2.1 Physical and Mental Health
COVID-19
- World Health Organization (WHO) and social problems
- Health: a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being
- The study of social problems is inherently intertwined with the study of health
- Pandemic: a worldwide disease outbreak
- COVID-19 is a pandemic
- Death rate: the number of people per 100,000 in a population that die in a specific period
- Contact tracing: focuses on identifying contacting people exposed to others with positive test results
- Positivity rate: the percentage of positive results for every 100 tests
- The first reported cases were identified in the Wuhan, Hubie province of China
Overview of Global Health
Classifying Countries
- When comparing health outcomes, sociologists generally classify countries by level of economic development
- High-income country: a country with a relatively high gross national income per capita
- Aka “most-developed countries”
- Middle-income country: a country with a relatively low gross national income per capita
- Aka “less-developed countries” or “developing countries”
- Low-income country: one of the poorest countries in the world
- Aka “least-developed countries”
- Figures such as life expectancy and cause of death vary significantly between countries with different levels of wealth
Key Concepts
- Life expectancy: the average number of years that individuals born during a \n specific year can expect to live
- Japan (84 years) versus Central African Republic (53 years)
- Higher in high-income countries
- Mortality: death
- Noninfectious versus infectious disease
- Vary globally, often correlated with a country’s level of economic development
- Infant mortality rate: the number of deaths of infants under 1 year of age per 1,000 live births
- Averages 4 to 48 deaths/1,000 live births around the globe
- Under-5 mortality rate: the number of deaths of children under age 5 per 1,000 live births
- Both of these rates are much higher in low- and middle-income countries than in high-income countries
- Maternal mortality rate: the number of deaths from complications associated with pregnancy, childbirth, and unsafe abortion
- More than 94% of maternal deaths occur in low-income countries
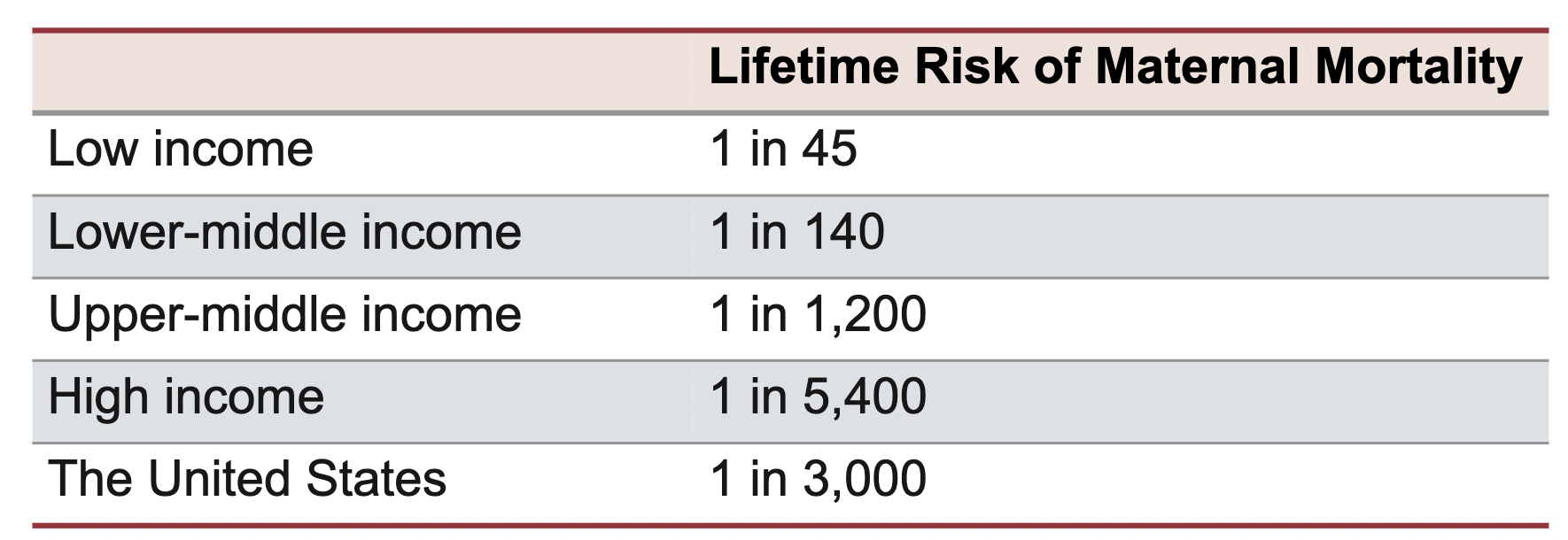
- Herd immunity: the point at which enough people in a population have been exposed to or immunized from an infectious agent to stop its spread
Globalization and Health
- Globalization
- International organizations monitor and report outbreaks of disease, disseminate guidelines for controlling and treating disease, and share medical knowledge and research findings
- Global travel is the primary means through which illnesses are transmitted between countries
- International trade agreements influence health
- Access to range of goods including tobacco and processed foods
- Globesity is a consequence of growing middle-class in poor countries
- Globesity: the high prevalence of obesity around the world
- Medical tourism: a global industry that involves traveling, primarily across international borders, for the purpose of obtaining medical care
- Medical tourism takes place for three main reasons:
- To obtain medical treatment that is not available in their home country
- To avoid waiting periods for treatment
- To save money on the cost of medical treatment
Applying Sociological Theories
Structural-Functionalist Perspective
- Health care is a social institution that functions to maintain the well-being of individuals and the society
- Failures in the health care system are dysfunctions that impact large numbers of people and other social institutions such as the economy
- Social change impacts health, and health concerns impact social change
- Latent dysfunctions: unintended or unrecognized consequences
- Use of antibiotics in agriculture and the connection to antimicrobial resistance among humans
Conflict Perspective
- Socioeconomic status or social class, power, and profit motive have an impact on illness and health care
- Health care industrial complex
- Powerful groups and wealthy corporations influence health-related policies and laws
- 600 million was spent by health industry in 2019 lobbying Congress
- Pharma corporations decide which drugs and products to develop
Symbolic Interactionist Perspective
- Meanings, definitions, and labels influence health, illness, and health care
- Meanings are learned through interaction with others and through media messages and portrayals
- Society or groups come to decide and agree what social conditions are defined as illnesses or diseases
- Medicalization: labeling behaviors and conditions as medical problems
- Individual experiences of distress into shared experiences of illness
- Eg. childbirth, menopause, death, etc.
Health Disparities in the United States
- Health disparity: a preventable difference in exposure to disease or injury or in opportunities to achieve optimal health across social groups
- Social stratification: systems of social inequality by which a society divides people into groups with unequal access to wealth, material and social resources, and power
- Socioeconomic status or social class
- Educational attainment, occupation, and household income
- Low socioeconomic status and poor communities linked to:
- Lower life expectancy and leading causal factor of poor health
- Greater stress and fewest resources to cope
- Hospitals more likely to be understaffed and lack life-saving equipment
- COVID-19 deaths in U.S. are higher in low-income counties
- Food deserts: areas that lack access to grocery stores
- Health also affects socioeconomic status and ability to pursue education, employment training, and employment itself
- Race/ethnicity
- Income, education, housing, toxins, and access to healthcare
- Black Americans, Native Americans, and Alaska Natives have lower than average health outcomes
- COVID-19 disproportionately impacts underserved groups
- Overcrowded and collective-living arrangements
- Employed in essential jobs
- Higher rates of chronic conditions
- Hispanic Paradox
- Hispanic cultural values promote family and community closeness, and traditional healthy diets which control for risk factors
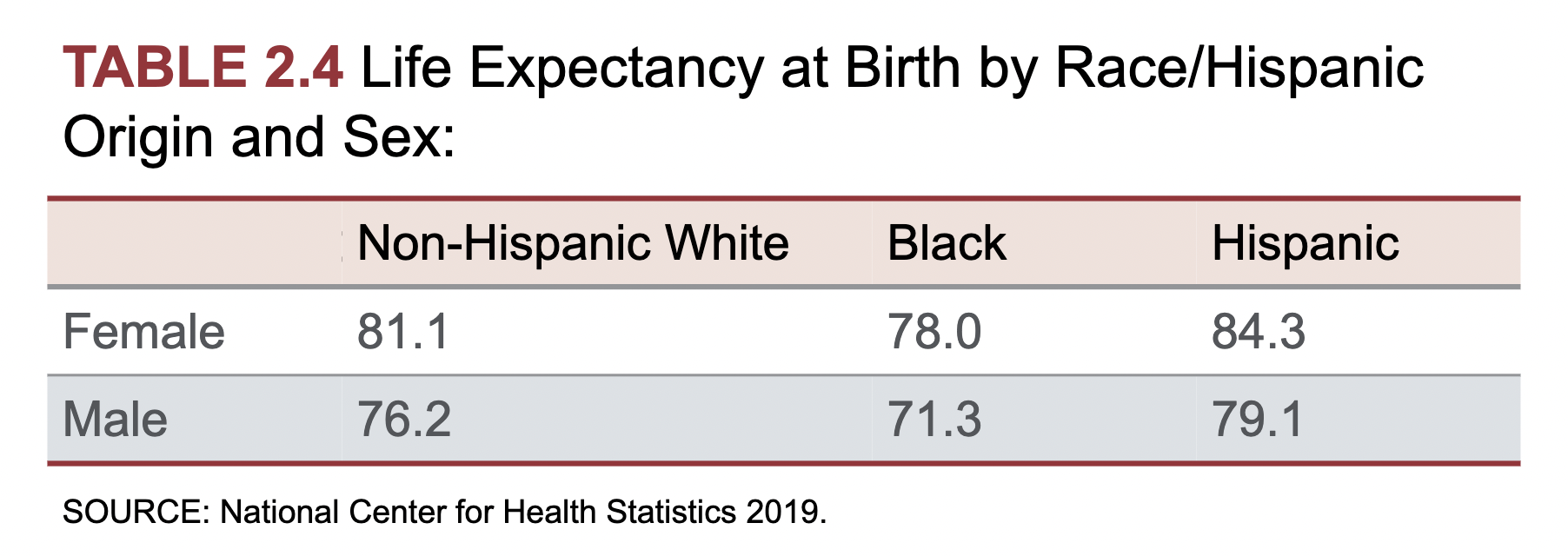
- Gender
- Men have more access to social power, privileges, resources, and opportunities but lower life expectancy
- Greater exposure to occupational hazards
- Social norms encourage risk-taking behaviors
- Less likely to seek health care and disclose symptoms
- Less likely to take COVID-19 seriously and take precautions
- Higher rates of antisocial personality disorder, and alcohol abuse
- Women’s health is impacted by gender inequalities
- Economic, political, and spousal inequalities
- Higher rates of depression and anxiety
Mental Illness: The Hidden Epidemic
- Mental health: psychological, emotional, and social well-being
- Mental illness: all mental disorders characterized by sustained patterns of abnormal thinking, mood, or behaviors that are accompanied by significant distress and/or impairment in daily functioning
- Stigma: a discrediting label that affects an individual’s self-concept and disqualifies that person from full social acceptance
- Stigma surrounding mental illness is partly due to misconceptions about their causes, such as that mental illness is caused by personal weakness, or results from engaging in immoral behavior
- The media often reinforces violent stereotypes through selective news reports and stereotypical portrayals in fictional crime shows and dramas
- Extent and impact of mental illness
- In 2019, nearly 1 in 5 adults had a mental illness in the past year
- The highest prevalence was among 18- to 25-year-olds
- About 65% received treatment
- Almost half of adolescents (13-18) had been diagnosed with a mental disorder in their lifetime
- Depression and anxiety are the most common in U.S. and around globe
- Untreated mental illness has many social consequences
- Suicide is the 10th leading cause of death in the U.S. and second leading cause of death among 10- to 34-year-olds
- Mental illness among college students
- In 2019, 1 in 3 college students had been diagnosed or treated for a mental \n health condition in the past year
- 24% had been diagnosed for depression
- 22% had been diagnosed for anxiety
- 12% had been diagnosed for panic attacks
- More than 1 in 4 college students reported that anxiety affected their academic performance; 1 in 5 reported that depression affected their academic performance
- Treatment of mental illness
- Deinstitutionalization: the shift during the 1960s from in-patient care to community-based mental health centers and drug therapies
- Legislation passed prohibiting committing people to psychiatric hospitals against their will unless they posed a danger to themselves
- Community-based mental health centers have not adequately met mental health care needs as millions of Americans go without care
- Criminalization of mental illness: the view that correctional facilities have replaced the mental health asylums of the past
Strategies for Action
- Improving health in middle- and low-income countries
- Access to adequate nutrition, clean water, and sanitation
- Increase immunizations and distribute mosquito nets to prevent malaria
- Provide access to quality reproductive care and family planning services
- Provide women education and income-producing opportunities
- Improving mental health care
- Eliminate stigma surrounding mental illness
- Improve access to mental health services
- Recruit more mental health professionals
- Improve health insurance coverage
- Expand mental health screening
- Make mental health screenings a standard practice reimbursed by insurance companies
- Support the mental health needs of college students

