Cardiovascular System
5.0(4)Studied by 249 people
Card Sorting
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:47 PM on 2/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
1
New cards
Blood circulation-Overview
\
__**Right side**__
Deoxygenated blood enters through either the superior or inferior vena cava then will travel through the right atrium through the tricuspid valve then through the right ventricle then goes up to the pulmonary valve to release deoxygenated blood to the lungs where gas exchange occurs in the capillaries and makes deoxygenated blood into oxygenated
\
\
__**Left side**__
Then oxygenated blood comes back through the lungs into the pulmonary vein to the left atrium to the bicuspid valve and dumps into the left ventricle and then leaves through the aortic valve to the aorta
\
\
\
__**Right side**__
Deoxygenated blood enters through either the superior or inferior vena cava then will travel through the right atrium through the tricuspid valve then through the right ventricle then goes up to the pulmonary valve to release deoxygenated blood to the lungs where gas exchange occurs in the capillaries and makes deoxygenated blood into oxygenated
\
\
__**Left side**__
Then oxygenated blood comes back through the lungs into the pulmonary vein to the left atrium to the bicuspid valve and dumps into the left ventricle and then leaves through the aortic valve to the aorta
\
\
\
2
New cards
Artery and veins
Arteries=Brings blood __**Away**__
Veins: Brings deoxygenated blood __**towards**__
Veins: Brings deoxygenated blood __**towards**__
3
New cards
Thoracic Cavity
__**Right pulmonary cavity**__
* Houses right lung
__**Mediastinum**__
* Houses heart and great vessels
__**Left pulmonary cavity**__
* Houses left lung
* Houses right lung
__**Mediastinum**__
* Houses heart and great vessels
__**Left pulmonary cavity**__
* Houses left lung
4
New cards
Superior Mediastinum
* Located between pleural cavities
* Superiorly terminates at the superior thoracic aperture
* Inferiorly terminates at the level of the sternal angle
* Superiorly terminates at the superior thoracic aperture
* Inferiorly terminates at the level of the sternal angle
5
New cards
Inferior border of sternum
* Inferiorly terminates the inferior thoracic aperture
* Located between pleural cavities
* Inferiorly terminates at the level of the sternal angle
* Divided into three sections: Anterior, Middle, Inferior
* Located between pleural cavities
* Inferiorly terminates at the level of the sternal angle
* Divided into three sections: Anterior, Middle, Inferior
6
New cards
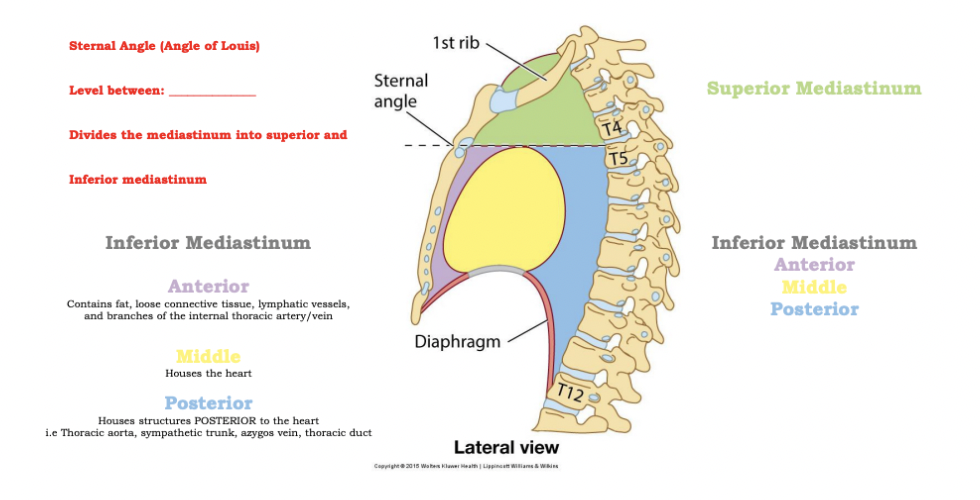
The Thoracic Cavity
==**Sternal Angle (Angle of Louis)**==
* Level between: __**T4-T5**__
* Divides the mediastinum into superior and inferior mediastinum
* **Anterior:** Contains fat, loose tissue, lymphatic vessels, and branches of the internal thoracic artery/vein
* **Middle:** Houses heart
* **Posterior:** Houses structures posterior to the heart i.e. Thoracic aorta, sympathetic trunk, azygous vein, thoracic duct
* Level between: __**T4-T5**__
* Divides the mediastinum into superior and inferior mediastinum
* **Anterior:** Contains fat, loose tissue, lymphatic vessels, and branches of the internal thoracic artery/vein
* **Middle:** Houses heart
* **Posterior:** Houses structures posterior to the heart i.e. Thoracic aorta, sympathetic trunk, azygous vein, thoracic duct
7
New cards
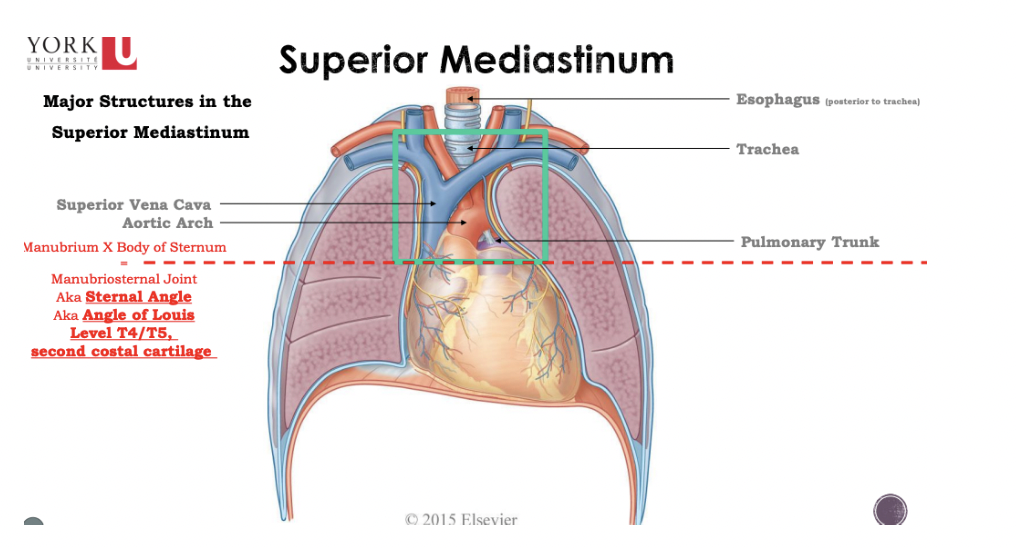
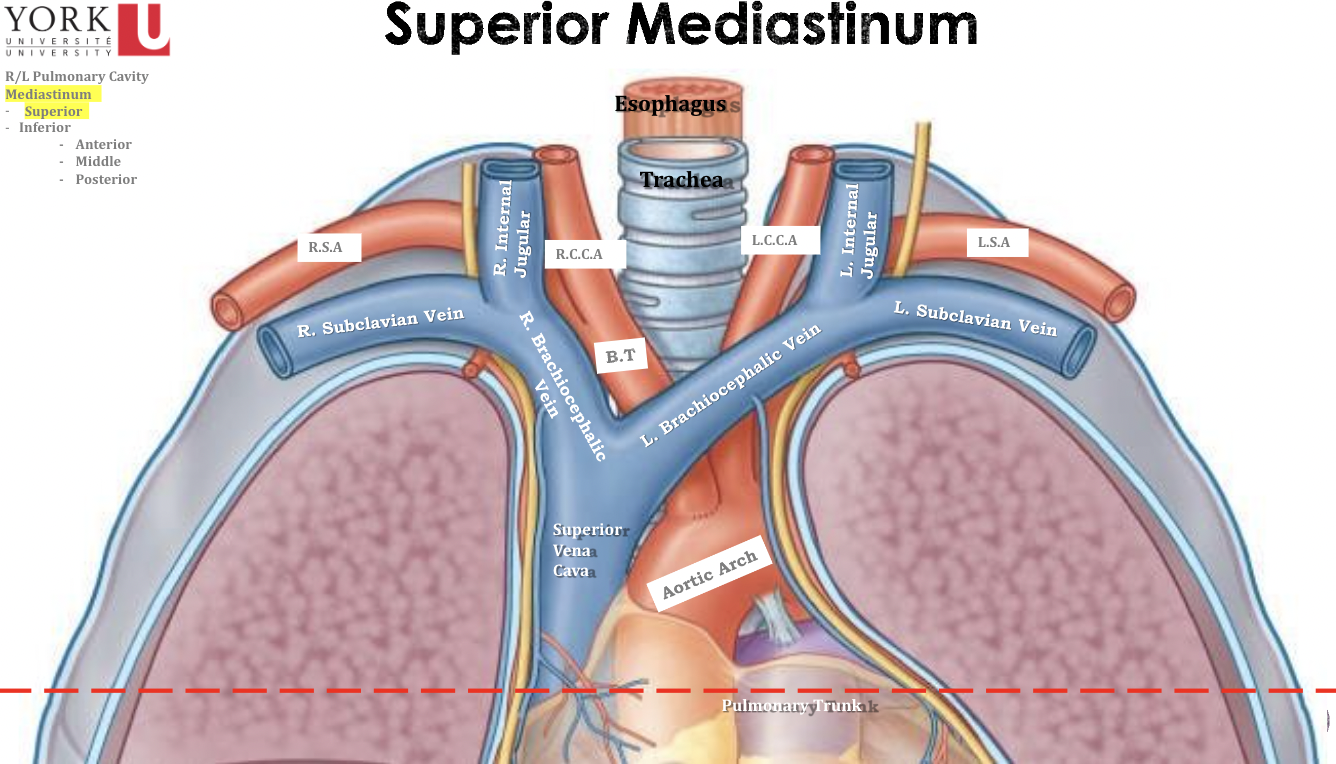
Superior Mediastinum
* Trachea is only found in the superior part of the mediastinum because it bifurcates
* The pulmonary trunk is found at the level of the sternal angle
* Esophagus is found in the posterior inferior mediastinum and superior mediastinum
* The pulmonary trunk is found at the level of the sternal angle
* Esophagus is found in the posterior inferior mediastinum and superior mediastinum
8
New cards
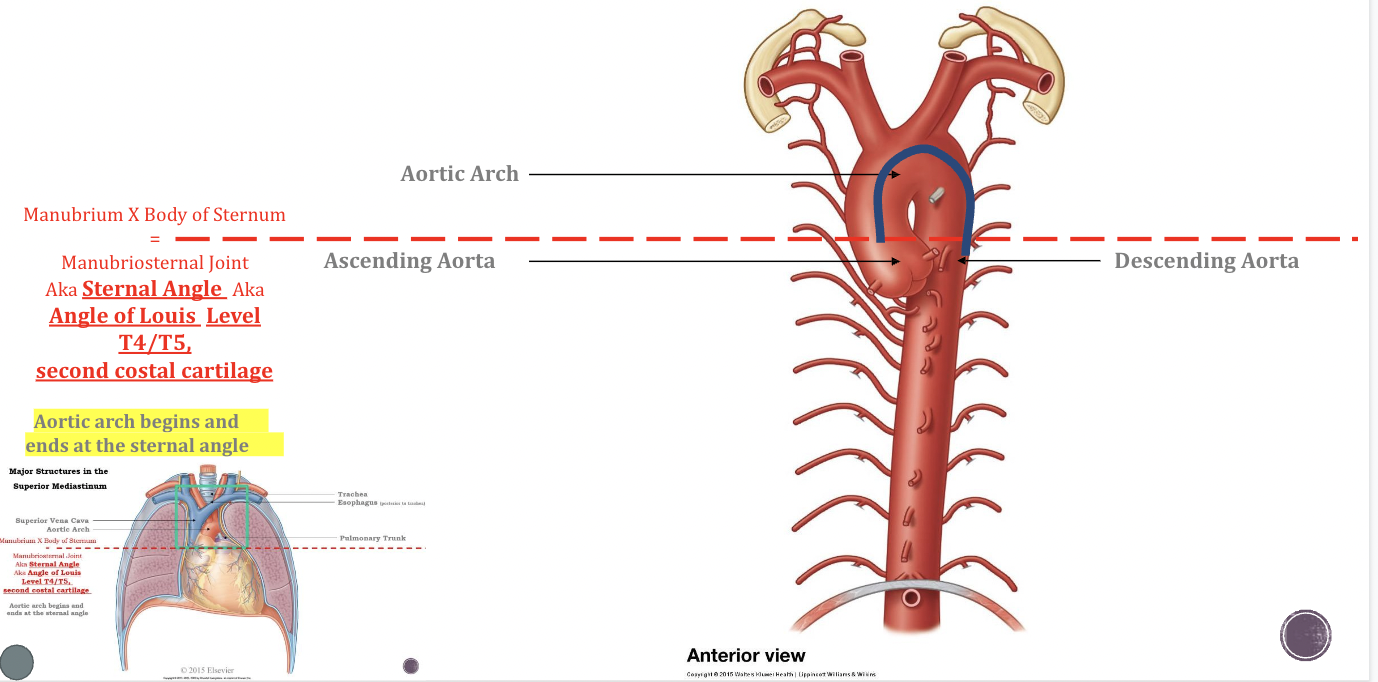
Superior Mediastinum
\*ROLLERCOASTER METHOD
Ascending Aorta: Waiting Area
Aortic Arch: Stuck before the drop
Descending Aorta: Finally drop
\
Ascending Aorta: Waiting Area
Aortic Arch: Stuck before the drop
Descending Aorta: Finally drop
\
9
New cards
Sternal Angle Significance
1- Easy locate and palpate
2-Junction between ascending aorta, aortic arch, and descending aorta
3-Bifurcation of the trachea
4-Bifurcation of the pulmonary trunk
\
2-Junction between ascending aorta, aortic arch, and descending aorta
3-Bifurcation of the trachea
4-Bifurcation of the pulmonary trunk
\
10
New cards
The Pericardium
Fibrous Pericardium: Thick/outer layer
Serous Pericardium
* Parietal: Second layer
* Visceral: Interact with organ, within the heart, Third layer
Serous Pericardium
* Parietal: Second layer
* Visceral: Interact with organ, within the heart, Third layer
11
New cards
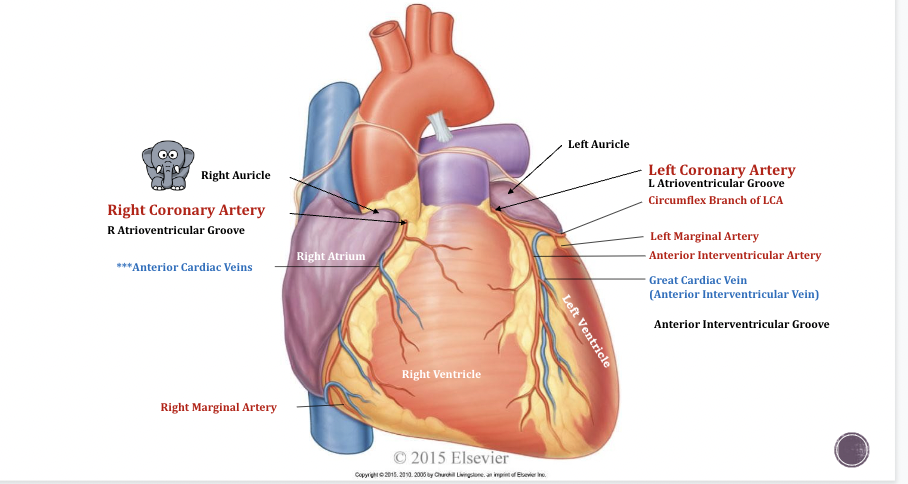
Coronary Vessels of the Heart
* Heart has four chambers
* Both left/right Coronary arteries come from aorta
* **Auricle (elephant ears):** increases the volume and allows for more blood to sit into the atriums
* **Anterior cardiac veins** dumps deoxygenated blood from cardiac muscle into right atrium
* **Left coronary artery:** Comes up from the ascending aorta to the pulmonary trunk and branches off and creates circumflex branch of LCA
* **Right coronary artery:** Between right atrium and ventricle, known as atrioventricular groove
* **Anterior Interventricular Artery:** Sits between ventricles
* Both left/right Coronary arteries come from aorta
* **Auricle (elephant ears):** increases the volume and allows for more blood to sit into the atriums
* **Anterior cardiac veins** dumps deoxygenated blood from cardiac muscle into right atrium
* **Left coronary artery:** Comes up from the ascending aorta to the pulmonary trunk and branches off and creates circumflex branch of LCA
* **Right coronary artery:** Between right atrium and ventricle, known as atrioventricular groove
* **Anterior Interventricular Artery:** Sits between ventricles
12
New cards
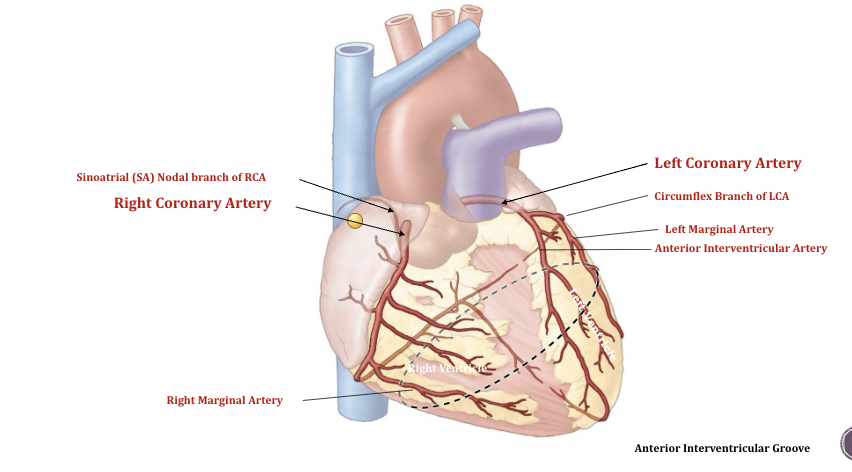
Coronary vessels of the heart
__**Sinoatrial Nodal branch of RCA**__
* Pacemaker of the heart
\
__**Left Coronary Artery**__
* Swings behind the left pulmonary trunk
\
Anastomosis, when vessel A meets up with vessel B and intertwined
* Two vessels connect together which helps supply blood in one
* Lots of this around the heart, protect the heart, incase of a blockage or severed artery
* Pacemaker of the heart
\
__**Left Coronary Artery**__
* Swings behind the left pulmonary trunk
\
Anastomosis, when vessel A meets up with vessel B and intertwined
* Two vessels connect together which helps supply blood in one
* Lots of this around the heart, protect the heart, incase of a blockage or severed artery
13
New cards
Coronary Vessels of the Heart
* **Coronary Sinus:** Dumps into the right atrium, and gets blood from the great cardiac vein
* **Posterior interventricular groove**
* Posterior interventricular artery
* Posterior interventricular vein
* Travels down and join at the apex of the heart
* **Posterior interventricular groove**
* Posterior interventricular artery
* Posterior interventricular vein
* Travels down and join at the apex of the heart
14
New cards
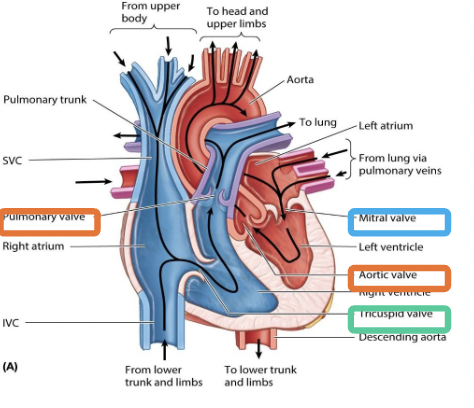
Blood circulation
\
\
Four heart chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles)
%%**1 right atrioventricular valve (tricuspid valve)**%%
* 3 cusps
%%**1 left atrioventricular valve (bicuspid valve)**%%
* 2 cusps
* Try before you buy
%%**2- Pulmonary and Aortic Valves (semilunar valves)**%%
* Pulmonary valve=right ventricle to the lung
* Aortic valve=Left ventricle to the aorta
* Semilunar valve (3 cusps): Mercedes benz logo
%%**1 right atrioventricular valve (tricuspid valve)**%%
* 3 cusps
%%**1 left atrioventricular valve (bicuspid valve)**%%
* 2 cusps
* Try before you buy
%%**2- Pulmonary and Aortic Valves (semilunar valves)**%%
* Pulmonary valve=right ventricle to the lung
* Aortic valve=Left ventricle to the aorta
* Semilunar valve (3 cusps): Mercedes benz logo
15
New cards
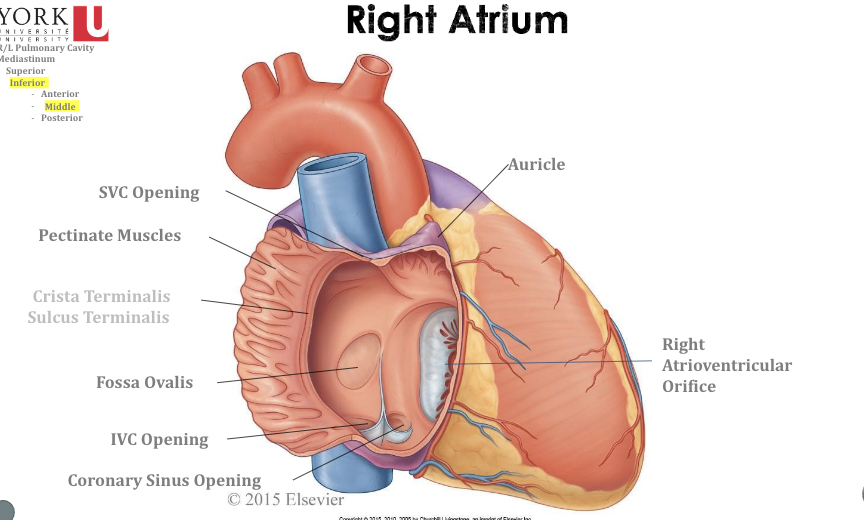
Right Atrium
* **Fossa Ovalis:** Used to be an opening between the right and left side, as a fetus and seals up when you develop
16
New cards
Right Ventricle
* **Interventricular Septum:** Separates the right and left ventricles of the heart
* **Chordae Tendinae:** Ligaments of the valve-Connects the cusps to the papillary muscles which are finger like projects that help the valve do its job
* **Traberculae Carneae:** Rough wall
* **Moderator Band:** Conduction system and helps the heart beat, base of the anterior papillary muscle and extends to the interventricular septum
* **Chordae Tendinae:** Ligaments of the valve-Connects the cusps to the papillary muscles which are finger like projects that help the valve do its job
* **Traberculae Carneae:** Rough wall
* **Moderator Band:** Conduction system and helps the heart beat, base of the anterior papillary muscle and extends to the interventricular septum
17
New cards
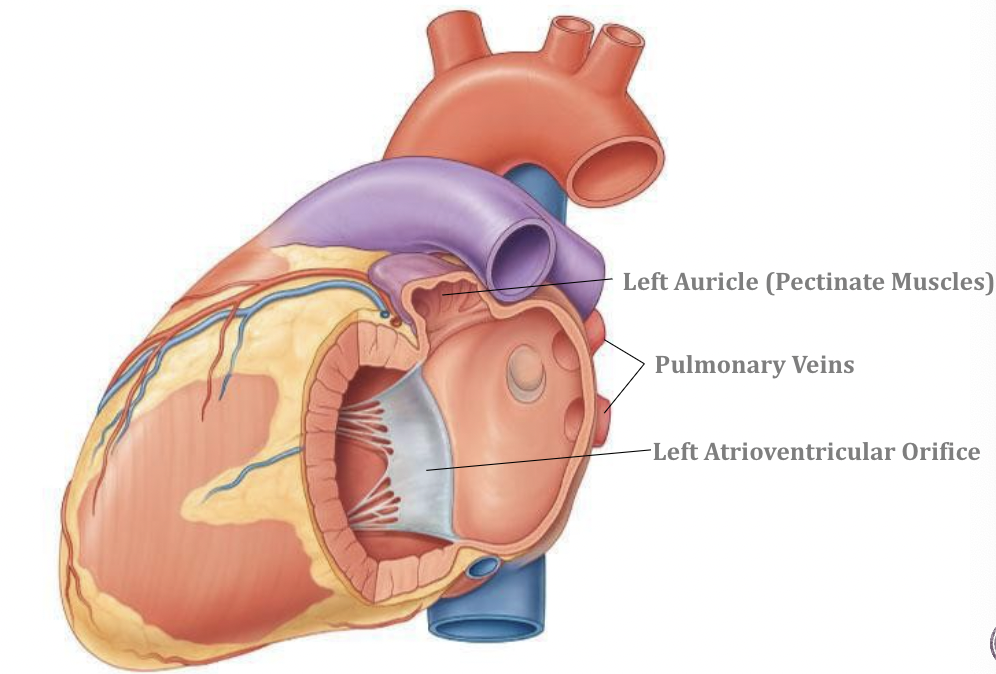
Left Atrium
18
New cards
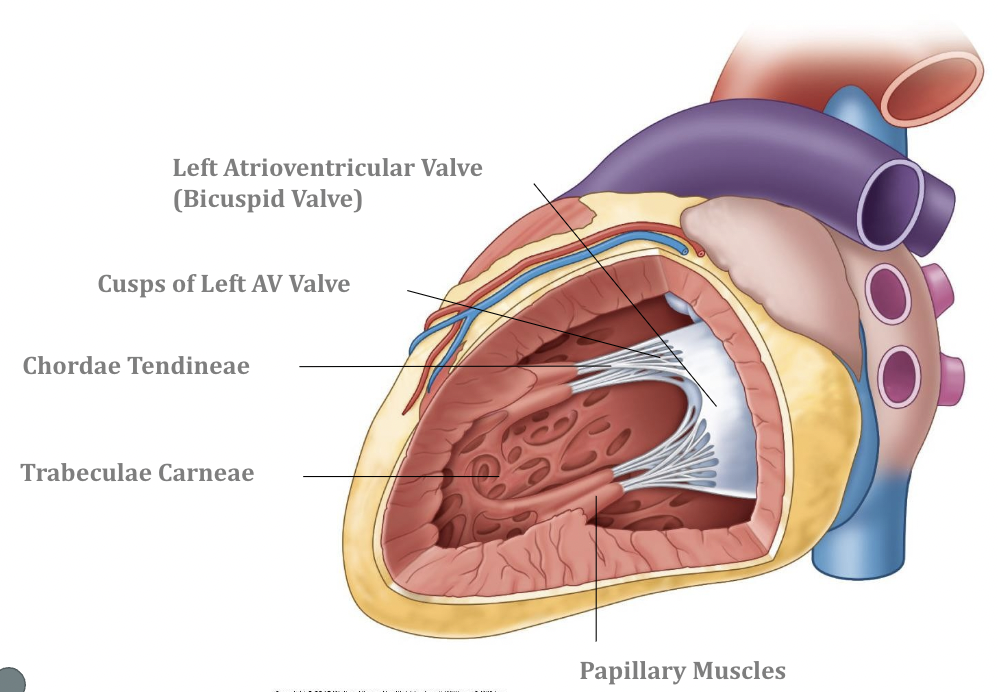
Left Ventricle
19
New cards
Superior Mediastinum
Anterior Glands (thymus)
* Veins
* Arteries
* Airway (Trachea)
* Alimentary tract (esophagus)
* Lymphatic trunks
* Veins
* Arteries
* Airway (Trachea)
* Alimentary tract (esophagus)
* Lymphatic trunks
20
New cards
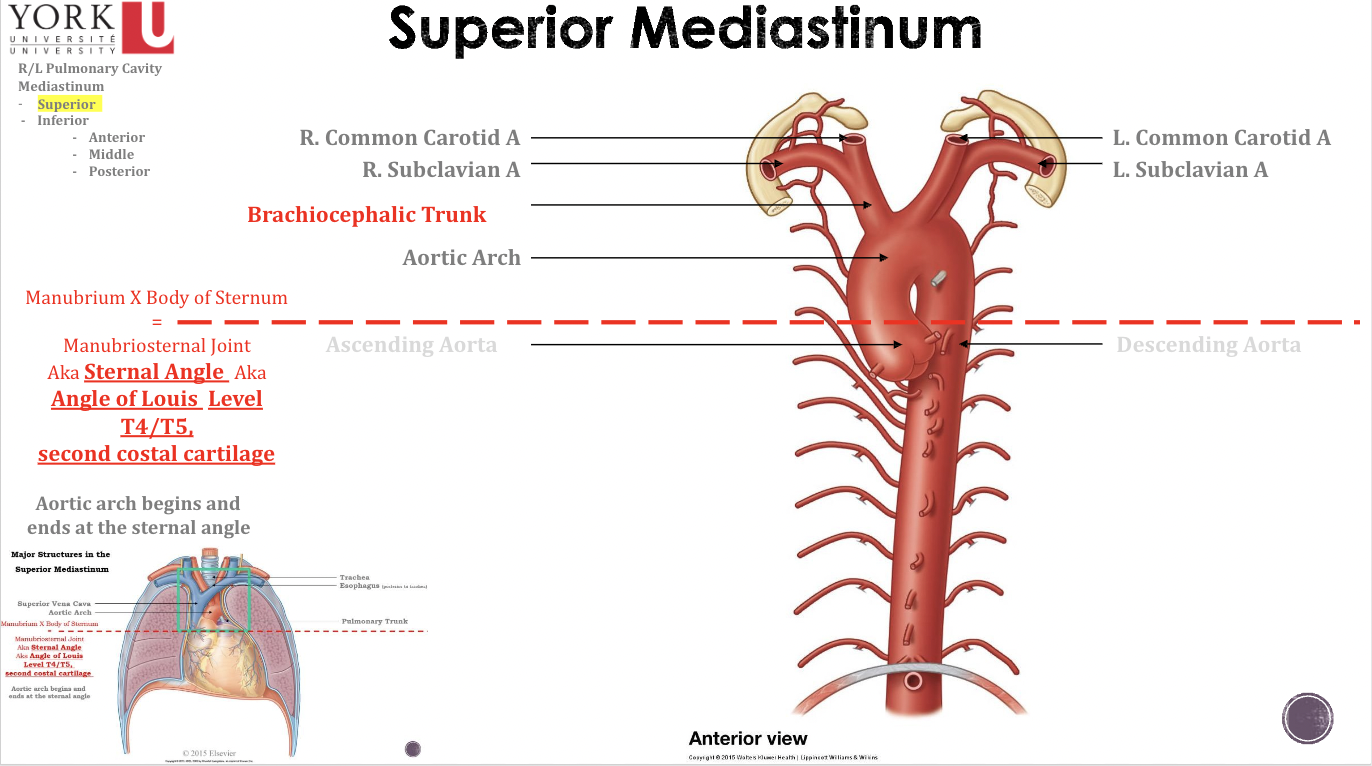
Superior mediastinum
21
New cards
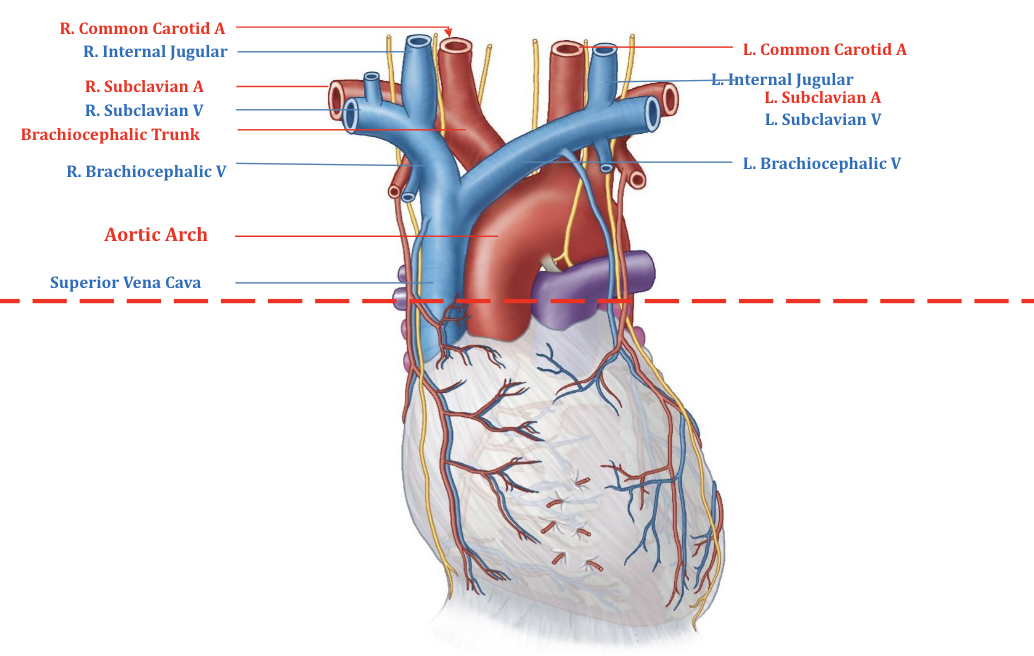
Superior Mediastinum
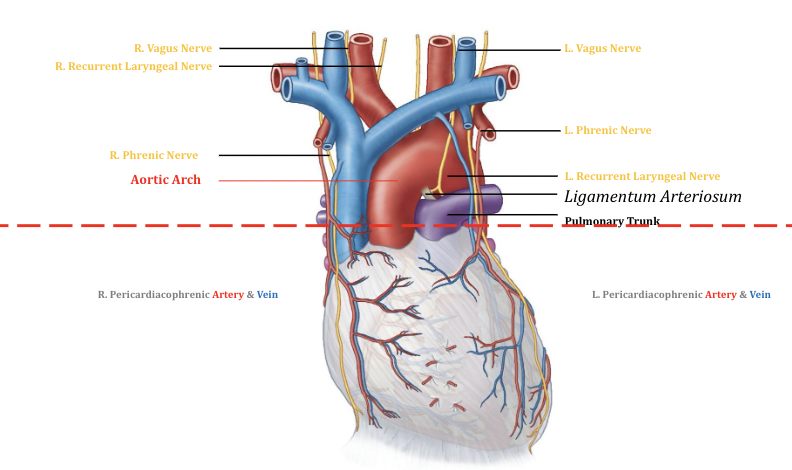
22
New cards
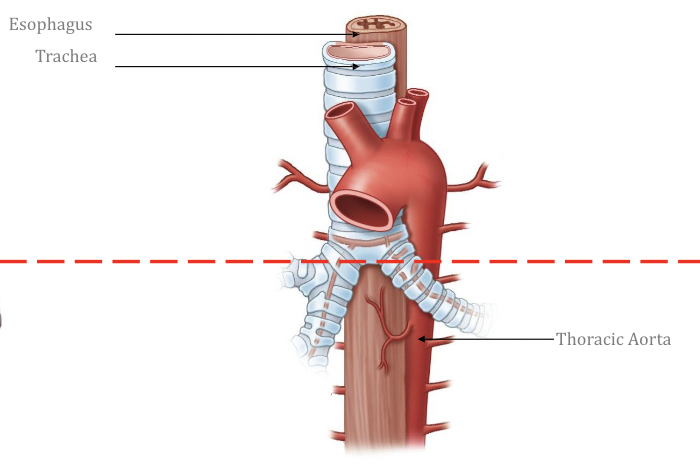
The “Dancers”
23
New cards
Pulmonary and systemic circuits
* **Right side of the heart:** Recieves poor blood and sends lungs to get O2 (deoxygenated blood)
* **Left side of the heart:** Recieves rich blood from lungs and sends out to body (oxygenated blood)
\
\
* **Left side of the heart:** Recieves rich blood from lungs and sends out to body (oxygenated blood)
\
\
24
New cards
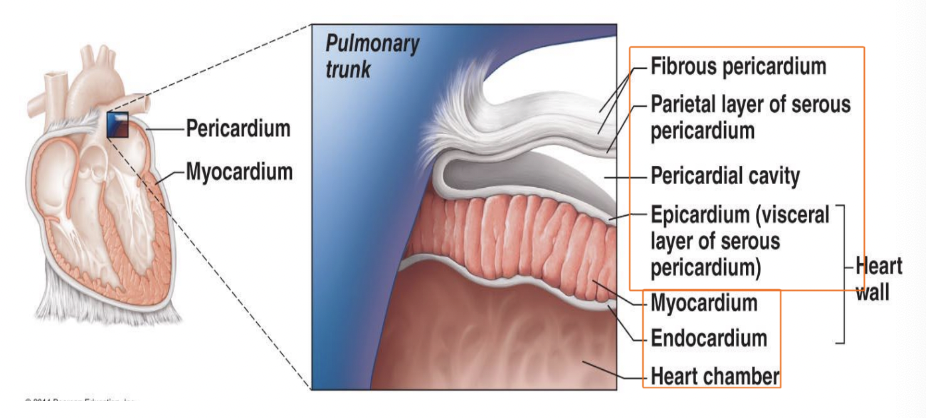
Pericardium
* **Fibrous Pericardium:** Thickest layer on the outside, second protective layer that sits on top of the heart
* **Serous Pericardium:** Responsible for serous fluid and allows for frictionless movement to allow your heart to beat
* **Visceral Pericardium:** Innermost layer
* **Pericardial Cavity:** Space between two serous pericardium
* **Serous Pericardium:** Responsible for serous fluid and allows for frictionless movement to allow your heart to beat
* **Visceral Pericardium:** Innermost layer
* **Pericardial Cavity:** Space between two serous pericardium
25
New cards
Valve incompetence
* Valve does not close properly due to scar tissuem congenitals
* Blood backflows
* Blood backflows
26
New cards
Valve Stenosis
* Valve becomes stiff (Ca2+ deposits, scar tissue, common with ages, blood flow is reduced)
* Constricts opening
* Prevent from going out
* Constricts opening
* Prevent from going out
27
New cards
Upper Circulatory pathway
* **Aorta:** Gives common carotid arteries which is responsible for head and neck
* **Upper limb:** Has the subclavian artery and so the aortic arch gives the head, neck, upper limb blood supply and once used up deoxygenated go back to the superior vena cava to the right atrium
* **Upper limb:** Has the subclavian artery and so the aortic arch gives the head, neck, upper limb blood supply and once used up deoxygenated go back to the superior vena cava to the right atrium
28
New cards
Lower circulatory pathway
1. **Thoracic Aorta:** Blood going to the intercostal muscles around the thorax
2. **Abdomen:** Pelvis and lower lim and will travel all that blood will travel once deoxygenated and back to the heart to the inferior vena cava
29
New cards
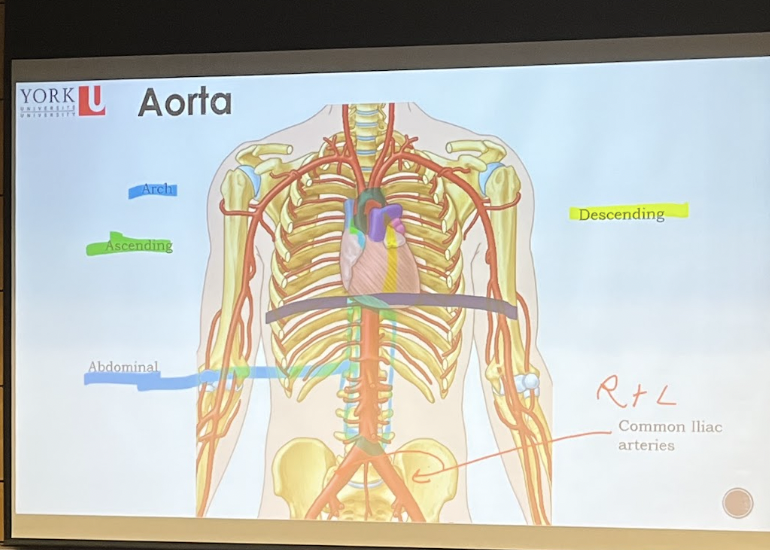
Aorta
* Line in middle: Diaphragm
* **Descending aorta**: separated by sternal angle
* Blood will leave the heart from the left ventricle of the heart through the ascending aorta
* **Descending aorta**: separated by sternal angle
* Blood will leave the heart from the left ventricle of the heart through the ascending aorta
30
New cards
How do you go from the lungs to the right lower limb
* Travelling from the lungs into the left atrium and then into the left ventricle through the tricuspid valve from the left ventricle to the ascending aorta through the aortic valve ascending aorta to ascending arch then thoracic aorta then through the diaphragm into abdominal aorta and bifurcate the common iliac arteries to the right common iliac artery
31
New cards
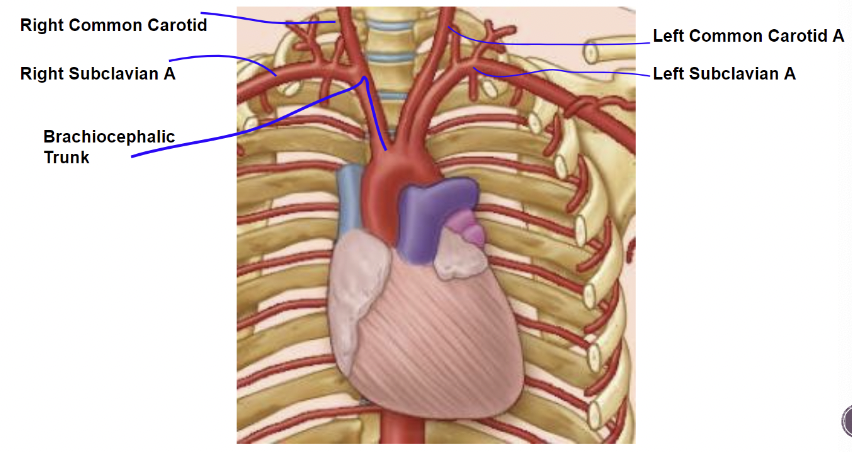
Recall: Branches of the Aorta
Right side
* Brachiocephalic trunk which will **split** into the subclavian artery which is responsible for the upper limb and then the right common carotid artery which goes to head and neck
\
Left side
* Does not have brachiocephalic trunk
* Left common carotid artery and left subclavian artery directly come off the aortic arch
* Brachiocephalic trunk which will **split** into the subclavian artery which is responsible for the upper limb and then the right common carotid artery which goes to head and neck
\
Left side
* Does not have brachiocephalic trunk
* Left common carotid artery and left subclavian artery directly come off the aortic arch
32
New cards
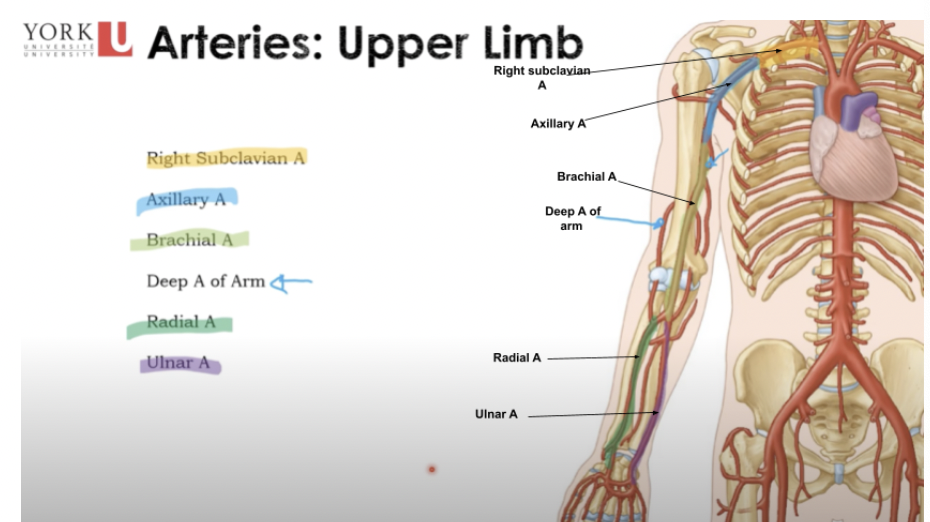
Arteries: Upper Limb
* **Right subclavian A** (by the heart in the thorax)
* **Axillary A** (armpit)
* **Brachial A** (upper limb)
* **Deep A of Arm** (goes to the posterior arm region responsible for triceps brachii) \*Big artery\*
* **Radial A** (thumb)
* **Ulnar A**
* **Axillary A** (armpit)
* **Brachial A** (upper limb)
* **Deep A of Arm** (goes to the posterior arm region responsible for triceps brachii) \*Big artery\*
* **Radial A** (thumb)
* **Ulnar A**
33
New cards
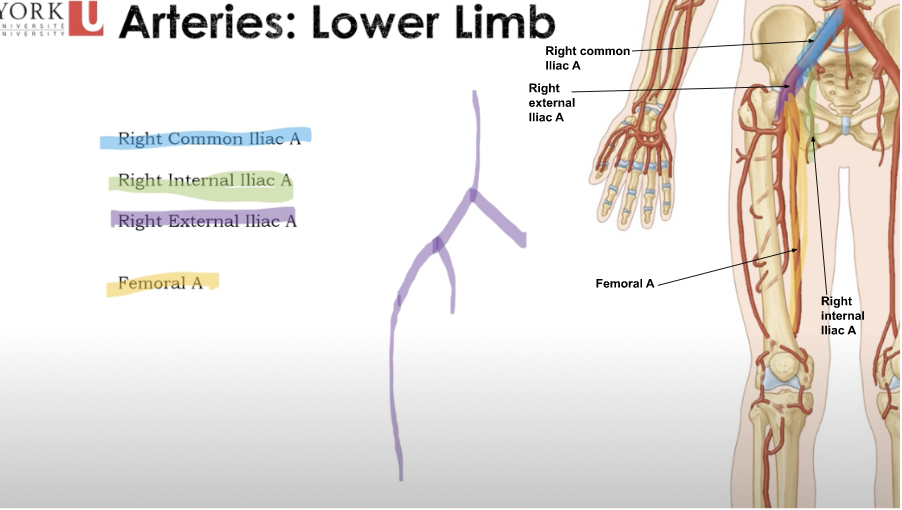
Arteries: Lower Limb
* **Right Common Iliac A** (bifurcate into a right internal/external iliac artery)
* **Right Internal Iliac A** (into/within the pelvis)
* **Right External Iliac A** (outside the pelvis)
* **Femoral A** (Comes from the right external artery which comes from the right common iliac)
* **Right Internal Iliac A** (into/within the pelvis)
* **Right External Iliac A** (outside the pelvis)
* **Femoral A** (Comes from the right external artery which comes from the right common iliac)
34
New cards
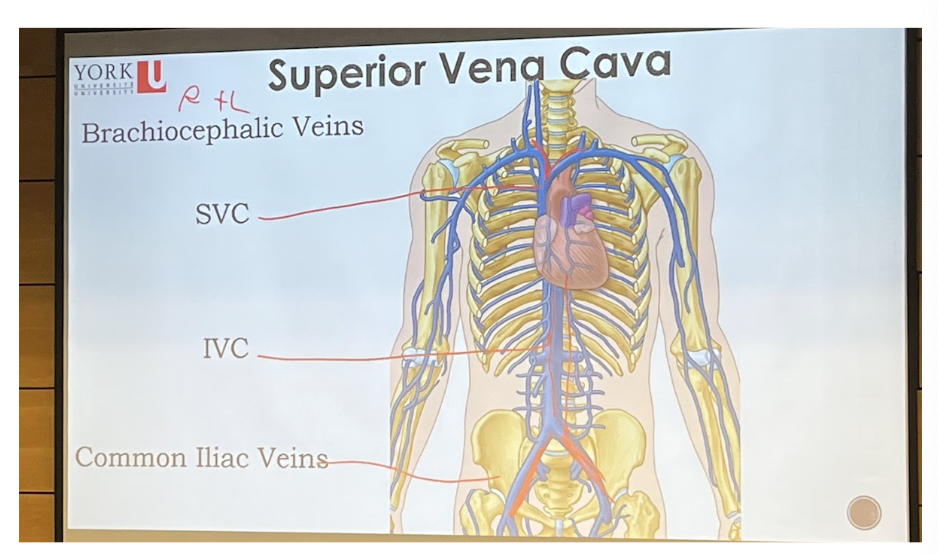
Superior Vena Cava
__**Major vessels**__
* Superior and inferior vena cava being capable of dumping blood into the right atrium
%%**SVC (3 branches)**%%
* Right and Left
* Bifurcate into a left and right brachiocephalic veins
* Brings blood from the upper limb head and neck to the heart
\
%%**IVC (2 branches)**%%
* Travels down the abdomen
* Tributaries right and left common iliac veins
* Brings blood from lower limb and abdomen into the heart
\
***Common Iliac Veins**
* Superior and inferior vena cava being capable of dumping blood into the right atrium
%%**SVC (3 branches)**%%
* Right and Left
* Bifurcate into a left and right brachiocephalic veins
* Brings blood from the upper limb head and neck to the heart
\
%%**IVC (2 branches)**%%
* Travels down the abdomen
* Tributaries right and left common iliac veins
* Brings blood from lower limb and abdomen into the heart
\
***Common Iliac Veins**
35
New cards
Blood vessels
* Delivery system of dynamic structures that begins and ends at heart
* Complex delivery tunnels and their job with the arteries and to take blood away from the heart
* Complex delivery tunnels and their job with the arteries and to take blood away from the heart
36
New cards
Arteries
Carry blood away from heart, oxygenated except for pulmonary circulation and umbilical vessels of fetus
37
New cards
Capillaries
* Contact tissue cells, directly serve cellular needs
* Tissue gets oxygen, rich blood gives back the oxygen-deficient blood or the nutrition-rich blood and nutrient enriched blood
* Tissue gets oxygen, rich blood gives back the oxygen-deficient blood or the nutrition-rich blood and nutrient enriched blood
38
New cards
Veins
* Carry blood towards the heart
39
New cards
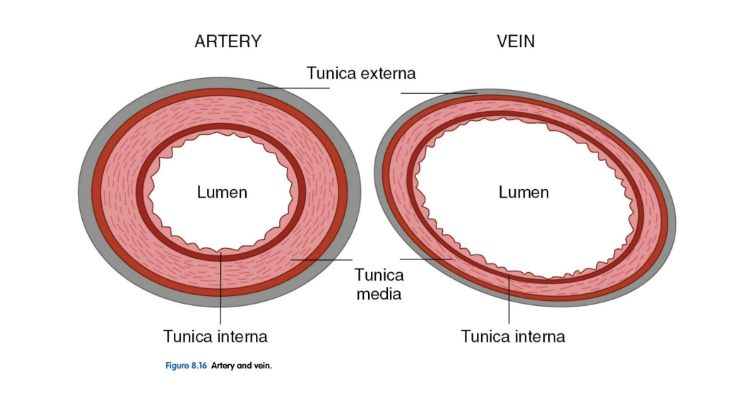
Structures of blood vessel walls
==__**Arteries**__==
* Handle much higher pressure
* Have thicker walls
* Contain muscle to control flow
* Ex. when you get a cut the arteries will jump in and stop the bleeding from happening
* Have more elasticity
* Can take some of the blunt force so as the heart is pressuring each time there is an unsmooth and uneven amount of pressure coming in
* Stop/preventing blood because of smooth muscle within they can constrict
==__**Veins**__==
* Thinner wall
* Pressure has been decreased
* Experience a smooth low pressure amount going through
* Their biggest job is to get blood back to the heart against gravity
* Handle much higher pressure
* Have thicker walls
* Contain muscle to control flow
* Ex. when you get a cut the arteries will jump in and stop the bleeding from happening
* Have more elasticity
* Can take some of the blunt force so as the heart is pressuring each time there is an unsmooth and uneven amount of pressure coming in
* Stop/preventing blood because of smooth muscle within they can constrict
==__**Veins**__==
* Thinner wall
* Pressure has been decreased
* Experience a smooth low pressure amount going through
* Their biggest job is to get blood back to the heart against gravity
40
New cards
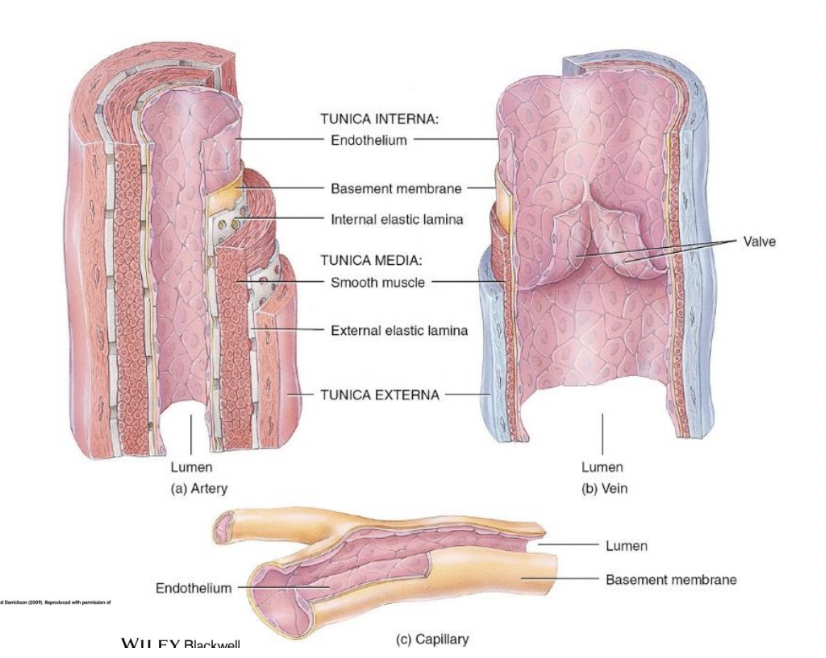
Tunica Interna/Tunica Intima, Tunica Media, Tunica Externa
^^**Tunica Interna/Tunica Intima**^^
* Composed on one layer which is the __***endothelium***__ which forms a slick surface for the blood
* Innermost layer
* In a large vessel you can have an extra endothelial layer aka a __***basement membrane (sub-endothelial layer)***__
\
^^**Tunica Media**^^
* Intermediate layer
* has a smooth muscle layer
* Controlled with the CNS allowing for vasoconstriction
\
^^**Tunica Externa/Tunica Adventitia**^^
* Most external/outermost layer
* Offer protection and reinforcement
* Give blood vessel its structure, shape and solidity
* Anchors the blood vessel to nearby structures
* Composed of loose collagen fibers
* Could be supplied by their own blood vessels aka **VASA vasorum**
* Composed on one layer which is the __***endothelium***__ which forms a slick surface for the blood
* Innermost layer
* In a large vessel you can have an extra endothelial layer aka a __***basement membrane (sub-endothelial layer)***__
\
^^**Tunica Media**^^
* Intermediate layer
* has a smooth muscle layer
* Controlled with the CNS allowing for vasoconstriction
\
^^**Tunica Externa/Tunica Adventitia**^^
* Most external/outermost layer
* Offer protection and reinforcement
* Give blood vessel its structure, shape and solidity
* Anchors the blood vessel to nearby structures
* Composed of loose collagen fibers
* Could be supplied by their own blood vessels aka **VASA vasorum**
41
New cards
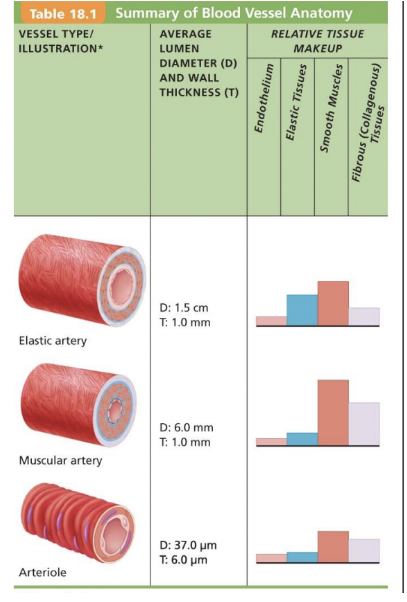
Arterial System
**Elastic Arteries (conducting) largest**
* Thick-walled, highly elastic
* Near heart
* Ex.Aorta
* Large amount of smooth muscle
\
**Muscular Arteries (disturbing)**
* Deliver to organs, more distal
* Most of named arteries
* Very active in vasoconstriction
* Ex.Ulnar artery, radial artery, axillary artery
* Have more smooth muscle allows for vasoconstriction
\
**Arterioles**
* Fine control of flow to capillaries
* Smallest arteries
* Give fine control to flow to capillary
* Nice flowing, much lower pressure
* Very thin
* Composed of one single smooth muscle layer and an endothelial lining
* Thick-walled, highly elastic
* Near heart
* Ex.Aorta
* Large amount of smooth muscle
\
**Muscular Arteries (disturbing)**
* Deliver to organs, more distal
* Most of named arteries
* Very active in vasoconstriction
* Ex.Ulnar artery, radial artery, axillary artery
* Have more smooth muscle allows for vasoconstriction
\
**Arterioles**
* Fine control of flow to capillaries
* Smallest arteries
* Give fine control to flow to capillary
* Nice flowing, much lower pressure
* Very thin
* Composed of one single smooth muscle layer and an endothelial lining
42
New cards
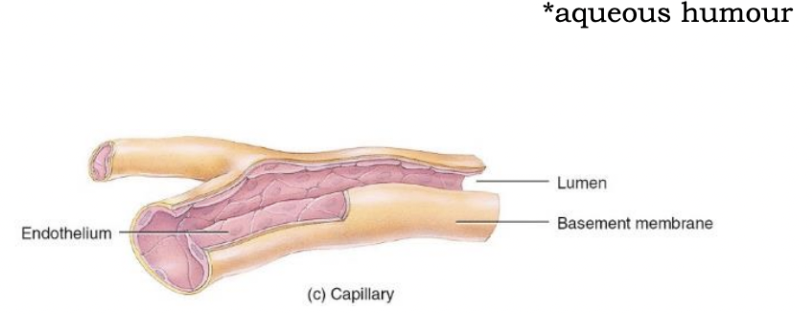
Capillaries
* Smallest blood vessels
* Thin walls to allow exchange
* Most areas of body have rich capillary supply
* Sometimes you only have one single endothelial cell
* Exceptions:
* Tendons and ligaments (poorly vascularized)
* Cartilage, Epithelia, Cornea, Lens (no capillaries)
* Cornea and lens receive their nutrients from aqueous humour
* Thin walls to allow exchange
* Most areas of body have rich capillary supply
* Sometimes you only have one single endothelial cell
* Exceptions:
* Tendons and ligaments (poorly vascularized)
* Cartilage, Epithelia, Cornea, Lens (no capillaries)
* Cornea and lens receive their nutrients from aqueous humour
43
New cards
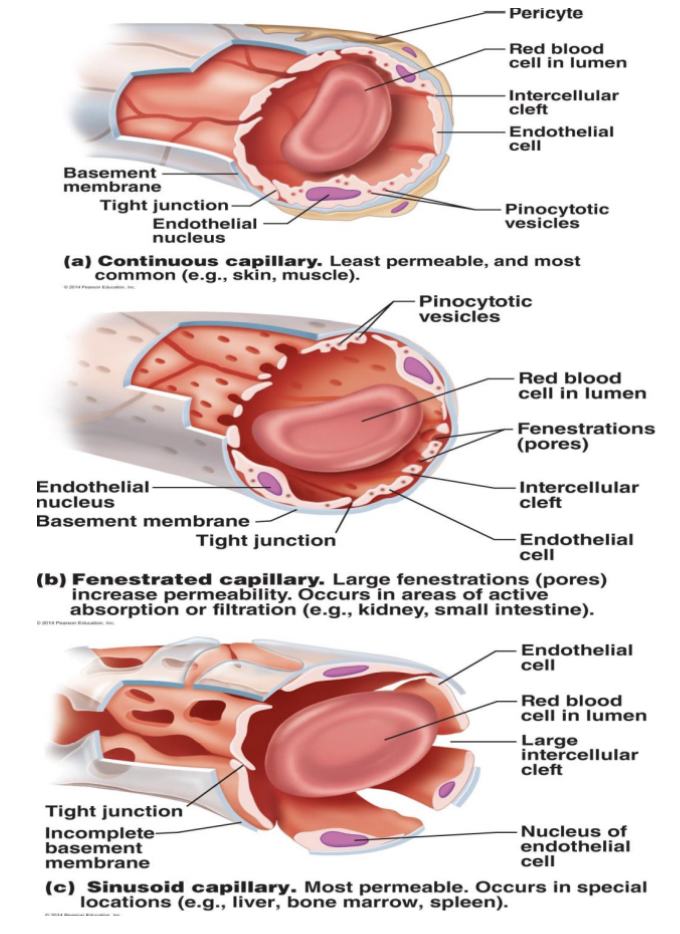
Types of Capillaries (least to most permeable)
1. @@**Continuous (LEAST)**@@
* Allows smaller things to pass over their walls
* Abundant in skin and muscles
* Allow for oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass back and forth
* The reason for why its tight is because the endothelial cells the tunica intima are joined by **tight junctions (hard for things to get through in/out except for intracellular cleft such as O2 and CO2)** and the tight junctions job is to hold everything tight together so there is less space for things to cross over
* **Intercellular Cleft:** Very small openings between epithelial cells that will allow for passage of O2 and CO2
* Found in skin, muscles and in the brain
2. @@**Fenestrated**@@
* Have pores which are known as fenestrations
* Fenestration allows capillaries to pass bigger things that require absorption such as kidneys, intestines and endocrine organs
* Easier for larger stuff to cross over
3. @@**Sinusoid** @@
* Super leaky
* Lots of space
* Larger intercellular clefts
* Have fewer junctions and allows for bg things to pass across including red blood cells, bone marrow, liver, spleen
44
New cards
Capillary Beds
* Under local control
* Controlled by chemicals
* Terminal arterial and blood is flowing
* All diffusion happens
* Ex. Blood diffusion, oxygen, CO2 exchange
* Precapillary sphincters: Happens when capillary is emerging
* **Vascular shunt (Middle part):** Cancel out the capillary beds and blood will flow back to the veins and go back to the postcapillary venule and then back to the heart
* Bypass when using these sphincters could be regulated locally through chemical conditions or the central nervous system
* Controlled by chemicals
* Terminal arterial and blood is flowing
* All diffusion happens
* Ex. Blood diffusion, oxygen, CO2 exchange
* Precapillary sphincters: Happens when capillary is emerging
* **Vascular shunt (Middle part):** Cancel out the capillary beds and blood will flow back to the veins and go back to the postcapillary venule and then back to the heart
* Bypass when using these sphincters could be regulated locally through chemical conditions or the central nervous system
45
New cards
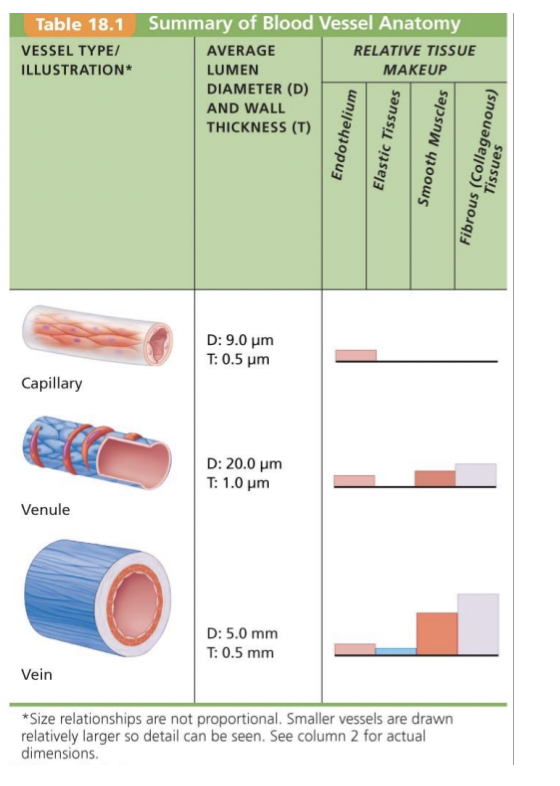
Veins
* **Venules**
* Thin walled
* **Veins**
* Tunica externa largest layer (Collagen + elastin)
* Accomodate large blood volume (up to 65% of bodys blood at one)
* Thin walled
* **Veins**
* Tunica externa largest layer (Collagen + elastin)
* Accomodate large blood volume (up to 65% of bodys blood at one)
46
New cards
Venous valves
Job is to be a one way valve and prevent blood from going back so blood can go back to the heart and backflow
47
New cards
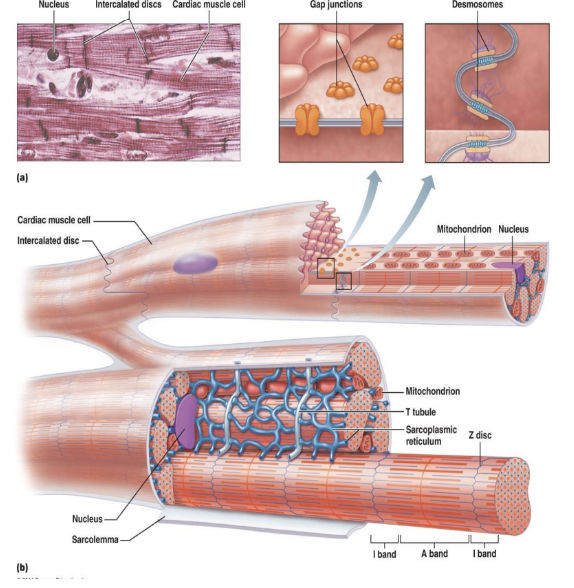
Cardiac Muscle Fibers
%%__**Similar to Skeletal**__%%
* Striated
* Sliding filament mechanism
\
%%__**Unlike Skeletal**__%%
* Short
* Fat
* Branches
* Interconnected
* Striated
* Sliding filament mechanism
\
%%__**Unlike Skeletal**__%%
* Short
* Fat
* Branches
* Interconnected
48
New cards
Intercalated Discs
* Junction between two cardiac muscle cells
* Allow all cells to behave as one unit
* **Desmosomes**
* Act like hair clips and their job is to connect one fiber to the other so that there are __no separation__ between these two muscle fibers
* **Gap Junctions**
* Little pods and their job is allow the signal to pass from one cell to the other and is done really fast, everything will contract as one single unit
* Allow all cells to behave as one unit
* **Desmosomes**
* Act like hair clips and their job is to connect one fiber to the other so that there are __no separation__ between these two muscle fibers
* **Gap Junctions**
* Little pods and their job is allow the signal to pass from one cell to the other and is done really fast, everything will contract as one single unit
49
New cards
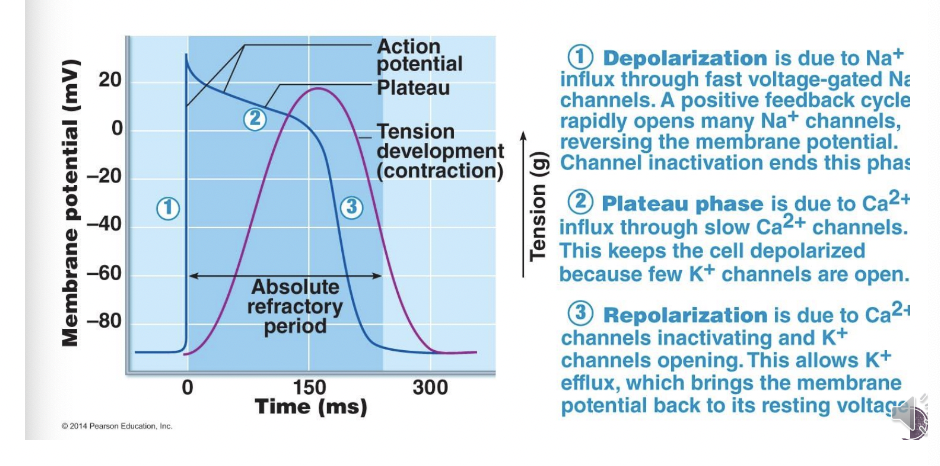
Mechanism of Contraction
Blue line=Membrane Potential
* More negative=Negative ions within the cell
* More positive=Positive ions outside of the cell
* Ex. Sodium, potassium, calcium
* Starts at negative membrane potential of -90mv
\
@@__**Has 3 phases**__@@
1. **Depolarization**
2. **Plateau Phase**
3. **Repolarization**
* More negative=Negative ions within the cell
* More positive=Positive ions outside of the cell
* Ex. Sodium, potassium, calcium
* Starts at negative membrane potential of -90mv
\
@@__**Has 3 phases**__@@
1. **Depolarization**
2. **Plateau Phase**
3. **Repolarization**
50
New cards
Depolarization
* Due to Na+ influx through fast voltage gated Na channels. A positive feedback cycle rapidly opens many Na+ channels, reversing the membrane potential. Channel inactivation ends this phase
* ==**Sodium channels open up and starts flooding right into the muscle cell from the outside**==
* ==**Since sodium is positively charged there is a huge influx jump (increase) in the membrane potential because the inside of the cell is starting to receive positive ions (inside of the cell is now becoming positive) this happens because of an electrical signal**==
* ==**Sodium channels close known as depolarization (look at blue line at 30mv)**==
* ==**Sodium channels open up and starts flooding right into the muscle cell from the outside**==
* ==**Since sodium is positively charged there is a huge influx jump (increase) in the membrane potential because the inside of the cell is starting to receive positive ions (inside of the cell is now becoming positive) this happens because of an electrical signal**==
* ==**Sodium channels close known as depolarization (look at blue line at 30mv)**==
51
New cards
Plateau Phase
* Stop letting sodium in
* Membrane potential starts dropping right away and the reason for it happening is because inside the cell there's a lot of potassium and is positively charged and starts to leak outside of the cell
* Calcium channels (Ca2+) open up which allows calcium to slowly start going in slowly and lasts longer and gives enough time for contraction
* Membrane potential starts dropping right away and the reason for it happening is because inside the cell there's a lot of potassium and is positively charged and starts to leak outside of the cell
* Calcium channels (Ca2+) open up which allows calcium to slowly start going in slowly and lasts longer and gives enough time for contraction
52
New cards
**Repolarization** \n
* Held the action potential as high as it could be
* Slow calcium gates have closed
* Potassium leaking out, Potassium channels are opening, Positive ion is going out
* Inside is becoming more negative and go back to the resting potential
* Efflux=All potassium exiting the cell and membrane potential drop to a resting potential of -90mv
\*Highest amount of force in regards to the tension contraction tension is occurring right at the end of the second stage which is the Plateau phase
* Absolute refractory period
* We cannot start a new contraction
* Goes from when the sodium channels first open to just the end of everything
* Slow calcium gates have closed
* Potassium leaking out, Potassium channels are opening, Positive ion is going out
* Inside is becoming more negative and go back to the resting potential
* Efflux=All potassium exiting the cell and membrane potential drop to a resting potential of -90mv
\*Highest amount of force in regards to the tension contraction tension is occurring right at the end of the second stage which is the Plateau phase
* Absolute refractory period
* We cannot start a new contraction
* Goes from when the sodium channels first open to just the end of everything
53
New cards
Purple line (Tension developmental contraction)
* It is a force the development of the contraction happening within the heart
* Starts as the sodium influx goes through and is so fast and is not going to last long
* Calcium gates close
* Starts as the sodium influx goes through and is so fast and is not going to last long
* Calcium gates close
54
New cards
Cardiac vs. Skeletal Muscle
==__**Skeletal Muscle**__==
**Stimulation:** Each fibre stimulated by a neuron
**Contraction:** Each fibre works on its own
**Refractory Period:** 1-2 ms (full contraction is 15-100ms), contractions can build on one another (tetany)
\
==**Cardiac Muscle**==
**Stimulation:** A few self excitable cells stimulate themselves and all other cells
**Contraction:** All cells work as a team and contract as one
**Refractory Period:** 200 ms, No tetany
**Stimulation:** Each fibre stimulated by a neuron
**Contraction:** Each fibre works on its own
**Refractory Period:** 1-2 ms (full contraction is 15-100ms), contractions can build on one another (tetany)
\
==**Cardiac Muscle**==
**Stimulation:** A few self excitable cells stimulate themselves and all other cells
**Contraction:** All cells work as a team and contract as one
**Refractory Period:** 200 ms, No tetany
55
New cards
Tetany
* Building on one force over the other and holding that contraction for a longer period of time
56
New cards
Self excitable cells
* In the right atrium and fire at regular intervals and send an electrical signal to the heart muscle (contract) (Nervous system can step in and can regulate/upregulate or down regulate the contraction to allow your heart to pump faster/ slower etc
57
New cards
Contraction
* ^^**Skeletal muscle**^^
* The simplest unit is one motor unit where one fiber and one muscle cell that contracts
* ^^**Cardiac Muscle**^^
* We want them to all work in unison (all at the same time) in order to give us a strong enough contraction to move blood (all work together as one team)
* The simplest unit is one motor unit where one fiber and one muscle cell that contracts
* ^^**Cardiac Muscle**^^
* We want them to all work in unison (all at the same time) in order to give us a strong enough contraction to move blood (all work together as one team)
58
New cards
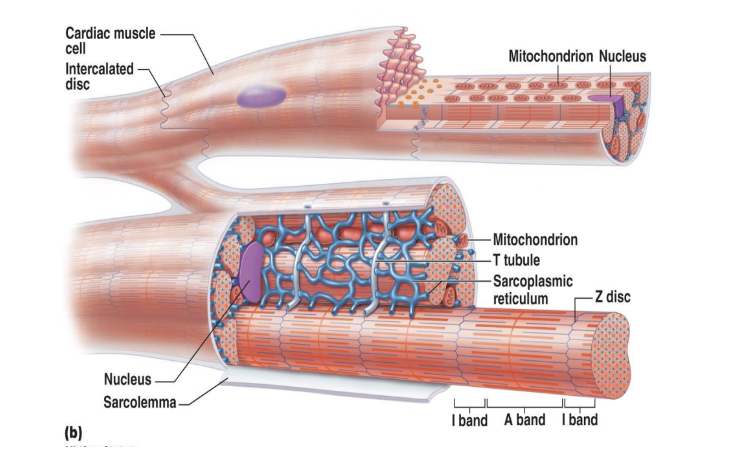
Energy requirements of cardiac muscle
* Mitochondria
* Powerhouse of the cell
* Make up approximately 25-35% of the whole cell volume of cardiac muscle
* Lots of energy being produced
* Highly dependent on **aerobic metabolism** in the heart which means that they rely on **oxygen** to metabolize the fuel
* Long lasting
* Fuel
* Very **flexible** (Glucose, fatty acids, lactic acid from skeletal muscles)
* Will take fat, glucose, protein in order to make energy and will continuously fuel the heart throughout
* Powerhouse of the cell
* Make up approximately 25-35% of the whole cell volume of cardiac muscle
* Lots of energy being produced
* Highly dependent on **aerobic metabolism** in the heart which means that they rely on **oxygen** to metabolize the fuel
* Long lasting
* Fuel
* Very **flexible** (Glucose, fatty acids, lactic acid from skeletal muscles)
* Will take fat, glucose, protein in order to make energy and will continuously fuel the heart throughout