POG100 - MIDTERM
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
Power is the ability to _____________. (textbook definition)
achieve goals + to get others to do what you want.
What is Power (Max Weber)?
the probability that one actor within a social relationship will be in a position to carry out his own will depite resistance
Is Power Neutral?
Yes. It is an objective, scientific way of laying out what we are learning.
What are the 3 ways to look at power?
CAP
The ability to win on contested decisions.
(peasants are scared 2 contest bc of conflict - feudalism: power from above, ruling class)
The ability to get your issues on the agenda and to keep other issues off.
(the power to say “idc abt the issue so we arent talking abt it”)
The ability to shape others’ perceptions and preferences.
(raised 2 live along preconceived social hierarchy, what u learn from society shapes your “role”)
The study of politics is often described as a….
social science. Like a “natural” science, one of its goals is to find predictable rules and regularities to explain past events and predict future ones. This is why you’ll often hear about “political science”—a term that became increasingly common around the turn of the 20th century.
What are the 4 subfields of POG?
Theory
International
Canadian
Comparative - method of political analysis that compares different systems of political authority based on system type, time period, or form of leadership
Where does the word “theory” originate from?
the word "theory" comes from the Greek word "theoros: a witness or spectator
Political Theory is about…
trying to make sense of political events at a higher level of abstraction.
putting ideas together → leading to a higher understanding + potential solutions (ie. supply and demand - think abt causes + solutions)
theorists ask things like:
“what is happening?”
“why is it happening?”
“what should be done about it?”
What meanings come with “theory” ? ancient Greece sending ppl to athletic games or a festival (LBR)
Think of “theory” as having meanings of looking at, bearing witness, and reporting back what you see.
What does “bear witness” mean?
means to understand the issue on a deeper, general level + explaining it to others (“what are the forces behind everything?”)
This is one thing theories do in the physical sciences: e.g., the theory of gravitation or the theory of evolution. They explain seemingly disconnected events at a higher level of abstraction or generality.
PLATO - Why are so many states badly ruled?
- states are badly ordered + don’t reserve power for people with knowledge of the good
- ppl w philosophical knowledge should rule the state
THOMAS HOBBES - What causes violent conflict and civil war? How can we make these less likely?
People don’t understand how much better it is to
have a state than to live without one. If people were rational, they’d agree to live under an absolute and arbitrary sovereign.
live under a singular ruling (king), submit yourself to something.
EDMUND BURKE - Revolutions that start for understandable reasons can get out of hand and become destructive.
think about how traditions and institutions embody more wisdom that individuals
traits of conservatism
HARRIET TAYLOR MILL - Why does the law give overwhelming power to men when women are just as intelligent?
We should think of the reasons why people are afraid to depart from the status quo, even when it’s unjust.
Political Change
KARL MARX - Humanity is increasingly productive, but individuals are increasingly miserable. Why?
Capitalism is a system that generates huge
wealth and productive power, but only through
exploitation
FRANTZ FRANTON - Why has imperialism lasted so long?
Imperialist systems repress subject peoples with
violence, but also treats them as less than human—an idea they often internalize.
What types of questions do PT’s ask (3-CPN)?
conceptual questions: clarify the meanings of key political ideas, “what is equality?”
historical questions: how political ideas changed overtime + how political conditions shaped the ideas that thinkers developed
normative questions: questions using evaluative terms like should, ought, best, and right, “What is the best form of government?”
What is an ideology?
It is a political belief system. It can be thin (feminism etc.) or thick (broader concepts like liberalism)
Those beliefs can be about government, the economy, the nature of human beings, the good
life, etc. In general, they are supposed to lead to political action.
What are some key parts of liberal ideology (4)?
Protection of individual rights, including religious, expressive, and property rights
The state’s main reason for being is to safeguard those rights, especially from violence and unchecked authority
Limits on government to protect individual rights
Toleration and neutrality on “the good life” - anyone can o what they want, the state will not have a say on ppl belief's + philosophies
Liberalism: thick or thin ideology?
thick - it remains the most dominant ideology in most western democracies
how do liberalism and democracy fit together? Is liberal democracy a “marriage of convenience,” or something else?
Liberalism and democracy are closely intertwined in a liberal democracy. It's not merely a "marriage of convenience" but a system where democratic governance and the protection of individual rights and freedoms are combined to create an inclusive and respectful political order.
who best represents liberalism’s concern with freedom, “classical liberals,” or “social liberals”?
"Classical liberals" best represent liberalism's concern with freedom, emphasizing individual liberty and limited government intervention, while "social liberals" also value freedom but may prioritize social and economic equality, sometimes requiring more government intervention.
what kinds of assumptions does liberalism make about human beings? Are these viable assumptions?
Liberalism assumes that individuals are rational, equal, and capable of peaceful coexistence. While these assumptions guide liberal principles, their viability can vary in practice and is subject to ongoing debate.
The state is…
“a recognized political unit, considered to be sovereign, with a defined territory and people and a central government responsible for administration”
sovereign - must be recognized by other states (taiwan)
defined territory + people
highest authority
holds access to legitimate use of forces within the territory (max weber) - tax vs stealing
IT IS NOT = GOVERNMENT gov is merely apart of it
state is the most dominant form of political organization today - but historically it is not (monarchy)
What does sovereign mean?
having ultimate political authority
Legitimacy is…
a “political community’s belief that those in authority are there for justifiable and worthy reasons; what is lawful, proper, and conforms to the standards of a political system.”
Where is the sovereignty in democracy?
its complicated. power is mostly w ppl but we cant exactly change the constitution
many different definitions (parliament etc.)
sovereignty in other countries gets messy can other countries step in when there is a humanitarian crisis?
political or social system based on the relationship between landholders and those with permission to use and live on the property in exchange for fees, political loyalties, or other commitment
What is the term^
feudal rule
Authoritarianism is a...
political system requiring absolute obedience to a constituted authority
analytical approach is a perspective that views politics as an …..
empirical discipline rather than a science; argues that politics cannot be broken down into parts but must be seen comprehensively
empirical approach is …
analysis based not on concepts and theory but on what can be observed or experimented upon
traditional approach is a method….
method in politics drawing heavily on fields of law, philosophy, and history and relying on subjective evaluation of the observer; also called the analytical approach
What is globalization?
intensification of economic, political, social, and cultural relations across border
ie. The globalization of the current era, where information about other systems and cultures is readily available to us from media sources, our educational system, and the Internet, affects both how we get information and how we use it.
order is a condition …
in which both units and interaction within a political system are marked by regularity and stability with the imposition of accepted and enforced rules, structures, and practices
anarchy is …
absence of a supreme authority over global politics and international relations
what is a nation?
group of persons who share an identity based on, but not limited to, shared ethnic, religious, civil, cultural, or linguistic qualities
etc. quebec or indigenous communities
What is Agency?
capacity to exercise free will and act independently
What is the difference between law, legislation, and policy?
law - rules imposed on society by the governing authority
legislation - laws enacted by a governing authority
policy - law or principle of performance adopted by a government
What is the role of the government?
- serve different kind of needs (ie. welfare, security)
- but whose needs count?
expectations change, major source of debate
The primary objective of every government is to provide for the independence, stability, and economic and social well-being of all its citizens.
What are failed states?
When states can no longer perform their core functions and broadly lose support, we can consider them failed states.
“State failure is a cumulative development that could encompass any or all of the following factors: poor economic performance; lack of growth and innovation; vulnerability to natural disasters; poverty and food shortages; corrupt political institutions and actors; human rights violations; and, poor relationships with other states and international actors.”
What are the 4 regime types we looked at? (LATH)
liberal democracy
authoritarianism
totalitarianism
hybrid regimes
what is an ideology?
it is a set or system of ideas that form the basis of a political or economic system and provide guidance and direction for political leadership and collective action
political stance that champions “the common people” (often defined in nationalistic or ethnic terms) as opposed to “the elite” (bankers, railroads, big corporations, “the politicians in Ottawa”); in Canada, populism has been associated with both the right (e.g., the Social Credit Party and the Reform Party) and the left (notably Saskatchewan CCF Premier and federal NDP leader Tommy Douglas)
what stance is this?
populism
liberalism is a view of politics that…
favours liberty, free trade, and moderate social and political change
neoliberalism → new current liberalism (vieled capitalism, that helps rich and punishes the poor)
What is self-determination? is is the…
ability to act freely without external compulsion
similar to agency
Explain Adam Smiths’ invisible hand theory
Adam Smith’s notion that economic forces will lead to maximum efficiency and economic growth over time as they engage in competition against each other; benefits to society as a whole exist without political interference
Under market economics, self-interested individuals will maximize efficiency and economic growth over time as they engage in competition against each other, thereby benefiting society as a whole. However, these advantages will not be distributed equally, nor is it guaranteed that all individuals will benefit.
NEO LIBERALISM.. CAPITALISM?
What is neoliberalism?
reinvigoration of classical liberalism in the last decades of the twentieth century, emphasizing free markets, free movement of capital, free trade, and the efficient (i.e., profit-maximizing) allocation of resources, and rejecting the reform liberalism of the Keynesian welfare state identified by more state involvement in the economy and social welfare
utilitarianism is a branch of political thought that states …
that the worth of a particular action is determined by its contribution to overall utility, meaning the balance of happiness and unhappiness in society
explain Mill’s toleration principle (related to individualism)
toleration - the acceptance or protection of individuals, groups, and types of behaviour that may be disapproved of by the majority in society
mill saw that democracy was in danger of suppressing individuality as the masses dominated minorities and that conformity would bring about a mediocre society.
what is conservatism?
political ideology that reveres tradition and the status quo, views humans as imperfect and imperfectible, upholds law and order over equality and freedom, and tolerates only gradual change in the structures of society
edmund burke
what is representative democracy?
political system in which voters elect others to act on their behalf; also called indirect democracy
what is communism?
political theory, based on the writings of Marx and Engels, that espouses class conflict to form a system where all property is publicly owned and each citizen works to his or her own best ability and is compensated equitably
related to socialism
what is socialism?
ideology focused on human community and society, on the group as a social organism more than on the individual, with an emphasis on state involvement in social welfare and on human and economic equality and dignity
differences on communism:
gradual power to the people
capitalism can still exist
democratic government
what is proletariat?
working class
what is the bourgeois?
according to socialists such as Marx, the property-owning class that exploits the working class (proletariat)
ideology that seeks the separation of one nation from others and strives to create and protect the political institutions and mechanisms needed to ensure the prosperity of that nation, its values, traditions, and culture
quebec!
nationalism
balance of power
situation in international politics in which states strive to achieve equilibrium of power in the world in order to prevent any other country or coalition of countries from dominating the system
“to let be”; economic theory that suggests a reduction in political control will benefit the economic system, adam smith
laissez-faire
What is the constitution? And what does it do?
Constitutions are the “basic law” of a state. They can be written or unwritten.
Some things that constitutions do:
- Formalize institutions of government and their relationships
- Create a framework for lawmaking
- Define relationship between government and individuals
- Act as a national symbol
In Canada, the Constitution is not one document, but is made up of the 1867 and 1982 Constitution Acts, and the Charter of Rights and Freedoms.
Other important constitutional documents include the 1763 Royal Proclamation and the 1774 Quebec Act.
Canada also has important unwritten constitutional conventions (or practices), like responsible government and the office of the PM.
What are the branches of government in canada?
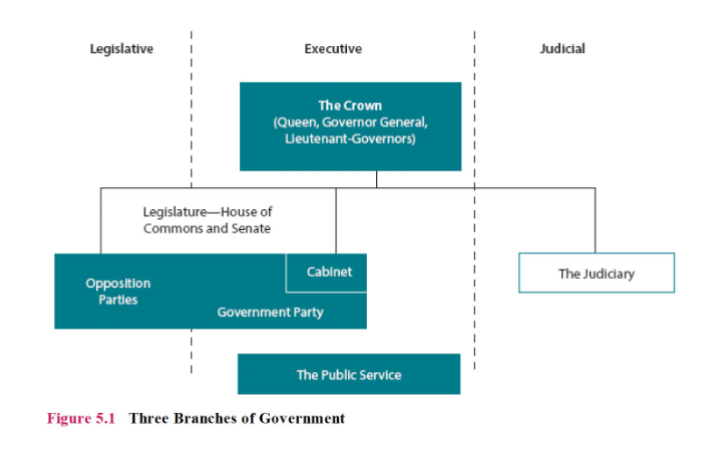
What does the executive government do?
In parliamentary systems, the executive is part of the legislative body and is responsible to parliament.
usually the top level of government or the leader; maintains leadership of the entire political system and often reflects the leadership and preoccupations of the dominant political party
The PM generally chooses the Cabinet from among Members of Parliament (MPs).
In presidential systems, the executive is separate from the legislature.
What does the Presidential system (US) look like?
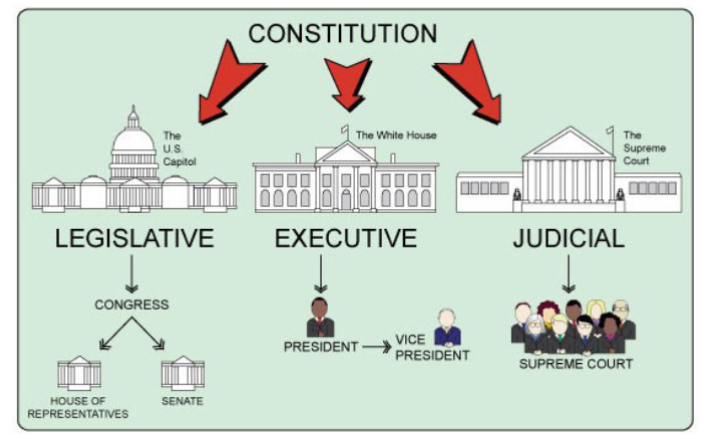
What does the legislative branch do?
referring to the body of a political system with the responsibility to make laws; known as the legislature
What is the role of the judiciary?
judicial (courts) level of governance
What is the role of the bureaucracy?
Finally, the bureaucracy or public service carries out directives from the legislature.
A key question here has to do with the level of political control of the bureaucracy.
pluralism
society in which several disparate groups (minority and majority) maintain their interests and a number of concerns and traditions persist
multiculturalism
What are the central components of liberal democracy? (MEPF)
Equality of political rights: This type of equality allows every member of the society to participate
Political participation: Related to the equality of political rights, this factor refers to distributing political responsibilities among the ruled and the rulers.
Majority rule
(Political) Freedom: A citizen’s right to participate freely in the political process is limited only by the laws of the community
What is authoritarianism?
having ultimate control over government activities + citizens
political system requiring absolute obedience to a constituted authority
totalitarianism
authoritarian political system that not only controls most social interaction but is also marked by a government’s desire to force its objectives and values on citizens in an unlimited manner
nazi germany
opposition is…
one or more political parties that are not part of government but form a check on the ruling power of the elected party in Parliament
what is cronyism?
in politics, the practice of choosing or preferring friends or associates for positions of authority
disallowance
when provincial legislation is rejected or vetoed by the federal cabinet
devolution
political system in which some authority is given to regional governments, but the power to oversee, dismiss, or entrench these authorities is still held by the central government
process in decentralization
decentralization
process whereby power and authority is taken from the central government and conferred to non-central (e.g., state, regional, or provincial) governments
centralization
concentration of power in a single body, usually the principal government
unitary systems
political systems that concentrate political authority and powers within one central government, which is singularly responsible for both the domestic and foreign activities of the political unit
delegated authority
in a unitary system, the transfer of certain powers from the national government to subnational authorities
centralized federalism
process whereby federal government increases its power relative to that of the regional governments, such as provinces or states
power in the provinces but the federal gov gets more
concurrent powers
sharing of control between provincial and federal levels of government
what is reservation? when a lieutenant-governor…
puts provincial legislation up for the federal cabinet’s consideration
What is the difference between co-operative federalism and executive federalism ? (together + apart)
co-operative federalism: co-operation and coordination of policy between the federal and provincial levels of government
executive federalism generally conflictive relationship between the provinces and the federal government, created when provinces try (often successfully) to achieve greater autonomy from the federal government, which resists such attempts
conditional grants
funds given to provincial authorities from the federal government, which assigns controls and conditions on how the monies may be spent
unconditional grants
payments from the federal government that may be spent by the provinces in any way they see fit
sovereignty-association
arrangement by which a state or province acquires independence from the federal government but retains strong links to the country, generally in the form of economic policy