BIOL 1406 - Lecture Exam 1
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Accuracy
How close measurements are to a true value
Precision
How close measurements are to each other
What is Biology?
The study of life
Showing order
All living things are made of one or more cells, the basic units of life
Homeostasis
Maintain a constant internal environment despite changes to external environment
Responds to environment
Organisms can detect and respond to changes in their environment
Growth and Development
Living things increase in size and undergo changes throughout their lives
Able to Reproduce
Organisms produce new individuals to pass on their genetic information to the next generation
Process energy
Organisms obtain and use energy through a series of chemical reactions to carry out life processes
Able to evolve
Over time, organisms evolve and adapt to their environments, which contributes to the survival of the species
NO
Are viruses alive
Prokaryotes
single celled organisms (including bacteria and archaea) that lack a membrane bound nucleus and organelles
Eukaryotes
organisms whose cells contain a true, membrane bound nucleus and other specialized membrane bound organelles such as mitochondria
Domain
Highest level of classification with three domains: Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
Kingdom
Consists of organisms that share just a few basic similarities. There are 5: Fungi, Plantae, Animalia, Protista, Monera
Domain Bacteria
Consists entirely of prokaryotic organisms
Domain Eukarya
Contains all organisms with complex cells that have a membrane bound nucleus and organelles. Includes: Plantae, Animalia, Fungi, and Protista
Hypothesis
A temporary explanation based on known information and must be testable
Element
a substance that can’t easily be broken down
CHONPS
an acronym for the six most abundant chemical elements in living organisms: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorous, and Sulfur
Ionic Bonds
Atoms lose or gain unpaired valence electrons to become oppositely charged ions that attract each other
Very different electronegativity
Covalent Bonds
Nonmental Atoms share unpaired valence electrons
Identical or similar electronegativity
Electronegativity
attraction of an atom’s nucleus to shared electrons
Polar covalent bond
Covalent bond that forms between atoms with similar but not identical electronegativity. Unequal electron sharing
Cohesive and Adhesive
Polarity makes water molecules ____________.
Cohesive
molecules attracted to each other because of hydrogen bonds
Adhesive
molecules attracted to anything else with a charge
pH
Reflects the concentration of H+ in a solution
Continuous random variable
Hydroxyl group
What chemical group is this?
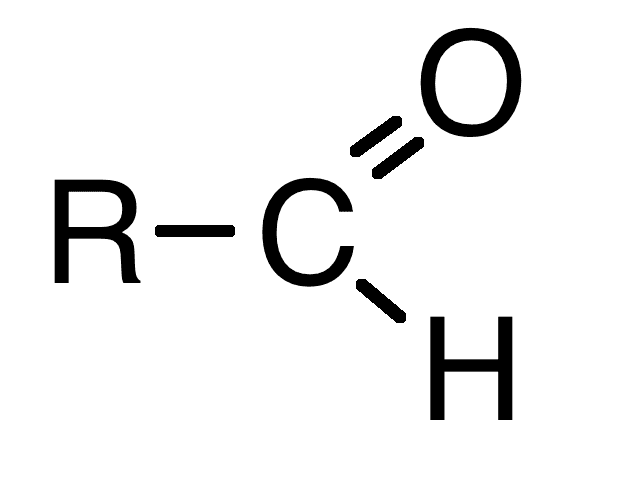
Carbonyl group
What chemical group is this?
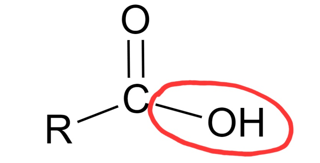
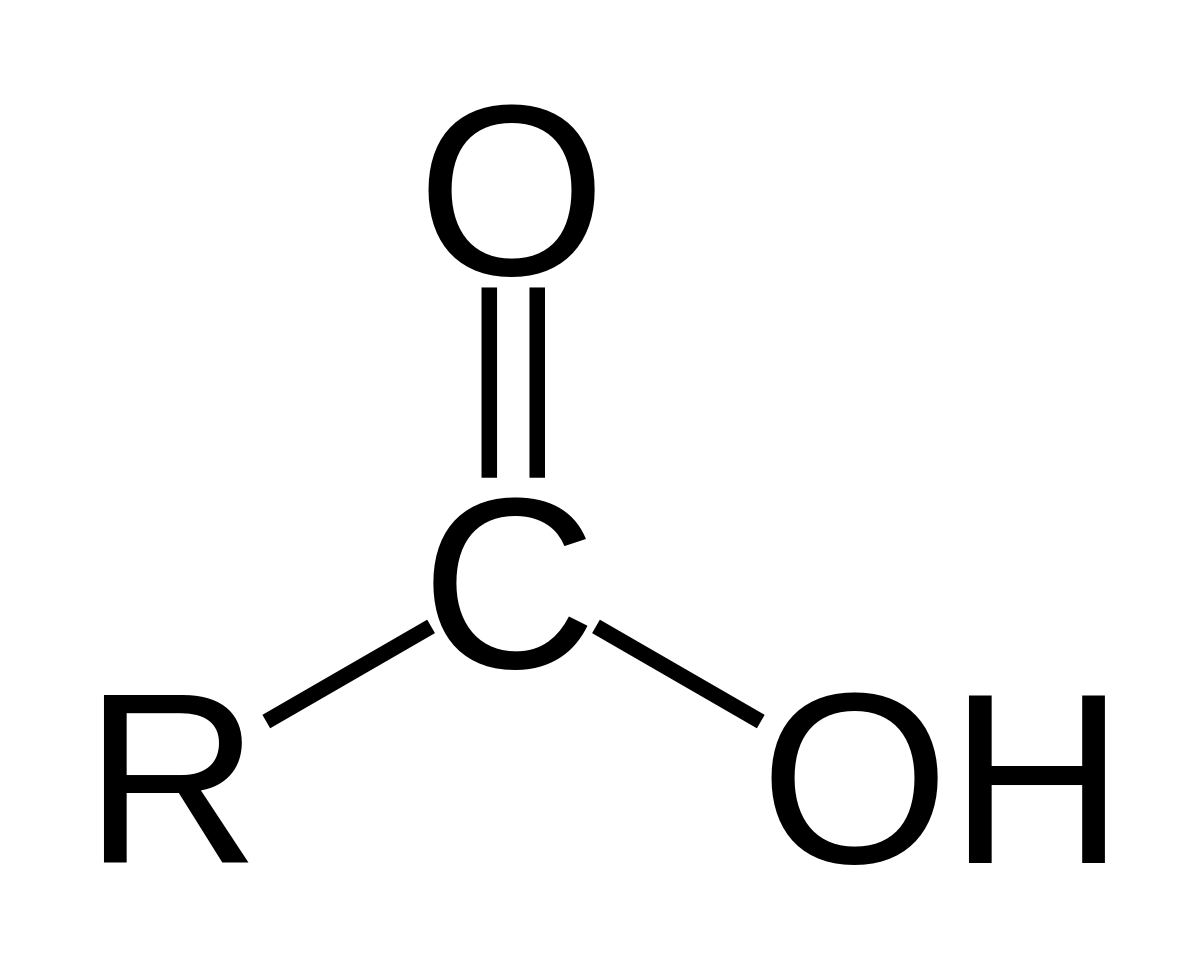
Carboxyl group
What chemical group is this?
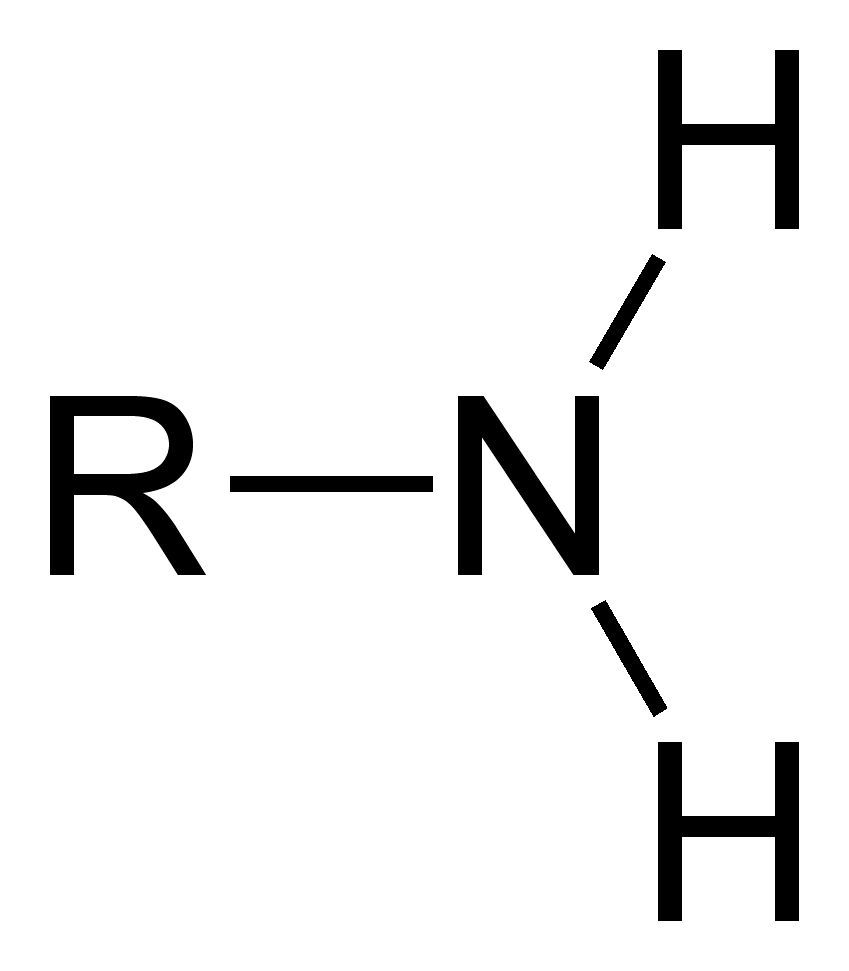
Amino group
What chemical group is this?
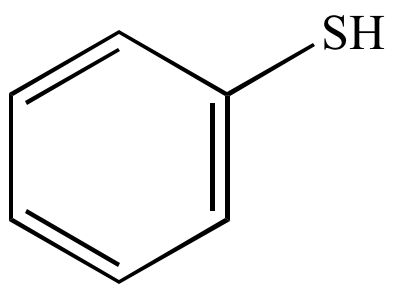
Sulfhydryl group
What chemical group is this?
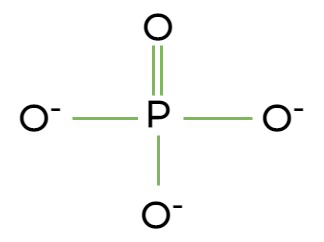
Phosphate group
What chemical group is this?
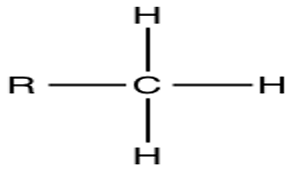
Methyl group
What chemical group is this?
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Nucleic Acids
Proteins
Four types of organic molecules found in all organisms
Dehydration reaction
chemical reaction to form covalent bond
Hydrolysis reaction
chemical reaction to break covalent bond
Yes, partially, making them soluble in water
Do carbohydrates have charge(s)?
Carbohydrates
serve as a primary energy source for living organisms, are used for structural support, and are classified by size into monosaccharides (glucose), disaccharides (sucrose), and polysaccharides (cellulose)
basic have no net charge, but some modified have slight (+) or (-)
Lipids
perform crucial roles in long-term energy storage, forming cell membranes, insulation, and signaling.
characterized by their nonpolar hydrocarbon chains and can be amphipathic (having both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts)
Saturated fat
shape is stick straight due to only single covalent bonds
Unsaturated fat
shape is bent due to at lease one double covalent bond
Nucleic acids
essential, large biomolecules that store, transmit, and express an organism's genetic information, directing cell growth, development, and protein synthesis
(-) charge
RNA
ribonucleic acid
a single-stranded nucleic acid that carries genetic instructions from DNA to the cell's machinery to synthesize proteins
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid
double helix nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions for the development and function of all living organisms
Proteins
composed of long chains of amino acid residues linked by peptide bonds.
act as enzymes, provide structural support, signaling and other basic cell functions
Primary structure
Linear sequence of amino acids linked by covalent bonds
Secondary structure
Regular, repeating structures within the polypeptide chain, such as alpha-helices and beta-pleated sheets, stabilized by hydrogen bonds
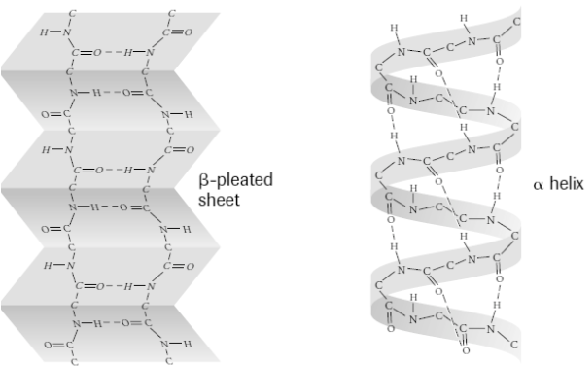
Tertiary structure
The overall 3-dimensional shape of a single polypeptide chain, resulting from interactions between the side chains of amino acids.
covalent, hydrogen, and ionic bonds
Quaternary structure
Found in some proteins, this level involves the arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains to form a functional protein complex
hydrogen and ionic bonds
Common cell parts
cell/plasma membrane
cytosol/cytoplasm
DNA
ribosomes