3.3.3 Economies and diseconomies of scale
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
ECONOMIES OF SCALE
EoS- advantages of large scale production that enable a large business to produce at a lower average cost than a smaller business
so firm is able to experience increasing returns to scale where an increase in inputs by a certain % will lead to a greater % increase in output
DISECONOMIES OF SCALE
DoS- disadvantages that arise in large businesses that reduce efficiency and cause average costs to rise
firm experiences decreasing returns to scale, where output increases by a small % than inputs
CONSTANT RETURNS TO SCALE
where firms increase inputs and receive an increase in output by the same %
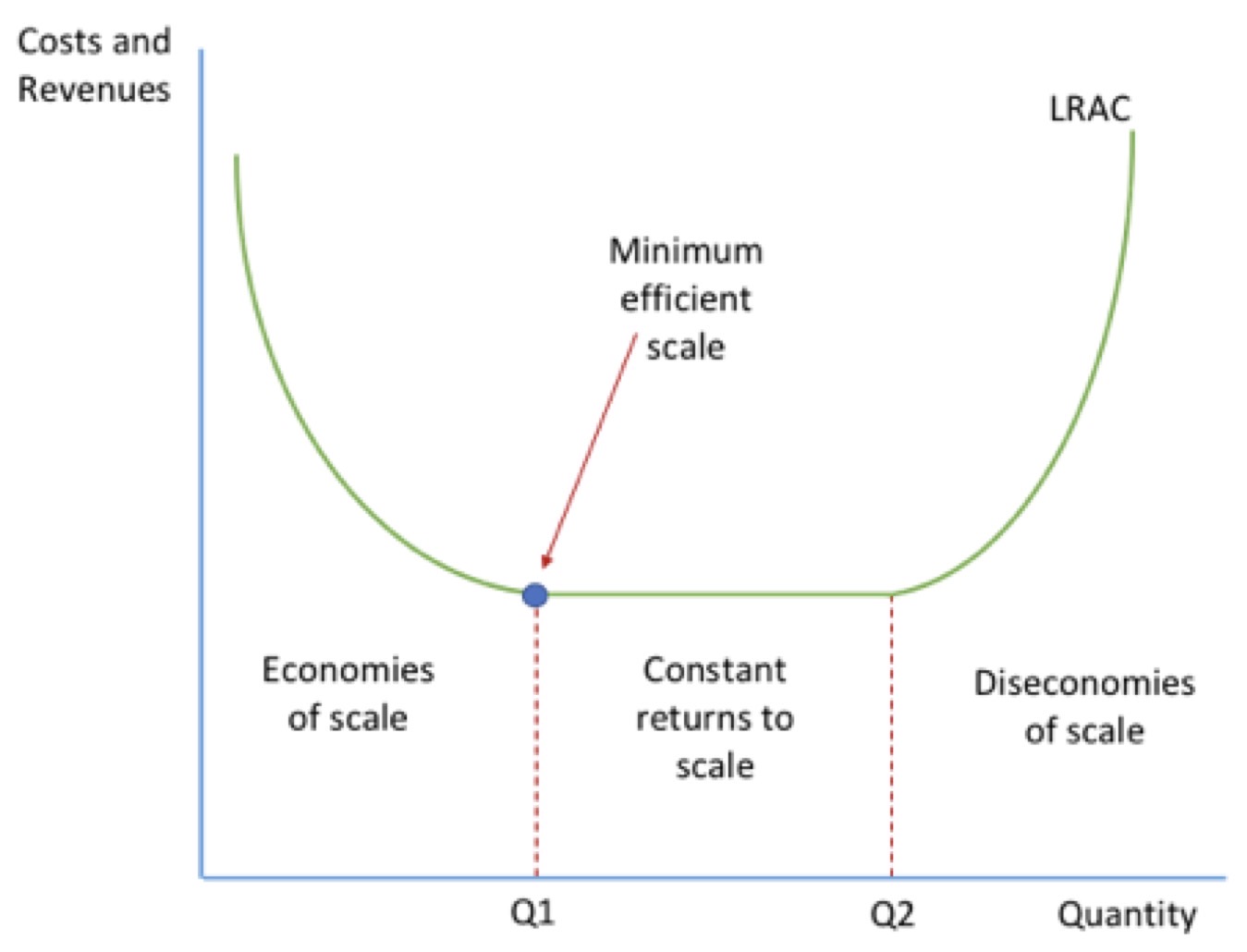
MINIMUM EFFICIENT SCALE
minimum level of output needed for a business to fully exploit economies of scale
point where LRAC curve first levels off and when constant returns to scale is first met
INTERNAL ECONOMIES OF SCALE
advantage that a firm is able to enjoy because of a growth in firm, independent of anything happening to other firms or industry in general
TYPES OF INTERNAL ECONOMIES OF SCALE- TECHNICAL ECONOMIES
technical economies
specialisation
balanced teams of machines
increased dimensions
invisibility of capital
research and development
TYPES OF INTERNAL ECONOMIES OF SCALE- OTHER ECONOMIES
financial economies
risk-bearing economies
managerial economies
marketing and purchasing economies
buying in bulk
specialisation
distribution
TECHNICAL ECONOMIES
arise as a result of what happens to production process
TECHNICAL ECONOMIES- SPECIALISATION
large firms will be able to appoint specialist workers and buy specialist machines which will be able to do their jobs more quickly and better than machines/workers which are not specialised
TECHNICAL ECONOMIES- BALANCED TEAMS OF MACHINES
large firms can afford to buy a no. of every kind of machine for each stage of production
by combining these machines, they can ensure they run each machine at its optimal level
smaller companies may only be able to afford one machine for each stage and if one stage of production runs faster than the other, machines will spend a long time turned off
TECHNICAL ECONOMIES- INCREASED DIMENSIONS
if you double the size of a container you increase the amount it can carry
all occurs w/out doubling the cost
spend less of shipping costs
TECHNICAL ECONOMIES- INVISIBILITY OF CAPITAL
some processes require huge items of machinery and investment that make it only possible for them to produce on a large scale
TECHNICAL ECONOMIES- RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT
often only large firms can afford to carry out large scale R&D
means they can gain a large advantage over their competitor
FINANCIAL ECONOMIES
large firms have greater security because they have more assets and are therefore less likely to be forced out of business overnight
so easier for them to obtain finance and lower interest rates due to lower risk
makes investment more accessible
RISK BEARING ECONOMIES
large companies able to operate in a range of diff markets, producing diff products which means that if one area of business fails, their whole business will not collapse
MANAGERIAL COMPANIES
large companies can afford to appoint specialist managers in every field, who are specialised and so are likely more efficient
staff represent an indivisibility and so small firms cannot employ specialist staff
PURCHASING ECONOMIES- BUYING IN BULK
large firms able to buy in large no. so may be able to buy their raw materials at a cheaper price than competitors
MARKETING AND PURCHASING ECONOMIES- SPECIALISATION
businesses can afford to take on specialist buyers and sellers who could be more efficient due to extra time and knowledge
MARKETING ECONOMIES- DISTRIBUTION
large businesses can establish regional distribution centres which enables them to reduce transport costs by using large transporters over long distances and storing goods in distribution centre
EXTERNAL ECONOMIES OF SCALE
advantage which arises from growth of industry w/in which the firm operates, independent to firm itself
cause the LRAC curve to shift downwards
EXTERNAL ECONOMIES OF SCALE- HIGH CONC OF FIRMS IN AN AREA
businesses established in an area w/ other successful firms from same industry find that labour tends to come to that area if they want a job in that industry
e.g. Silicon Valley
reduces cost and time take to recruit
EXTERNAL ECONOMIES OF SCALE- SKILL IMPROVEMENT
local education and training providers are more likely to develop courses to prepare people to take up jobs in these businesses
firms be able to hire staff who have been trained by other businesses, which is cheaper and more efficient for the firm than training the workers themselves
EXTERNAL ECONOMIES OF SCALE- SUPPORT SERVICES
businesses who provide products or services for large businesses will naturally move to area where those businesses are based, which reduces transport cost/time delays for business
DISECONOMIES OF SCALE- TYPES
workers
geography
change
price of materials
management
DISECONOMIES OF SCALE- WORKERS
in a large business, people can think their efforts go unnoticed and have less chance of promotion so lose motivation and work less hard
can also have less personal commitment w/ the business
DISECONOMIES OF SCALE- GEOGRAPHY
firm may have to transport finished products huge distances and firms may find it harder to control parts of business which is miles away
DISECONOMIES OF SCALE- CHANGE
takes longer and is more difficult for a large firm to respond to change
DISECONOMIES OF SCALE- PRICES OF MATERIALS
as business grows so does their demand for raw materials and equipment
although this can increase their bargaining power as they buy in bulk, an increase in demand can cause prices to rise and therefore increase production costs
this could also occur if whole industry increases and so firms bid up prices
DISECONOMIES OF SCALE- MANAGEMENT- COORDINATION AND CONTROL
as a business grows, it will become progressively more difficult to coordinate and control of all diff parts of business
could lead to poorer quality to work and business decisions which don’t work well together
DISECONOMIES OF SCALE- MANAGEMENT- COMMUNICATION
w/in a large business, communication can be slow and lose accuracy because of distance and no. of people it has to be passed through