curved mirrors & lenses
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
2 types of curved mirrors
Concave & Convex
Concave
Converging mirrors
To meet in a common place
Convex
Diverging mirrors
To spread apart
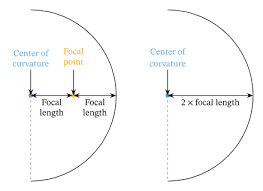
Center of curvature
Center of the larger sphere (circle) of the mirror
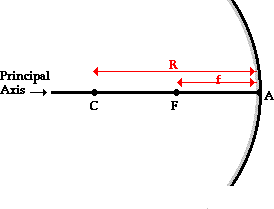
Principal axis
Line thru the center of curvature to the midpoint of the mirror
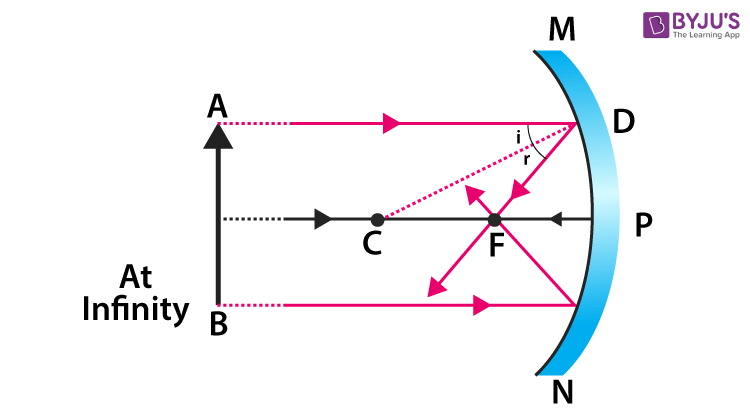
Focus
Point where light parallel to the principal axis meets
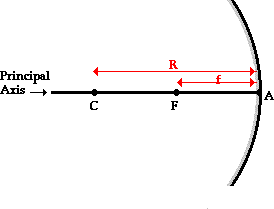
Vertex
Point where the principal axis meets the mirror
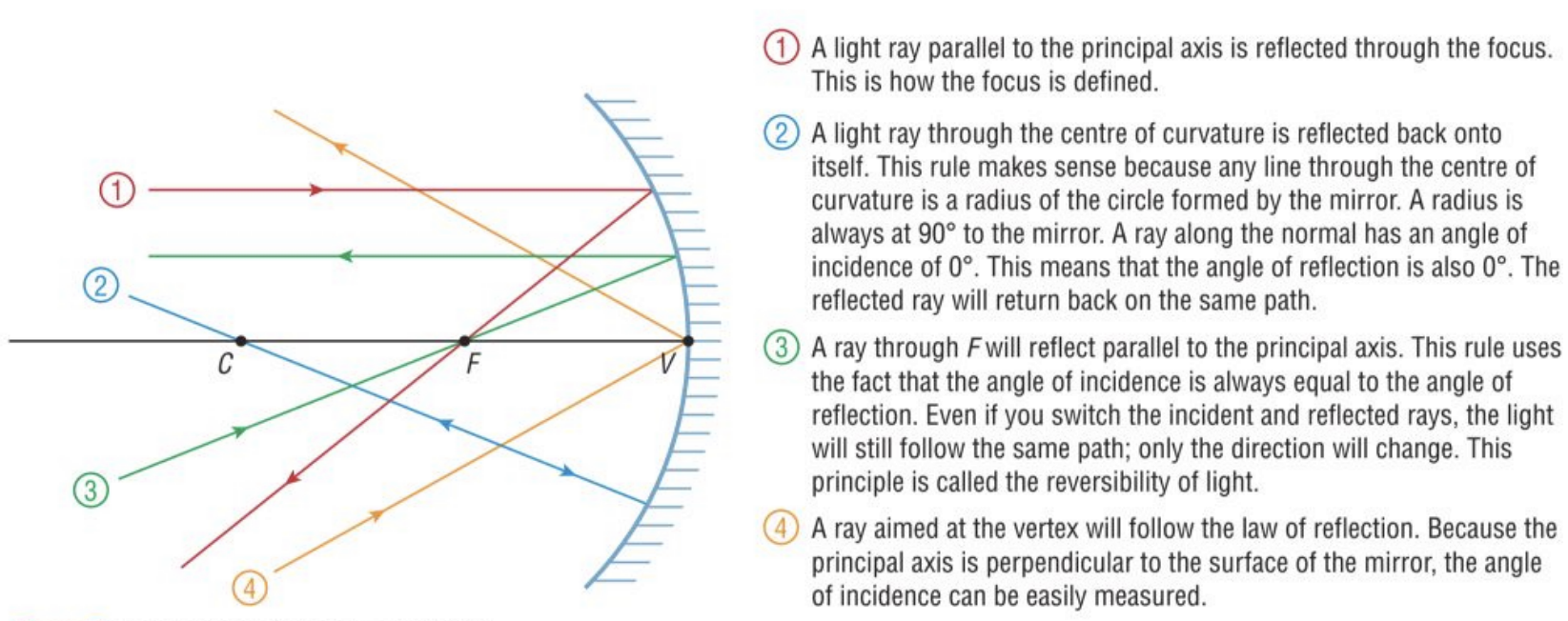
Concave rules
Parallel ray bounces thru the focus
Thru the focus bounces parallel
Thru the center reflects back to the way it came
Thru the vertex reflects like a flat mirror
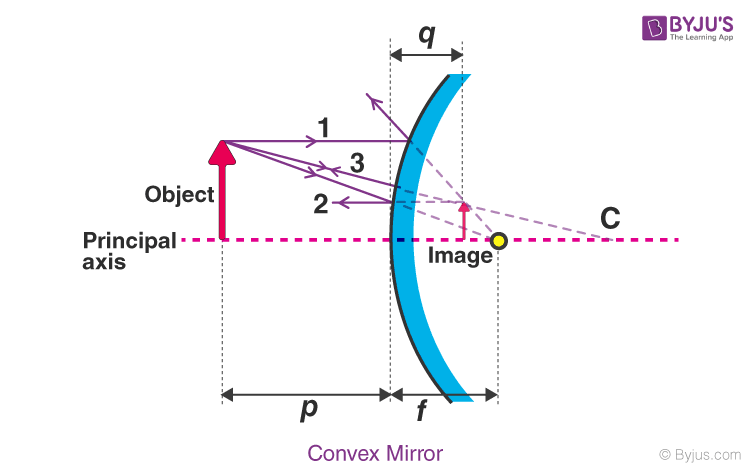
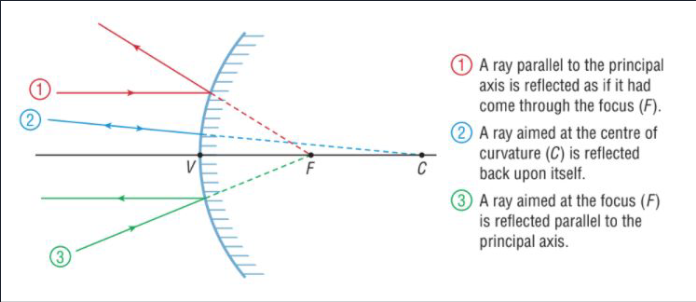
Convex rules
ray parallel to the principal axis is as if it had come through the focus
ray aimed to the centre of curvature on the other side is reflected
ray aimed to the focus is reflected parallel to principal axis
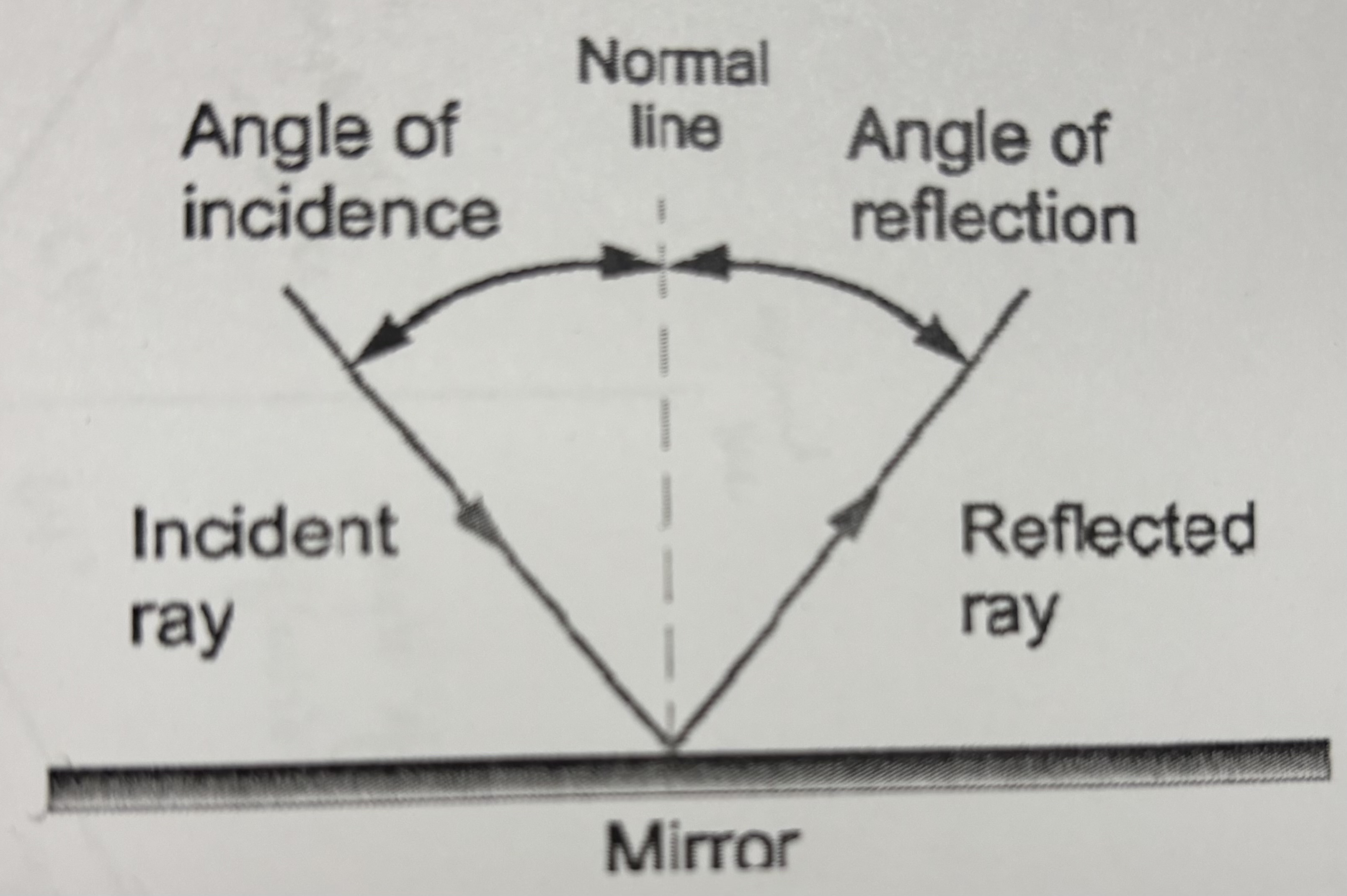
The law of reflection states that…
When an object hits a surface, its angle of incidence will equal the angle of reflection. Only true when the object is light and the surface is a flat smooth mirror
Transparent
All light goes thru
Translucent
Some light goes thru
Opaque
No light goes thru
Normal line
Imaginary line perpendicular to the surface
Angle of incidence
Angle in which the light enters
angle in between the normal and the incident ray
Angle of reflection
Angle in which the reflected ray bounces off the surface
Angle in between the normal and the reflected ray
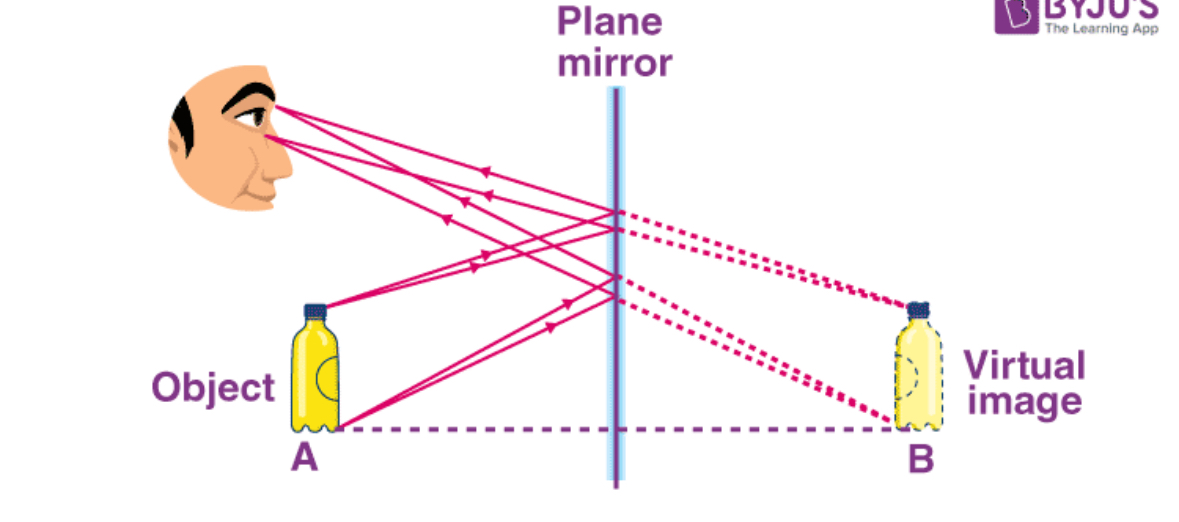
Virtual image
Image formed by light coming to an apparent
Upright
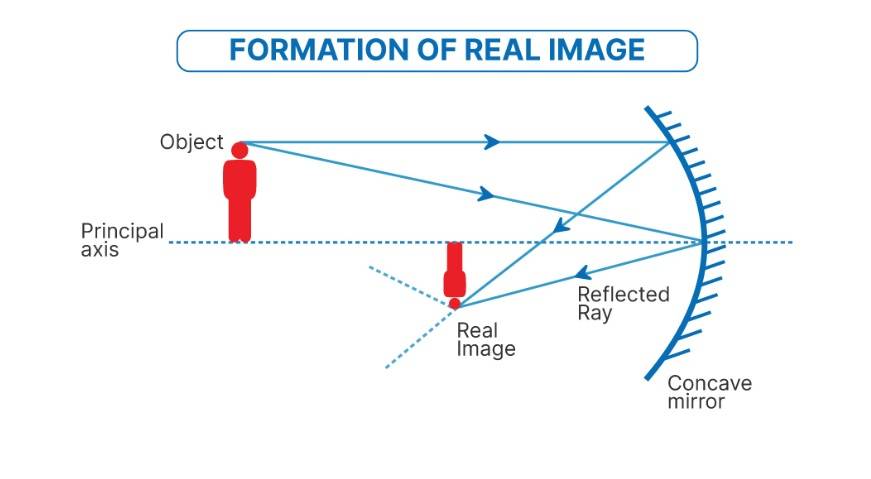
Real image
Reproduction of an object, produced by an optical device
Inverted
Lateral Inversion
Placement of image in a plane mirror that is backwards and in reverse order
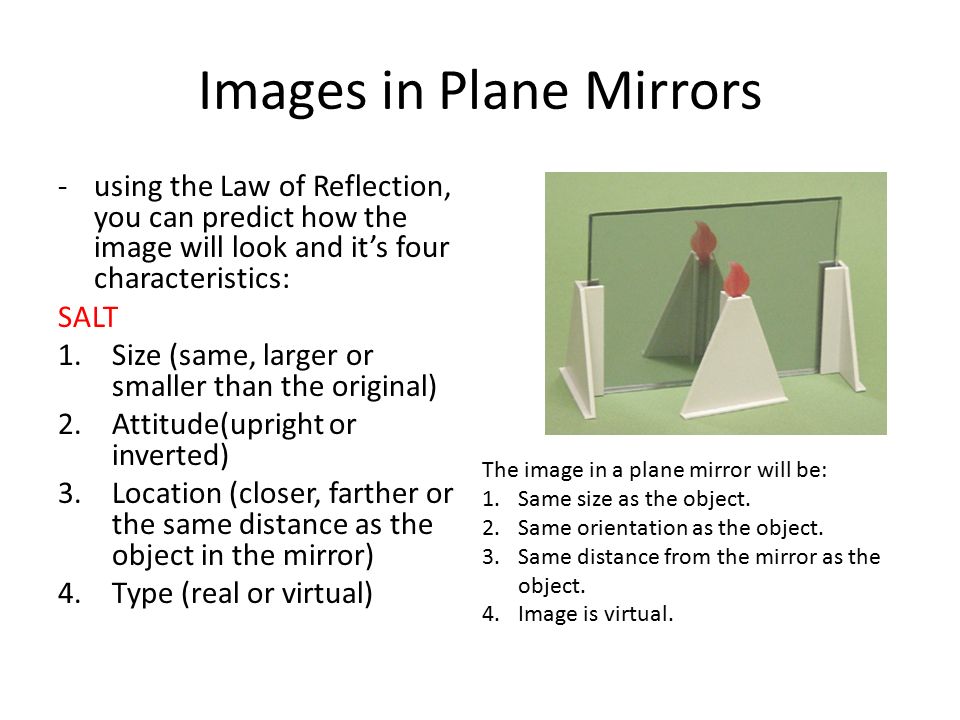
SALT
S - Size of an image (size, smaller, larger)
A - Attitude of an image (upright/inverted)
L - Location of image
T - Type of image (real/virtual)
2 types of lenses
converging and diverging
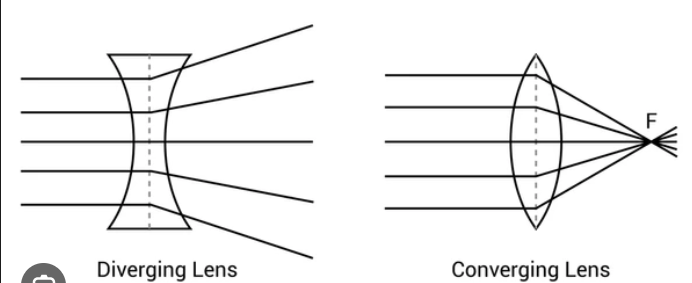
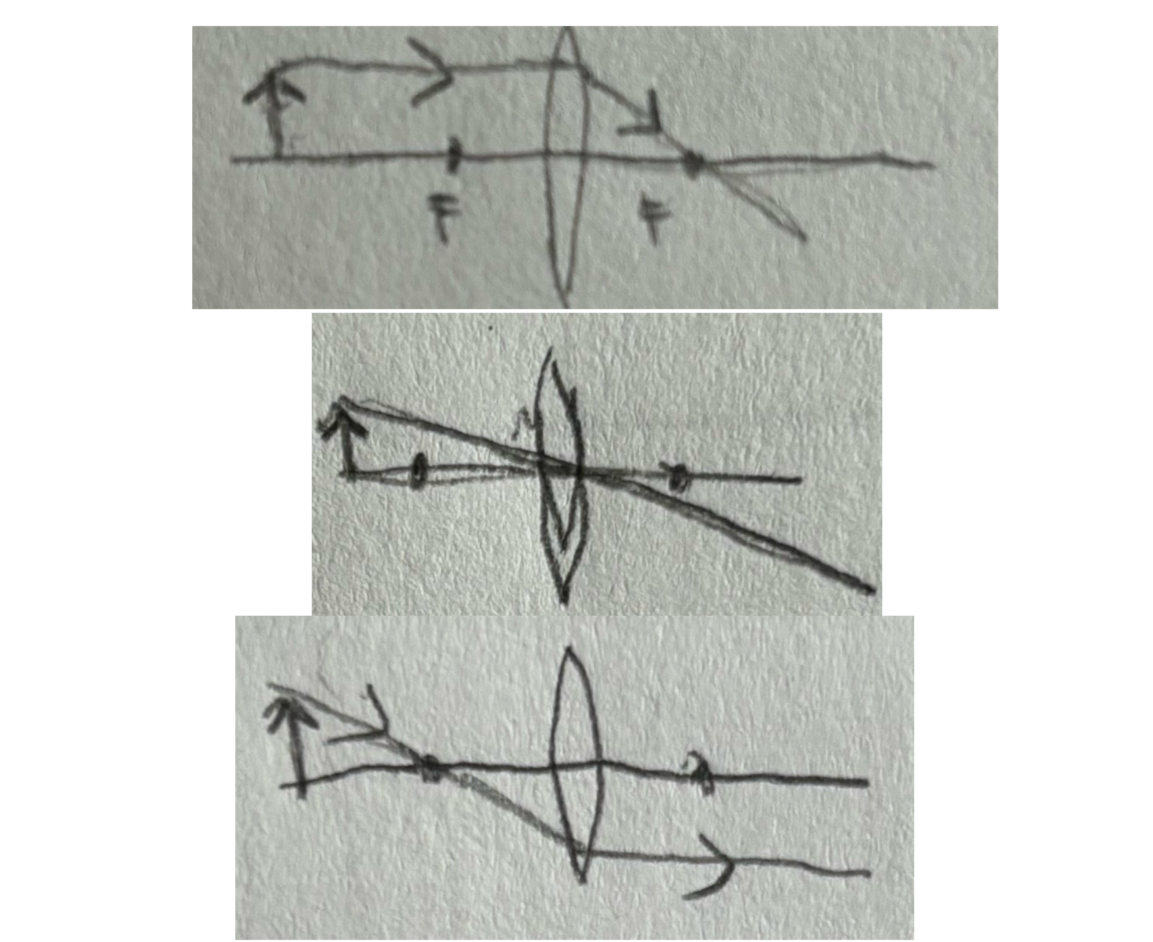
converging lens rules
ray parallel to the principal axis passes thru focal point on the other side
ray passes thru center of lens doesn’t get reflected
ray passes thru focal point in front of lens emerges parallel to the principal axis on the other side
can make both real and virtual images
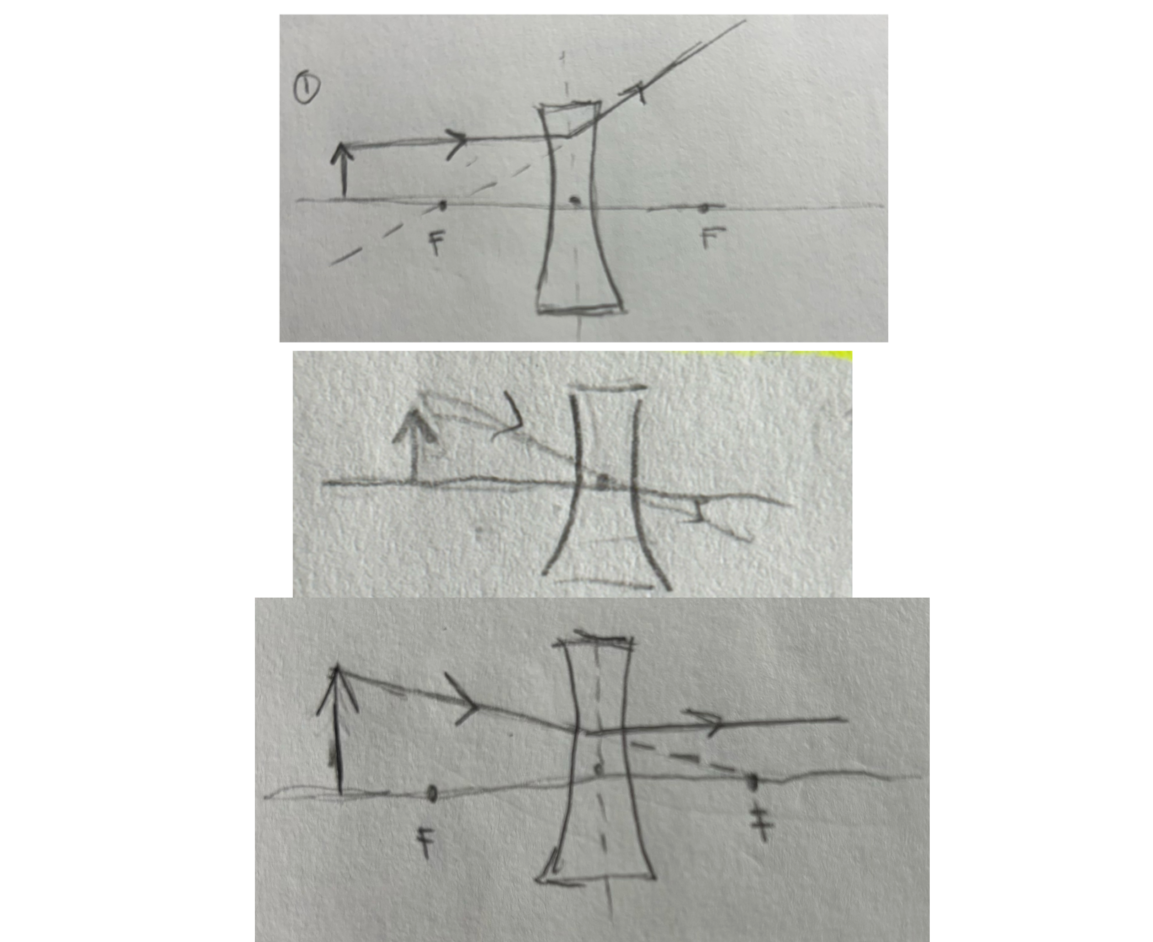
diverging lens rules
ray parallel to the principal axis deflects and appears to come from the focal point in front of lens
ray passes thru center of lens doesnt deflect
ray would pass thru focal point on the other side of lens but instead emerges parallel to the principal axis
always produces same image characteristics.
S - small
A - upright
L - same side of lens as object
T - virtual
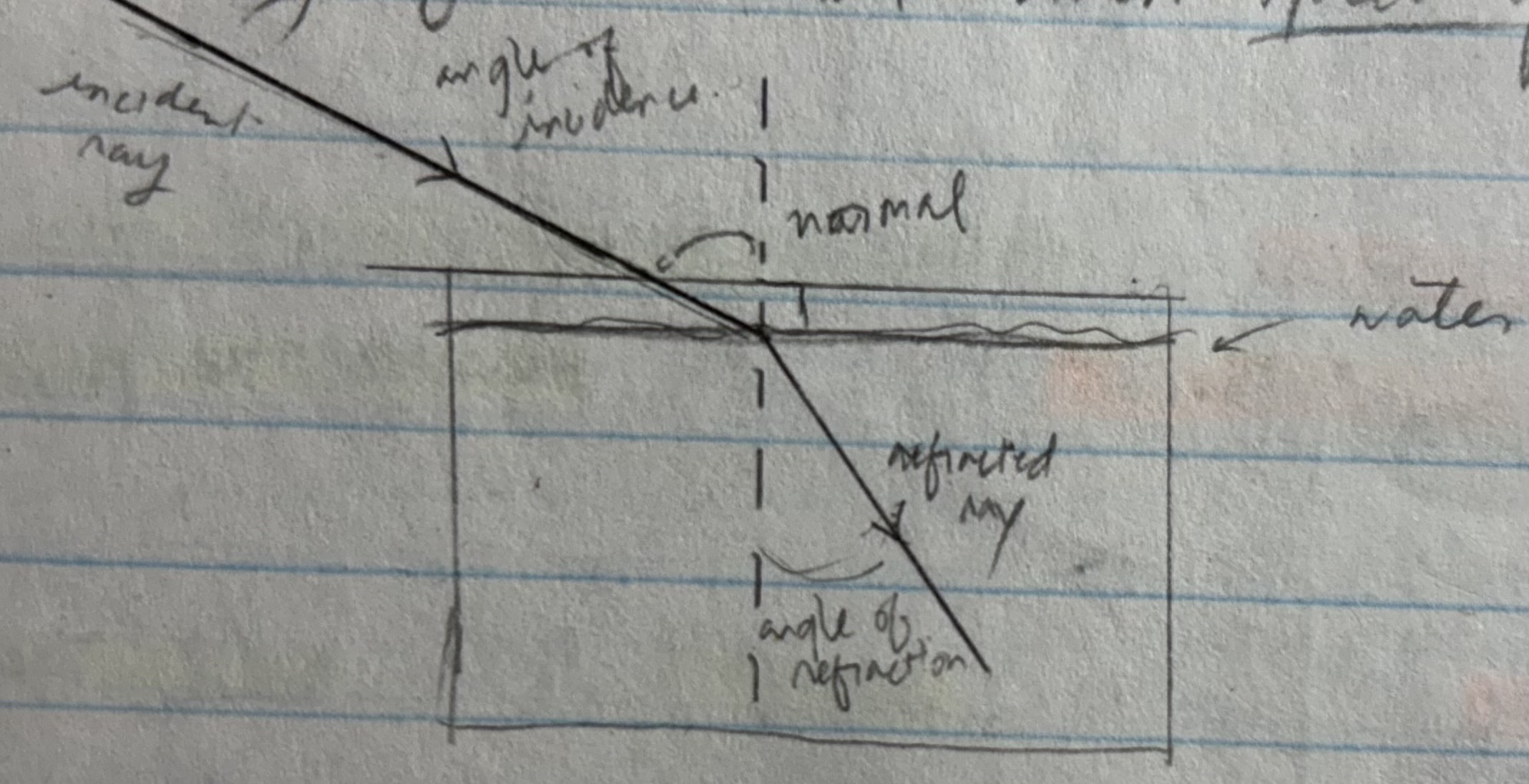
refraction
bending/change in direction of light when it travels to one medium to another
angle of refraction
angle between the refracted ray and the normal
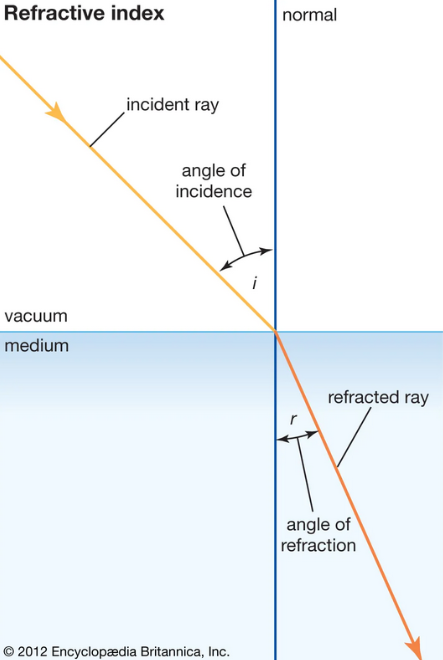
rules of refraction
incident ray, refracted ray, normal are all in the same plane. incident and refracted ray are on the opposite sides of the line that separates the two media
light bends towards the normal when speed of light in 2nd medium is slower than the speed of light in the first medium
light bends away from the normal when speed of light in the 2nd medium is faster
slower towards, faster away
lens equation
1/f = 1/do + 1/di
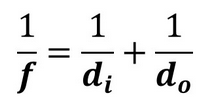
magnification equation
how big image is compared to the object
m = hi/ho = -di/do
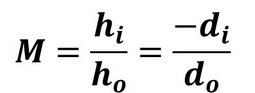
conventions of lens equation
do = ALWAYS positive
di = positive is real img, negative is virtual img
ho & hi positive = upright, negative = inverted
f = positive for converging, negative for diverging
magnification equation = if negative, image is inverted

what are the 2 conditions needed for total internal reflection
light must travel to more dense medium to less dense medium
angle of incidence is large enough that refraction does not occur in the 2nd medium (angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle)
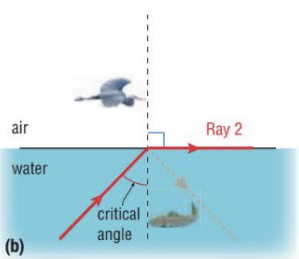
critical angle
the angle of incidence that produces a 90° refracted ray
symbol: θc
θc = θi
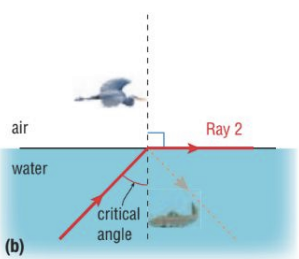
with a _____ critical angle, you will get more internal reflection
with a small critical angle, you will get more internal reflection
with a ___ critical angle, you will get less internal reflection
with a big critical angle, you will get less internal reflection
when angle of incidence is ____ ____ the critical angle, light ray is reflected like a mirror
when angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle, light ray is reflected like a mirror