Quiz 5 KRS-353
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/204
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:25 AM on 3/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
205 Terms
1
New cards
clavicle
Two Pectoral Girdle
1. \
1. \
2
New cards
scapula
Two Pectoral Girdle
2. \
2. \
3
New cards
shoulder girdle
Accompany glenohumeral joint movement to increase ROM
4
New cards
shoulder girdle
To stabilize the scapula and clavicle during glenohumeral joint movements.
5
New cards
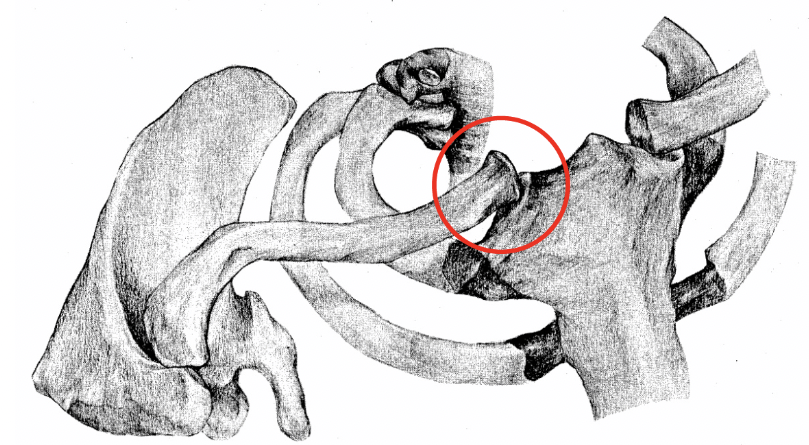
sterno-clavicular joint
Where is the only bony contact the shoulder girdle has with the axial skeleton?
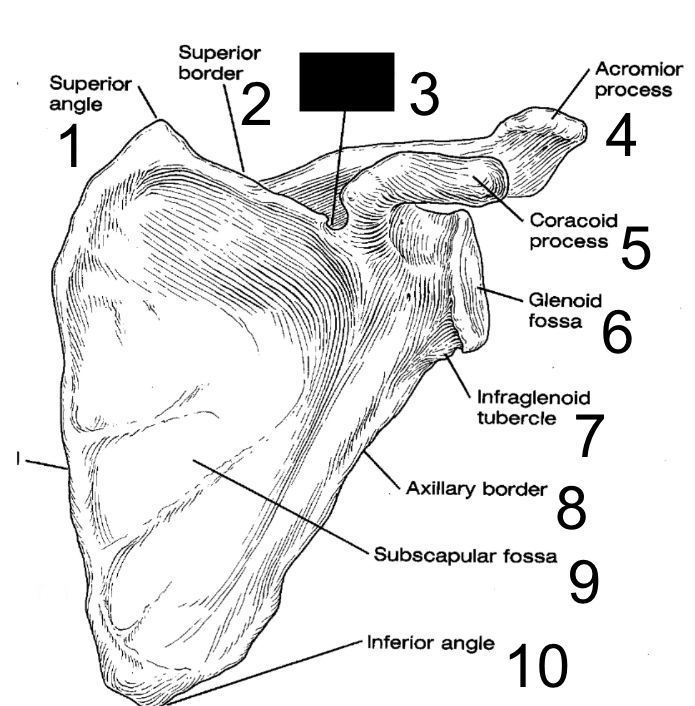
6
New cards
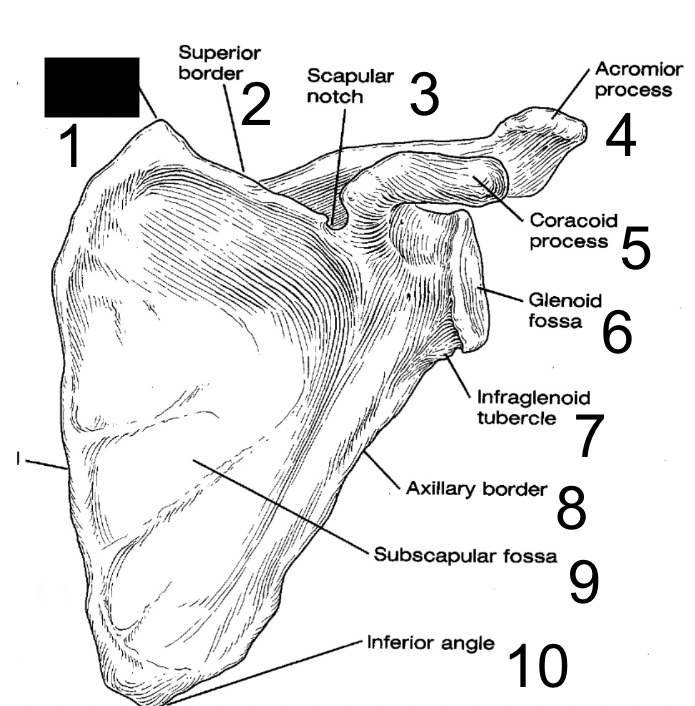
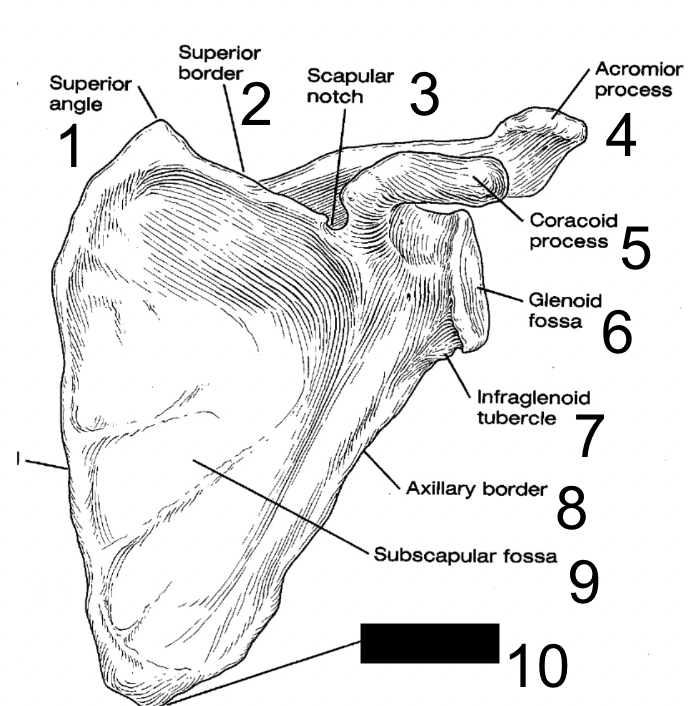
superior angle
what is this?
7
New cards
superior border
what is this?
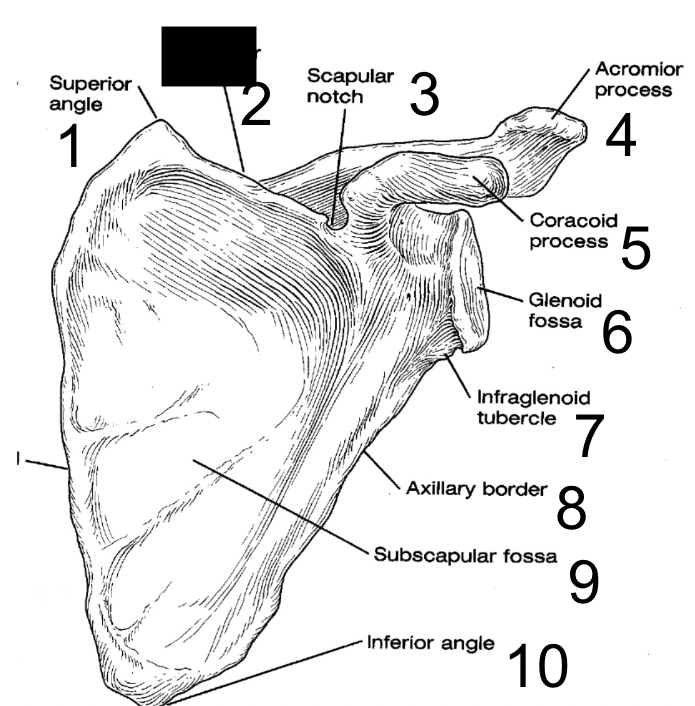
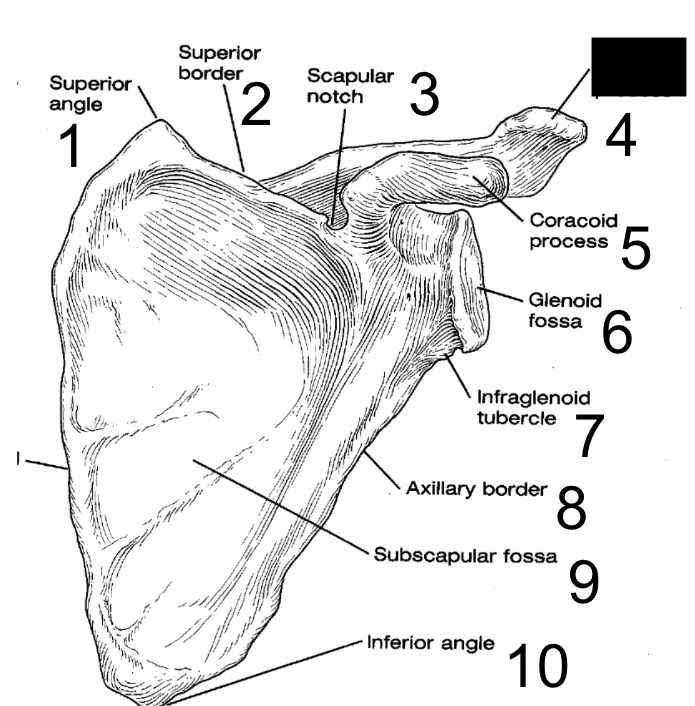
8
New cards
scapular notch
what is this?
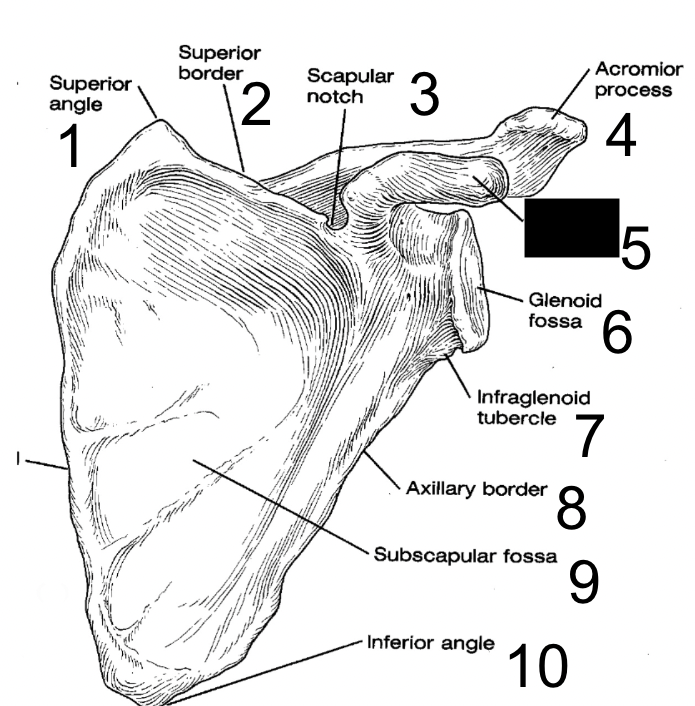
9
New cards
acromion process
what is this?
10
New cards
coracoid process
what is this?
11
New cards
glenoid fossa
what is this?
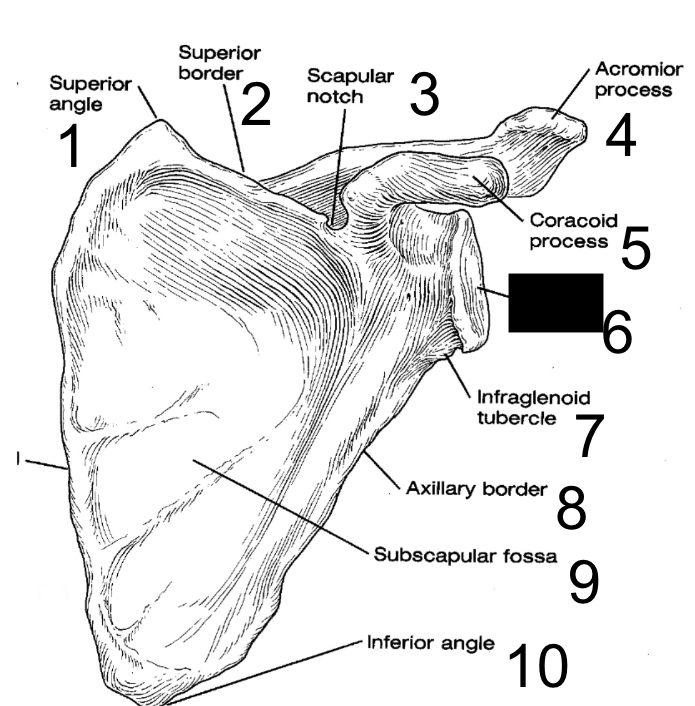
12
New cards
infraglenoid tubercle
what is this?
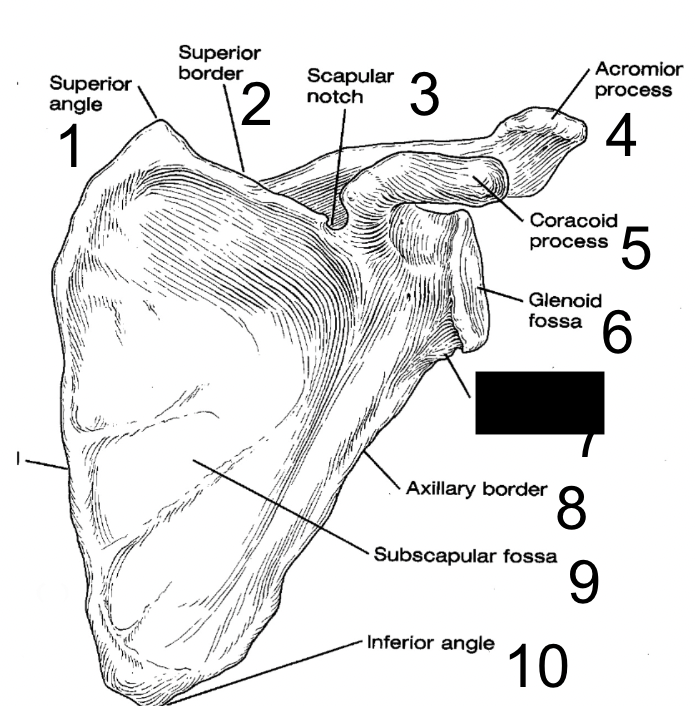
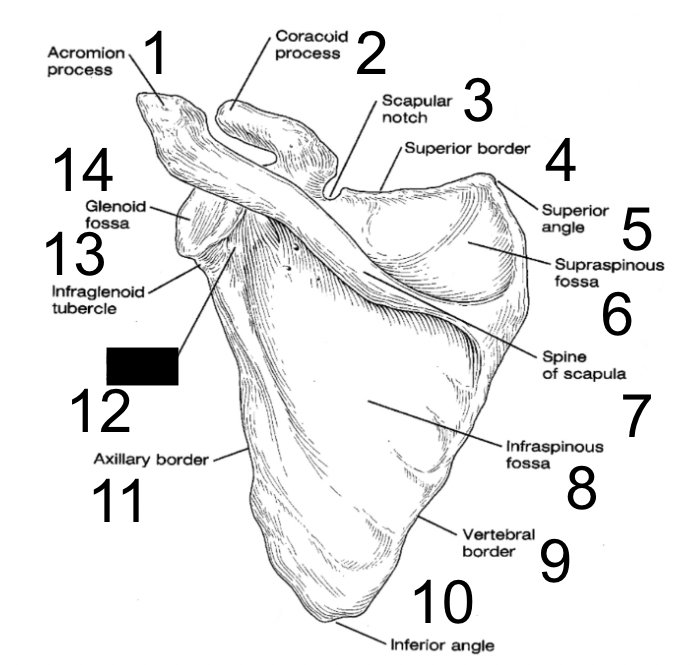
13
New cards
axillary border
what is this?
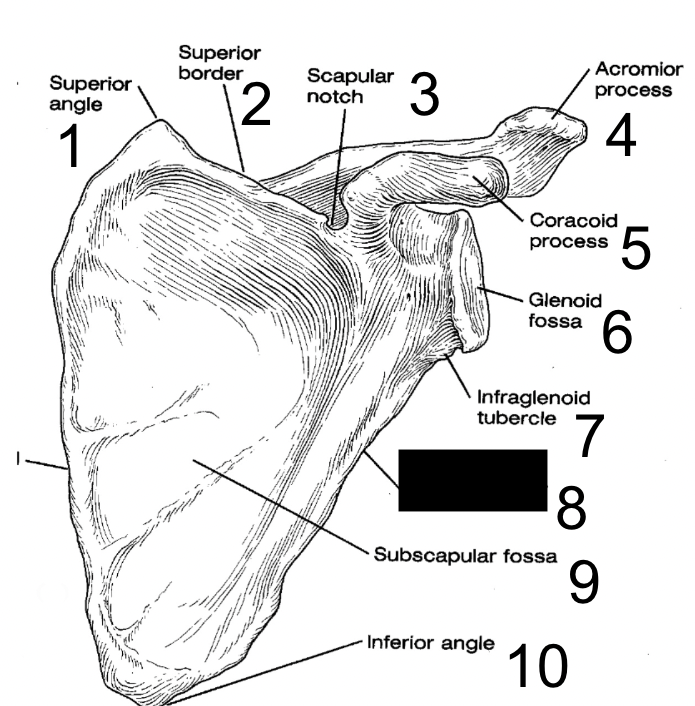
14
New cards
subscapular fossa
what is this?
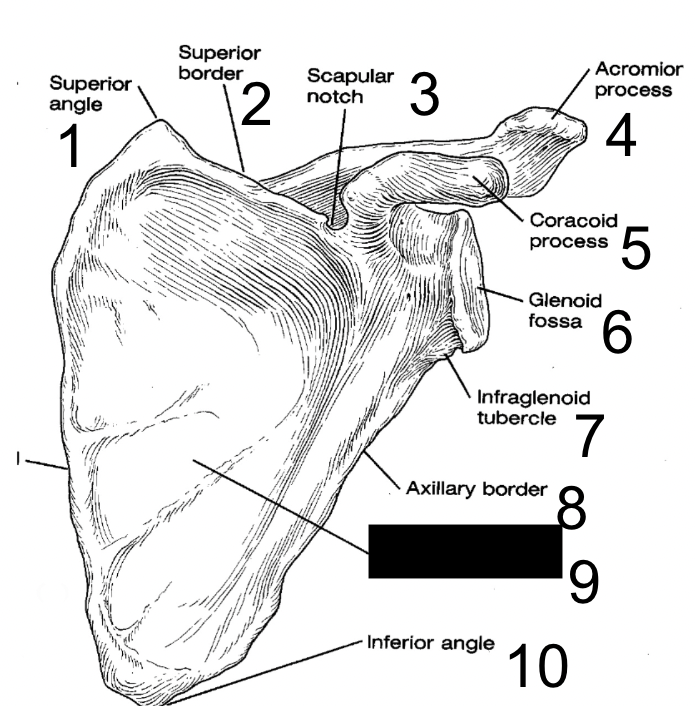
15
New cards
inferior angle
what is this?
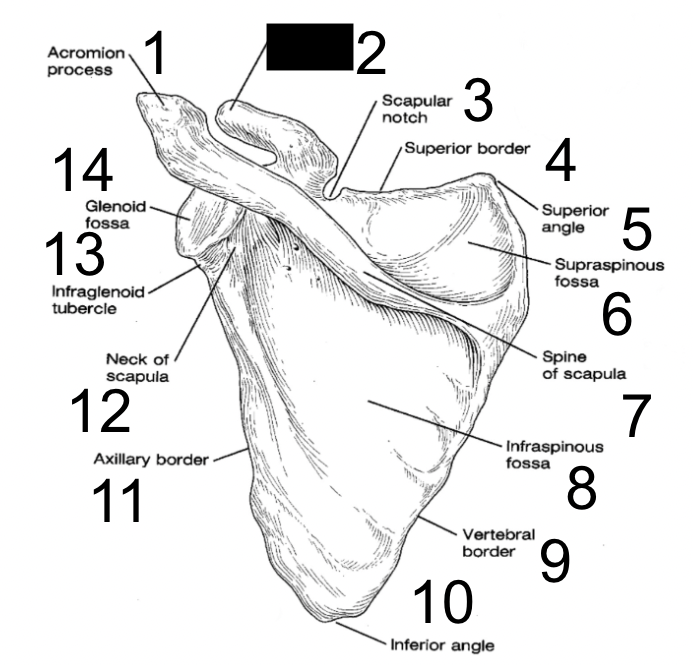
16
New cards
acromion process
what is this?
17
New cards
coracoid process
what is this?
18
New cards
scapular notch
what is this?

19
New cards
superior border
what is this?
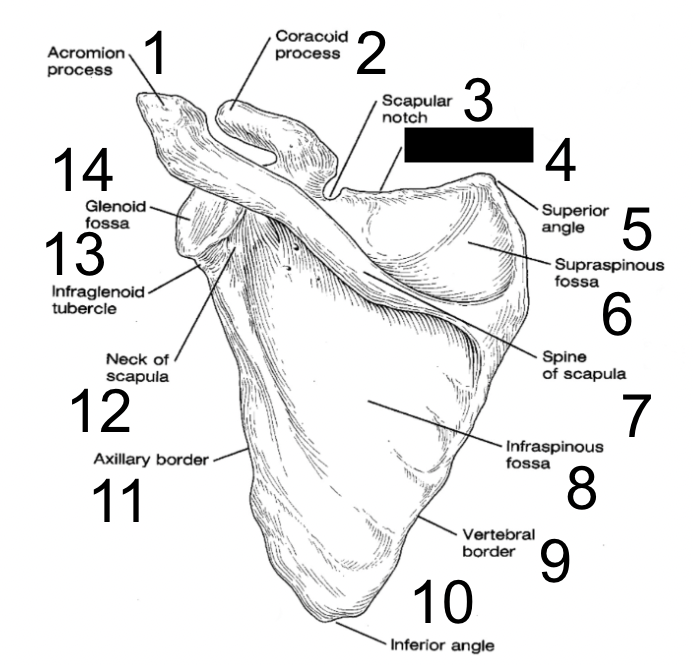
20
New cards
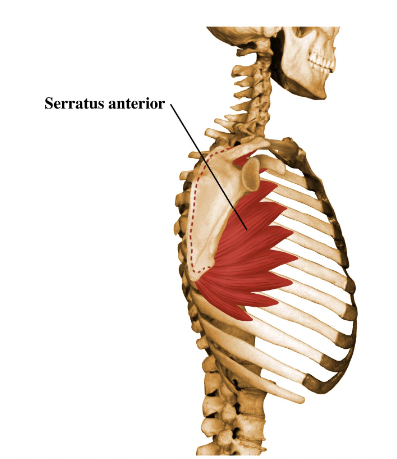
superior angle
what is this?
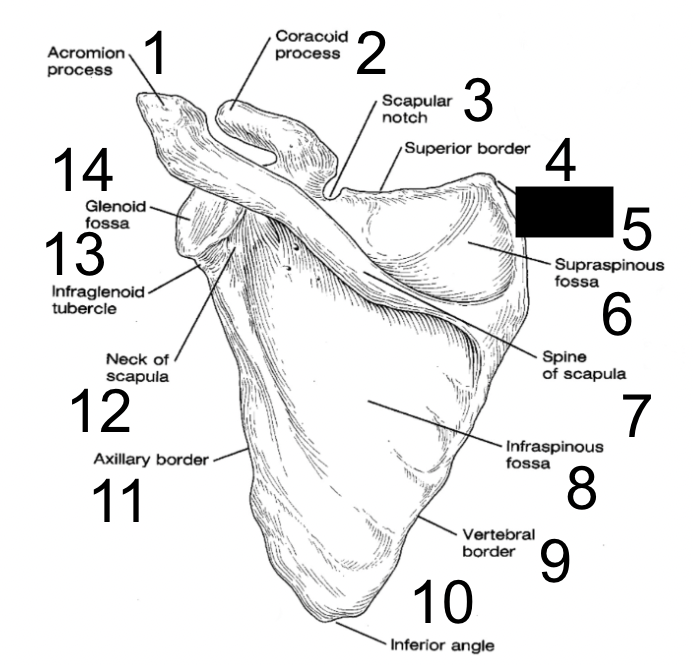
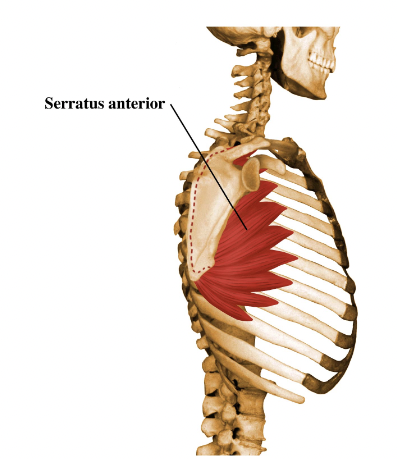
21
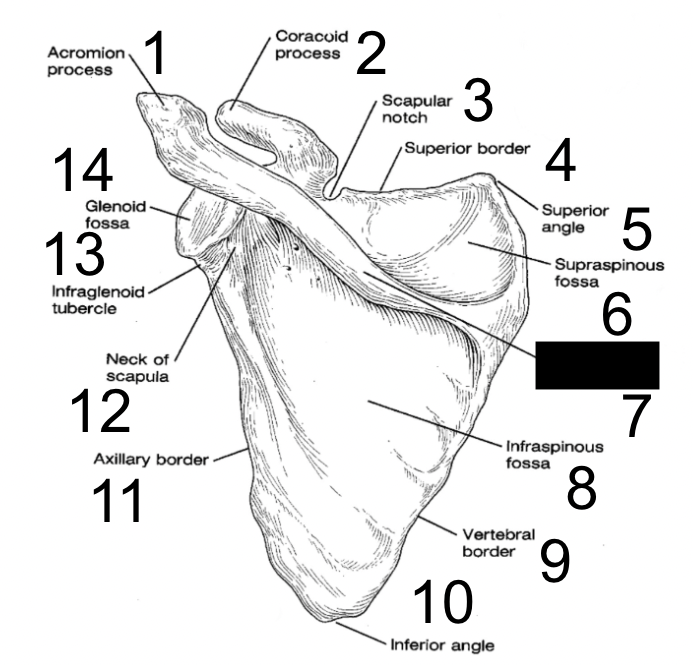
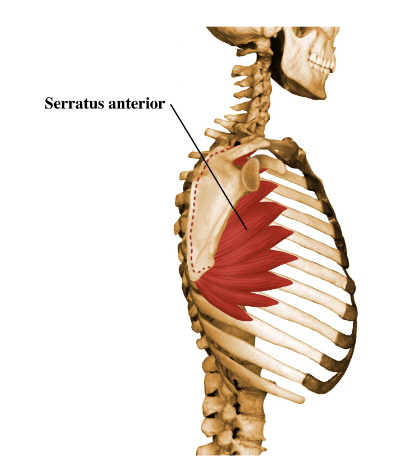
New cards
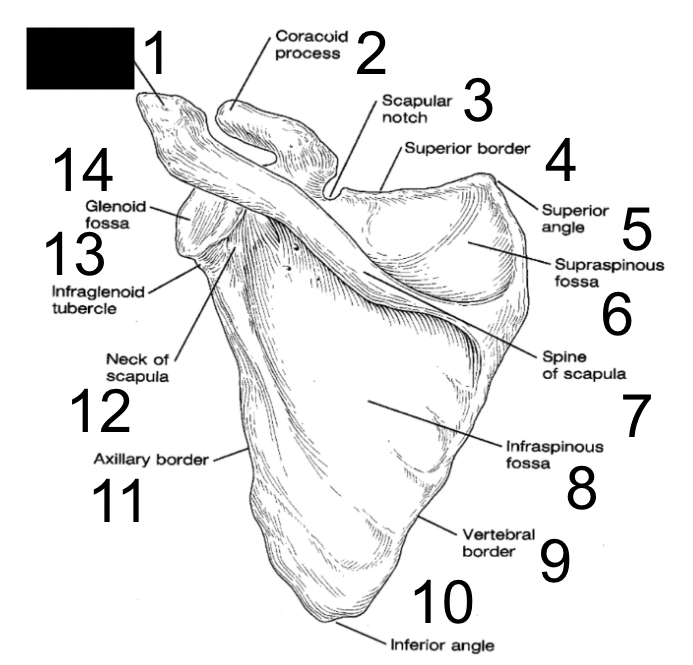
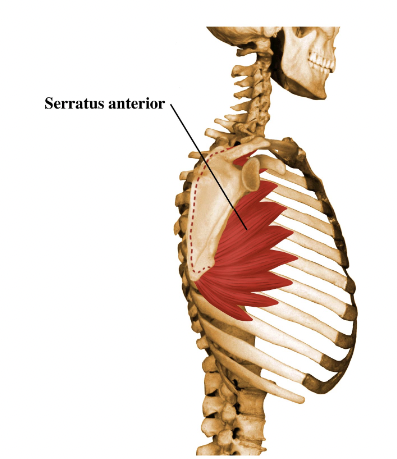
supraspinous fossa
what is this?
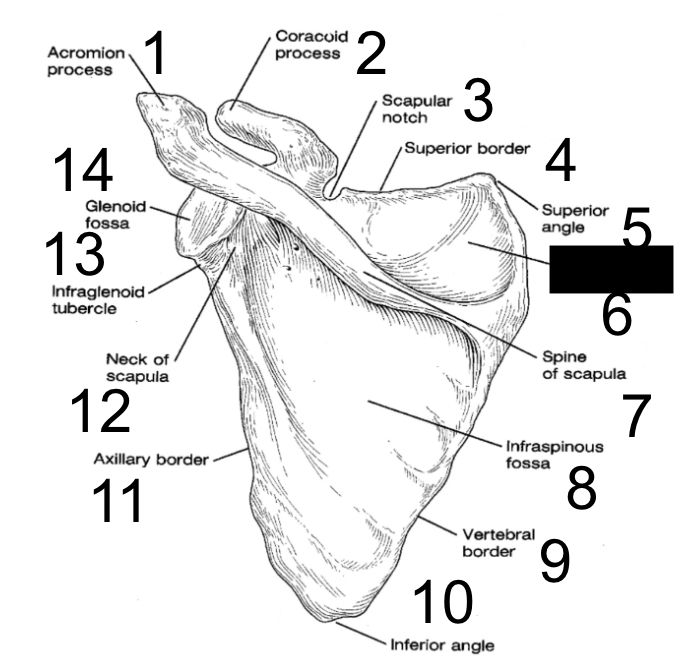
22
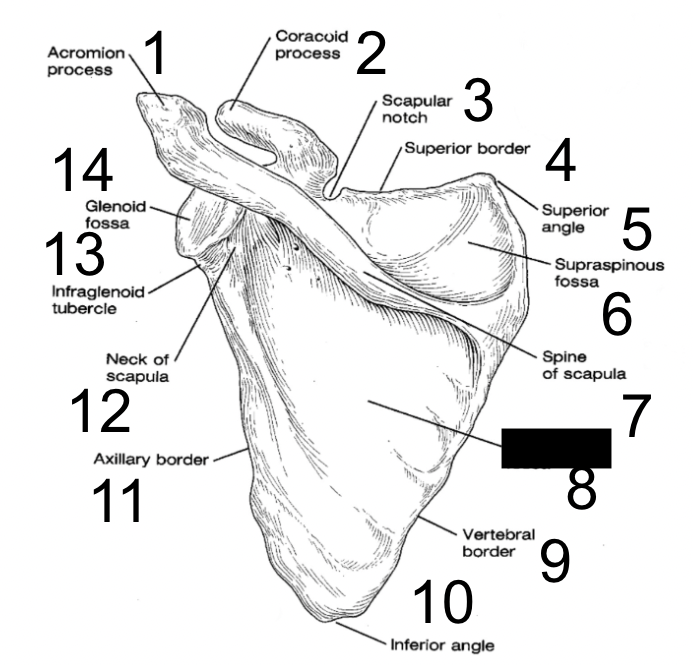
New cards
spine of scapula
what is this?
23
New cards
infraspinous fossa
what is this?
24
New cards
vertebral border
what is this?
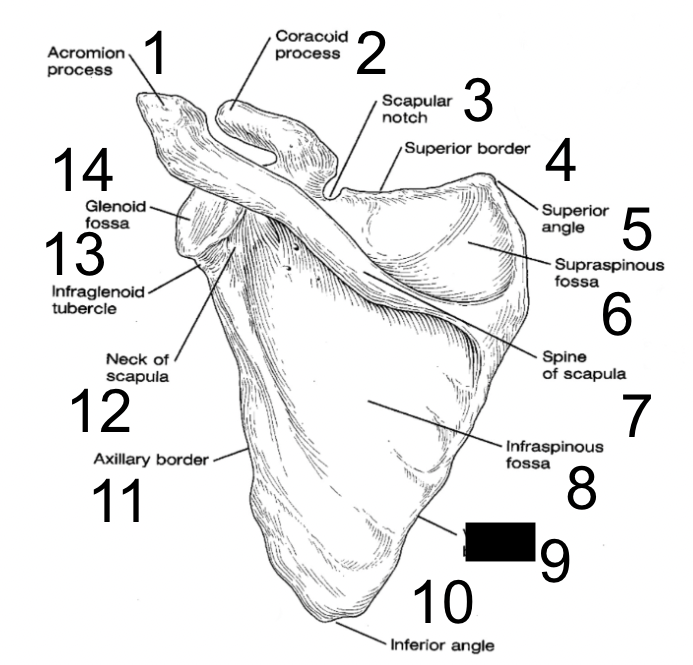
25
New cards
inferior angle
what is this?
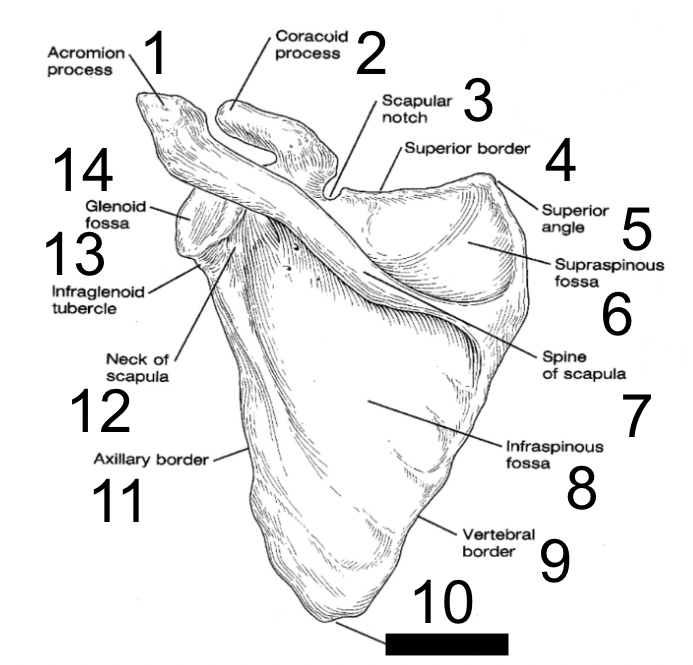
26
New cards
axillary border
what is this?
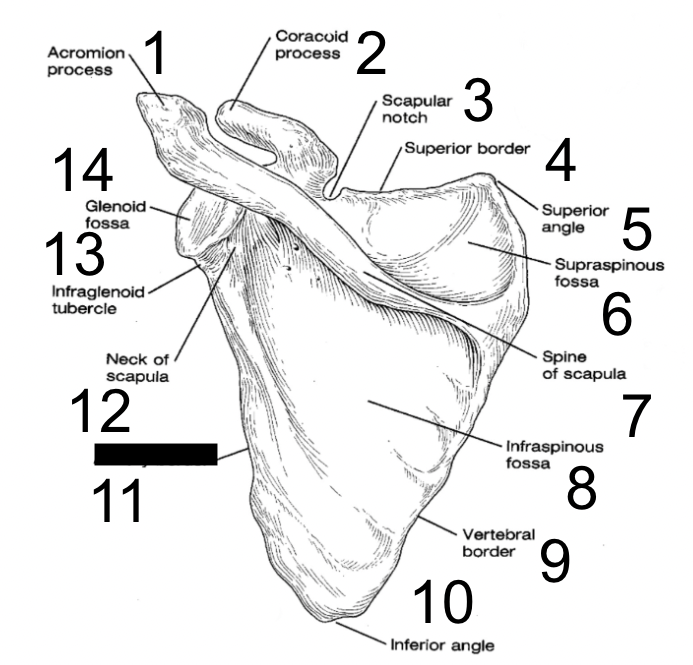
27
New cards
neck of scapula
what is this?
28
New cards
infraglenoid tubercle
what is this?
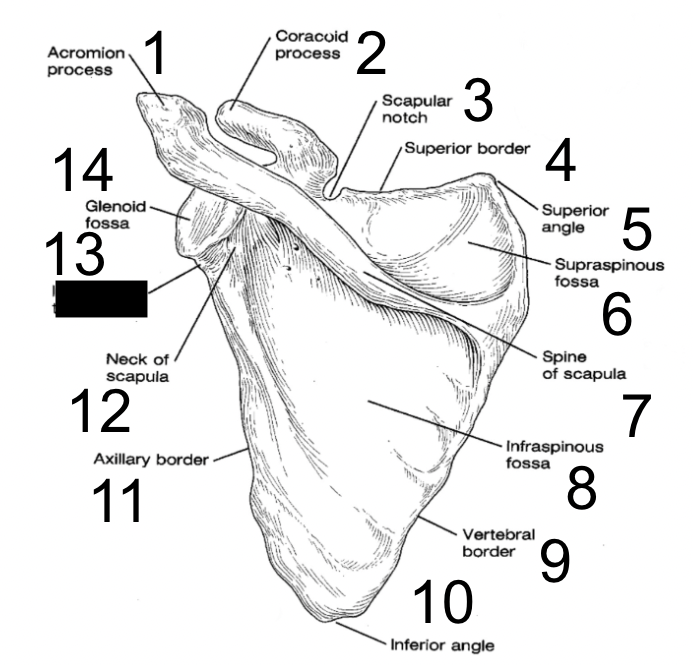
29
New cards
glenoid fossa
what is this?
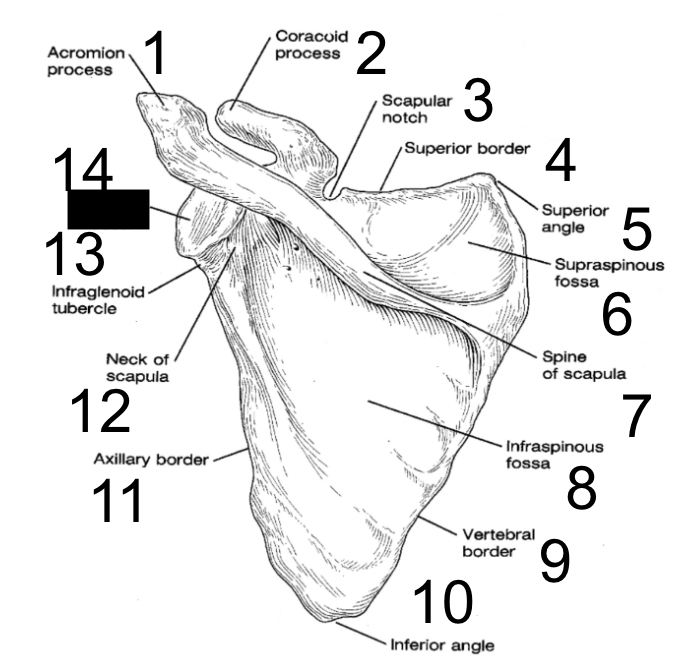
30
New cards
sterno-clavicular joint
Classification: Ball & Socket
Ball - Sternal end of clavicle.
Socket – Clavicular notch of the sternum.
Ball - Sternal end of clavicle.
Socket – Clavicular notch of the sternum.
31
New cards
ball and socket
classification of sterno-clavicular joint
32
New cards
3
How many planes can this joint move in?
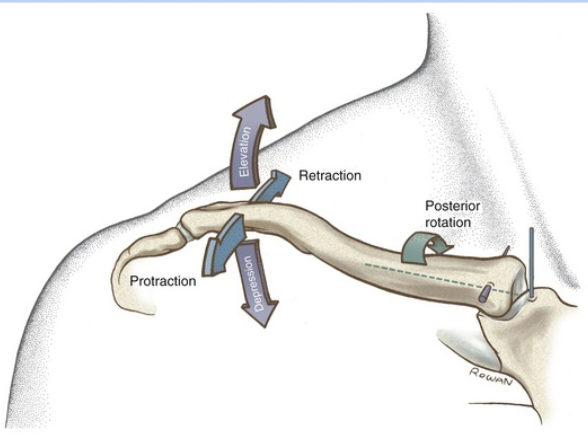
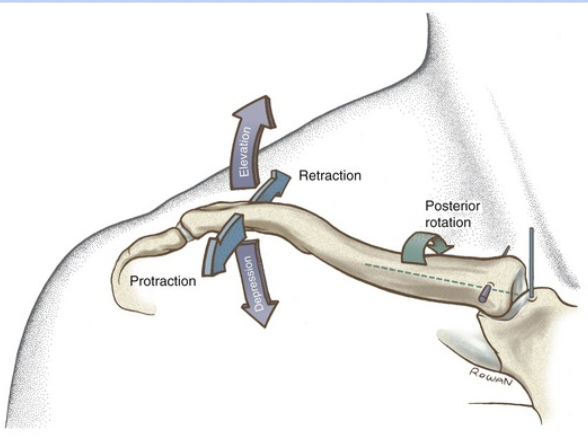
33
New cards
rotational
What movement can this joint do?
34
New cards
sterno-clavicular disk
Attached to both ends of the joint. Divides the joint cavity into 2 parts. Fibro-cartilage
35
New cards
sterno-clavicular disk
Prevent superior dislocation of the head of the clavicle.
36
New cards
sterno-clavicular disk
Absorb compression stress.
37
New cards
sterno-clavicular disk
Improve bony fit.
38
New cards
ant/post sterno-clavicular ligament
two ligaments
1. \
1. \
39
New cards
costoclavicular ligament
two ligaments
2. \
2. \
40
New cards
costoclavicular ligament
Attaches from the clavicle to the costal cartilage of the first rib.
41
New cards
sterno-clavicular joint
Movements of the shoulder girdle complex occur around the…
42
New cards
acromio-clavicular joint
Classification: Planar, synovial, non-axial.
43
New cards
acromio-clavicular joint
Medial edge of the acromion process attached to the lateral end of the clavicle.
44
New cards
acromio-clavicular
A lateral blow to the… joint will dislocate the clavicle superiorly to the acromion. This is a “shoulder separation”.
45
New cards
coraco-clavicular ligament
Composed of
* Conoid Ligament
* Trapezoid Ligament
* Conoid Ligament
* Trapezoid Ligament
46
New cards
costco-clavicular
Coraco-clavicular ligament
Similar to the ___________ lig.
Similar to the ___________ lig.
47
New cards
very strong, doesn’t cross joint
Why are the coraco-clavicular ligament and costo-clavicular ligament similar?
48
New cards
fracture
Injury or trauma to the Clavicle
the most common…
the most common…
49
New cards
sterno-clavicular
movements at shoulder girdle at what joint?
50
New cards
axilla
Anterior wall: formed by pectoralis major & minor.
51
New cards
axilla
Medial wall: formed by the serratus anterior.
52
New cards
axilla
Posterior wall: formed by shoulder mm. – latissimus dorsi & teres major.
53
New cards
axilla
Lateral wall: formed by intertubercular groove of the humurus
54
New cards
abduction
upward rotation
55
New cards
adduction
downward rotation
56
New cards
flexion
elevation
57
New cards
extension
depression
58
New cards
internal rotation
protraction 1
59
New cards
external rotation
retraction 1
60
New cards
horizontal adduction
protraction 2
61
New cards
horizontal abduction
retraction 2
62
New cards
abduction
what is this?
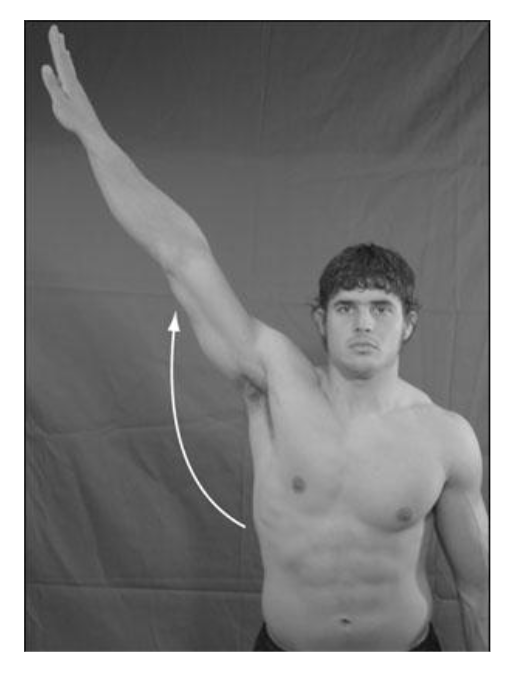

63
New cards
flexion
what is this?
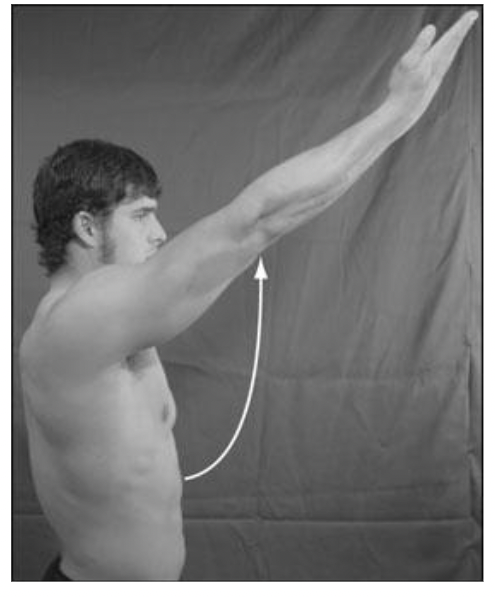
64
New cards
adduction and flexion
what is this?
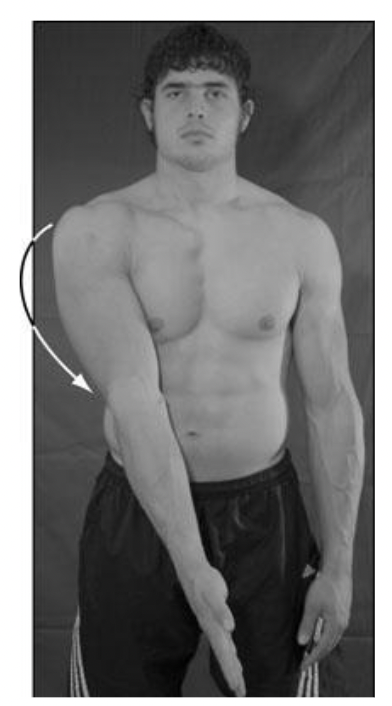
65
New cards
horizontal adduction (protraction)
what is this?
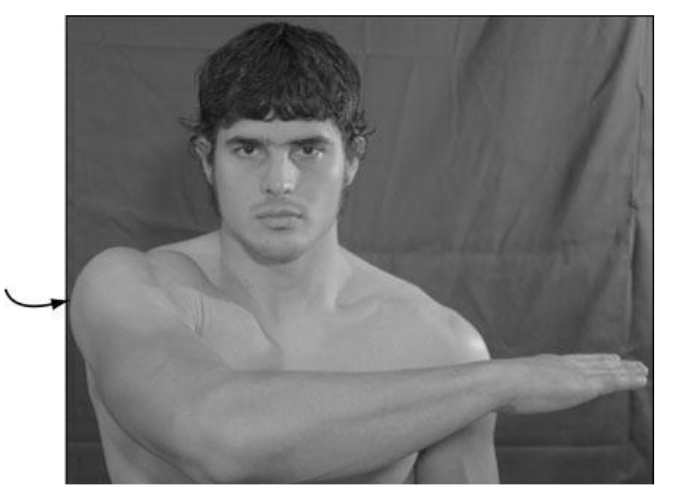

66
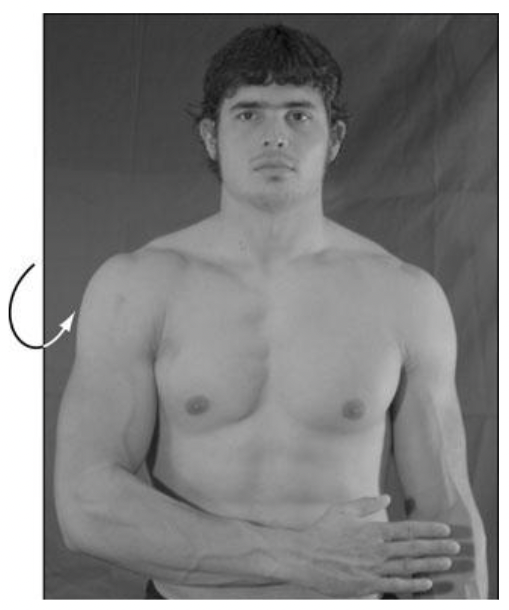
New cards
external rotation (retraction)
what is this?

67
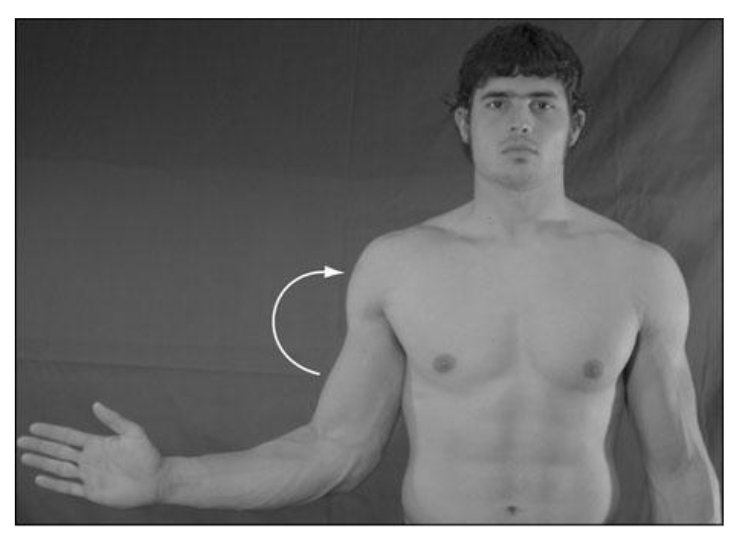
New cards
internal rotation (protraction)
what is this?

68
New cards
horizontal abduction (retraction)
what is this?
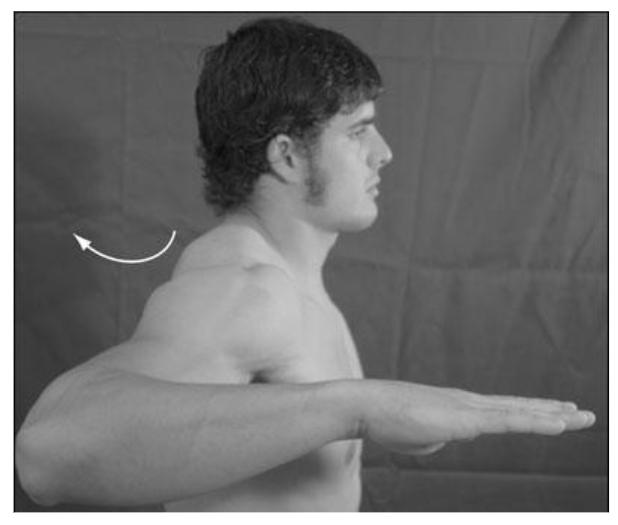

69
New cards
extension
what is this?
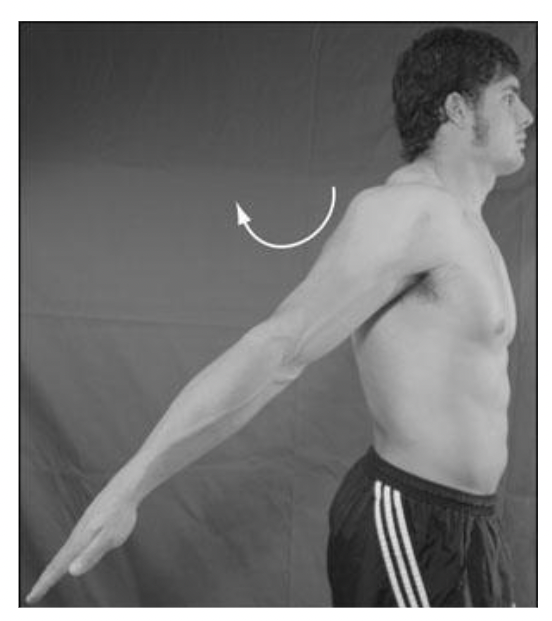
70
New cards
shoulder girdle
Accompany glenohumeral joint movement to increase ROM.
71
New cards
shoulder girdle
To stabilize the scapula and clavicle during glenohumeral joint movements.
72
New cards
shoulder girdle
Scapulo-humeral rhythm
73
New cards
stabilization
The importance of muscle function in…
74
New cards
proximal stabilization
Movements associated with joint motion require…
75
New cards
origin
Proximal attachment, generally considered the __least movable part__
76
New cards
origin
the part that attaches closest to the midline or center of the body.
77
New cards
stable
Muscles can only exert force and cause limb movement __if one end remains…__
78
New cards
insertion
*The* distal attachment, generally considered the __most movable part__
79
New cards
insertion
*the part that attaches farthest from the midline or center of the body.*
80
New cards
6
…muscles primarily involved in shoulder girdle movements
81
New cards
muscles
6… primarily involved in shoulder girdle movements
82
New cards
muscles
Do not attach to humerus & do not cause shoulder joint actions.
83
New cards
muscle
Essential in providing dynamic stability of the scapula so it can serve as a __relative base of support__ for shoulder joint activities such as throwing, batting, & blocking.
84
New cards
dynamic stability
muscles are Essential in providing… of the scapula so it can serve as a __relative base of support__ for shoulder joint activities such as throwing, batting, & blocking.
85
New cards
scapula
muscles are Essential in providing dynamic stability of the … so it can serve as a __relative base of support__ for shoulder joint activities such as throwing, batting, & blocking.
86
New cards
base of support
muscles are Essential in providing dynamic stability of the scapula so it can serve as a relative … for shoulder joint activities such as throwing, batting, & blocking.
87
New cards
primary
There are 6… muscles of the shoulder girdle.
88
New cards
nerves
Shoulder girdle muscles primarily innervated by *cervical* & brachial plexus
89
New cards
cervical
nerves
Shoulder girdle muscles primarily innervated by *…* & brachial plexus
Shoulder girdle muscles primarily innervated by *…* & brachial plexus
90
New cards
brachial plexus
nerves
Shoulder girdle muscles primarily innervated by *cervical* & …
Shoulder girdle muscles primarily innervated by *cervical* & …
91
New cards
serratus anterior
Anterior muscles of the shoulder girdle
1. \
1. \
92
New cards
pectoralis minor
Anterior muscles of the shoulder girdle
2. \
2. \
93
New cards
subclavius
Anterior muscles of the shoulder girdle
3. \
3. \
94
New cards
upper 9 ribs
serratus anterior
origin: superiors surfaces of ….
origin: superiors surfaces of ….
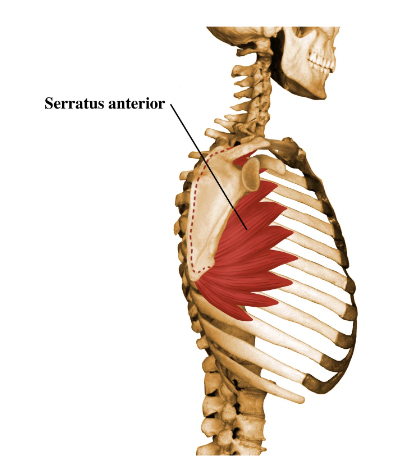
95
New cards
serratus anterior
__Origin__
Superior surfaces of upper 9 ribs.
Superior surfaces of upper 9 ribs.
96
New cards
medial border of scapula
serratus anterior
insertion: costal aspect of ….
insertion: costal aspect of ….
97
New cards
serratus anterior
__Insertion__
Costal aspect of medial border of scapula.
Costal aspect of medial border of scapula.
98
New cards
long thoracic nerve
serratus anterior
innervation: …. arising from the ventral rami of C5, C6, C7, before the brachial plexus.
innervation: …. arising from the ventral rami of C5, C6, C7, before the brachial plexus.
99
New cards
serratus anterior
innervation: Long thoracic nerve arising from the ventral rami of C5, C6, C7, before the brachial plexus.
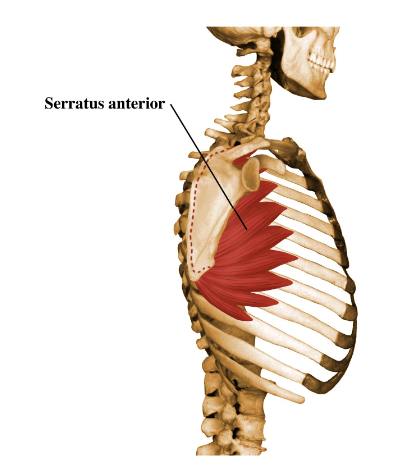
100
New cards
stabilization
Primary role of Serratus Anterior
…. of the shoulder girdle
…. of the shoulder girdle