biochem exam 4
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/265
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
266 Terms
1
New cards
Which of the following removes the RNA nucleotides from the primer and adds equivalent DNA nucleotides to the 3' end of Okazaki fragments?
DNA POL 1
2
New cards
Which of the following statements is true of chromatin?
Heterochromatin is highly condensed, whereas euchromatin is less compact.
3
New cards
Which of the following techniques could help a researcher inhibit the expression of a target gene?
RNAi
4
New cards
how many base pair codons do we have total
64
5
New cards
Shine-Dalgarno sequence is
upstream from AUG
6
New cards
A polysome could be best described as
an active site for protein biosynthesis
7
New cards
Identify the false statement regarding the control and secretion of insulin
High intracellular ATP opens the ATP-sensitive potassium ion channel.
8
New cards
DNA replication occurs ( ), while transcription and protein translation take place ( ), respectively
in the nucleus, in the nucleus and on ribosomes
9
New cards
Binding of high level of insulin molecules to their receptors will () - in regards to appetite
inhibit the production of appetite-stimulating neuropeptide Y and induce the production of appetite-suppressing -MSH
10
New cards
Insulin stimulates glucose uptake in
muscle and adipose where glucose is converted to glucose 6 phosphate
11
New cards
insulin in liver activates
glycogen synthase and inactivates glycogen phosphorylase, so that much of the glucose-6-phosphate is channeled into glycogen.
12
New cards
lipoprotein lipase breaks down
triglycerols in the lipoproteins to smaller fatty acids and monoglycerides that are transported into your tissues and either burned for fuel or re-assembled into triglycerides for storage
13
New cards
specialized pancreatic cells that secrete important hormones:
alpha- glucagon
beta cells- insulin
delta- somatostatin
beta cells- insulin
delta- somatostatin
14
New cards
somatostatin inhibits
insulin and glucagon
15
New cards
where are the alpha beta and delta cells found
the islets of Langerhans in pancreas
16
New cards
beta cells secrete what in response to increasing blood glucose levels
insulin
17
New cards
glucose enters what cells via what
enters beta cells via GLUT2
-glycolysis, ATP increases
-glycolysis, ATP increases
18
New cards
ATP binds to
ATP gated K+ channels then K+ channels close depolarizing plasma membrane
19
New cards
the closing of K+ channels triggers opening of
Ca2+ voltage gated ion channels and theres an increase of Ca2+ in cytosol through exocytosis
20
New cards
maturation of insulin
-24 AA−long signal sequence targets proinsulin into the endoplasmic reticulum where the storage vesicles form
-formation of disulfide bonds occurs within storage vesicles
-Ca2+ activated proteases that cleave C-peptide from proinsulin
-tests of insulin levels measure C-peptide
-formation of disulfide bonds occurs within storage vesicles
-Ca2+ activated proteases that cleave C-peptide from proinsulin
-tests of insulin levels measure C-peptide
21
New cards
1 glucose forms how many ATP
30-32
22
New cards
Ca2+ is also released from
endoplasmic reticulum in response to initial elevation of Ca2+ levels in cytosol
23
New cards
depolarizing the membrane
internal is less positive
24
New cards
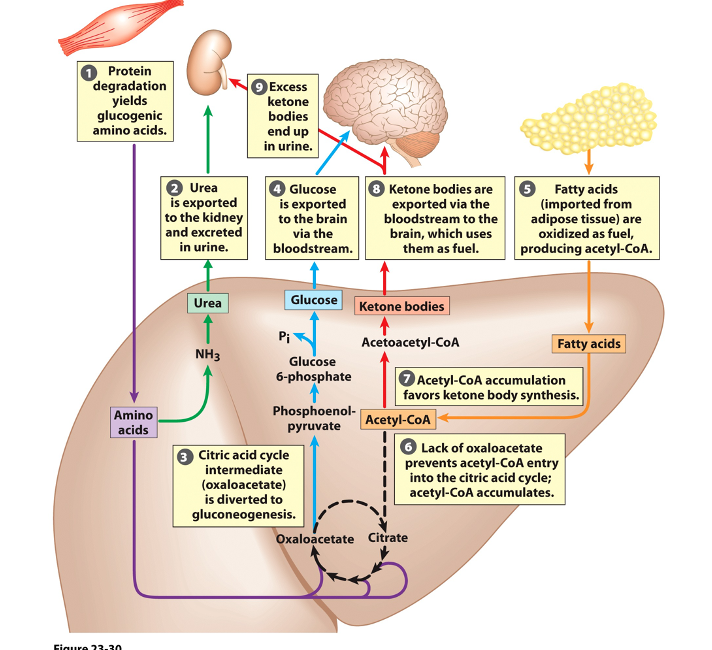
process of fuel metabolism due to prolonged fasting or type 1
leads to CAC inhibition, ketone body formation, and eventual coma/death due to ketoacidosis
-glycolysis isn’t stimulated leading to muscle and fat breakdown, so the oxaloacetate produced is used to send glucose to your brain
-without oxalo staying in CAC it’s inhibits so the fat broken down remains acetyl coa and is used for ketone bodies which provide some fuel also for the brain but accumulate in your kidneys
-glycolysis isn’t stimulated leading to muscle and fat breakdown, so the oxaloacetate produced is used to send glucose to your brain
-without oxalo staying in CAC it’s inhibits so the fat broken down remains acetyl coa and is used for ketone bodies which provide some fuel also for the brain but accumulate in your kidneys
25
New cards
Fuel Use Over Four Hours of Normal Human Metabolism
right after eating- glucose rises
-insulin stimulates glycolysis and glycogen synthesis
-two hours after eating blood glucose drops- glycogen secreted liver glycogen releases glucose
-four hours after eating more glucagon from pancreatic alpha cells, more TAG hydrolysis, FA becomes fuel for muscle and liver
-insulin stimulates glycolysis and glycogen synthesis
-two hours after eating blood glucose drops- glycogen secreted liver glycogen releases glucose
-four hours after eating more glucagon from pancreatic alpha cells, more TAG hydrolysis, FA becomes fuel for muscle and liver
26
New cards
two forms of diabetes
type 1- insufficient production of insulin:
-due to autoimmune destruction of B-cells
-develops early in life
-genetic
-ie insulin dependent or juvenile diabetes
type 2- insulin resistance
-worse type
-more common
-develops in late adulthood
-associated with obesity
-cells dont respond appropriately to insulin
-due to autoimmune destruction of B-cells
-develops early in life
-genetic
-ie insulin dependent or juvenile diabetes
type 2- insulin resistance
-worse type
-more common
-develops in late adulthood
-associated with obesity
-cells dont respond appropriately to insulin
27
New cards
diabetes symptoms
in both forms of diabetes, blood sugar becomes elevated
body tries to dilute glucose and this causes excessive urination and thirst
body tries to dilute glucose and this causes excessive urination and thirst
28
New cards
in type 1 diabetes fat breakdown is accelerated which leads to
high production of ketone bodies
this raises H+ and leads to ketoacidosis
Bicarbonate buffering system activated, leads to altered breathing
Breakdown of ketone body acetoacetate produces acetone, which is expelled via the breath
Untreated diabetes leads to dramatic weight loss
this raises H+ and leads to ketoacidosis
Bicarbonate buffering system activated, leads to altered breathing
Breakdown of ketone body acetoacetate produces acetone, which is expelled via the breath
Untreated diabetes leads to dramatic weight loss
29
New cards
Physiological Effects of Blood Glucose Levels
Blood glucose is normally determined after several hours of fasting
High fasting blood glucose level (126 or higher) is a warning sign for diabetes
Low fasting blood glucose level below 50 (in men) or 40 are warning signs of various hypoglycemic conditions
Blood glucose levels after meal (postprandial) are typically higher (up to 145 mg/100 mL is normal)
High fasting blood glucose level (126 or higher) is a warning sign for diabetes
Low fasting blood glucose level below 50 (in men) or 40 are warning signs of various hypoglycemic conditions
Blood glucose levels after meal (postprandial) are typically higher (up to 145 mg/100 mL is normal)
30
New cards
long term effects on elevated blood sugar
Compromises O2 delivery, especially in extremities (feet, etc.)
Increases risk of cardiovascular disease, renal failure, and damage to small blood vessels and nerves
Increases risk of cardiovascular disease, renal failure, and damage to small blood vessels and nerves
31
New cards
adipose tissue releases
peptide hormones called adipokines which carry info about fuel stores to brain
32
New cards
hormones that control eating
alpha MSH suppresses appetite- eat less metabolize more
neuropeptide Y (NPY)- inceat more metabolize less
neuropeptide Y (NPY)- inceat more metabolize less
33
New cards
Both leptin and insulin are peptide hormones both trigger production of ( ) and act upon what cells
acts on anorexigenic neurosecretory cells to increase production of alpha MSH
34
New cards
Leptin and insulin also act on orexigenic neurosecretory cells to inhibit the release of
NPY
35
New cards
leptin
Stimulates production of anorexigenic (appetite-suppressing) hormones
Stimulates sympathetic nervous system
Triggers cascade that regulates gene expression
May be involved in hard-wiring of neuronal circuits during development
Stimulates sympathetic nervous system
Triggers cascade that regulates gene expression
May be involved in hard-wiring of neuronal circuits during development
36
New cards
neuropeptide Y
orexigenic (appetite-stimulating) hormone
Sends signal to eat
Levels rise in starvation
Levels rise in ob/ob and db/db mice
Inhibited by leptin and insulin
Sends signal to eat
Levels rise in starvation
Levels rise in ob/ob and db/db mice
Inhibited by leptin and insulin
37
New cards
alpha melanocyte stimulating hormone (a-MSH)
is an anorexigenic (appetite-suppressing) hormone
Sends signal to stop eating
Release is stimulated by leptin
Acting through melanocortin 1 receptor, α-MSH stimulates the production and release of melain, by melanocytes in skin and hair.
Sends signal to stop eating
Release is stimulated by leptin
Acting through melanocortin 1 receptor, α-MSH stimulates the production and release of melain, by melanocytes in skin and hair.
38
New cards
leptin increases transcription of gene yielding
a-MSH
39
New cards
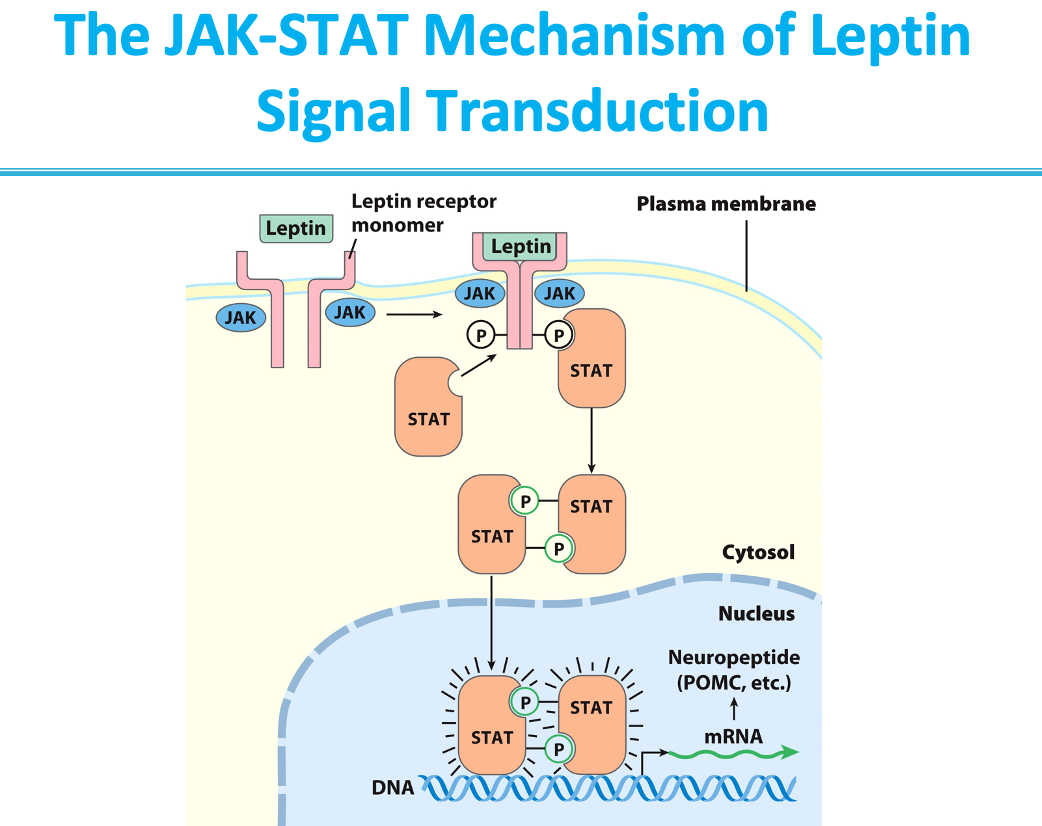
what happens to leptin receptor when leptin binds
it dimerizes and JAK phosphorylates 2 Tyr in receptor dimer
40
New cards
after JAK is phosphorylated in the receptor dimer what happens
Receptor becomes docking site for STAT3, STAT5, STAT6 (Signal Tranducers and Activators of Transcription)
STATs are phosphorylated by the same JAK
STATs are phosphorylated by the same JAK
41
New cards
once that STATs dimerize they
move the nucleus stimulate transcription of gene for precursor to anorexigenic a-MSH
42
New cards
JAK-STAT mechanism of leptin signal transduction
43
New cards
folic acid helps treat
stroke and heart attacks
44
New cards
high blood glucose levels cause hemoglobin to become
glycosylated
45
New cards
insulin also inhibits appetite by interacting with
hypothalamus
46
New cards
The orexigenic neurons have insulin receptors to Regulate
wakeful appetite
47
New cards
insulin binding to orexigenic neurons
Inhibits release of appetite-stimulating NPY
Stimulates appetite-suppressing a- MSH
Stimulates appetite-suppressing a- MSH
48
New cards
there can be cross talk between
insulin and leptin pathways
49
New cards
Leptin makes liver and muscle more sensitive to
insulin
common 2nd messenger may enable leptin and insulin to trigger same downstream pathways
common 2nd messenger may enable leptin and insulin to trigger same downstream pathways
50
New cards
type 2 diabetes epidemic
90% of diabetes cases are type 2
300 million diagnosed cases world-wide and growing
Hallmark is resistance to insulin
Initially, the body responds by making more insulin
Over time, some individuals have to supplement with insulin
300 million diagnosed cases world-wide and growing
Hallmark is resistance to insulin
Initially, the body responds by making more insulin
Over time, some individuals have to supplement with insulin
51
New cards
type 2 diabetes syndrome
Believed to affect 27% of adult U.S. population
Cluster of symptoms along with insulin resistance:
Abdominal obesity
High triglycerides (TAGs)
Low HDL Good high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol
They act as cholesterol scavengers, picking up excess cholesterol in your blood and taking it back to your liver where it's broken down. The higher your HDL level, the less "bad" cholesterol you'll have in your blood.
High blood pressure
Elevated blood glucose (but may not be full-blown diabetic)
Often includes other signs of inflammation
Cluster of symptoms along with insulin resistance:
Abdominal obesity
High triglycerides (TAGs)
Low HDL Good high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol
They act as cholesterol scavengers, picking up excess cholesterol in your blood and taking it back to your liver where it's broken down. The higher your HDL level, the less "bad" cholesterol you'll have in your blood.
High blood pressure
Elevated blood glucose (but may not be full-blown diabetic)
Often includes other signs of inflammation
52
New cards
functions of nucleotides
Energy for metabolism (ATP)
Enzyme cofactors (NAD+)
Signal transduction (cAMP)
Enzyme cofactors (NAD+)
Signal transduction (cAMP)
53
New cards
functions of nucleic acids
Storage of genetic info (DNA)
Transmission of genetic info (mRNA)
Processing of genetic information (ribonucleic acid enzymes)
Protein synthesis (tRNA and rRNA)
Transmission of genetic info (mRNA)
Processing of genetic information (ribonucleic acid enzymes)
Protein synthesis (tRNA and rRNA)
54
New cards
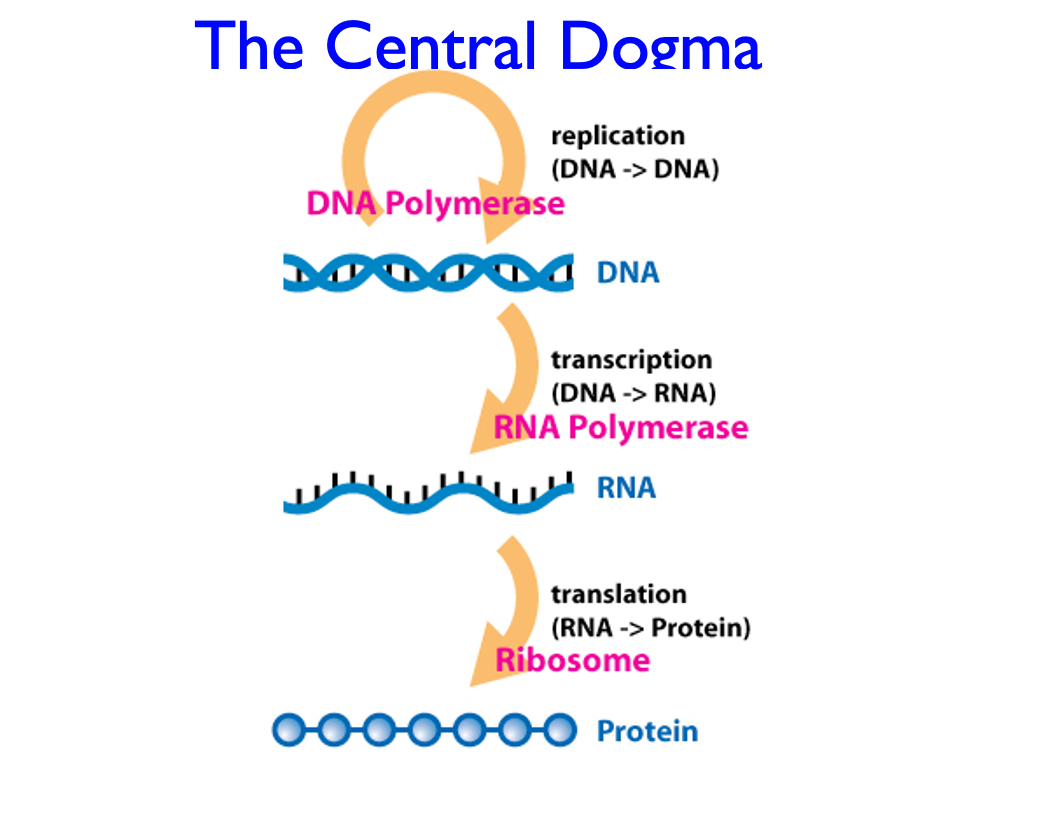
central dogma
replication - DNA- transcription- RNA- translation- protein
55
New cards
nucleotide=
nitrogenous bases
pentose
phosphate
pentose
phosphate
56
New cards
nucleoside=
nitrogenous base
pentose
pentose
57
New cards
nucleobase=
nitrogenous base
58
New cards
pentose in nucleotides
beta-D-ribofuranose in RNA
beta-2-deoxy-D-ribofuranose in DNA
beta-2-deoxy-D-ribofuranose in DNA
59
New cards
nucleobases
Derivatives of pyrimidine or purine
Nitrogen-containing heteroaromatic molecules
Planar or almost planar structures
Absorb UV light around 250–270 nm
Nitrogen-containing heteroaromatic molecules
Planar or almost planar structures
Absorb UV light around 250–270 nm
60
New cards
pyrimidine bases
Cytosine is found in both DNA and RNA
Thymine is found only in DNA
Uracil is found only in RNA
Thymine is found only in DNA
Uracil is found only in RNA
61
New cards
purine bases
adenine
guanine
guanine
62
New cards
B-N-glycosidic bond
in nucleotides the pentose ring is attached to the nucleobase through this bond
bond is formed to position N1 in pyrimidines and to position N9 in purines
bond is stable toward hydrolysis especially in pyrimidines
bond is formed to position N1 in pyrimidines and to position N9 in purines
bond is stable toward hydrolysis especially in pyrimidines
63
New cards
how does B-N-glycosidic bond get cleaved
catalyzed by acid
64
New cards
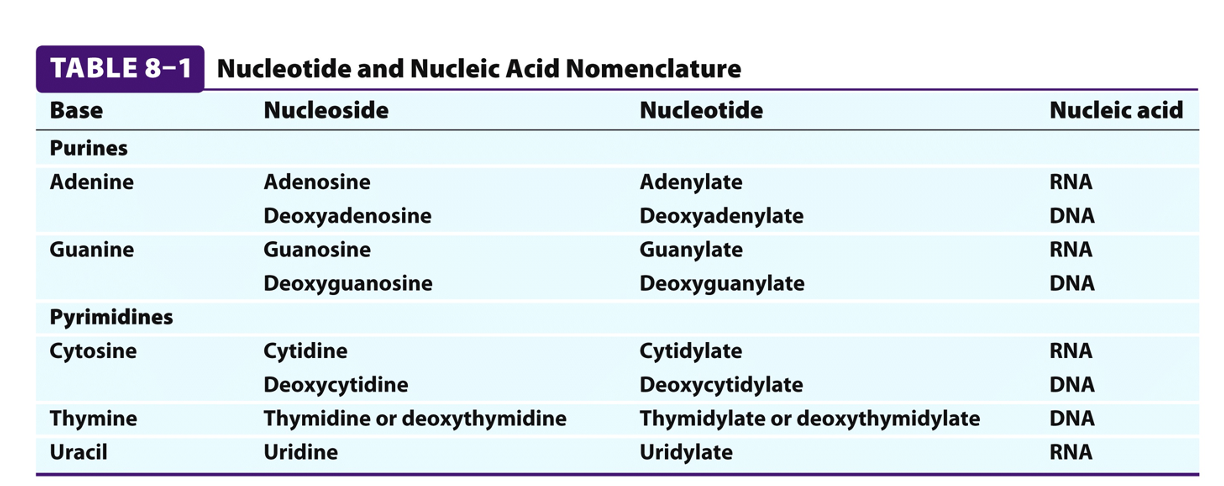
nucleotide and nucleic acid nomenclature
65
New cards
what minor nucleoside (modification done after DNA synthesis) in DNA is common in eukaryotes, also found in bacteria
5-Methylcytosine
66
New cards
what minor nucleoside (modification done after DNA synthesis) in DNA is common in bacteria, but not found in eukaryotes
N6-Methyladenosine
67
New cards
epigenetic marker
Way to mark own DNA so that cells can degrade foreign DNA (prokaryotes)
Way to mark which genes should be active (eukaryotes)
Could the environment turn genes on and off in an inheritable manner?
Foreign DNAs (not methylated) that are introduced into the cell are degraded by sequence-specific restriction enzymes and cleaved
Way to mark which genes should be active (eukaryotes)
Could the environment turn genes on and off in an inheritable manner?
Foreign DNAs (not methylated) that are introduced into the cell are degraded by sequence-specific restriction enzymes and cleaved
68
New cards
DNA can be methylated in
epigenetic
69
New cards
hydrogen bonding between what base pairs is easier to break and why
AT because it has 2 H bonds while CG has 3 bonds
70
New cards
mRNA - messenger RNA
Is synthesized using DNA template
Contains ribose instead of deoxyribose
Contains uracil instead of thymine
One mRNA may code for more than one protein
Together with transfer RNA (tRNA) transfers genetic information from DNA to proteins
Contains ribose instead of deoxyribose
Contains uracil instead of thymine
One mRNA may code for more than one protein
Together with transfer RNA (tRNA) transfers genetic information from DNA to proteins
71
New cards
gene expression control in Eukaryote-
Monocistronic- one promotor controls expression of one gene
72
New cards
gene expression control in prokaryotes-
polycistronic- one promotoer controls several genes
73
New cards
Palindromic sequences can form
hairpins and cruciforms
74
New cards
Different strands are read like
a palindrome read in reverse
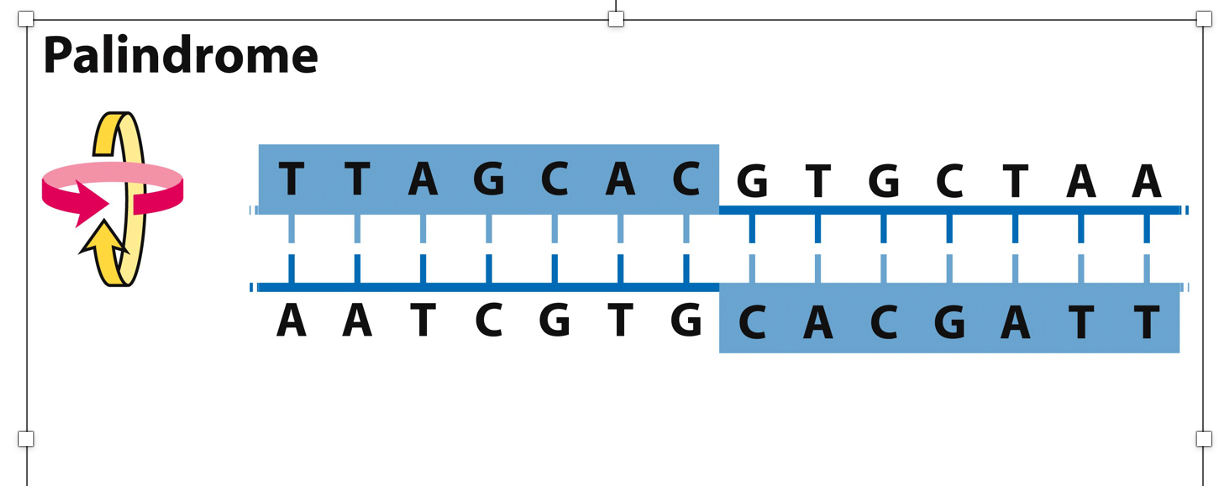
75
New cards
same strands are read like
mirror- they repeat
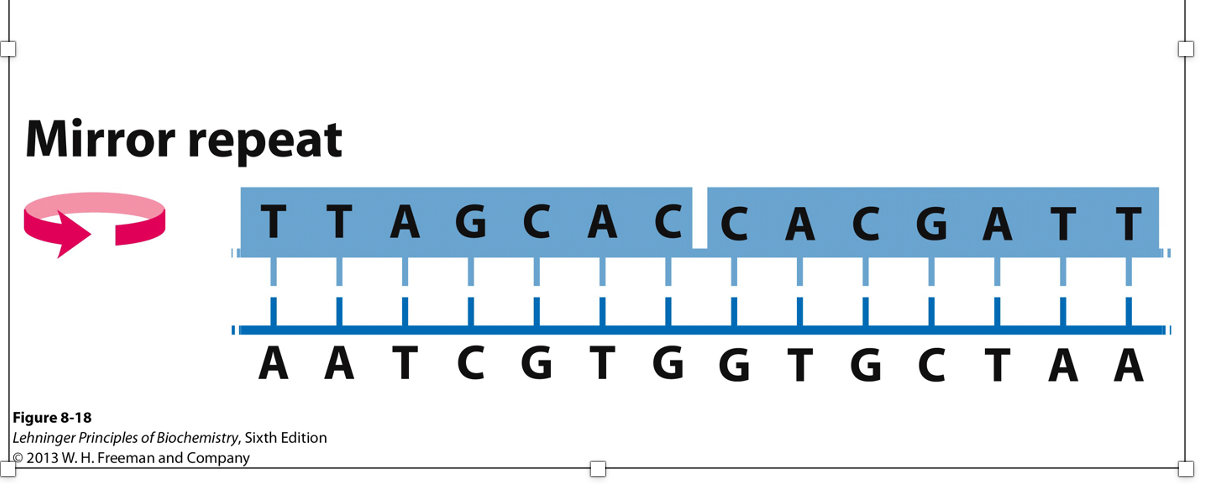
76
New cards
When only a single DNA (or RNA) strand is involved, the structure is called
a hairpin
77
New cards
Tm of DNA
heat denaturation of DNA
it depends on pH and ionic strength and on the size and base composition of the DNA.
Tm= 50% of DNA becoming single stranded
it depends on pH and ionic strength and on the size and base composition of the DNA.
Tm= 50% of DNA becoming single stranded
78
New cards
factors that affect DNA denaturation
The midpoint of melting (Tm) depends on base composition
High CG increases Tm
Tm depends on DNA length
Longer DNA has higher Tm
Important for short DNA
Tm depends on pH and ionic strength
High salt increases Tm
High CG increases Tm
Tm depends on DNA length
Longer DNA has higher Tm
Important for short DNA
Tm depends on pH and ionic strength
High salt increases Tm
79
New cards
what bases melt at a lower temp
AT
80
New cards
increase C and G nucleotides what happens to Tm graph
the temp increases
linear
linear
81
New cards
Molecular Mechanisms of Oxidative and Chemical Mutagenesis
Oxidative damage
Hydroxylation of guanine
Mitochondrial DNA is most susceptible
Chemical alkylation
Methylation of guanine
Cells have mechanisms to correct most of these modifications
Hydroxylation of guanine
Mitochondrial DNA is most susceptible
Chemical alkylation
Methylation of guanine
Cells have mechanisms to correct most of these modifications
82
New cards
alkylating agent
chemical agents that cause DNA damage
S-adenosylmethionine
nitrogen mustard
dimethylsulfate
dimethylnitrosamine
S-adenosylmethionine
nitrogen mustard
dimethylsulfate
dimethylnitrosamine
83
New cards
which alkylating agent acts enzymatically
S-adenosylmethionine
84
New cards
molecular mechanisms of radiation induced mutagenesis
UV light induces dimerization of pyrimidines; this may be the main mechanism for skin cancers.
Ionizing radiation (X-rays and y-rays) causes ring opening and strand breaking .
These are difficult to fix.
Cells can repair some of these modifications, but others cause mutations. Accumulation of mutations is linked to aging and carcinogenesis.
Ionizing radiation (X-rays and y-rays) causes ring opening and strand breaking .
These are difficult to fix.
Cells can repair some of these modifications, but others cause mutations. Accumulation of mutations is linked to aging and carcinogenesis.
85
New cards
deamination is removal of
NH group
86
New cards
depurination is removal of
prune group through hydrolysis
87
New cards
process by which DNA gets unwound from histones
acetylation
88
New cards
start codon
AUG (RNA)
89
New cards
stop codon
UAA UAG UGA (RNA)
90
New cards
what other amino acid only has one codon - and what is the code
Trp - UGG
91
New cards
bacteria also contains extra chromosomal double stranded circular
plasmids about 2000-10000 base pairs
92
New cards
E. coli
4,639,675 DNA 1 chromosome about 4400 genes
93
New cards
true or false: circular plasmids can be swapped easily in bacteria
true
94
New cards
what is one way bacteria can acquired antibiotic resistance
plasmid exchange
95
New cards
eukaryote DNA is in
multiple discrete chromosomes
96
New cards
composition of human genome
-only a small fraction (1.5%) of the total genome encodes for proteins
-Some DNA regions directly participate in the regulation of gene expression (promoters, termination signals, etc.)
-Some DNA encodes for small regulatory RNA with poorly understood functions
-Some DNA may be junk (pieces of unwanted genes, remnants of viral infections
-Some DNA regions directly participate in the regulation of gene expression (promoters, termination signals, etc.)
-Some DNA encodes for small regulatory RNA with poorly understood functions
-Some DNA may be junk (pieces of unwanted genes, remnants of viral infections
97
New cards
exons
are expressed sequences (translated into amino acid sequence)
Exons account for only 1.5% of human DNA!
Exons account for only 1.5% of human DNA!
98
New cards
introns
are regions of genes that are transcribed but not translated
They do not encode polypeptide sequence
They do not encode polypeptide sequence
99
New cards
introns are removed after
transcription and the exon mRNA sequences are spliced together and creates “mature transcripts”
100
New cards
transposons are
sequences that can move within genome