Bio Quiz 1 Unit 3: complete dominance, incomplete dominance, codominance, sex linked diseases, blood types, gel interpretation, and pedigrees
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
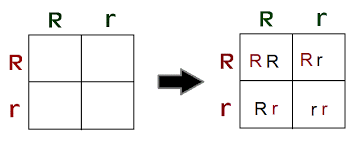
punnett square
A diagram used to predict the genetic outcomes of a cross between two individuals, illustrating the possible allele combinations of offspring. It applies rules of probablility that predict that outcome of a genetic cross. It helps to determine observable traits.
Genotype
The allelles of a person’s gene. Ex: 50% Aa
Phenotype
The physical characteristics that occur from a genotype. Ex: 50% blue eyed
gene
a unit of heredity which goes from the parent to the offspring and determines the charactersistcs of the offspring
Allele
The different forms of a gene
complete dominance
gregor mendel’s theory with dominant and recessive alleles. Ex: RR, Rr, rr
Homozygous
It can be homozygous dominant or homozygous recessive, but either way there is no carrier. In other words, the individual has two identical alleles for a trait. Ex: TT. Ex: tt.
Heterozygous
An individual having two different alleles for a trait. Ex: The individual has one dominant allele and one recessive allele, such as Aa.
Multiple alleles
Multiple alleles control 1 trait
Blood types
The human blood types are blood type A, B, AB, and O. It is controlled by Codominance and multiple alleles. There are two dominant alleles: I^A and I^B, and one recessive allele: i.
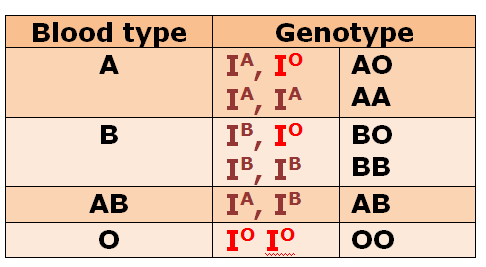
Blood Type A
The genotype is I^A I^A or I^Ai. It can donate blood to types AB and A. It can recieve blood from types A and O. It has the antibody Anti-B and a A antigen.
Blood Type B
This genotype is I^BI^B or I^Bi. It can donate blood to AB and B. It can receive blood from blood types O and B. It has the antibody Anti-A and a B antigen
Blood Type AB
This genotype is I^AI^B. It can donate blood to blood type AB. It can receive blood from A, B, AB, and O (universal reciever). It has no antibodies and A and B antigens.
Blood Type O
This genotype is ii. It can donate blood to A, B, AB, and O (universal donor). It can receive blood only from type O. It has the antibodies Anti-A and Anti-B, and no antigens.
dominant allele
the gene that masks the recessive gene; represented by a capitol letter
recessive allele
the masked gene; represented by a a lowercase letter
Incomplete dominance
a mixed trait is possible, portraying a blended characteristic. Ex: C exponent R, C exponent W
Codominance
Both alleles are fully expressed, showing a mix. Ex: RW
sex-linked inheritance
the traits that are created by sex linked inheritance. Male: XY. Female: XX. Allele is like an exponent on each chromosome
amount of chromosomes in humans
In humans, the twenty-third pair is the sex chromosomes, while the first 22 pairs are called autosomes
In sex linked inheritance, females are more often ________ than males
carriers
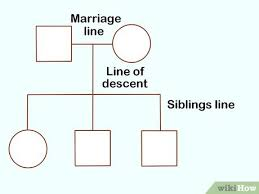
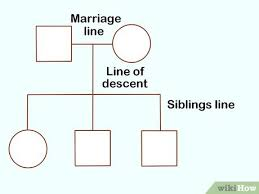
Pedigrees
diagrams that show the inheritance of traits in a family across generations, used to analyze genetic disorders and relationships. Similar to a family tree.
Autosomal
a disease/condition that affects males and females equally
X-linked
a disease/condition that affects males more than females, because it is sex linked
Dominant
a disease/condition that is found in every generation
Recessive
a diesease/condition that skips a generation
sign for males
square
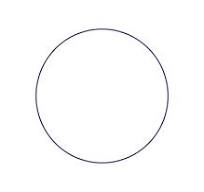
sign for females
circle
sign for affected person
filled shape, darkly shaded
sign for carrier person
half-shaded circle or square, pale gray
sign for unaffected person
a blank circle or square
line of marraige
the line between a square and a circle that indicates a union between partners in a pedigree chart.
Lane
A, B, C, D, E, F, G
Band
Colored lines
Well
white lines on top
If there are a lot of bands, they can be used as a ___________ to compare the sizes of the bands
reference
The section of the gel sample that is negatively charged
the DNA
If bands are lighter colored, then an _______ has occured
error
If there are more nucleotides, the bands are ________, meaning they will move slower and be higher up. If there are less nucleotides, the bands are ________, lighter, meaning they will move faster and farther down
heavier; lighter
electrophoresis
the running of gels
how to show siblings in a pedigree chart
a line and bracket going from the line of marraige