BIBC 100 EXAM 1
1/179
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
180 Terms
Study of the molecular composition of living cells
Organization of biological molecules within the cell, and the structure and function of these biological molecules
Biological marcomolecules
Proteins, polysaccharides, and polynucleic acids (DNA and RNA)
Proteins
The workhorse molecule of life
Nucleic acids
Make up genetic information and encode proteins
Lipids
Utilized for energy, signaling and structural organization of the cell
Carbohydrates
Energy storage and structural components
Water
Most abundant molecule in our body and cells
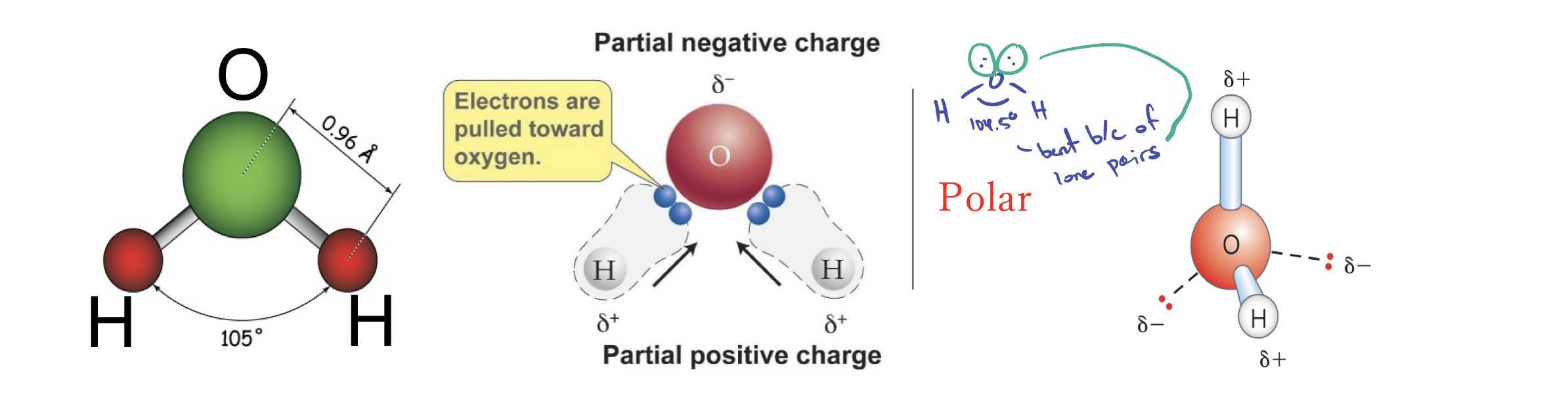
Structure of water (H2O)
Bent, polar, and has a bond angle of 105 degrees
Macromolecule relationship with water
Non-covalent
Covalent interactions
Pairs of electrons shared by two atoms
Noncovalent interactions
Not involved in sharing a pair of electrons
The four types non-covalent interactions
Hydrogen bonding, ionic interactions, van der waals interaction, and hydrophobic interactions
What kind of interaction is hydrogen bonding?
Dipole-Dipole interaction
Why is H2O arranged as a tetrahedral?
Due to repulsions of the shared/unshared electrons
What does tetrahedral of the H2O allow?
Allow interaction with up to four other water molecules.
Why are hydrogen bonds weaker than O-H covalent bonds?
Hydrogen bonds are longer making it weaker.
How come water has a high melting, boiling, and heat of vaporization?
There are multiple hydrogen bonds summing to make water highly cohesive.
Ion-Ion interactions
Between two oppositely charged ions
Hydration
Water molecule form a cell around cation (Oxygen surround atom) and anions (hydrogen surround atom)
Van Der Waals Interactions (London dispersion forces)
Transient, induced dipole-dipole interactions, weak, universal, and require any two atoms within proximity
Van der waals diameter
Distance where repulsive force = attractive force
Van der Waals radius
Half the distance of van der waals diameter
Hydrophobic interactions
Nonpolar molecules aggregating together to avoid water
Entropy
State of disorder/randomness
What happens to the entropy of a closed system?
Increase spontaneously
What occurs when non-polar molecules enter water?
Water create cages around the non-polar molecules by holding onto other water molecules
More separate water cages
More ordered water and less entropy
Less separate water cages (more surface area)
Less ordered water and more entropy
Polar molecules (Hydrophilic)
Have bonds between atoms that differ greatly in electronegativity (has all interactions except for hydrophobic)
Nonpolar molecules (Hydrophobic)
Have bonds between atoms that don’t differ greatly in electronegativity (has hydrophobic and van der waals interacttion)
Amphipathic molecule
Have both polar and nonpolar bonds (has all weak interactions)
How does hydrophobic interaction cause the formation of lipid bilayer and micelles?
Effects amphipathic lipid molecules since they have a polar (head) and nonpolar region (tail) allowing water molecules to interaction with the head while the tails are caged causing the tails to congregate together to form micelles and lipid bilayers.
How does weak molecular interactions effect protein folding?
Proteins fold because of the hydrophobic residue causing it to be in the inner fold of the protein and then the charged/polar amino acid will be on the surface of the fold so they can electrostatically interact with each other.
How does weak interactions cause stability for bio molecules?
Multiple interactions causes more stability since the complex will be less likely to be disrupted due to the vast amount interactions weak interactions.
Draw an amino acid with alpha C and identify the 4 substituents
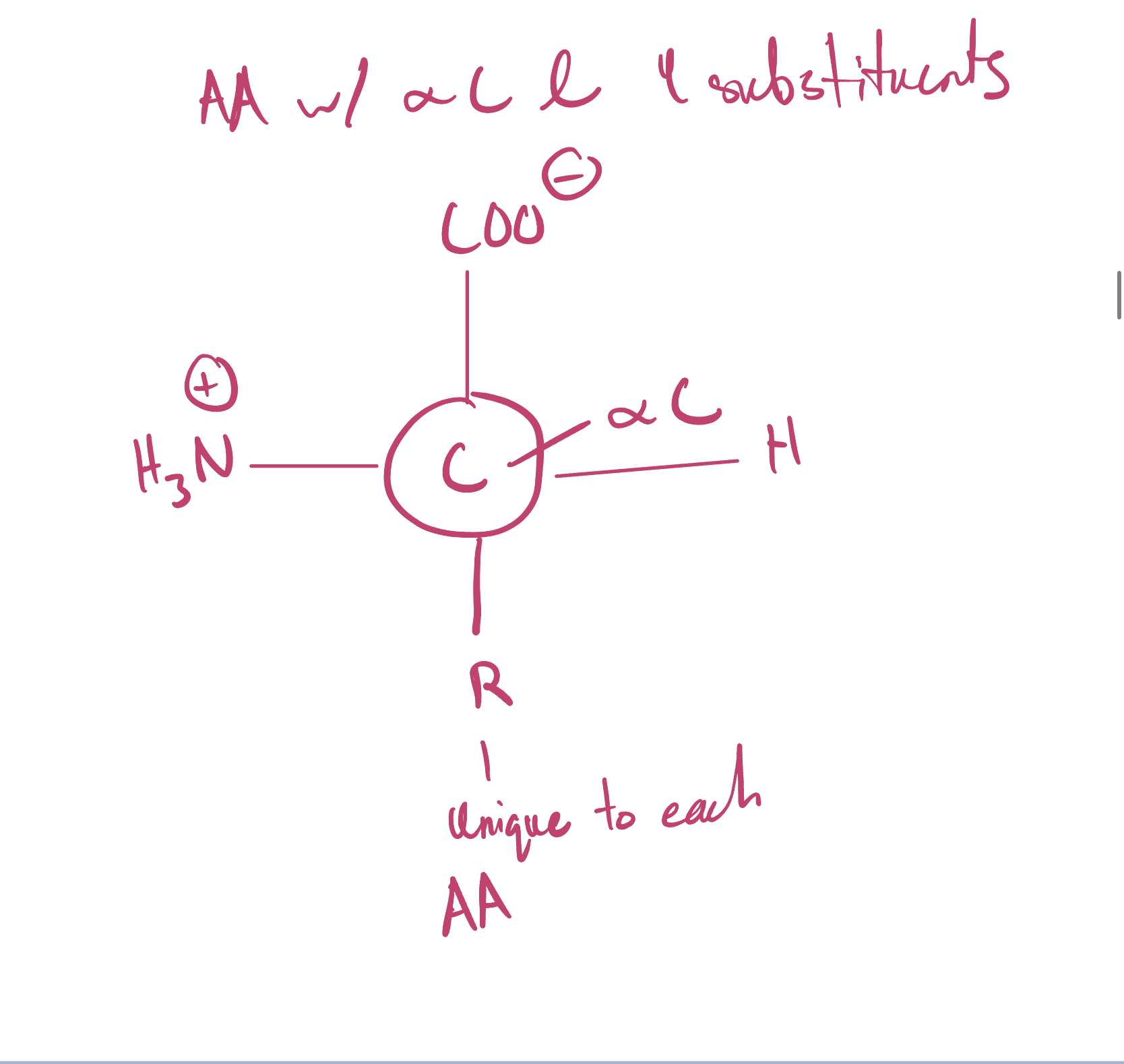
What amino acid(s) are achiral and chiral?
All amino acids are chiral except for Glycine since two of the four substituents are the same.
What specific amino acid enantiomer exist in proteins?
L-Amino acids
At pH less than 2 what groups are protonated?
The amino and carboxyl group
At pH 7.4 what groups are protonated?
Amino group
At pH greater than 10, which groups are protonated?
None
What causes the acid to be more likely to give out protons?
Lower the pKa causes the higher Ka making it more likely to give out protons.
What is the pKa of the carboxyl group?
Has a pKa of 2 causing it to give up its’ proton at a pH greater than 2.
What is the pKa of the amino group?
Has a pKa of 9 causing it to be protonated until the pH is at a pH of 9 or above.
The pKa of Lysine’s amino group?
10.5
The pKa of Arginine’s amino group?
12.5
The pKa of Histidine’s amino group?
6.0
The pKa of Aspartate’s carbpxyl group?
3.7
The pKa of Glutamate’s carboxyl group?
4.3
Zwitterion
Has both positively and negatively charged groups with the net charge being zero
How can amino acids can act as a proton donor?
Can give proton on amino group at a higher pH (9).
How can amino acids act as a proton acceptor?
Can accept proton on the carboxyl group at a lower pH (2).
Buffers
Solutions that can resist change in pH whne acid or bases are added.
pI
The pH when the net electric charge of a molecule is zero
Equation for pI
pI = (pK1 + pK2)/2
Acetylation (Lys)
Key for epigenetic regulation, histone structure and interactions with DNA
Carboxylation (Glu)
Increases affinity for calcium because it is postively charged and wants to attach
Glycosylation (Ser, Thr, Asn)
Protein stability, recognition. At least 40 known human diseases are caused by mis-glycosylation
Phosphorylation (Thr, Ser, Tyr in eukaryotes, and His in bacteria and plants)
Regulation of enzyme activity, protein/proetin interactions, and signal transduction
Ubiquitination (Lys)
Protein degradation
Lipidation (Glys, Cys)
Target the proteins to membranes
How does disulfide bonds stabailize 3D structure of proteins?
Close in proximity and form bond with same polypeptide or different polypeptides stabilizing the structure of proteins
What are the 3 common properties used to separate proteins?
Size, charge, and affinity for a ligand
Size exclusion Chromatography
Column filled with beads that allow small molecules to enter but exclude large molecules so smaller molecules will elute slower while bigger molecules will elute faster.
Ion exchange chromatography
Columns have charged resin where depending on the charge of the resin, the charge molecules will move faster if it is the same charge as resin due to repulsion or slower due to having opposite charges causing attrcation
Affinity Chromatography
Columns filled with resin that are coupled to ligands that capture tagged protein of interest allowing proteins that are not of interest to travel through and proteins of interest to be eluted at a high concentration.
Which bonds in a polypeptide chain have a partial double bond character?
The C-N bond in the polypeptide bond.
What does it mean to have a double bond character?
When bond has the potential to form a double bond due to resonance causing the bond to be shorter than neighboring bonds, and it cannot rotate.
Why can’t polypeptide bonds (C-N) character bonds rotate?
Because of its rigid double bond character.
What are the dihedral angles?
Phi and Psi
Phi
Rotation angle of N-C alpha bond
Psi
Rotation angle of C-C alpha bond
What hinders the angle of peptide bond angles?
Steric hinderance between backbone and side chains
Amino acid that contribute to the Ramachadran diagrams
Glycine, Proline, and pre-proline
Identify secondary structure associated with regions of a Ramachandran diagram
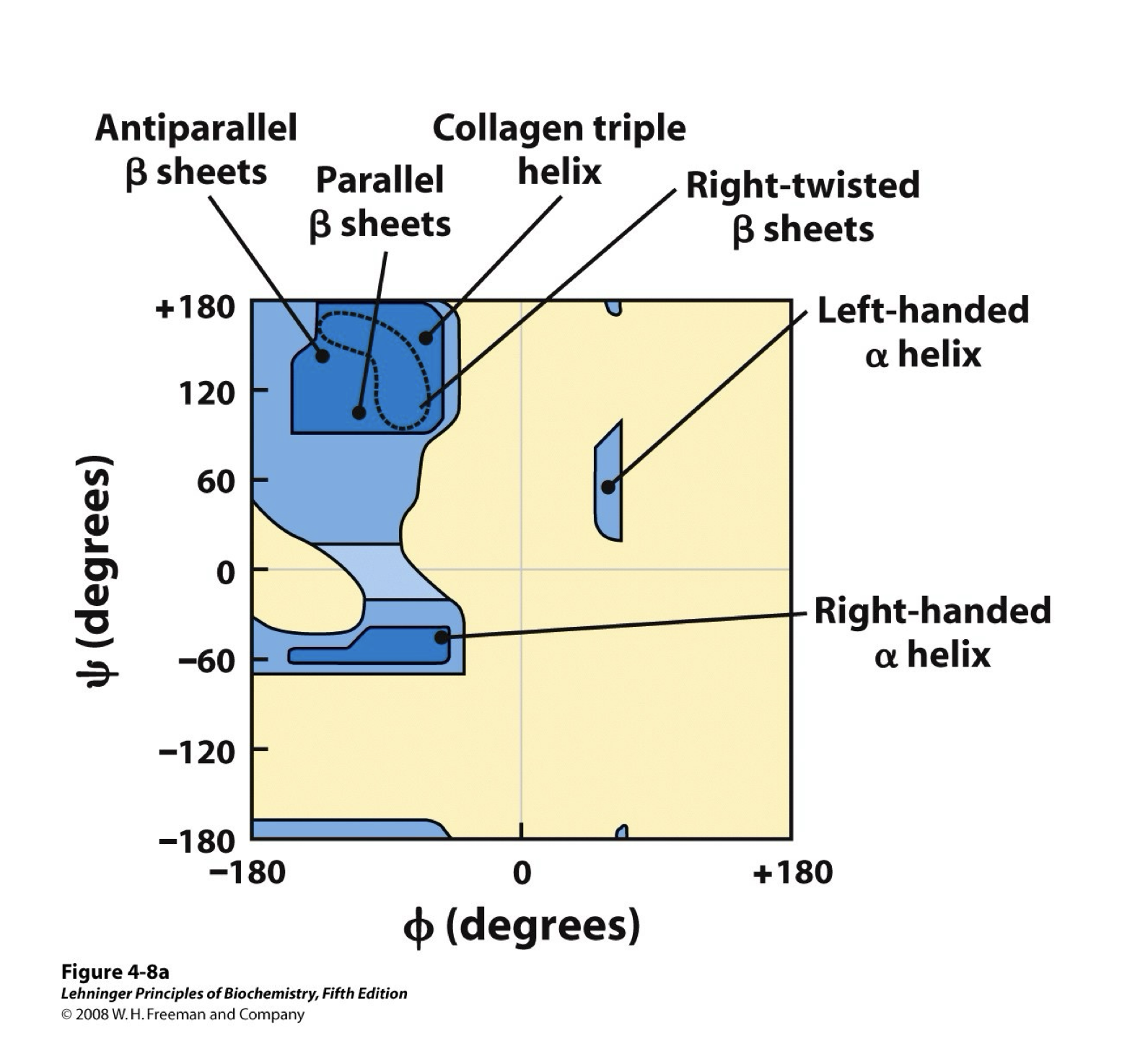
Alpha helix
Spiral structure of polypeptide, side chains pointing outward, every helical turn held together by 3-4 hydrogen bonds, and stabilized by a large number of hydrogen bonds between electronegative O of residue n and electropositive amide H of residue n+4.
Beta Strand
Zig zag shape, alt side chains point in opposite directions, two or more segments of the same polypeptide chain run alongside each other, and nearby strands are parallel or antiparallel which means they are stabilized with inter-strand hydrogen bond
What do all alpha folds have in common?
Has an EF hand (helix - loop - helix), helix bundle (made of amphipathic helices where one side is hydrophobic and the other side is polar/charged and are exposed)
What do all beta fold have?
Beta barrel (usually antiparallel beta sheets that wrap around to various sizes), interior could be hydrophobic or hydrophilic, have beta propellers (has blades which have twisted beta sheets with 4 antiparallel beta strands
Alpha/Beta fold
Has alternating alpha helices and beta strands, most frequent domain structure in proteins and alternation leads to variety of diverse shapes such as a horseshoe (important for binding many ligands from nucleic acids to peptides)
Alpha + Beta Folds
Contain both alpha helices and beta strands but don’t alternate, beta strands mostly antiparallel, less common
How many folds can a tertiary structure hold?
Contain one or mold folds
How do quaternary structure form?
By assembly of multiple subunits (each subunit is a polypeptide) into a larger functional cluster.
How are quaternary structures held together?
By non-covalent interactions and sometimes S-S bonds.
Globular protein
Functional role, found in all kingdoms of life
Globular shape
No repetitive AA sequence
Usually soluble in water
Fibrous Proteins
Structural proteins, very common but only in animals
Long fiber or sheet, very tough, and stretchy
Repeated AA sequence
Long parallel polypeptide chains
Usually insoluble in aqueous solution or lipid bilayer
Examples of fibrous proteins
Alpha-Keratin and Collagen
What is alpha-Keratin used for?
The main structural component of hair and nails.
Structure of alpha-Keratin
Super-Bundle of Coiled-coil
Two very long alpha helices twist together to form a coiled coil
Two coiled coils are arranged in a staggered fashion in tetramer
Three tetramers are staggered to make the protofilament
Protofilament polymerizes to make a filament
The coiled coil has a heptad repeat pattern meaning it has a repeating pattern of 7 amino acids/residues
Structure of the heptad repeat
a = often nonpolar
b,c,f = charged or polar, exposed to solvent
d = often Leu, hence also called the leucine zipper
e,g = often charged
How are the coiled coils stabilized?
Hydrophobic and Ionic interactions
How are alpha keratin stabilized?
Disulfide bonds
Structure of Collagen
Main structural component of our connective tissue
Some are stronger than steel
It’s a superhelix of three left-handed helices rich in Glycine and Proline
Sequence of collagen (Glycine - Proline - Hydroxyl proline)
Secondary structure = left-handed helix (3.3 residues per turn, looser than the alpha helix)
Three of the left-handed helices bundle together into a triple helix
Glycine in interior allows for tight packing
Has similar H-Bond pattern as B-sheets
Filaments are stabilized by H bonding btwn Gly hydrogen of one chain and Pro carbonyl oxygen of another chain
What is the name of a folded protein?
Native fold
Do all proteins have the same 3D structure and function?
Each adopt a unique 3D structure and have a specific function.
Are the covalent peptide bonds different in the peptide chain when unfolded compared to the native state?
No they are the same
Are the non-covalent interactions different in the peptide chain when unfolded compared to the native state?
Differ significantly
How is the native structure stabilized?
By non-covalent interactions
Denaturation
A loss of native folding that leads to a loss if function
Full denaturation
Native state to primary sequence
Partial denaturation
Loss of some structure