Biology Test: Unit 3
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
When the volume of a cell increases, its surface area
increases at a slower rate
Surface area is an important factor in limiting cell growth because
The cell may become too large to take in enough food and to remove enough wastes.
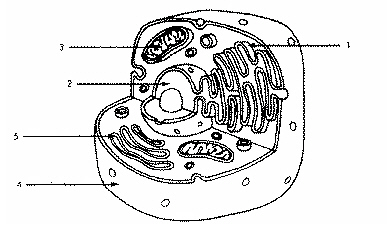
Refer to the illustration above. Which structure immediately identifies this cell as a eukaryote?
Structure 2
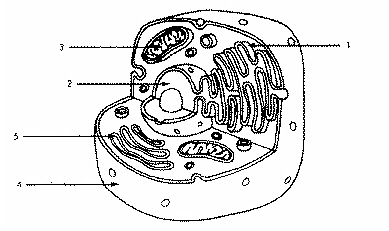
Refer to the illustration above. In eukaryotic cells, DNA is found in
Structure 2
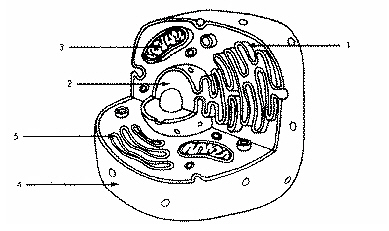
Refer to the illustration above. Structure 2 is
The nucleus.
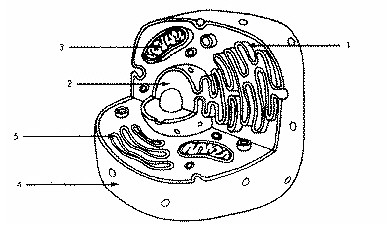
Refer to the illustration above. Which structure produces vesicles filled with proteins?
Structure 1
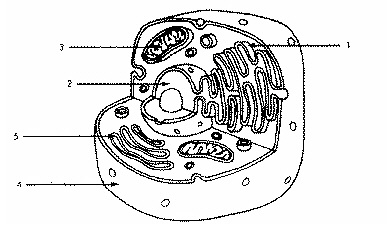
Refer to the illustration above. Structure 5 is
The golgi apparatus
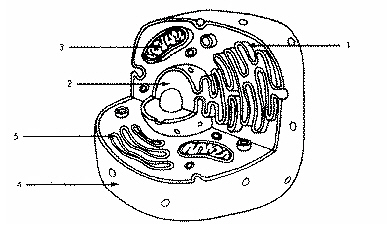
Refer to the illustration above. The cell uses structure 3 to
transport material from one part of the cell to another.
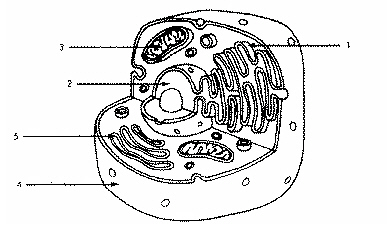
Refer to the illustration above. The cell shown is probably an animal cell because it
does not have a cell wall.
What kind of cytoskeleton fibers could help a cell change shape to fit into a space?
microtubules
The double membrane surrounding the nucleus is called the
nuclear envelope.
The organelle that moves proteins and other substances through the cell is the
endoplasmic reticulum.
The organelle that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins is the
Golgi apparatus. (Function)
Which organelles contain enzymes that break down old cell parts?
lysosomes
Which organelles are involved in defending a cell against viruses?
lysosomes (Virus Question)
Mitochondria and chloroplasts are both sites of
Energy Conversion
Which invention played the biggest role in the discovery of cells by early scientists?
compound microscope
What is the term for the jellylike substance that is contained inside the cell membrane?
cytoplasm (Jellylike)
Specialized structures that work together inside a cell are called
organelles
Which of the following is a network of proteins that supports and gives shape to a cell?
cytoskeleton
Which of the following organelles can be found in the cytoplasm and on the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum?
ribosomes
Which organelle contains enzymes that break down damaged cell parts?
lysosomes (Break Down)
What are the three parts of the cell theory?
All cells come from previous cells. All living things are made of a cell or cells. A cell is the basic structure for all life.
What are three kinds of cytoskeleton in eukaryotic cells
Microfilaments, Microtubules, intermediate filaments.
Where are ribosome parts made and assembled.
In the nucleolus
Phospholipids are molecules that have?
One polar phosphate head and two nonpolar fatty acid tails.
The interior of the lipid bilayer of a cell membrane forms a nonpolar zone that…?
Repels ions and most polar molecules.
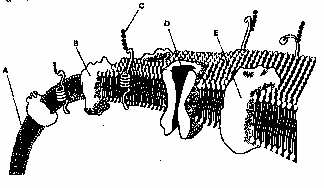
Refer to the illustration above, the structure labeled D is an
Transport Protein.
Proteins in the cell membrane that identify the cell are called…?
Receptor proteins
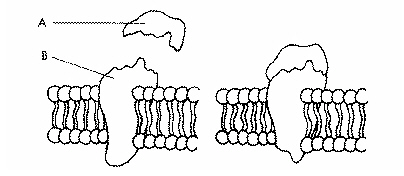
Refer to the illustration above. What happens when the structure labeled A binds to the structure labeled B?
Information is sent into the cell
What change takes place in the cell membrane if a signal molecule causes a transport protein to open.
Permeability change
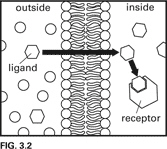
What type of receptor is shown in the diagram in Figure 3.2?
Intracellular
A protein that detects a signal molecule and performs an action in response is called a…?
Receptor
Which model did scientists develop to describe the cell membrane?
Fluid mosaic model
Which word best describes the structure of the cell membrane?
Layered
Which phrase best describes the property of selective permeability?
Some molecules pass
In addition to it’s function as a gatekeeper, what are three other functions of the cell membrane?
Helps the cell maintain structure, homeostasis, and protection.
In the lipid bilayer, what causes one layer of polar heads to face the cell’s cytoplasm and the other layer of heads to face the cell’s surroundings?
The non-polar tails of the lipid bilayer avoid the water which is both in and outside of the cell, which is why there are two layers and why the heads face outwards.
What are the four types of proteins in cell membranes?
Transport proteins, enzymes, receptors, and cell surface markers.
What is one function of the molecules (B) that are embedded in the layers of part A?
They allow the transport of molecules in and or out of the cell.
Diffusion is the movement of a substance…?
From an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Proteins the serve as tunnels for specific substances through the lipid bilayer are?
Channel Proteins
Sugar molecules cross the cell membrane by…?
Facilitated diffusion.
Which of the following does not require energy?
Diffusion
Ion move through ion channels by?
Passive transport
The diffusion of water into or out of a cell is called?
Osmosis
How does water pass through the cell membrane?
Through channel proteins just for water
Which of the following statements about an isotonic solution and a cell is correct?
The solution has the same solute concentration that the cytoplasm does.
Unlike passive transport, active transport…?
Requires energy
The sodium-potassium pump usually pumps
potassium ions into the cell
Proteins and polysaccharides that are too large to move into a cell through diffusion or active transport move in by
Endocytosis
Water enters a cell when the solution surrounding the cell is…?
hypotonic to the cell
Which of the following phrases best describes active transport?
Moves substances against concentration gradient.
Which sentence best describes exocytosis?
A vesicle fuses to the cell membrane and its contents leave the cell.
What happens to the vesicle membrane of a vesicle that migrates to the cell membrane and releases proteins to the outside of the cell.
It combines with the rest of the cell
What is the difference between how a molecule crosses the cell membrane in simple diffusion and in facilitated diffusion?
In facilitated diffusion, the molecule is transferred by transport proteins.
Why are some water molecules not free to move across the cell membrane?
Water molecules are polar and have a hard time passing through the lipid bilayer.
A biologist conducts an experiment designed to determine whether a particular type of molecule is transported into cells by simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, or active transport. He collects the following information:
I disagree it can accumulate inside of the cell and the molecule is small, I think it's simple diffusion.
Distinguish between facilitated diffusion and active transport.
Facilitated diffusion uses transport proteins to diffuse into the cell and active transport uses the pumps.
Why is it dangerous for humans to drink seawater?
Too much salt and bacteria can destroy the cells in our body. The salt can absorb most of the water in our bodies.