Emotion and Mood
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is emotion?
Positive or negative reaction to an evocative stimulus that involves:
1. cognitive appraisal
2. physiological arousal
3. subjective feeling
4. expressive behaviour
5. goal-directed activity.
What is mood?
A frame of mind or emotional state defined by internal state rather than external behaviour. They last longer and are less spontaneous than emotions.
What are the 6 basic emotions? (Ekman, 1971, 1984).
1. happiness
2. sadness
3. fear
4. anger
5. disgust
6. surprise
What is Plutchik's Wheel of Emotions? (1994)
4 pairs of opposite emotions:
- Joy/sadness
- Affection/disgust
- Anger/fear
- Expectation/surprise
All other emotions are derived from a combo of these.

List the 4 factors involved in processing emotion.
1. Appraisal
2. Arousal
3. Expression
4. Action readiness.
Explain the 1º appraisal factor for processing emotion. (Lazarus, 1968).
Evaluate relevance of current situation to personal wellbeing - 'am i in trouble or am i OK?'
Explain the 2º appraisal factor for processing emotion. (Lazarus, 1968).
Evaluate capacity to deal with it - Can I cope with it? ‘What can be done about it ?’ what can be done?'
If it's a bad situation and coping level is low, then you're likely to be sad or anxious. If it's a good situation it produces hope.
Explain the results from appraisal
Negative appraisal leads to anxiety/sadness, while positive results generate happiness+hope.
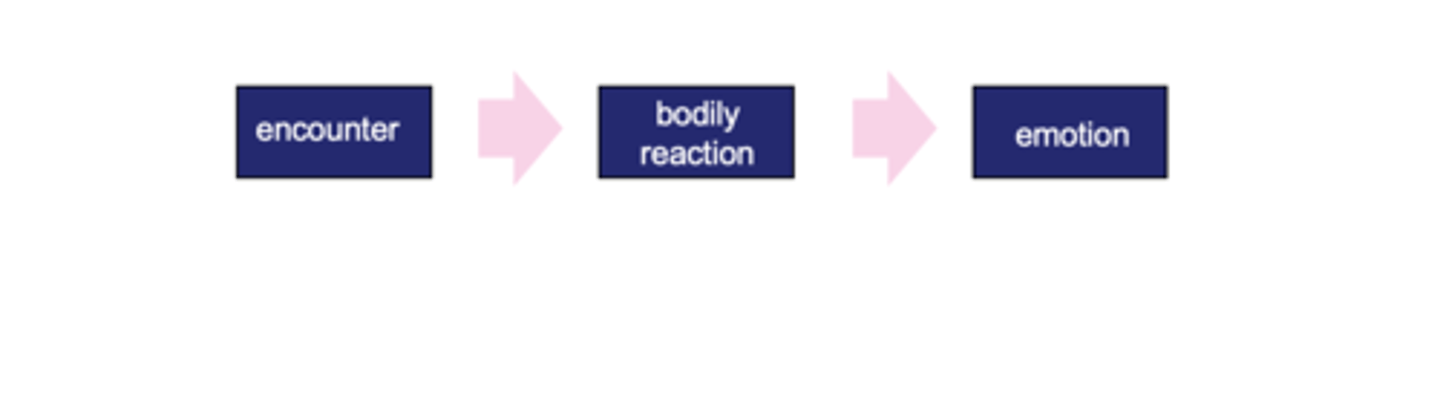
Explain the arousal factor for processing emotion. (James-Lange, 1890).
Emotions are based on feedback of bodily changes. They are cognitive responses to information from physiology.
("We feel sorry because we cry, angry because we strike, afraid because we tremble")
it’s not the stimulus (the dog) that makes you feel the emotion. It’s the physical reaction (the racing heart) that makes you feel it.
What is the support and evidence against arousal being a factor in emotion?
Support: Beta-blockers reduce anxiety eg. BP and muscle tightening + useful in lie-detection industry.
Against: Physiological changes accompany many emotions which are similar and are difficult to differentiate. Spinal cord injury patients still experience emotions.
What is Cannon's theory in regards to the arousal factor of emotion? (1927)
SNS and PNS act in balance when non-excited. When balance is upset, SNS prepares body for fight or flight with increased adrenaline.
Emotional experience and physiological reactions are separate but can happen at the same time. Esentially saying there is 2 different tracks (one to the cortex (emotion - fear) and one to ANS (physical action - heart races))
What is Canon-Bard's theory in regards to the arousal factor of emotion?
Physiological changes and subjective emotional feeling as a response to a stimulus are separate and independent.
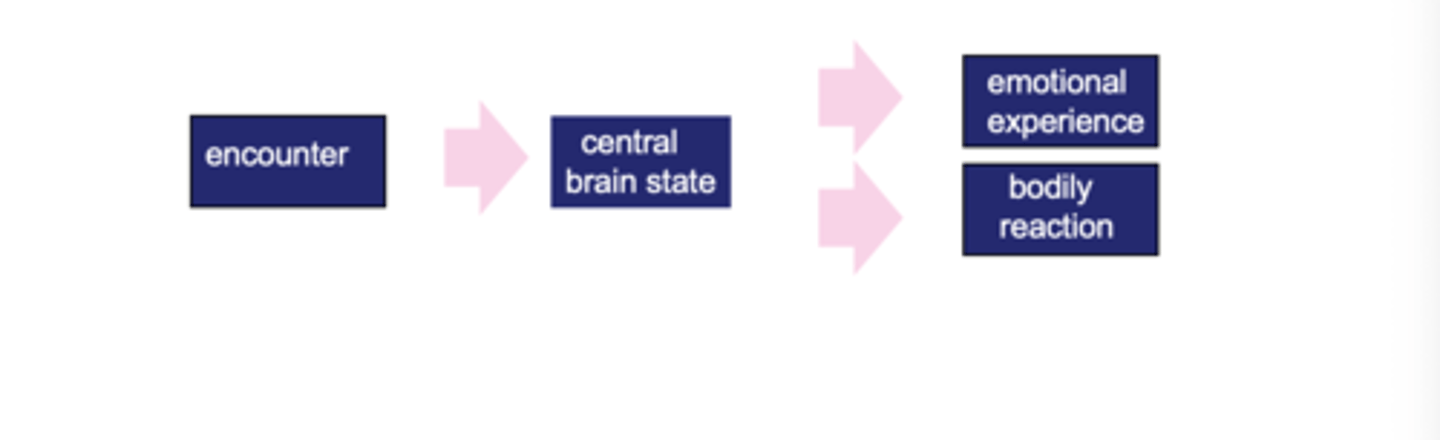
What is a Point against the Cannon-Bard Theory
The emotion we feel is irrelevant to the subjective awareness of emotion triggered in the cortex
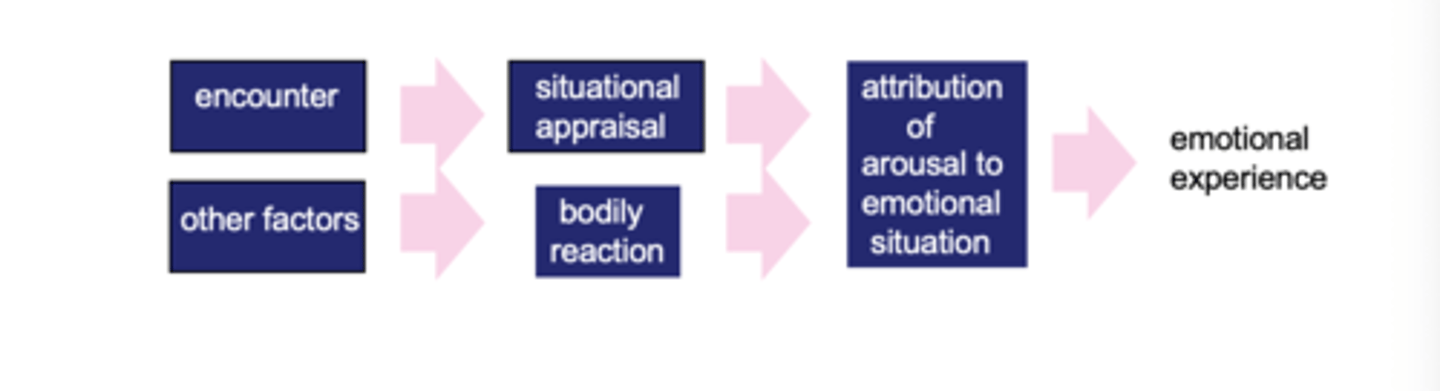
What is Schachter's 2-factor theory in regards to the arousal factor of emotion? What is the drawback of this theory?
Emotion arises from physiological arousal and its interpretation based on situational cues.Said to feel an emotion you need both physcial arousal (heart race) and cognitive label ..
i.e. emotion depends on how the arousal is interpreted by the person experiencing it. Combines Lange and Canon-Bard's theories.
Drawback: Doesn't account for other sources of emotionally relevant info which can affect eg. facial expression or feedback from emotional action.
Explain the expression factor for processing emotion. (Darwin, 1873 and Duchenne).
Expressing emotion is mostly innate but some need practice before being developed.
Duchenne: specific facial muscles produce emotion through facial expressions.
What is the Duchenne smile?
A false smile by electrically stimulating appropriate facial muscles - different mm are associated with different emotions.
What regions of the brain control voluntary and involuntary facial movements?
Voluntary: Pyramidal motor system that includes the motor cortex.
Involuntary: eg. genuine smile, extrapyramidal motor system depending on subcortical areas.
Brain damage can disrupt either system.
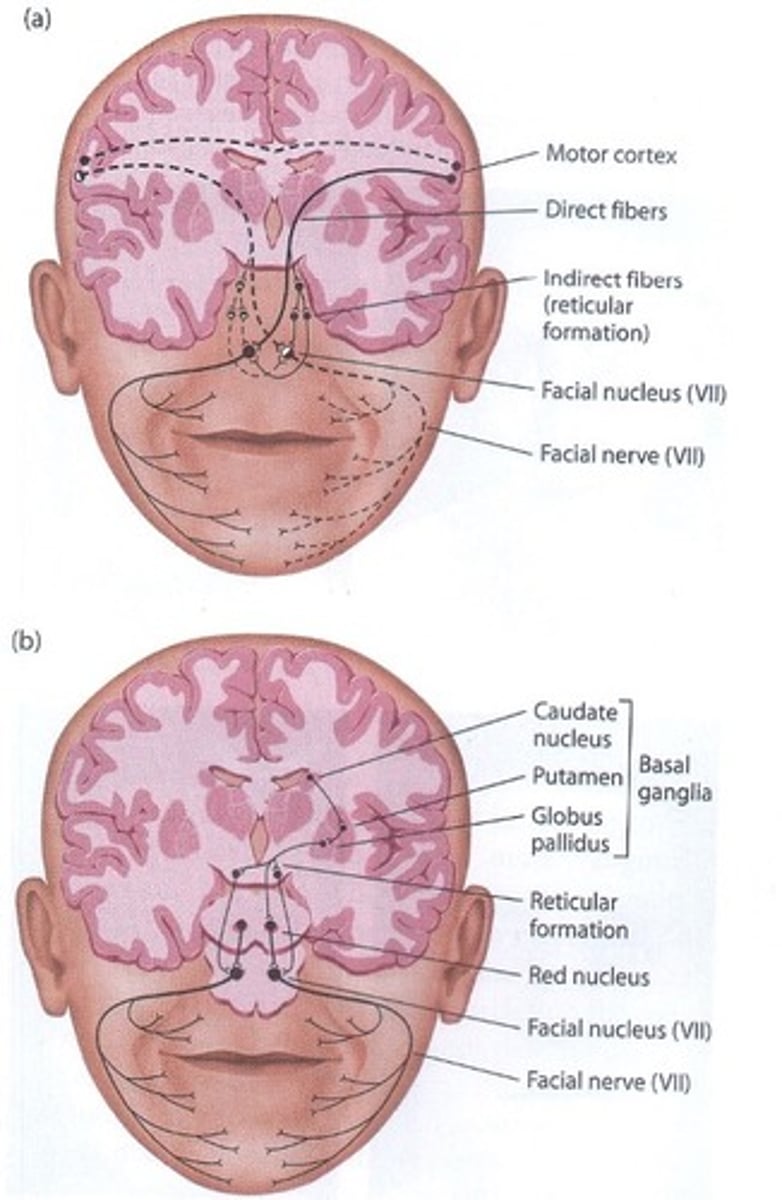
What is the facial feedback hypothesis?
Pattern of mm during facial expression feeds back to brain, giving it information for the subjective feel of an emotion.
Darwin says the intensity of the emotion can be altered by altering intensity of facial expression.
So smile bigger = feel more happier
Explain the action-readiness factor for processing emotion. (Frijda's 4-factor theory).
Emotion serves as impulse for specific action for emotion.
Emotional processes are manifestations of common underlying process. Emotion involves the 4 factors - appraisal, arousal, expression and readiness.
State what each theory’s primary focus is .
James-Lange Cannon-Bard , Schachter-Singer , Frijda's Four-Factor
James-Lange = Physiological Arousal
Cannon-Bard = Brain/Cortex Awareness
Schachter-Singer = Physiological Arousal + Appraisal
Frijda's Four-Factor = Integrated Process
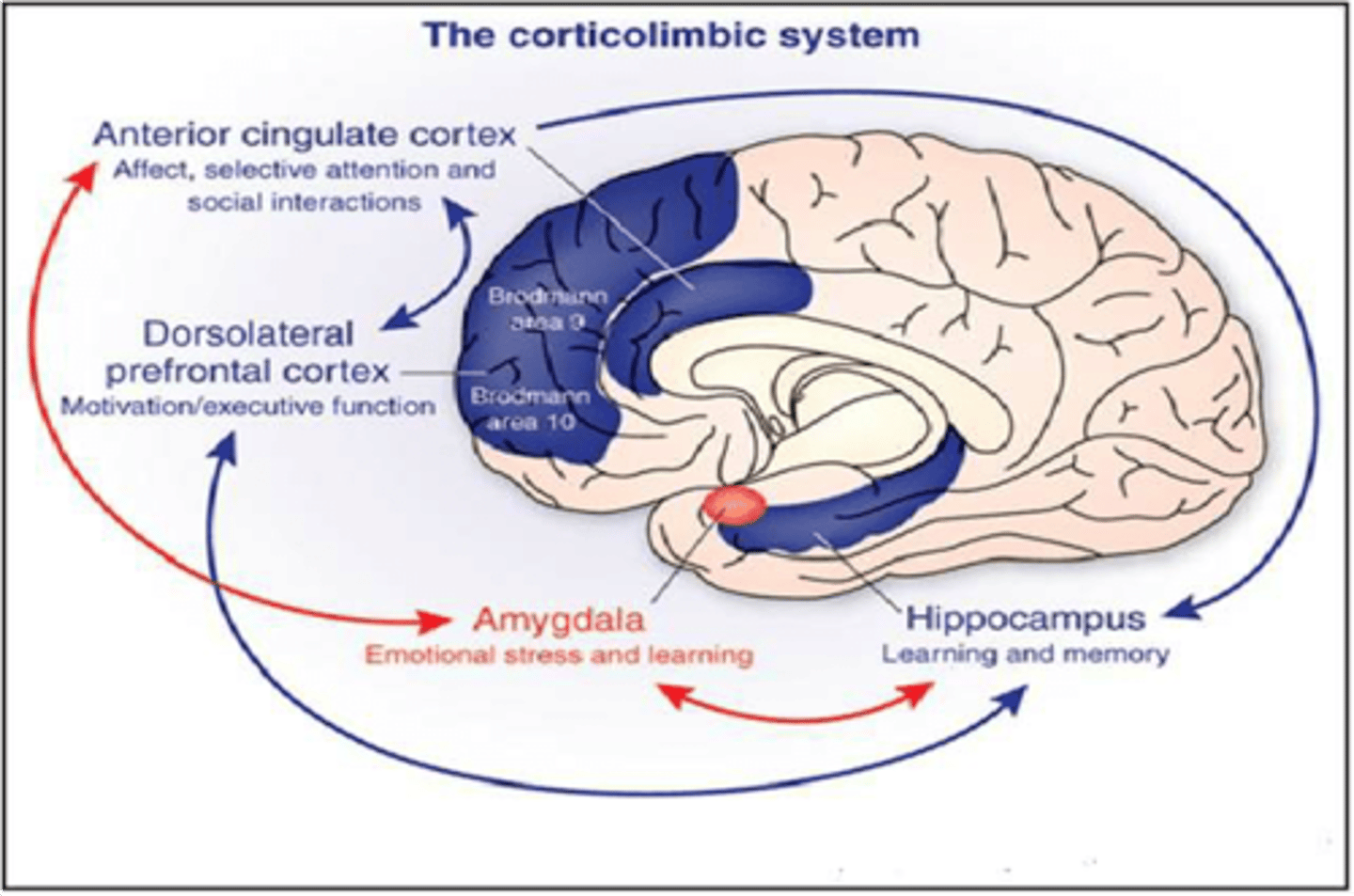
What is the role of the limbic system in regulating emotion?
Influences motivation, attention, learning + memory. Influences endocrine system and the ANS.
Is tightly connected to prefrontal cortex, (mood and appetite) creating cortico-limbic network.
What is role of the amygdala in emotion appraisal?
-Receives visual, auditory, taste + smell from thalamus and uses it to make a quick and rough eval about potential harm or benefit of stimulus. Meanwhile the visual cortex responds slowly and accurately.
- Mediates both autonomic expression + cognitive experience of emotion.
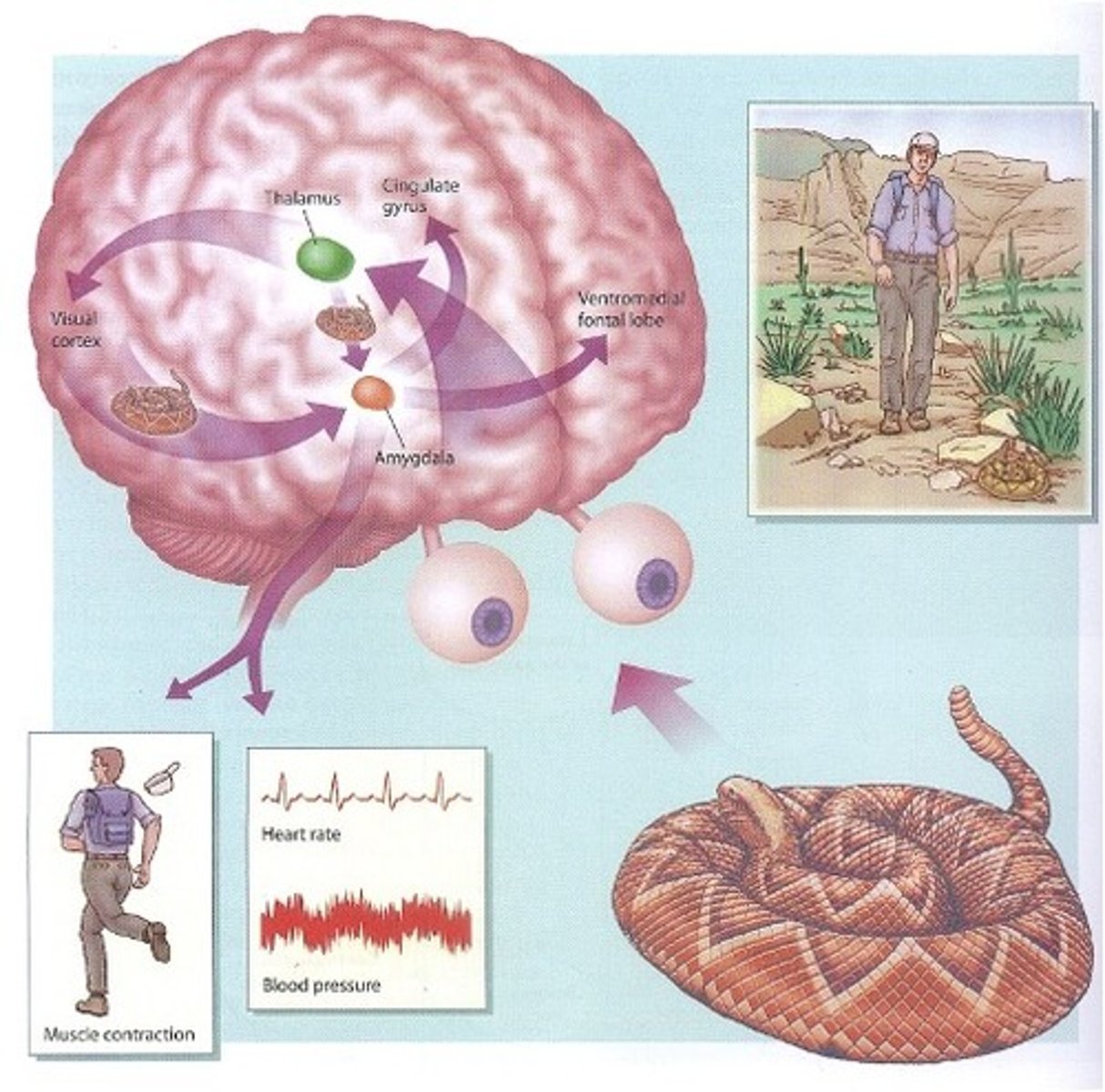
Amygdala - fill in the gaps
Processes visual, auditory, and sensory information for —- ?
Crucial in —— conditioning and quick “—— responses.
Role is emotional appraisal?
The visual thalamus sends info to —— + —— → amygdala process this quickly → mistakingly it sees the stimulus as a —— → prepares for ——- automatically → visual cortex responds —— + accurately
Supports —— theory
So it works at the ——- level
Processes visual, auditory, and sensory information for rapid appraisal/evaluation of threats (is the stimulus a threat or not - determined by the amygdala).
Crucial in fear conditioning and quick “fight or flight” responses.
Is the role emotional appraisal?
The visual thalamus sends info to amygdala + visual cortex→ amygdala process this quickly → mistakingly it sees the stimulus as a threat → prepares for flight/fight automatically → visual cortex responds slowly + accurately
Supports james + frijda theory
So it works at the subliminal level
How does fear activate the amygdala?
Involved in autonomic and preconscious detection of threat and danger to quickly act. Subliminal presentations of fearful faces (for short time) without conscious detection still activate amygdala.
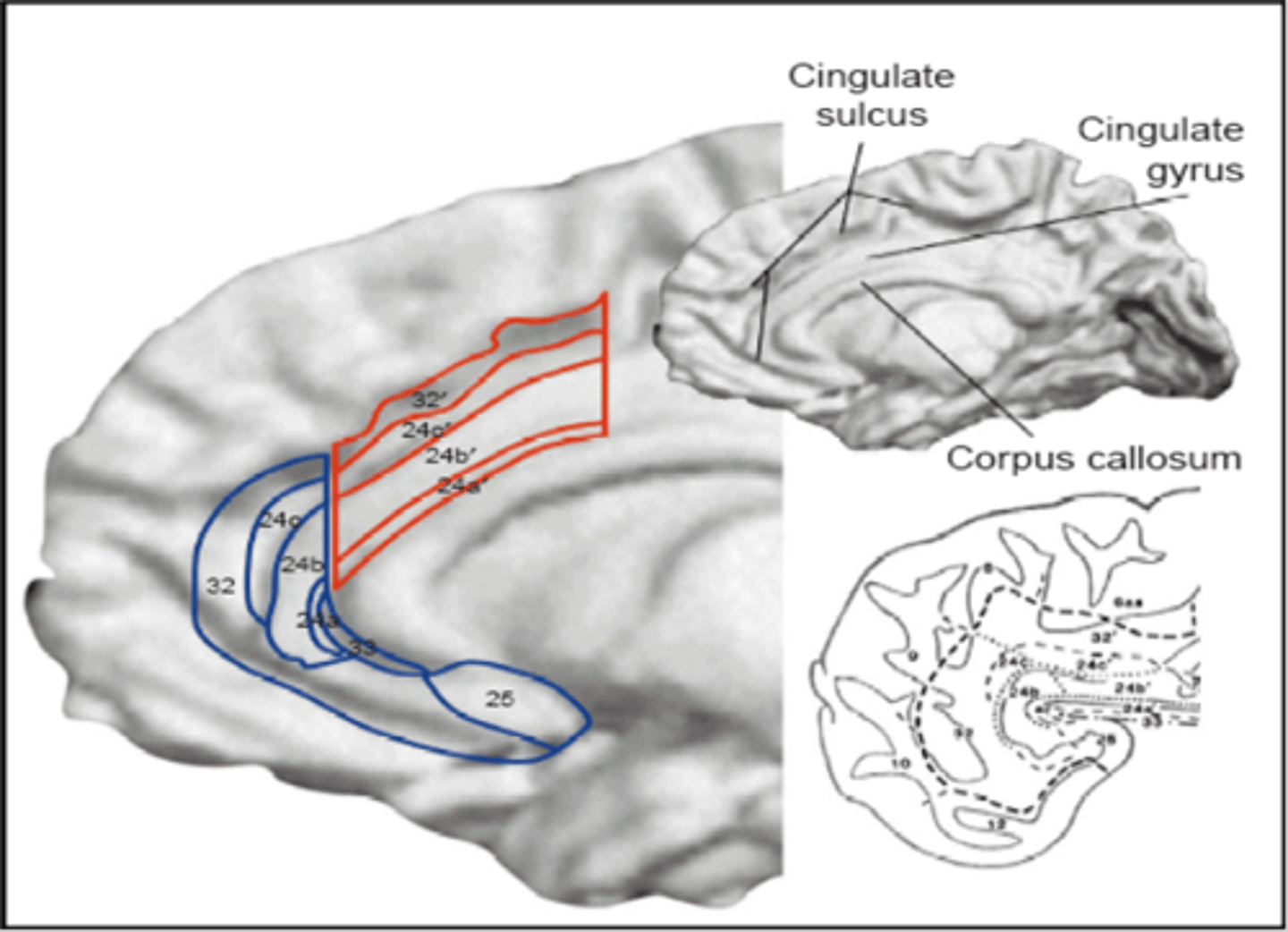
What is the role of the anterior cingulate cortex in emotional regulation?
Involved in attention to regulate cognitive + emotional processing. It has 2 separate divisions for cognitive (dorsal) and emotional (rostral) processing.
involved in a form of attention that serves to regulate both cognitive and emotional processing.
Like the mediator - acts as a junction between the emotional limbic system and the rational prefrontal cortex
Regulates cognitive and emotional processing.
Subdivided into dorsal (cognitive) and rostral (emotional) sections.
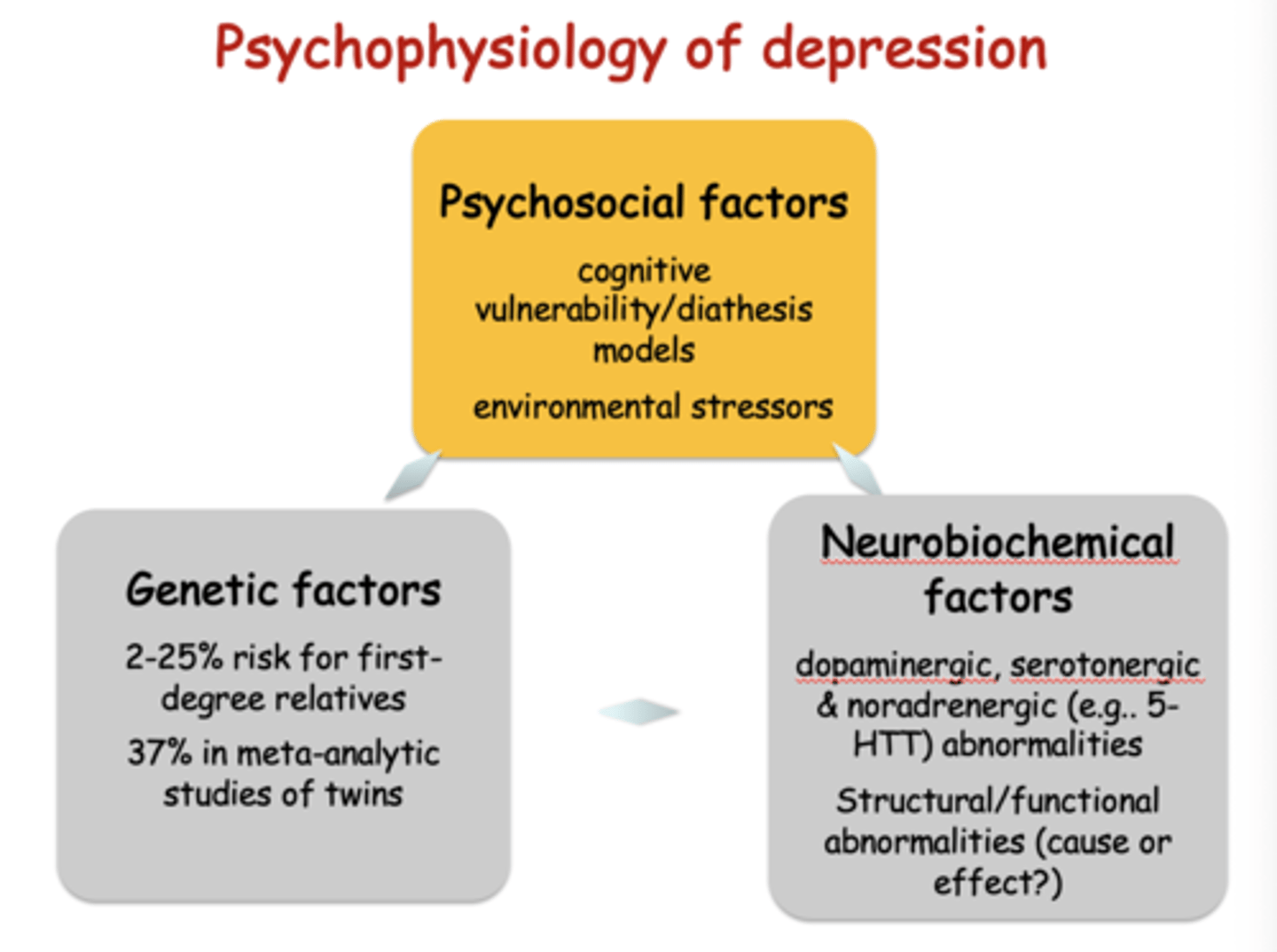
Outline the psychophysiology of depression i.e. its components. (3)
Psychosocial: cognitive vulnerability models and environment
Genetic: 2-25% risk for 1º degree relatives.
Neurobiochemical: DA, 5HT3, NA abnormalities.
How does anxiety and low mood affect emotional processing tasks?
Perform worse in response to emotion-laden stimuli or feedback that triggers emotional reactions.
Explain the transdiagnostic emotional sign - flat affect.
Which disorders can it occur in?
Can occur in major depression, schizophrenia and Parkinson's.
- Lack of emotional response in facial + vocal.
- Linked to brain dysfunction.
- May not reflect actual subjective emotional experience in schizophrenic patients.
Explain the transdiagnostic emotional sign - inappropriate effect.
Seen in psychotic disorders eg. schizoprehnia where there is disorganised thought and associated effect.
- Emotional display isn't suitable to context; may laugh on hearing bad news.
Outline the presentation of patients with mood disorders. (3)
1. Emotional processing deficits in affective tasks
2. Functional abnormalities in corticolimbic circuit (prefrontal, amygdala, hippocampus)
3. Overactive dorsal cortical, hypofunctional ventral paralimbic
Dorsol corticol decreases and ventric paralimbic increases = ventral is higher → means that emotions take over → prevents patients using their cognitive thinking in certain situations
Outline the presentation of patients with psychotic disorders. (2)
Typically in a psychotic disorder like in schizo, there are behavioural + neural deficits.
Dysregulation in both:
1. top-down control via prefrontal
2. bottom-up control via limbic areas.
What is the Abnormal Affect in Mood and Psychotic Disorders model
This model shows you how the limbic system functions differently in depressed states , it looks at
Psychological factors
Cognitive - that individual predispositions (diathesis) interact with life experiences to trigger depressive states
Environmental stressors- External pressures can act as triggers for the emotional and cognitive circuits
Genetic factors
risk of developing depression has a significant hereditary component
There is a 2-25% risk for those with an affected close relative
37% concordance rate in twins
Neurobiochemical factors
Neurobiochemical factors - chemical and structural changes that occur within the brain's emotional centers
Irregularities occur in the dopaminergic, serotonergic, and noradrenergic systems
structural abnormalities
Interms of Neurobiological Factors , how does this cause sympotoms of mood diorder
Dysfunction in cortico-limbic networks:
Overactive paralimbic regions (emotional response).
Underactive dorsal cortical regions (cognitive control).
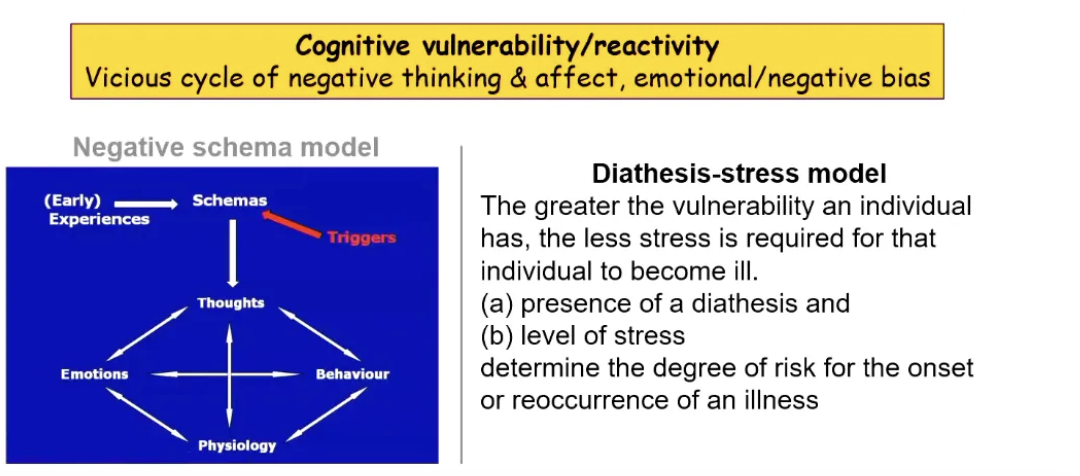
What are the 2 models of depression
Beck’s Negative Schema Model: Negative thought patterns perpetuate depression.
Diathesis-Stress Model: Interaction of vulnerability and stress determines illness risk.