The Human Body: An Orientation
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering core anatomy and physiology terms, body organization, directional terms, planes, and body cavities.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Anatomy
Study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another.
Physiology
Study of the function of body parts and how they work to carry out life-sustaining activities.
Gross (macroscopic) anatomy
Study of large, visible structures.
Microscopic anatomy
Study of structures too small to be seen with the naked eye.
Developmental anatomy
Study of anatomical and physiological development throughout life.
Chemical level
Atoms, molecules, and organelles—the simplest level of structural organization.
Cellular level
Single cell as the basic unit of life.
Tissue level
Groups of similar cells that perform a common function.
Organ level
An organ contains two or more types of tissues.
Organ system level
Organs that work closely together to accomplish a common purpose.
Organismal level
All organ systems working together to make the whole organism.
Integumentary System
Forms the external body covering; protects tissues; synthesizes vitamin D; houses receptors and glands.
Skeletal System
Protects and supports organs; framework for movement; blood cells form in bones; stores minerals.
Muscular System
Allows manipulation of the environment, locomotion, posture, and heat production.
Nervous System
Fast-acting control system; responds to changes by activating muscles and glands.
Endocrine System
Glands secrete hormones that regulate growth, reproduction, and metabolism.
Cardiovascular System
Blood vessels transport blood; the heart pumps blood.
Lymphatic System/Immunity
Picks up leaked fluid, houses lymphocytes, and mounts immune responses.
Respiratory System
Keeps blood supplied with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
Digestive System
Breaks down food into absorbable units for distribution in the body.
Urinary System
Eliminates nitrogenous wastes and regulates water, electrolytes, and acid-base balance.
Female Reproductive System
Production of offspring; ovaries produce eggs; mammary glands nurture the newborn.
Male Reproductive System
Production of offspring; testes produce sperm; delivery of sperm via ducts and glands.
Anatomical Position
Standard position: body erect, feet apart, palms facing forward, thumbs outward.
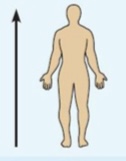
Superior (cranial)
Toward the head end or upper part of a structure.
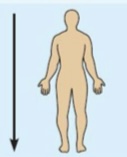
Inferior (caudal)
Away from the head end; toward the lower part of a structure.
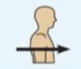
Anterior (ventral)
Toward or at the front of the body.
Posterior (dorsal)
Toward or at the back of the body.
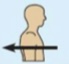
Medial
Toward or at the midline of the body; inner side.
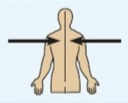
Lateral
Away from the midline; outer side.
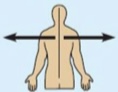
Intermediate
Between a more medial and a more lateral structure.
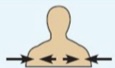
Proximal
Closer to the origin of the body part or point of attachment.
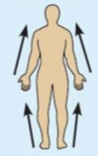
Distal
Farther from the origin of a body part or point of attachment.
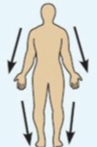
Superficial (external)
Toward or at the body surface.
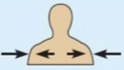
Deep (internal)
Away from the body surface; more internal.

Axial region
Head, neck, and trunk.
Appendicular region
Limbs (arms and legs).
Sagittal plane
A plane that divides the body vertically into right and left parts.

Midsagittal (Median) plane
A sagittal plane that divides the body exactly in the midline.
Parasagittal plane
A sagittal plane that is offset from the midline.
Frontal (Coronal) plane
Divides the body vertically into anterior and posterior parts.

Transverse (Horizontal) plane
Divides the body horizontally into superior and inferior parts.

Oblique section
A cut at an angle other than 90 degrees to the vertical plane.
Dorsal Body Cavity
Cavity protecting the nervous system; includes the cranial and vertebral cavities.
Cranial cavity
Encases the brain.
Vertebral (spinal) cavity
Encases the spinal cord.
Ventral Body Cavity
Cavities that house internal organs (viscera); divided by the diaphragm into thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities.
Thoracic cavity
Contains lungs and other thoracic organs; divided into pleural cavities and mediastinum; houses pericardial cavity.
Pleural cavities
Two cavities surrounding each lung.
Mediastinum
Contains pericardial cavity and other thoracic organs.
Pericardial cavity
Encloses the heart.
Peritoneum
Membrane associated with the abdominopelvic cavity.
Abdominopelvic cavity
Cavity that includes the abdominal and pelvic cavities.
Abdominal cavity
Contains stomach, intestines, spleen, liver.
Pelvic cavity
Contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum.
Pericardium
Membrane around the heart.
Pleurae
Membranes around the lungs.
Peritoneum
Membrane associated with the abdominal cavity.
Synovial cavities
Joint cavities lined with synovial membranes.
Oral cavity
Digestive cavity within the mouth.
Nasal cavity
Cavity within the nose.
Orbital cavities
House the eyes.
Middle ear cavities
Small cavities within the temporal bones housing auditory structures.