Bio Chem Exam #4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 1:49 AM on 5/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
1
New cards
enzyme whose endergonic nature depends on keto-enol tautomerism
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
pyruvate kinase
2
New cards
exported compound during high levels of beta oxidation which allosterically activates fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
citrate
3
New cards
product of the adrenal cortex that activates PEPCK and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase expression
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
cortisol
4
New cards
mitochondrial enzyme using a biotin cofactor
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
pyruvate carboxylase
5
New cards
redox enzyme that forms a thioester bond to substrate
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
GAPDH
6
New cards
source of GTP for PEPCK
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
succinyl coA synthetase in the CAC
7
New cards
gluconeogenic enzyme requiring especially high levels of ATP
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
phosphoglycerate kinase
8
New cards
enzyme with a high Km for glucose which invests an ATP for retention in the Islet beta cell
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
glucokinase
9
New cards
allosterically inhibits pyruvate kinase
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
alanine
10
New cards
compound whose low energy drives the exergonic nature of the production of "profit" ATPs during glycolysis
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
3-phosphoglycerate
11
New cards
enzyme with a low Km for glucose which invests an ATP for retention within the muscle cell
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
hexokinase
12
New cards
anchoring transcription factor for the GRs bound to weak GREs whose function is negated by Akt/PKB action
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
Fox01
13
New cards
cytoplasmic gluconeogenic enzyme using a biotin cofactor
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
PEPCK
14
New cards
reduced form of OAA that is channeled to the cytoplasm to feed gluconeogenesis
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
\
alanine
\
citrate
\
cortisol
\
FoxO1
\
GAPDH
\
glucokinase
\
hexokinase
\
malate
\
PEPCK
\
3-phosphoglycerate
\
phosphoglycerate kinase
\
pyruvate carboxylase
\
pyruvate kinase
\
succinylCoA synthetase in the CAC
malate
15
New cards
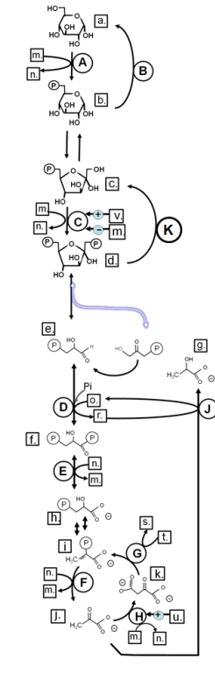
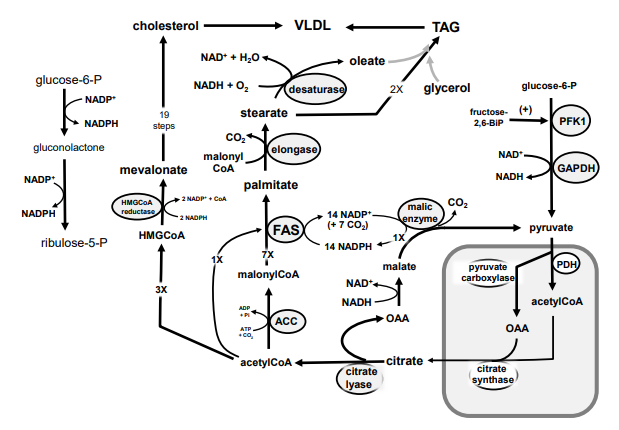
Match from CAPS to: PEPCK
G
16
New cards
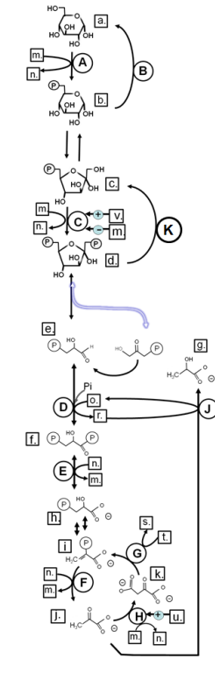
Match from CAPS to: PYRUVATE KINASE
F
17
New cards
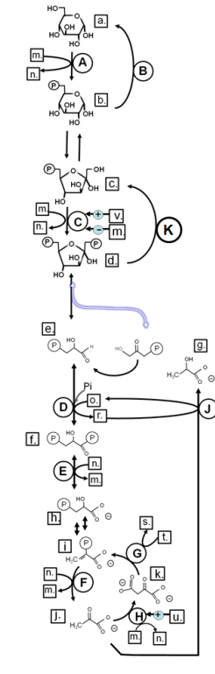
Match from CAPS to: HEXOKINASE
A
18
New cards
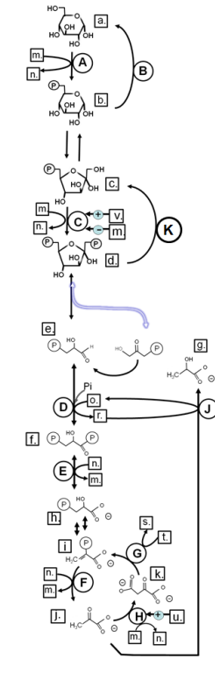
Match from lower case letters to: pyruvate
j
19
New cards
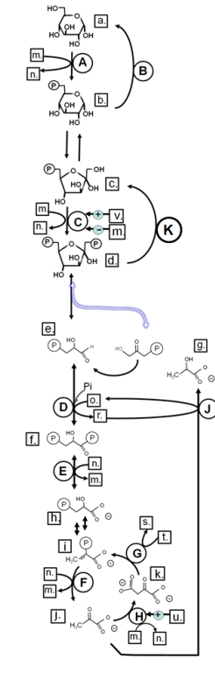
Match from CAPS to: LDH
J
20
New cards
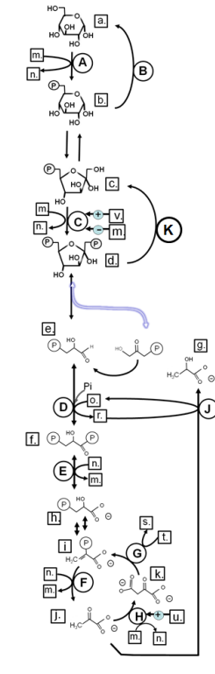
Match from lower case letters to: glucose
a
21
New cards
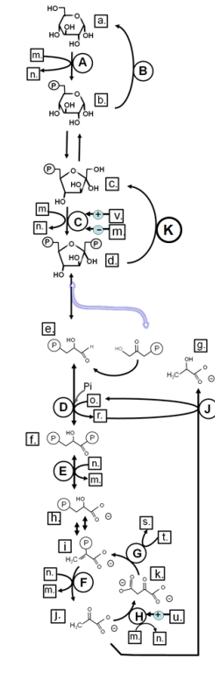
Match from CAPS to: FRUCTOSE-1,6-BISPHOSPHATASE
K
22
New cards
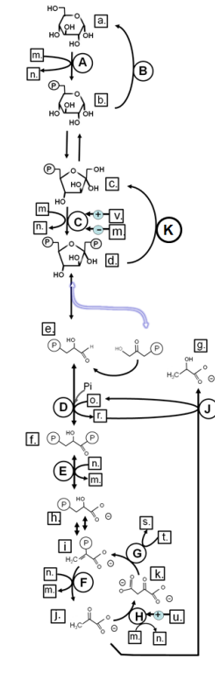
Match from lower case letters to: NADH
r
23
New cards
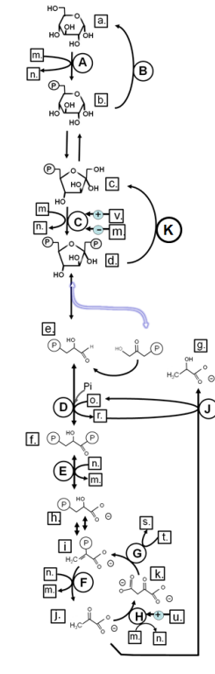
Match from lower case letters to: ATP
m
24
New cards
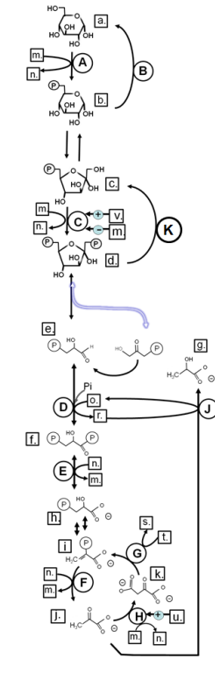
Match from lower case letters to: fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
d
25
New cards
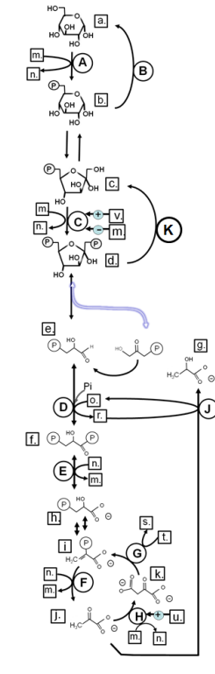
Match from lower case letters to: acetylCoA
u
26
New cards
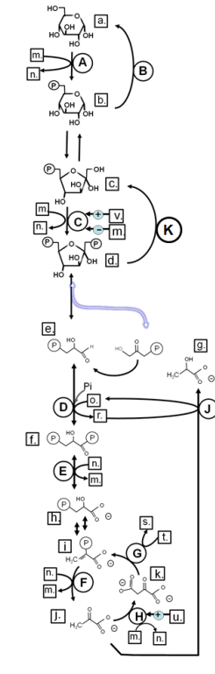
Match from lower case letters to: ADP
n
27
New cards
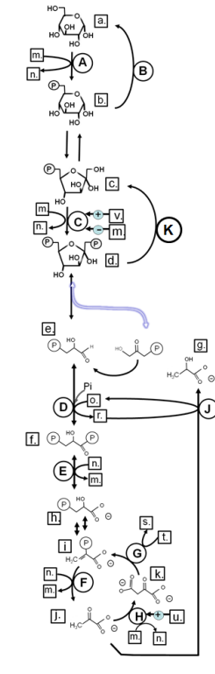
Match from lower case letters to: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
e
28
New cards
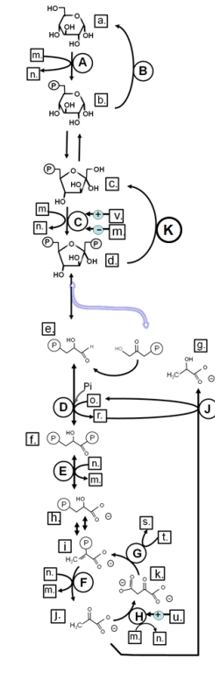
Match from lower case letters to: GDP
s
29
New cards
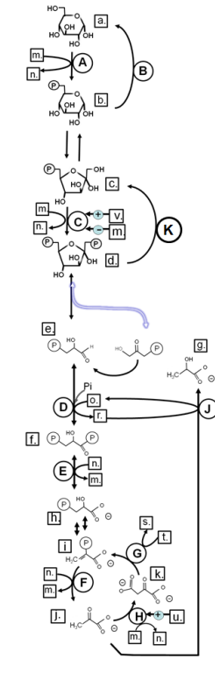
Match from lower case letters to: fructose-6-phosphate
c
30
New cards
Match from lower case letters to: NAD+
o
31
New cards
Match from lower case letters to: lactate
g
Match from lower case letters to: oxaloacetate
Match from lower case letters to: oxaloacetate
32
New cards
Match from lower case letters to: oxaloacetate
k
33
New cards
Match from lower case letters to: glucose-6-phosphate
b
34
New cards
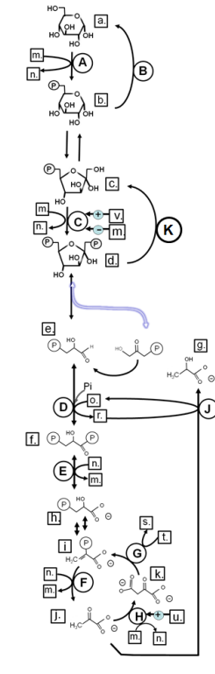
Match from lower case letters to: phosphoenolpyruvate
i
35
New cards
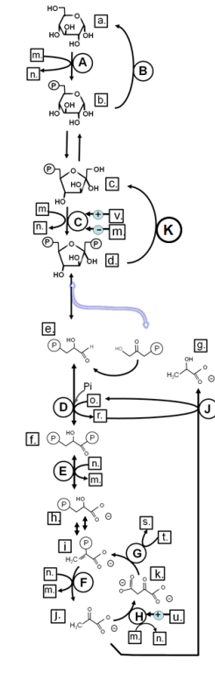
Match from CAPS to: PYRUVATE CARBOXYLASE
H
36
New cards
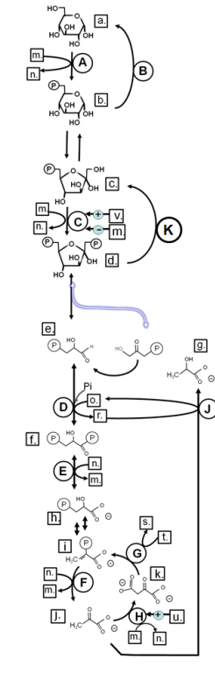
Match from lower case letters to: 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
f
37
New cards
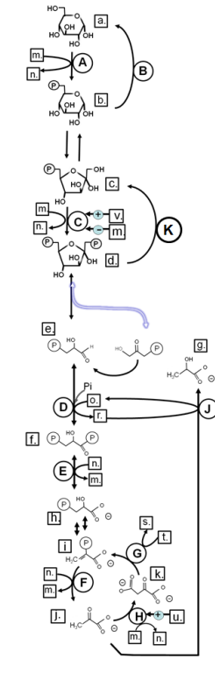
\
Match from lower case letters to: AMP
v
38
New cards
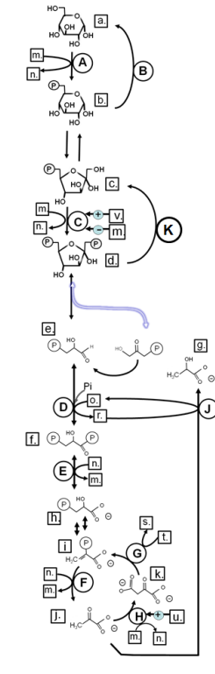
Match from CAPS to: GAPDH
D
39
New cards
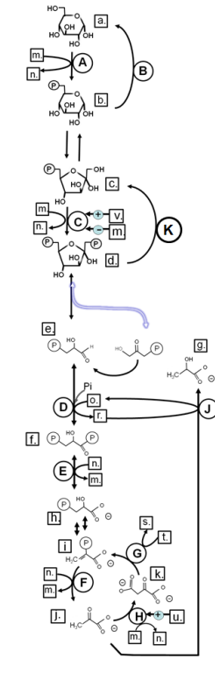
Match from CAPS to: PFK-1
C
40
New cards
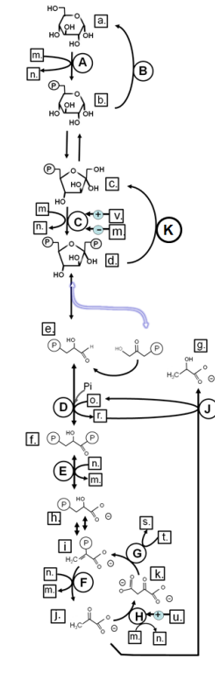
Match from CAPS to: GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATASE
B
41
New cards
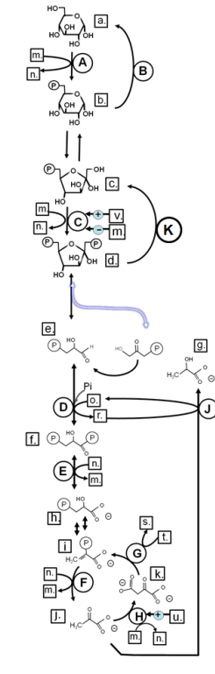
Match from lower case letters to: 3-phsophoglycerate
h
42
New cards
Match from lower case letters to: GTP
t
43
New cards
Match from CAPS to: PHOSPHOGLYCERATE KINASE
E
44
New cards
decarboxylates a three-carbon alpha keto acid, reducing NAD+ with the bond electrons, and producing a thioester bond of the remaining two-carbon product to CoA
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
PDH
45
New cards
hydrolyzes a thioester-bonded six-carbon intermediate in a highly exergonic standard state reaction
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
46
New cards
performs simple hydride transfer reduction of NAD+ combined with decarboxylation in an exergonic standard state reaction
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
isocitrate dehydrogenase
47
New cards
decarboxylates a five-carbon alpha keto acid, reducing NAD+ with the bond electrons, and producing a thioester bond of the remaining four-carbon product to CoA
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
48
New cards
phosphorylyzes a thioester-bonded four-carbon compound to produce an acyl-phosphate that participates in substrate-level phosphorylation
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
succinyl-CoA synthetase
49
New cards
inner membrane complex that conducts a redox reaction as part of the CAC to donate electrons directly to the ETS
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
succinate dehydrogenase
50
New cards
performs simple hydride transfer reduction of NAD+ in a highly endergonic standard state reaction
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
malate dehydrogenase
51
New cards
uses high energy electrons to both pump matrix protons and loading matrix protons on a ubiquinol to carry them to the intermembrane space
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex 1)
52
New cards
uses a covalently-bound FAD to donate CAC electrons and matrix protons reduce of ubiquinone
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
succinate dehydrogenase
53
New cards
delivers ubiquinone protons to the intermembrane space and electrons to multiple cytochrome-c-s
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
54
New cards
uses cytochrome-c provided electrons to reduce molecular oxygen to produce low energy water
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
cytochrome c oxidase
55
New cards
in order, each of the ten c subunits of the merry-go-round of ATP synthase first donate a proton from its _____ to the matrix when it comes into contact with the a subunit's half channel to the matrix
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
aspartic acid
56
New cards
the c subunit become negatively charged at first contact with a subunit because of its deprotonated ______
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
aspartate
57
New cards
movement of the merry-go-round is powered by the attraction of the negatively charged c subunit to _____ at the end of the a subunit's half channel from the intermembrane space
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
arginine
58
New cards
The a subunit's ____ protonates the c subunit and is itself re-protonated from protons delivered to it by the half channel from the intermembrane space
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
arginine
59
New cards
the turning of the merry-go-round turns a _____ cam-shaft which produces the changes among the three states of the three alpha/beta dimeric enzymes that synthesize ATP
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
gamma subunit
60
New cards
ADP + Pi bind to the ____ during ATP synthase action
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
alpha/beta subunit L state
61
New cards
a water molecule is withdrawn and trapped as ATP is synthesized in the _____ of ATP synthase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
alpha/beta subunit T state
62
New cards
a water molecule is withdrawn and trapped as ATP is synthesized in the _____ of ATP synthase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
alpha/beta subunit T state
63
New cards
a parallel beta sheet is disrupted by the spinning camshaft to release ATP and water in the ____ of ATP synthase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
alpha/beta subunit O state
64
New cards
in the water trap of ATP synthase what interacts with the polar H's of water?
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
glutamate
65
New cards
in the water trap of ATP synthase what interacts with the polar O of water?
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Citrate synthase
PDH
Cytochrome b-c1 complex (III)
Aspartic acid
Gamma subunit
Alpha/beta subunit T state
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I)
Succinate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome c oxidase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Alpha/beta subunit L state
Arginine
Malate dehydrogenase
Lysine
Alpha/beta subunit O state
Aspartate
Glutamate
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
lysine
66
New cards
When a cytoplasmic NADH is worth 2.5 ATPs in mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, matrix OAA is exported to the cytoplasm as _____.
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
aspartate
67
New cards
When a cytoplasmic NADH is worth 2.5 ATPs in mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, cytoplasmic OAA is imported into the matrix as reduced _____.
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
malate
68
New cards
When a cytoplasmic NADH is worth 1.5 ATPs, it is first used to reduce _____.
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
DHAP
69
New cards
When a cytoplasmic NADH is worth 1.5 ATPs, electrons are donated to the ETS at the inner membrane by _____.
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
glycerol 3P
70
New cards
In response to active thyroid hormone (T3), the protein _____ is produced to activate non-productive movement protons back through the mitochondrial inner membrane to the matrix.
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
UCP1
71
New cards
During thyroid hormone (T3) leakage of protons, the compound _____ is channeled from the matrix to the intermembrane space where it becomes protonated, and returns through the membrane to the matrix to deprotonate.
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
butyrate
72
New cards
In response to non-productive movement of protons back through the inner membrane to the matrix, reduced chemiosmosis leads to the production of heat due to increased activation of the _____.
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
ETS
73
New cards
In response to non-productive movement of protons back through the inner membrane to the matrix, reduced chemiosmosis leads to an increase in ____ which signals glucose uptake and activation of PFK1.
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
AMP
74
New cards
The rate of chemiosmosis is regulated mainly by the concentration of _____ which represents cytoplasmic energy demand.
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
ADP
75
New cards
In response to hyperglycemia, sensitive cells decrease the rate of chemiosmosis by decreased levels of ____.
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
ADP
76
New cards
During hyperglycemia, there is an abnormally large supply of electrons in the ETS, which with low matrix protons leads to the overproduction of _____.
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
Semiequinoes
77
New cards
Semiquinones most directly activate the production of ____.
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
superoxide
78
New cards
SOD converts superoxide into ____.
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
hydrogen peroxide
79
New cards
The major method of removing hydrogen peroxide within the cell is by reducing it with hydrides donated by a pair of cysteines in the protein ____.
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
peroxiredoxin
80
New cards
Oxidized peroxiredoxin is reduced by ____.
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
thioredoxin
81
New cards
Apoptosis signaling kinase-1 is prevented from forming its activating homodimeric, disulfide-bridged state by the formation of a competing disulfide-bridged heterodimer with ____.
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
thioredoxin
82
New cards
When supplies of reduced thioredoxin levels are lowered by ROS demand on the cell, Ask1 will phosphorylate ____ which unmasks the binding site found on the protein Bim.
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
JNK
83
New cards
Phosphorylated Bim removes ____ from the mitochondrial outer membrane leading to Bax-induced apoptosis.
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
BCl2
84
New cards
The most potent allosteric activator of PFK1 is _____ which acts to directly tetramerize that enzyme.
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
85
New cards
PKA-phosphorylated PFK2 produces the product ____.
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
Fructose 6-phosphate
86
New cards
Insulin-stimulated action of PP1 on PFK2 causes it to produce the product ____.
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
aspartate
AMP
UCP1
DHAP
ETS
glycerol 3P
butyrate
malate
hydrogen peroxide
Semiequinoes
superoxide
peroxiredoxin
thioredoxin
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Fructose 6-phosphate
BCl2
JNK
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
87
New cards
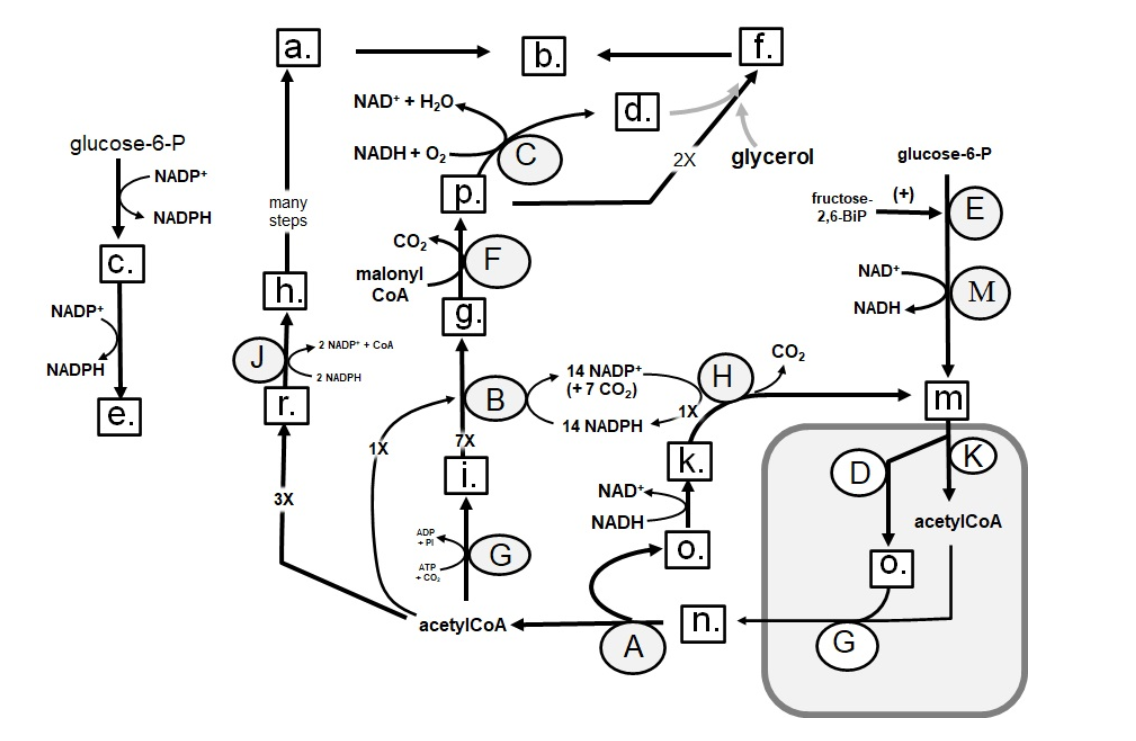
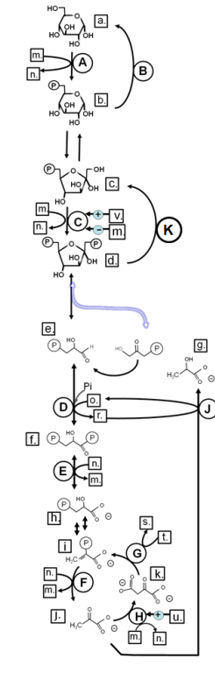
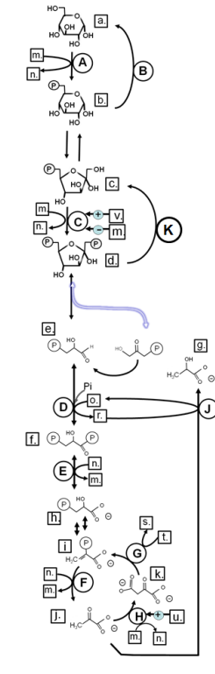
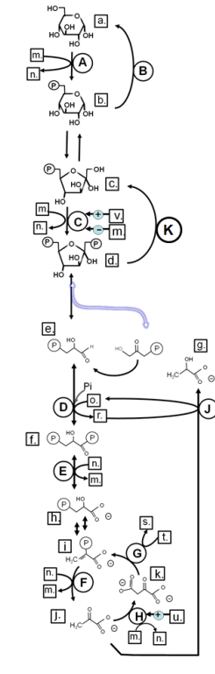
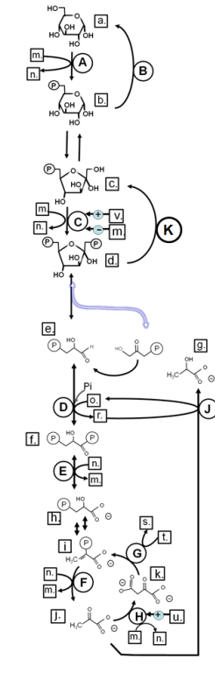
Identify in the circle using CAPS: GAPDH
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
M
M
88
New cards
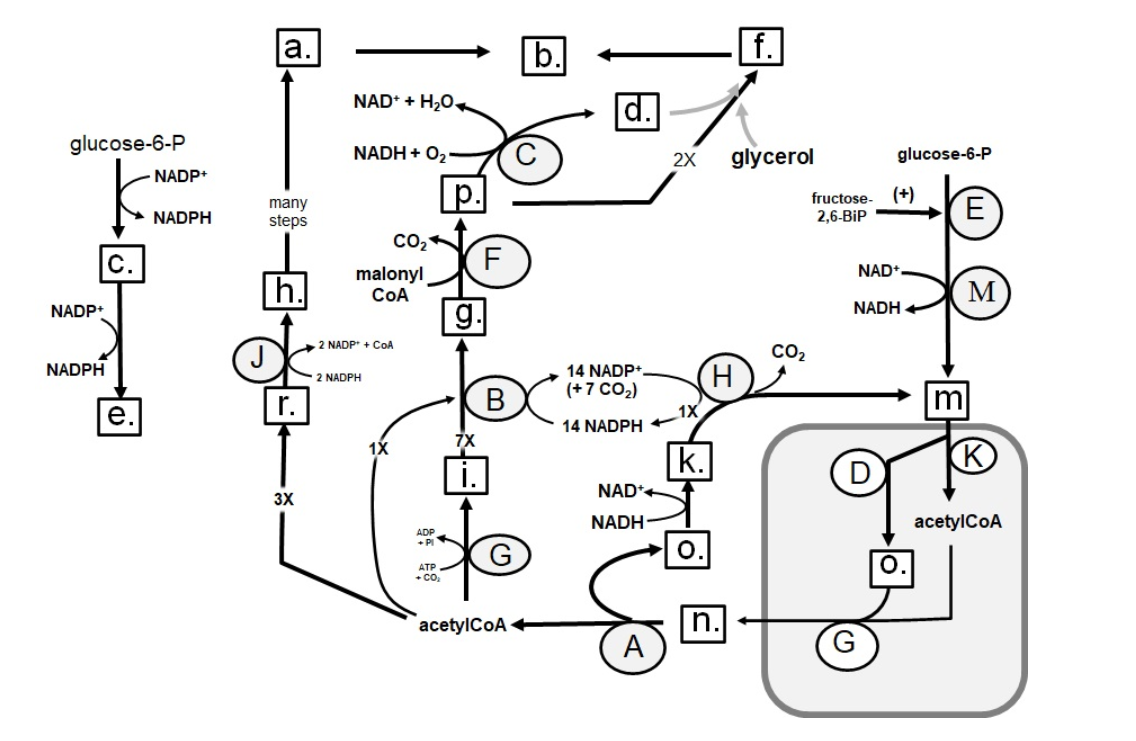
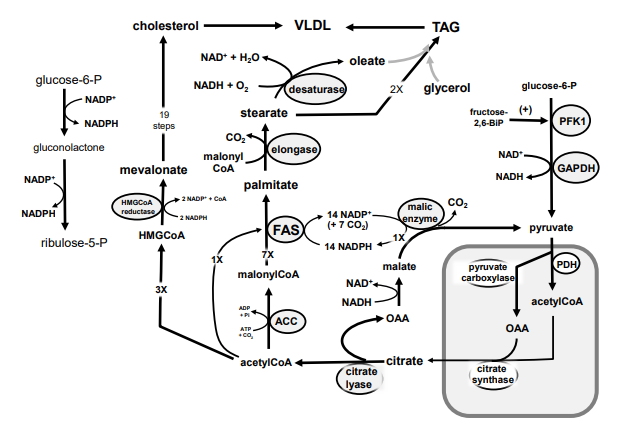
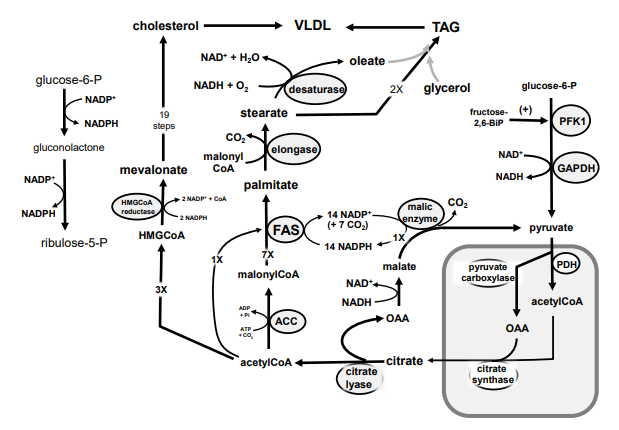
Identify in the circle using CAPS: FAS
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
M
B
89
New cards
Identify in the circle using CAPS: malic enzyme
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
M
H
90
New cards
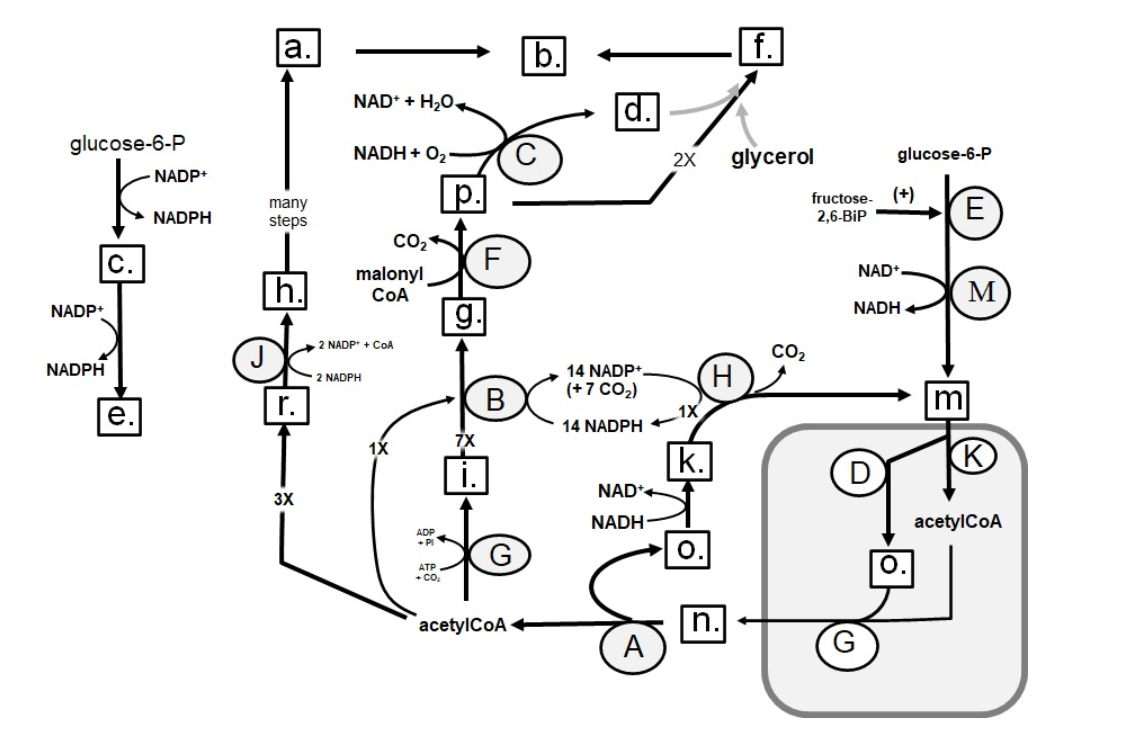
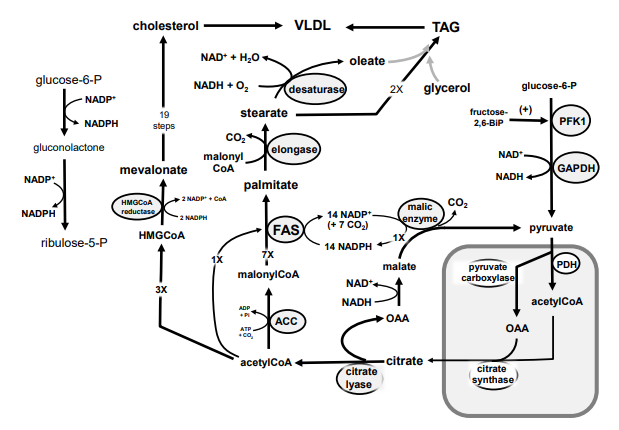
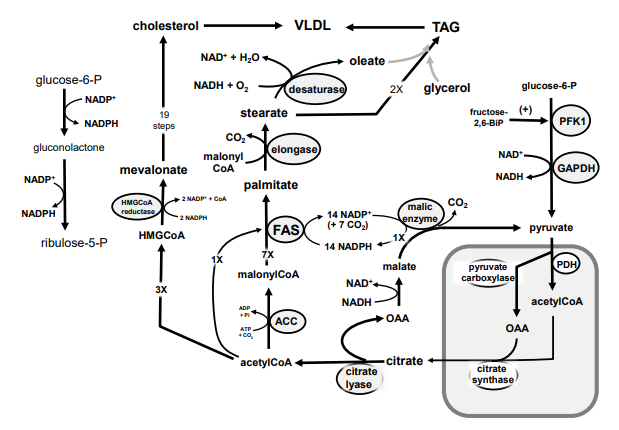
Identify in the square box using lower case letters: gluconolactone
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
i.
k.
m.
n.
o.
p.
r.
c.
91
New cards
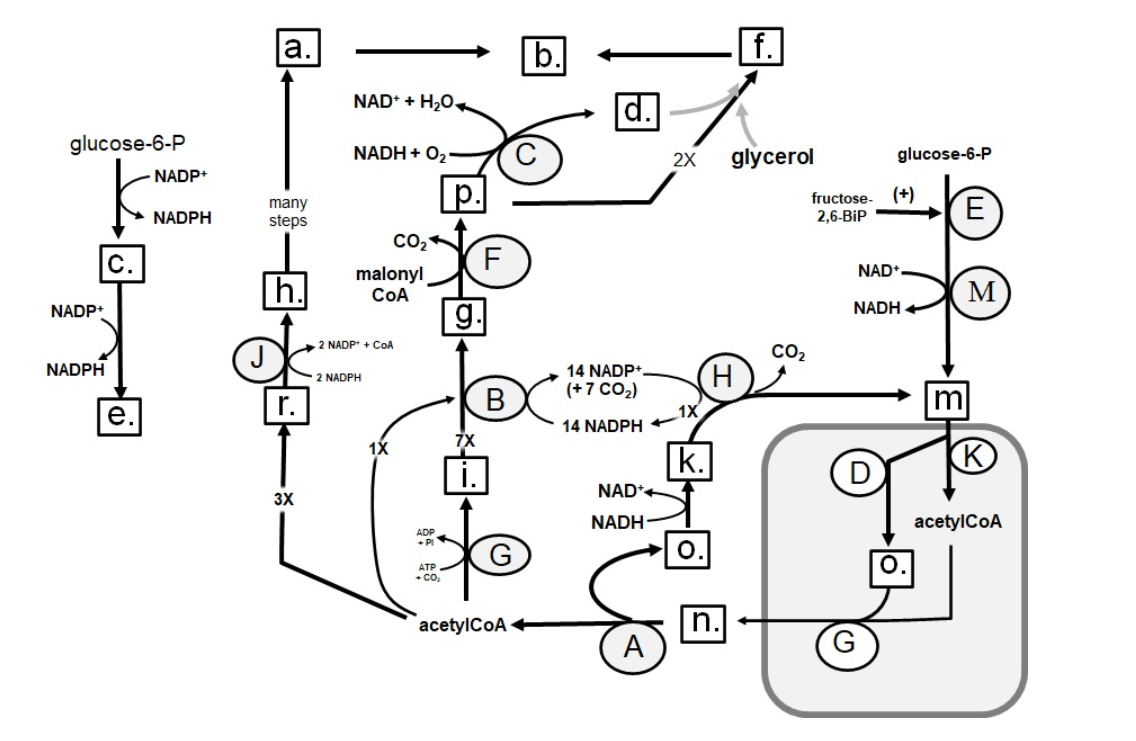
Identify in the square box using lower case letters: OAA
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
i.
k.
m.
n.
o.
p.
r.
o.
92
New cards
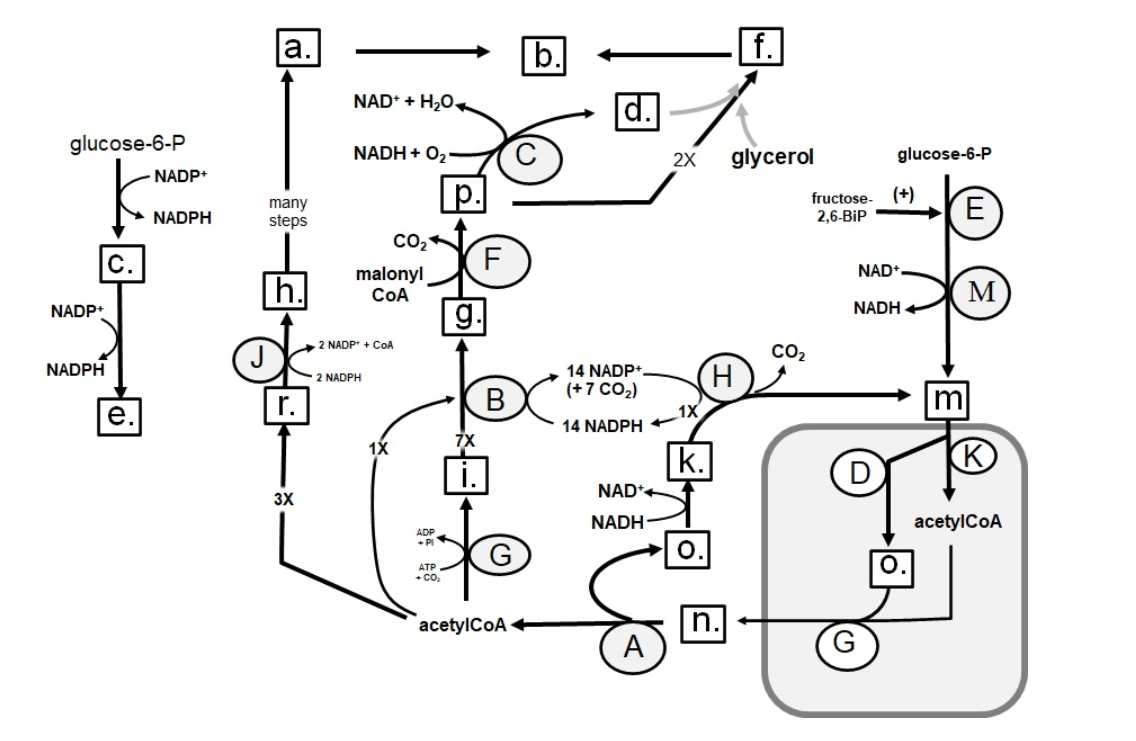
Identify in the square box using lower case letters: pyruvate
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
i.
k.
m.
n.
o.
p.
r.
m.
93
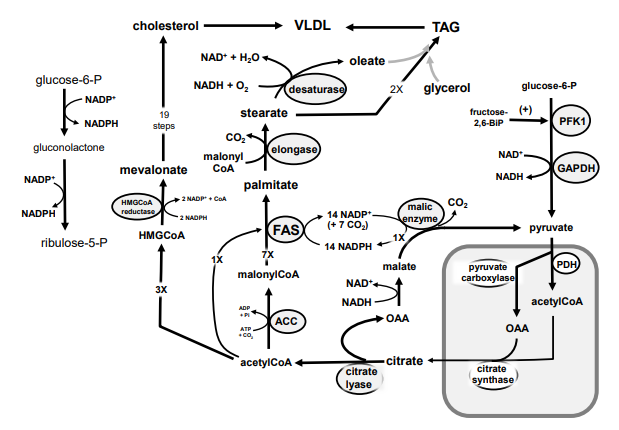
New cards
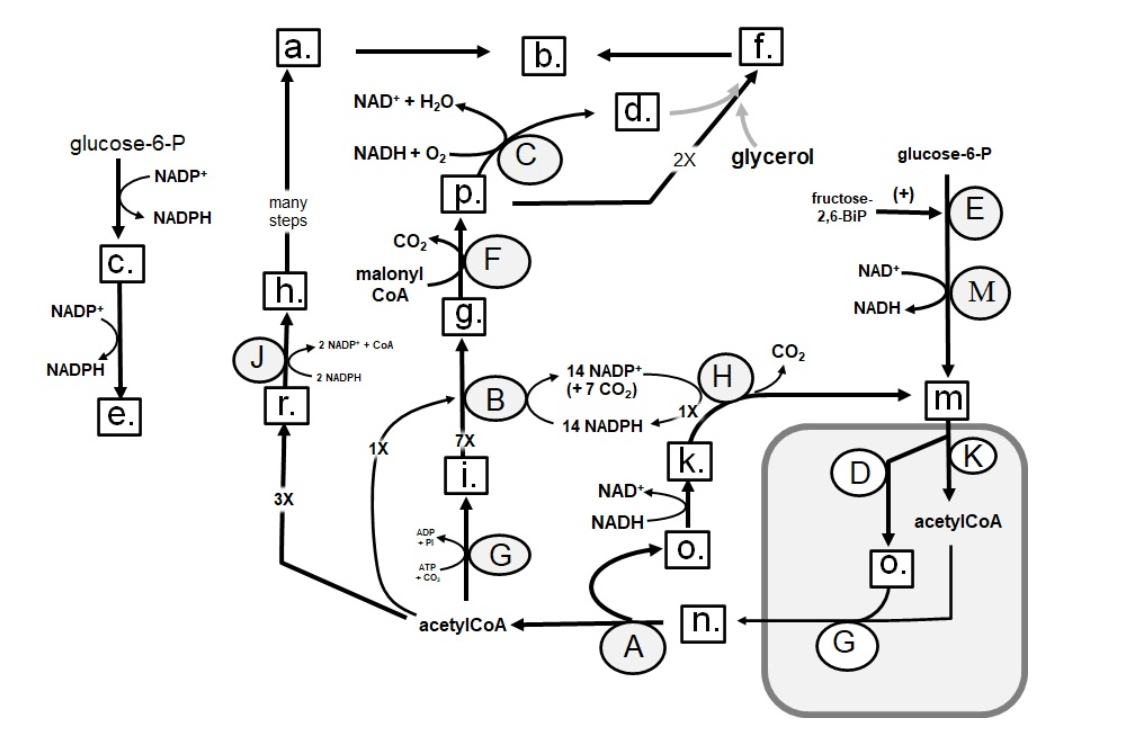
Identify in the circle using CAPS: ACC
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
M
G
94
New cards
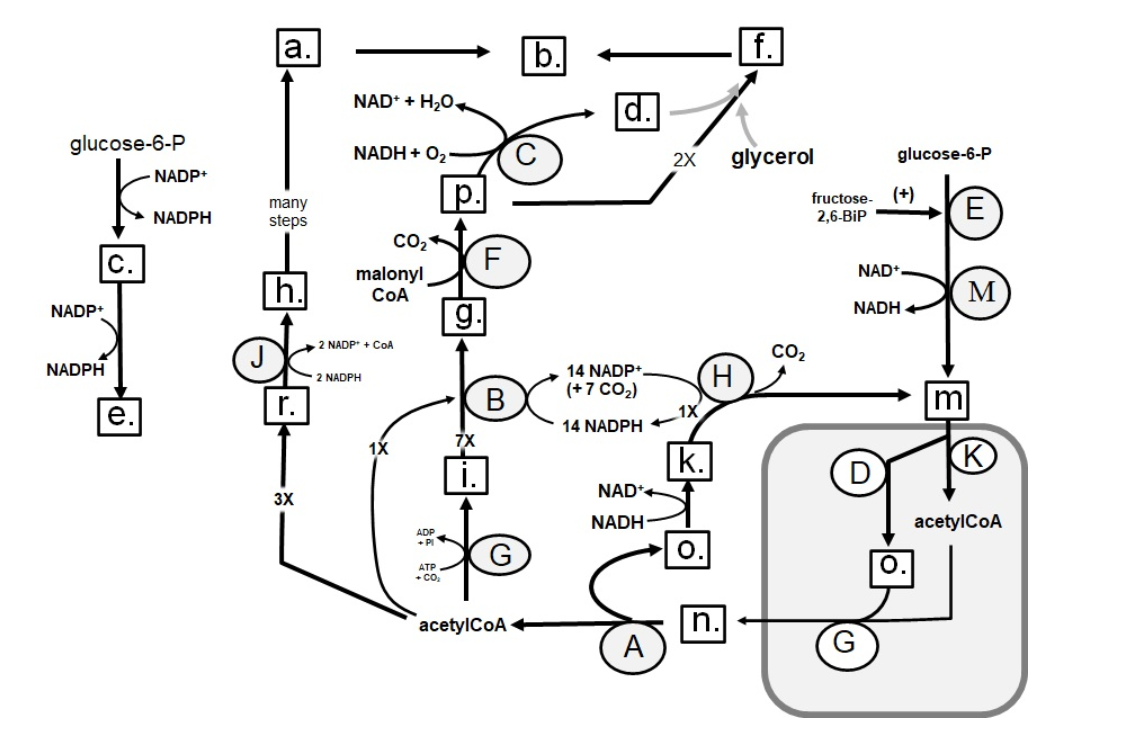
Identify in the circle using CAPS: elongase
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
M
F
95
New cards
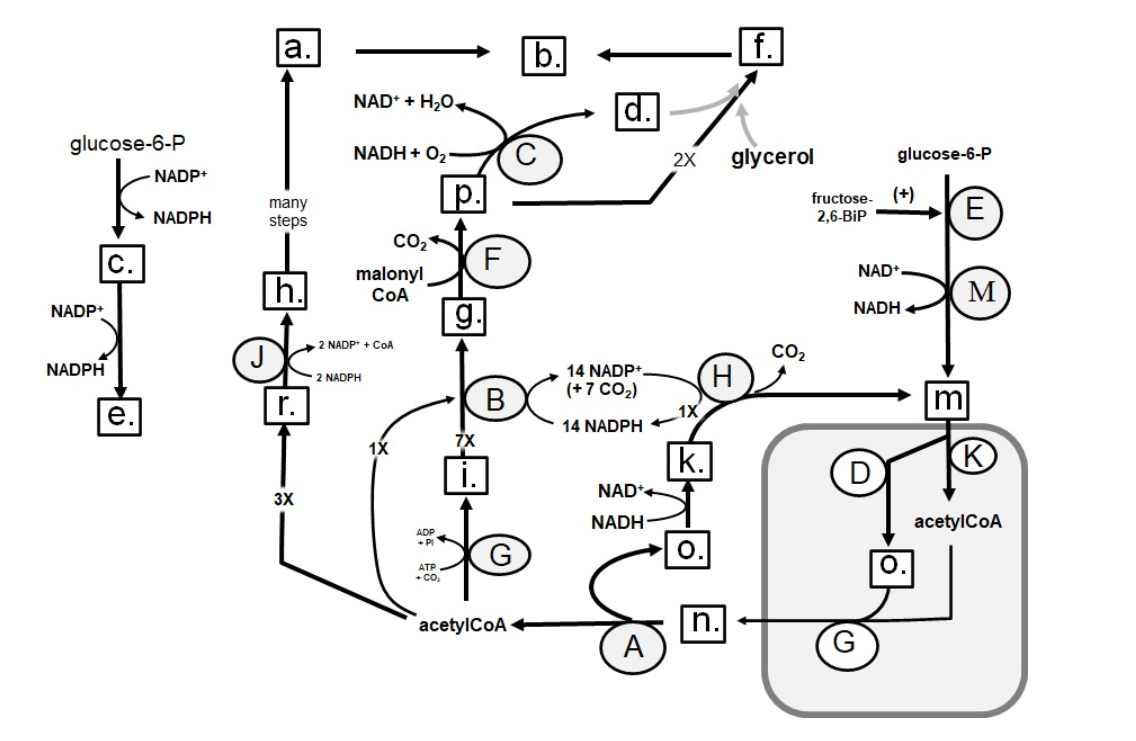
Identify in the circle using CAPS: desaturase
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
M
C
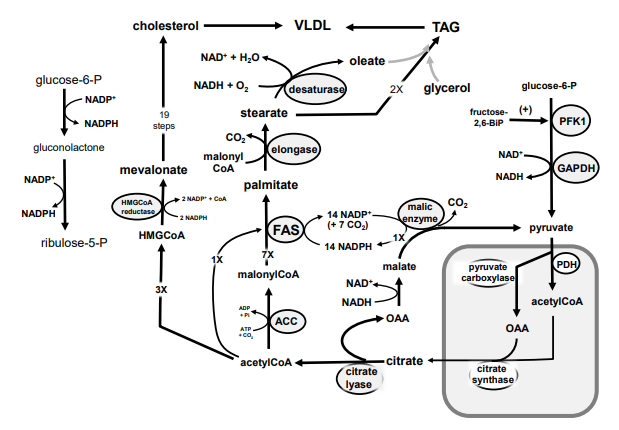
96
New cards
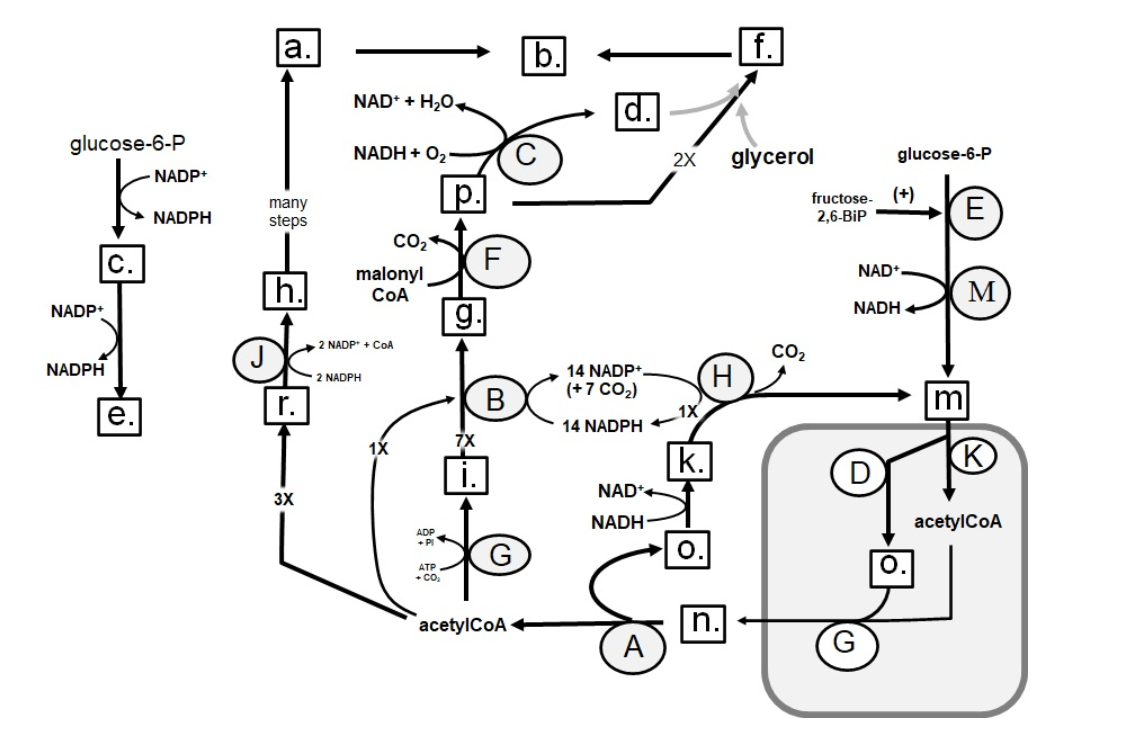
Identify in the square box using lower case letters: palmitate
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
i.
k.
m.
n.
o.
p.
r.
g
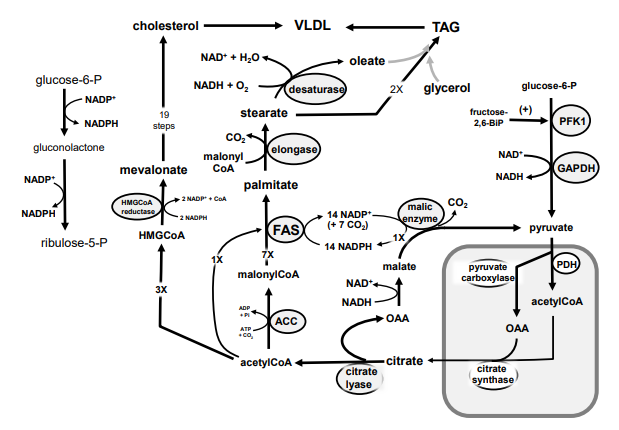
97
New cards
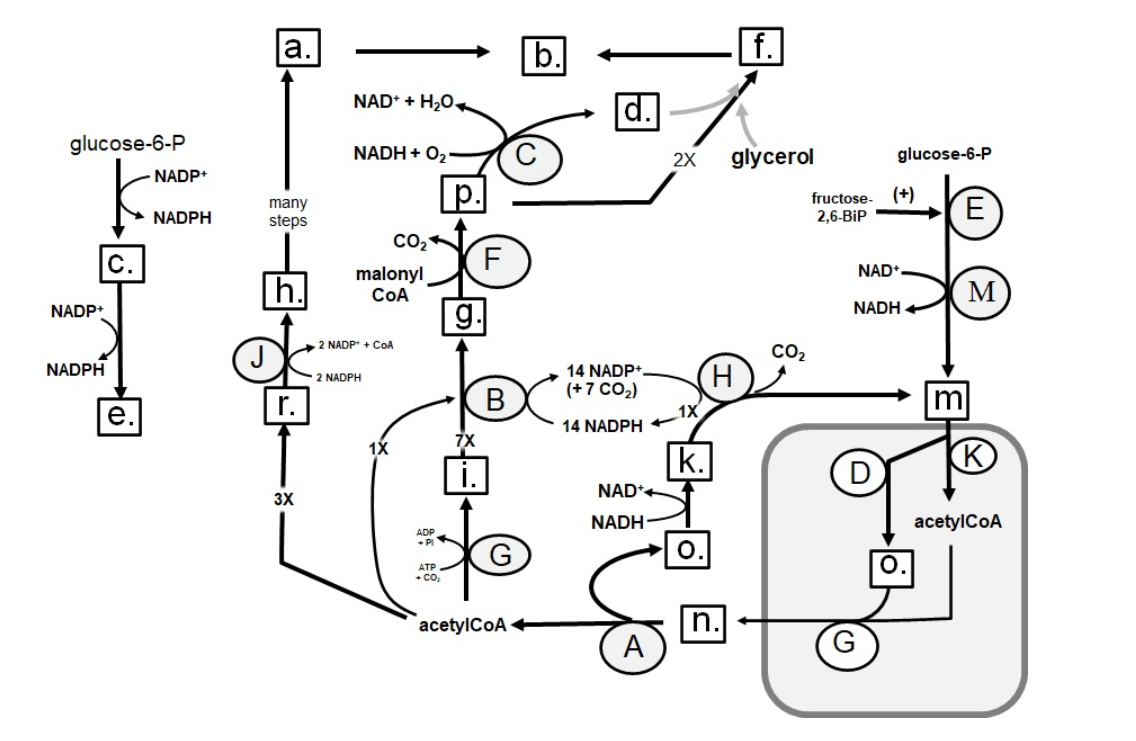
Identify in the circle using CAPS: HMGCoA reductase
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
M
J
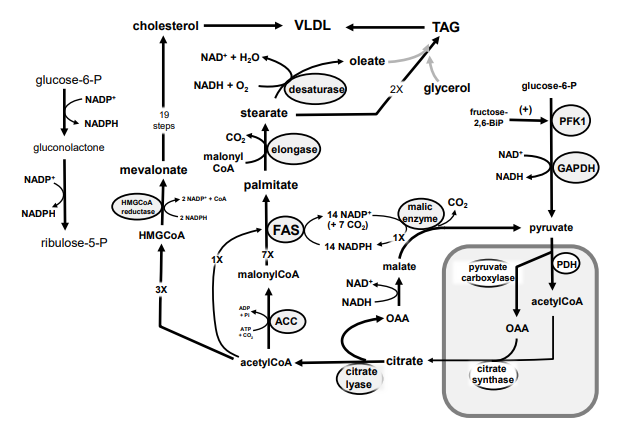
98
New cards
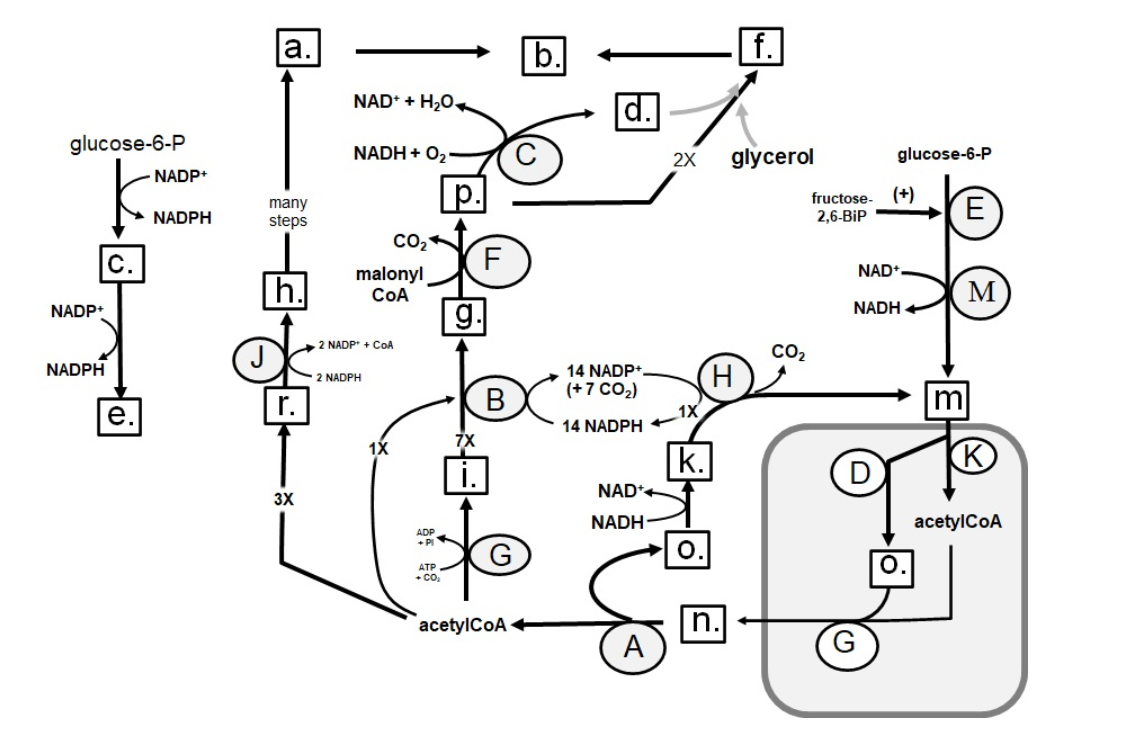
Identify in the square box using lower case letters: malonylCoA
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
i.
k.
m.
n.
o.
p.
r.
i.
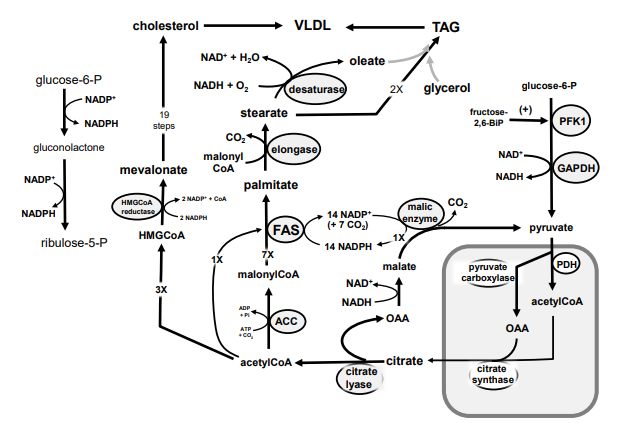
99
New cards
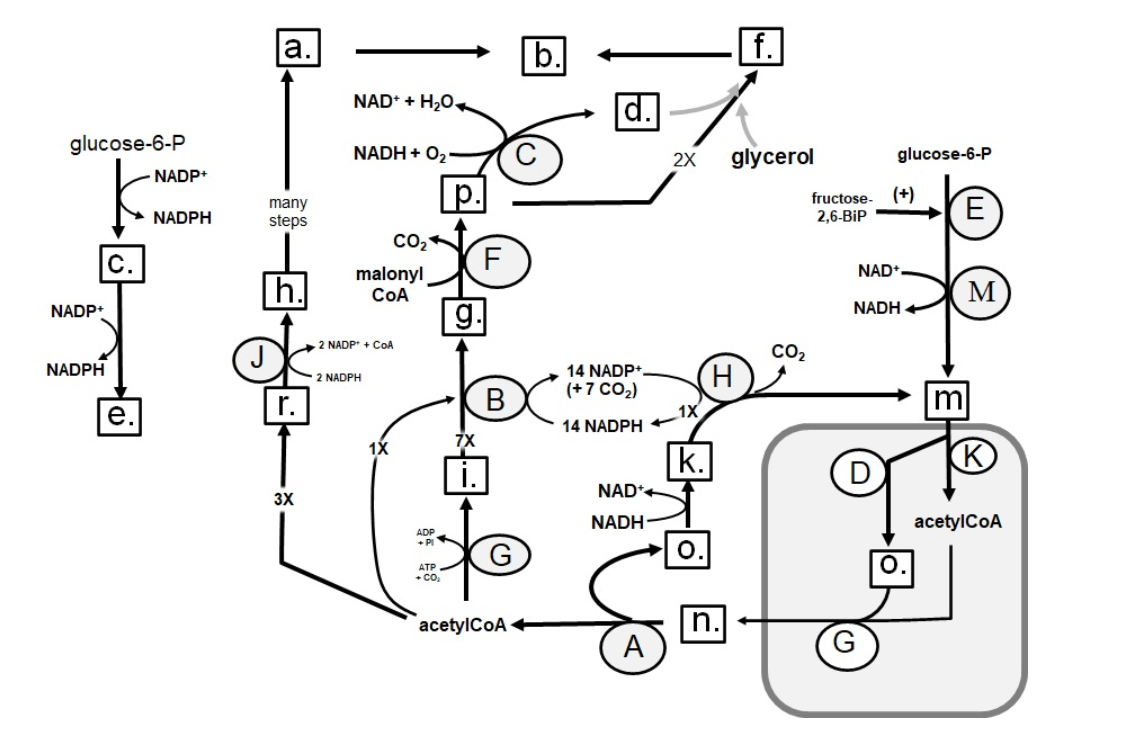
Identify in the circle using CAPS: pyruvate carboxylase
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
M
D
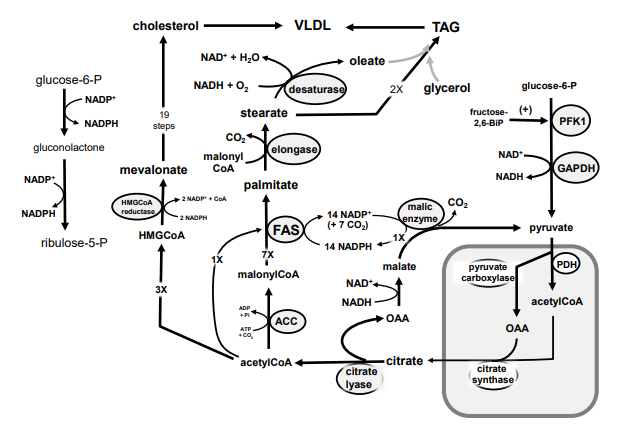
100
New cards
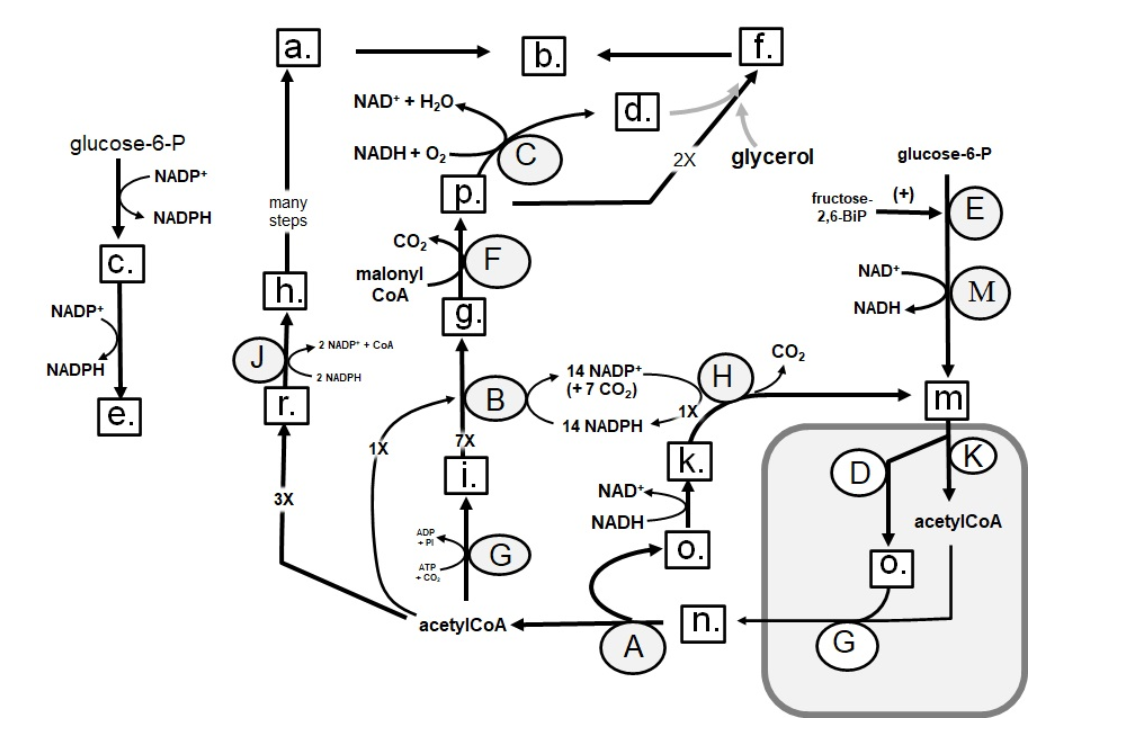
Identify in the square box using lower case letters: HMGCoA
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
i.
k.
m.
n.
o.
p.
r.
r.