electrode potentials
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
what happens when a piece of metal is dipped into a solution of its metal ions? (2)
an equilibrium is established between the metal atoms and its ions in the solution
a half cell
draw a diagram to show a half cell set up for zinc (2)
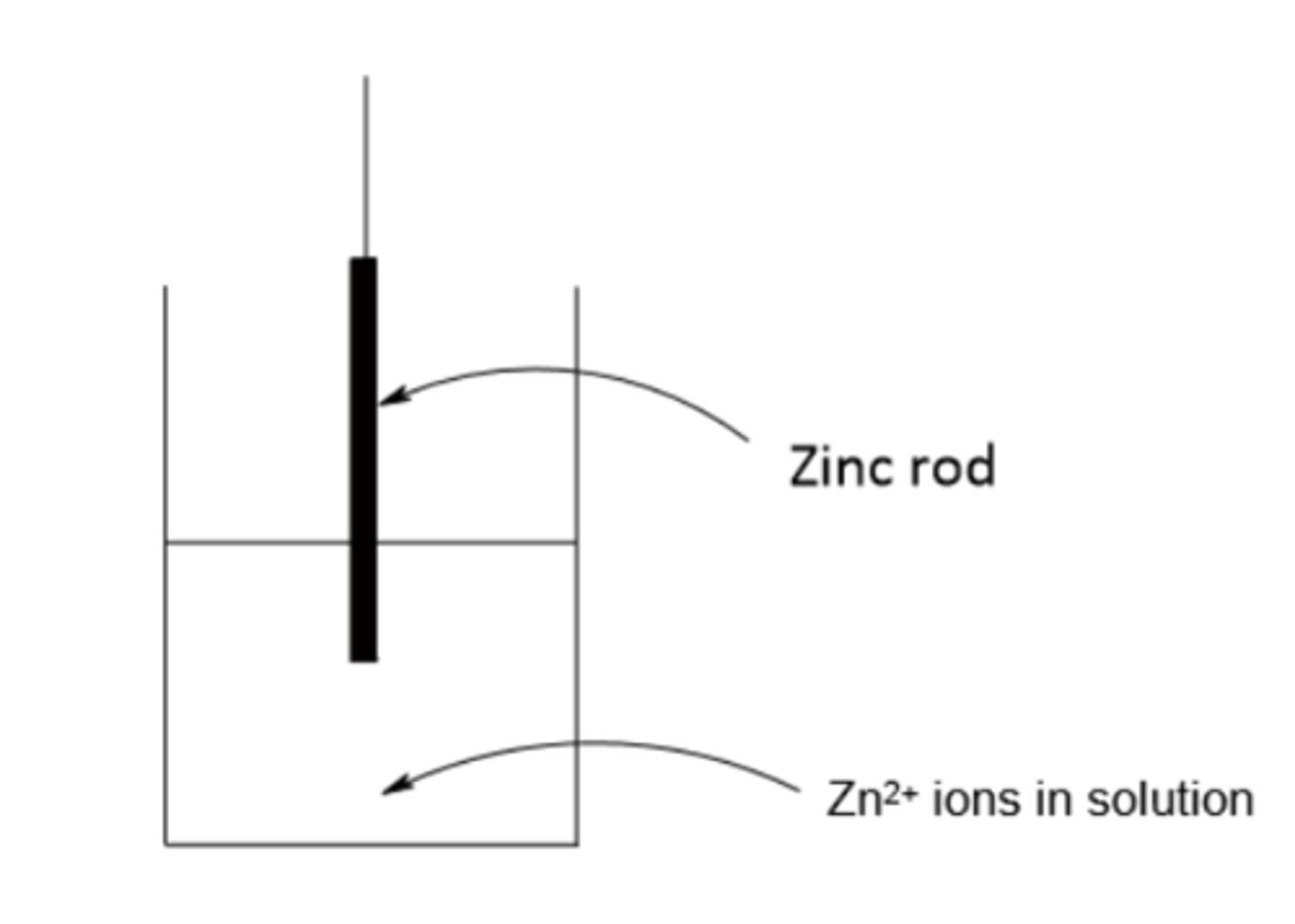
write an equilibrium reaction for zinc (2)
Zn2+ + 2e- ⇌ Zn
what is the electrode potential (E°)? (2)
the potential difference set up between the rod and the solution
measures how readily electrons are released by the metal
draw and label a basic diagram of an electrochemical cell (4)
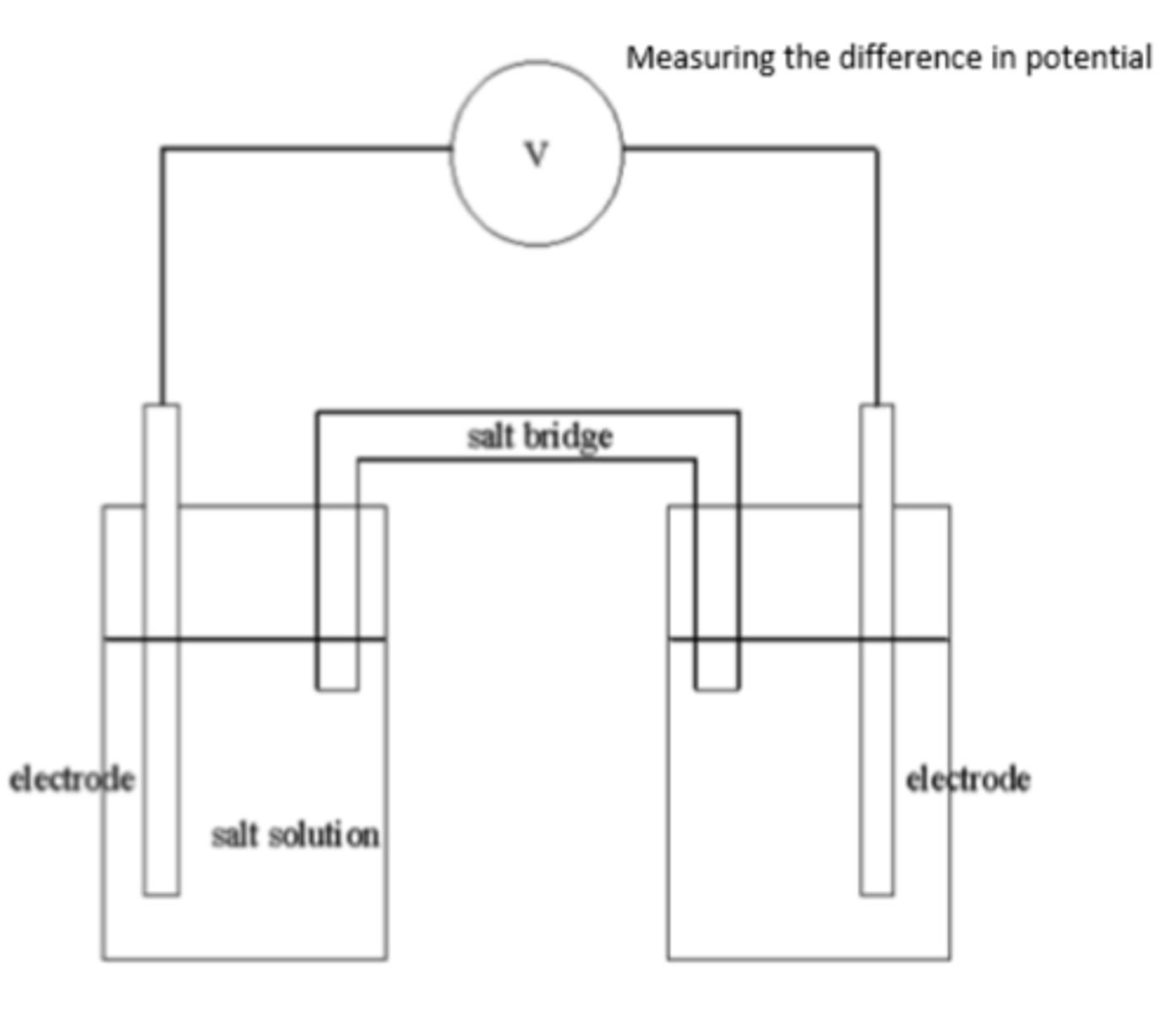
what does a voltmeter measure in an electrochemical cell? (1)
measures the potential pushing power of electrons through the circuit while keeping the current at zero
what is the function of the wire in an electrochemical cell? (1)
allows the movement of electrons
what are electrodes, and what is their role in an electrochemical cell? (1)
electrodes are where the half-equations take place, also referred to as the half-cells
what is a salt bridge? (1)
a piece of filter paper soaked in solution of KNO3
what is the purpose of the salt bridge in an electrochemical cell? (2)
allows the movement of ions to complete the circuit
compensates for changes in ion concentration in each half-cell
why is KNO3 a suitable solution for the salt bridge? (1)
it doesn’t react with any of the ions in solution, so it does not interfere with the redox reaction
why is KCl not used as a salt bridge solution for a cell containing Ag⁺ ions? (1)
KCl contains Cl-, which would react with Ag+ to form a white precipitate
what are the three types of electrodes? (3)
metal electrodes - consists of a metal surrounded by a solution of its ions
gas electrodes - for a gas and a solution of its ions. An inert metal is the actual electrode to allow the flow of electrons
redox electrodes - for two different ions of the same element, where two types of ions are present in solution with an inert metal electrode to allow the flow of electrons
why is a standard electrode potential used? (1)
to compare the tendency of different metals to release electrons and determine which electrode will be positive or negative
what is the role of the Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE)? (1)
it’s the primary standard assigned a potential of 0 volts as a reference
draw the standard hydrogen electrode (3)
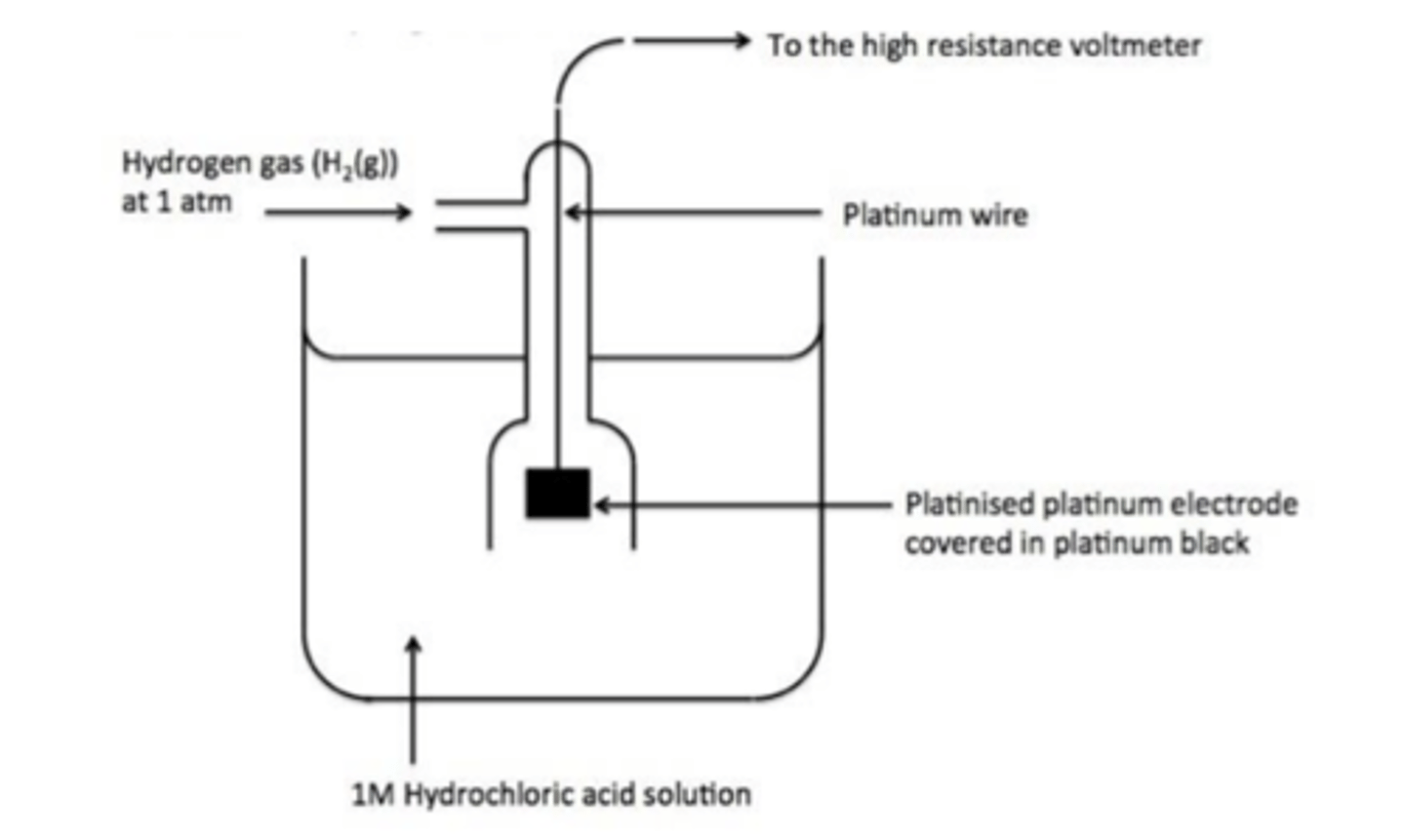
what is the half-equation for the Standard Hydrogen Electrode? (1)
H⁺(aq) + e⁻ ⇌ ½H₂(g)
what is the E° value of the Standard Hydrogen Electrode? (1)
0.00 V
what are the standard conditions for the Standard Hydrogen Electrode? (3)
1.00 mol dm⁻³ HCl (pH = 0)
100 kPa pressure
298 K temperature
what are the components of the Standard Hydrogen Electrode? (3)
1.00 mol dm⁻³ HCl
H₂ gas
platinum electrode coated in platinum black
what is the checklist for drawing half cells? (3)
solution needs to be in contact with the salt bridge and electrode
check if a Pt electrode is needed (if nether species is in the solid state)
label all parts of diagram and give concentrations of solutions and state symbols
what is an electrochemical series? (1)
the electrode potentials of different ions after they have been measured using the SHE
what are the best reducing agents in terms of electrochemical series? (1)
very negative potentials
what are the best oxidising agents in terms of electrochemical series? (1)
very positive potentials
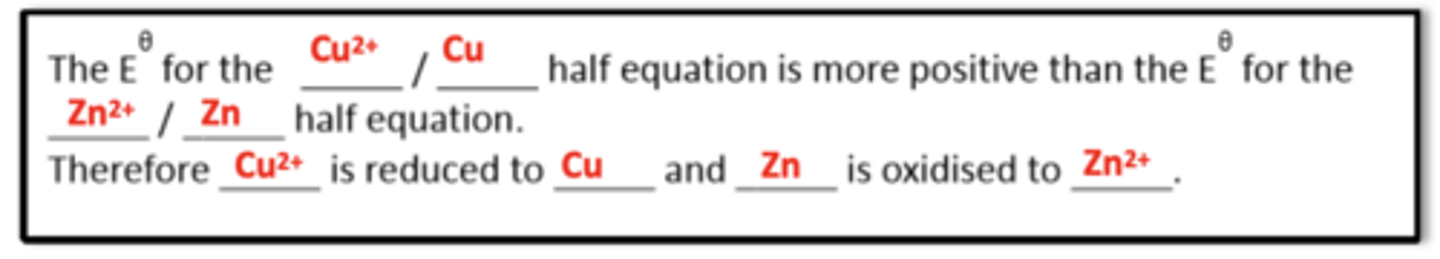
what template answer do you use to explain why a reaction is feasible using electrode potentials? (3)
the Eo for the __ half equation is more positive than the Eo for the __ half equation
therefore __ is reduced to __ and __ is oxidised to __
what is the E∘ cell also known as? (1)
electromotive force (potential difference) across two electrodes
what does a positive E∘ cell value indicate about the reaction? (1)
the reaction is feasible
what does a negative E∘ cell value indicate about the reaction? (1)
the reaction is not feasible
what is the formula for calculating E∘ i.e. EMF of a cell? (1)
E∘ cell = E∘(reduction) - E∘(oxidation)
[E∘ cell = E∘(right) - E∘(left)]
what does a more positive E∘ value indicate about a reaction? (1)
the more positive the value, the more feasible the reaction
give an example of a conventional cell diagram (1)
Zn(s) | Zn2+(aq) || Cu2+(aq) | Cu(s)
what do single lines (|) in a cell diagram represent?
phase boundaries i.e. different states
what do commas in a cell diagram indicate?
used if the phases of the components are in the same phase or are liquid and aqueous
what does a double line (||) in a cell diagram represent?
salt bridge
which species is placed on the LHS of a cell diagram?
the species being oxidised (negative electrode)
which species is placed on the RHS of a cell diagram?
the species being reduced (positive electrode)
when are H+ and H2O included in a cell diagram? (1)
if they are the species undergoing oxidation or reduction
how is a platinum electrode represented in a cell diagram when no solid is present? (1)
Pt
how is the order of elements determined in a cell diagram?
based on the direction of their half-equations
how does shifting equilibrium in a redox half-equation affect the E∘ value? (2)
a shift to the right (oxidation direction) makes the E∘ more positive or less negative (depending on sign of E∘)
a shift to the left (reduction direction) makes the E∘ more negative or less positive (depending on sign of E∘)
(example given)

What are the risks of using hydrogen fuel cells? (4)
- Need constant supply of fuels.
- Hydrogen is flammable and explosive.
- Hydrogen usually made using fossil fuels.
- High cost of fuel cells.