MRI Pulse Sequences
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Which of the following echo train lengths generate a set of images with the greatest signal-to-noise, assuming all other parameters are the same?
A. 3 ETL
B. 6 ETL
C. 12 ETL
D. 16 ETL
A. 3 ETL

In order to produce an echo in a gradient echo pulse sequence, a ________ is used.
A. RF pulse
B. Gradient field
C. Combination of two RF pulses
D. 180 pulse, then 90 pulse
E. All of the above
F. A & B only
F. A & B only

Which RF pulse refocuses a decaying spin echo?
A. 90 deg
B. 180 deg
C. 67 deg
D. 30 deg
B. 180 deg

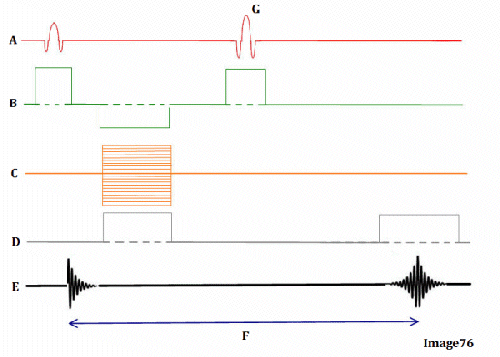
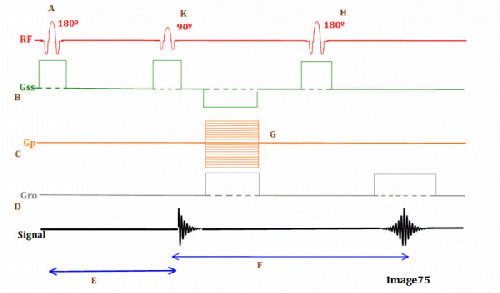
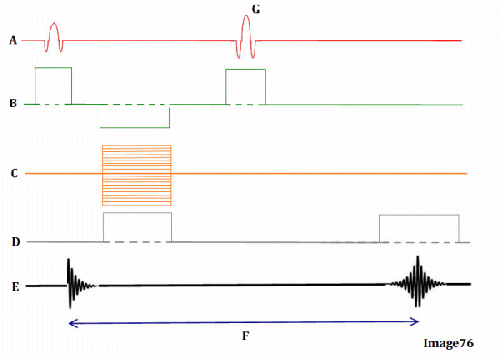
Image 76 is a diagram of which pulse sequence?
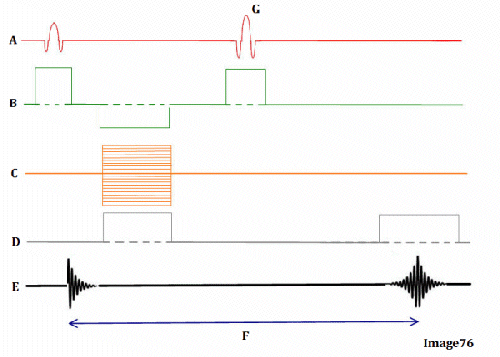
A. Inversion recovery
B. Spin echo
C. Fast spin echo
D. Dual echo spin echo
E. Gradient echo
B. Spin echo

Conventional spin echo sequences begin with a _______ RF excitation pulse.
A. 25
B. 45
C. 180
D. None of the above
D. None of the above

What specifically is a SPGR sequence spoiling?
A. The hippocampus
B. Longitudinal magnetization
C. Transverse magnetization
D. Gradient amplitude
C. Transverse magnetization

The echo time is the
A. Time between the 180 inverting pulse and the 90 RF excitation pulse
B. Time between the 90 RF pulse and the peak of the signal in the receiver coil
C. Time it takes for the flip angle to reach the Ernst angle of peak signal
D. Time between two 90 RF pulses
B. Time between the 90 RF pulse and the peak of the signal in the receiver coil

Letter D in Image 76 represents:
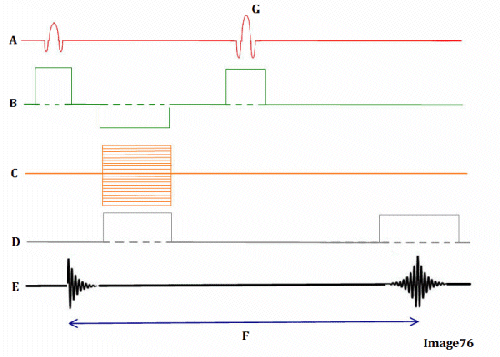
A. Radiofrequency (RF)
B. MR signal
C. Phase encoding gradient
D. Frequency encoding gradient
E. Slice select gradient
D. Frequency encoding gradient

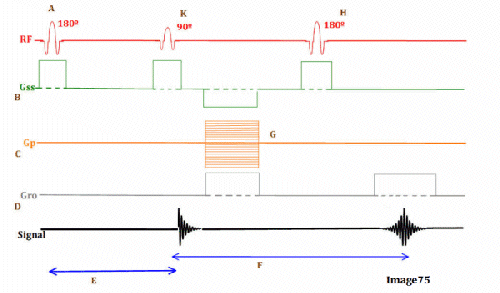
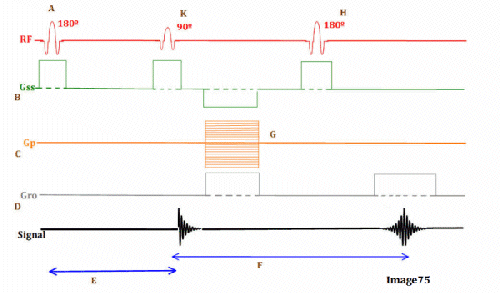
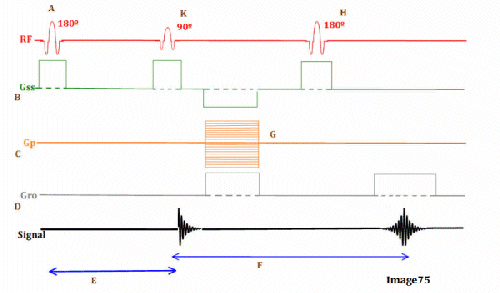
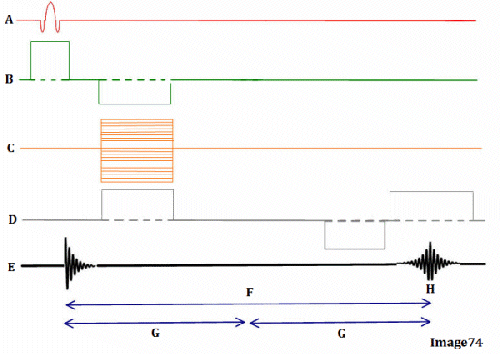
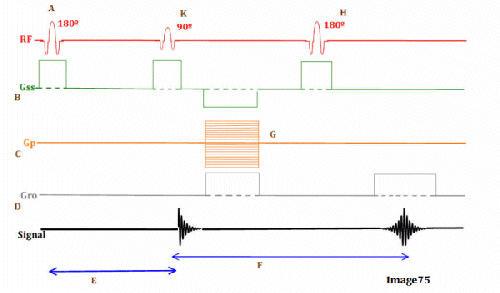
Letter F in Image 75 represents:
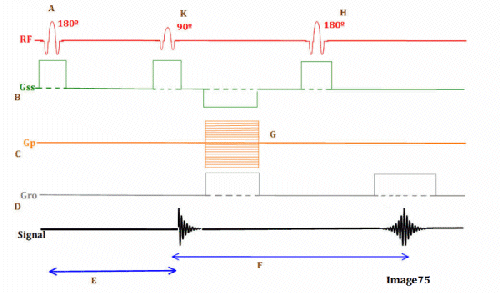
A. Repetition time (TR)
B. Inversion time (TI)
C. Echo time (TE)
D. Tau (1/2 TE)
E. Peak signal for echo
C. Echo time (TE)

A pulse sequence that begins with a 180 RF pulse, followed by a 90 RF excitation pulse, would be a(n):
A. Inversion recovery
B. Spin echo
C. Gradient echo
D. Dual echo spin echo
A. Inversion recovery

Letter K in Image 75 represents:
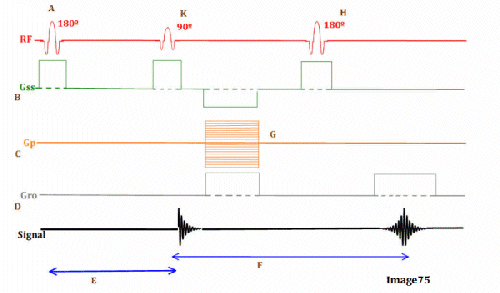
A. Repetition time (TR)
B. 180 RF pulse (inverting)
C. 90 RF excitation pulse
D. 180 RF pulse (refocusing)
E. Peak signal for echo
C. 90 RF excitation pulse

Which RF pulse is always absent in a gradient echo sequence?
A. 90 excitation pulse
B. 180 refocusing pulse
C. Presaturation pulse
D. Flip angle pulse
B. 180 refocusing pulse

Image 77 is a diagram of which pulse sequence?
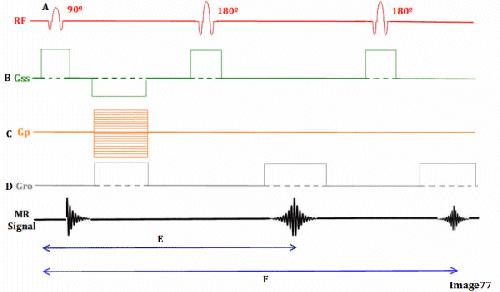
A. Inversion recovery
B. Spin echo
C. Fast spin echo
D. Dual echo spin echo
E. Gradient echo
D. Dual echo spin echo

Letter G in Image 76 represents:
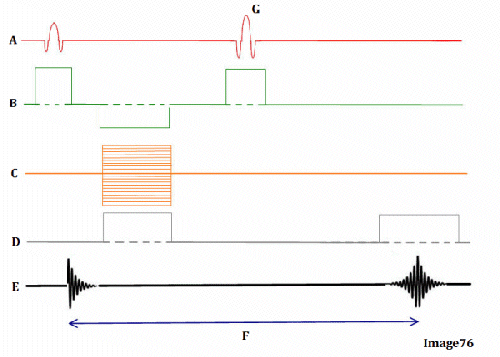
A. Refocusing 180 RF pulse
B. MR signal
C. Faraday equation
D. Free induction decay (FID)
E. TE (echo time)
A. Refocusing 180 RF pulse

When performing a gradient echo pulse sequence, what is used to refocus the protons and create the echo?
A. A focus group
B. Shim coils
C. RF coils
D. Gradient coils
D. Gradient coils

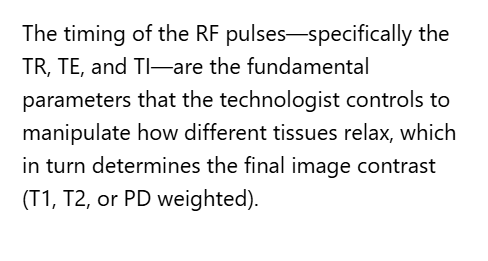
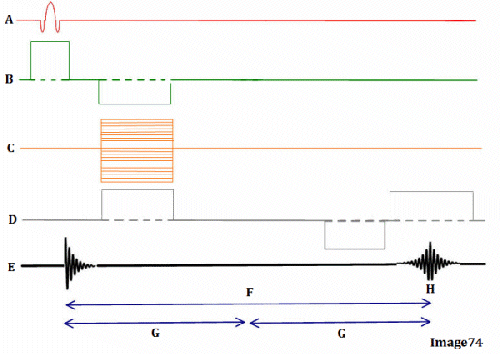
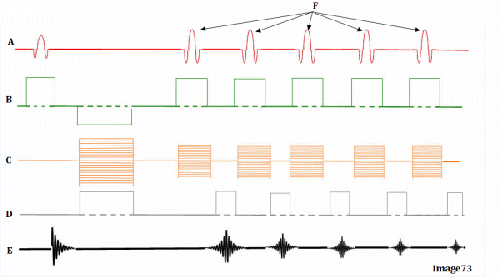
Letter D in Image 73 represents:
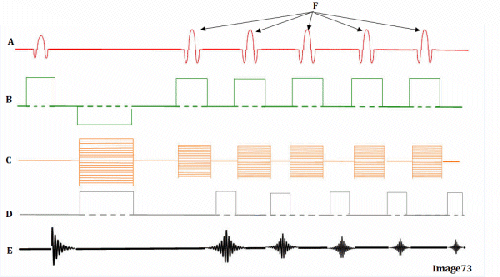
A. Radiofrequency (RF)
B. 180 RF pulses (echo train)
C. Phase encoding gradient
D. Frequency encoding gradient
E. Slice select gradient
D. Frequency encoding gradient

Letter B in Image 76 represents:
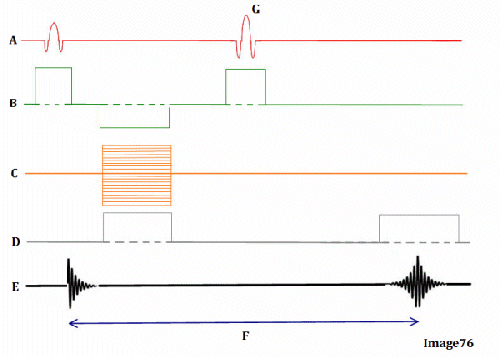
A. Radiofrequency (RF)
B. Frequency encoding gradient
C. Phase encoding gradient
D. 180 RF pulse (refocusing)
E. Slice select gradient
E. Slice select gradient

Letter E in Image 76 represents:
A. Radiofrequency (RF)
B. MR signal
C. Phase encoding gradient
D. Frequency encoding gradient
E. Slice select gradient
B. MR signal

Letter B in Image 75 represents:
A. Radiofrequency (RF)
B. 180 RF pulse (inverting)
C. Phase encoding gradient
D. Frequency encoding gradient
E. Slice select gradient
E. Slice select gradient

In a fast spin echo pulse sequence, if the TSE factor (echo train length) is increased by a factor of 3, the scan time will be:
A. Twice as fast
B. Three times faster
C. Six times faster
D. Nine times as fast
B. Three times faster

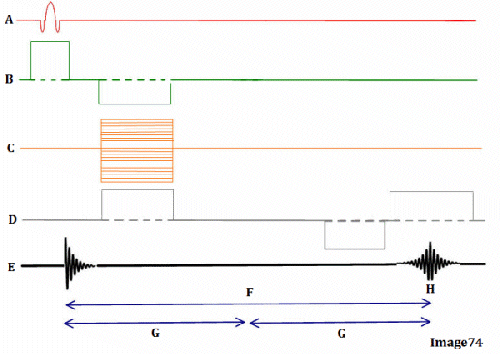
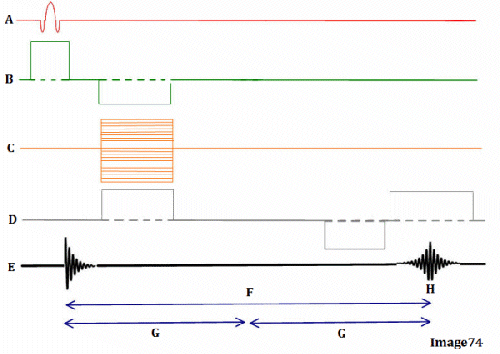
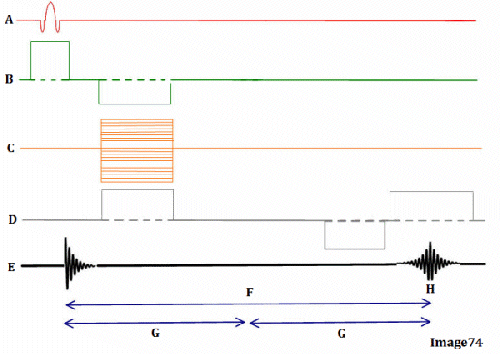
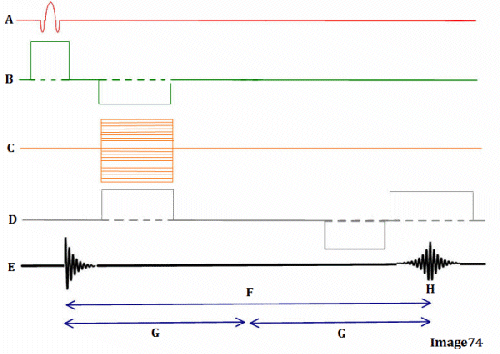
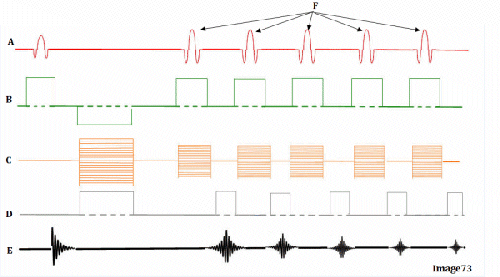
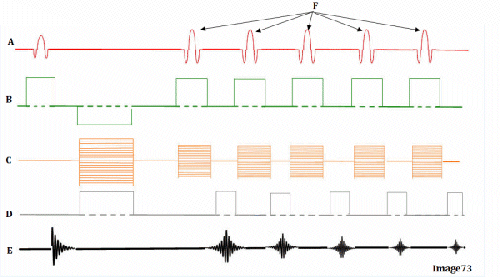
Letter H in Image 74 represents:
A. Repetition time (TR)
B. Inversion time (TI)
C. Echo time (TE)
D. Tau (1/2 TE)
E. Peak signal for echo
E. Peak signal for echo
What is the correct scan time for a spin echo sequence with the following parameters: TR 500 ms, TE 30 ms, matrix 208 × 208, 2 NEX, FOV 200mm?
A. 2 minutes 8 seconds
B. 3 minutes 46 seconds
C. 3 minutes 28 seconds
D. 5 minutes 14 seconds
C. 3 minutes 28 seconds

In a spin echo sequence, the time between the 90 RF pulse and the 180 RF pulse is known as the:
A. TR
B. TE
C. ½ TE
D. TI
E. Double Echo
C. ½ TE

Letter B in Image 74 represents:
A. Radiofrequency (RF)
B. 180 RF pulses (echo train)
C. Phase encoding gradient
D. Frequency encoding gradient
E. Slice select gradient
E. Slice select gradient

Letter A in Image 74 represents:
A. Radiofrequency (RF)
B. 180 RF pulses (echo train)
C. Phase encoding gradient
D. Frequency encoding gradient
E. Slice select gradient
A. Radiofrequency (RF)

Letter C in Image 75 represents:
A. Radiofrequency (RF)
B. 180 RF pulses (echo train)
C. Phase encoding gradient
D. Frequency encoding gradient
E. Slice select gradient
C. Phase encoding gradient

Image 75 is a diagram of which pulse sequence?
A. Inversion recovery
B. Spin echo
C. Fast spin echo
D. Dual echo spin echo
E. Gradient echo
A. Inversion recovery

As the TR is increased,
I. SNR is increased
II. Available number of slices is increased
III. T2 information is maximized
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. I only
D. II only
E. I, II and III
A. I and II only

Image 74 is a diagram of which pulse sequence?
A. Inversion recovery
B. Spin echo
C. Fast spin echo
D. Dual echo spin echo
E. Gradient echo
E. Gradient echo

A patient is being scanned for multiple sclerosis. Which sequence is specifically designed to suppress the signal from CSF to aid in the detection of periventricular lesions?
A. FLAIR
B. STIR
C. FISP
D. SPGR
A. FLAIR

The timing of RF pulses in an MRI pulse sequence controls:
A. Resolution capabilities
B. Amount of signal in the image
C. The time the coil receives the echo
D. Image contrast
D. Image contrast
The repetition time is the:
A. Time between the 180 inverting pulse and the 90 RF excitation pulse
B. Time between the 90 RF pulse and the peak of the signal in the receiver coil
C. Time it takes for the flip angle to reach the Ernst angle of peak signal
D. Time between two 90 RF pulses
D. Time between two 90 RF pulses

For a given number of slices, which of the following pulse sequences uses the most 180 RF pulses during each TR period?
A. Spin echo
B. Gradient echo
C. Dual contrast spin echo
D. Inversion recovery
C. Dual contrast spin echo

Image 73 is a diagram of which pulse sequence?
A. Inversion recovery
B. Spin echo
C. Fast spin echo
D. Dual echo spin echo
E. Gradient echo
C. Fast spin echo

The gradient that is on during the production of the echo is the:
A. Slice select gradient
B. Phase encoding gradient
C. Frequency encoding gradient
D. Inversion recovery gradient
C. Frequency encoding gradient

Letter D in Image 74 represents:
A. Radiofrequency (RF)
B. 180 RF pulses (echo train)
C. Phase encoding gradient
D. Frequency encoding gradient
E. Slice select gradient
D. Frequency encoding gradient

The fastest sequence commonly and currently available is:
A. Fast spin echo
B. Inversion recovery
C. Echo planar imaging
D. Gradient echo
C. Echo planar imaging

Letter E in Image 75 represents:
A. Repetition time (TR)
B. Inversion time (TI)
C. Echo time (TE)
D. Tau (1/2 TE)
E. Peak signal for echo
B. Inversion time (TI)

Letter A in Image 73 represents:
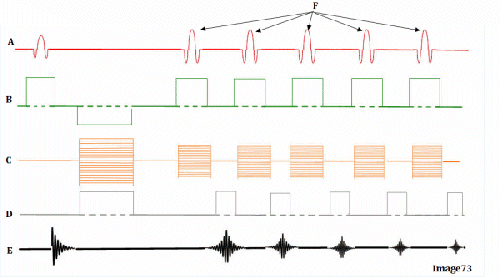
A. Radiofrequency (RF)
B. 180 RF pulses (echo train)
C. Phase encoding gradient
D. Frequency encoding gradient
E. Slice select gradient
A. Radiofrequency (RF)

In a Fast Spin Echo sequence, the effective TE are the echoes that are encoded:
A. In the first portion of the sequence
B. In the outer edges of k-space
C. With a high amplitude phase encoding gradient
D. With a low amplitude phase encoding gradient
D. With a low amplitude phase encoding gradient

In an inversion recovery sequence, the time interval between the 180 RF pulse and the 90 RF pulse is the:
A. TR
B. TI
C. TE
D. 3T
B. TI

In a spin echo pulse sequence, an echo is produced from:
A. Flip angle
B. A gradient
C. A combination of two or more RF pulses
D. A 90 RF pulse
C. A combination of two or more RF pulses

Letter F in Image 73 represents:
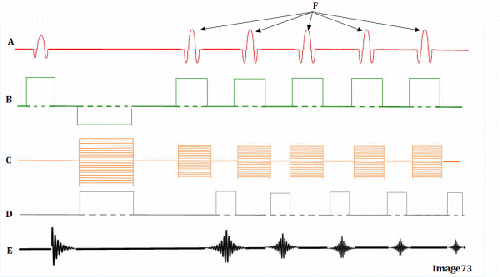
A. Radiofrequency (RF)
B. 180 RF pulses (echo train)
C. Phase encoding gradient
D. Frequency encoding gradient
E. Slice select gradient
B. 180 RF pulses (echo train)

All of the following are types of inversion recovery sequences EXCEPT:
A. STIR
B. DWI
C. FLAIR
D. 3D-IR
B. DWI

As the TE is increased, what is the effect on the number of slices available for a given TR?
A. The available number of slices is increased
B. The available number of slices is decreased
C. SNR increases
D. T1 contrast is maximized
B. The available number of slices is decreased

Letter A in Image 76 represents:
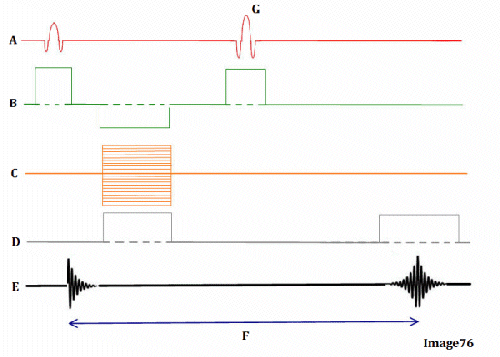
A. Radiofrequency (RF)
B. Frequency encoding gradient
C. Phase encoding gradient
D. 180 RF pulse (refocusing)
E. Slice select gradient
A. Radiofrequency (RF)

Letter G in Image 74 represents:
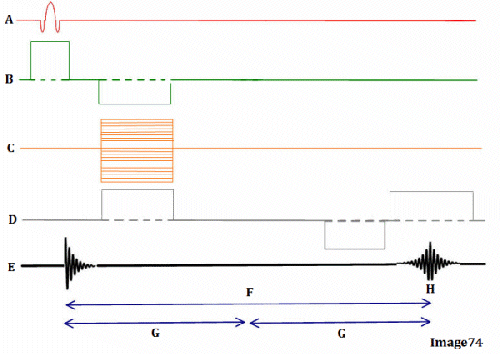
A. Repetition time (TR)
B. Inversion time (TI)
C. Echo time (TE)
D. Tau (1/2 TE)
E. Peak signal for echo
D. Tau (1/2 TE)

A technologist needs to perform a rapid, dynamic, contrast-enhanced scan of the liver, requiring a very short TR. Which of the following pulse sequences is best suited for this?
A. Fast spin echo
B. Inversion recovery
C. Gradient echo
D. Spin echo
C. Gradient echo

A patient has a metallic implant that causes significant field inhomogeneity. Which of the following sequences would be the most INSENSITIVE to this artifact and provide the most diagnostic image?
A. RF spoiled gradient echo
B. Steady state rephased gradient echo
C. Echo planar
D. Spin echo
D. Spin echo
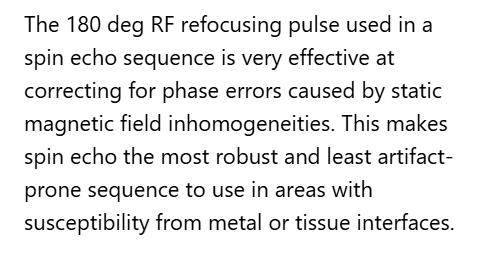
Letter B in Image 73 represents:
A. Radiofrequency (RF)
B. 180 RF pulse (echo train)
C. Phase encoding gradient
D. Frequency encoding gradient
E. Slice select gradient
E. Slice select gradient

Letter C in Image 74 represents:
A. Radiofrequency (RF)
B. 180 RF pulse (echo train)
C. Phase encoding gradient
D. Frequency encoding gradient
E. Slice select gradient
C. Phase encoding gradient

Each train of echoes has what effect on the pulse sequence in a fast spin echo?
A. Increases SAR absorption
B. Reduces scan time
C. Lowers SNR
D. All of the above
D. All of the above

Letter E in Image 73 represents:
A. Radiofrequency (RF)
B. 180 RF pulses (echo train)
C. Phase encoding gradient
D. Larmor equation
E. MR signal
E. MR signal

Letter D in Image 75 represents:
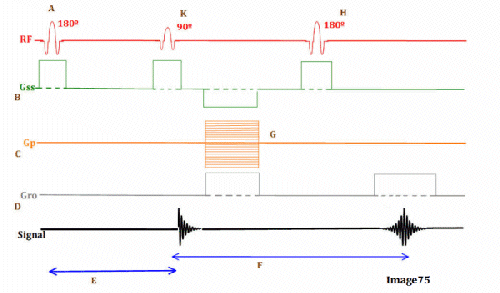
A. Radiofrequency (RF)
B. 180 RF pulse (inverting)
C. Phase encoding gradient
D. Frequency encoding gradient
E. Slice select gradient
D. Frequency encoding gradient

Letter F in Image 74 represents:
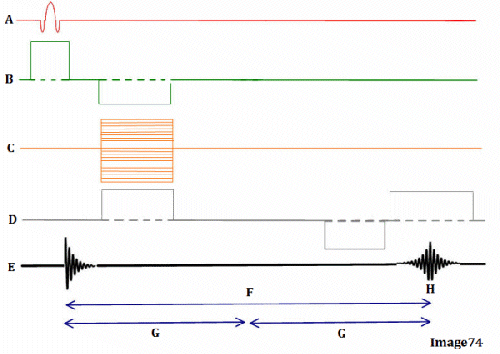
A. Repetition time (TR)
B. Inversion time (TI)
C. Echo time (TE)
D. Tau (1/2 TE)
E. Peak signal for echo
C. Echo time (TE)

Which of the following combinations of flip angle (FA) and TR would produce a T2 weighted gradient echo?
A. 45 TR; 30 deg flip angle
B. 45 TR; 90 deg flip angle
C. 450 TR; 30 deg flip angle
D. 450 TR; 90 deg flip angle
C. 450 TR; 30 deg flip angle

Letter C in Image 76 represents:
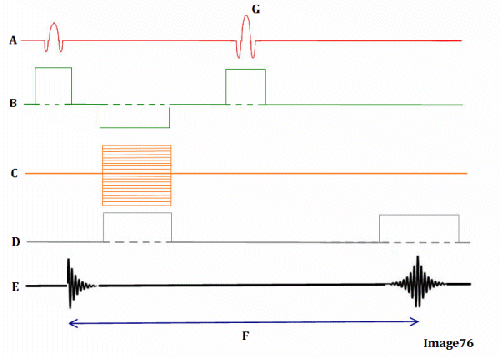
A. Radiofrequency (RF)
B. MR signal
C. Phase encoding gradient
D. Frequency encoding gradient
E. Slice select gradient
C. Phase encoding gradient

Letter H in Image 75 represents:
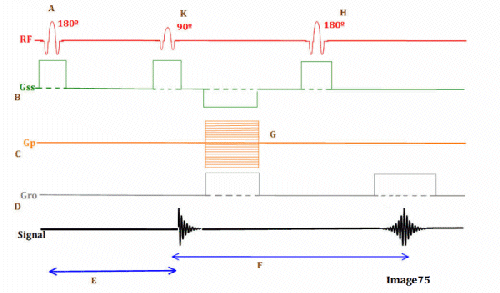
A. Repetition time (TR)
B. 180 RF pulse (Inverting)
C. 90 RF excitation pulse
D. 180 RF pulse (refocusing)
E. Peak signal for echo
D. 180 RF pulse (refocusing)

A technologist needs to shorten a fast spin echo sequence. Which of the following echo train lengths would result in the shortest scan time?
A. 3 ETL
B. 6 ETL
C. 12 ETL
D. 16 ETL
D. 16 ETL

A STIR sequence with a TI time of 160 ms will null signal from fat at what field strength?
A. 0.5 Tesla
B. 1 Tesla
C. 1.5 Tesla
D. 3 Tesla
C. 1.5 Tesla

In a dual contrast spin echo sequence with echo times of 25ms and 90ms, the second echo image has _______ than the first echo image
I. more T2 contrast
II. Lower signal-to-noise ratio
III. More T1 contrast
A. I only
B. III only
C. I & II only
D. I & III only
C. I & II only

Letter F in Image 77 represents:
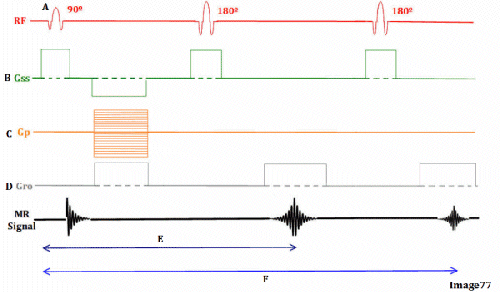
A. Refocusing 180 RF pulse
B. TE 1 (shorter TE)
C. TE 2 (longer TE)
D. Free induction decay (FID)
E. Slice select gradient
C. TE 2 (longer TE)

A fast spin echo sequence is faster than a conventional spin echo pulse sequence because:
A. Several echoes for each slice are collected during each TR period
B. T2* contrast takes less time
C. A shorter TR is used for fast spin echo
D. A smaller pixel size is utilized
A. Several echoes for each slice are collected during each TR period

Letter E in Image 77 represents:
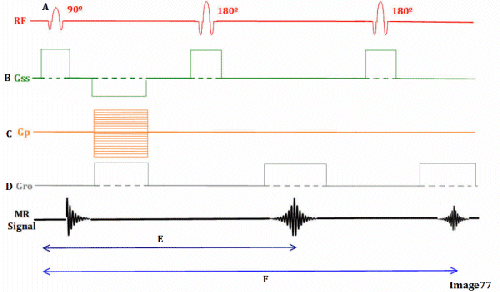
A. Refocusing 180 RF pulse
B. TE 1 (shorter TE)
C. TE 2 (longer TE)
D. Frequency encoding gradient
E. Slice select gradient
B. TE 1 (shorter TE)

A technologist wants to generate a proton density weighted image. To do this, they should select a spin echo sequence with which parameters?
A. Long TR, Long TE
B. Short TR, Short TE
C. Long TR, Short TE
D. Short TR, Long TE
A. Long TR, Long TE
Fast spin echo sequences are fast because:
A. The TE used is very short
B. More than 1 line of k-space is acquired in each TR period
C. No 180 refocusing pulses are used
D. The excitation flip angle is very small
B. More than 1 line of k-space is acquired in each TR period

Letter G in Image 75 represents:
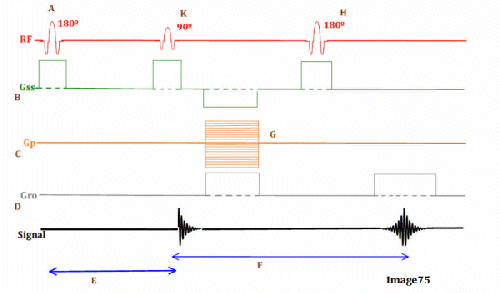
A. Radiofrequency (RF)
B. Frequency encoding step
C. Phase encoding step
D. Free induction decay (FID)
E. Peak signal for echo
C. Phase encoding step

Letter C in Image 73 represents:
A. Radiofrequency (RF)
B. 180 RF pulses (echo train)
C. Phase encoding gradient
D. Frequency encoding gradient
E. Slice select gradient
C. Phase encoding gradient

Letter F in Image 76 represents:
A. Repetition time (TR)
B. Inversion time (TI)
C. Echo time (TE)
D. Tau (1/2 TE)
E. Peak signal for echo
C. Echo time (TE)

Letter A in Image 75 represents:
A. Refocusing 180 RF pulse
B. Inverting 180 RF pulse
C. Phase encoding step
D. Tau (1/2 TE)
E. Peak signal for echo
B. Inverting 180 RF pulse
