Chapter 46 Gas exchange
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
160 Terms
What is the advantages ventilating in the air
There is a 30x higher concentration of air then in water
O2 diffuse faster
Air is less viscous than water
How is air being less viscous than water a benefit
we require less energy to ventilate
What is the disadvantage of using air to breather rather than water
Requires secretion to keep surface moist and allow for gas exchange
What is the requirement of gases to go through gas exchange
Gases must be soluable in liquids (in all respiratory surfaces (gills, book lungs, lungs, etc.)
What is the advantage of using water to breathe
The surface of the repository tract is always wet
What is the disadvantages of using water to breathe
Water and ion movement
Gas solubility
Gas concentration
How is Water and ion movement a disadvantage
There are things dissolved in the liquid which impacts how much things can dissolve in water, this also impacts tonicity and osmotic pressure
How is Gas solubility a disadvantage
There is more CO2 than O2 in the water
How is Gas concentration a disadvantage in water breathing
There is less O2 around
What is true about water solubility with oxygen and temperature
The warmer the water the less oxygen is in that water
What is positive pressure ventillation
forcing water/air across respiratory surface
Where do we see positive pressure
frogs, toads, and fishes
What animals has lost it’s reparatory muscles and uses ram ventilation
sharks and tuna
What is ram ventilation
swimming with an open mouth to rub water across gills
What is negative pressure ventilation
Increasing in volume to drop pressure and allow air to come in.
What animals have negative pressure ventilation
animals with a diaphragm (all mammals)
How do small animals with thin skin breathe
they breathe through the surface
What is the requirement for a small animal
animals have a high surface area:volume ratio and a low metabolic rat
What is the requirement for all respiratory surfaces
moist surface (all)
blood supply (most)
ventilation (most)
What kind of animals breathe through their surface
nudibranch mollusks, most annelids (earthworms), and amphibians
What is important to know about amphibians breathing
In the surface lungs/gills will be their way of breathing
In water they breathe through their skin
these are toads/frogs
What is the spiracel
opening of the body surface to the outside to allow air to get into trachea, seen in insects
What is the tracheal tube
air passage way you can find this in insects
What is the tracheole tube
a branched segment of trachea and it’s fluid filled and contacts the alveoli cells
How do we, insects, and some other arthropods ventilate
Movement: Just by moving it causes pressure change to move air into tubes
Muscle Contraction: Changing the diameter of tubules
Mini explosions: A build up of bicarbonate which results in mini explosions to cause a vacuum
What are gills and lungs made up of
epithelium
What are the 3 different type of gills
External
Internal
dermal
What has external gills
some annelids (polychaeta)
What has internal gills
aquatic mollusks, crustaceans, fishes, and amphibians
What has dermal gills
echinoderm
What is the characteristics of epithelium
it’s moist and thin
Outer gills are exposed too…
water
inner gills are exposed too…
blood vessels
What are dermal gills
The dermis is extending upward from the body surface, this is not epithelium but it’s covered via epithelium
What is the disadventage of going concurrent vs counter
there is an equilibrium in concurrent
How does lung form
invagination
Do fishes have internal or external gills
internal, they have an operculum
What is counter current exchange
When blood flows in opposite direction of another mediym
(seen in fish)
What is the benefit of counter current exchange in gills
maximize o2 concentration between blood
When do we humans have the highest concentration of oxygen in the blood
Exactly after gas exchange happens at the site of gas exchange
How is countercurrent set up in fishes
their gills are thin and rich in capillaries,
How is the air move in birds when breathing
it’s a one way flow through the lungs and associated structures
How is the movement of air in humans
mixing of incoming and outgoing air
How does the lung surface areas of an animal with very low activity look like
it has low surface area, like a salamander
How does surface areas of an animal with very high activity look like
there is multiple invagination/air sacs, to increase number of gas exchange
What are the air sacs of birds
very large invaginations of the lungs
What are the three/four important structures of the bird respiratory structure
posterior/anterior lungs, lungs, parabronchi
What is an air sacs
extension of lung, they contract and relax to force air in and out
What is parabronchi
equivlent of aveoli they hold the air for gas exchange to happen within the capiallries
Where does gas exchange happen in birds
parabronuhi
What is the flow of birds
First inhalation→first exhalation→second inhalation→second inhalation
(2 cycles of breathing)
What is first inspiration
Air goes through trachea→posterior sacs and partly into the lungs
What is first exhalation
posterior sacs→lungs
What is secondary inhalation
they breathe in air which goes to the posterior sac, and the air they already have goes to the anterior sacs
What is the secondary exhalation
the air which has been moved all around is breathed out and the air they breathed in again goes to the lungs from the posterior sac
How is current in birds (blood flow to air flow)
Crosscurrent exchange
What is crosscurrent exchange
There is a large vessel which branches out and each branches cross over the medium
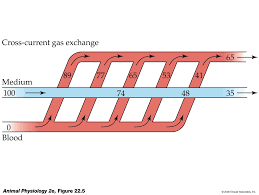
What is the ranking of the types of currents (based on oxygen concentration after we do gas change)
1 Counter current
2 Cross curent
3 Con current
What is the flow of air in humans
Nostrails→nasal cavity→ pharynx→larynx→trachea→bronchial→bronchioles→aveoli
Where does gas exchange happens in humans
In the aveoli
What is the conducting zone in humans made up of
trachea→bronchial tree→bronchioles→terminal bronchioles
What is the respiratory zone in humans made up of
Respiratory bronchioles→avlevoli
What is conducting zone
just moving air, NO EXCHANGE POSSIBLE
What is respiratory zone
where gas exchange happens
Thoracic cavity is a closed or open space
closed
What is pleural cavity
fluid filled sac where lungs reside
What is the parietal pleural membrane
the membrane which wraps the walls of the thoracic cavity
What is the visceral pleural membrane
a SEROUS membrane which surrounds the lungs, it decreases friction when breathing
What is an alveolus made up of
simple squamous epithelium
What proportionality should I remember
👆 volume= 👇 pressure
(increase in volume, decreases pressure)
What kind of cells are there in alveoli (cells involved in gas exchange)
type 1, type 2, and macrophage
What does type 1 cells do
gas exchange
What does type 2 cells do
it produces and secretes surfactants
What do macrophages do
clear the air of any invaders via phagocytosis
All gases must cross…
lung surface: (((respiratory membrane→ epithelium of type 1 cell)))→interstitum:(((basement membrane of blood vessel→ and then endothelial cells of capillary)))
What are the pressures involved in ventilation
atmospheric pressure, intrapleural pressure, transpulmonary pressure, and intraalveolar pressure
What is intrapleural pressure
Pressure within the pleural cavity
What is transpulmonary pressure
the pressure difference from pleural sac and pressure within the lungs (alveoli)
What is intraalveolar pressure
The pressure within the alveoli pocket.
What is the pressure that inflates the lung
increases transpulmonary pressure
What is the mechanism of inspiration
Diaphragm contracts and thoracic cavity increases and intrapleural pressure decreases, which increases transpulmonary pressure and the lung inflate, and intraalvelolar pressure drops below atm so air enter lungs
What are the properties of lung
elasticity, distensibility, and compliance,
What is distensiability
increase with in width
What is elasticity
able to return to original size after being inflated
What is compliance
how easily a lungs can increase it’s volume (stretch) due to pressure
What is compliance equation
∆V/∆P
but as volume increases we need more and more pressure to increase the volume by the same unit (not linear)
What happens when lungs are to compliance
pressure increases volume of the lungs a lot, so it’s easy to inflate and hard to deflate
What happens when lungs are not compliate
it’s easy to deflate and hard to inflate
As we get older what lung property changes
decrease in elasticity, so we get lower compliance
What does surfactant do
Add’s surfactant between water molecule, because without surfactant the alveoli will collapse due to high water tension (makes it hard in inflate)
(water molecules pull each other in=collapse)
what is surfactant made up of
a protein and lipid mixture
Lung capacity chart (Memorize it)
total lung capacity= 6,000
the rest memorize okay
What is dalton’s law of partial pressure
total pressure is the sum of each gas pressure
Ptotal=P1+P2+P3
What is Fick’s law of diffusion
Amount of gas that diffuses is due to:
partial pressure (NOT CONCENTRATION)
total surface area
What is tidal volume
Amount of air move into and out of the lungs with normal resting breathing
What is expiratory reserve volume
how much we can breathe out AFTER tidal volume
What is inspiratory reserve volume
how much we can breathe in AFTER tidal volume
What is residual volume
volume of air remaining in lungs at the end of maximal expiration,
(it’s always there (except death))
What is vital capacity
The maximum amount of air a person can exhale and inhale
What is functional residual capacity
the amount of air we start with during tidal volume