CH. 2: CHEMICALS OF LIFE
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/140
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:03 AM on 2/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
141 Terms
1
New cards
Matter definition
Anything that occupies space
2
New cards
What is chemistry?
the scientific study of **matter** and the interactions of matter
3
New cards
What is composed of matter?
the physical universe (living and nonliving)
4
New cards
What are elements?
substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by ordinary chemical means
5
New cards
How many out of 118 known elements are “naturally occurring”?
92
6
New cards
How many elements are involved in maintaining life?
24
7
New cards
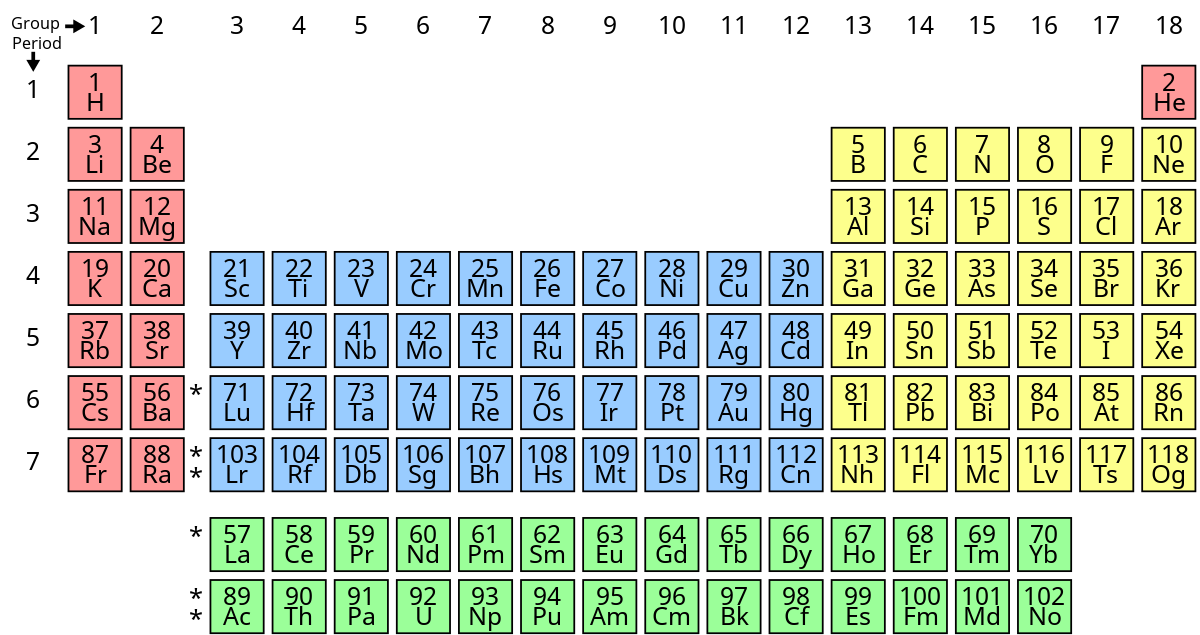
What’s group 1’s name?
alkali metals except hydrogen
8
New cards
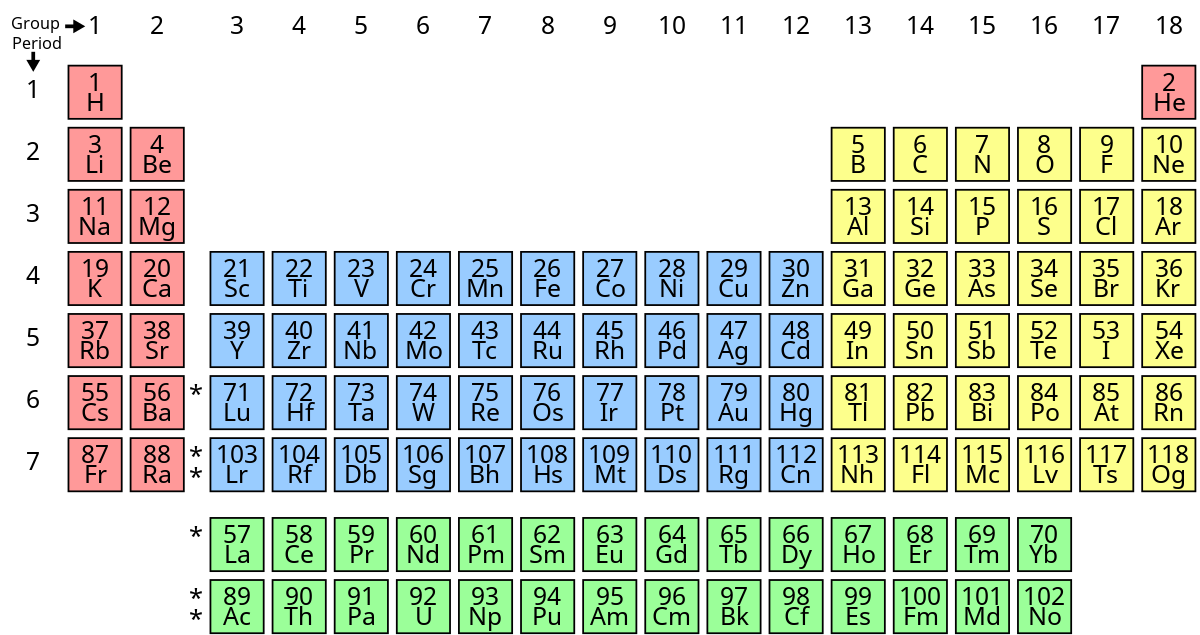
What’s group 2’s name?
alkali earth metals
9
New cards
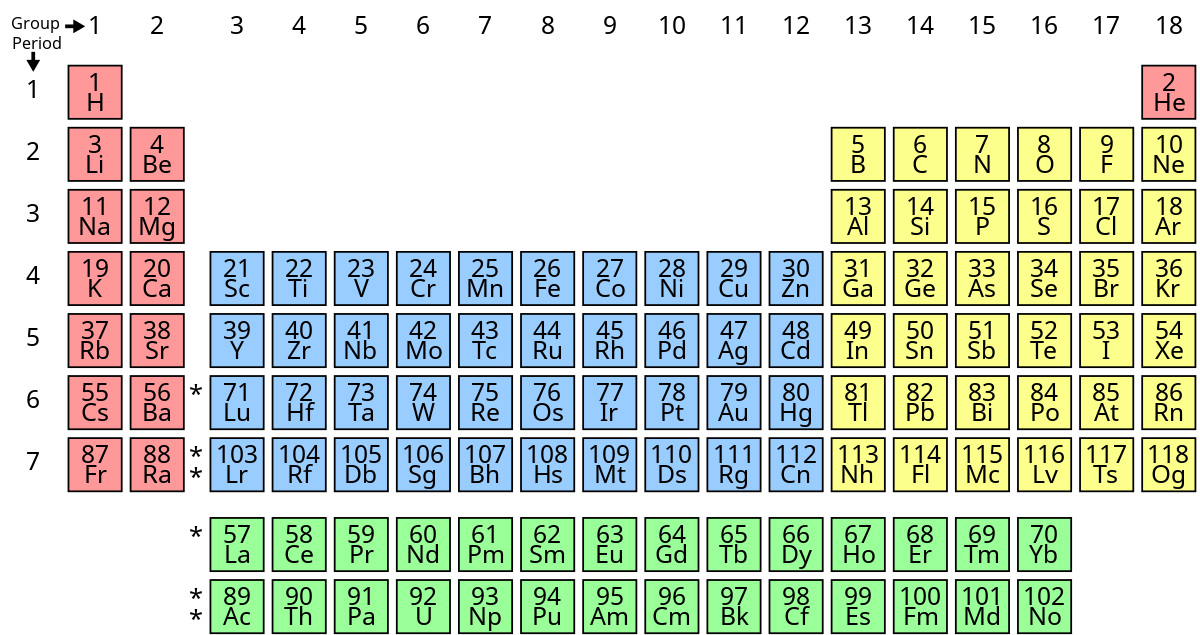
What’s group blue’s name?
transitional metals
10
New cards
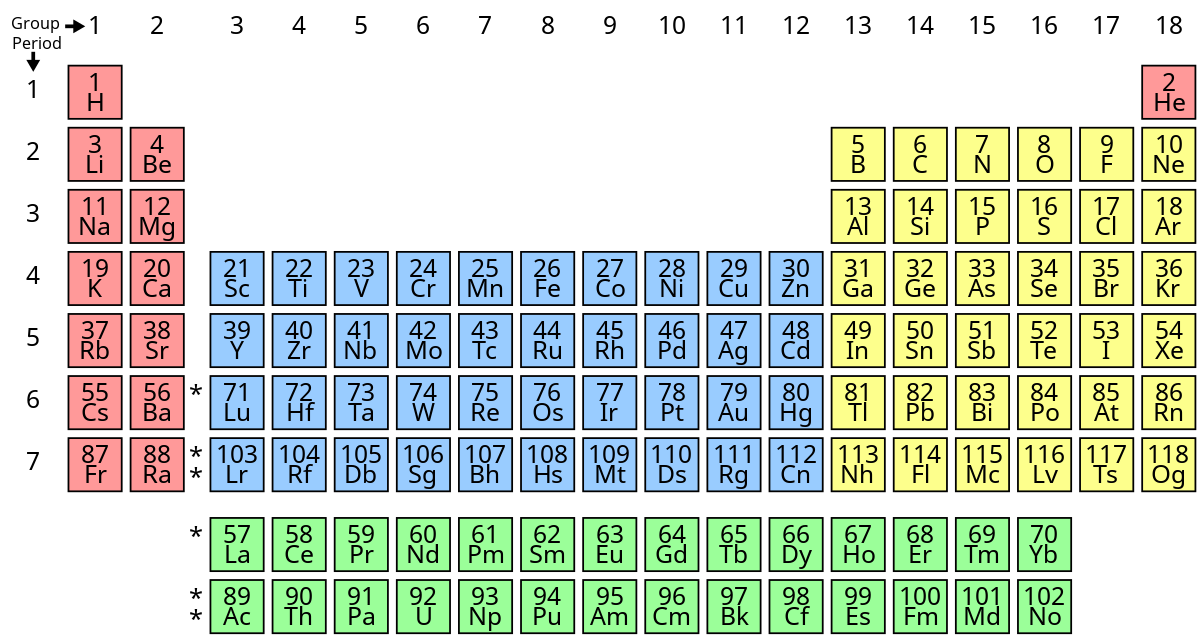
What’s group 7’s name?
halogens
11
New cards
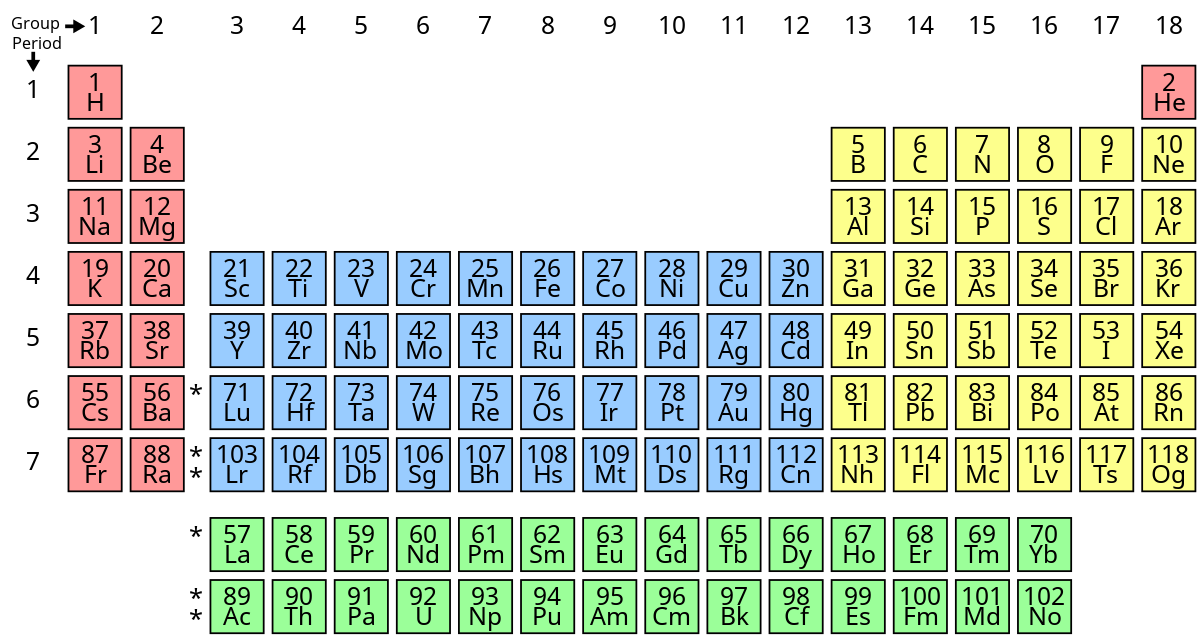
What’s group 0’s name?
noble gases
12
New cards
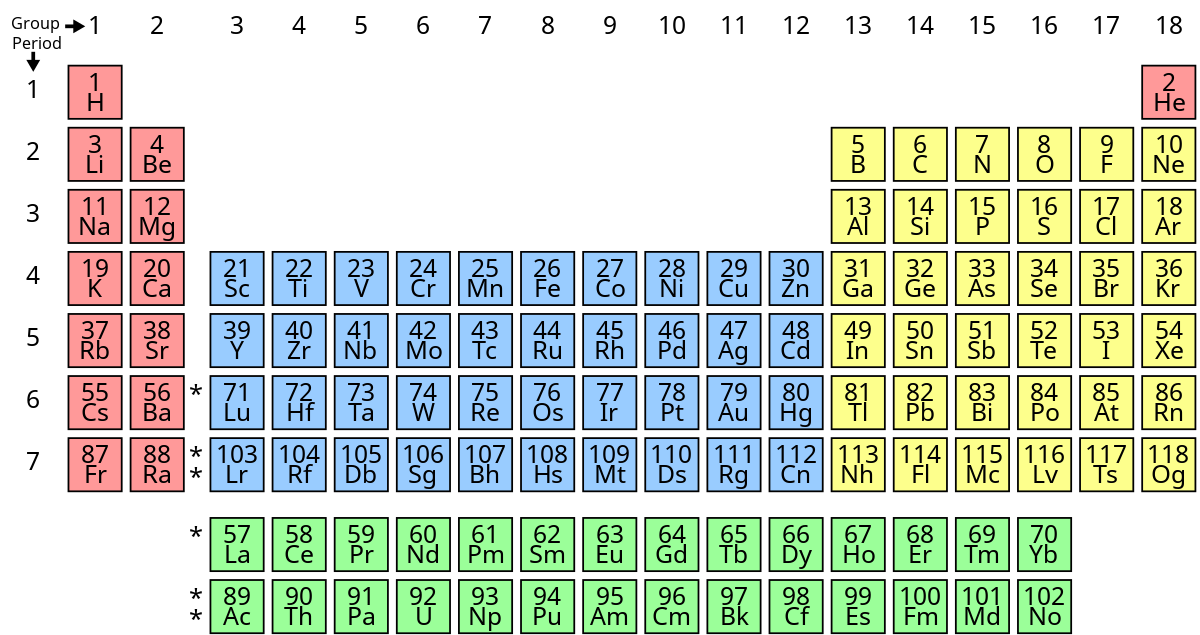
What group does carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur, and selenium belong to?
nonmetals
13
New cards
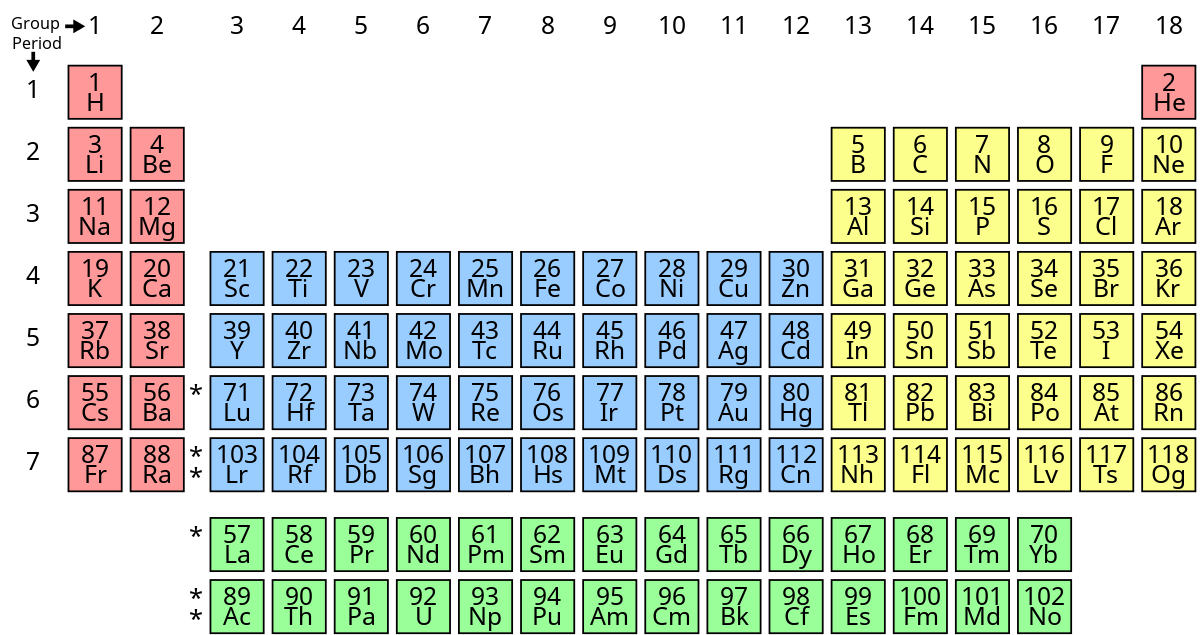
What group does boron, silicon, geranium, arsenic, antimony, tellurium, and polonium belong to?
metalloid
14
New cards
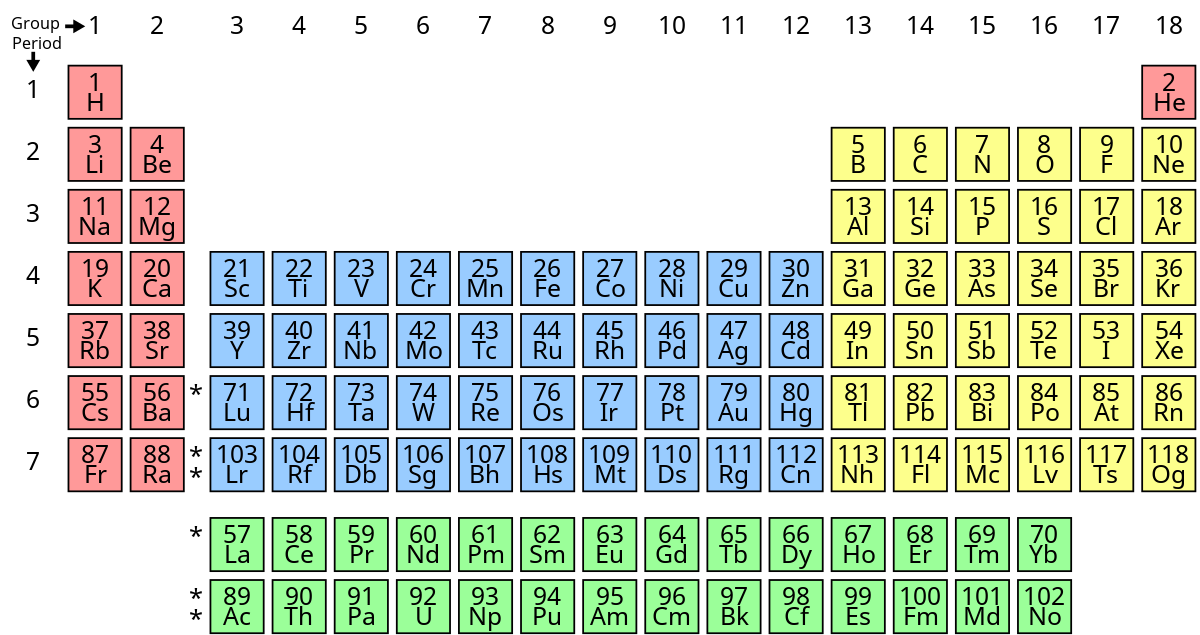
What does aluminum, gallium, indium, tin, thallium, lead, bismuth, ununtrium, flerovium, ununpentium, livermorium belong to?
basic metals
15
New cards
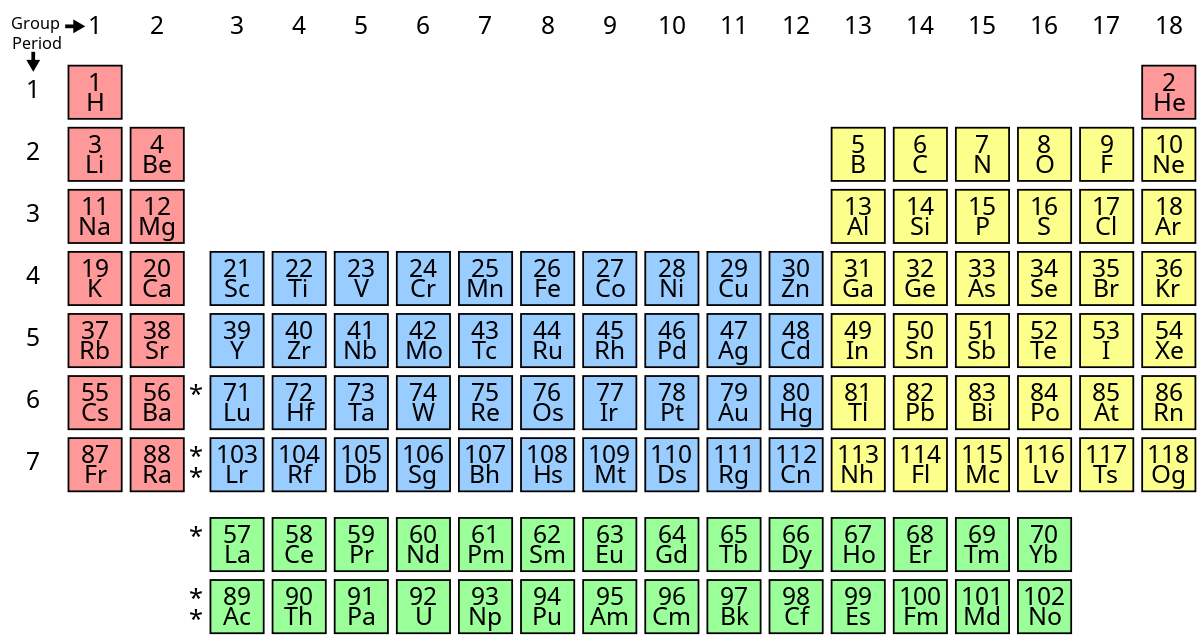
What group does the top green period belong to?
lanthanide
16
New cards
What group does the bottom green period belong to?
Actinide
17
New cards
What are the elements important to physiology?
C, N, O, F, S, O, H, Ca, P
18
New cards
Approximately, 96% is composed of the human body?
oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen
19
New cards
Atom definition
the smallest unit of an element.
20
New cards
What is a proton?
a positively charged particle in an atomic nucleus
21
New cards
What is a neutron?
a noncharged particle in an atomic nucleus.
22
New cards
What is an electron?
a negatively charged particle that revolves around an atomic nucleus
23
New cards
What is a nucleus comprised of ?
protons and neutrons
24
New cards
What are electron shells?
where electrons orbit, or revolve around, the nucleus at high speeds that are located at various distances from the nucleus
25
New cards
What are valence shells?
an atom’s outermost shell of electrons
26
New cards
The overall electrical charge of an atom is _______.
neutral
27
New cards
The number of protons = the number of ________.
electrons
28
New cards
Most neutral atoms are ________
unstable
29
New cards
How do atoms gain stability?
lose, gain, or share electrons
30
New cards
Atomic number definition.
the number of protons (the number of electrons)
31
New cards
Chemical symbol definition.
a shorthand for referring to an element or atom of an element
32
New cards
Atomic mass definition.
the sum of the number of protons and neutrons
33
New cards
What are isotopes?
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons
34
New cards
What are radioisotopes?
certain isotopes of some elements have an unstable nucleus that emits high-energy radiation as it breaks down to form a more stable nucleus
35
New cards
Molecule definition.
a substance formed by two or more atoms bonded together by covalent bonds only
36
New cards
A molecule can have what atoms?
identical or different
37
New cards
Compound definition
a substance formed by the atoms from two or more elements
38
New cards
What bonds are in a compound?
ionic and covalent
39
New cards
What is a chemical formula?
expresses the chemical composition of a substance
40
New cards
Molecular formula definition.
expresses the composition of the molecule or compound using chemical symbols and numbers but it does not describe how the atoms are arranged
41
New cards
Structural formula definition
is a diagram that indicates the composition and number of atoms but also shows how the atoms are linked to each other
42
New cards
Chemical bond definition
a force of attraction between two atoms
43
New cards
Ionic bond formation.
is the formation of 2 ions with opposing charges; cation (+) and an anion (-) that creates a force bond and an ionic compound
44
New cards
What are covalent bonds?
atoms that form molecules by sharing electrons
45
New cards
What are nonpolar covalent bonds?
they are shared electrons that spend equal time revolving between the two atoms
46
New cards
A characteristic of a nonpolar covalent bond?
are **hydrophobic**
47
New cards
What are polar covalent bonds?
they are an unequal sharing of electrons between the two atoms
48
New cards
What are characteristics of a polar covalent bond?
* One atom has greater electronegativity
* are **hydrophilic**
* are **hydrophilic**
49
New cards
What is a hydrogen bond?
weak attractive force between slightly positive and a slightly negative areas
50
New cards
How does a hydrogen bond occur?
occur within the same molecule, between different molecules, and between polar molecules and ions
51
New cards
What is a chemical reaction?
bonds between atoms are formed or broken
52
New cards
Synthesis (anabolic) reaction definition
the combining of smaller molecules to form more complex molecules
53
New cards
Decomposition (catabolic) reaction definition
the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules.
54
New cards
Exchange (rearrangement) reaction
a reaction in which two reactants exchange components to form two different products.
55
New cards
Reversible reaction definition
the reactants and products may convert in both directions
56
New cards
Inorganic substances definition
contain carbon or hydrogen but not both
57
New cards
Organic substances definition
always contain **both** carbon and hydrogen, usually oxygen as well
58
New cards
What is a major inorganic substance?
water
59
New cards
What are some facts about water?
* composes approximately 2/3 of body weight
* occurs in the body as part of an aqueous solution
* the solvent for electrically charged solutes
* serves as a site for chemical reactions
* used for transport of solutes
* serves as a lubricant
* aids in maintaining a constant body temperature
* serves as a reactant in the breakdown (hydrolysis) of organic molecules
* occurs in the body as part of an aqueous solution
* the solvent for electrically charged solutes
* serves as a site for chemical reactions
* used for transport of solutes
* serves as a lubricant
* aids in maintaining a constant body temperature
* serves as a reactant in the breakdown (hydrolysis) of organic molecules
60
New cards
What are water compartments?
specific locations where water is found in the body
61
New cards
Intracellular fluid (ICF) definition
fluid within cells; about 65% of the total body water
62
New cards
Extracellular fluid (ECF) definition
all fluid not in cells; about 35% of the total body water
63
New cards
Interstitial fluid (tissue fluid) definition
fluid in spaces between cells
64
New cards
Plasma definition
fluid portion of blood
65
New cards
Lymph definition
fluid in lymphatic vessels
66
New cards
Transcellular fluids definition
fluid in more limited locations/ more specific locations
67
New cards
What are electrolytes?
Ionic compounds ionize (dissociate) in water, releasing ions
68
New cards
Nonelectrolytes definition
do not ionize when they dissolve in water and are usually organic compounds
69
New cards
Acid definition
increases H+ concentration in solution and releases H+ ions (protons)
70
New cards
Base definition
decreases the H+ concentration in a solution
71
New cards
What is pH?
a measure of the H+ concentration in a solution
72
New cards
What is a pH scale?
indicates the measure of acidity or alkalinity of a solution
73
New cards
What is a buffer?
* Maintain normal pH of body fluids because slight pH changes can be harmful to body cells
* Chemical or chemicals that either picks up or releases H+ to keep a solution’s pH constant
* Chemical or chemicals that either picks up or releases H+ to keep a solution’s pH constant
74
New cards
What are salts?
are ionic compounds that ionize in water but do not produce H+ and OH-
75
New cards
What is the dehydration synthesis?
removes water to join molecules
76
New cards
What is hydrolysis?
adds water to break apart molecules
77
New cards
What are carbohydrates?
an organic molecule composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio.
78
New cards
Carbohydrates are what to the body?
the primary source of nutrient energy for cells of the body
79
New cards
What are monosaccharides?
a simple sugar; a structural unit of carbohydrates.
80
New cards
What is glucose?
the monosaccharide that is the primary energy source for cells
81
New cards
Disaccharide definition
a molecule composed of two monosaccharides chemically combined
82
New cards
Polysaccharide definition
an organic macromolecule formed of many monosaccharide units
83
New cards
What are fructose and galactose?
isomers of glucose
84
New cards
What is an isomer?
molecules with the same molecular formula but different structures
85
New cards
Where are pentose sugars found in?
DNA nad RNA
86
New cards
What is maltose?
aka malt sugar; glucose + glucose
87
New cards
What is sucrose?
aka table sugar, glucose + fructose
88
New cards
What is lactose?
aka dairy sugar; glucose + galactose
89
New cards
What is glycogen?
the polysaccharide that is the storage form for carbohydrates in the body for animals
90
New cards
Starch definition
* plant carbohydrate storage
* a common polysaccharide in foods derived from plants
* a common polysaccharide in foods derived from plants
91
New cards
What are lipids?
* a class of organic macromolecules that includes steroids, triglycerides, and phospholipids
* diverse group composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms
* diverse group composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms
92
New cards
What are triglycerides?
a lipid molecule composed of three fatty acids attached to glycerol; a fat molecule.
93
New cards
What are phospholipids?
a molecule containing two fatty acids and a phosphate group attached to glycerol
94
New cards
What are steroids?
a group of lipids that includes sex hormones and cholesterol.
95
New cards
What forms triglycerides?
Formed of one **glycerol** molecule and three **fatty acid** molecules
96
New cards
What is glycerol?
an organic molecule that is the backbone of triglyceride and phospholipid molecules.
97
New cards
What is a fatty acid?
an organic molecule that forms part of a triglyceride
98
New cards
Triglycerides are nonpolar molecules, meaning that they are ______
hydrophobic
99
New cards
What are triglycerides classified as?
saturated or unsaturated fats
100
New cards
Where are triglycerides found in?
adipose tissue around internal organs and beneath the skin