unit 1 - plate tectonics
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/49
Last updated 4:58 AM on 1/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
1
New cards
coastline fit
- close land fit between the
coastlines of the continents
- coastlines fit together like puzzle pieces
- south america fits really well into africa
coastlines of the continents
- coastlines fit together like puzzle pieces
- south america fits really well into africa
2
New cards
geological fit
- close geological correlation across landmasses
- shield and non-shield areas align, mountain ranges fit into mountain ranges
- shield and non-shield areas align, mountain ranges fit into mountain ranges
3
New cards
paleoclimatology
- study of past climates show that certain areas had the same climatological history that would only be possible had they been attached/in the same location
- some of the strongest evidence
- some of the strongest evidence
4
New cards
paleoglaciation
- continental glaciation that correlated between land masses would have been impossible unless these continents were once united
5
New cards
fossil correlation
- fossil remains of pre-mesozoic life are uniform and correlate between the southern continents
- would be impossible for these plants and animals to have crossed the oceans as they are today
- would be impossible for these plants and animals to have crossed the oceans as they are today
6
New cards
paleomagnetism
- within ocean basins where molten magma is extruded, there is evidence of plate movement as the magma shows signs of reversal of magnetic polarity over time
- in the ocean basin, the molten magma is thrusting through the earth, north is true north, but over time true north reverses
- in the ocean basin, the molten magma is thrusting through the earth, north is true north, but over time true north reverses
7
New cards
3 types of plate movement
- diverging, converging, and transforming
8
New cards
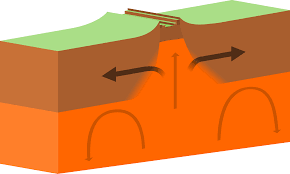
divergent/diverging plate boundaries
- moving away from each other
- forms new lithosphere and is the youngest land on
earth
- creates mid-ocean ridges or rift zones (ex. east african rift valley)
- seafloor spreading can lead to mid-ocean ridges
- forms new lithosphere and is the youngest land on
earth
- creates mid-ocean ridges or rift zones (ex. east african rift valley)
- seafloor spreading can lead to mid-ocean ridges
9
New cards
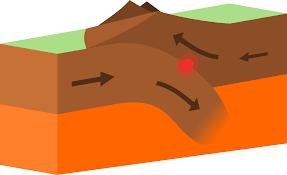
converging plate boundaries
- moving together
- when 2 plates are moving towards each other, 1 plate will eventually be pushed down under the other plate due to variations in density
- 2 continental plates converge: may form mountains
- continental plate and oceanic plate converge: oceanic plate will subduct and create a trench
- 2 oceanic plates converge: process is longer, eventually one will begin to descend and be reclaimed by the mantle (may form a string of volcanic islands)
- when 2 plates are moving towards each other, 1 plate will eventually be pushed down under the other plate due to variations in density
- 2 continental plates converge: may form mountains
- continental plate and oceanic plate converge: oceanic plate will subduct and create a trench
- 2 oceanic plates converge: process is longer, eventually one will begin to descend and be reclaimed by the mantle (may form a string of volcanic islands)
10
New cards
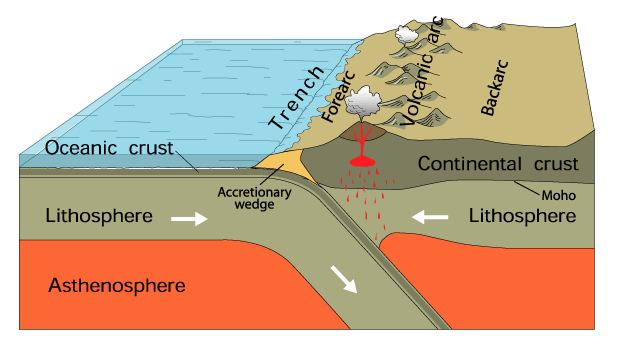
subduction zone
- where the lithospheric crust is being pushed under and reclaimed by the mantle (where the oldest rock material is found)
- occurs when an oceanic and continental plate meet
- occurs when an oceanic and continental plate meet
11
New cards
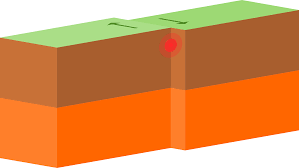
transforming plate boundaries
- occurs when 2 plates slide horizontally past each other
- surface area is neither created or destroyed
- known as a tear or strike-slip fault
- great friction between the 2 plates, and if they become locked massive earthquakes can occur when the pressure releases
- surface area is neither created or destroyed
- known as a tear or strike-slip fault
- great friction between the 2 plates, and if they become locked massive earthquakes can occur when the pressure releases
12
New cards
types of faults
* normal, reverse (compression), strike-slip, horst, graben
13
New cards
normal fault
* plates move away from each other
* one goes up, one goes down
* one goes up, one goes down
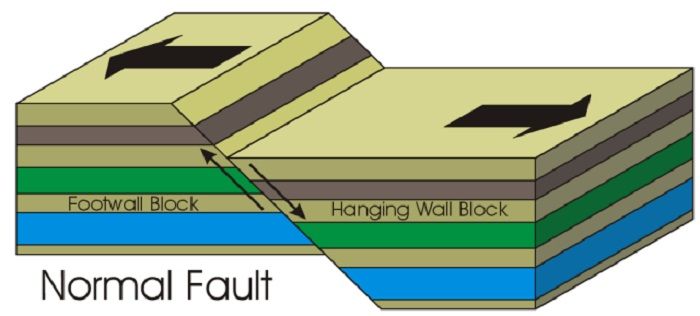
14
New cards
reverse (compression) fault
* plates converge, one goes up, one goes down
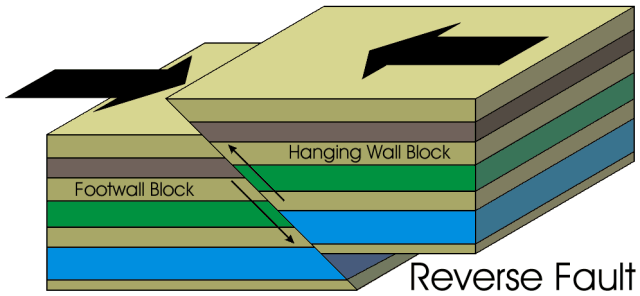
15
New cards
strike-slip fault
* transform boundary
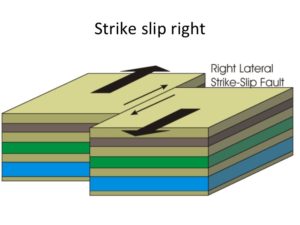
16
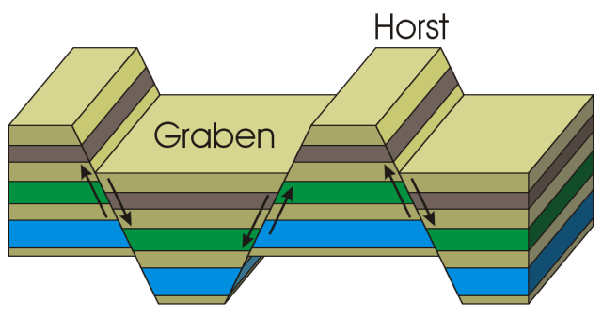
New cards
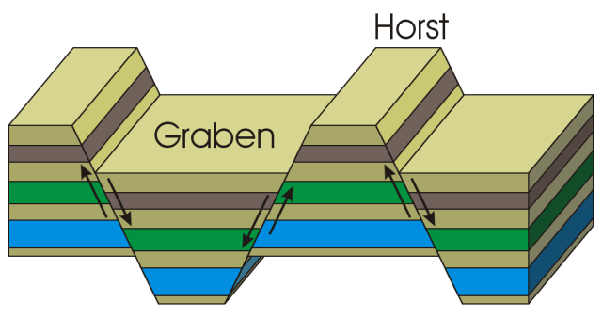
horst fault
* block mountain, occurs under tension
* like a horse, you can mount it
* like a horse, you can mount it
17
New cards
graben fault
* rift valley, also created under tension
* looks like someone grabbed chunks out of it
* looks like someone grabbed chunks out of it
18
New cards
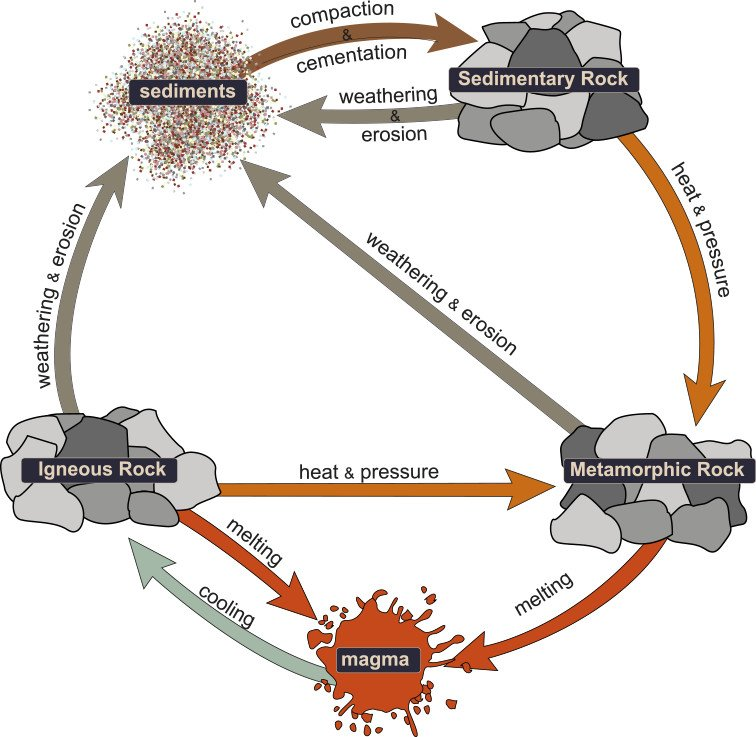
types of rocks
- sedimentary, metamorphic, igneous
19
New cards
sedimentary rocks
- formed from layers of sand, silt, dead plants, and animal skeletons, mainly found in watery areas
ex. sandstone
ex. sandstone
20
New cards
metamorphic rocks
- formed from other rocks that are changed by heat and pressure underground, found in mountainous regions
ex. marble, quartz, slate
ex. marble, quartz, slate
21
New cards
igneous rocks
* formed from melted rock deep inside the earth, found in volcanic regions ex. gabbro, basalt (in oceanic crust), granite, andesite (continental crust)
22
New cards
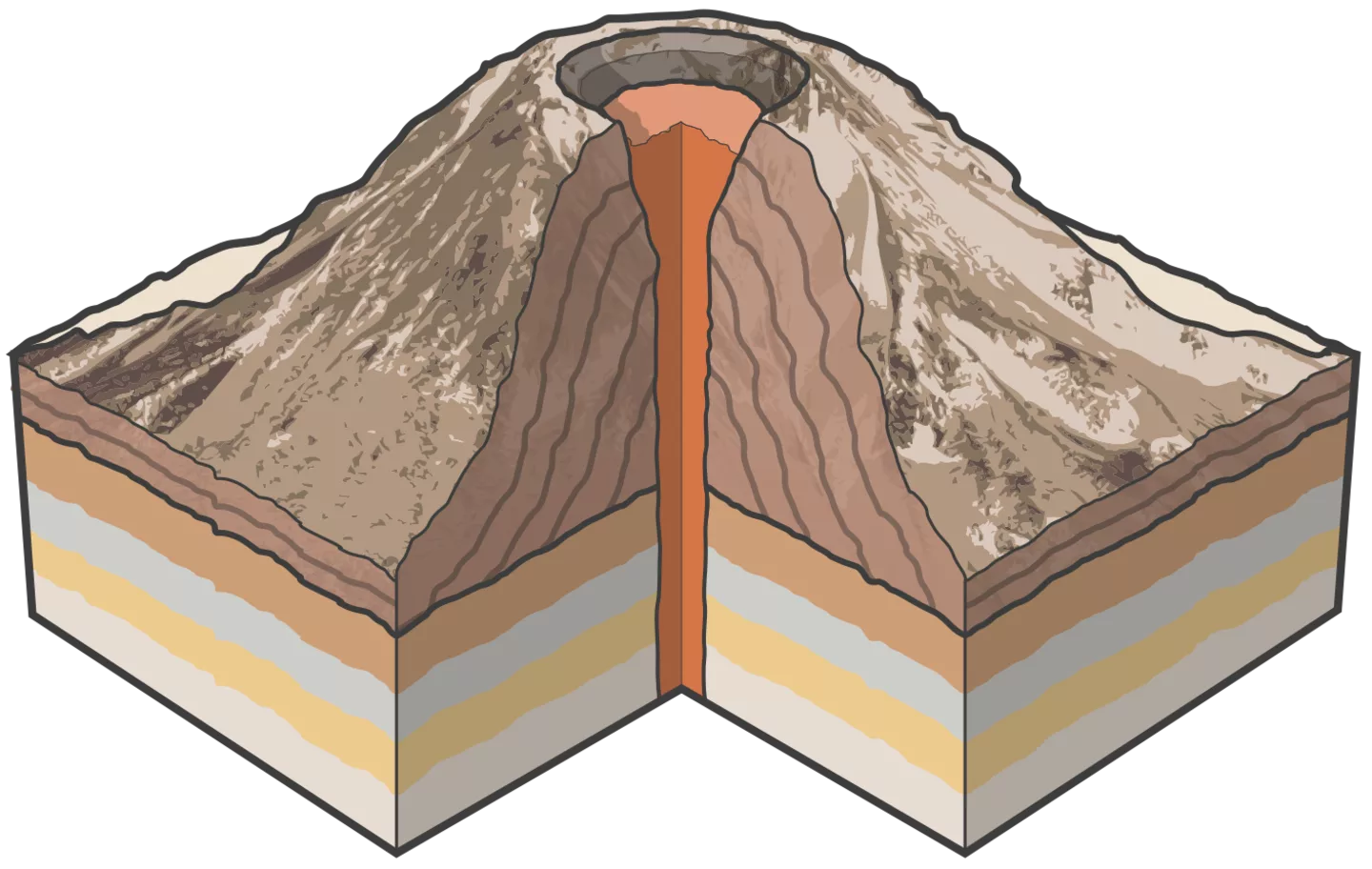
types of volcanoes
- cinder cone, shield cone, composite cone
23
New cards
cinder cone
- predominantly found on continents
- made up of acidic lava
- made of layers of cinder and ash
- compact/small in size
- highly violent and explosive
- associated with pyroclastic flows
- fast cooling = can cause clogged neck
ex. Mt. Fuji
- made up of acidic lava
- made of layers of cinder and ash
- compact/small in size
- highly violent and explosive
- associated with pyroclastic flows
- fast cooling = can cause clogged neck
ex. Mt. Fuji
24
New cards
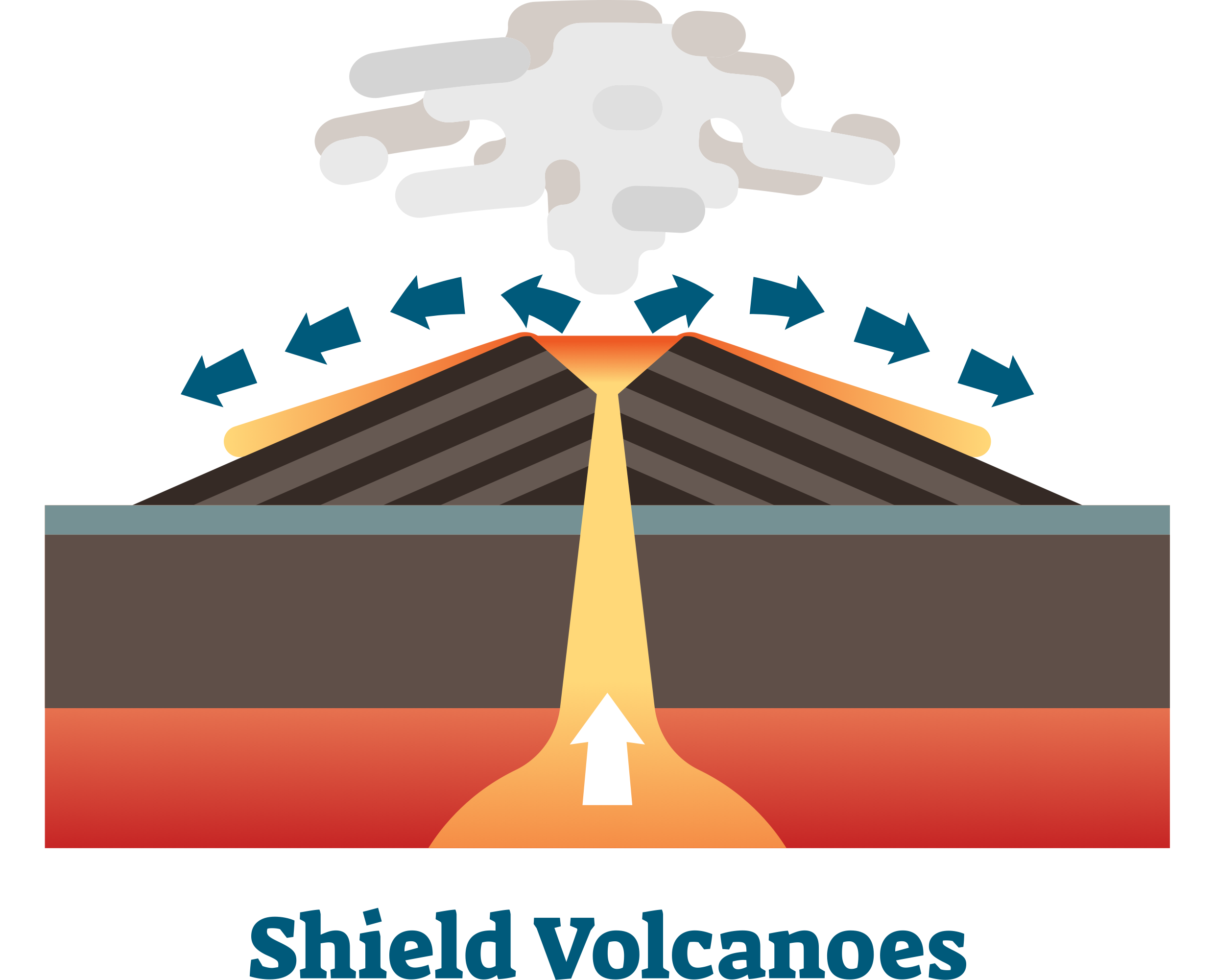
shield cone
- large and gentle sloping
- basic lava (basaltic lava) = wet like concrete
- do not violently erupt, instead ooze
-> any accounts of violent eruption tend to be from steam as the lava comes in contact with the water
- cools very slowly and spreads over large areas
- predominantly found on ocean floors
ex. Hawaiian Islands
- basic lava (basaltic lava) = wet like concrete
- do not violently erupt, instead ooze
-> any accounts of violent eruption tend to be from steam as the lava comes in contact with the water
- cools very slowly and spreads over large areas
- predominantly found on ocean floors
ex. Hawaiian Islands
25
New cards
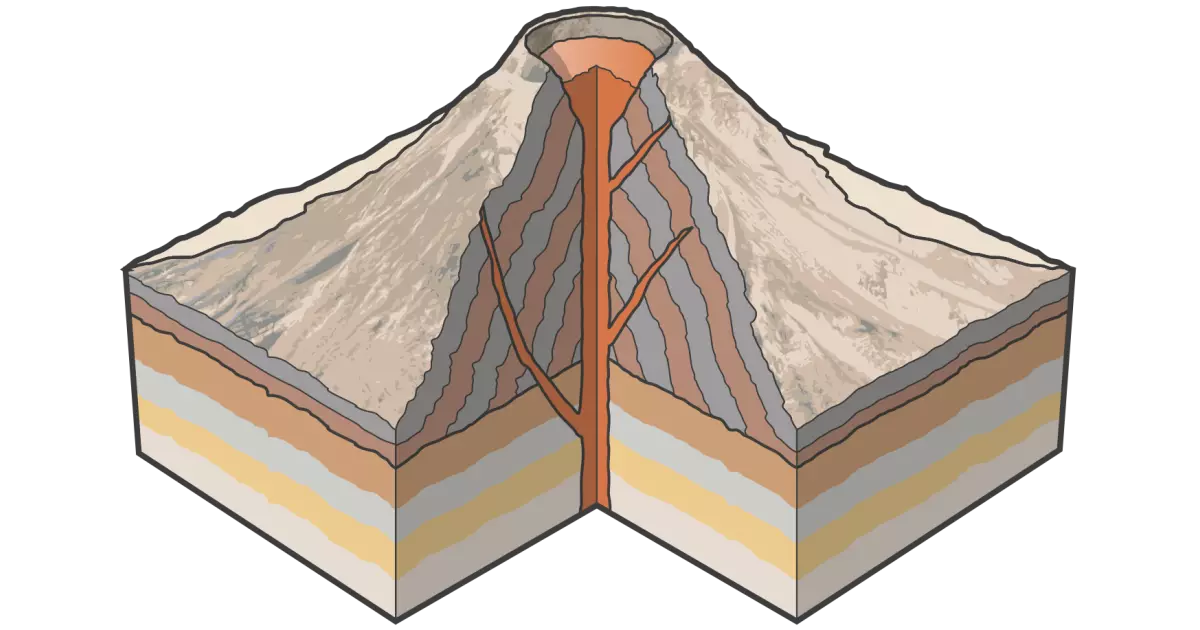
composite cone
- most often formed over subduction zones (Pacific Ring of Fire)
- symmetrical formation with cake-like layers of lava and ash
- snow and ice-capped
- more moderately sloped than cinder cones
- tend to be larger in size
- sudden and violent eruptions
ex. Pacific Ring of Fire
- symmetrical formation with cake-like layers of lava and ash
- snow and ice-capped
- more moderately sloped than cinder cones
- tend to be larger in size
- sudden and violent eruptions
ex. Pacific Ring of Fire
26
New cards
fissure
- juicy crack
- more associated w/ oceanic crust and occur when magma flows up through cracks in the crust and "erupts"
- more associated w/ oceanic crust and occur when magma flows up through cracks in the crust and "erupts"
27
New cards
hotspot
- an area on the earth's mantle where magma rises up to melt through the crust, creating volcanoes or volcanic islands
28
New cards
types of eruptions
- lava flows, tephra flows, pyroclastic flows, mudflows
29
New cards
lava flows
* pour or ooze out of vents or cracks
* causes majority of harm to non-moveable objects (trees, cars)
* basaltic lava can travel vast distances vs. andesite lava that rarely goes past \~8 km.
* objects and terrain are either surrounded, buried or ignited
* causes majority of harm to non-moveable objects (trees, cars)
* basaltic lava can travel vast distances vs. andesite lava that rarely goes past \~8 km.
* objects and terrain are either surrounded, buried or ignited
30
New cards
tephra flows
- made up of cinder and ash (super concentrated)
- majority of fragments fall back onto the slope, enlarging it
- alters climate
- majority of fragments fall back onto the slope, enlarging it
- alters climate
31
New cards
pyroclastic flows
- hot and dry rocks, gases and lava pieces
- fast-moving and dense
- fast-moving and dense
32
New cards
mudflows
- same consistency as cement
- happens when the steam, heat or lava from the volcano melt the snow-capped tops and ice, and that watery runoff mixes with ash, debris and dirt to create a mudflow
- happens when the steam, heat or lava from the volcano melt the snow-capped tops and ice, and that watery runoff mixes with ash, debris and dirt to create a mudflow
33
New cards
pros of volcanoes
* creates igneous rocks that can be used as building materials
* creates fertile soil
* a source of geothermal energy
* tourism! (slay)
* creates fertile soil
* a source of geothermal energy
* tourism! (slay)
34
New cards
cons of volcanoes
- destructive
- can cause lots of air pollution b/c of the ash (like Mt. St. Helens)
- can have many casualties if they erupt aggressively and without fair warning
- gas will kill you
- can cause lots of air pollution b/c of the ash (like Mt. St. Helens)
- can have many casualties if they erupt aggressively and without fair warning
- gas will kill you
35
New cards
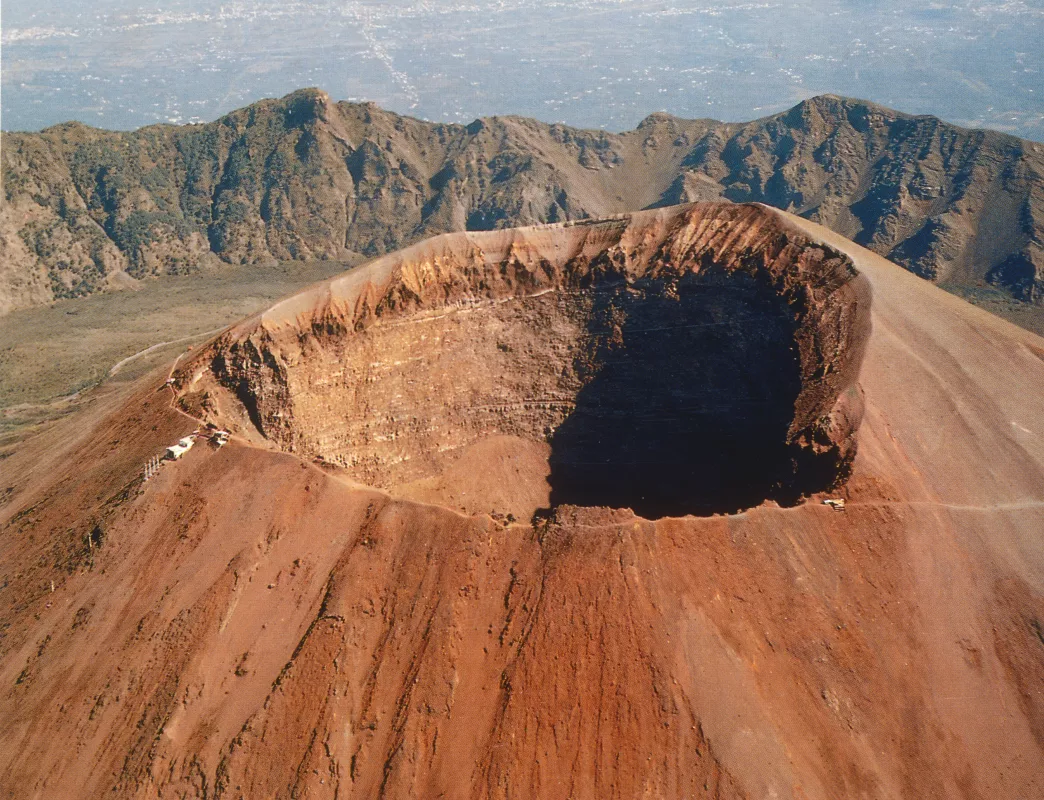
caldera
- forms because the magma chamber empties/oozes out so fast that the volcanoes lose their structural integrity
- also forms because the explosion is so violent that the volcano blows its top off
- also forms because the explosion is so violent that the volcano blows its top off

36
New cards
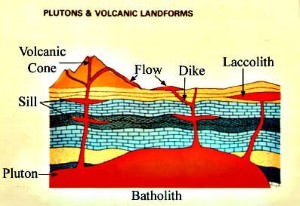
batholith
* largest feature, looks like a giant pool of magma underground
37
New cards
laccolith
* 2nd largest feature
* found between layers
* usually dome-shaped but smaller
* found between layers
* usually dome-shaped but smaller
38
New cards
dike
* cuts through multiple layers (across)
39
New cards
sill
* stuck between layers
* cuts in between layers
* cuts in between layers
40
New cards
earthquake
- when stress-deformed rocks break or release pressure by elastic rebound or sudden shift in position and severe shaking of the ground may occur
- lasts ~10-30 s
- lasts ~10-30 s
41
New cards
wave types
- body waves and surface waves
- primary waves, secondary waves, surface waves
- primary waves, secondary waves, surface waves
42
New cards
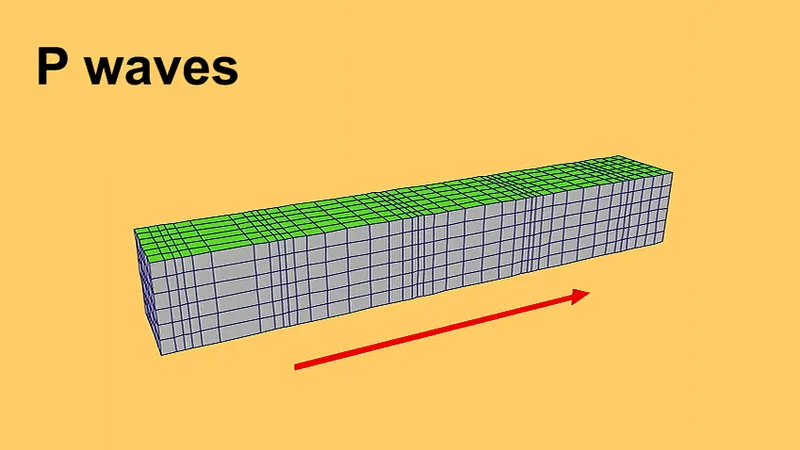
primary wave
- aka compression wave
- a type of body wave (much smaller)
- travels by compressing and expanding the ground
- the fastest
- first to reach the earthquake recording stations
- a type of body wave (much smaller)
- travels by compressing and expanding the ground
- the fastest
- first to reach the earthquake recording stations
43
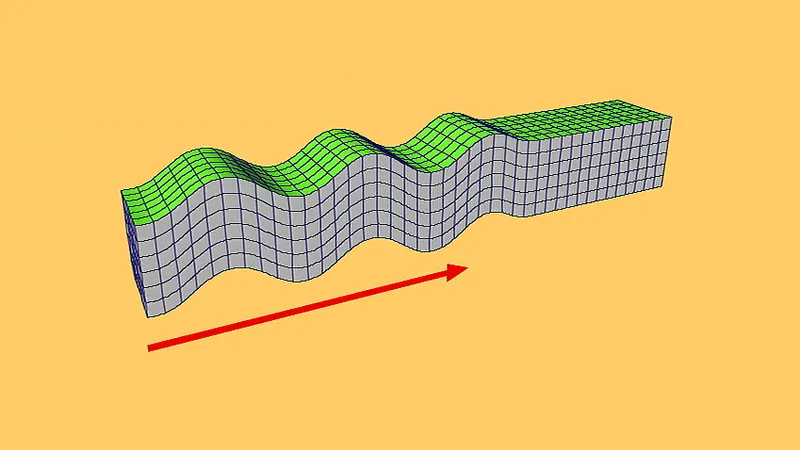
New cards
secondary wave
- aka shear wave
- second wave generated by quakes
- slower than the primary waves and travels in a side-to-side motion
- second wave generated by quakes
- slower than the primary waves and travels in a side-to-side motion
44
New cards
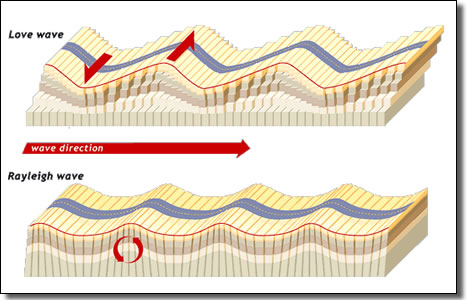
surface wave
- more extreme + aggressive
- travels like ripples through calm water
- responsible for ground shaking which causes much of the damage during earthquakes
- includes love waves (move back + forth) and Rayleigh waves (rolling)
- travels like ripples through calm water
- responsible for ground shaking which causes much of the damage during earthquakes
- includes love waves (move back + forth) and Rayleigh waves (rolling)
45
New cards
aftershocks
- smaller earthquake that follows a larger earthquake
- occurs in the same area of the crust/fault
- occurs in the same area of the crust/fault
46
New cards
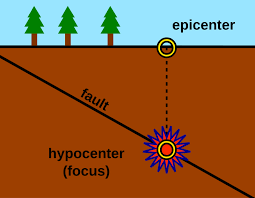
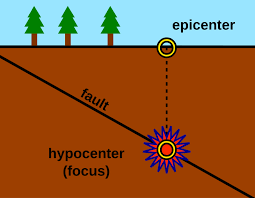
focus
- the location where the fracture/shift occurs and the seismic waves originate
- depth varies but can be as deep as ~700km
- depth varies but can be as deep as ~700km
47
New cards
epicentre
- located on the surface of the earth directly above the focus point
48
New cards
tsunami
- a series of waves caused by the displacement of water from an earthquake
49
New cards
magnitude
- a measure of the size/amplitude of the seismic waves generated by an earthquake
- recorded by seismographs
- recorded by seismographs
50
New cards
richter scale
- goes from 1 to 8.9
- each number is 10x stronger than the previous
- usually a tremor less than 3 will not be felt
- a 6.5 and above will cause extensive damage
- each number is 10x stronger than the previous
- usually a tremor less than 3 will not be felt
- a 6.5 and above will cause extensive damage