Hematologic system
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
Components of the blood
plasma
Rbc
WBC
Platelets
Plasma
caries antibodies and nutrients to tissues
Carries waste away
Consists mainly of proteins
What proteins do we find in the plasma
albumin
Globulin
Fibrinogen
Coagulation factors
Will be found in the plasma which will be part of the coagulation cascade
Erythrocytes (RBC) shape and why
donut shape
Have no nucleus
The can deform to fit in narrow capillaries
Erythrocytes RBC life span
80 to 120 days
Cannot divide
Erthropoiesis
Formation of new red blood cells
If the kidneys that filter the blood realize there is low oxygen
The kidney will secrete Erythropoietin
which is the signal for proliferation and maturation in the bone marrow
The stem cells will cause the proliferation of the stem cells leading it to maturation
Once matured the cell will extrude the nucleus
The nucleus will combine with the reticulocytes
Then you have red blood cells
Don’t need to know
Reticulcocytes
Are the precursors for the red blood cell
Chronic kindny failure
Usually bare going to be suffering from anemia
Low red blood cell, htc, hemoglobin,
Leukocytes WBC
Help fight infections
WBC count
5,000 to 10,000
Higher than 10,000
Means infection or inflammation
Leukocytes divided into 2
granulocytes
Agranulocytes
Granulocytes
Neutrophils
Basophils
Eosinophils
Agranulocytes
Macrophages
Lymphocytes ( B cells,T cells, and natural killers)
Leukocytes distribution
Never let monkeys eat bananas
Neutrophils - most
Lymphocytes
Monocytes
Eosinophils
Basophils- least
Thrombocytes (platelets) concentration
150k to 450k
Thrombocytes (platelets) Is
Essential to normal blood clotting.innate the coagulation cascade.
Blood dyscrasis - problems in the blood
trauma
Chronic disease
Surgery
Malnutrition
Drugs
Toxins
Radiation
Genetics and congenital Defects
Sepsis
She said just read for summary 👀
Hemoglobin men
14-16.5
Hemoglobin women
12- 15
Hematocrit men
40% to 50%
Hematocrit Women
37% to 47%
Mean corpuscular volume - normocytic
Size of RBC
80 to 100 Fl/red cell
Macroscytic anemia
Bigger than 100
Microcytic anemia
Smaller than 80
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentrations
How much hemoglobin is in red bleed cell
Low; pale in color
Anemia
Low hemoglobin, low hematocrit , low red blood cells
Anemias overall
Is less than 12 hemoglobin
Nutritional anemia
iron deficiency anemia
Vitamin B12 anemia
Folic acid Anemia
Hemolytic anemia
Red blood cells that break down
sickle cell anemia
Thalassemia
Aplastic anemia
Bone marrow depression
low RBC, Low WBC, Low Platelets
Can be caused by chemotherapy
Microcytic
Less than 80
iron deficiency
Thalassemia
Anemia of chronic disease
Iron deficiency anemia caused
Caused by blood loss. Because we can’t recycle RBC but we can reuse iron from those other RBC, but if we don’t have enough RBC we will lose iron
Iron deficiency examples
trauma
Loss blood in the GI normally unknown
Women if the have heavy menstrual
Loss blood through urine
Inadequate diet
Pregnancy
Symptoms of anemia start showing when
Hemoglobin is 7-8
General anemia symptoms
fatigue
Weak
Shortness of breath causing them to have tachycardia
Pallor skin
Brittle nails
Glossititus (inflammation of tongue
Decrease mental alertness
Pica (eating dirt and other random things)
Pagophagia (eat ice constantly)
Anemia lab findings for iron deficiency
Low ferritin
Microcytic RBC
Hypochromic: low MCHC ,pale blood cells
Increase Total iron binding capacity
Increase Total iron binding capacity for iron deficiency
total Iron finding capacity has a inverse relationship with iron. So if you have a lot of iron, you will have low iron finding capacity, but if you have low iron, you have an increase of total iron finding capacity.
Iron deficiency Anemia treatment
Fe iron supplement
Vitamin C improves reabsorption of iron
Improve diet
What will prohibit iron from being absorbed?
Milk
Thalassemia
Genetic defect that result in a or b chain hemoglobin
A thalassemia genetic defect
Asian population
A thalassemia has 4 genes that are involved of the synthesis of the alpha-chain
4 genes that are involved of the synthesis of the a-chain
Asymptomatic = a-chain
1 defective gene
Fatal= a -chain
All 4 alpha genes are defective
Control of synthesizing of the B chain for B-thalassemia are
2 genes
Asymptomatic - B thalassemia minor
1 defective gene
B thalassemia major or cooley’s anemia
2 defective genes
Will need blood transfusions
B thalassemia effects
Mediterranean
Italy and Greece peoples
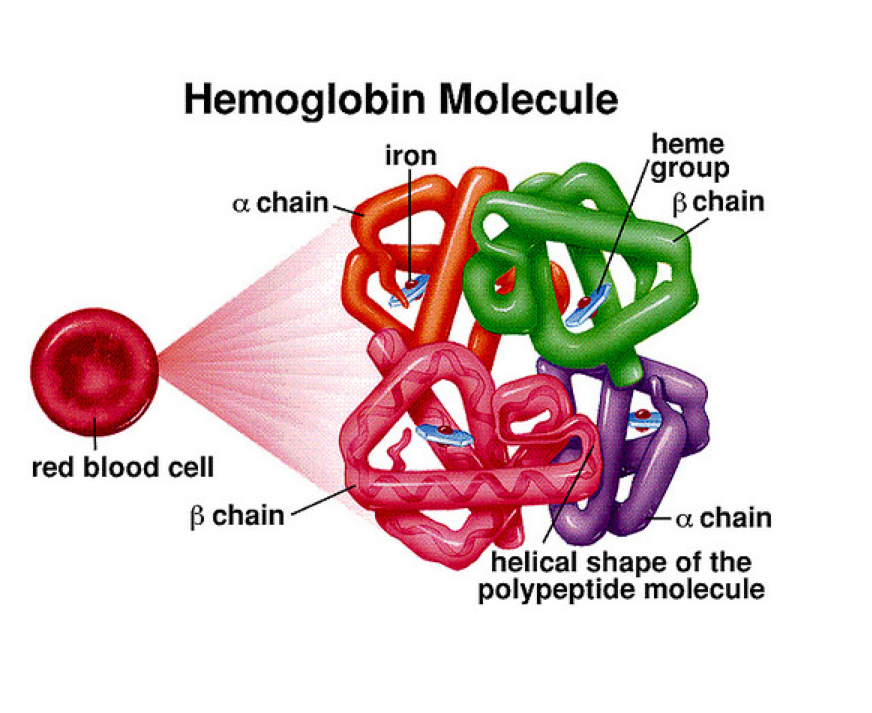
Hemoglobin molecule
Is found in red blood cell, it helps us move iron around (so iron can help move oxygen around the body)
We have 2 A chains and 2 B chains, but they are mutated
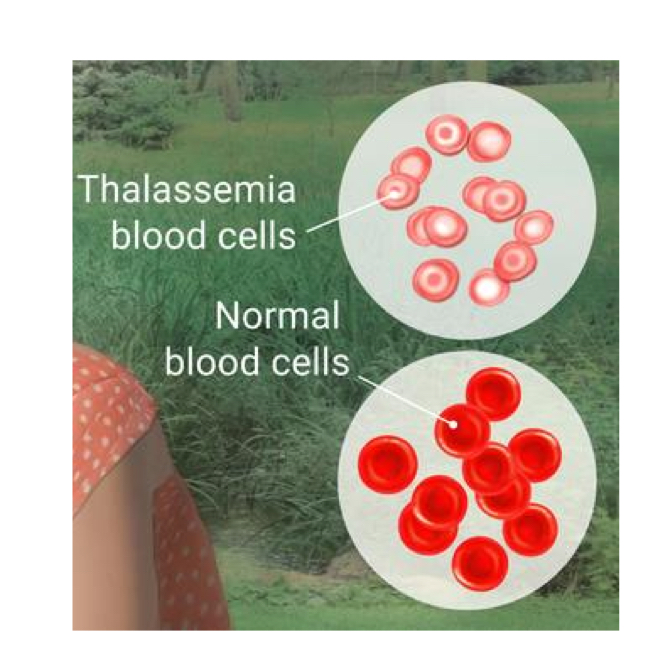
Thalassemia blood cells
Are smaller and pale
Macrocytic
Over 100
vitamin B12 deficiency
Folate deficiency
Pernicious anemia
Vitamin B 12 found in animal products need to attach to intrinsic factor but can’t because we have low amount
Pernicious anemia Causes
autoimmune disorder that destroy parietal cells (make intrinsic factors)
Gastrectomy removal (also takes parietal cell that make intrinsic factors that absorb vitamin b12)
Vitamin B12 deficiency manifestations
Gastrointestinal
glossitis
Anorexia
Diarrhea
Neurological
numbness and parenthesis in extremities
Weakness
Ataxia
Vitamin12 last stage vs beginning stage
If you’re in the last stage, you can’t reverse it. If you were in the beginning stage and have numbness and all of the symptoms of the neurological, you can reverse it.
Vitamin B 12 deficiency diagnosis
Low Hbg and HTC
Over 100
Schilling test - they give a person marked vitamin b12 and then check there urine for 24 hrs. If in the urine absorption was done and if not then it would come out in the poop. So
So now they know that the are missing intrinsic factor and can treat the person
When you can have vitamin b12 deficiency
You can have vitamin B 12 deficiency and not pernicious anemia. There’s anemia is only when you’re lacking of intritic factor.
Vitamin B12 pernicious anemia
give vitamin B12 shots there whole life every week and later 1 time a month
Folic acid deficiency anemia causes
Larger than 100
Poor nutrition
ETOH alcoholism
Folic acid manifestation
pallor
Fatigue
Palpitations
GI symptoms
No neurological symptoms
Folic acid deficiency treatment
supplements
Increase dietary intake, fruits, nuts, and vegetables
Sickle cell anemia
Defective hemoglobin molecule instead have HBG S
The issue with these S shaped hemoglobins is that they’re going to have a difficult time going through tiny capillaries and will end up plugging the cite
This leads to ischemia and pain because since it’s plugged, no oxygen can go through
Factors/ triggers that exhibit sickling all lead to decrease O2
Hypoxia
cold - Extreme temperatures
Stress
Physical exertion
Dehydration*
Illness
Excessive exercise
Infection
Elevated blood viscosity
High altitudes cause low oxygen
People with sickle cells it’s important to keep them
Hydrated
Sickle cell occlusion
In b hemoglobin we have a mutation
The hemoglobins when the oxygenated will begin sickling
There’s a point that it will be irreversibly sickled
Causing vessel occlusion leading to ischemia and infraction
Sickle cell manifestations
pain
Hemmat hematuria
Lethargy
Irritability
Pale lips, tongue, palms, and nail beds
Stroke
Splenomegaly - gets swollen
babies will be OK until they’re six months old
Sickle cell diagnosis
genetic testing
Hemoglobin electrophoresis
Increase erythrocytes sedimentation rate mean inflammation
High iron
Low RBC survival
Reticulocytosis high number
Treatment for sickle
hydration
Avoid low oxygen
Give oxygen
Pain management
Sickle cell anemia type
Autosomal recessive disorder
But in homozygous both are effect 80-90%
With heterozygous normally, they are not affected they’re just carriers, but with sickle cells 40% of them will be altered
Normocytic
anemia of chronic disease
Aplastic anemia
Chronic renal failure
Post hemorrhagic
Thrombocytopenia plaletes normal
150k - 450k
If we have abnormal amount of platelets
You will have bleeding
Thrombocytopenia levels
Less than 150,000
Causes of of decrease plaletes - thrombocytopenia
Immune thrombocytopenia purpura
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Secondary thrombocytopenia
Immune thrombocytopenia purpura
Autoimmune disorder
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
ADAMTS 13
Secondary thrombocytopenia
Due to medication such as heparin example HIT
HIT (heparin induced thrombocytopenia)
Person is receiving Heparin and they began making antibodies against heparin
The are making antibodies against the plaletes
Those plaletes get removed by the spleen
Causing low platelets in blood causing thrombocytopenia
HIT (heparin induced thrombocytopenia)
It’s called this when more than 50% reduction of plaletes
HIT (heparin induced thrombocytopenia) Treatment
Stop heparin
HIT manifestation
start bleeding
epistaxis (nose bleed)
Menorrhage (leading to excess menstral cycle)
Hematuria
GI bleeding blood in fecces
Petechia or purpura
Tachycardia
Shortness of breath
Change in mental status
Death
Thrombocytopenia diagnosis
CBC- plaletes count
Coag studies - PT/PTT
Platelet antibodies studies
Coagulation studies
PT/PTT check because if higher than normal
It tells them if coagulation is take too long due to low platelets count
If they make thrumbus quickly they will have low PT/PTT
Thrombocytopenia treatment
steroids
Platelet transfusions
Splenectomy
Educate on risk of bleeding
Thrombocytopenic precautions
Hemostasis
Vessel spasm- vascular construction
Formation of platelet plug aggregation
Formation of insolvable, fibrin clot - blood clotting coagulation cascades
Once healed clot dissolution
Coagulation casacade
Intrinsic and extrinsic pathway make fiber 10 xa and ca++
Fiber 10 makes prothrombin
Prothrombin makes Thrombin
Thrombin makes the transformation from fibrinogen to fibrin
What stops fibrin when it’s done
Anti thrombin 3 will inhibit thrombin and factor 10 when you don’t need anymore fibrin
Anti thrombin works
With heparin to stops factor 10 and fibrin
Other anticoagulant
Coumadin stop 2,6,4,5 need blood test constantly, taken by mouth
10 factor medication
Rivoroxaban
Coagulation casacade medications
Heparin
What dissolves fibrin in last stage
plasminogen gets activated by TPA and makes plasmin that dissolves Thrombus
Anti coagulation
Is to prevent thrombus
Anti plaletes medication
Avoid new aggregation of plaletes
Formation plug
We have vessel that broken down cause you got a cut
Outside that vessel is going to be exposed to the plaletes
Meaning collagen will be exposed
Von willeband factor will be attached to collagen
Next to it will have factor 8 and a platelet
Platelet plug release
ADP and TXA2 To attract more plaletes
2 medications that will effect ADP and thromboxane
Aspirin- inhibit thromboxane
Clopidogrel = plavix inhibit ADP
these are anti platelets
Regulation of blood coagulation factors
Protein C and protein S the work the same way as anti thrombin
work as anticoagulant - protein c
Accelerates the action of protein c- protein s