Exercise Physiology
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms

The sympathetic nervous system causes vasoconstriction to the digestive area and muscle however, active muscle produces waste products that cause vasodilation. Metabolic waste products overrise the vasoconstriction.
An individual is placed on Inderal, which is a drug sometimes used to treat migraines. It blocks sympathetic action, and reduces maximal heart rate. Explain why healthy patients on Inderal have a reduced peak work output as a side effect of their migraine medicine.

If the maximal heart rate is at its peak, then we would also have the stroke volume at its peak. Since the heart rate can’t reach to its max then it will be low, causing your cardiac output to go down. So, the peak work output goes down too.
At the onset of exercise, veins holding blood contract, thus increasing venous return. Explain how this effects heart function (specific variables)

This effects heart function because if the venous return is increasing, stroke volume would increase as well, heart muscles would stretch, stronger contractions. This would cause the cardiac output to increase. helping the heart reach to the high demands of physical activity.
A person with heart disease has a heart that cannot increase stroke volume at all, yet following training they are able to do more work. Explain which adaptations have taken place that allows the individual to do more work.
a. Hint- there are 3 variables related to work… not just cardiac output! Ask Fick

If you can’t increase the stroke volume, you can’t increase cardiac output. However, you can increase the A-VO2 difference by extracting more oxygen to do so you would by growing more capillaries and mitochondria which would increase the capillary density. That would help extract more oxygen.
Explain why prescribing exercise intensity using a target heart rate ( a specific range of heart rate) may be problematic when individuals are exercising in hot environments. What could happen to the heart rate (why?)

Using a specific range of heart rate may be problematic because if the runner is in hot temperatures they will sweat, making them lose plasma. That will also decrease the stroke volume if they continue running the heart rate will increase to maintain the same cardiac output.
Studies have shown that within 12 days of beginning exercise, there is an increase in plasma volume (due to the Kidneys retaining fluid). For an individual who trains at the same intensity each session, how will they note that they have experienced this plasma volume expansion?

If there’s an increase in plasma, we can also measure the stroke volume We have the same intensity each session so the cardiac output would stay the same and since the stroke volume is increasing the heart rate would be lower to have the same cardiac output.
A deconditioned Dad is helping his daughter move into her new apartment. He has to lift a very heavy couch. What is happening to his blood pressure during the lift, and how is this affecting his blood vessels and heart rate? Explain (reflex?)

His blood pressure would be increasing which would trigger the baroreceptor reflex which is sensitive to change in pressure. It would want to do the opposite and lowering it down so the heart rate would go down, the blood vessels would need to dilate.
You get a new client and have them walk on the treadmill at 3.0mph for 10 minutes. Their heart rate is 127. You then aerobically train them for 3 months. Now you test them again by walking them at 3.0mph. Their heart rate is 107. Explain 2 adaptations that occurred to cause this lowered heart rate at the same work intensity.

Two adaptations have occurred in this would be a decreased sympathetic sensitivity. Possibly also the increase of parasympathetic when doing the workout because the heart rate did not go as higher than before.
Two cyclists are both cycling at 75 watts (assume they are the same person, two different sessions). However, in one condition the cyclist is doing the work in a reclined (recumbent) body position. Explain how the recumbent position will affect Cardiac Output, Heart Rate and Stroke Volume. How would a recumbent position cause any difference?

The position would affect all three because the one reclined body position will have the venous return to increase. If that increases it will increase the stroke volume, meaning the blood will come back to the heart quicker and will pump more blood out, increasing the contractions and being able to hold more blood in. The heart rate won’t increase as much and the Cardiac output will also increase.
Following aerobic training, a conditioned athlete has a lower resting heart rate, and also a faster recovery heart rate. Which heart rate controlling variable has been trained?
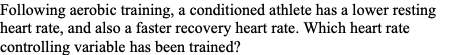
Parasympathetic Nervous System
If he also has a (slightly)lower maximal heart rate, what control system has also been affected
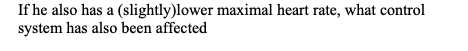
The sympathetic Sensitivity
How does plasma volume affect stroke volume?
Loss of plasma volume (dehydration reduces blood volume, lowering stroke volume and cardiac output.
Increase in plasma volume (hydration or training) helps maintain or increase stroke volume, improving cardiac output
What is steady state?
Steady state is the point at which the body’s oxygen consumption, heart rate, and other cardiovascular variables stabilize during moderate-intensity exercise, meaning energy supply meets energy demand
Why doesn’t diastolic pressure change much during aerobic exercise, but it increases during strength training ?
Aerobic exercise: diastolic pressure remains stable or decreases decreases slightly due to vasodilation in active muscles, which reduces peripheral resistance
Why doesn’t diastolic pressure change much during aerobic exercise, but it increases during strength training ?
Strength training: Diastolic pressure increases because of increased vascular resistance during muscle contraction, which raises the overall resistance in the circulatory system
How does a sudden change in pressure affect heart rate?
A drop in pressure (ex. standing up quickly) triggers the baroreceptor reflex, which increases heart rate to restore blood pressure
A rapid increase in pressure (ex.lifting heavy weights) can initially cause a decrease in heart rate as the body adjusts to the new pressure levels
How does an increase in venous return affect heart rate?
Increased venous return (more blood returning to the heart) increases stroke volume. This enhanced stroke volume can lead to a temporary decrease in heart rate due to the Frank-Starling mechanism (which states that the heart pumps more efficiently when it is more filled). However, heart rate may still increase as intensity rises to meet overall oxygen demands
Why might a bout of heavy weight lifting cause a higher heart rate during running?
Heavy lifting stimulates the sympathetic nervous system and increase muscle fatigue, leading to a higher heart rate during subsequent aerobic exercise (like running) due to prolonged elevated sympathetic tone and body’s need for oxygen to recover from the weightlifting bout.
How does the left ventricle change after chronic aerobic training?
The left ventricle increases in size (hypertrophy) and becomes more efficient, which allows it to pump a greater volume of blood per beat. This results in an increase in stroke volume and cardiac output during exercise
Why is resting heart rate lower after aerobic training?
Increased parasympathetic tone: Aerobic training enhances the vagus nerve (parasympathetic) influence, which slows the heart rate
Improved cardiac efficiency: the heart pumps more blood per beat (due to increased stroke volume), so it doesn’t need to beat as frequently at rest.
What are the two key components of VO2max?
Cardiac output (Q): The amount of blood the heart pumps per minute (HR x SV)
A-VO2 difference: The difference in oxygen content between arterial blood and venous blood, indicating how much oxygen is extracted by the tissues.
Why is resting cardiac output the same btu peak cardiac output higher after aerobic training?
Resting cardiac output remains the same because resting oxygen demand doesn’t change
Peak cardiac output increases due to a higher stroke volume from an enlarged left ventricle, allowing more efficient blood circulation during exercise, even though heart rate might not be higher
Who has a higher peak heart rate: a sedentary person or an aerobically trained person?
A sedentary person typically has a higher peak heart rate because their heart is less efficient at delivering oxygen to muscles, so it needs to beat faster during intense activity. An aerobically trained person has a lower peak rate due to a more efficient heart (larger stroke volume)
What causes vasoconstriction and vasodilation in blood vessels?
Vasoconstriction: caused by sympathetic nervous system activation (ex.during stress or cold) or hormones like norepinephrine and angiotensin II
Vasodilation: caused by increased metabolism demand (ex. during exercise), heat, or local release of nitric oxide from the endothelium
Why is a warm-up beneficial for exercise performance?
A warm-up increase blood flow to active muscles through vasodilation, which improves oxygen and nutrient delivery. It also helps redirect blood away from less active areas (ex. the digestive system) to ensure that muscles are adequately perfused during exercise.