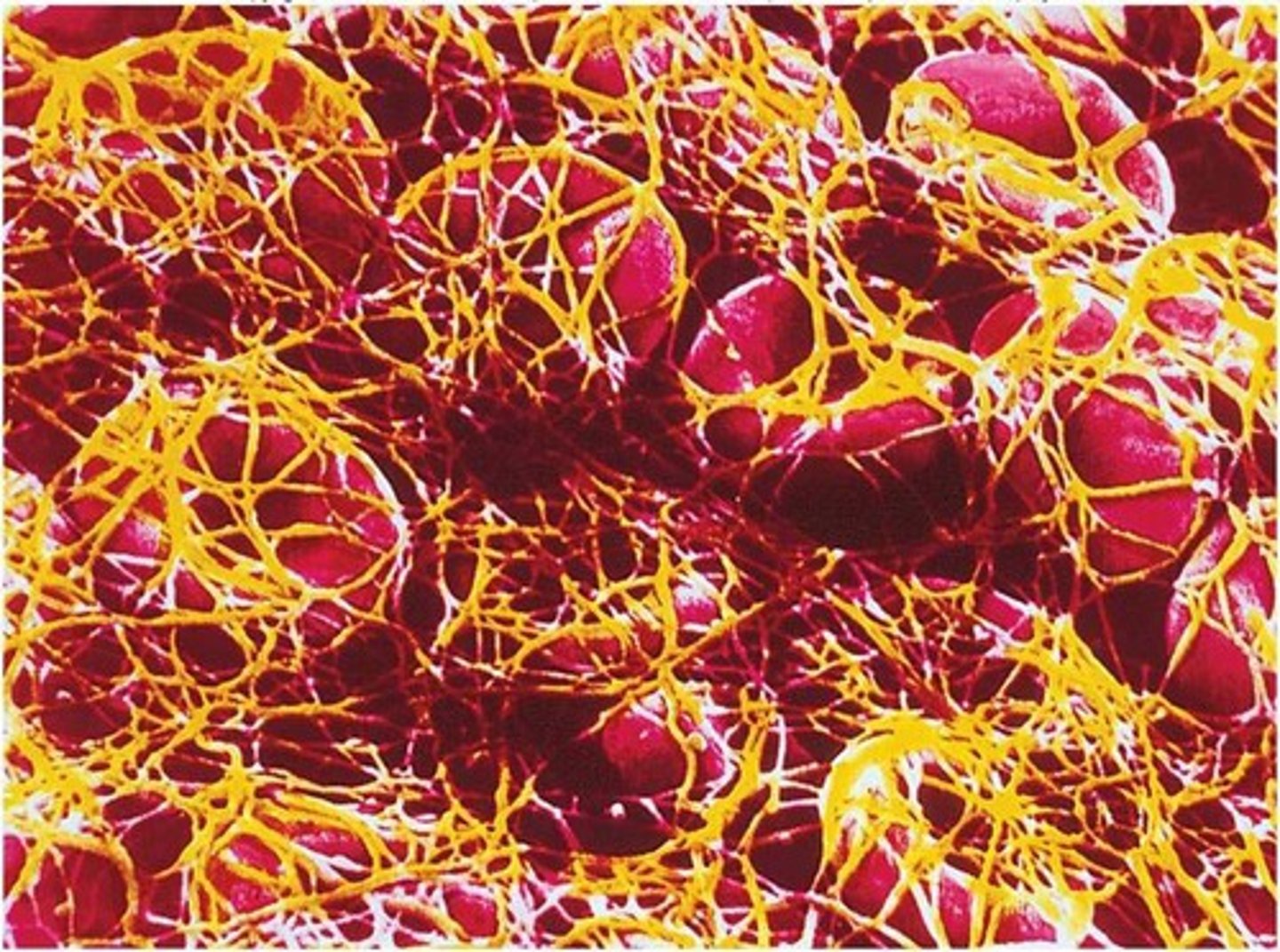
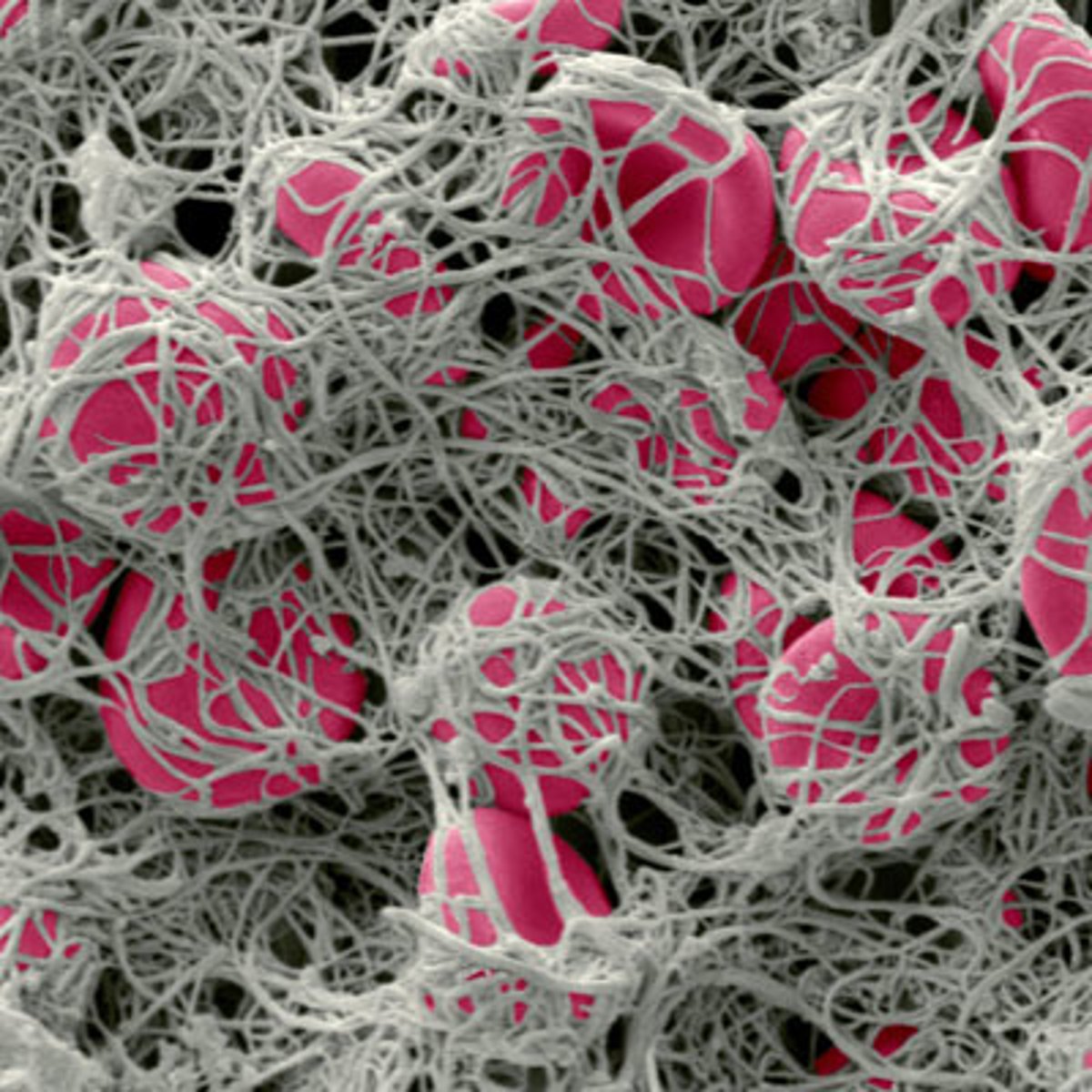
Clotting (coagulation)
Complex process by which blood components form a plug to stop bleeding
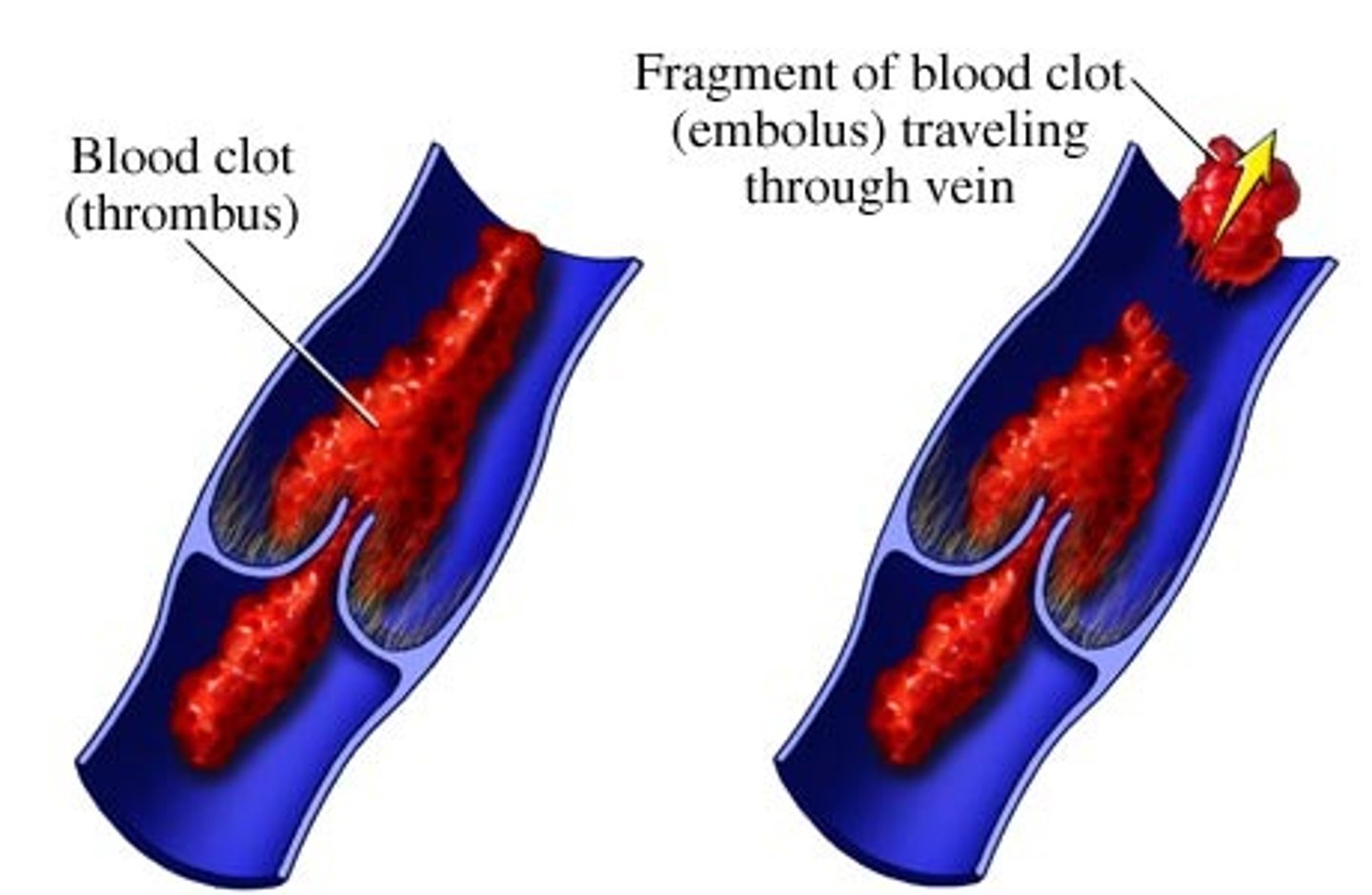
blood clot (thrombus)
The conversion of blood from a liquid form to solid through the process of coagulation
fibrinogen
plasma protein that is converted to fibrin in the clotting process
fibrin
protein that forms the basis of a blood clot
clotting factors
any of the various plasma components involved in the clotting process
coagulation cascade
Complex series of steps by which blood flow stops.
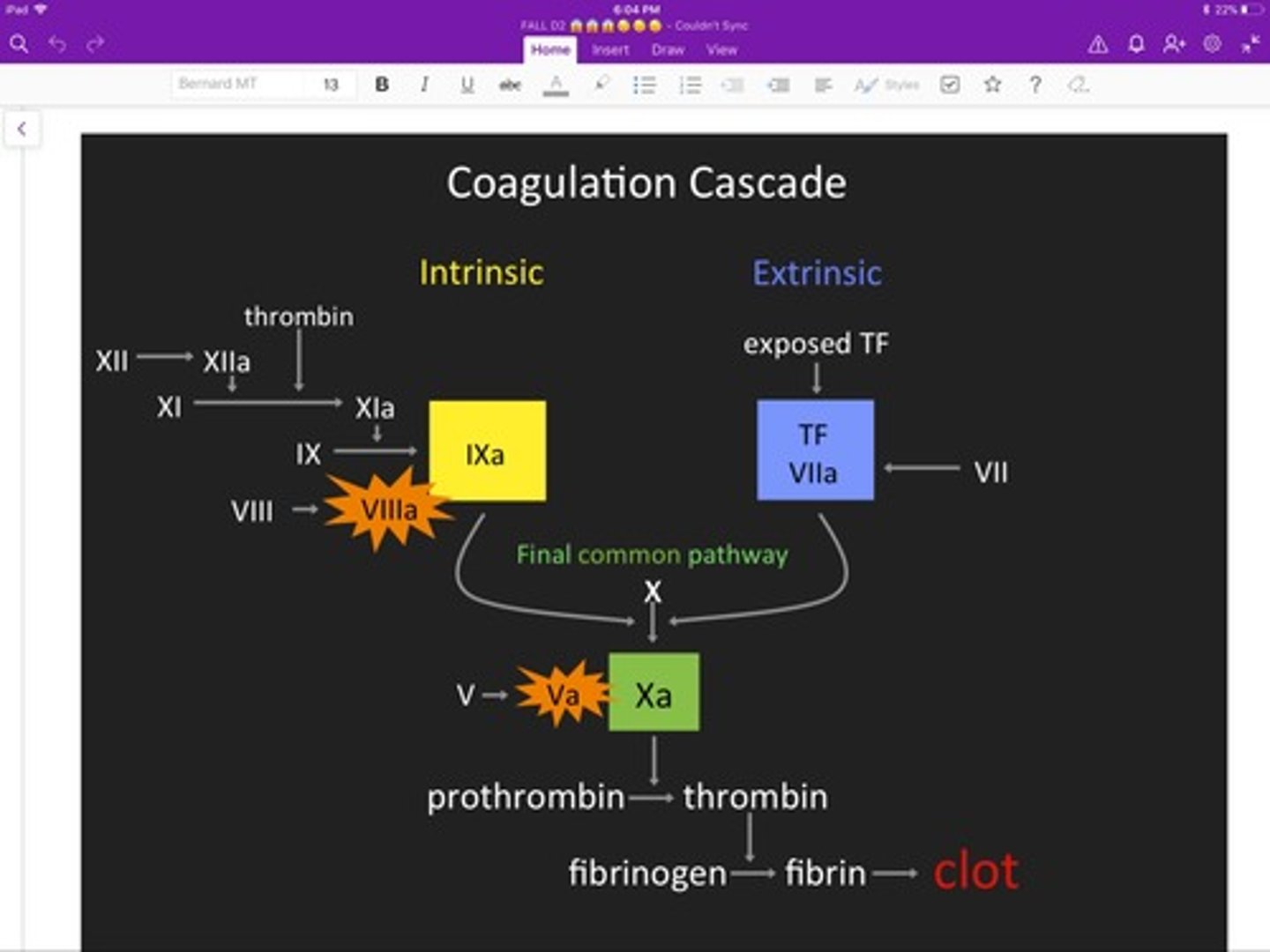
intrinsic pathway
cascade of clotting factors leading to the formation of a clot within an injured vessel
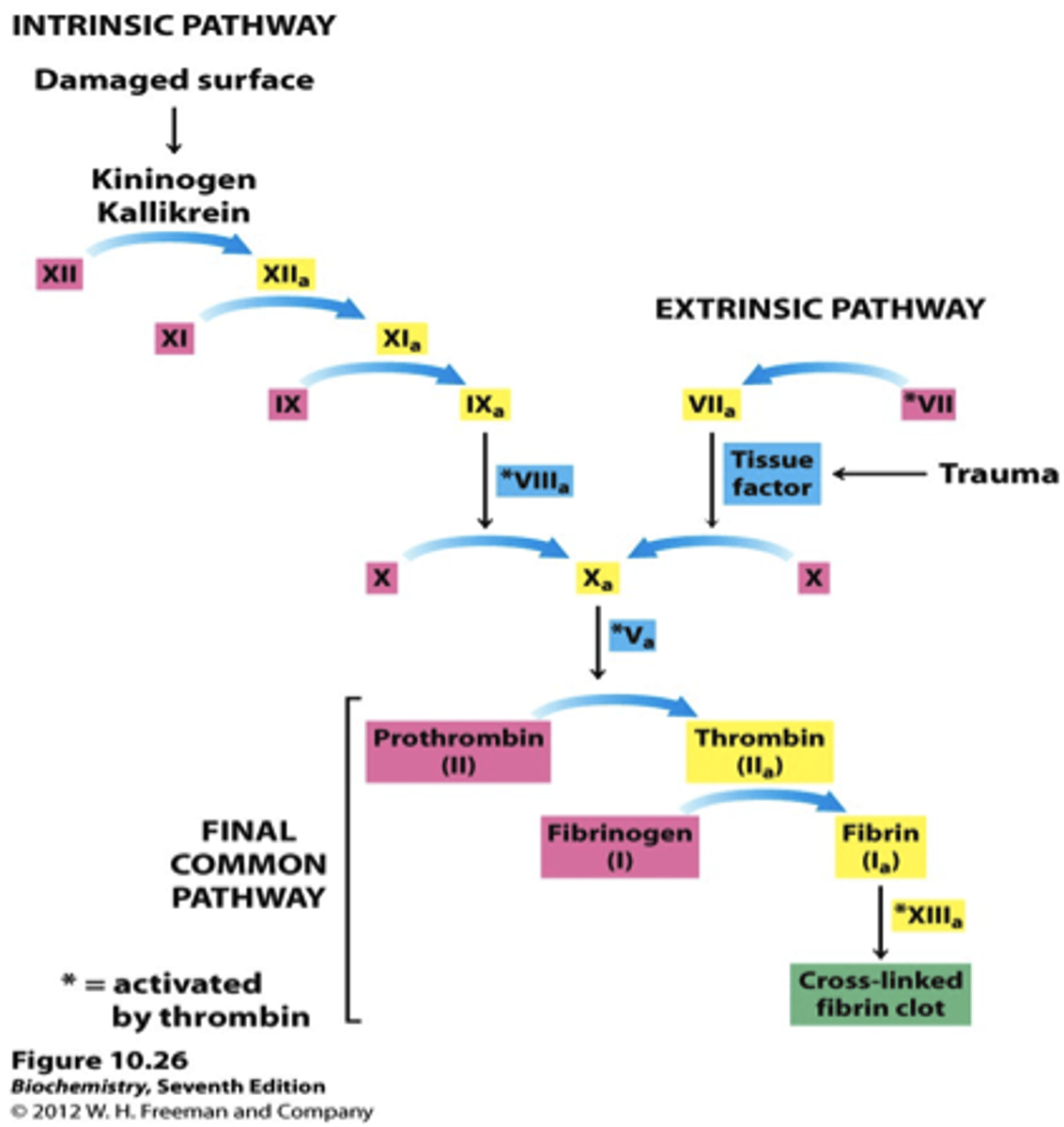
extrinsic pathway
initial coagulation pathway that begins with tissue damage and results in the activation of the common pathway
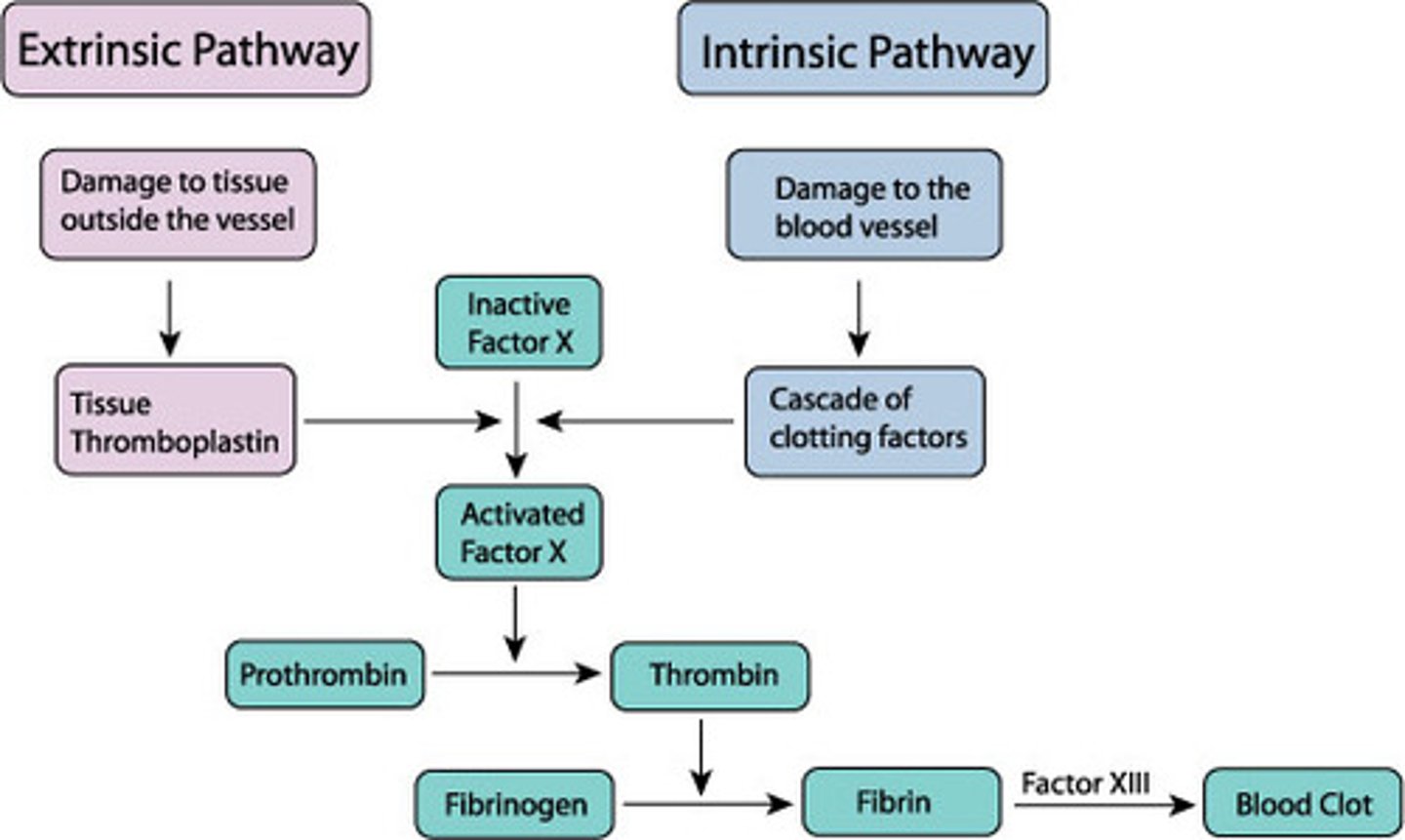
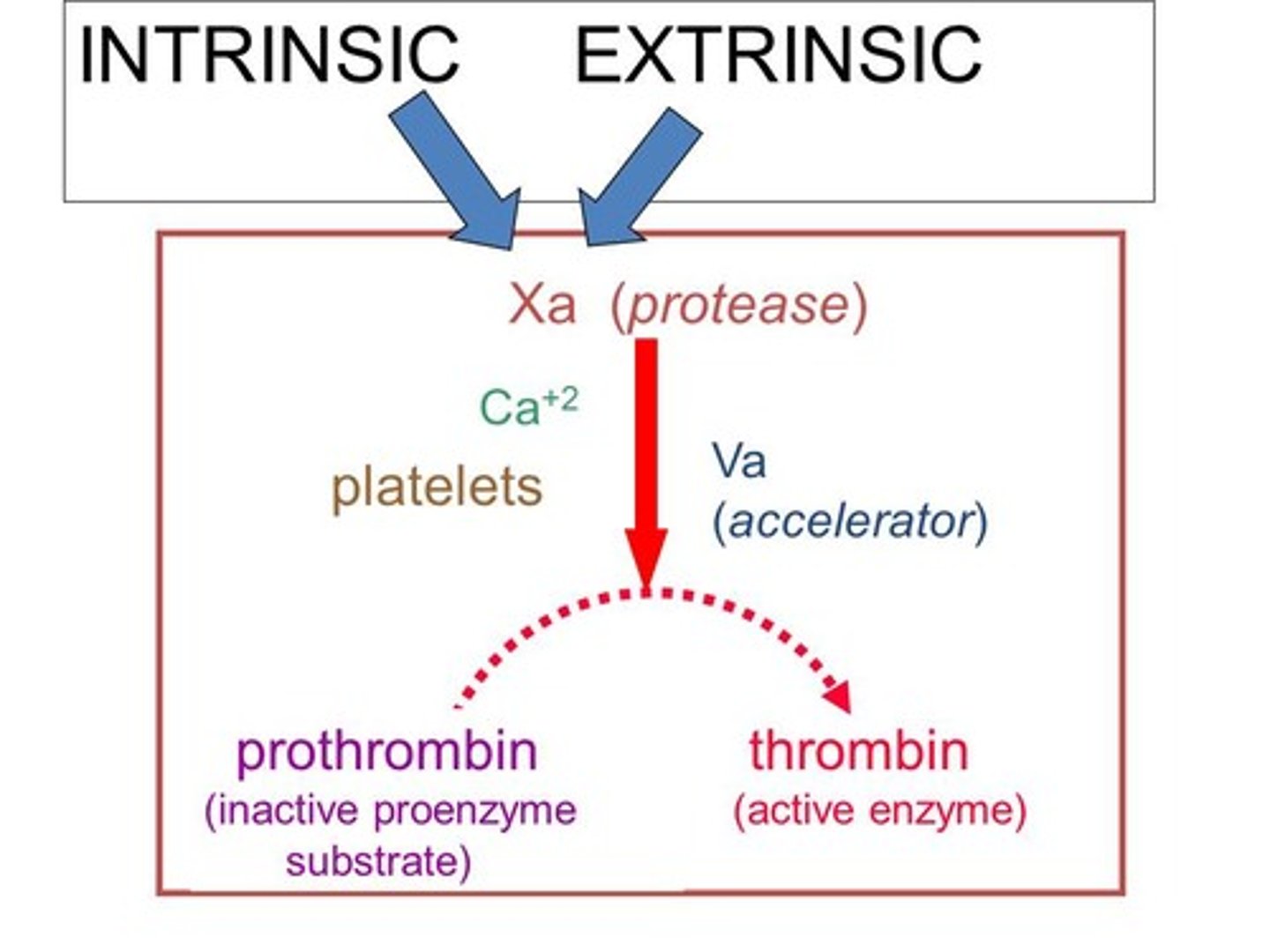
common pathway
where intrinsic and extrinsic pathways converge
thrombin
enzyme that converts fibrinogen to fibrin during coagulation
vitamin k
Helps blood clot

clot retraction
after coagulation, platelets contract pulling torn blood vessel together