L78: microanatomy of the liver
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
what is the largest gland in the animal?
liver
what covers the lobes of the liver?
serosa and a capsule of connective tissue with smooth muscle cells
where does the connective tissue from the capsule extend into the liver lobe as?
interlobular connective tissue to surround each individual liver lobule to provide support to vascular and bile ducts
hepatocytes
primary cells of the liver parenchyma
describe hepatocytes
Polygonal epithelial cells with abundant eosinophilic granular cytoplasm and large, centrally located round nuclei
what cellular features are in hepatocytes?
mitochondria
smooth and rough ER
golgi apparatus
inclusions
what does the microscopic appearance of the hepatocyte depend on?
nutritional state of the animal
what are most cytoplasmic changes in hepatocytes due to?
intracytoplasmic glycogen and lipid
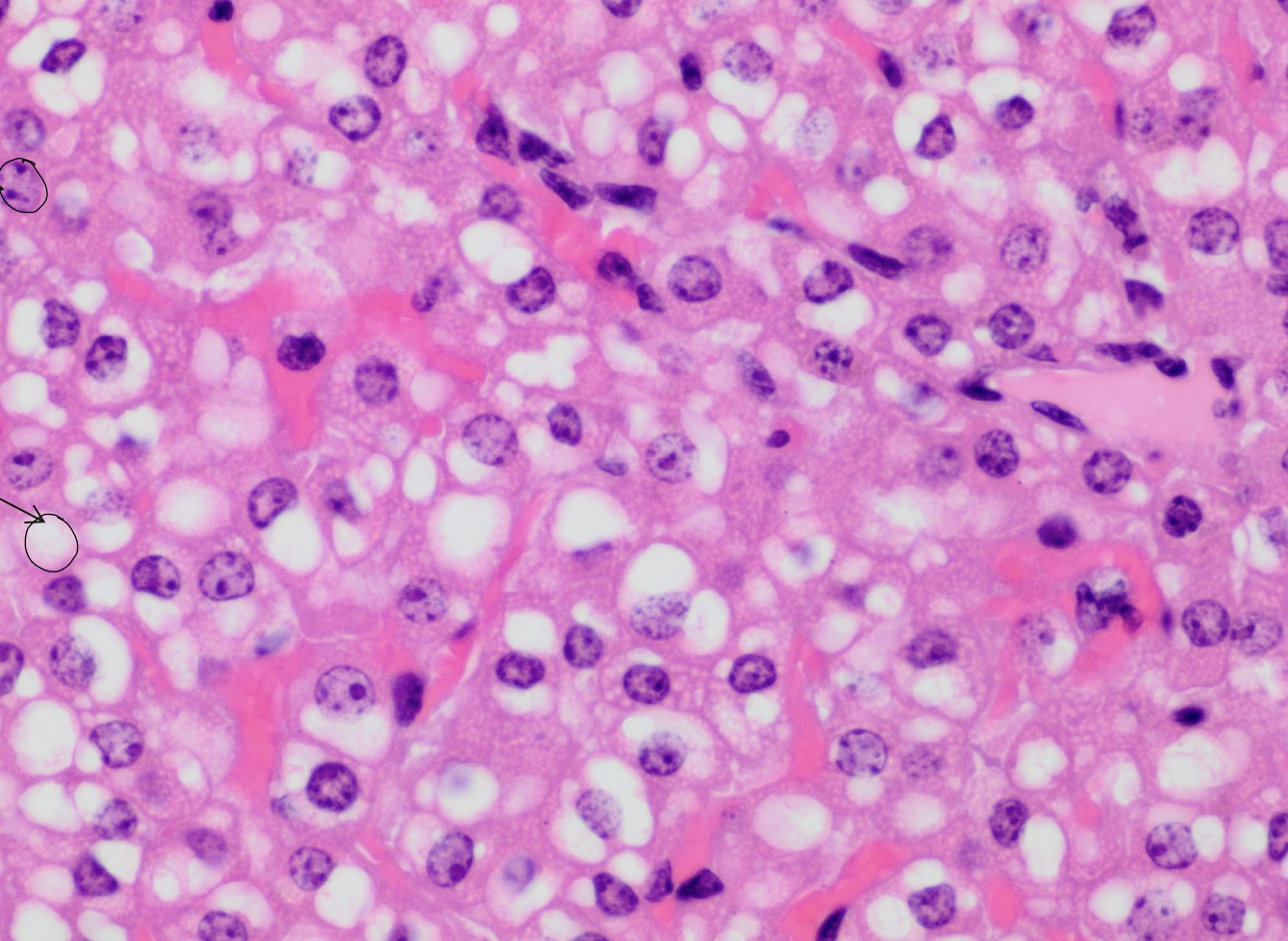
what are the neon pink spots?
hepatocyte sinusoids
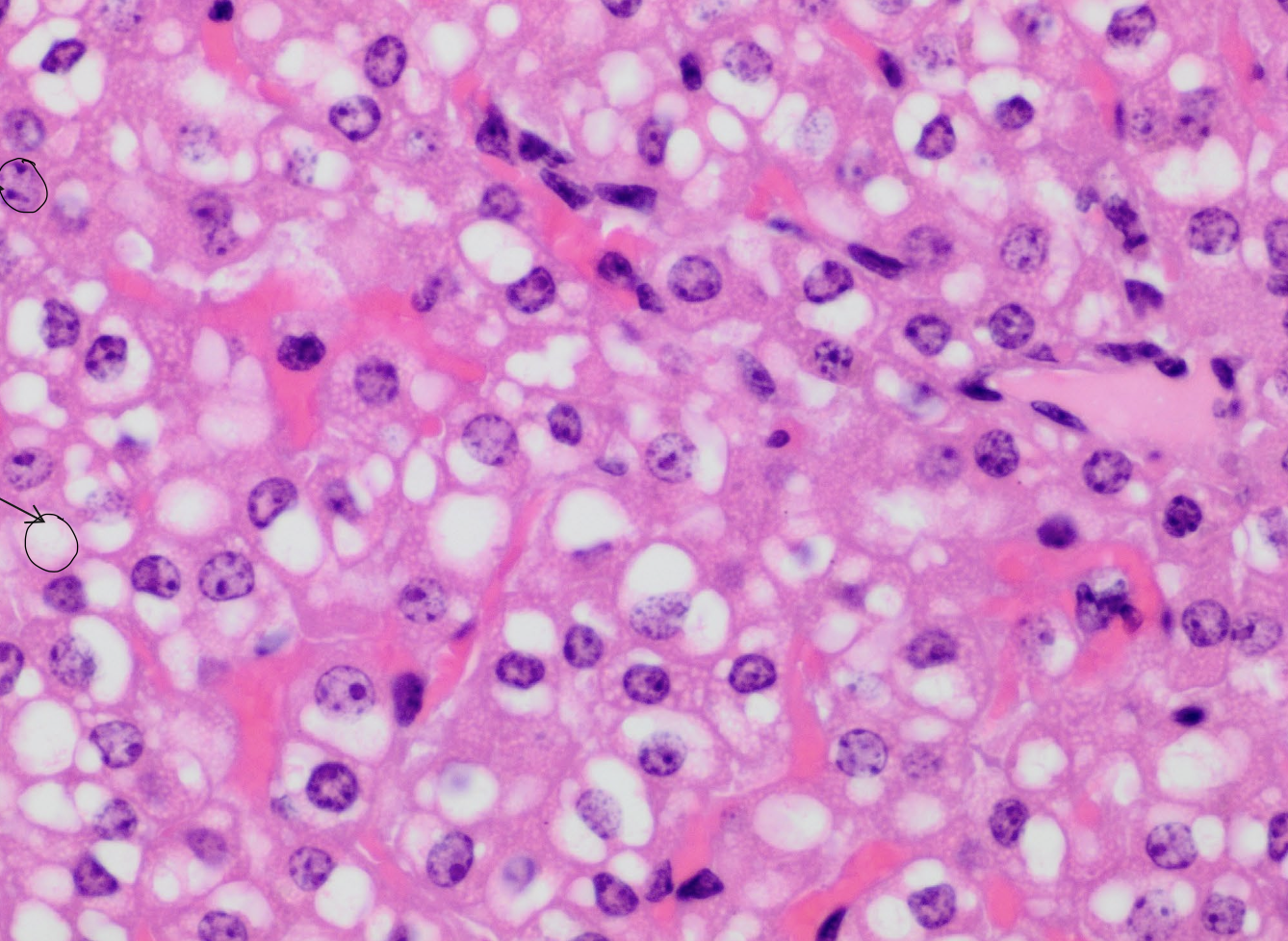
what are the purple spots?
hepatocyte nuclei
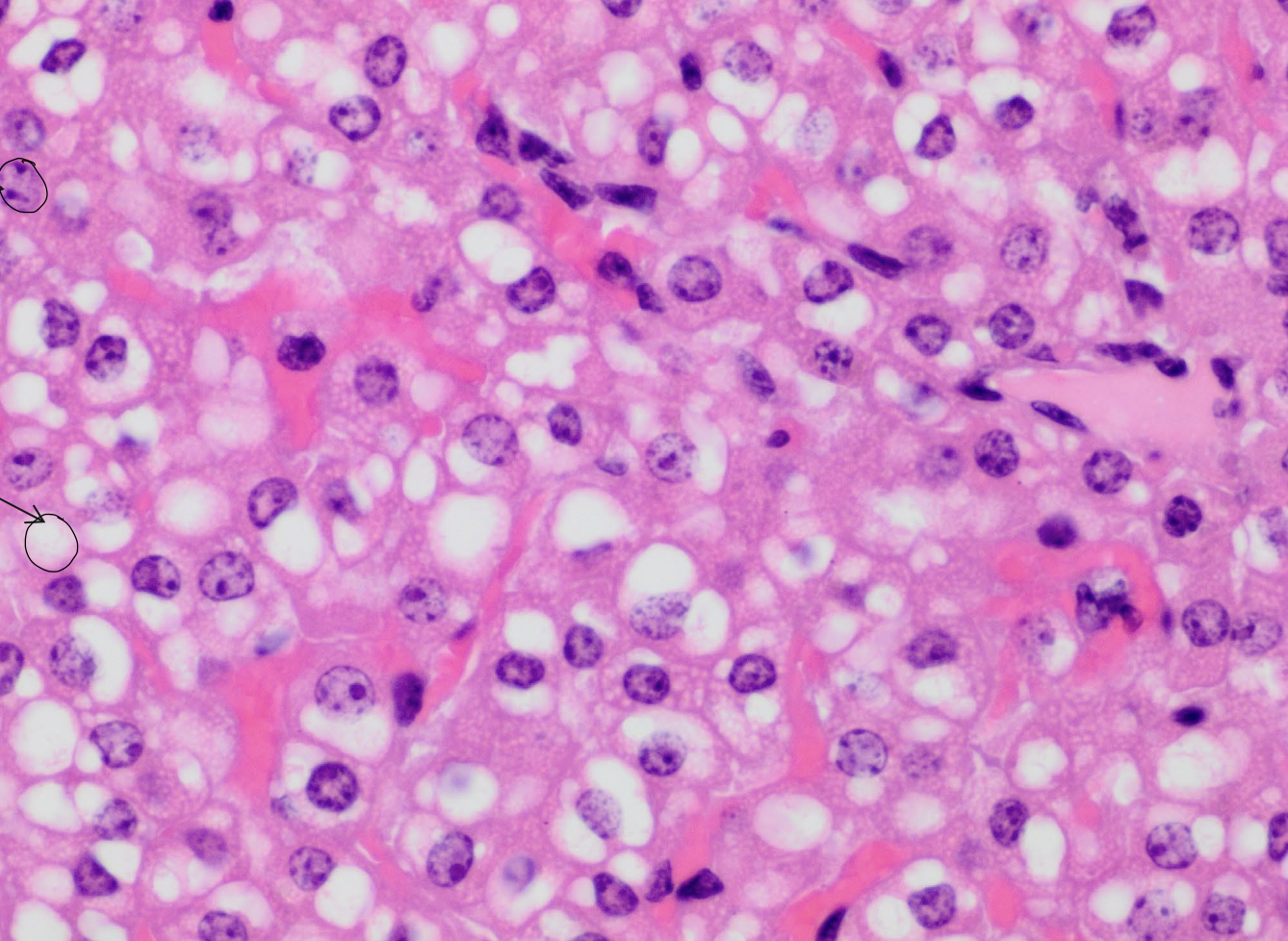
what are the white spots?
lipid vacuoles within hepatocytes
how are hepatocytes arranged?
arranged in radiating cords
what are adjacent hepatic cords separated by?
sinusoids
sinusoids
blood vessels lined by endothelial cells that separate adjacent hepatic cords in the liver
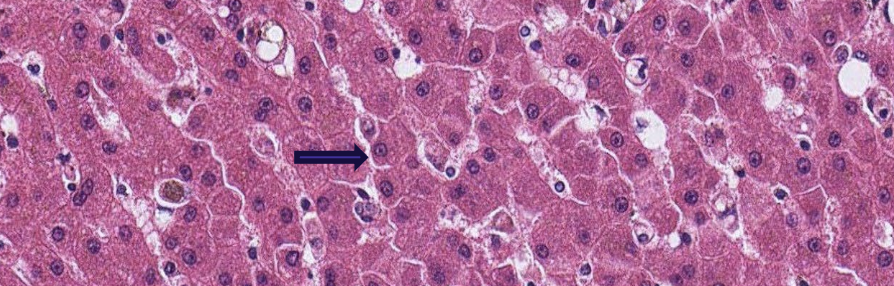
what is the arrow pointing to?
sinusoids
what surrounds the hepatocytes and sinusoids?
a fine network of reticular fibers to help keep everything together
how many surfaces are present on the hepatocyte?
six surfaces, three different types
what are the three different types of surfaces present on the hepatocyte?
microvillous
canalicular
intraceullular surface
what is the surface of the hepatocyte that faces the perisinusoidal space?
microvillous surface
what is the surface of the hepatocyte that borders the bile canaliculi?
canalicular surface
what is the surface of the hepatocyte that is between adjacent hepatocytes?
intracellular surface
what type of surface may you find in hepatocytes where apposed cell membranes may have tight junctions and desmosomes?
intercellular surface
what are ito cells also known as?
stellate cells
fat storing cells
lipocytes
where are ito cells located in the liver?
reside in the perisinusoidal region known as “space of disse”
space of disse
narrow region located between the endothelial cells and hepatocytes where ito cells reside
what are ito cells identified by?
their large lipid vacuoles
what are the functions of ito cells?
uptake, storage, and maintenance of vitamin A
production of extracellular matrix
regulation of sinusoidial blood flow
hepatic tissue repair after injury
kupffer cells
phagocytes derived from monocytes that are found within the vascular spaced of hepatic sinusoids lining the endothelial surfaces
what are the functions of kupffer cells?
remove aged red blood cells from circulation
phagocytize adn remove blood borne pathogens absorbed from GI tract
what cells are difficult to identify on histology unless they have phagocytized cytoplasmic material?
kupffer cells
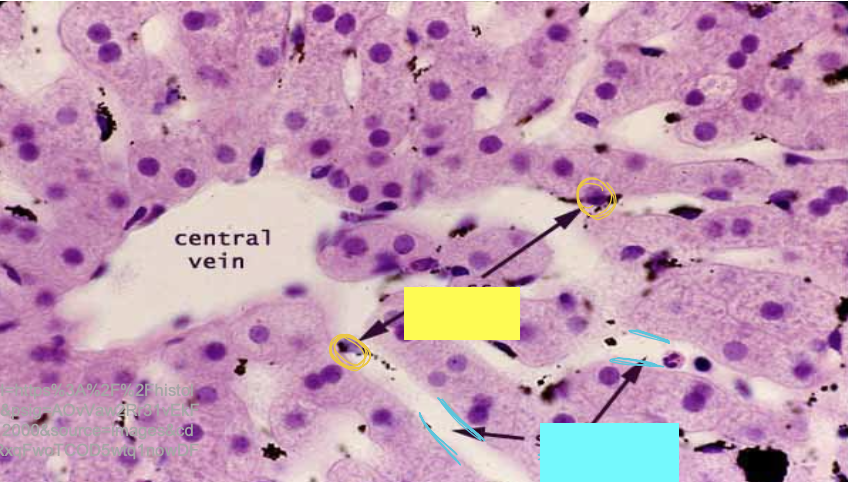
what are the yellow circles indicating?
kupffer cells
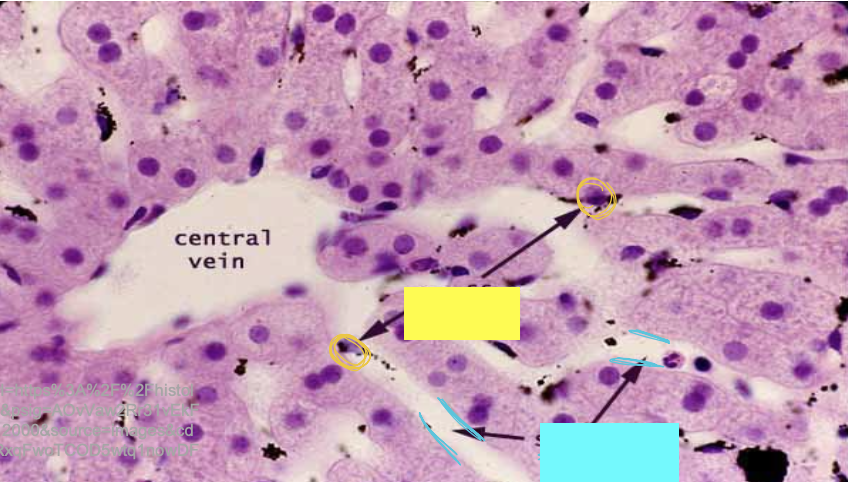
what are the blue lines indicating?
sinusoids
oval cells
pluripotent stem cells that differentiate into several cell types
what is the function of oval cells?
replacement of damaged liver cells and regeneration of liver tissue
pit cells
short-lived granular lymphocytes that reside within hepatic sinusoids and contribute to immunity
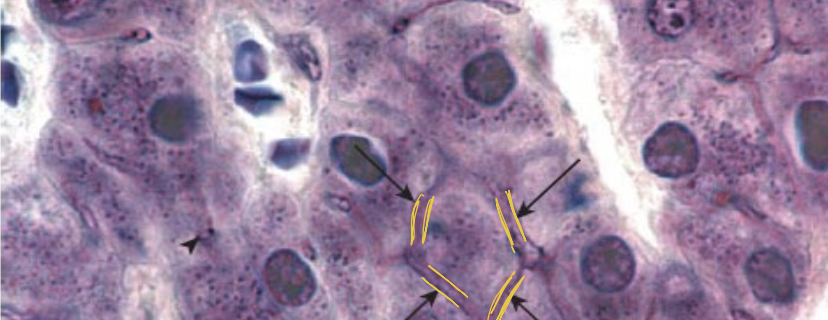
what are the yellow lines indicating
bile canaliculi
bile canaliculi
tiny canals between apposed hepatocytes
what structure is bile secreted into?
bile canaliculi
why are tight junctions important in regards to bile?
prevents bile from escaping into the narrow intercellular space adjacent to the canaliculus
where is bile produced?
hepatocytes
canaliculi
expanded intercellular spaces bordered by cell membranes with short microvilli projecting into the lumen
canals of hering
larger canals formed when bile canaliculi join near the periphery of the lobule
where do the canals of hering empty into?
bile ductules within the portal triad
what type of cells line bile ductules?
low simple cuboidal epithelium
what do bile ductules join within the portal canals?
interlobular bile ducts
what cells line the interlobular bile ducts?
simple cuboidal or simple columnar epithelium
intrahepatic ducts
are structures formed by the merging of interlobular bile ducts, transporting bile out of the liver through hepatic ducts
what is the flow of bile starting from the hepatocytes?
hepatocytes
bile canaliculi
canals of hering
bile ductules
interlobular bile duct
intrahepatic duct
hepatic duct
gall bladder
bile duct
duodenum
what duct drains the gallbladder?
cystic duct
extrahepatic biliary passages
composed of hepatic ducts, cystic ducts, bile duct, and gall bladder
what ducts unite to form the bile duct?
hepatic ducts and cystic ducts
what duct empties into the duodenum?
bile duct
what type of cells line all extrahepatic ducts?
simple columnar epithelium
MCQ: What cell is responsible for removing broken blood cells, and blood-borne microbes from the liver?
kupffer cells
MCQ: What description is accurate concerning the bile canaliculi?
Lumens are entirely sealed by junctional complexes.
what does the liver receive blood from?
hepatic artery and portal vein
what suppplies most of the blood to the liver?
portal vein
where does blood from the hepatic artery and portal vein empty into?
adjacent peri-portal hepatic sinusoids that flows towards the central vein
what does venous blood from the GI tract contain?
digested nutrients, toxins, and microbes
what is the major role of the liver in receiving this portal circulation?
to metabolize nutrients and eliminate toxins/microbes
hepatic artery
delivers highly oxygenated blood to the liver
what is important to understand about the blood in the liver?
receives highly oxygenated blood from the hepatic artery which mixes with poorly oxygenated blood from the portal vein
where are hepatic sinusoids located?
between hepatic laminae
what two types of cells line sinusoids?
endothelial cells
stellate macrophages (kupffer cells)
what does the microvilli of hepatocytes extending into the perisinusoidal space allow for?
a direct exchange of substances between blood and hepatocytes
what do the sinusoids of the ruminant liver contain?
nonporous endothelium
describe the hepatic lobule
hexagonal structure with a central vein in middle and hepatocytes forming
what are the hepatocullular regions within the classical lobule?
portal
midzonal
centrilobular
how does bile flow from the hepatocyte?
from central vein to portal triad
how does blood flow into the hepatocyte?
from portal triad to central vein
portal lobule
a functional unit developed to emphasize the exocrine function (bile secretion) of the liver
what is important to understand about the portal lobule?
cannot observe in a microscope
describe the portal lobule
a triangular area consisting of the parenchyma of three adjacent classic lobules
what is the axis of the portal lobule?
interlobular bile ductule and the peripheral angles
hepatic acinus
functional unit that describes the vascular supply to the parenchyma
describe the structure of hepatic acinus
diamond shaped made of 2 hepatic lobules supplied by terminal branches of the interlobular portal venule and interlobular hepatic arteriole
what are the zones of the hepatic acinus?
zone 1
zone 2
zone 3
which zone of the hepatic acinus is nearest to the vascular axis and what does this mean?
zone 1
excellant oxygen and nutrient supply = most metabolically active
what zone of the hepatic acinus is responsible for the production of proteins?
zone 1
what zone of the hepatic acinus is the zone of intermediate activity?
zone 2
what zone of the hepatic acinus borders the central vein and what does this mean?
zone 3
least oxygen and nutrient supply
what zone of the hepatic acinus is more susceptible to ischemic necrosis?
zone 3
what zone of the hepatic acinus is involved with lipid formation and drug detoxification?
zone 3
what does the acinus highlight and what is it useful for?
hepatic blood flow and metabolic activity
considering liver disease or pathology
where is bile concentrated and stored?
gallbladder
how does the gallbladder mucosa look in its contracted state?
has numerous folds (plicae)
what lines the luminal surface of the gallbladder?
tall simple columnar epithelium
what covers the epithelial surface of the gallbladder?
microvilli
tight junctions
what species may have goblet cells in the epithelium of their gallbladder?
cattle
what is the propria submucosa composed of in the gallbladder?
loose connective tissue with lymphatic tissue and glands
what is the tunica muscularis composed of in the gallbladder?
thin bundles of smooth muscle cells
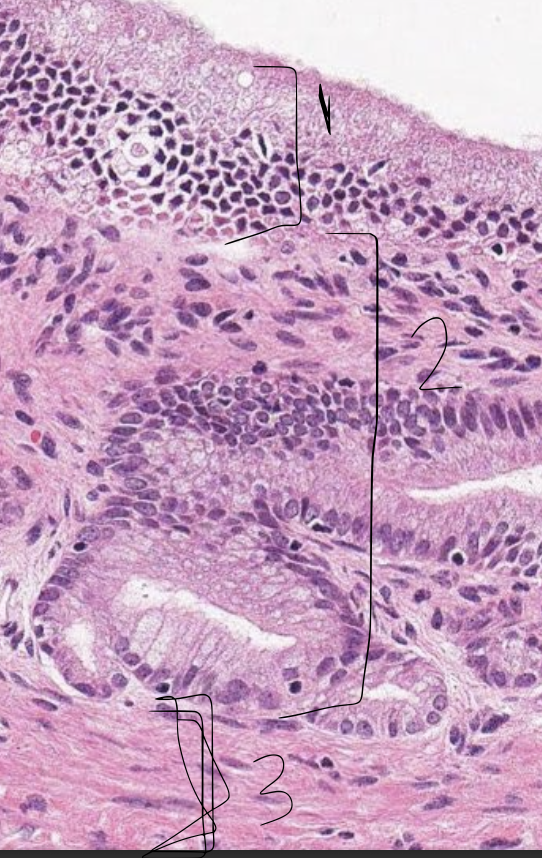
what is 1?
epithelium of gallbladder
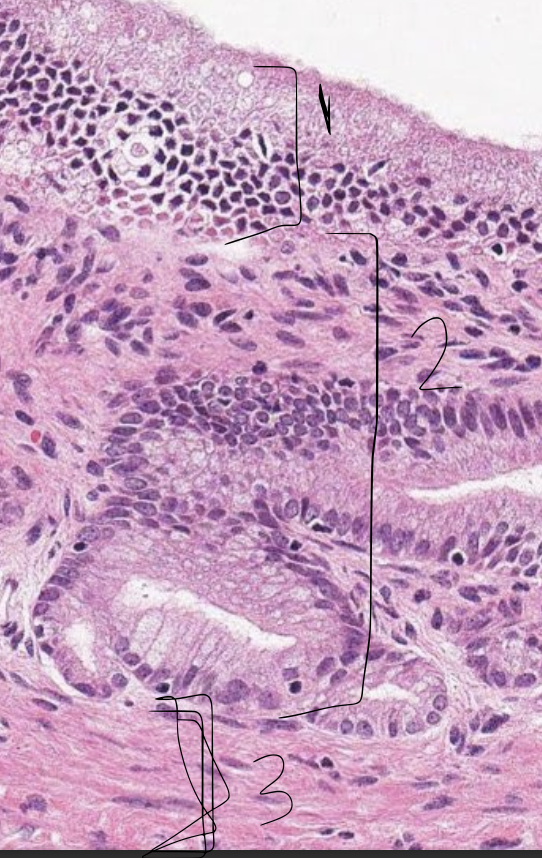
what is 2?
propria submucosa of gallbladder
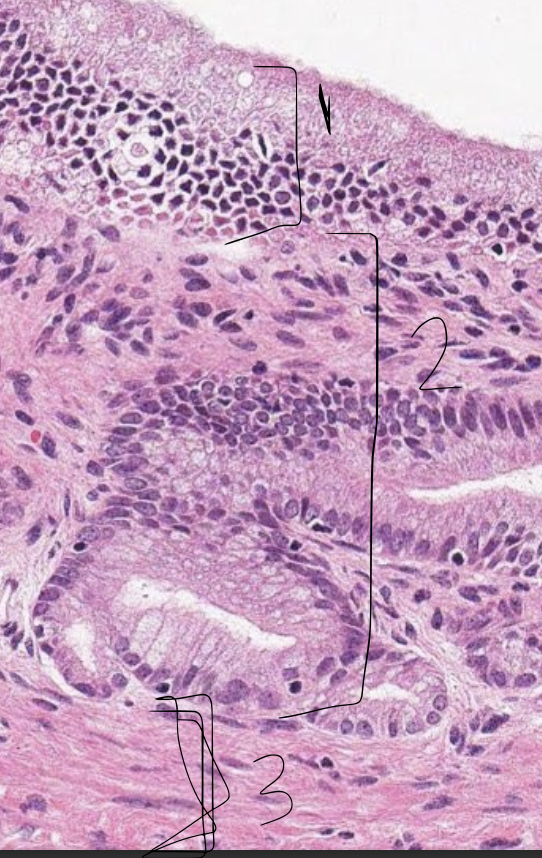
what is 3?
tunica muscularis of gallbladder