Questions that were answered incorrectly
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Name and describe five ways substances can move across the cell surface membrane into a cell (5)
Simple diffusion of small/non-polar molecules down a concentration gradient
Facilitated diffusion down a concentration gradient via protein carrier/channel
Osmosis of water down a water potential gradient
Active transport against a concentration gradient via protein carrier using ATP
Co-transport of 2 different substances using a carrier protein
The movement of substances across cell membranes is affected by membrane structure. Describe how. (5)
Phospholipid bilayer allows movement/diffusion of non-polar/lipid soluble substances
Phospholipid bilayer prevents movement/diffusion of polar substances (or) proteins allow polar-charged substances to cross the membrane
Carrier proteins allow active transport
Channel/carrier proteins allow facilitated diffusion/co-transport
Shape/charge of channel/carrier determines which substances move
Number of channels/carriers determines how much movement
Membrane surface area determines how much diffusion
Cholesterol affects fluidity/rigidity/permeability
Contrast how an optical microscope and a transmission electron microscope work and contrast the limitations of their use when studying cells. (6)
TEM uses electrons and optical uses light
TEM allows greater resolution
(TEM) smaller organelles can be observed/observed in greater detail
TEM can only view dead specimens and optical can only view live
TEM does not show colour and optical can
TEM requires thinner specimens
TEM requires a more complex preparation
TEM uses magnets and optical uses lenses/glasses
Describe and explain the processes that occur during meiosis that increase genetic variation (5)
Homologous chromosomes pair up
Independent segregation of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I, and of chromatids in meiosis II
Random allocation of chromosomes into each daughter cell (maternal and paternal chromosomes are re-shuffled in any combination)
Crossing over leads to exchange of parts of non-sister chromatids/alleles between homologous chromosomes
(Both) create new combinations of alleles
Describe how vaccination can lead to protection against a disease (7)
Vaccine contains antigens from pathogen which are injected into bloodstream
Antigen-presenting cell/B-cell presents antigens on its surface
T cell with complementary receptor protein binds to antigen
Activates/stimulates B cell to divide by mitosis/produce clones
B cells develop into plasma cells/memory cells
Plasma cells release antibodies
Antibodies cause pathogens to agglutinate which are killed/engulfed by phagocytes
On second exposure memory cells rapidly produce antibodies/produces more antibodies
Describe the process involved in the absorption and transport of digested lipid molecules from the ileum into lymph vessels (5)
Micelles contain bile salts and fatty acids/monoglycerides
Make fatty acids/monoglycerides more soluble in water
(or) bring/release fatty acids/monoglycerides to cell lining of the ileumFatty acids/monoglycerides absorbed by simple diffusion
Triglycerides reformed in cells and cholesterol and lipoproteins added to form chylomicrons
Chylomicrons released by exocytosis
Describe how a polypeptide if formed by translation of mRNA (6)
mRNA attaches to ribosome
tRNA anticodons bind to complementary mRNA codons
tRNA brings a specific amino acid
Amino acids join by peptide bonds
Amino acids join together with the use of ATP
tRNA released (after amino acid joined to polypeptide)
The ribosome moves along the mRNA to form the polypeptide
Describe how mRNA is produced in a plant cell (6)
Hydrogen bonds between DNA bases break
Only one DNA strand acts as a template
Free RNA nucleotides align by complementary base pairing
Uracil base pairs with adenine/used in the place of thymine
RNA polymerase joins (adjacent) RNA nucleotides by making phosphodiester bonds
Pre-mRNA is spliced (or introns are removed)
Describe how the structure of glycogen is related to its function (4)
Helix/coiled/branched so compact
Polymer of glucose so easily hydrolysed
Branched so more ends for faster hydrolysis
Glucose (polymer) so provides respiratory substrate for energy
Insoluble so does not affect water potential/osmosis
Explain why viruses are described as acellular and non-living? (2)
No cell surface membrane
(or) not made of cells
(or) do not have organelles/cell structuresHave no metabolic reactions
(or) cannot independently replicate/respire
One reason why antibiotics are not effective against viruses (1)
Do not have bacterial structures/enzymes
(or) do not have metabolic processes
(or) do not have a cell wall/murein
Explain the importance of one adaptation of the gas exchange surface in the tracheal system of an insect (2)
Tracheole wall thin/one cell thick
So rapid diffusion into cells/short diffusion pathway
(or)
Tracheoles are highly branched
So short diffusion pathway
(or) So large surface area for diffusion
Explain the importance of the xylem being kept open as a continuous tube (3)
Allows unbroken water column/no barrier to water movement
Cohesion from H bonds between water molecules
Transpiration/evaporation creates tension
(or) water moves from xylem into cells to create tension
(or) pull up water creates tension in xylem
What is meant by genetic diversity? (1)
The number of different alleles of each gene
(or) number of different base sequences found of each gene
Suggest two reasons why populations might show very low levels of genetic diversity (2)
Population might have been very small/genetic bottleneck
Population might have started with a small number of individuals/founder effect (one pregnant female)
Inbreeding
Describe the induced-fit model of enzyme action and how an enzyme acts as a catalyst (3)
Substrate binds to the active site
(or) Enzyme-substrate complex formsActive site changes shape so that it is complementary to the substrate
(or) Active site changes shape, distorting/breaking bonds in the substrateReduces activation energy
Describe the complete digestion of starch by a mammal. (4)
Hydrolysis
of glycosidic bonds
Starch to maltose by amylase
maltose to glucose by maltase/disaccharidase
disaccharidase/maltase is membrane-bound
Define ‘gene mutation’ and explain how a gene mutation can have:
• no effect on an individual
• a positive effect on an individual. (4)
Gene mutation is a change in the base/nucleotide sequence of DNA
Results in the formation of new allele
(Has no effect because)
Genetic code is degenerate (so amino acid sequence may not change)
(or)
Mutation is in an intronDoes change amino acid but no effect on tertiary structure
(New allele) is recessive so does not influence phenotype
(Positive effect because)
Results in change in polypeptide that positively changes the properties of the protein
May result in increased reproductive success or increased survival chances
Describe how viruses are replicated (4)
Virus attachment proteins attach to cell receptors
Viral nucleic acid/genetic information enters cell
Viral nucleic acid is replicated (or) reverse transcriptase produces DNA from RNA
Viral protein is produced
Viral components assembled and released from cell
Describe and explain how the structure of DNA results in accurate replication (4)
2 strands therefore semi-conservative replication (if possible)
base pairing/hydrogen bonds hold strands together
hydrogen bonds weak and easily broken, allows strands to separate
base sequence exposed so acts as a template
A with T, C with G, complementary copy
DNA one parent and one new strand
Describe the behaviour of chromosomes during mitosis and explain how this results in the production of two genetically identical cells. (7)
chromosomes shorten/thicken/supercoiling
each chromosome has 2 identical chromatids (due to replication)
chromosomes/chromatids move to equator
attach to individual spindle fibres
spindle fibres contract/centromeres divide
sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles
each pole receives identical copies of each chromosome
nuclear envelope forms around each group of chromosomes at each pole
Describe the role of haemoglobin in the loading, transport and unloading of oxygen (5)
Hb loads/associates oxygen in the lungs
At high partial pressure of oxygen
Binding of an oxygen molecule to Hb makes binding of subsequent oxygen easier (positive co-operativity)
Oxygen transported as oxyhaemoglobin in red blood cells
Hb unloads/dissociates in the respiring cells/tissues
At a low partial pressure of oxygen
Describe the cohesion-tension theory of water transport in the xylem (5)
Water is lost from leaf due to transpiration/evaporation of water from stomata
Lowers water potential of mesophyll/leaf cells
Water pulled up xylem (creating tension)
Water molecules cohere/stick together by hydrogen bonding
Forming a continuous water column
Adhesion of water molecules to the walls of xylem
Describe and explain how the structure of the mammalian breathing system enables efficient uptake of oxygen into the blood (6)
alveoli provide a large surface area
walls of alveoli thin to provide short diffusion pathway
walls of capillary thin to provide short diffusion pathway
cell membranes permeable to gases
many blood capillaries provides a large surface area
intercostal/diaphragm muscles/ventilate lungs/maintain diffusion gradient
wide trachea/branching of bronchi and bronchioles for efficient flow of air
cartilage rings keep airways open
Describe how the structure of the insect gas exchange system
- provides cells with sufficient oxygen
- limits water loss (5)
spiracles allow diffusion (of oxygen) / oxygen diffusion through trachea or tracheoles
Tracheoles are highly branched so large surface area
Tracheole (walls) thin so short diffusion distance to cells
(or) Highly branched so short diffusion distanceTracheole walls are permeable to oxygen/air
Exoskeleton (impermeable) so reduces water loss
Spiracles can close so no/less water loss
Hairs around spiracles reduce water loss
Describe how oxygen in the air reaches capillaries surrounding alveoli in the lungs. Details of breathing are not required (4)
Trachea and bronchi and bronchioles
down pressure gradient
down diffusion gradient
across alveolar epithelium
across capillary endothelium
Describe the structure and function of the nucleus [4]
Nuclear envelope/double membrane and pores
Chromosomes/chromatin (or) DNA with histones
Nucleolus
Stores genetic information/material for polypeptide production (or) is the code for polypeptides
DNA replication occurs
Production of mRNA/tRNA (or) transcription occurs
Production of rRNA/ribosomes
Explain how the use of antibiotics has led to antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria becoming a common cause of infection acquired when in hospital (3)
Some bacteria have resistant alleles
Exposure to antibiotics acts as a selection pressure
(or) Resistant bacteria survive/reproduce
(or) Non-resistant bacteria dieMore antibiotics used in hospital (compared with elsewhere)
(or) Patients already have weakened immune systems
(or) High frequency of resistance allele within bacterial population
NHE3 actively transports one sodium ion into the cell in exchange for one hydrogen ion out of the cell
Use your knowledge of transport across cell membranes to suggest how NHE3 does this (3)
Co-transport
Uses hydrolysis of ATP
Hydrogen ion and sodium ion bind to carrier protein
Protein changes shape (to move sodium/hydrogen across the membrane)
Describe how bacteria divide (2)
Binary fission
Replication of circular DNA
Cytoplasm divides to produce 2 daughter cells
Each with single copy of circular DNA
Suggest one advantage to a bacterium of secreting an extracellular protease in its natural environment (2)
To digest protein
So they can absorb amino acids for growth/reproduction/protein synthesis of organelles
(or) To destroy a toxic substance/protein
In DNA replication, why can new nucleotides only be added in a 5’ to 3’ direction? (4)
Reference to DNA polymerase
Which is specific
Only complementary with/binds to 5’ end (of strand)
Shapes of 5’ end and 3’ end are different/description of how different
Describe the mass flow hypothesis for the mechanism of translocation in plants (4)
In source/leaf sugars actively transported into phloem (co-transport with hydrogen ions)
By companion cells
Lowers water potential of sieve tube element and water enters by osmosis
Increase in pressure causes mass movement of sucrose towards sink
Sugars used/converted in root for respiration or storage (starch)
Describe the structure of proteins (5)
Polymer of amino acids
Joined by peptide bonds
Formed by condensation reaction
Primary structure is the order of amino acids
Secondary structure is folding of polypeptide chain due to hydrogen bonding (alpha helix and beta pleated sheet)
Tertiary structure is 3D folding due to hydrogen bonding, ionic bonding and disulphide bridges
Quaternary structure is two or more polypeptide chains
Describe how proteins are digested in the human gut (4)
Hydrolysis of peptide bonds
Endopeptidases break polypeptides into smaller polypeptide chains
Exopeptidases remove terminal amino acids
Dipeptidases hydrolyse/break down dipeptides into amino acids
[Cognito]
Suggest one advantage and one disadvantage of replanting hedges (2)
(Advantage)
Increased biodiversity may increase predation of pests
Increased predation of pests would mean fewer pesticides required
Increase in pollinators leading to increased yield/outcome
(Disadvantages)
Reduced land area for growth of crops
Greater biodiversity may increase number of pests
Increase in pest population may reduce yield/income
Seeds/plants from hedges may be blown onto fields and compete with crops
There is currently no effective vaccine available for HIV. Suggest one reason why (1)
Because HIV RNA mutates often, this means a higher genetic diversity (vaccines may not be effective against all strains of the virus)
A groups of scientists thought that pesticide in some flies was related to increased activity of an enzyme called PM that breaks down insecticides.
They then
exposed non-resistant flies to insecticide
exposed resistant flies to insecticide
exposed resistant flies with an inhibitor of PM to insecticide
Explain why the scientists carries out the control experiment with the non resistant flies (2)
for comparison with resistant flies/other groups
to see death rate (in non resistant)/to see effects of insecticide on non resistant flies
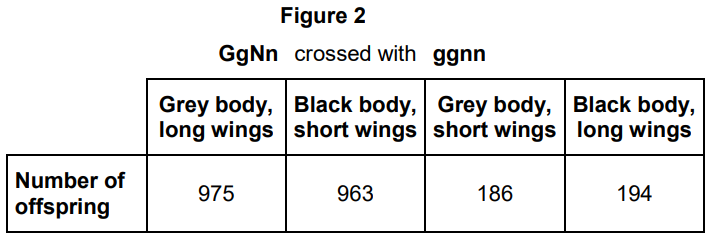
G = dominant allele for grey body
g = recessive allele for black body
N = dominant allele for long wings
n = recessive allele for short wings
Use your knowledge of gene linkage to explain these results (4)
GN and gn linked
GgNn individual produces mainly GN and gn gametes
Crossing over produces some/few Gn and gN gametes
So fewer Ggnn and ggNn individuals
Describe how red blood cells are adapted for their function [6] (Socrative)
Haemoglobin carries oxygen
Detail of no. of oxygen molecules transported
Small size/large SA:V, so haemoglobin never far from cell surface
Flexible/elastic/changes shape
Small size/’stretchiness’ allows RBCs to fit/squeeze into capillaries
Bioconcave shape gives increased surface area relative to volume, for diffusion
No nucleus to maximise room for haemoglobin/oxygen