Clin-Chem Lab AA Part 3
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Principle:
Measures total protein based on nitrogen content
KJELDAHL
What is the Reaction of KJELDAHL method.
• (Proteins + sulfuric acid)
• Nitrogen → Ammonium Sulfate → Distillation into Ammonia → Titration
What are the Disadvantages of KJELDAHL?
• Time-consuming, labor- intensive.
• Cannot differentiate protein nitrogen from nonprotein nitrogen.
Three (3) steps of KJELDAHL method?
(1) Digestion
(2) Neutralization and Distillation
(3) Titration
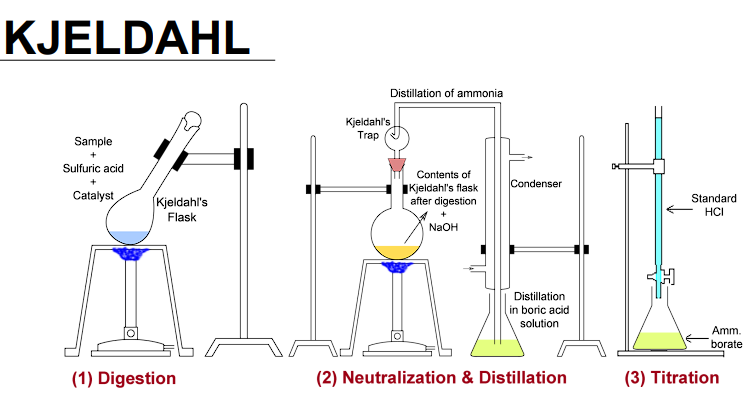
Formula of (1) Digestion
Proteins + H2SO4→(NH4)2SO4
In this step, Serum proteins are precipitated with an organic acid (Trichloroacetic acid or tungstic acid)
(1) Digestion
In (1) Digestion, the protein pellet is digested in:
Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) with heat (340°C to 360°C)
This is the Catalyst in (1) Digestion.
Cupric sulfate (to speed up the reaction)
This is used to increase the boiling point in (1) Digestion.
Potassium sulfate (improves the efficiency of digestion).
Formula of (2) Neutralization and Distillation
(NH4)2SO4+2NaOH→2NH3+Na2SO4+2H2O
In this step, the digested solution is neutralized with a strong base
(2) Neutralization and Distillation
What is the strong base used in (2) Neutralization and Distillation?
NaOH (sodium hydroxide).
In this step, ammonia (NH₃) gas is released, which is distilled into a receiving solution containing boric acid (H₃BO₃), forming ammonium borate.
(2) Neutralization and Distillation
In this step, the ammonium borate (NH4H2BO3) formed is then titrated with a standard solution of HCl to determine the amount of nitrogen in the original protein solution.
(3) Titration
Final calculation in KJELDAHL method:
Total Protein (g/dL)=Nitrogen (g/dL)×6.25
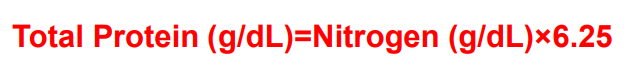
Why do we multiply the Nitrogen content by 6.25, in determining the Total Protein in KJELDAHL method?
The factor 6.25 is derived from the assumption that proteins are 16% nitrogen: 100% ÷ 16% = 6.25
Principle:
Cupric ions (Cu²⁺) react with peptide bonds in an alkaline environment to form a violet-colored complex
BIURET method.
• Most widely used method
• Recommended by IFCC for determination of TP
BIURET method.
Reaction that takes place in BIURET method:
Cu²⁺ + Peptide bonds → Violet color (measured at 540 nm)
Disadvantages of BIURET method:
Hemoglobin and lipemia interference
What are the components of BIURET REAGENT?
Potassium hydroxide
Sodium potassium tartrate
Potassium iodide
Under Biuret Reagent this:
Provides an alkaline medium so that the reaction can take place
Potassium hydroxide
Under Biuret Reagent this:
Contains Complex cupric ions
Sodium potassium tartrate
Under Biuret Reagent this:
Acts as an antioxidant.
Potassium iodide
Biuret Reagent’s absorbance is measured at?
540 nm
Principle:
• Proteins bind to certain dyes, causing color change proportional to protein concentration
• Used to stain protein bands after electrophoresis.
DYE-BINDING
Common dyes used in DYE-BINDING (Total Protein):
• Bromophenol blue
• Ponceau S
• Amido black 10B
• Lissamine green
• Coomassie brilliant blue
In Dye-Binding (Total Protein):
Relies on the binding to protein
Coomassie brilliant blue 250
Coomassie brilliant blue 250 has a shift absorbance maximum of the dye from?
465 to 595 nm
In Coomassie brilliant blue 250, absorbance at 595 nm = ?
protein concentration