Carbohydrate Metabolism Overview and Pathways
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Carbohydrate Metabolism
Biochemical process converting carbohydrates into energy.
Seager et al.
Authors of the textbook on biochemistry.
Cengage
Publisher of the biochemistry textbook used.
General Biochemistry
Study of biochemical processes in living organisms.
Organic Biochemistry
Focus on carbon-containing compounds in biological systems.
Carbohydrate digestion
Hydrolysis of di- and polysaccharides to monosaccharides.
Blood glucose level
Amount of glucose in blood, mg per 100 mL.
Hypoglycemia
Lower-than-normal blood sugar level.
Hyperglycemia
Higher-than-normal blood sugar level.
Renal threshold
Blood sugar level where kidneys stop reabsorbing glucose.
Glucosuria
Excretion of glucose in urine due to high blood sugar.
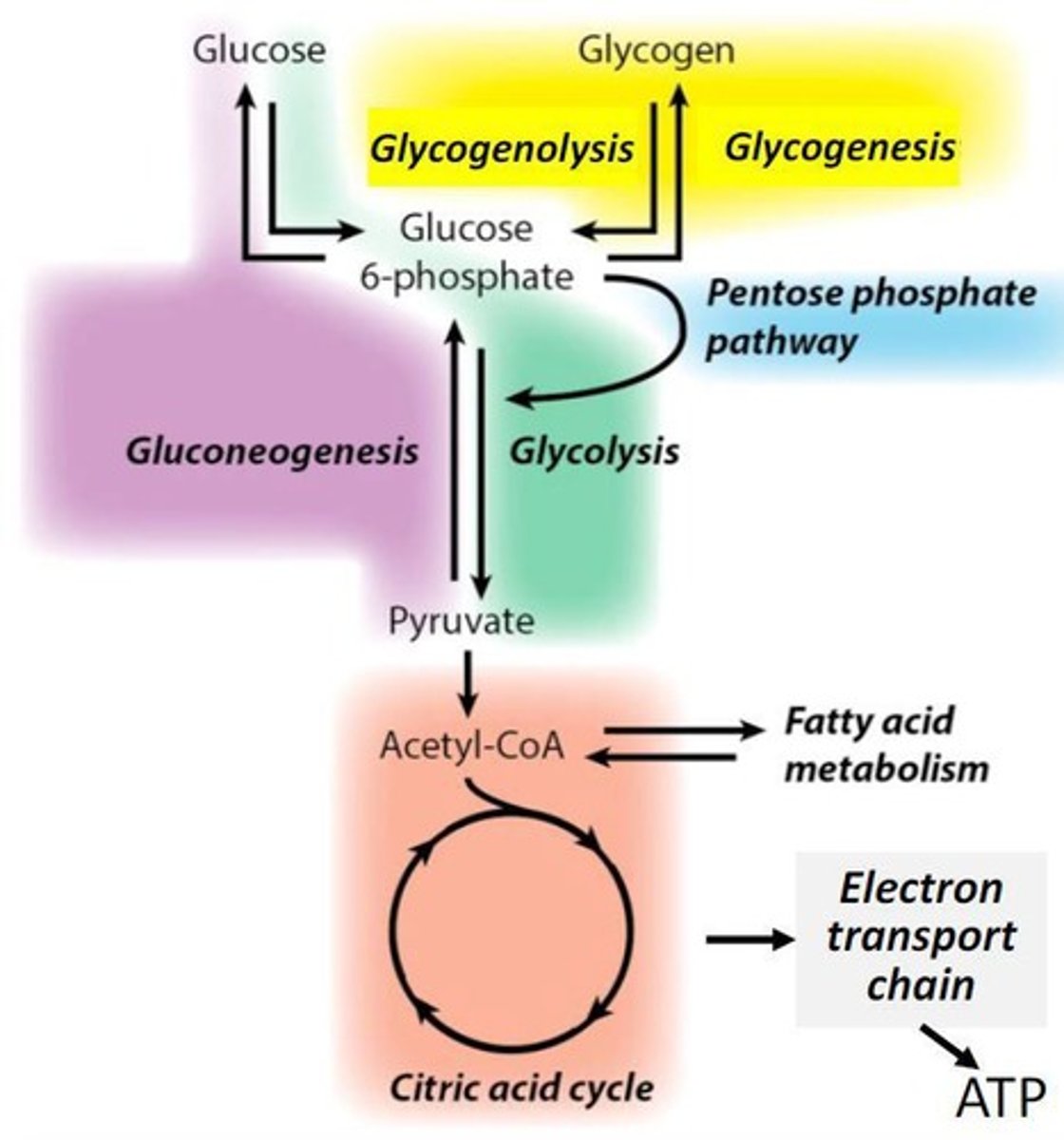
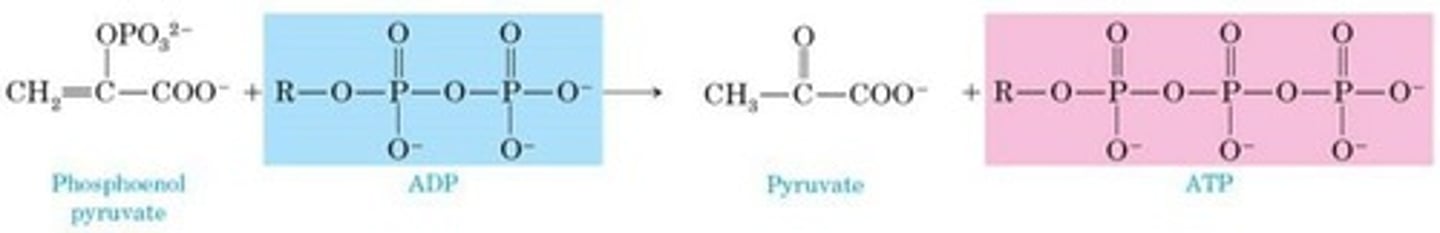
Glycolysis
Pathway converting glucose to pyruvate, producing ATP.
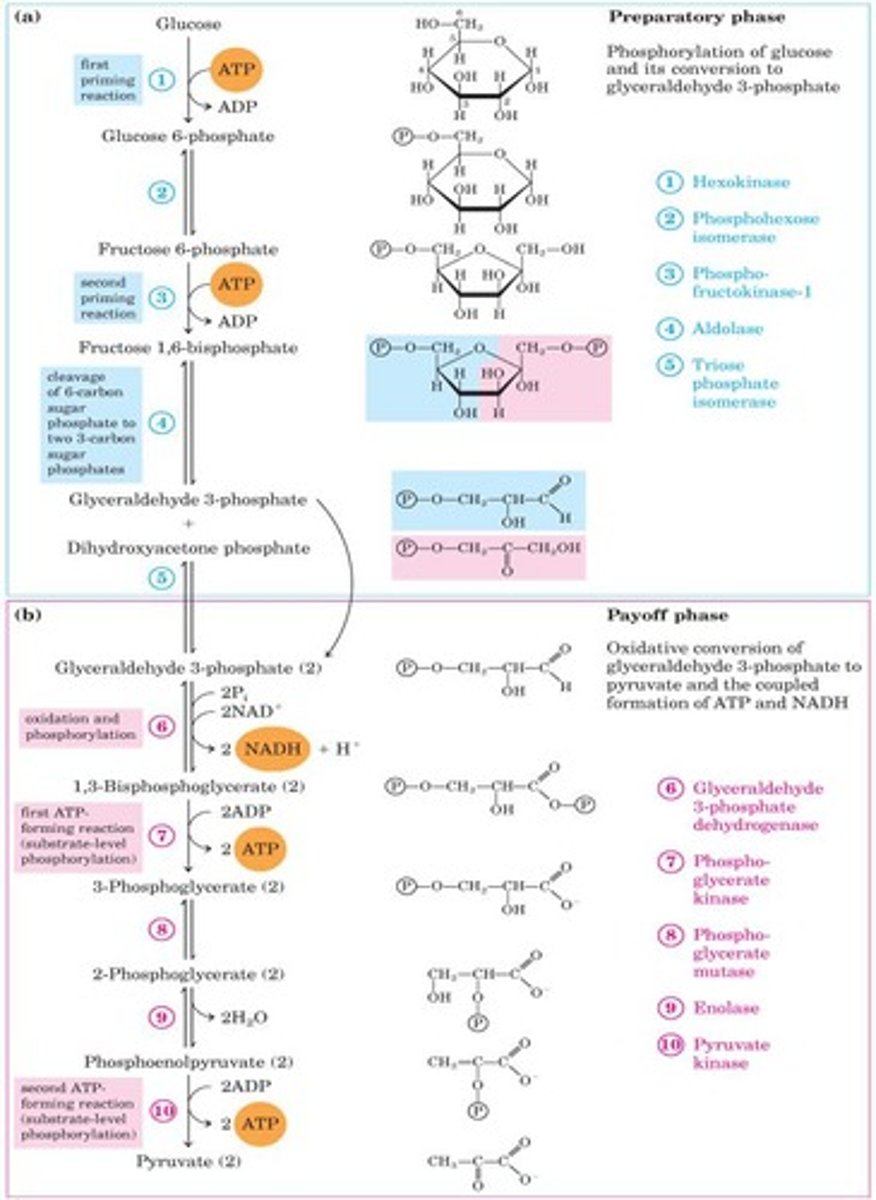
Net reaction of glycolysis
glucose + 2Pi + 2ADP + 2NAD+ → 2Pyruvate + 2ATP.
Fates of pyruvate
Oxidized to acetyl CoA, reduced to lactate or ethanol.
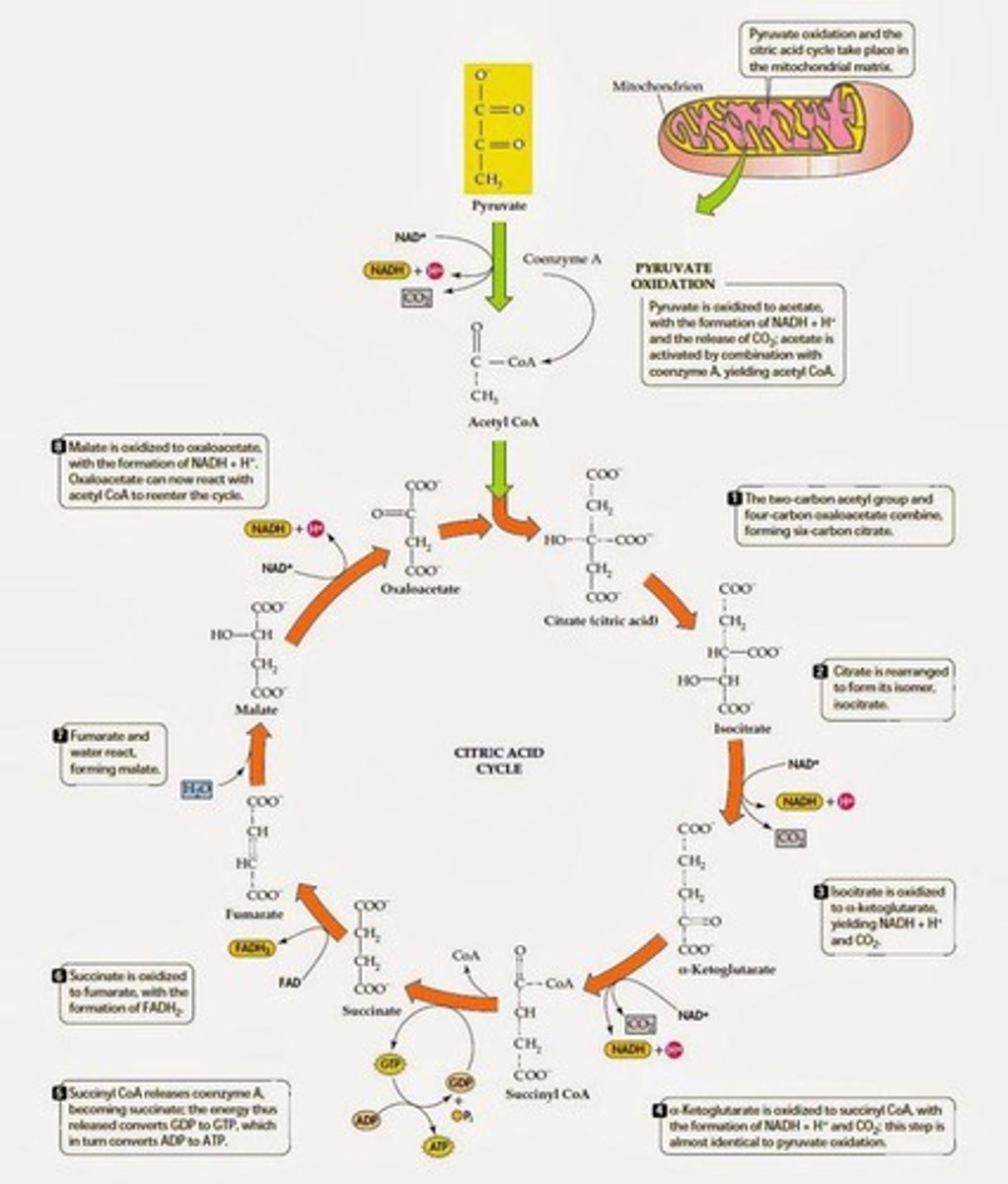
Citric acid cycle
Oxidizes acetyl CoA to CO2, generates NADH and FADH2.
Regulation of glycolysis
Controlled by hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, pyruvate kinase.
Feedback inhibition
Glucose-6-phosphate inhibits hexokinase activity.
Oxidative phosphorylation
Process converting ADP to ATP during electron transport.
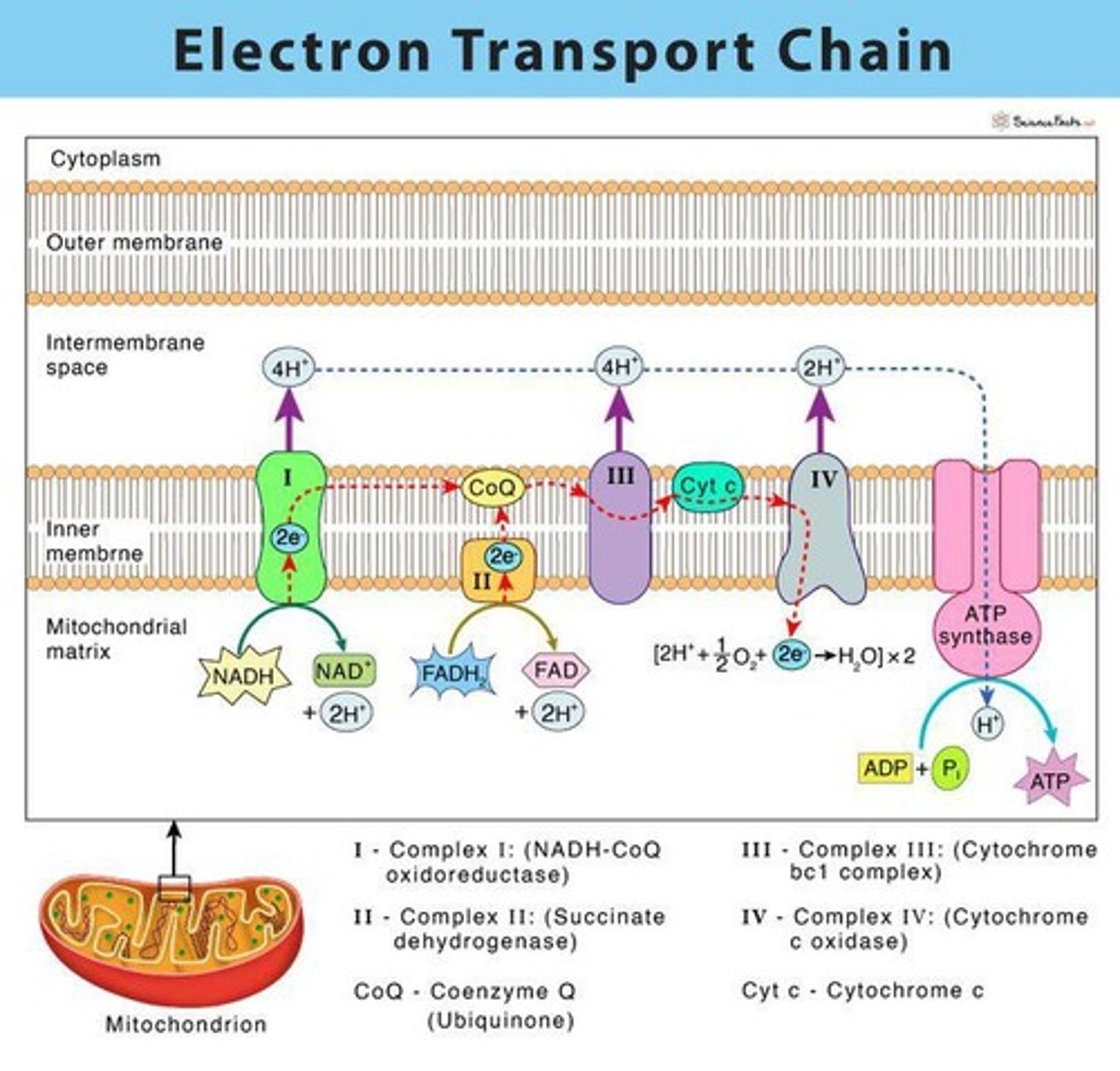
ATP yield from NADH
Each NADH generates 2.5 ATP during oxidation.
ATP yield from FADH2
Each FADH2 generates 1.5 ATP during oxidation.
Chemiosmotic hypothesis
Proton flow drives ATP synthesis in mitochondria.
Complete oxidation of glucose
Total ATP yield from glycolysis, citric acid cycle, and electron transport.
Glycogenesis
Process of converting glucose to glycogen for storage.
Glycogenolysis
Breakdown of glycogen to release glucose.
Gluconeogenesis
Synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors.
Cori cycle
Recycles lactate to glucose in the liver.
Acetyl CoA
Key metabolite entering the citric acid cycle.
Electron transport chain
Series of reactions reducing oxygen to water.
Cytochromes
Iron-containing enzymes in the electron transport chain.
Lactate fermentation
Anaerobic conversion of glucose to lactate.
Alcoholic fermentation
Anaerobic conversion of glucose to ethanol.
Energy yield from glucose
Net yield of 32 ATP from complete oxidation.
ATP production from GTP
1 GTP is equivalent to 1 ATP.
Oxidation of pyruvate
Conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA in mitochondria.
Regulation of citric acid cycle
Stimulated by low ATP and high ADP levels.
Proton flow
Drives ATP synthesis via ATP synthase.
NAD+ regeneration
Necessary for glycolysis to continue after pyruvate processing.
Glucose Oxidation
Releases 686 kcal/mol of energy.
ATP Synthesis
Captures 234 kcal/mol from glucose oxidation.
Overall Reaction
C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 32ADP + 32Pi → 6CO2 + 32ATP + 38H2O.
Energy Efficiency
34% of free energy captured by cells.
Automobile Engine Efficiency
20-30% energy from gasoline is usable.
Glycogenesis
Synthesis of glycogen from glucose.
Glycogen Storage in Liver
Liver can store 110 g of glycogen.
Glycogen Storage in Muscles
Muscles can store 245 g of glycogen.
Glycogen Synthase
Enzyme forming α(1→4) linkages in glycogen.
Amylo (1,4-1,6)-trans-glycosylase
Inserts α(1→6) branch points in glycogen.
Glycogenolysis
Breakdown of glycogen to glucose.
Glycogen Phosphorylase
Enzyme cleaving α(1→4) linkages.
Debranching Enzyme
Cleaves α(1→6) linkages during glycogenolysis.
Glucose-6-Phosphate Hydrolysis
Converts glucose-6-phosphate to glucose.
Muscle Cell Limitations
Cannot form free glucose from glycogen.
Liver Function
Maintains blood glucose levels by releasing glucose.
Gluconeogenesis
Synthesis of glucose from noncarbohydrate sources.
Cori Cycle
Glucose-lactate cycle between muscle and liver.
Lactate Conversion
Lactate converted back to glucose in liver.
Insulin
Hormone enhancing glucose absorption into cells.
Glucagon
Hormone increasing blood glucose levels.