Biology Final
1/163
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
164 Terms
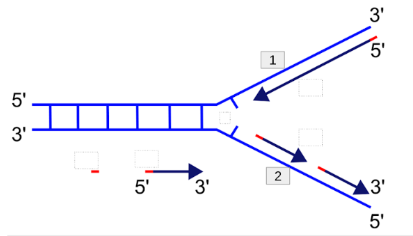
Which stand is the leading strand?
1
DNA controls the formation of ____ that allow you to express your ___
proteins, traits
What does this diagram show
DNA contains instructions for making proteins
How does the DNA in body cells compare to each other?
The DNA in body cells is the same, but cells use different parts of DNA
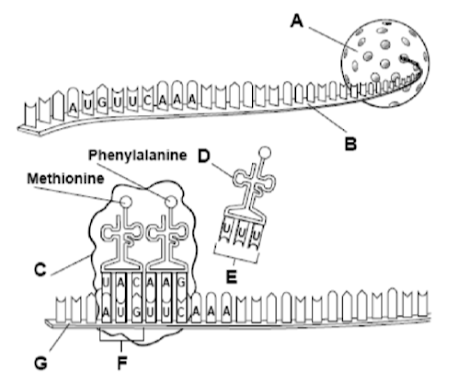
Identify each label in the diagram.
Cells build specific proteins, like enzymes, based on the....
sequence of nitrogen bases in the DNA
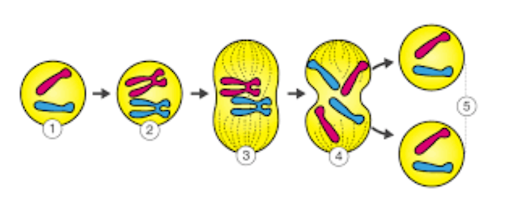
The diagram shows mitosis. What is the result of mitosis?
Two daughter cells with the same DNA as the parent cell.
Which of the following is true of interphase?
Interphase is longer than mitosis.
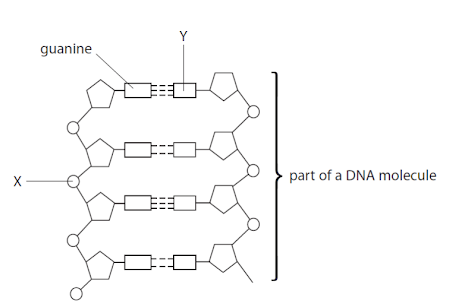
Component Y is a . . .
Nitrogen Base
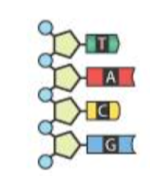
What is the complementary DNA Strand?
adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine
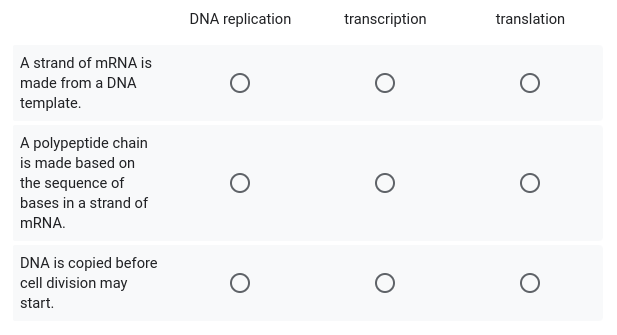
Match the definition with the name of the process.

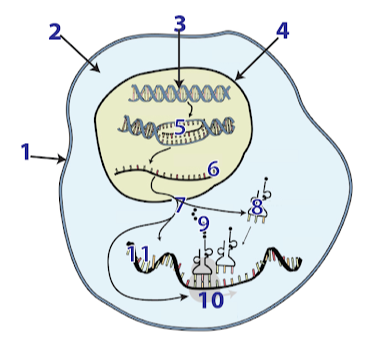
Match the terms with the parts labeled in the diagram of a cell.

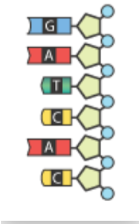
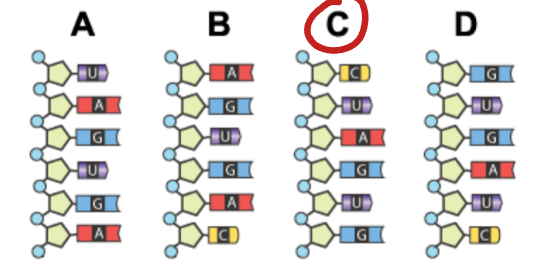
Which mRNA sequence complements the DNA sequence below?
Sequence C
Which statement is true about the nitrogen bases in DNA and RNA?
Uracil is found in RNA only. Thymine is found in DNA only.
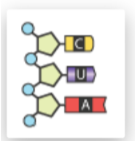
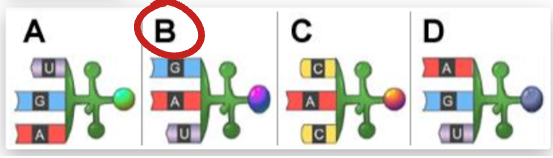
Which tRNA anticodon will complement this mRNA codon?
Anticodon B
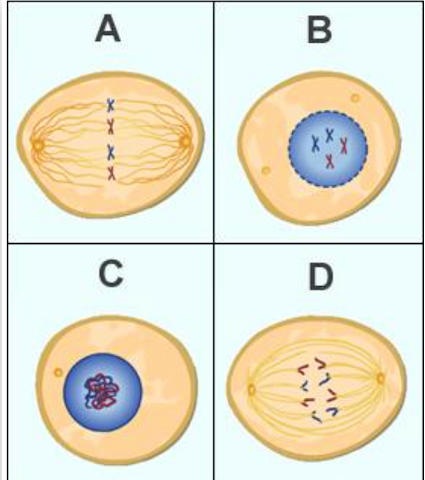
Place the four images from the cell cycle in the correct chronological order.
image C, image B, image A, image D
If you were to examine a sample of 1000 cells, in which of the phases listed below would you expect to find most of the cells?
Interphase
What is the role of DNA?
Contains instructions for making proteins that run cellular processes.
Both DNA and RNA:
contain phosphate groups
The result of replication is two DNA molecules:
each with one original strand and one new strand
What is the function of DNA in cells?
It stores the information that directs the ribosomes in protein synthesis.
Each strand of the DNA molecule can be used to make another strand during replication. This is because the two sides are ______ to each other.
Complementary
Griffith’s transformation experiments
caused harmless bacteria to become deadly.
Using radioactive tracers to determine the interactions of bacteriophages and their host bacteria, Hershey and Chase demonstrated without question that
DNA is the molecule that stores genetic information in cells.
All of the following are true about the structure of DNA except
short strands of DNA are contained in chromosomes inside the nucleus of a cell.
Which of the following is not part of a molecule of DNA?
ribose
The part of the molecule for which deoxyribonucleic acid is named is the
phosphate group.
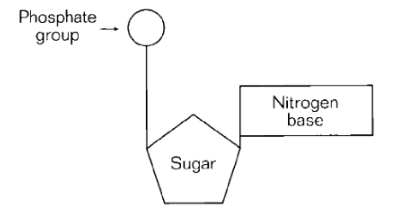
The entire molecule shown in the diagram above is called a(n)
nucleotide.
Purines and pyrimidines are
classification groups for nitrogen bases.
The scientists credited with establishing the structure of DNA are
Watson and Crick.
X-ray diffraction photographs by Wilkins and Franklin suggested that
DNA molecules are arranged as a tightly coiled helix.
During DNA replication, a complementary strand of DNA is made for each original DNA strand. Thus, if a portion of the original strand is CCTAGCT, then the new strand will be
GGATCGA
The attachment of nucleotides to form a complementary strand of DNA
is accomplished by DNA polymerase
Which of the following is not true about DNA replication?
The process is catalyzed by enzymes called DNA mutagens.
The enzymes that unwind DNA are called
DNA helicases
RNA differs from DNA in that RNA
All of the above
RNA is chemically similar to DNA except that its sugars have an additional oxygen atom, and the base thymine is replaced by a structurally similar base called
uracil
Transcription proceeds when RNA polymerase
binds to a strand of DNA.
Each nucleotide triplet in mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid is called a(n)
codon
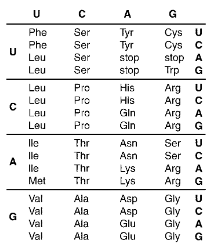
What is the portion of the protein molecule coded for by the mRNA: CUCAAGUGCUUC ?
Leu—Lys—Cys—Phe
What is the correct sequence of anticodons for the codons in the mRNA: CUCAAGUGCUUC?
GAG—UUC—ACG—AAG
Transfer RNA
carrier RNA.
Transfer RNA
carries an amino acid to its correct codon
During translation, the amino acid detaches from the transfer RNA molecule and attaches to the end of a growing protein chain when
the transfer RNA anticodon binds to the messenger RNA codon.
Cells must control gene expression so that
their genes will be expressed only when needed.
Enzymes that cut DNA molecules at specific places
are restriction enzymes.
Watson and Crick built models that demonstrated that
DNA is made of two strands that twist into a double helix.
The enzymes responsible for adding nucleotides to the exposed DNA template bases are
DNA polymerases.
During transcription, the genetic information for making a protein is “rewritten” as a molecule of
messenger RNA.
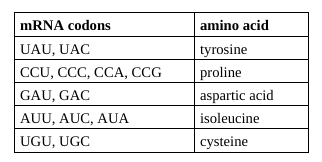
Refer to the illustration above. Suppose that you are given a protein containing the following sequence of amino acids: tyrosine, proline, aspartic acid, isoleucine, and cysteine. Use the portion of the genetic code given to determine which of the following contains a DNA sequence that codes for this amino acid sequence.
ATGGGTCTATATACG
In order for translation to occur, mRNA must migrate to the
ribosomes
Sex cells, found in the reproductive organs of men and women, are known as ___________________.
Gametes
Which of the following describes a homologous pair?
A pair of chromosomes that have the same genes, but different alleles. One is inherited from each parent.
The process that produces gametes is called ___________.
meiosis
Which of the following processes help to produce genetic variation in offspring? Select all the apply.
independent Assortment of homologous chromosomes during metaphase I of meiosis
Crossing Over before meiosis I
. How many rounds of cell division does the original cell undergo during meiosis?
2

Vocabulary: Match the vocabulary term with the correct definition.
1. What is the man’s genotype?
In humans, brown eyes are dominant over blue. A brown-eyed man marries a blue-eyed woman and they have three children, two of whom are brown-eyed and one of whom is blue-eyed.
Bb
2. What are the genotypes of the Brown-eyed children?
In humans, brown eyes are dominant over blue. A brown-eyed man marries a blue-eyed woman and they have three children, two of whom are brown-eyed and one of whom is blue-eyed.
Bb
3. What is the genotype of the mother?
In humans, brown eyes are dominant over blue. A brown-eyed man marries a blue-eyed woman and they have three children, two of whom are brown-eyed and one of whom is blue-eyed.
bb
4. What term best describes the genotype of the father?
In humans, brown eyes are dominant over blue. A brown-eyed man marries a blue-eyed woman and they have three children, two of whom are brown-eyed and one of whom is blue-eyed.
Heterozygous
If Parent A (Type AB blood) is crossed with Parent B (Type O blood), which of the following is not a possible offspring for that cross?
Offspring A- Type O blood
If a somatic (body) cell in an organism has 48 chromosomes, how many chromosomes would an egg cell contain?
24
If a person has type AB blood then they have an A allele and a B allele in their genome. This means that…
Both the A and B allele are expressed
A red snapdragon and a white snapdragon are crossed. All of the resulting snapdragons are pink. This is an example of what pattern of inheritance?
Incomplete Dominance
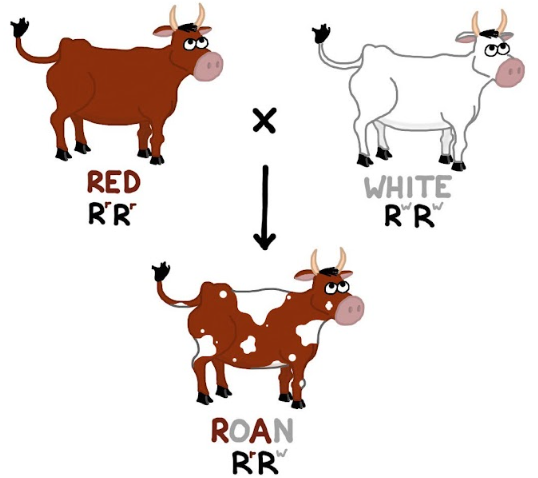
What pattern of inheritance is demonstrated by this image?
codominance
In cattle, roan color (mixed red and white hairs) occurs in the heterozygous offspring of red and white homozygotes. Cross 2 Roan cattle. What percentage of the off spring will have Roan coloring?
50%
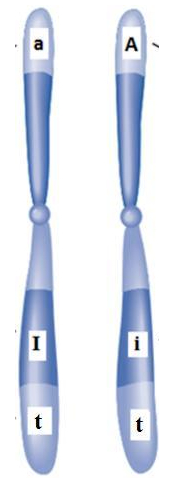
Which of the following statements describes the genotype of this homologous pair?
Heterozgyous for genes A and I. Homozygous recessive for gene T
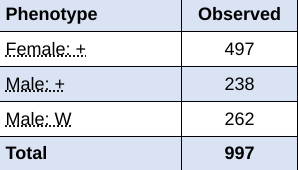
You cross two red-eye flies. Red is dominant to white, and the gene for eye color is found on the X chromosome. The image below shows the results of the cross. What are the phenotype probabilities?
50% female red eyes, 25% male red eyes, 25% male white eyes
Color-blindness is a RECESSIVE, sex-linked disorder. Rob is colorblind, and Linda carries the gene for color-blindness. What is the probability that their children could be carriers?
50%
A woman who is heterozygous for Type A blood married a man with Type B blood, and they had a child with type O blood. Which 2 statements are true: (Disregard positive and negative blood type)
The father must be heterozygous for type B blood.
Each new child from this couple will have a 25% chance of being type A, B, AB or O
. In fruit flies, eye color is located on the X chromosome. Red eye color is dominant to white eyes. Cross a Heterozygous red eye female with a red-eyed male. What is the probability that any of the offspring will have white eyes?
25%
Snapdragons are flowers. Their flower colors follow Incomplete Dominance rules for inheritance. Flowers can be white, red, or pink. What do you expect the GENOTYPE ratio to be if two pink snapdragons were to produce offspring?
1 RR: 2 RW: 1 WW
The scale-color of a made-up lizard is inherited as a codominant trait. The homozygous phenotypes of the trait are yellow scales, and blue scales. What do you expect the heterozygous form of the trait to look like?
some yellow scales, and some blue scales
Different versions of genes for a trait, such as the gene for brown eyes and the gene for green eyes, are called _______
Alleles
In reality, most traits in humans, and other organisms, are too complicated to predict using Punnett Squares. These traits are controlled by more than one gene, which is called a __________ pattern of inheritance?
Polygenic
If a disease was sex-linked recessive, what would you expect to see, on average, in the family over generations?
More males would have the disease than females
A father can pass an x-linked recessive trait to his son.
false
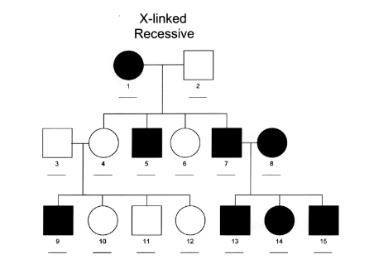
The pedigree below shows a sex-linked recessive disorder called hemophilia. Use the pedigree to answer the questions. Shaded individuals have the disorder. You can use the letters H and h to indicate alleles.
What is the genotype of individual number 1?
X^h X^h
The pedigree below shows a sex-linked recessive disorder called hemophilia. Use the pedigree to answer the questions. Shaded individuals have the disorder. You can use the letters H and h to indicate alleles.
What is the genotype of individual number 3?
X^H Y
The pedigree below shows a sex-linked recessive disorder called hemophilia. Use the pedigree to answer the questions. Shaded individuals have the disorder. You can use the letters H and h to indicate alleles.
What is the genotype of individual number 4?
X^H X^H
What is the probability of Individual #14 having children with hemophilia if their spouse has no family history of this disorder?
50%
What is the probability of Individual #10 being a carrier of the Hemophilia allele?
0%
How many bands would be expected in gel electrophoresis for a sample that has one mutation in the p53 gene?
two bands
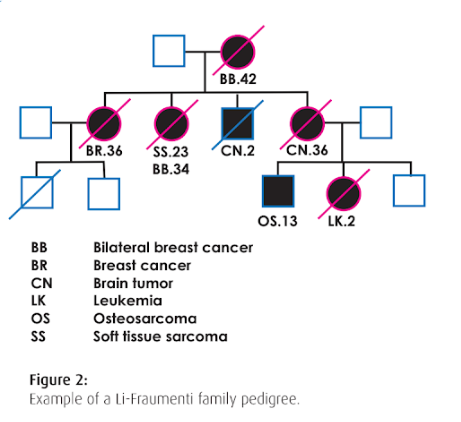
Which generation shows that a son died as an infant from cancer according to the pedigree?
Generation 2
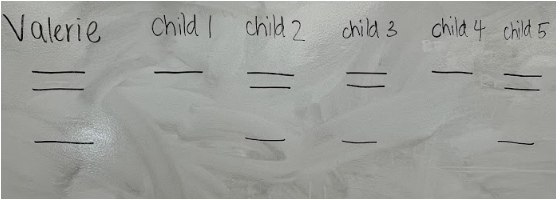
Valerie's children have decided to undergo genetic testing for the P53 gene. Below are the results from their gel electrophoresis genetic test. Which of the statements below are true?
Children 2, 3, and 5 have Li-Fraumeni Syndrome
Li-Fraumeni Syndrome is best characterized as which of the following?
A mutation in the p53 gene that a person could develop over the course of their lifetime
Which pattern of inheritance does Li-Fraumeni Syndrome follow?
Autosomal dominant
Separation of homologues occurs during
meiosis I.
The difference between anaphase of mitosis and anaphase I of meiosis is that
crossing-over occurs only in anaphase of mitosis.
When crossing-over takes place, chromosomes
exchange corresponding segments of DNA.
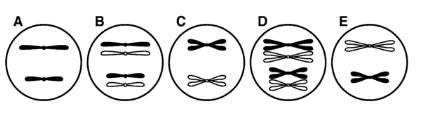
Using the information you have learned about cell reproduction, infer answers to the questions below about a cell with a diploid number of 4 chromosomes. Select from among the diagrams below, labeled A, B, C, D, and E, to answer the questions.
Which of the diagrams above depicts a cell at the end of meiosis I?
E
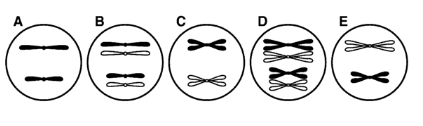
Using the information you have learned about cell reproduction, infer answers to the questions below about a cell with a diploid number of 4 chromosomes. Select from among the diagrams below, labeled A, B, C, D, and E, to answer the questions.
Which of the diagrams above depicts a cell at the end of meiosis 2?
A
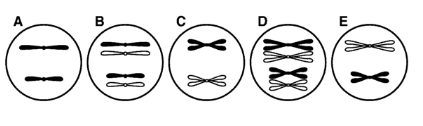
Using the information you have learned about cell reproduction, infer answers to the questions below about a cell with a diploid number of 4 chromosomes. Select from among the diagrams below, labeled A, B, C, D, and E, to answer the questions.
Which of the diagrams above depicts a cell at the end of mitosis?
B
Which of the following does not provide new genetic combinations?
cytokinesis
During cytokinesis in the female, what divides unequally?
cytoplasm
Mendel's law of segregation states that
pairs of alleles separate independently of one another after gamete formation.
The phenotype of an organism
is the physical appearance of a trait.
If an individual possesses two recessive alleles for the same trait, the individual is said to be
homozygous for the trait.
An individual heterozygous for a trait and an individual homozygous recessive for the trait are crossed and produce many offspring that are
of two different phenotypes.