COMPTIA A+ CORE 1 HARDWARE
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
Ethernet
a system for connecting a number of computer systems to form a local area network, with protocols to control the passing of information and to avoid simultaneous transmission by two or more systems.
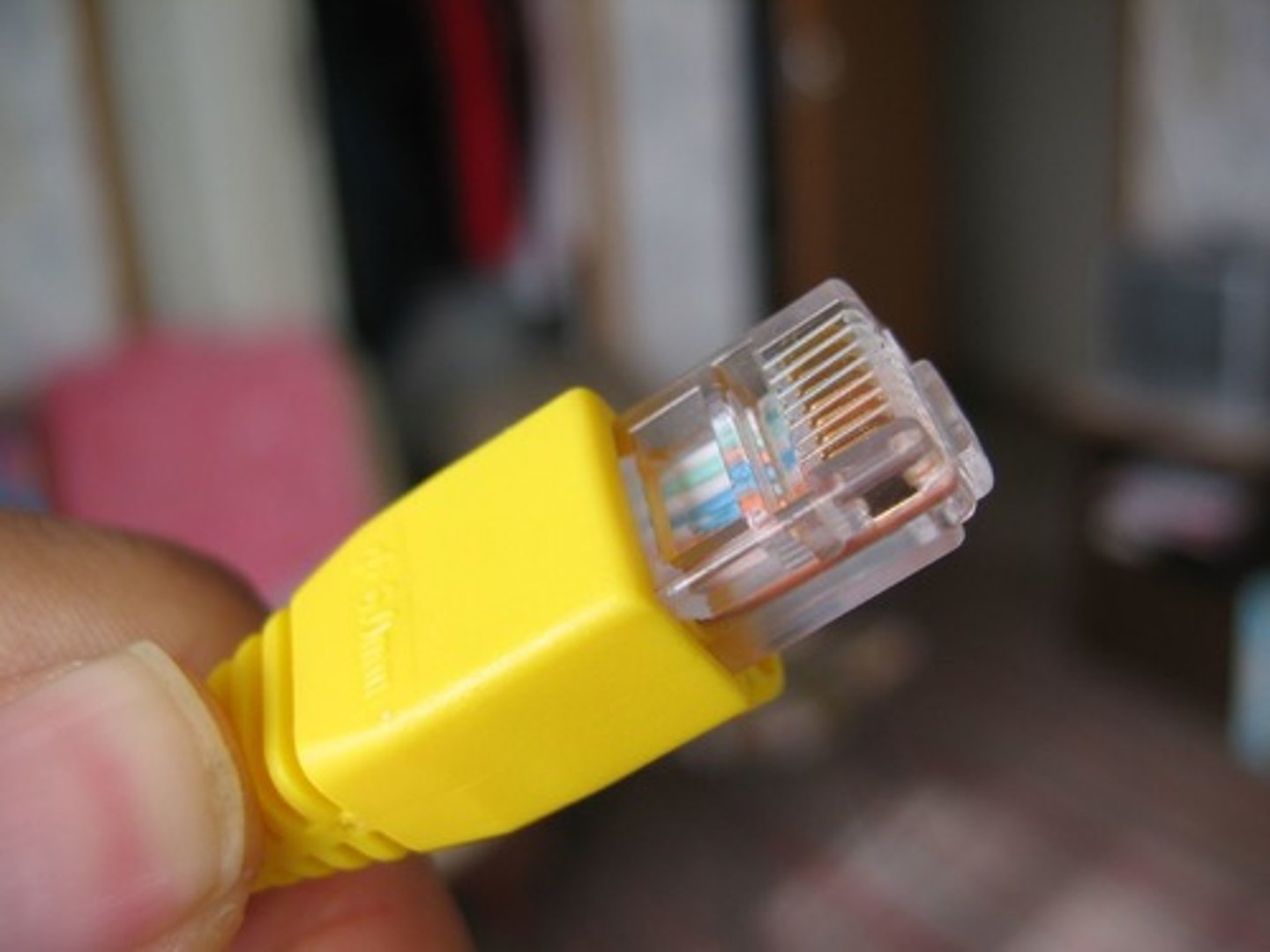

CAT-5 Cable
UTP capable of 100 Mbps. Four twisted wire pairs (eight wires). My be used for 10BaseT,10BaseT4, 10BaseT2, 100BaseTX and 1000BaseT Ethernet.
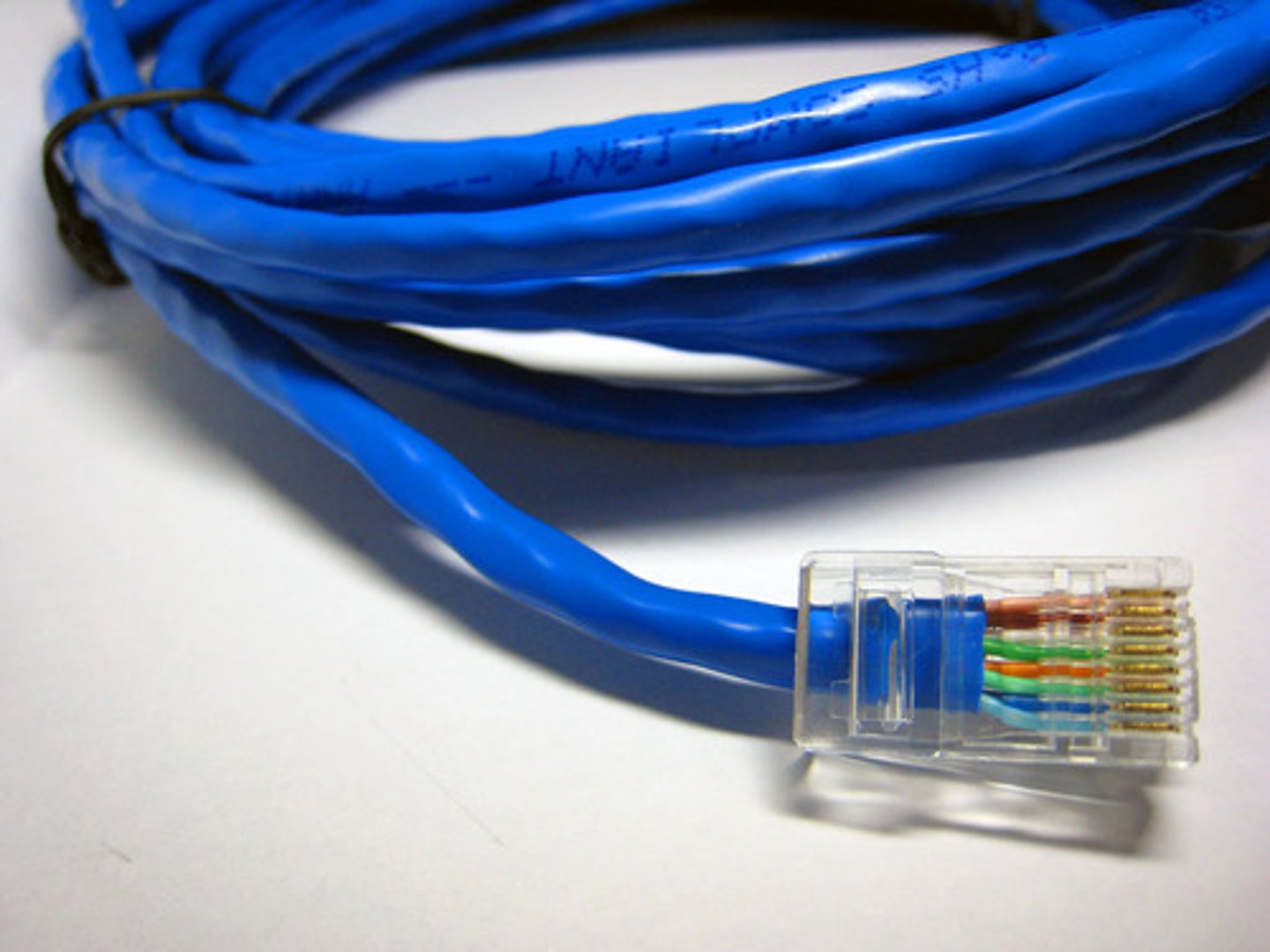

Cat 5e (Enhanced Category 5)
A higher-grade version of Cat 5 wiring that contains high-quality copper, offers a high twist ratio, and uses advanced methods for reducing cross talk. Enhanced Cat 5 can support a signaling rate of up to 350 MHz, more than triple the capability of regular Cat 5.
Cat 6 cable
A UTP cable type that provides more than 1 Gb/s of throughput.
plenum cable
Cabling approved for plenum areas because it has a special fire-resistant outer sheath that will not burn as quickly as PVC. (14)
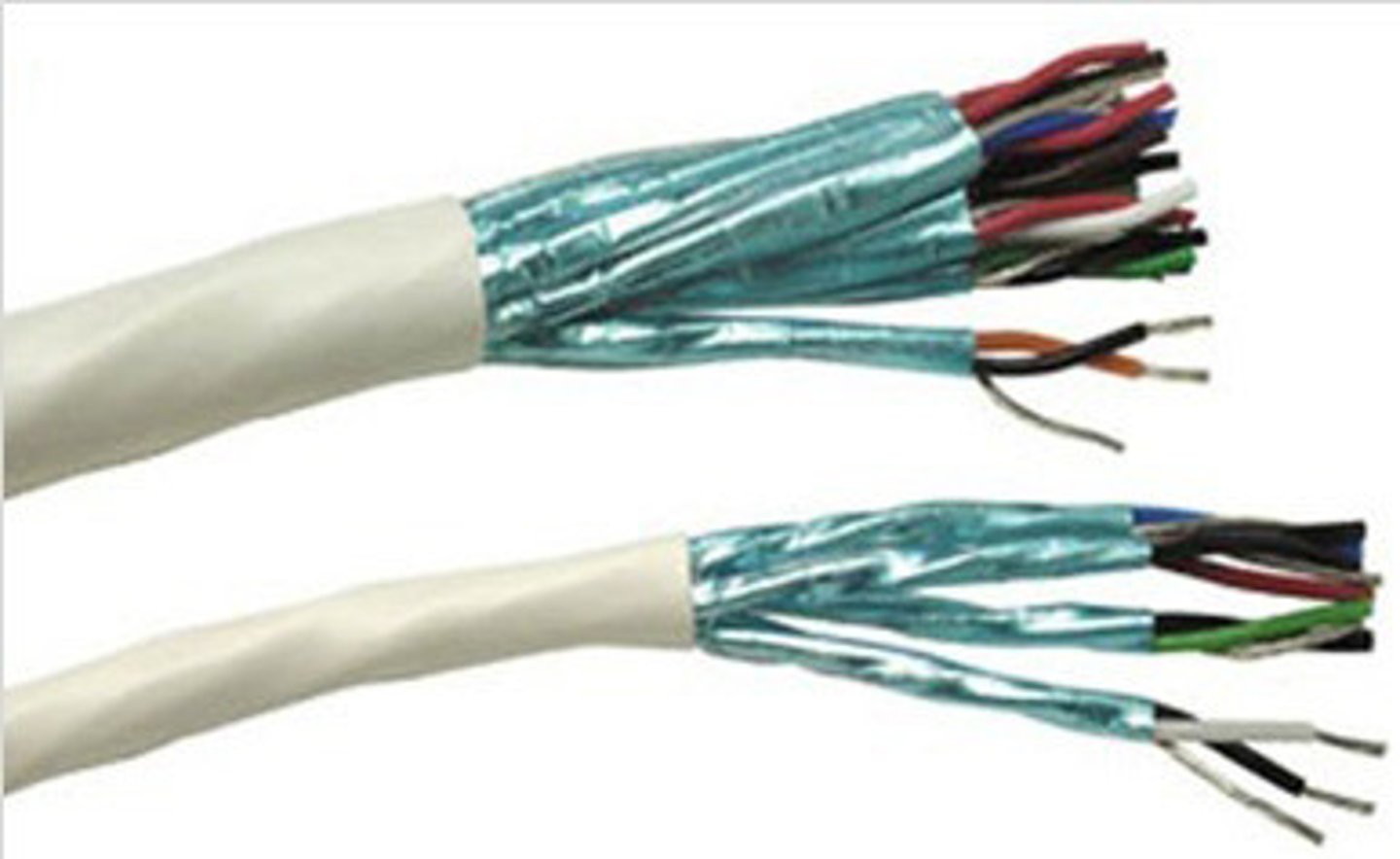
Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)
A twisted pair cable that has an aluminum shield inside the plastic jacket that surrounds the pairs of wires.
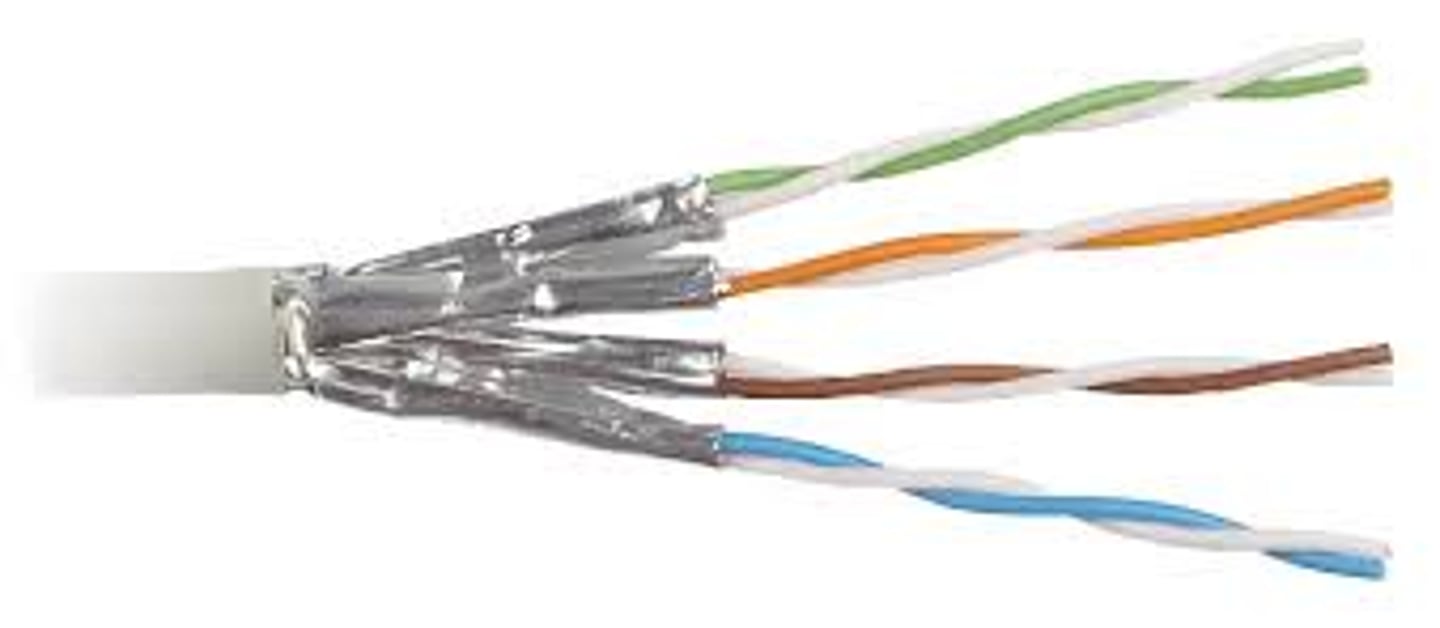

Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
Networking cable that has four twisted pairs of copper wire and a flexible outer coating.
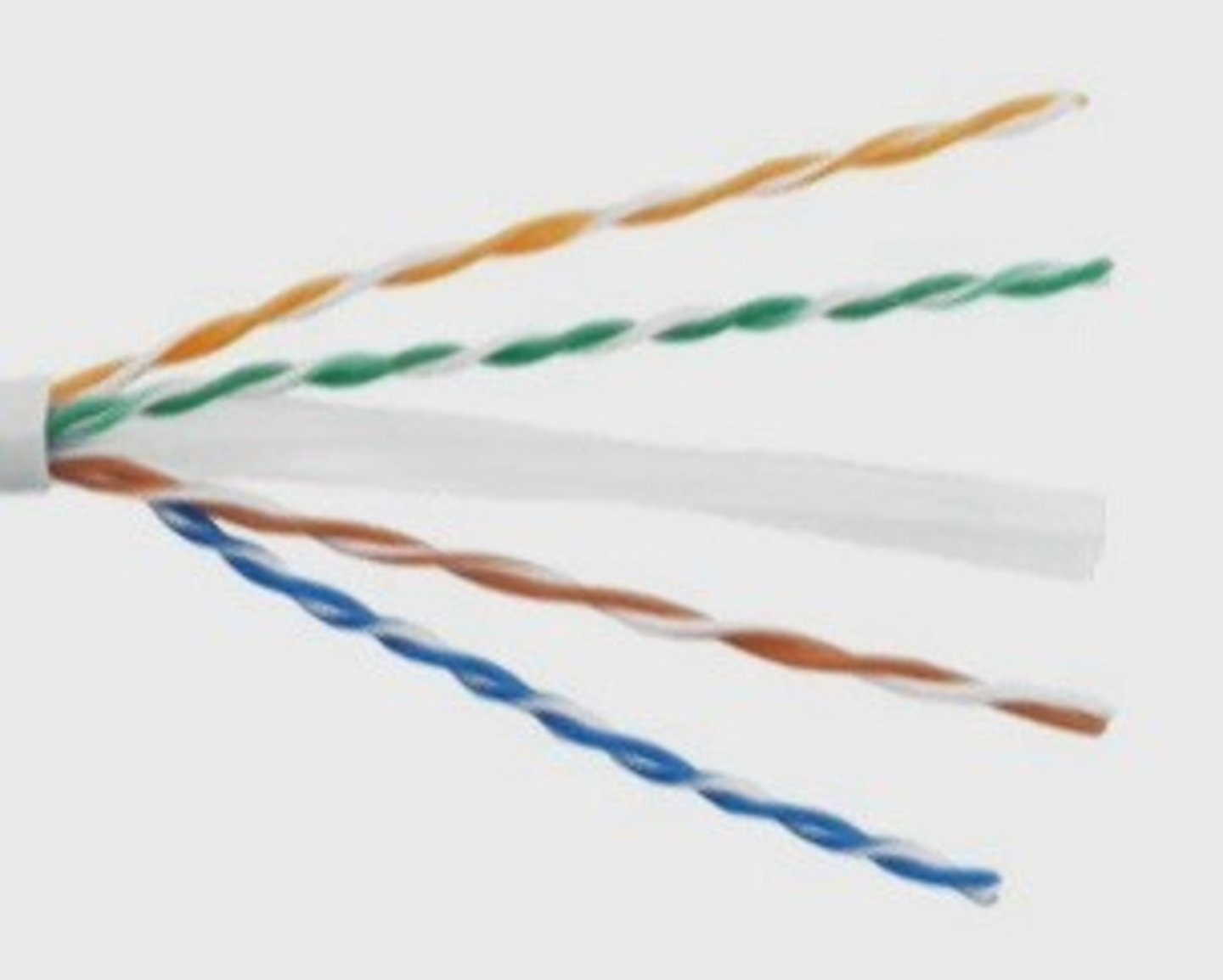

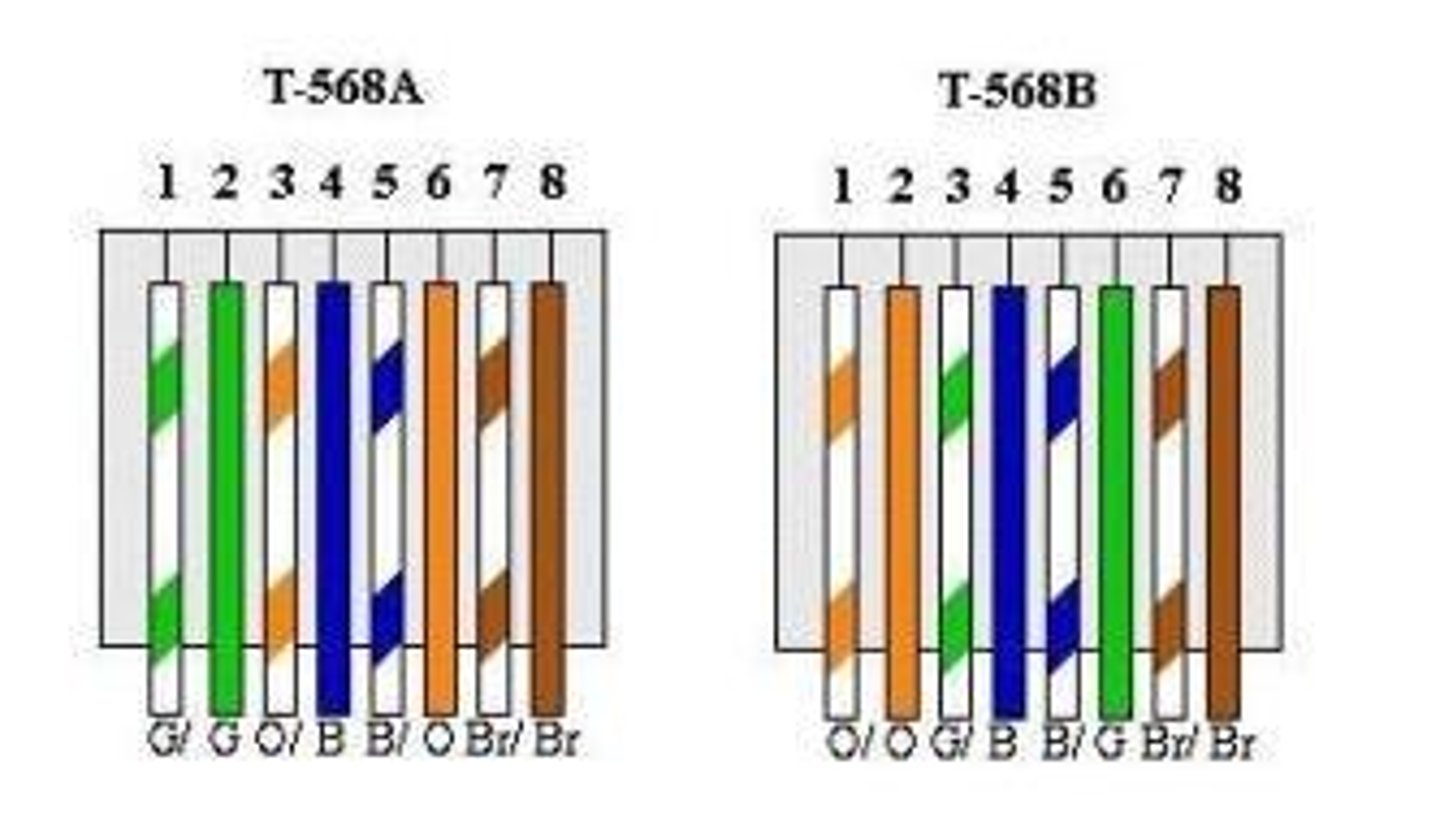
568A/B
network cable wire standards found in straight through and crossover cables.
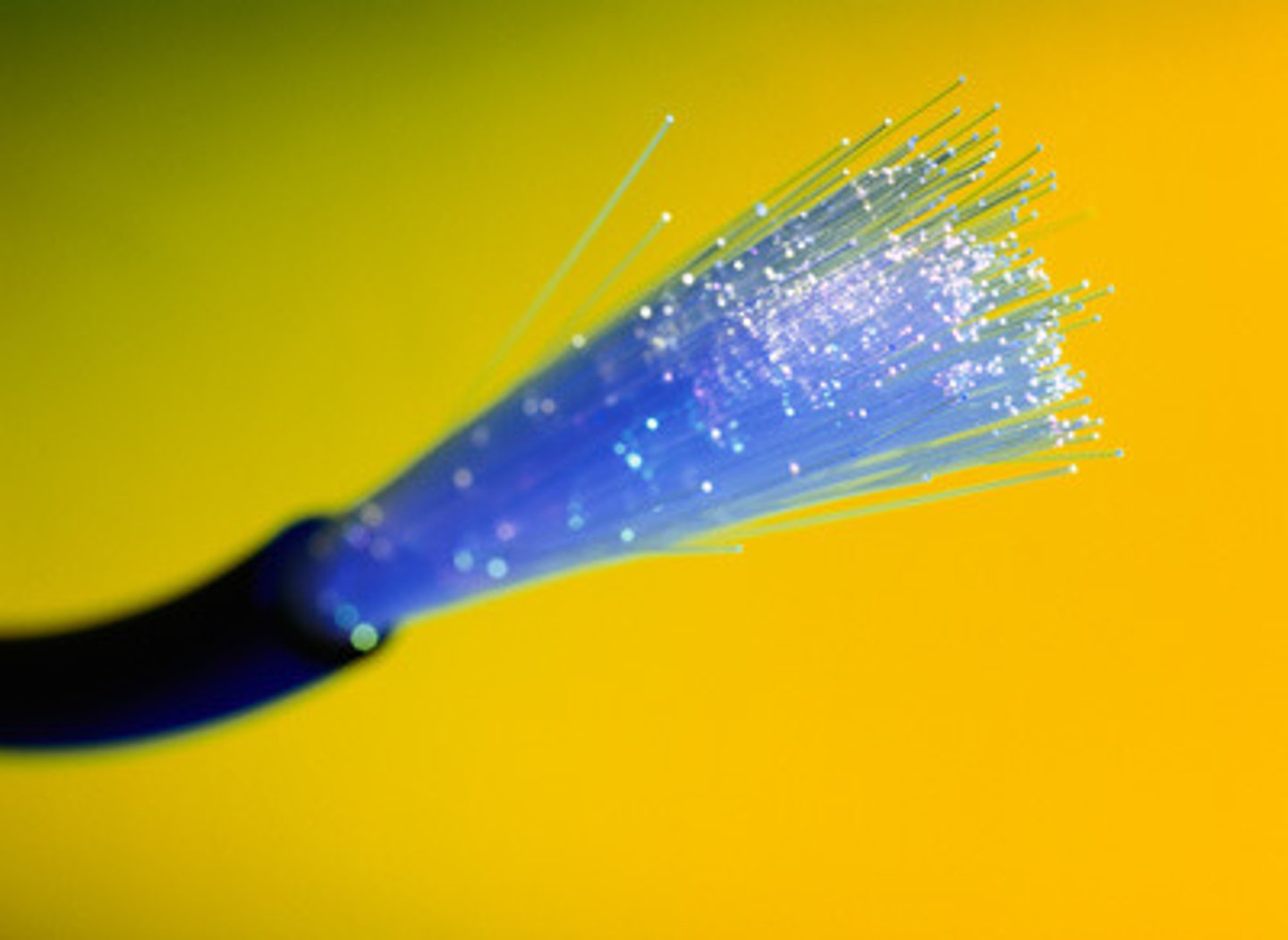
Fiber Cable
a glass tube and allows photons of light to be shot through cable. The fastest form of wired cabling
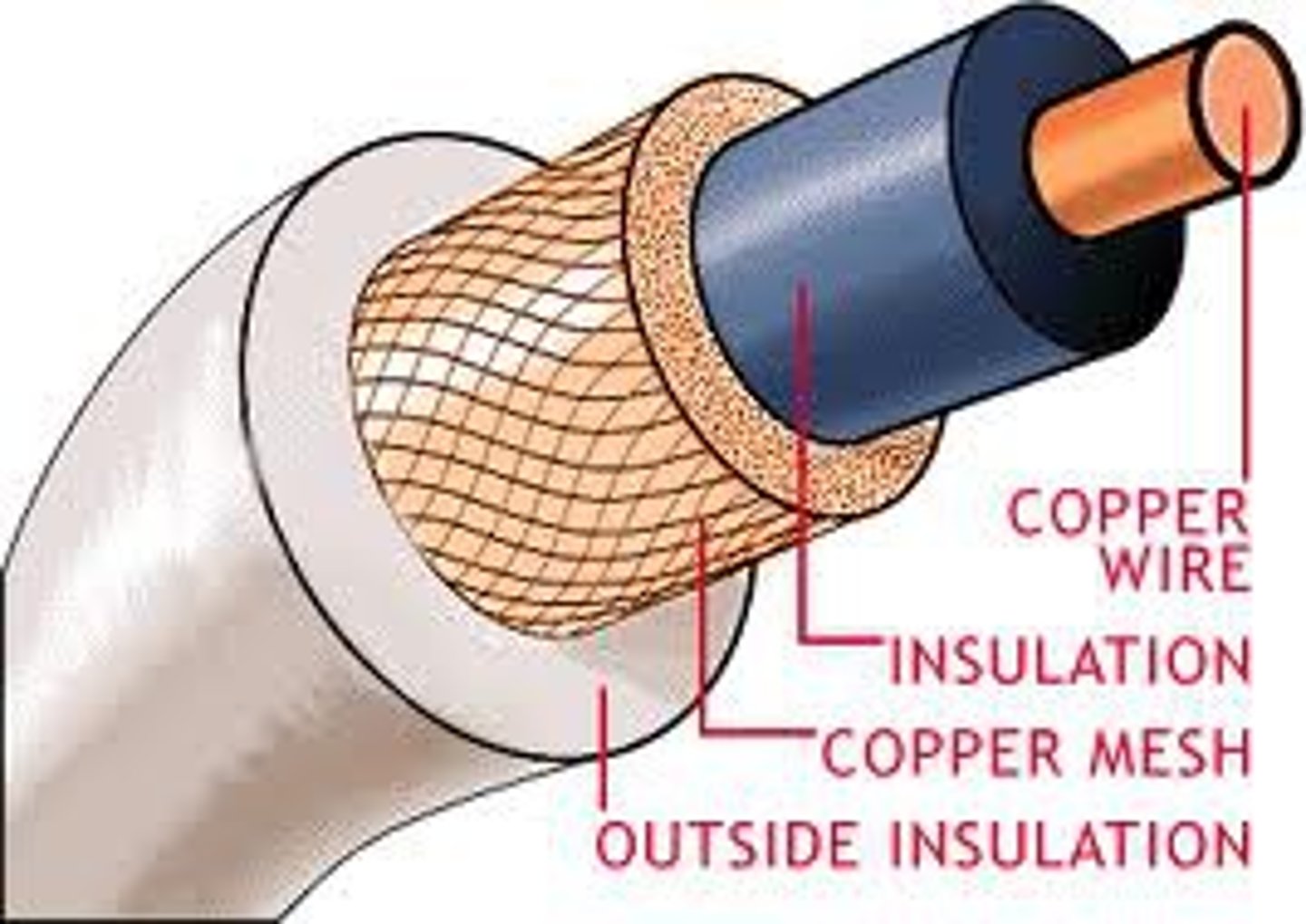
coaxial cable
insulated copper wire; used to carry high-speed data traffic and television signals
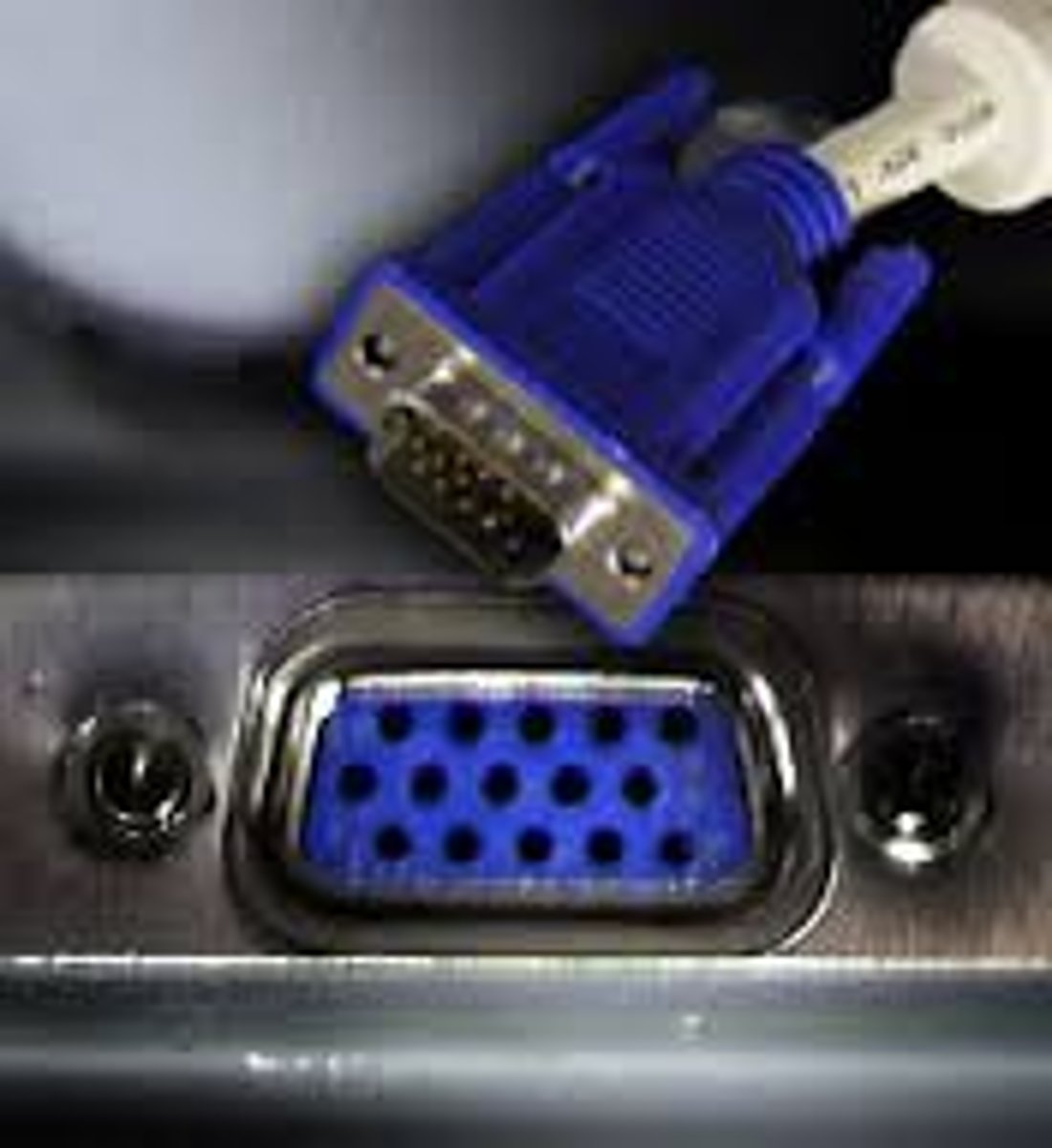
VGA (Video Graphics Array)
Standard for the video graphics adapter that was built into IBM's PS/2 computer. It supports 16 colors in a 640 × 480 pixel video display.

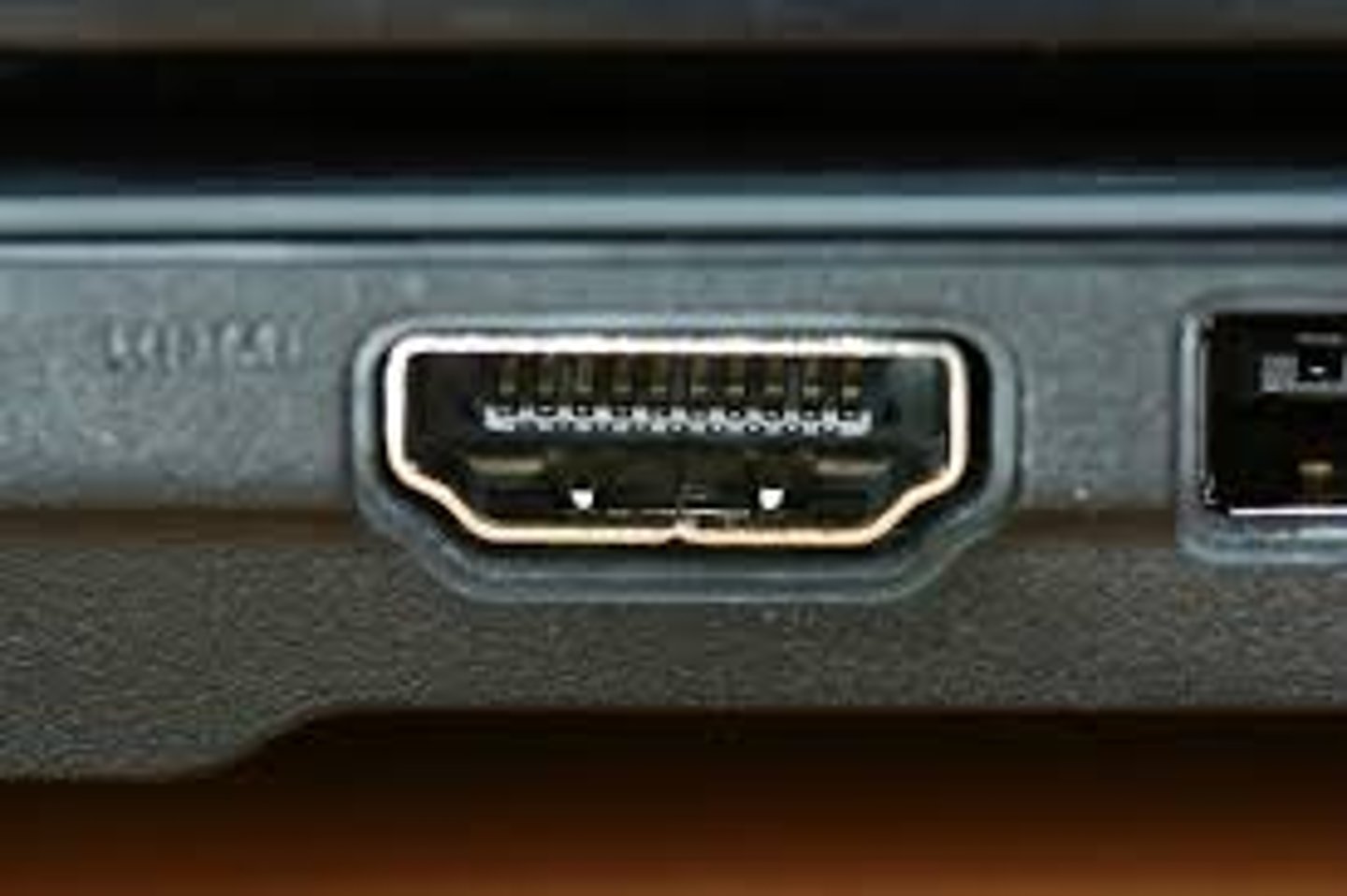
HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface)
transfers uncompressed digital data. Typically, it is used for
connecting high definition video and audio devices.

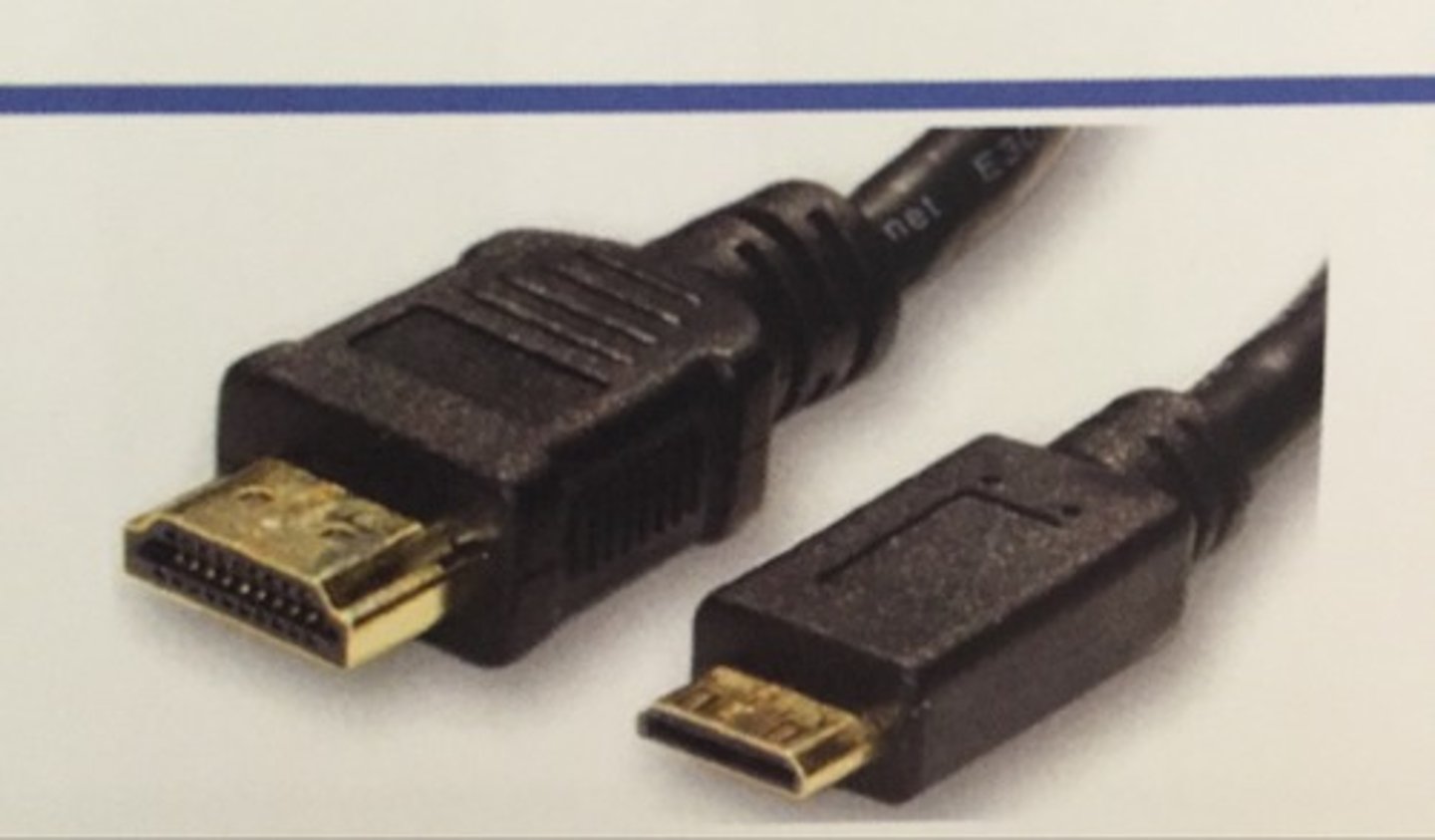
Mini HDMI
The HDMI Type C interface with the same 19 pins as the standard Type A interface. This compact HDMI interface allows smaller devices to output HDMI quality audio and video.

DisplayPort
a port that transmits digital video and audio (not analog transmissions) and is slowly replacing VGa and DVI ports on personal computers.

DVI (Digital Visual Interface)
Special video connector designed for digitalto-
digital connections; most commonly seen on PC video cards and LCD monitors.
Some versions also support analog signals with a special adapter.
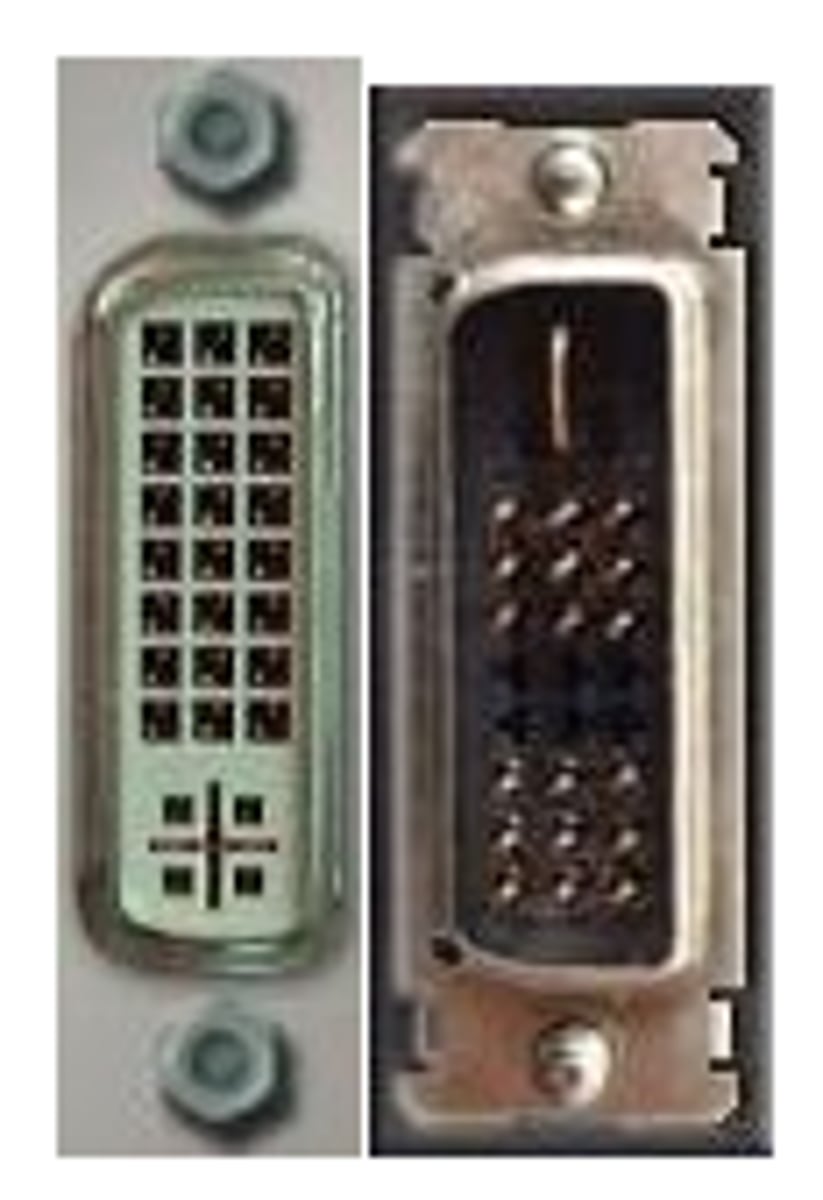

DVI-D
A DVI (Digital Visual Interface) video port that works only with digital monitors.
DVI-I
A DVI (Digital Visual Interface) video port that supports both analog and digital monitors.
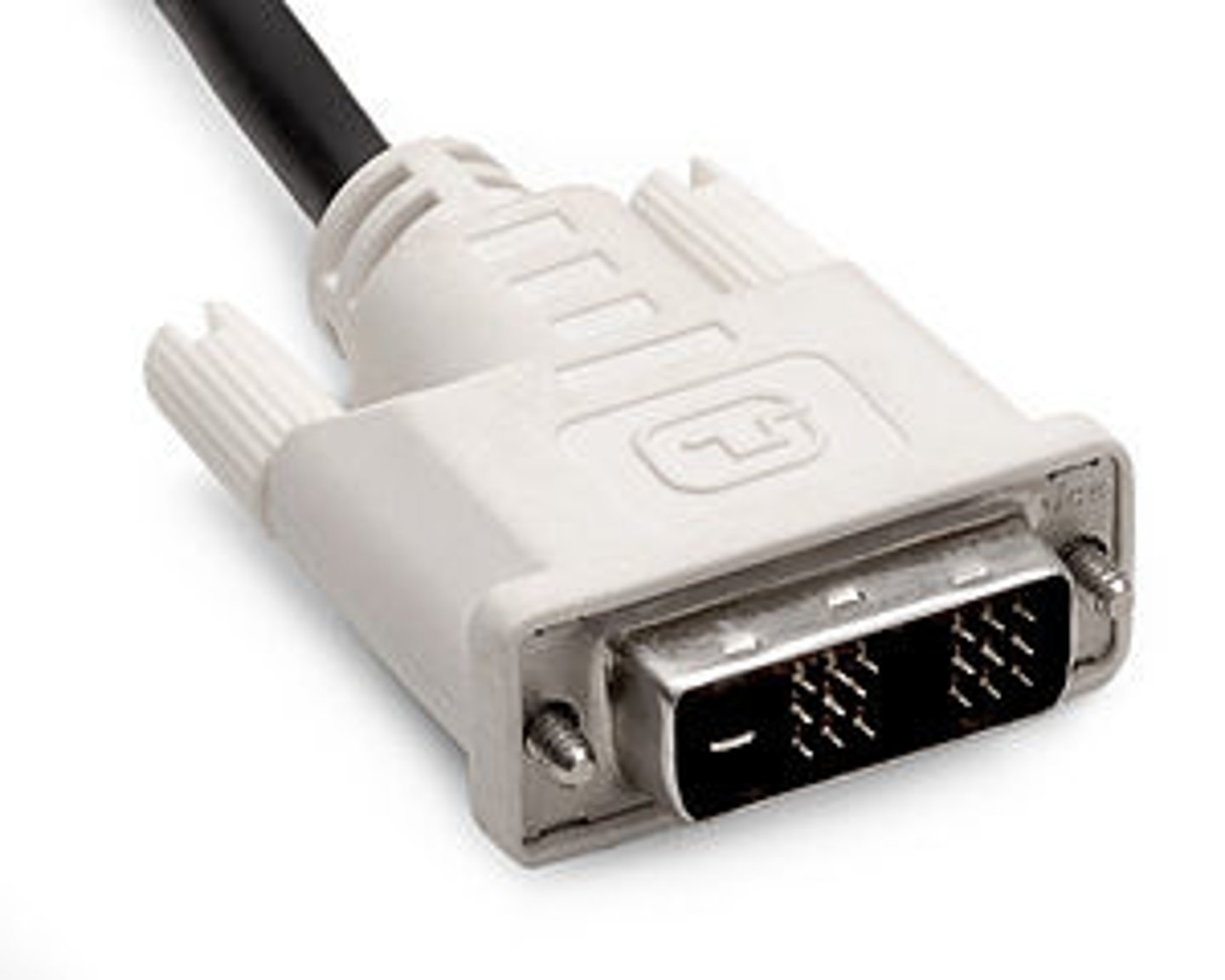

USB 2.0
runs at 480 Mb/s with aa max cable length of 5 meters.

USB-C
newer, reversible connector and port that supports charging, data transfer, and video all in one cable
Thunderbolt
a port that transmits both video and data on the same port and cable. The port is shaped the same as the DisplayPort and is compatible with DisplayPort devices.
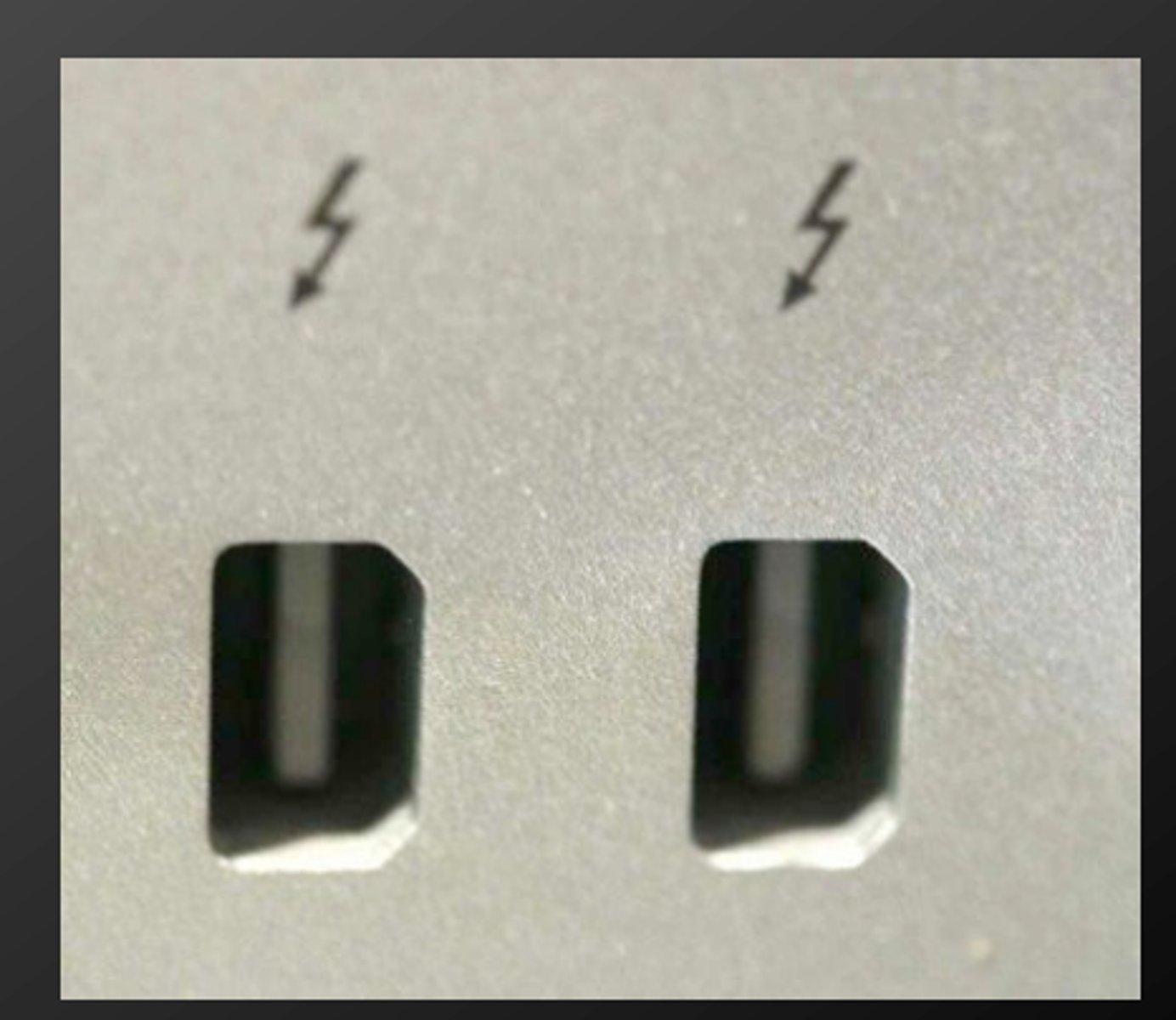
USB 3.0
5 gigabits per second, 3 meters

Serial Cable
A type of cable with many different styles of connectors used to connect a router to an external CSU/DSU on a leased-line installation.
Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA)
type of cable inside the computer connecting the mother board and
internal storage devices, such as the hard drive, CD- or DVD-ROM
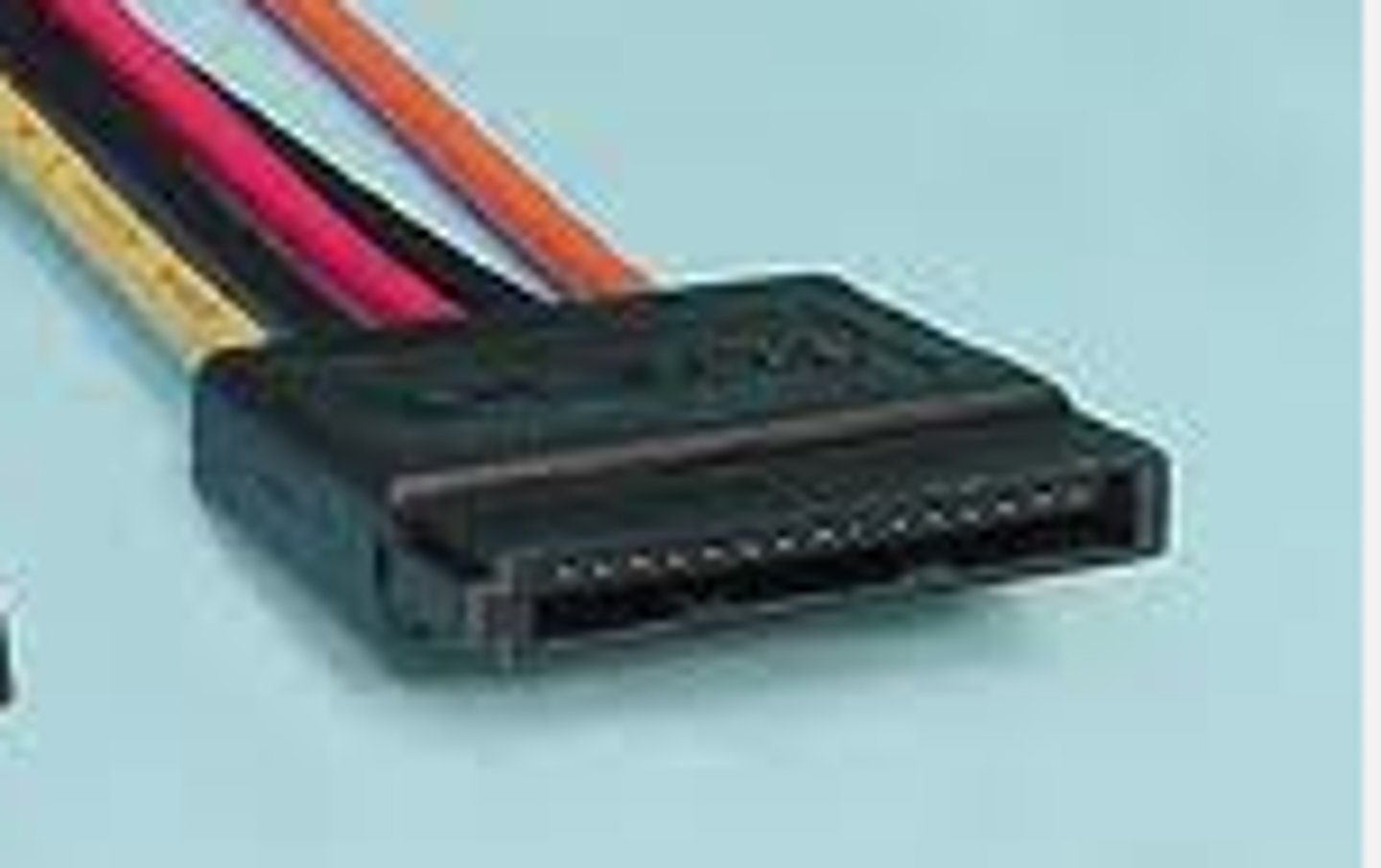

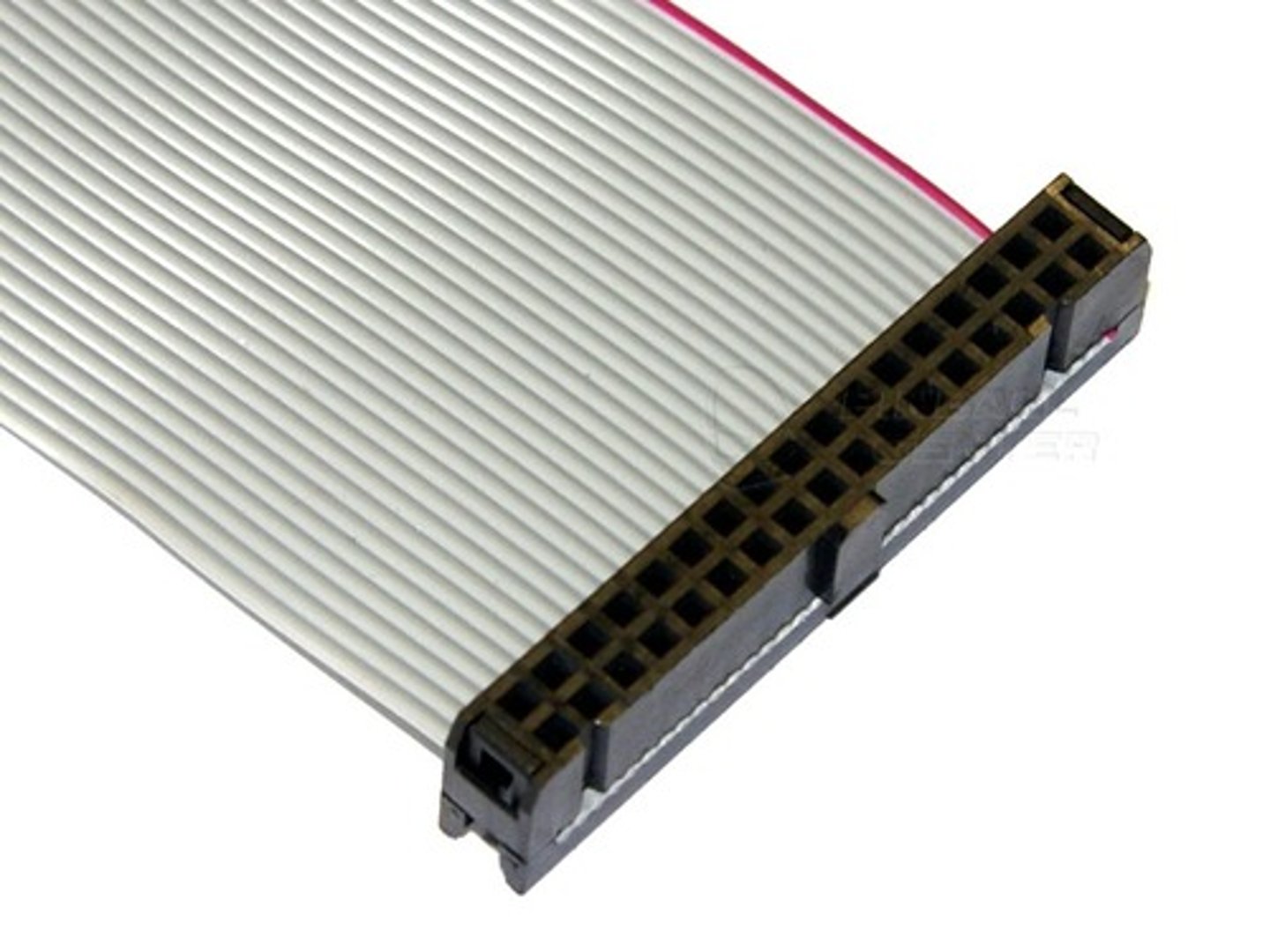
Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment (PATA)
A legacy hard disk technology that uses ribbon cables to typically attach up to four hard disk devices to a single computer.
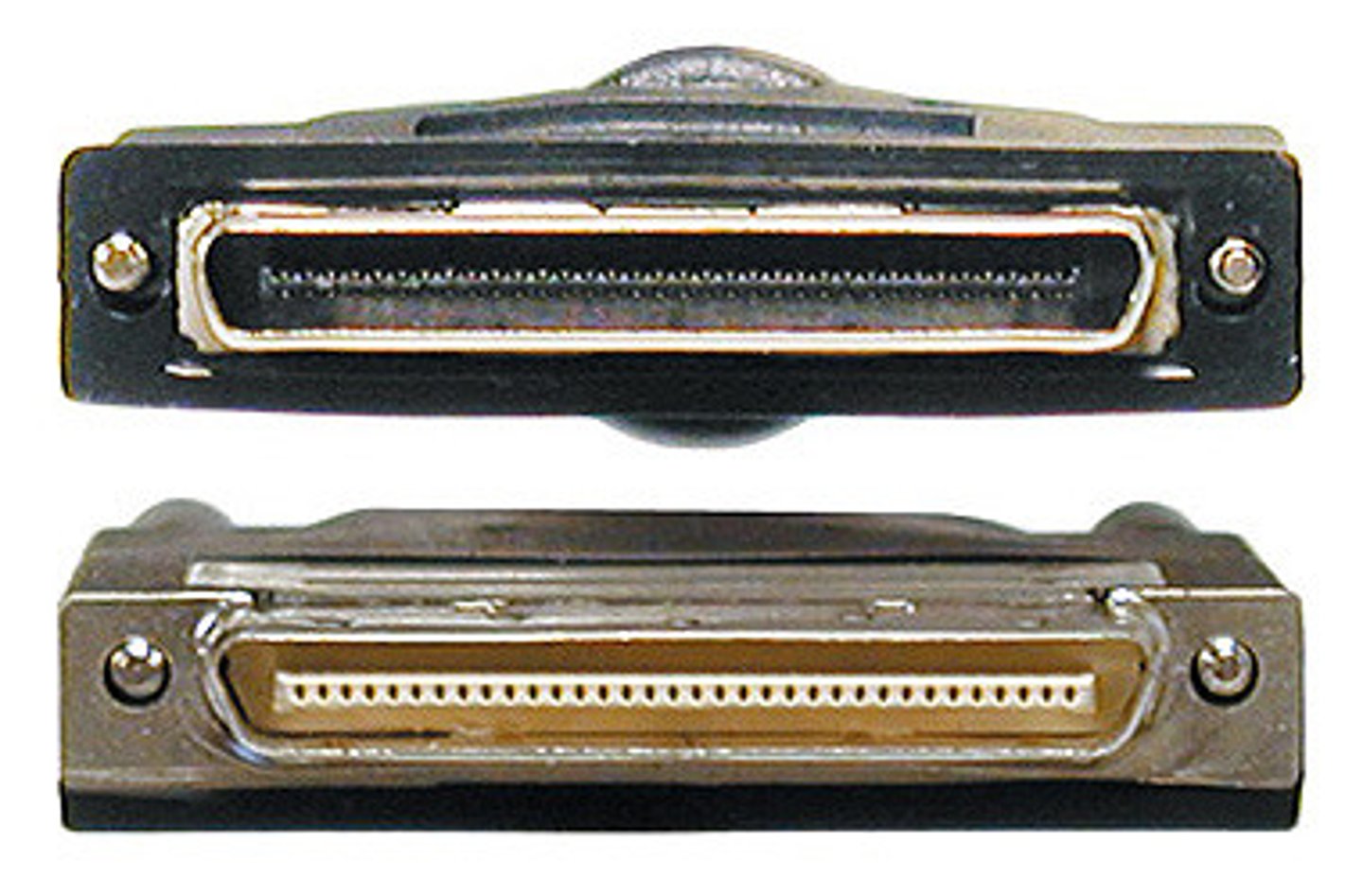
SCSI (Small Computer System Interface)
A fast interface between a host adapter and the CPU that can daisy chain as many as 7 or 15 devices on a single bus.
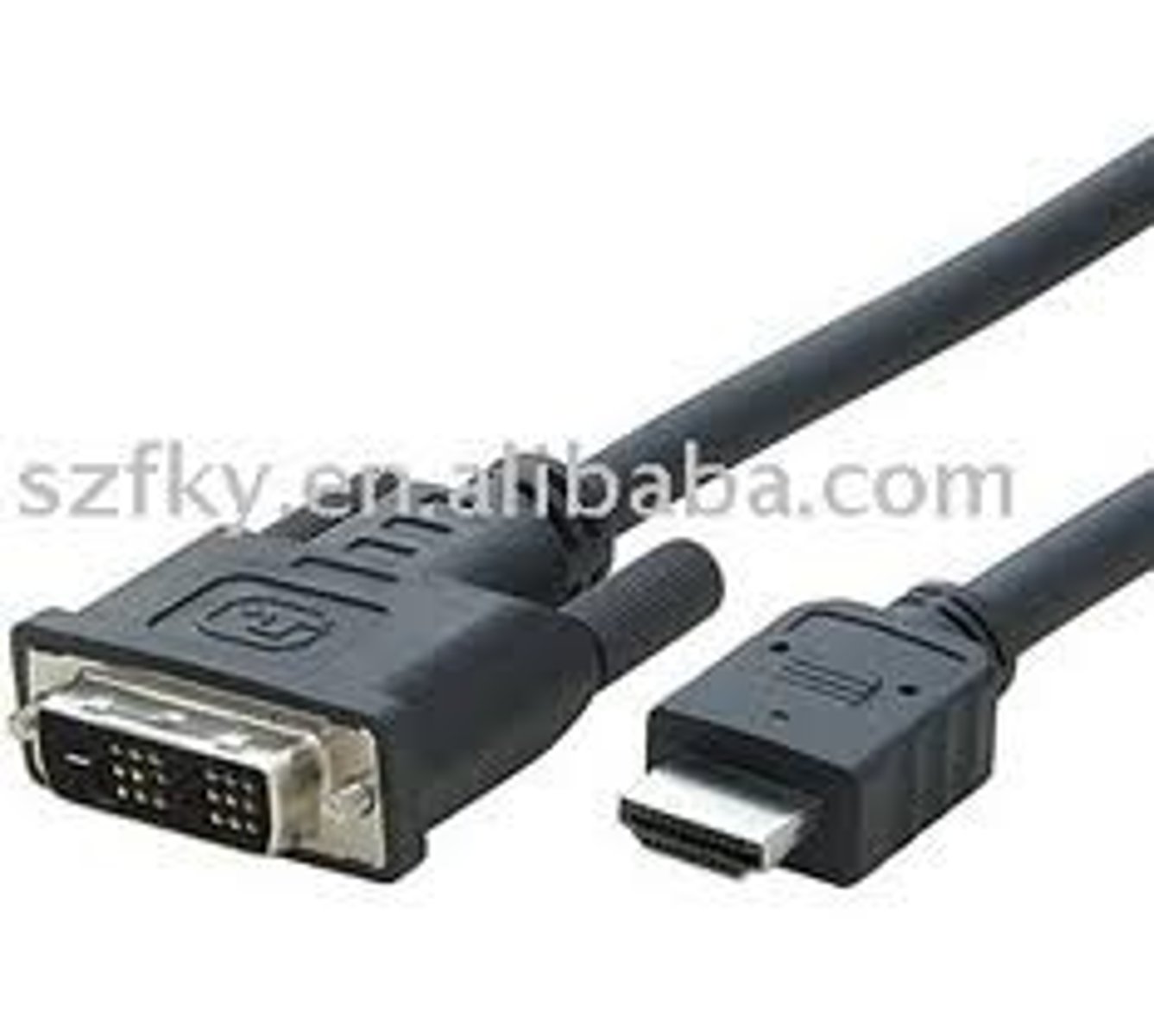
DVI to HDMI adapter
This adapter is used to connect an HDMI monitor to a DVI port.

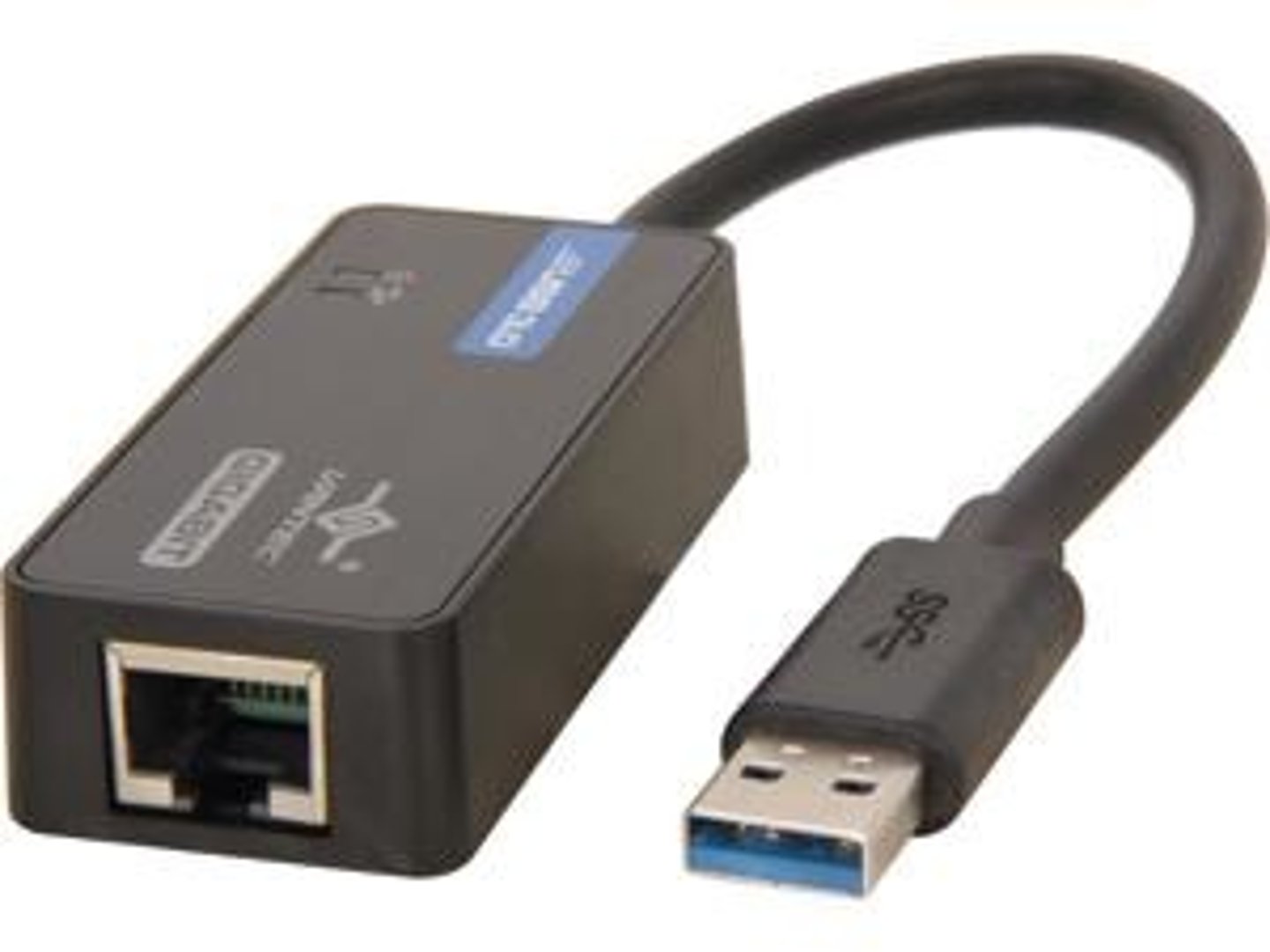
USB to Ethernet
Used to connect an RJ45 connector to a USB port

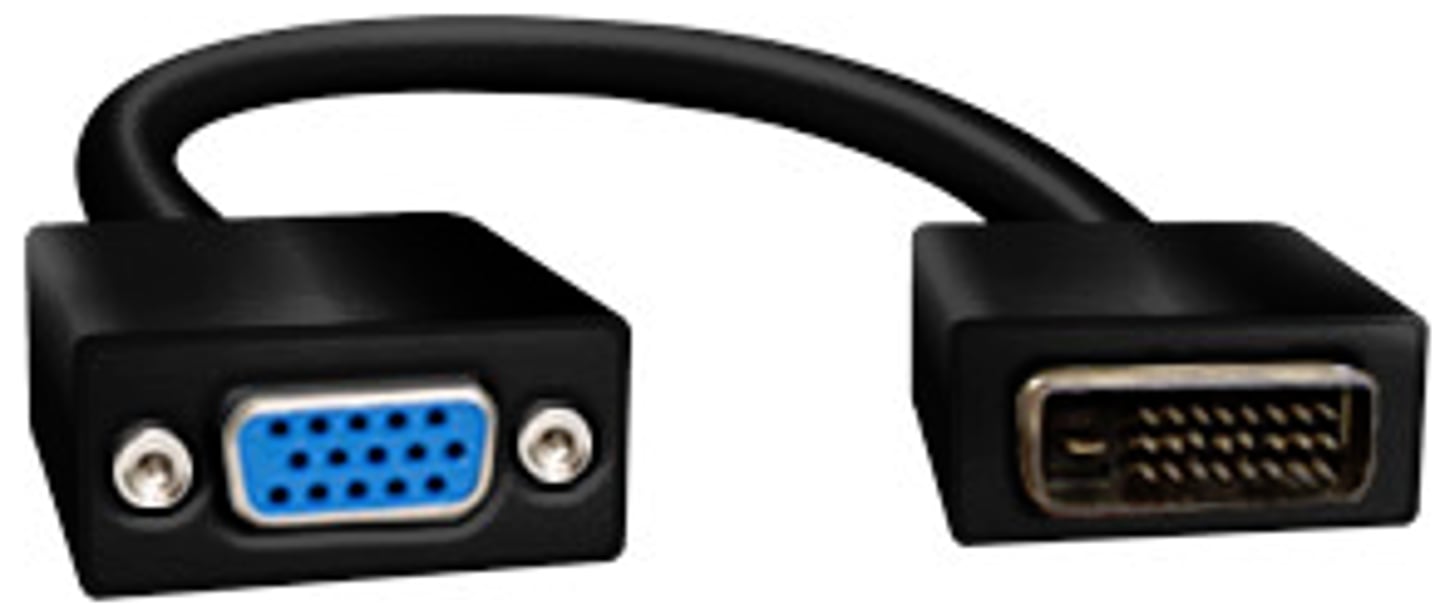
DVI to VGA adapter
This adapter is used to connect a VGA cable to a DVI port.

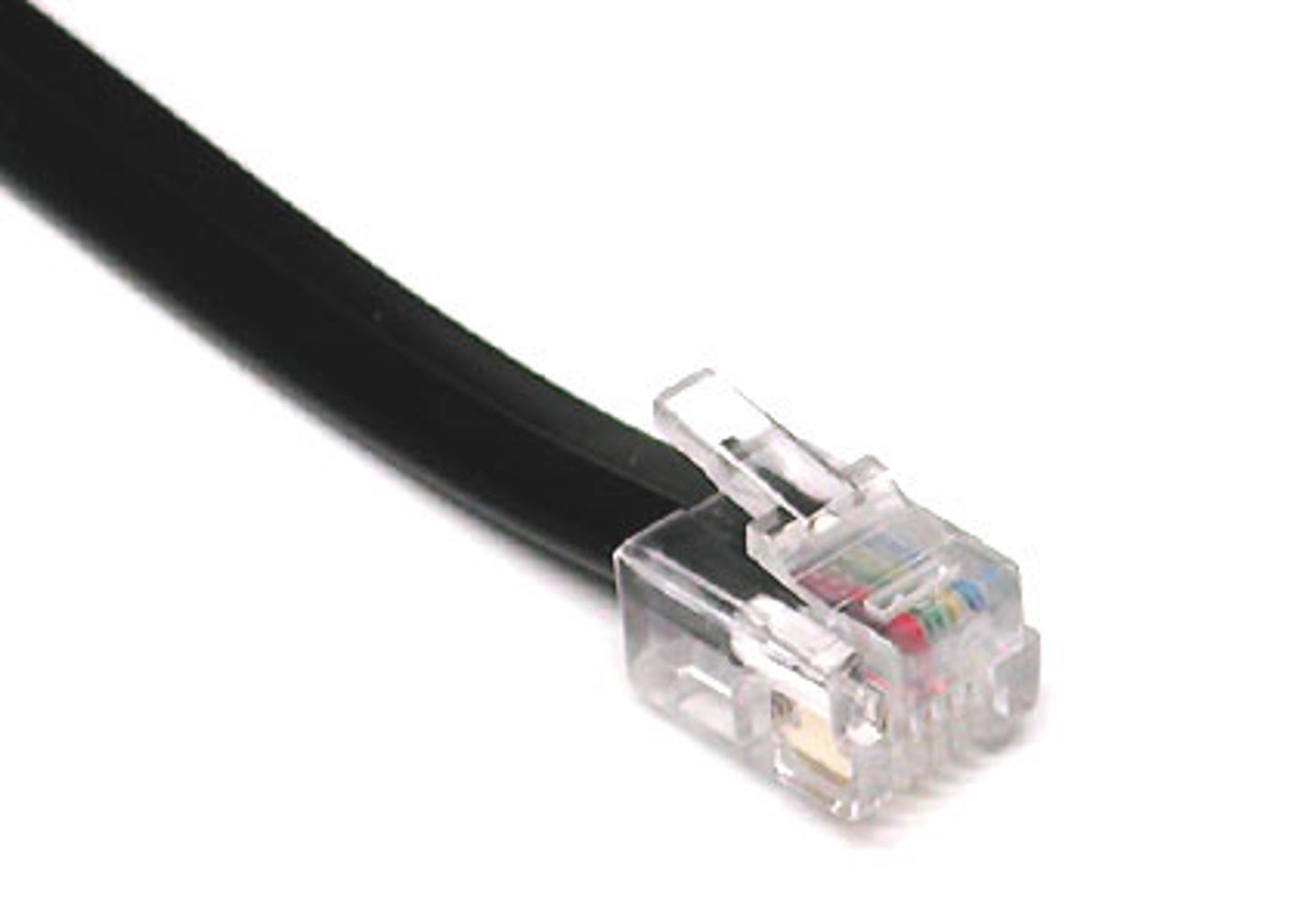
RJ-11
A phone line connection or port found on modems, telephones, and house phone outlets.

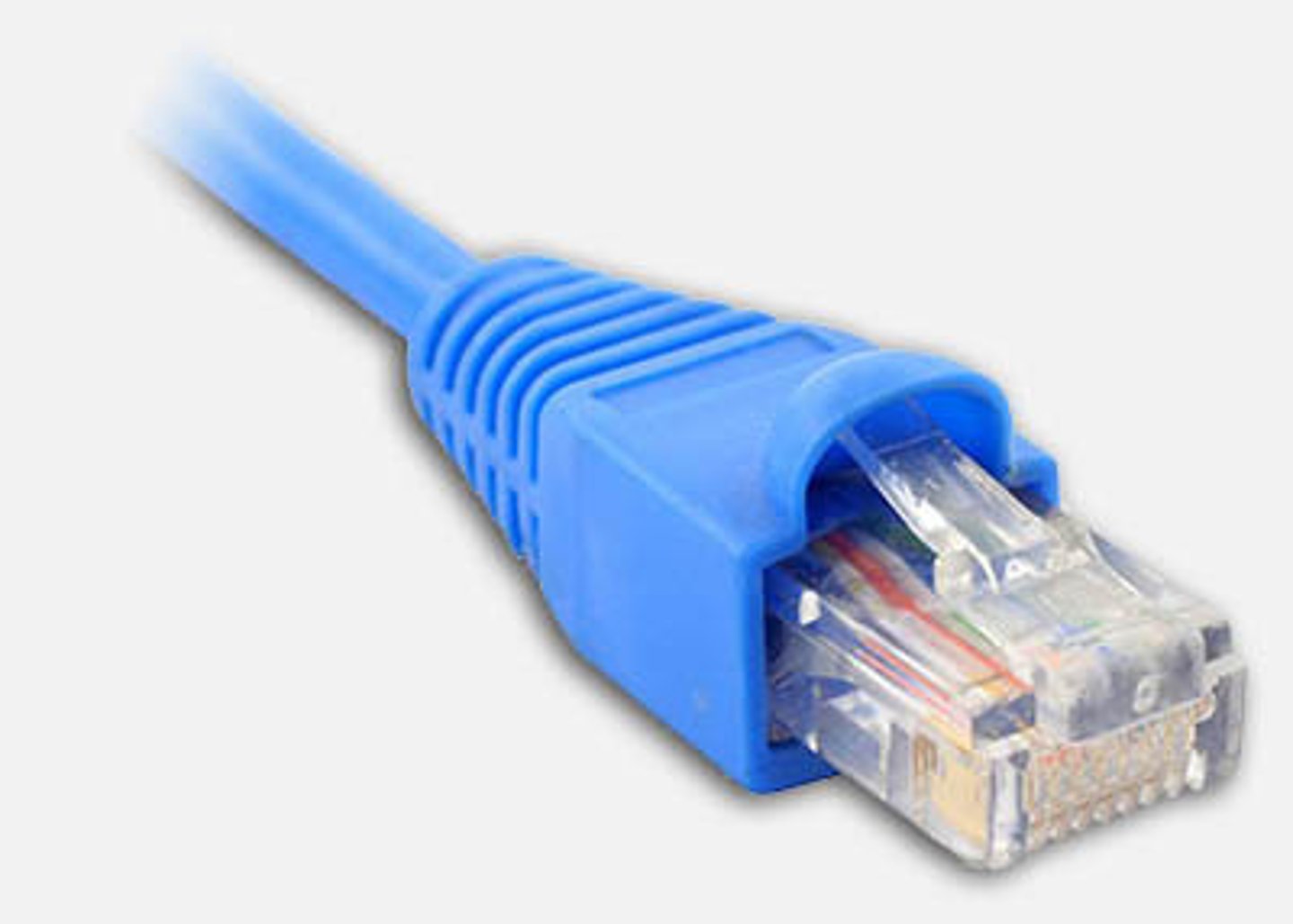
RJ-45 connector
An eight-position connector that uses all four pairs of wires. It is usually used for network connectivity

RS-232
The recommended standard (RS) upon which all serial communication takes place on a PC.
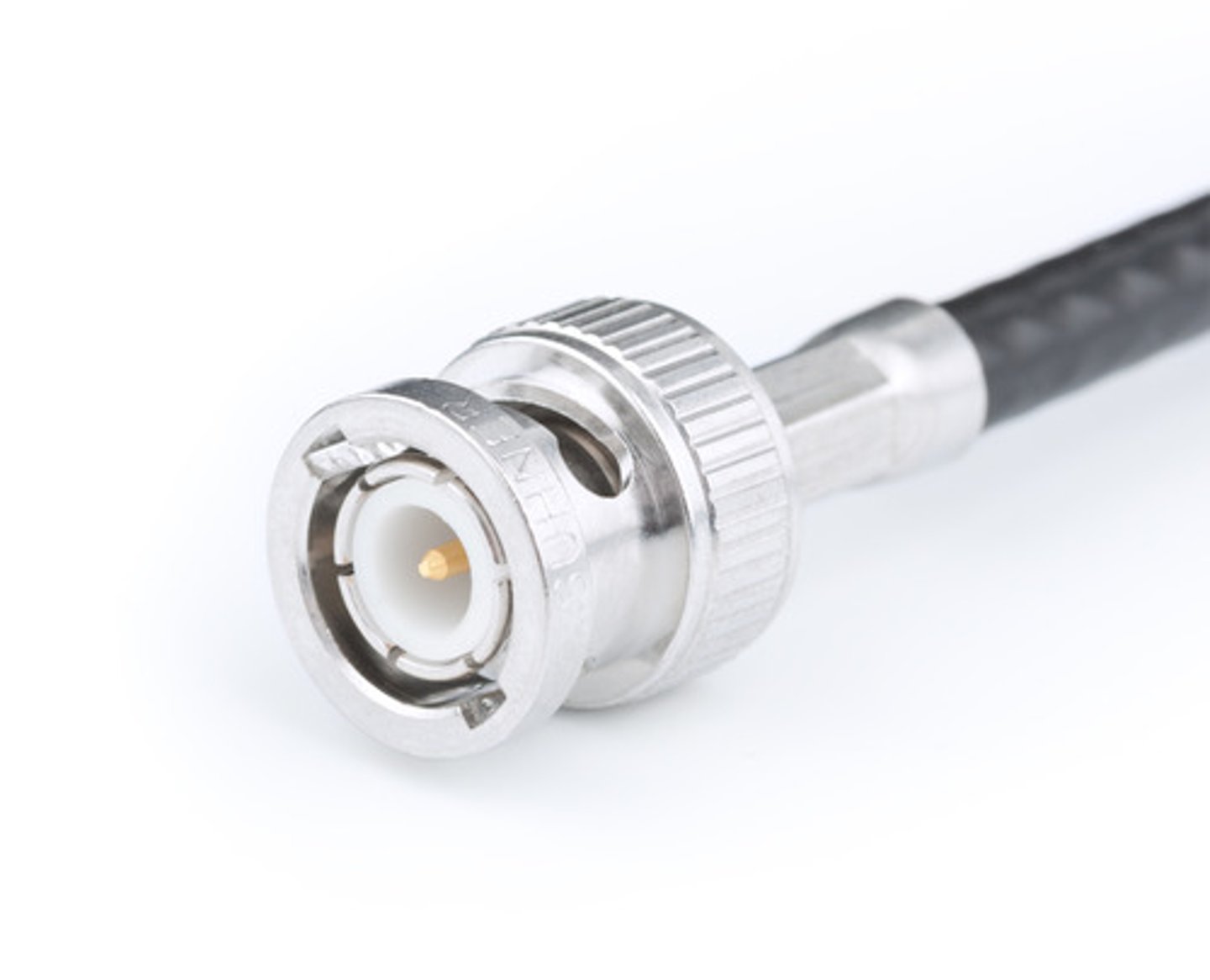
BNC cable
A miniature quick connect/disconnect connector used for coaxial cable. It features two blade-like lugs on the female connector. Connection is achieved with only a quarter turn of the coupling nut.

RG-59
A type of coaxial cable characterized by a 75-ohm impedance and a 20 or 22 AWG core, usually made of braided copper. Less expensive but suffering greater attenuation than the more common RG-6 coax, RG-59 is used for relatively short connections.
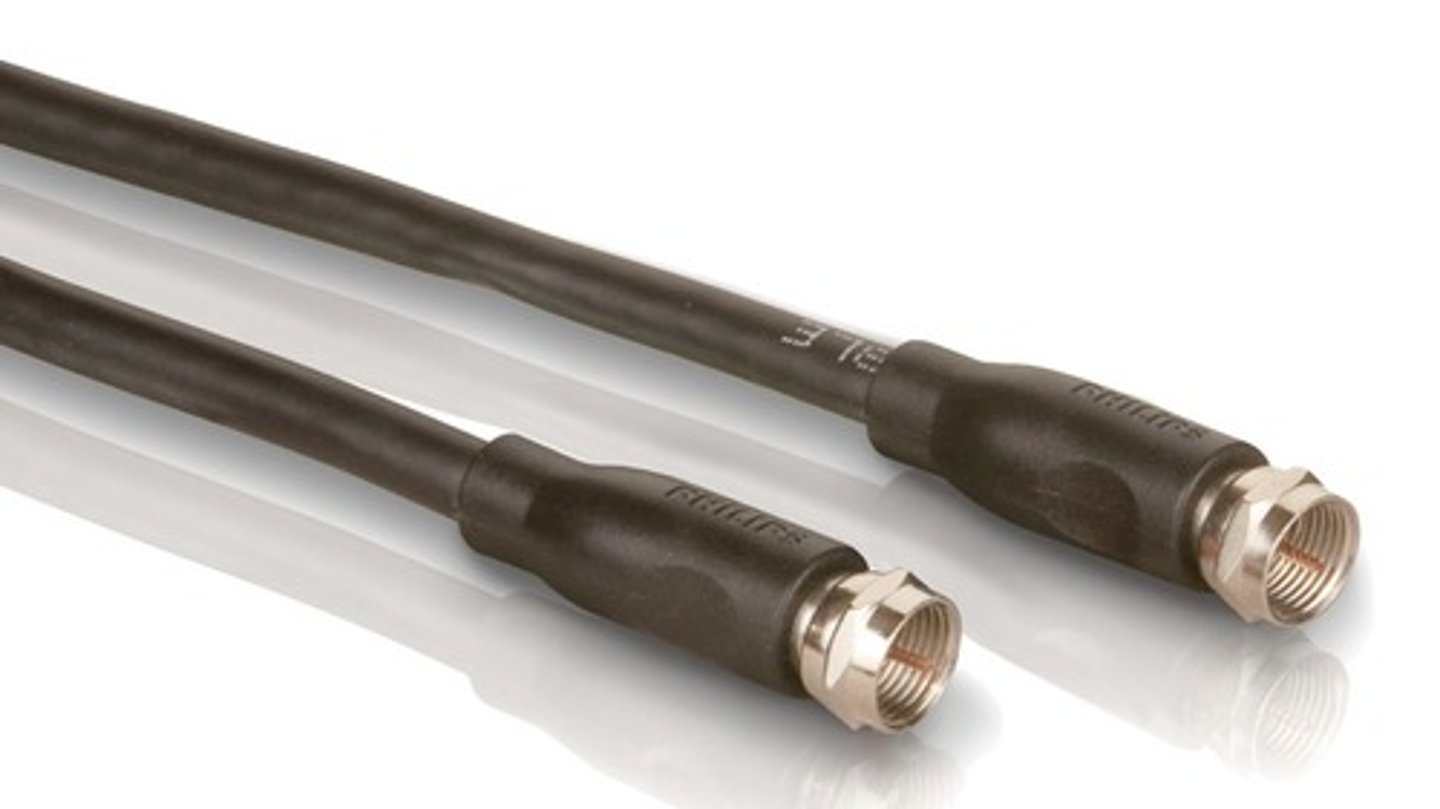

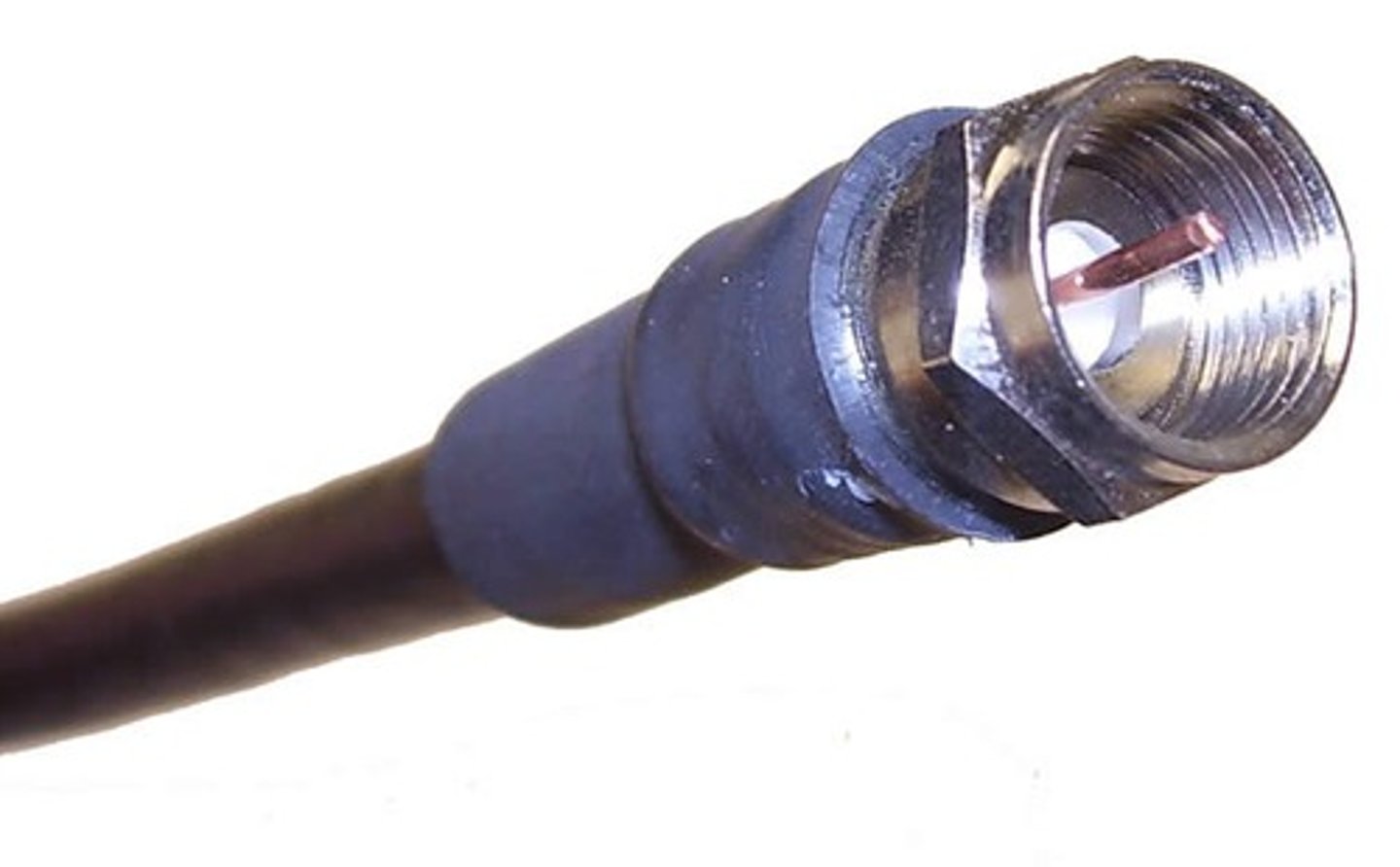
RG-6 Cable
Coaxial Cable used for connecting homes to cable networks. Larger conductor and higher frequencies than RG-59.

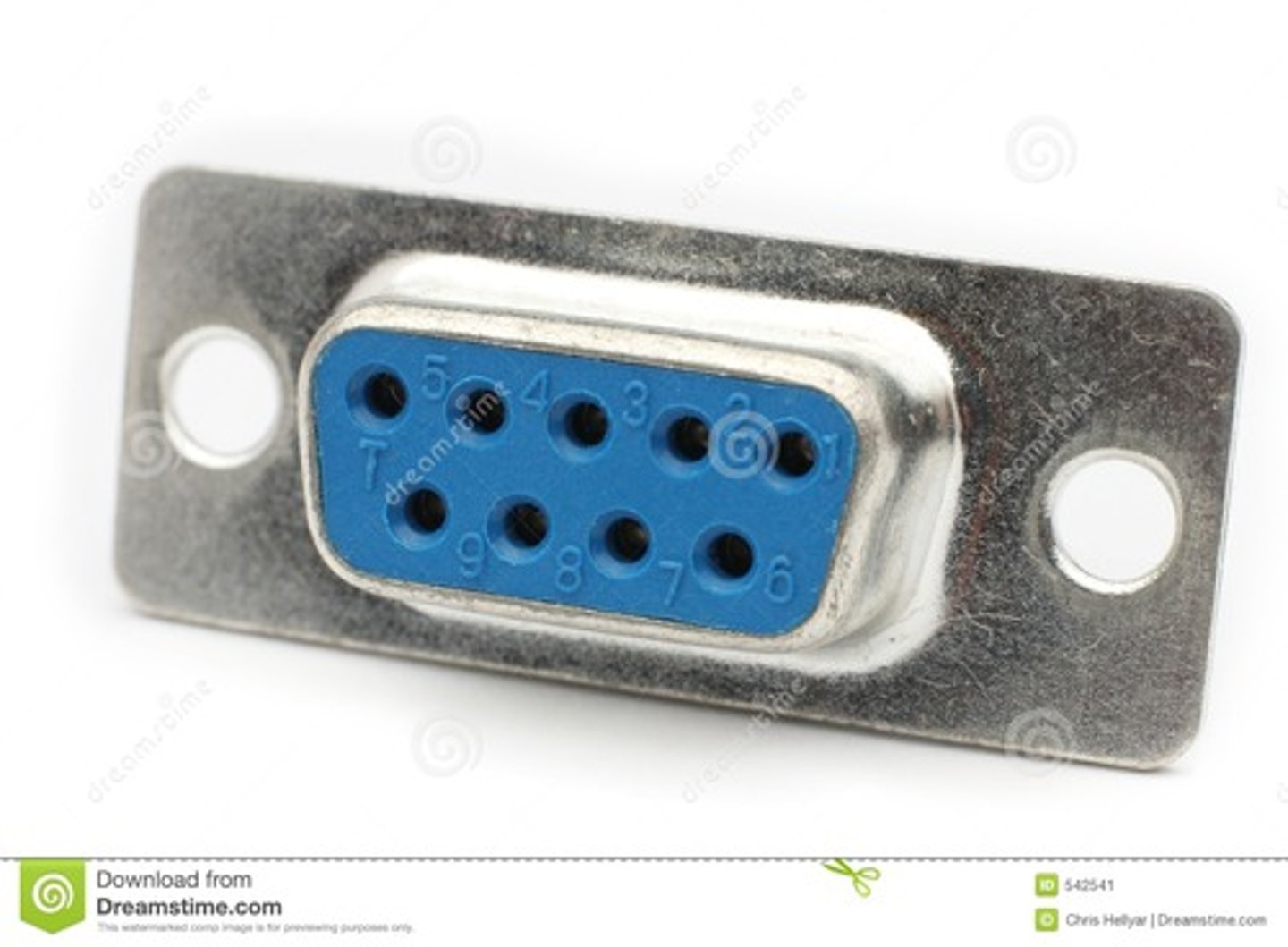
DB-9 connector
A type of connector with nine pins that's commonly used in serial communication that conforms to the RS-232 standard.

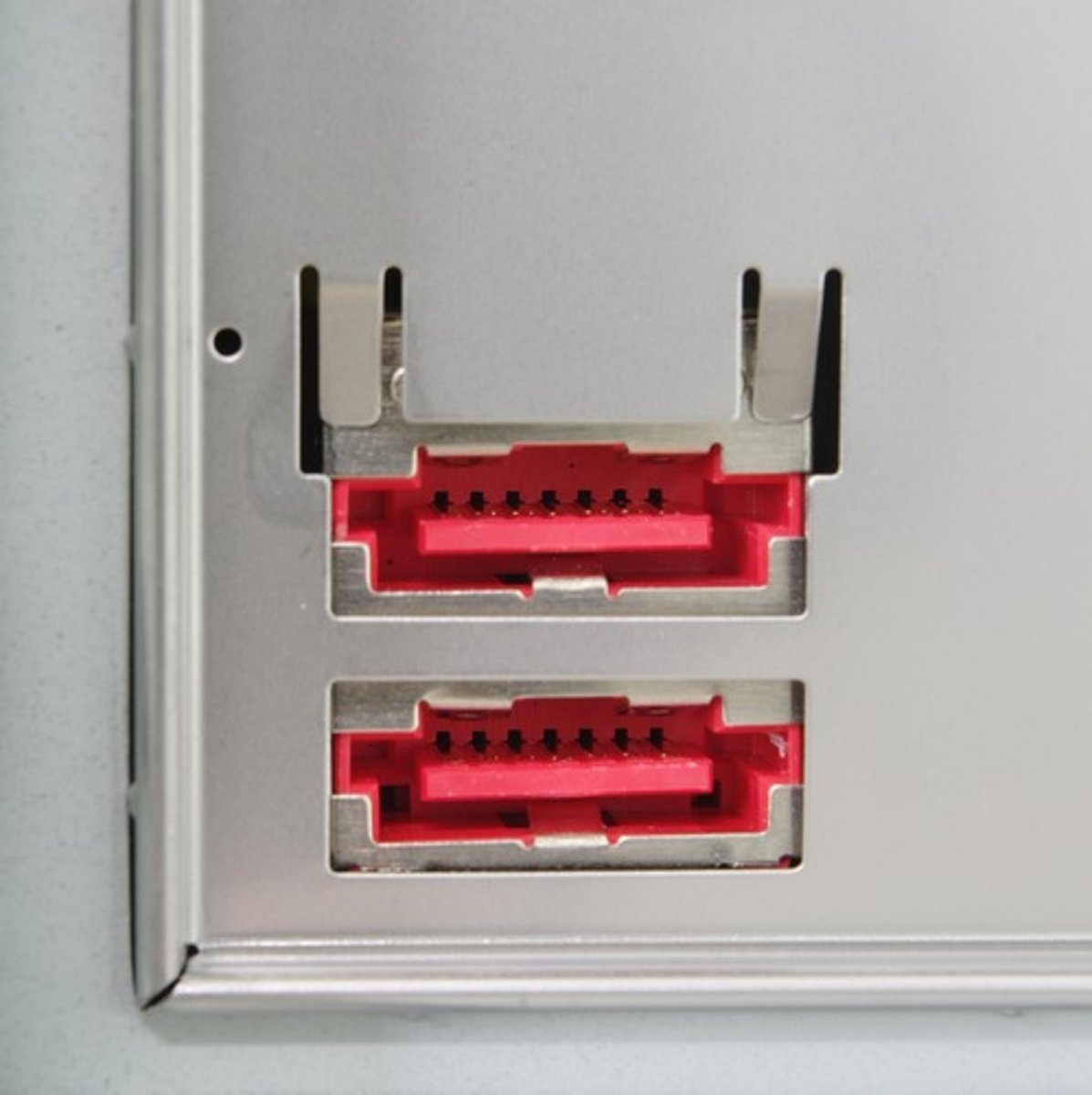
eSATA (External SATA)
Serial ATA-based connector for external hard drives and optical drives.

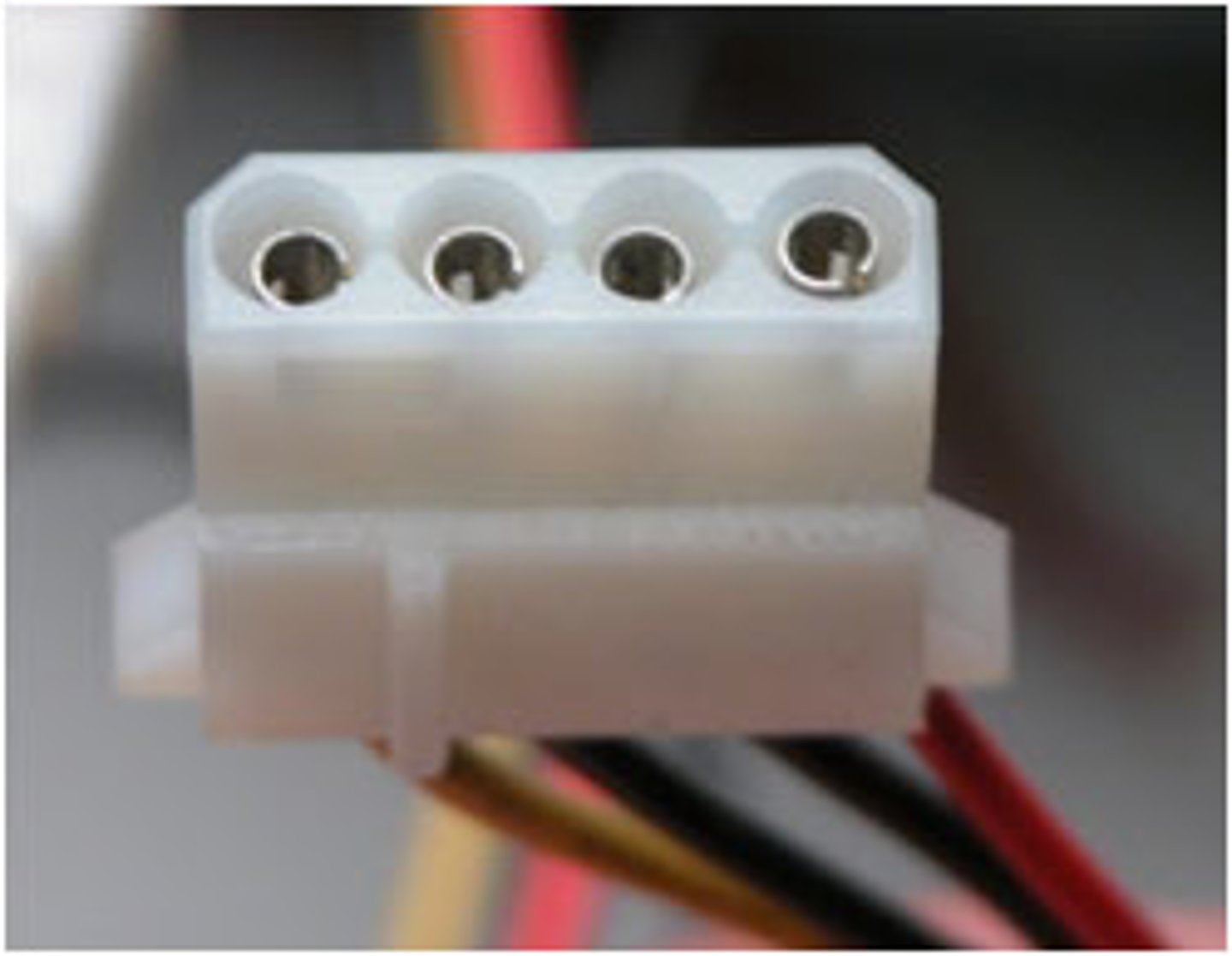
Molex connector
Computer power connector used by optical drives, hard drives, and case fans. Keyed to prevent it from being inserted into a power port improperly.
SODIMM (small outline dual in-line memory module)
A smaller version of a DIMM used in smaller devices such as laptop computers and some printers.

DDR2
A version of SDRAM that is faster than DDR and uses less power.

DDR3
A version of SDRAM that is faster than DDR2 memory and that can use triple channels.

DDR4
Memory that is faster and uses less power than DDR3.

single channel
The memory controller on a motherboard that can access only one DIMM at a time. Compare to dual channel and triple channel.
dual channels
A motherboard feature that improves memory performance by providing two 64-bit channels between memory and the chipset. DDR, DDR2, and DDR3 DIMMs can use dual channels.
Triple channel
A type of memory execution in which motherboards access three memory modules simultaneously
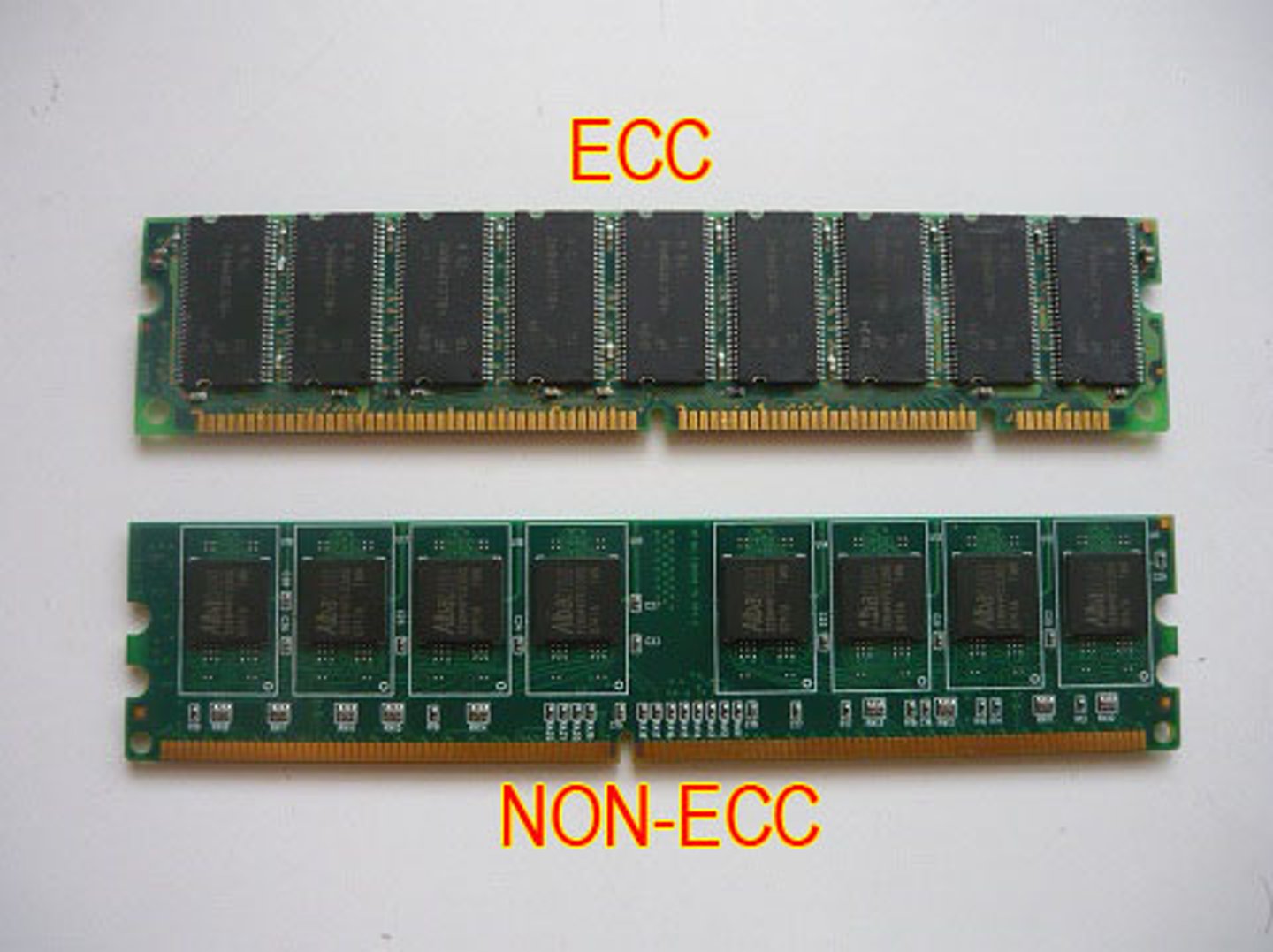
error-correcting code (ECC)
A method of memory error-checking that is more sophisticated than parity checking. Like parity checking, it adds an extra bit per byte. In addition, software in the system memory controller uses an algorithm to both detect and correct errors. (2)

parity bit
an extra bit added to every character; used to check transmission accuracy
Non-Parity RAM
- Type of RAM that doesn't have any error correction.
CD-ROM
Disk that can store up to 680 MB of data; data can only be read from it.
CD-RW
A CD that allows data to be erased and written again several times.

DVD-ROM
a high-capacity optical disc on which users can read but not write on or erase
DVD-RW
Digital versatile disc (DVD) discs that can be written to, and data can also be overwritten. This term also refers to the drives that can write to these discs. (2)
DVD-RW DL
Stands for DVD rewriteable memory, dual layers. Dual layers almost double the storage capacity of DVD-RW discs.
Blu-ray
A disk that enables the recording, rewriting and play back of high-definition video and the storing of large amounts of data. It has more than 5 times the storage capacity of traditional DVDs and can hold up to 25GB on a single layer disk and 50 GB on a dual layer disk.
BD-R
A Blu-ray disc on which you can record data once.
BD-RE (Blu-ray Disc-REwritable)
Blu-ray Disc equivalent of the rewritable DVD, allows writing and rewriting several times on the same BD. (See Blu-ray Disc.)
M.2 SSD
SSD form factor is that's directly installed onto the motherboard
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express)
SSD tech that supports a communication between the operating system and the SSD directly through a PCIe bus lane, reducing latency and taking full advantage of the speeds high-end SSDs. NVMe SSDs come in a couple of formats, such as an add-on expansion card and a 2.5 inch drive, like the SATA drives for portables. NVMe drives are a lot more expensive currently than other SSDs, but offer much higher speeds.
Magnetic hard drives speeds
- 5,400rpm
- 7,200rpm
- 10,000rpm
- 15,000rpm
Hybrid drives
Solid State Hybrid Drive (SSHD)
Both Spinning drive and SSD in a single device
SSD caches the slower spinning hard drive data

CompactFlash (CF) card
A flash memory device that allows for sizes up to 137 GB, although current sizes range up to 32 GB.

Mini-SD card
is a flash memory card designed for use primarily with cell phones, but they found use in other devices that supported the miniSD

Micro-SD card
T-Flash or TransFlash, is a small removable flash memory card that was first developed by SanDisk and approved as a standard on July 13, 2005. MicroSD are the smallest removable flash memory cards, range in available sizes of 128 MB to 4 GB

SD card
one of the more common types of memory cards used with electronics. The SD technology is used by over 400 brands of electronic equipment and over 8000 different models, including digital cameras and cell phones

RAID 0
A RAID array in which every time data is written to disk, a portion (block) is written to each disk in turn, creating a "stripe" of data across the member disks. uses the total disk space in the array for storage, without protecting the data from drive failure. (2)
RAID 1
Also called mirroring, this RAID array type provides fault tolerance because all the data is written identically to the two drives in the mirrored set. (2)
RAID 5
A technique that stripes data across three or more drives and uses parity checking, so that if one drive fails, the other drives can re-create the data stored on the failed drive increase performance and provide fault tolerance.
RAID 10
a combination of RaID 1 and RaID 0 that requires at least four disks to work as an array of drives and provides the best redundancy and performance.
hot-swappable
The ability to plug or unplug devices without first powering down the system. USB devices are hot-swappable.
ATX (Advanced Technology Extended)
The most common form factor for PC systems presently in use, originally introduced by Intel in 1995. ATX motherboards and cases make better use of space and resources than did the earlier AT form factor.
mATX
Micro Advanced Technology Extended. Fits cases that follows ATX 2.1 or higher.
ITX Form Factor
is a small motherboard form factor from VIA Technologies that was first introduced in November 2001 with the Mini-ITX.
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI)
Introduced in 1993, the most common expansion bus architecture in PCs in the mid 1990s. It transfers data in parallel over a data bus that is either 32- or 64-bits wide. (1)
PCIe (PCI Express)
• Serial communication - xl, x2, x4, x8, xl6, x32 lanes
• High performance for devices like high-end graphics adapters
• PCI Express throughput per-lane in each direction
• Speeds from 250 MB/s to 2 GB/s
Riser Card
is a board that plugs into the system board and provides additional slots for adapter cards. Because it rises above the system board, it enables you to connect additional adapters to the system in an orientation that is parallel to the system board and save space within the system case.

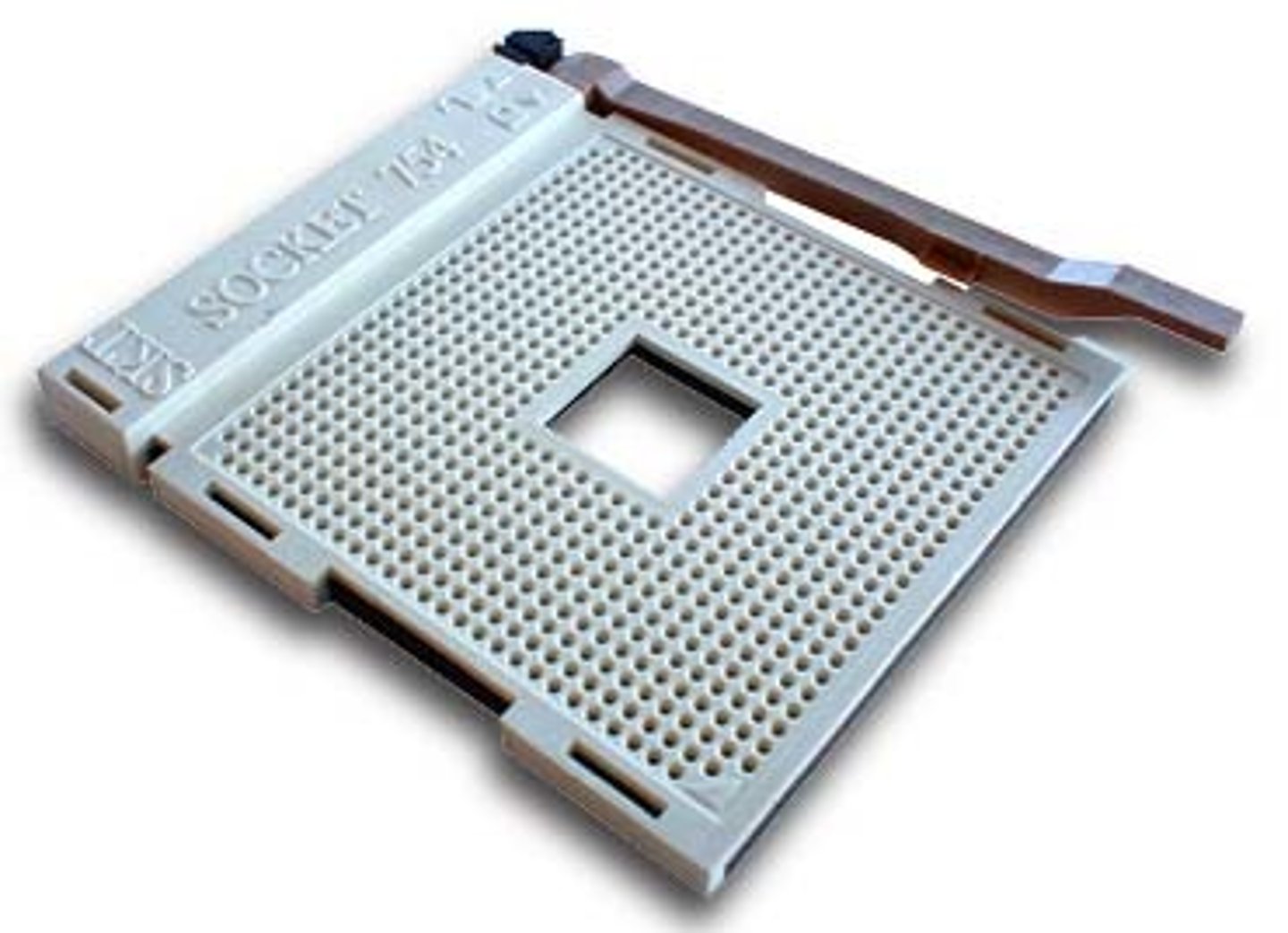
zero insertion force (ZIF) socket
A socket for a PGA CPU that has a retention lever as well as contacts to match the number of pins on the CPU. The lever is used to attach the CPU to the socket in a manner that does not require force to insert or to remove the CPU. (1)
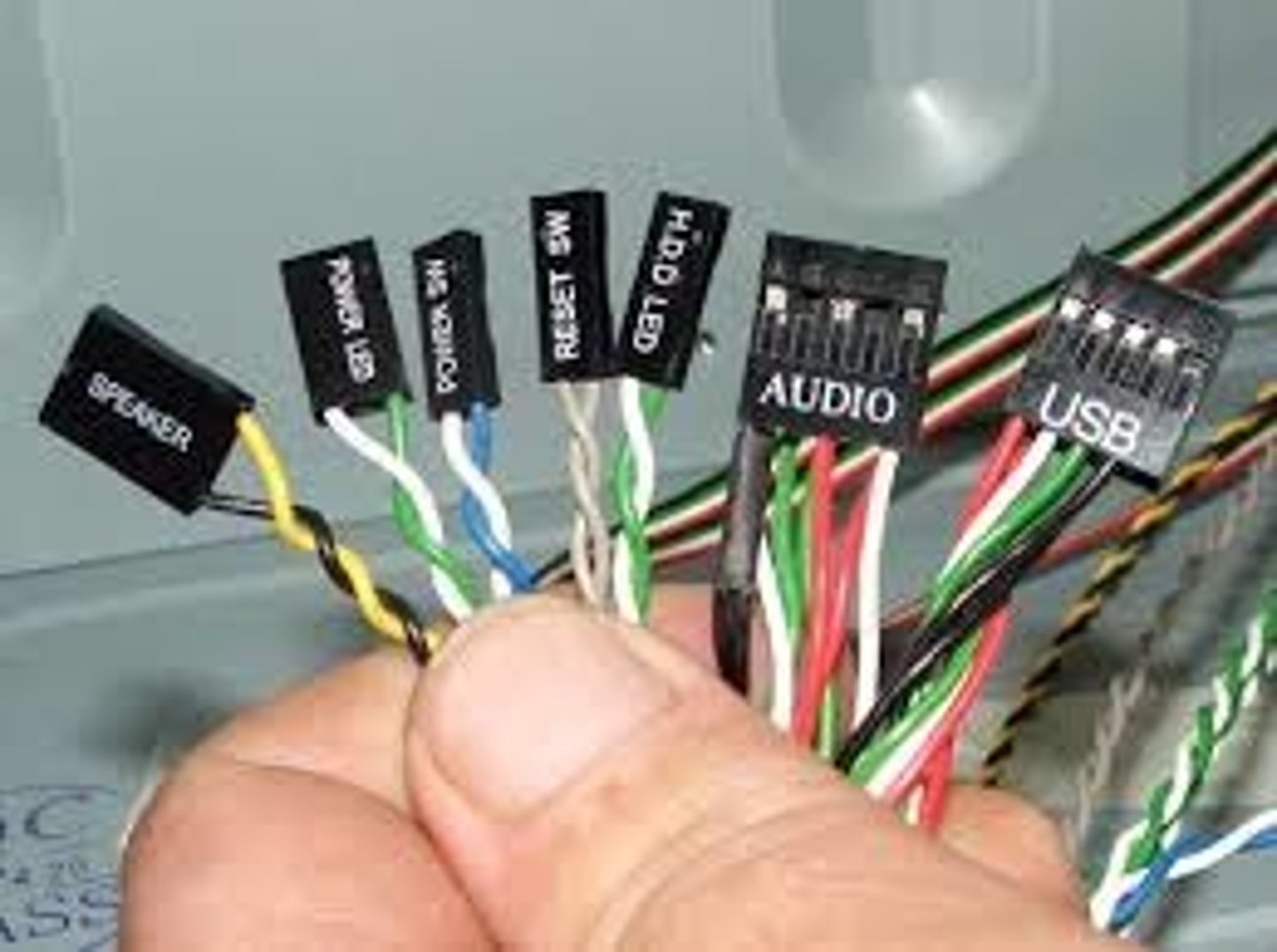
Front Panel Connectors
A group of wires running from the front of the computer case to the motherboard

Land Grid Array (LGA)
A feature of a CPU socket whereby pads, called lands, are used to make contact in uniform rows over the socket. Compare to pin grid array (PGA).
Firmware Updates
• Can have dramatic change on wireless performance
• May improve compatibility with chipsets from other devices
Secure Boot
A UEFI feature that prevents a system from booting up with drivers or an OS that are not digitally signed and trusted by the motherboard or computer manufacturer.
LoJack
A technology by Absolute Software used to track the whereabouts of a laptop computer and, if the computer is stolen, lock down access to the computer or erase data on it. The technology is embedded in the BIOS of many laptops.
TPM (Trusted Platform Module)
A chip on the motherboard used with software applications for security. It can be used with Windows BitLocker Drive Encryption to provide full-disk encryption and to monitor for system tampering.
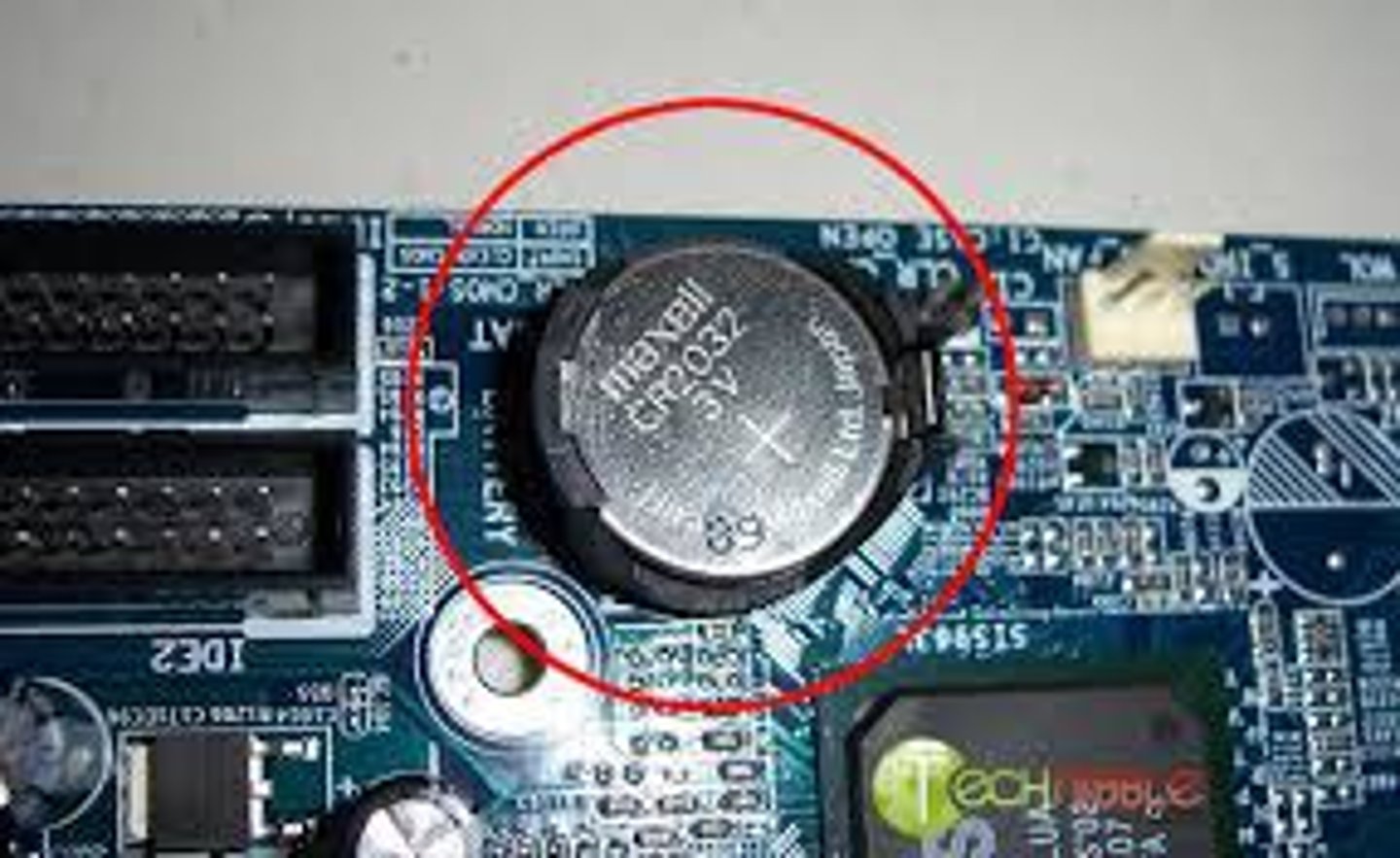
CMOS battery
The battery on the motherboard used to power the CMOS chip when the computer is unplugged.

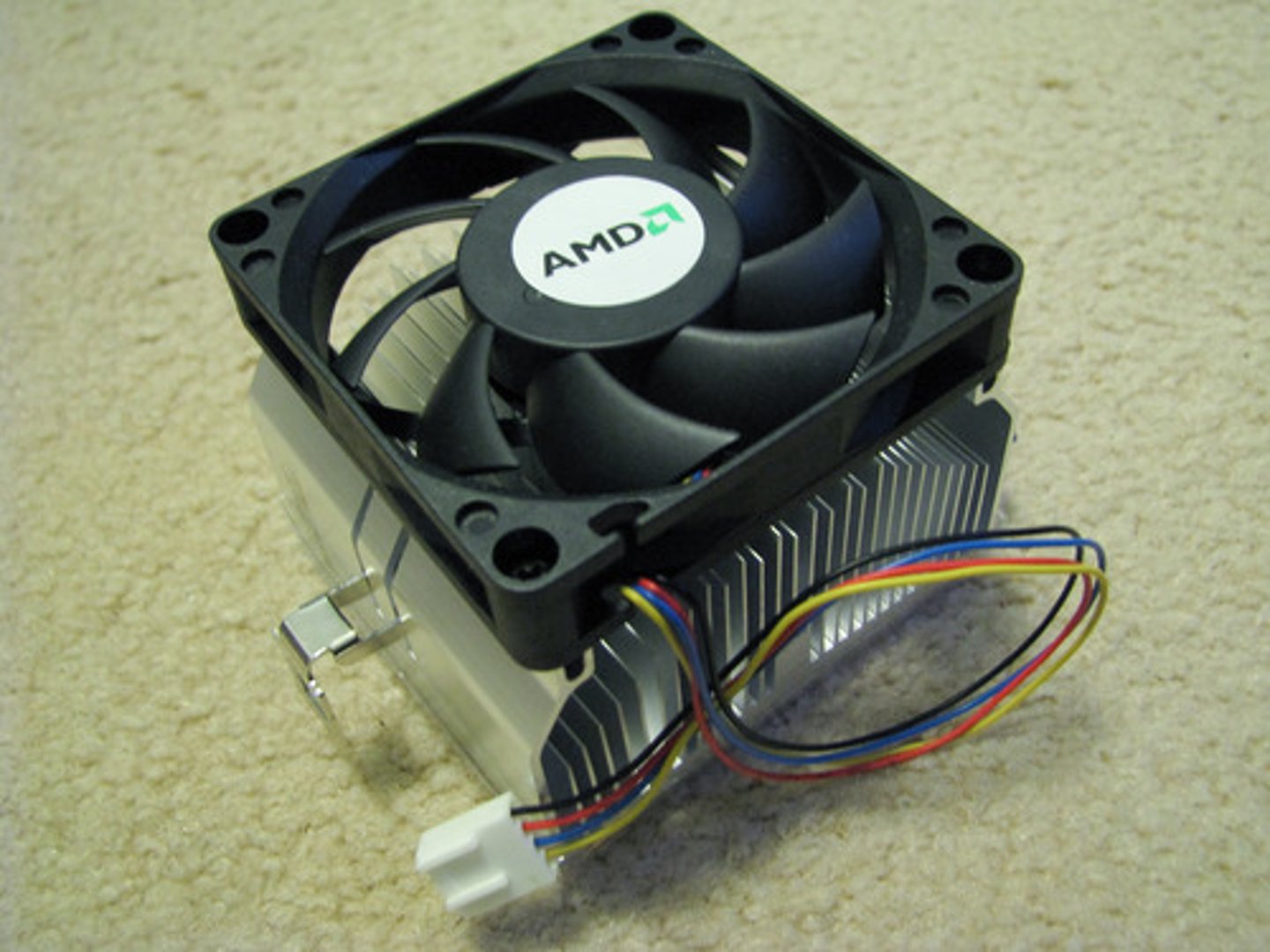
single-core processor
A CPU with one processor on the chip.
multicore processor
Integrated circuit to which two or more processors have been attached for enhanced performance, reduced power consumption and more efficient simultaneous processing of multiple tasks.
Virtualization
running multiple systems simultaneously on one physical computer
Hyperthreading
A technology that permits quicker processing of information by enabling a new set of instructions to start executing before the previous set has finished.
Overclocking
Running a processor at a higher frequency than is recommended by the manufacturer, which can result in an unstable system, but is a popular thing to do when a computer is used for gaming.
Integrated GPU (Graphics Processing Unit)
Located withing the CPU, improves processing graphical capabilities, but not intended for high-end usage
CPU Speeds
is the speed that the microprocessor executes each instruction or each vibration of the clock. The CPU requires a fixed number of clock ticks, or cycles, to execute each instruction.
Case Fan
A fan inside a computer case used to draw air out of or into the case.

heat sink
A piece of metal, with cooling fins, that can be attached to or mounted on an integrated chip (such as the CPU) to dissipate heat.

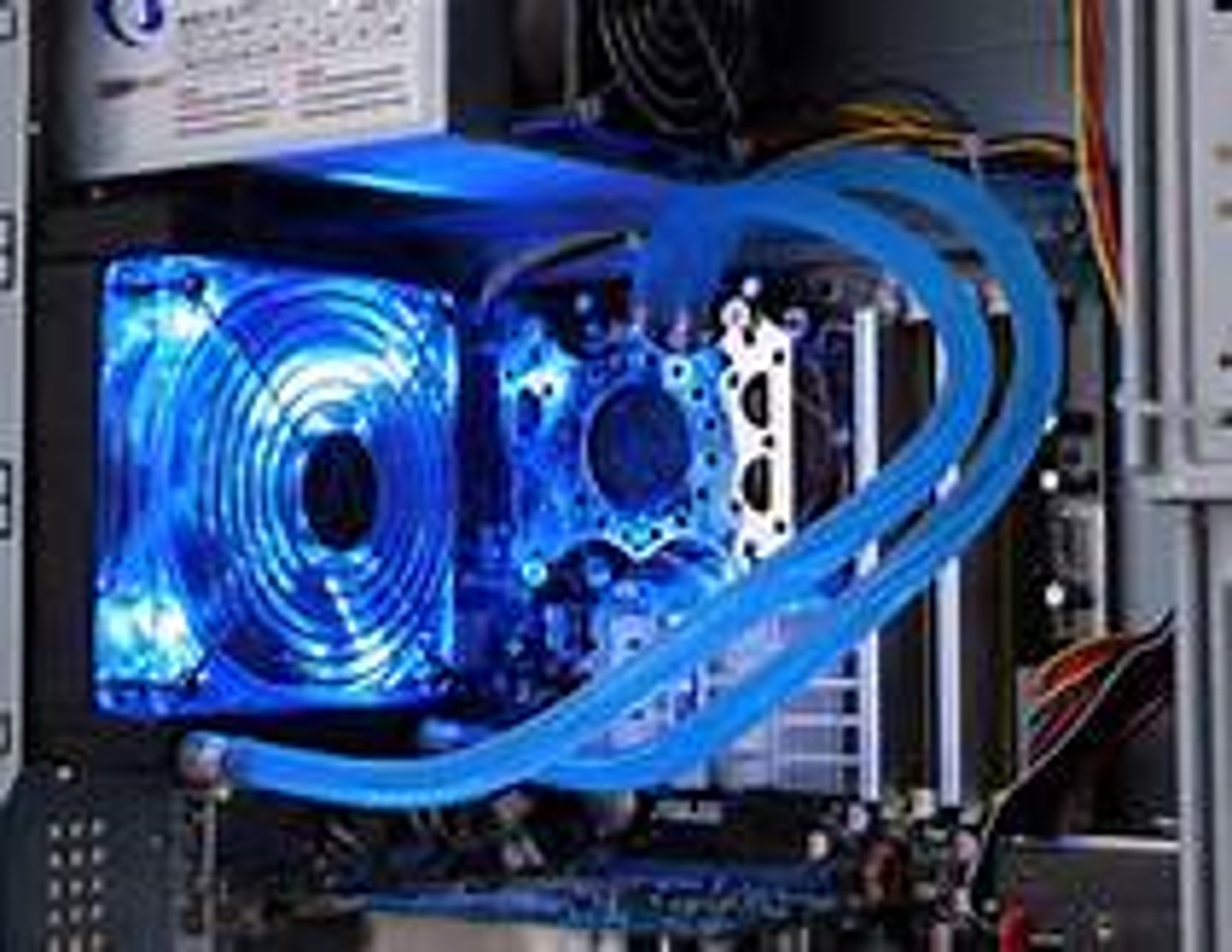
Liquid Cooling
A method of cooling a PC that works by running some liquid—
usually water—through a metal block that sits on top of the CPU, absorbing heat. The
liquid gets heated by the block, runs out of the block and into something that cools the
liquid, and is then pumped through the block again.

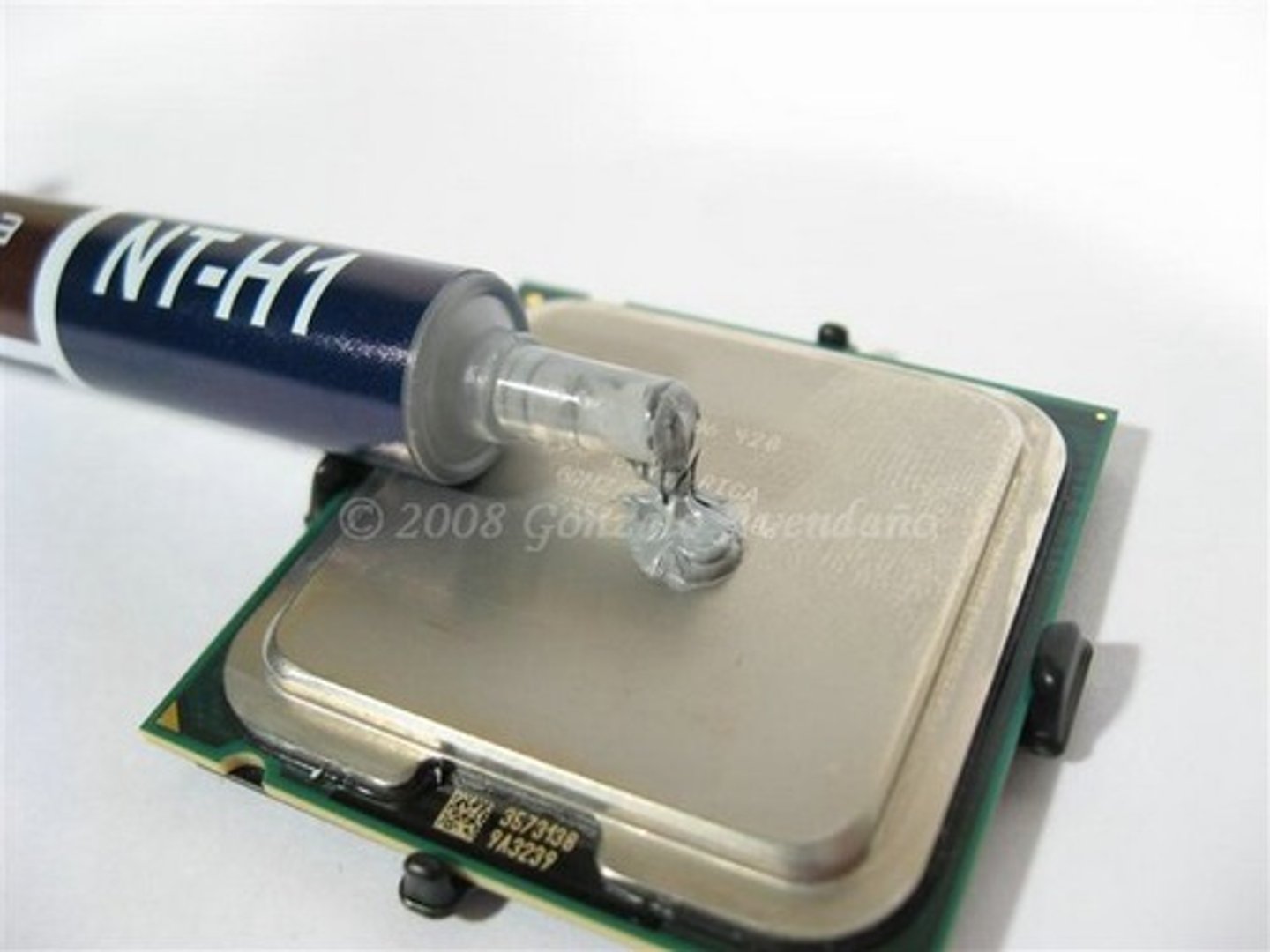
Thermal Paste
A special compound used between CPUs and heat sinks. It fills in microscopic gaps and helps draw heat from the CPU into the heat sink where it is dissipated.

Video cards
Connect to motherboards by way of x16 PCIe or PCI (uncommon) and cables include DVI, VGA, HDMI, Mini-HDMI, DisplayPort, Mini DisplayPort, S-Video, Component Video/RGB, and Composite.
Common color depths include 16-bit, 24-bit, and 32-bit.
Common Resolutions include:
1280x720 (720p 16:9 aspect ratio)
1920x1080 (HD 1080p, 16:9 aspect ratio)
1366x786 (16:9)
1680x1050 (WSXGA+, 8:5 aspect ratio)
1920x1200 (WSXGA, 8:5)
640x480 (VGA, 4:3).
TN is twisted nematic
IPS is in-plane switching. IPS has wider viewing angles.
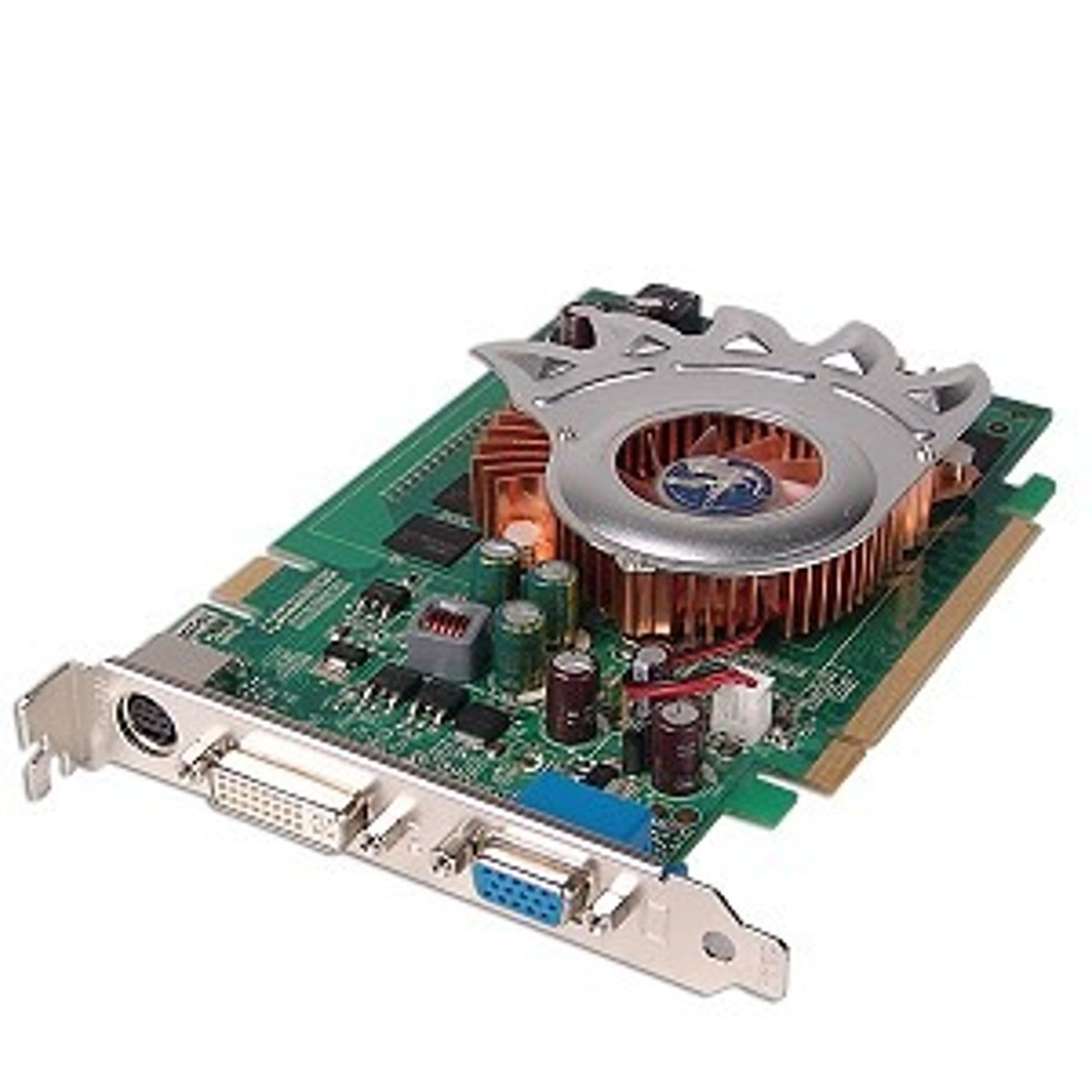

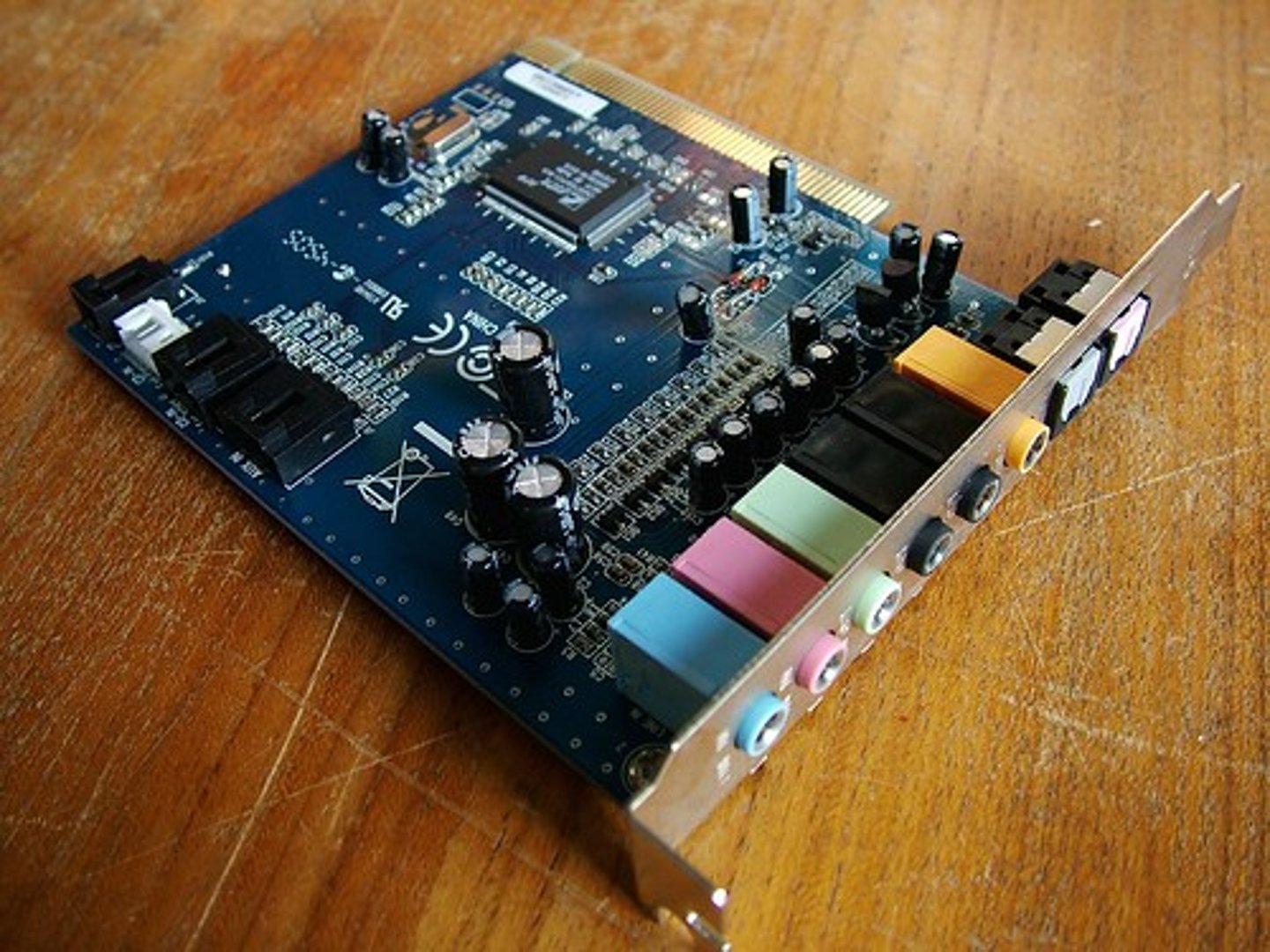
Sound Cards
connect as x1 PCIe or PCI cards and normally have PC 99 color-coded 1/8" mini-jacks for I/O and speakers and optical I/Os known as S/PDIF.
(Example: TOSLINK)
Network Interface Card (NIC)
An expansion card that enables a computer to connect other computers or to a cable modem to facilitate a high-speed Internet connection.

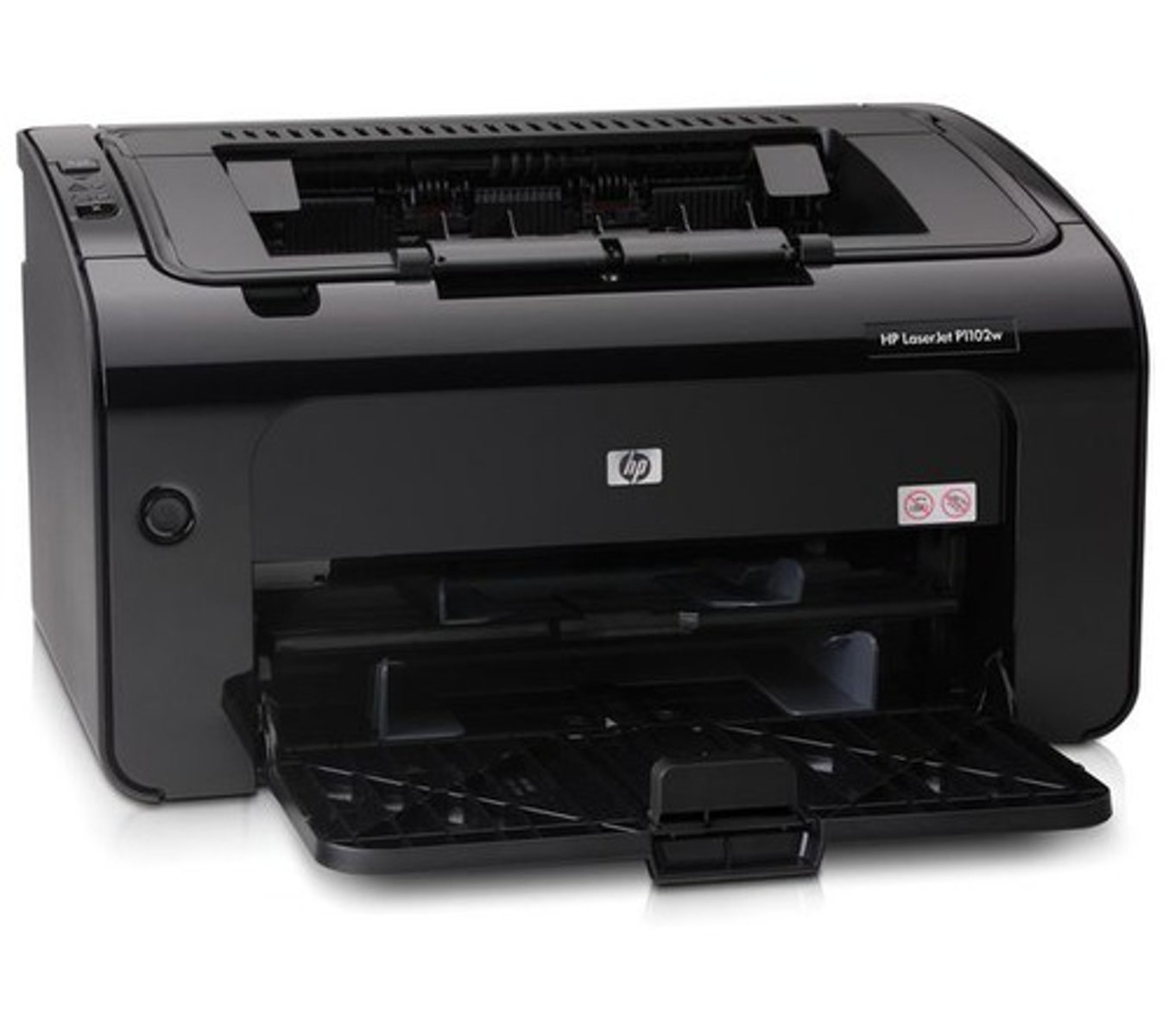
printer
an output device that prints the results of data processing

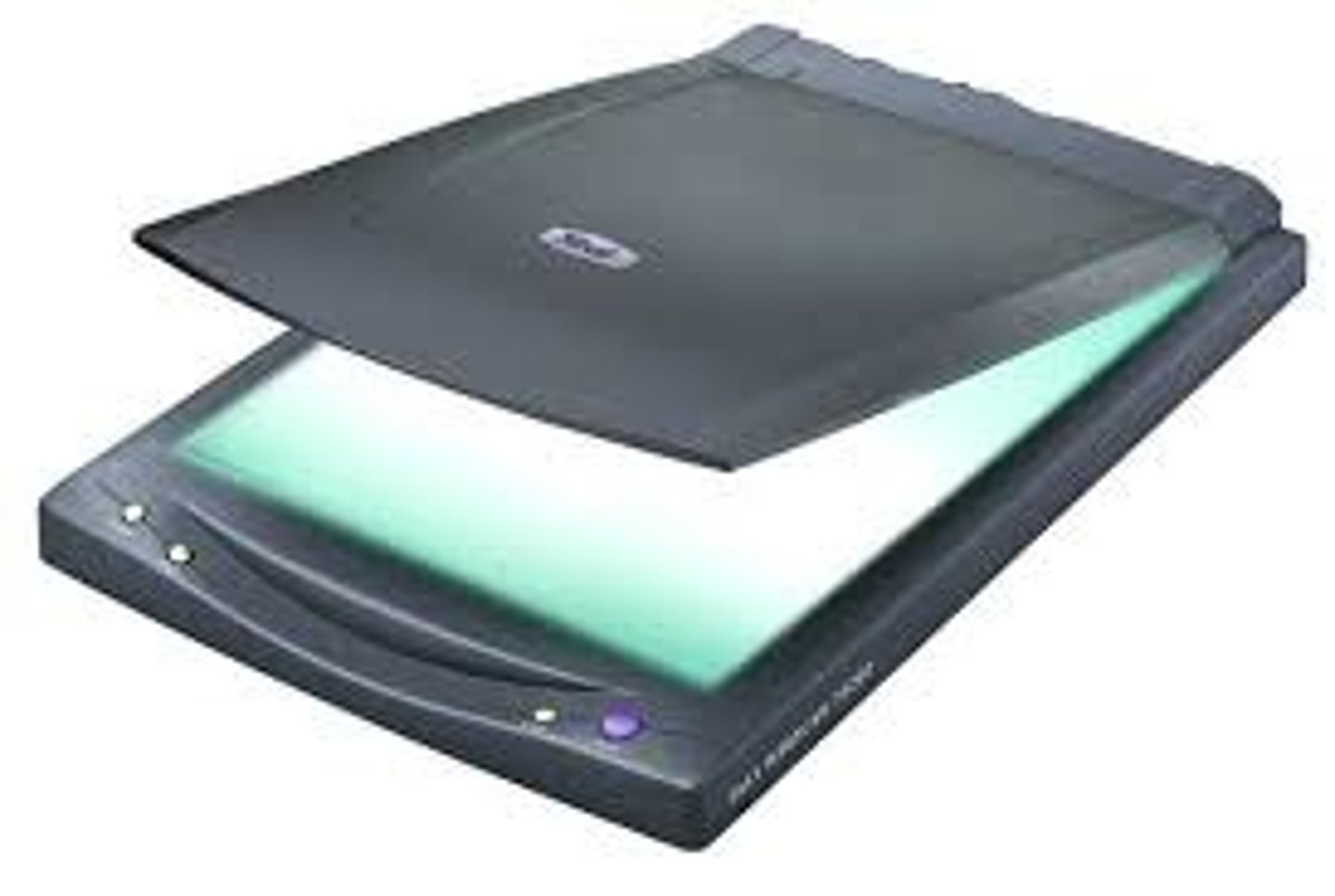
flatbed scanner
works in a manner similar to a copy machine except it creates a file of the document in memory instead of a paper copy

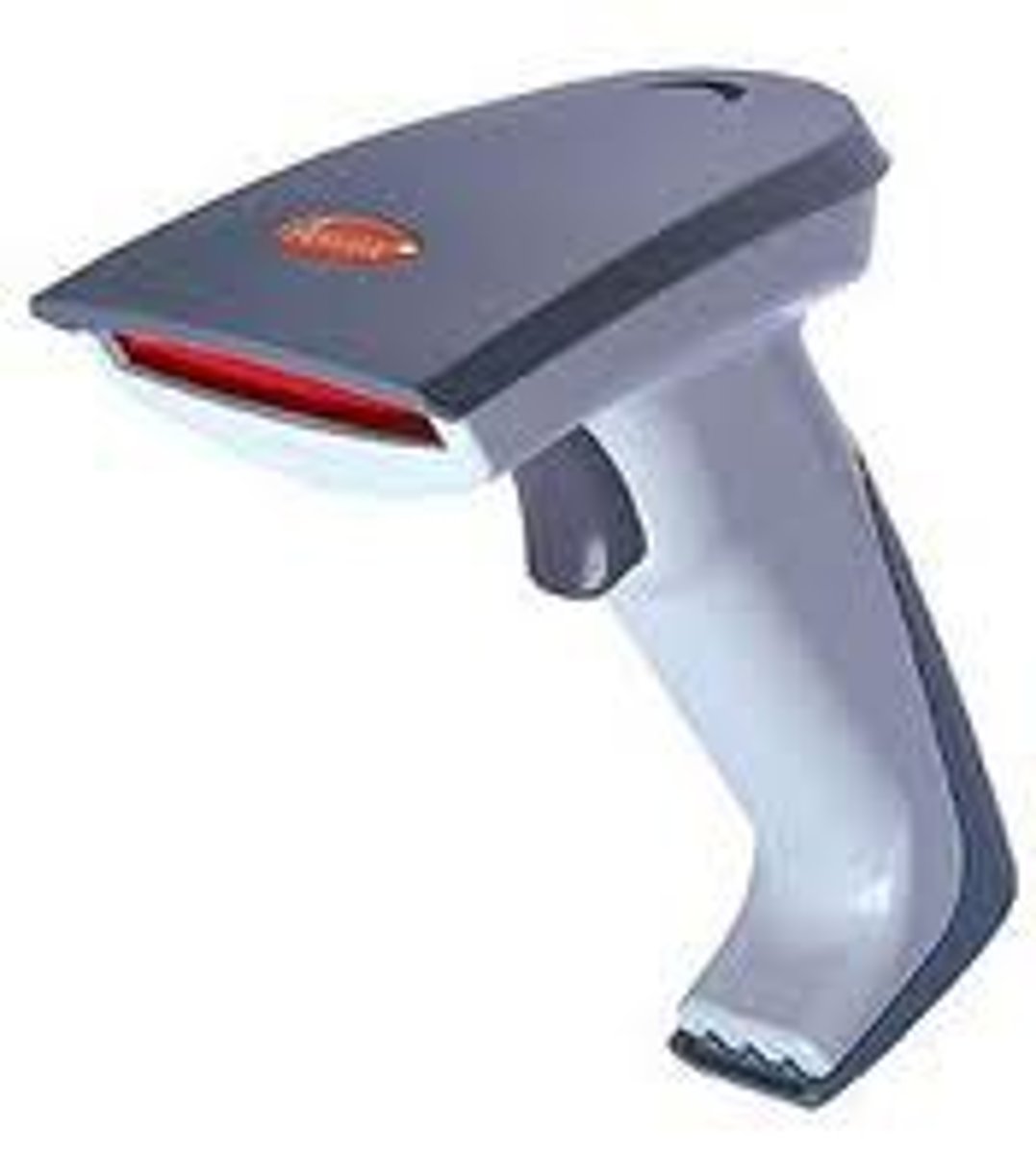
barcode scanner
Input devices that read bar codes that allow you to track both assets and inventory, check items in, manage item locations, maintain physical inventory, and control fixed assets.

Monitors
screens connected to a computer, which show information and instructions