Chemistry Semester 1 Review
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
1 cm3
1 mL
Density
mass/volume
q=mc∆T
represents the heat energy absorbed or released by a substance, where q is the heat energy, m is the mass, c is the specific heat capacity, and ∆T is the change in temperature.
physical properties
Physical properties can be seen or measured without changing the substance.
a) Density
b) Color
c) Melting point, boiling pt., freezing pt.
d) Smell
Chemical properties
require the substance to change to a new substance.
a) Flammability
b) Reactivity with certain chemicals.
physical change
when the physical properties of matter are changed but the substance itself does not change. This usually involves changing the state of matter (from liquid to gas, etc.)
chemical change
when a new substance is created. It involves either a color change, creation of a gas, formation of a precipitant (solid) or a temperature change.
homogeneous mixture
a mixture of two or more substances that are evenly distributed and which cannot be visually distinguished. (Mixture of sugar and water where the sugar is completely dissolved.)
heterogeneous mixture
a mixture of two or more substances that can still be seen as separate parts. (Mixture of salt and pepper.)
solute
a substance that is dissolved in a solution.
solvent
a substance that dissolves a solute in a solution.
solution
a homogeneous mixture formed when a solute is dissolved in a solvent.
protons, electrons, neutrons table
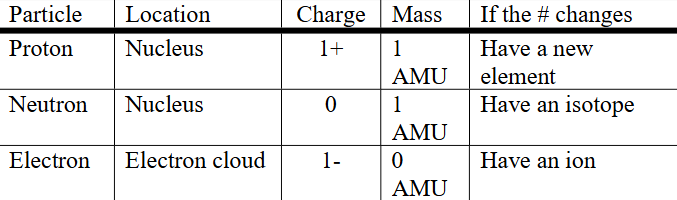
ion
when you change the number of electrons. There will be either a positive or negative charge. Charge is determined by the # of protons minus the number of electrons
cation
an ion with a positive charge
anion
an ion with a negative charge
isotope
an element with a different number of neutrons. An isotope is written with the symbol followed by a dash and the mass number. (Ex. Cl-37)
molar mass
the number on the Periodic Table with the unit ‘grams’ added to it.
Group 1
Alkali Metals
Group 2
Alkaline Earth Metals
Group 17
Halogens
Group 18
Noble gases
Melting point
The temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid.
Boiling point
The temperature at which a liquid becomes a gas.
Freezing point
The temperature at which a liquid becomes a solid.
Condensation point
The temperature at which a gas becomes a liquid.
Sublimation
The process in which a solid turns directly into a gas without passing through the liquid state.
Deposition
The process in which a gas turns directly into a solid without passing through the liquid state.
Vaporization
The process by which a liquid turns into a gas, occurring through boiling or evaporation.
Condensation
The process in which a gas turns into a liquid, typically when it loses heat.
Freezing
The process in which a liquid turns into a solid as it loses heat.
Melting
The process in which a solid turns into a liquid as it gains heat.