Honors Bio Unit 8 Study Guide
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/62
Last updated 3:58 AM on 4/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
1
New cards
What did James Hutton and Charles Lyell propose?
James Hutton and Charles Lyell proposed that the earth was very old.
2
New cards
What did Charles Darwin observe on his voyage?
Charles Darwin observed Natural Selection.
3
New cards
What was different about each island on the Galapagos Islands?
Each island had animals suited to its environment.
4
New cards
What is the definition of Variation?
Differences in physical traits.
5
New cards
What is the definition of an adaptation?
A feature that allows an organism to better survive in its environment.
6
New cards
What did Darwin discover about fossil and geologic evidence?
He discovered that fossil and geologic evidence changes over time.
7
New cards
How did Artificial Selection influence, Charles Darwin?
He compared what he learned about breeding to his idea of adaptation. He also said that in nature, environment creates selective pressure instead of humans in artificial selection.
8
New cards
What is Artificial Selection?
The process by which humans change species by breeding them for certain traits.
9
New cards
What are the four main principles of the theory of Natural Selection?
Variation, Overproduction(Lots of offsprings so few survive), Adaptation, Descent with Modificiation.
10
New cards
What is descent with modification?
Over time, natural selection will result in species with adaptations that are well suited for survival.
11
New cards
What does Natural Selection act on?
Phenotypes.
12
New cards
What is fitness?
The ability to survive until the age of reproduction, to find a mate, and produce offspring.
13
New cards
What evidence supported Darwin’s claims?
Fossils supported Darwin’s descent with modification, Geography made Darwin realize that finches found on the Galapagos islands closely resembled those found on the mainland and that over time new traits became well established in separate island populations which were caused by the different environments in each island that led to specific adaptations in diets, habits, and BEAK SHAPES, Embryology, and Anatomy where he compared body parts of different species.
14
New cards
What are analogous structures?
They perform a similar function but are not similar in origin(i.e. wings of bats and insects).
15
New cards
What are homologous structures?
Features that are similar in structure but have different functions(suggested common ancestor) (i.e. forelimbs of vertebrates).
16
New cards
What are vestigial structures?
Structures or organs that lack any useful function that had a function in an early ancestor(e.g. human appendix, wings of ostriches).
17
New cards
What is gene pool?
Genetic variation stored inside a population.
18
New cards
Meiosis is both…?
Recombination and Crossing over.
19
New cards
A bell curve is ___ distribution.
Normal.
20
New cards
What is directional slelection?
\
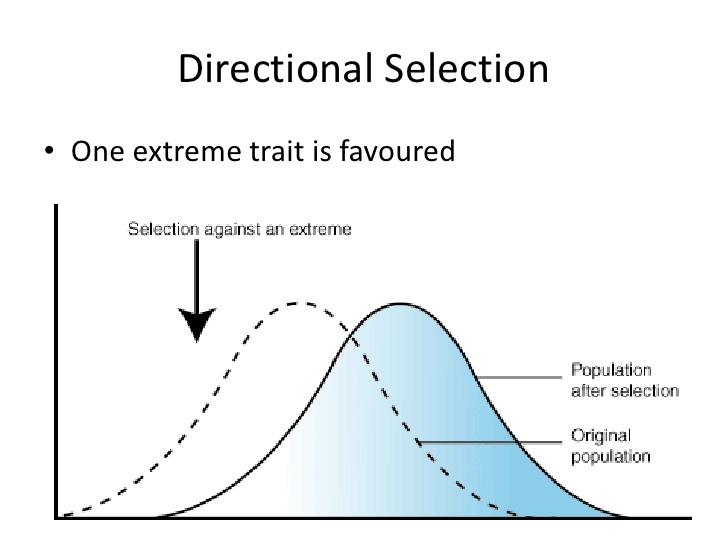
21
New cards
What is stabilizing selection?
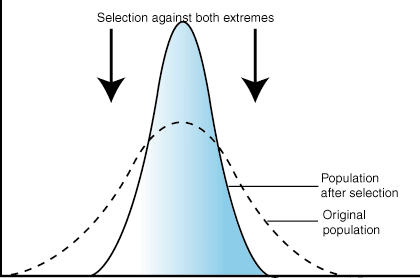
22
New cards
What is disruptive selection?
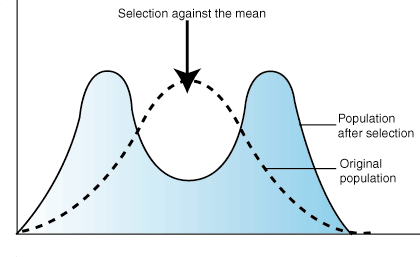
23
New cards
What is gene flow?
The movement of alleles from one population to another, the receiving population has increased genetic diversity.
24
New cards
What is genetic drift?
changes in allele frequency due to chance.
25
New cards
What is the bottleneck effect?
Genetic drift that occurs after an event.
26
New cards
What is the founder effect?
Genetic drift that occurs after a small number of individuals colonize a new area.
27
New cards
What are the effects of genetic drift?
Loss of genetic variation and lethal alleles may become more common.
28
New cards
What is sexual selection?
When certain traits increase mating success.
29
New cards
The Hardy-Weinberg Equillibrium describes…
populations that are not evolving.
30
New cards
The Hardy-Weinberg equation is used to predict…
genotype frequencies in a population.
31
New cards
What is reproductive isolation?
When members of different populations can no longer mate successfully with one another.
32
New cards
What is behavioral isolation?
Isolation caused by differences in courtship or mating behavior,
33
New cards
What is Geographic Isolation?
Involves physical barriers that divide populations like mountains and rivers.
34
New cards
What is temporal isolation?
Timing prevents reproduction between populations.
35
New cards
What is convergent evolution?
Evolution towards similar characteristics in unrelated species.
36
New cards
What is divergent evolution?
Related species evolve in different directions and become increasingly different.
37
New cards
What is Coevolution?
Two or more species evolve in response to changes in each other.
38
New cards
What is extinction?
Elimination of a species from earth.
39
New cards
What is punctated equillibrium?
Bursts of evolutionary activity.
40
New cards
What is adaptive Radiation?
Diversification of one ancestral species into many descendant species.
41
New cards
What is permineralization?
Minerals carried by water are deposited around or replace the hard structure (coal).
42
New cards
Where do most fossils form?
In sedimentary rock.
43
New cards
What is relative dating?
Estimate of date by comparing the placement of fossils in rock layers.
44
New cards
What is radiometric dating?
Technique using natural decay rate of unstable isotopes.
45
New cards
What are index fossils?
Organisms that existed only during specific spans of time over a geographical area.
46
New cards
Eras are seperated by…
mass periods of mass destruction.
47
New cards
Eras last…
tens of to hundreds of millions of years.
48
New cards
What is the first era?
Pre-cambrian.
49
New cards
What is the second era?
Paleozoic.
50
New cards
What is the third era?
Mesozoic.
51
New cards
What is the fourth era(the one we are in)?
Cenozoic
52
New cards
How old is earth?
4\.6 billion years old.
53
New cards
How did the atmosphere form on earth?
When it cooled, this caused water vapor to condense and rain to fall. Organic compounds soon formed.
54
New cards
The Miller Urey experiment demonstrated that…
Organic compounds could be made by simulating conditions on early earth.
55
New cards
What is the meteorite hypothesis.
Organic molecules may have arrived on earth through meteorite or asteroid impacts.
56
New cards
How did single-celled organisms change Earth’s surface?
They deposited minerals.
57
New cards
What allowed the evolution of aerobic prokaryotes?
Higher oxygen levels in the atmosphere.
58
New cards
What as the first photosynthetic life to evolve?
Cyanobacteria.
59
New cards
What is the endosymbiotic theory?
One organism lives within the body of another, and both benefit from the relationship.
60
New cards
What evidence proves the endosymbiotic theory?
Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA and ribosomes, and they are similar in shape.
61
New cards
The is the significance of asexual reproduction in cells?
First prokaryotes and eukaryotes reproduced asexually, this increased genetic variation and was the first step in the evolution of multicellular life.
62
New cards
What does Homo Sapien mean?
Modern man.
63
New cards
How long ago did Homo Sapiens appear?
200,000 years.