Bio Midterm
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
186 Terms
what is biology?
the study of living things and interaction of living things
interdependence
the concept that all living things depend on each other
characteristics of living things include:
the ability to reproduce, having an orderly structure, growing and developing, adjusting to changes in the environment
the steps of the scientific method
1. identify a problem
2. make a hypothesis
3. experiment
4. collect data
5. draw a conclusion
data
information collected from an experiment
hypothesis
a prediction to solving a scientific problem
quantitative data
measurements and other numbers collected during experiments
qualitative data
descriptions collected during experiments
in a controlled experiment, which is the variable that is being measured?
dependent variable
in a controlled experiment, what is the variable that is kept the same and is not tested?
control group
in a controlled experiment, which variable is being changed?
independent variable
what is used to measure length?
meters
what is used to measure temperature?
celsius
what is used to measure mass?
grams
what is used to measure volume?
liters
what is used to measure time?
seconds
a reaction type that can break apart a polymer into individual monomers and involves the addition of water molecules to break a bond
hydrolysis
polymers can be built from monomers by __________ reactions and involves the removal of a water molecule to break a bond
hydration synthesis
all polymers are held together by ________ bonds
covalent
lipids are formed from combinations of _____ (fatty/amino) acids and _______(glycogen/glycerol)
fatty acids, glycerol
two sugars joined together forms a _____
disaccharide
the two organic molecules used for energy are:
lipids and carbohydrates
enzymes are a type of ______(lipids/proteins) that _______(speed up/slow down) chemical reactions
proteins, speed up
starch is a _________(disaccharide/polysaccharide) made by _________(plants/animals)
polysaccharide, plants
enzymes bind _____(products/substrates) in their _____(active site/product site)
substrates, active site
the organic molecules that are responsible for our genetic information are _______(nucleic acids/proteins)
nucleic acids
what kind of molecule is used for making the exoskeletons of animals?
chitin
what is a chain of amino acids called?
polypeptide
what is a polysaccharide that makes up plant cells and provides structural support?
cellulose
what molecule is used for storing energy in animals?
glycogen
what are the characteristics of saturated fats?
unhealthy, solid, no double bonds
what are the characteristics of unsaturated fats?
liquid, healthy, has double bonds
what functions to provide structure and transports materials in and out of the cell?
proteins
all nucleotides consist of:
a 5 carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
what is the monomer of a lipid?
fatty acids/glycerol
what is the monomer of a protein?
amino acid
what is the monomer of a nucleic acid?
nucleotides
what is the monomer of a carbohydrate?
monosaccharide
what are two types of nucleic acids?
DNA and RNA
do all organic biomolecules contain carbon?
yes
enzymes speed up chemical reactions by _____(raising/lowering) the activation energy
lowering
the activation energy of a chemical reaction is the amount of energy required to ________(start/stop) a chemical reaction
start
enzymes act as biological _______(catalysts/inhibitors)
catalysts
the part of the enzyme or catalyst used in a chemical reaction is the _____(product site/active site)
active site
the reactants in a reaction using an enzyme are _______(substrates/products)
substrates
enzymes are what type of biological molecule? (nucleic acid/protein)
protein
are enzymes used up in reactions?
no
do enzymes bind to the active site of a substrate?
no
do enzymes only operate at certain temperatures and pHs?
yes
what is denaturing?
when an enzyme loses its shape
what is an enzyme?
proteins that speed up reactions
what is a catalyst?
anything that speeds up a reaction
what is an active site?
a place on an enzyme which the substrate binds to
what is a product?
material that is produced in a reaction
a hypertonic solution has ____ water and _____ solute concentrations so water always wants to leave a cell when it is placed in these solutions (more, less)
a hypertonic solution has LESS water and MORE solute concentrations
a hypotonic solution has ____ water and _____ solute concentrations so water always wants to enter a cell when it is placed in these solutions (more, less)
a hypotonic solution has MORE water and LESS solute concentrations
active transport always moves materials from _____ to ____ concentrations
low to high
passive transport always moves materials from _____ to ____ concentrations
high to low
what changes shape in endocytosis?
cell membrane
what changes shape in transport using protein pumps?
proteins
what kind of solution do animal cells do best in?
isotonic
what kind of solution do plant cells do best in?
hypotonic
what molecules will diffuse the fastest?
small molecules
what keeps plant cells from exploding?
cell wall
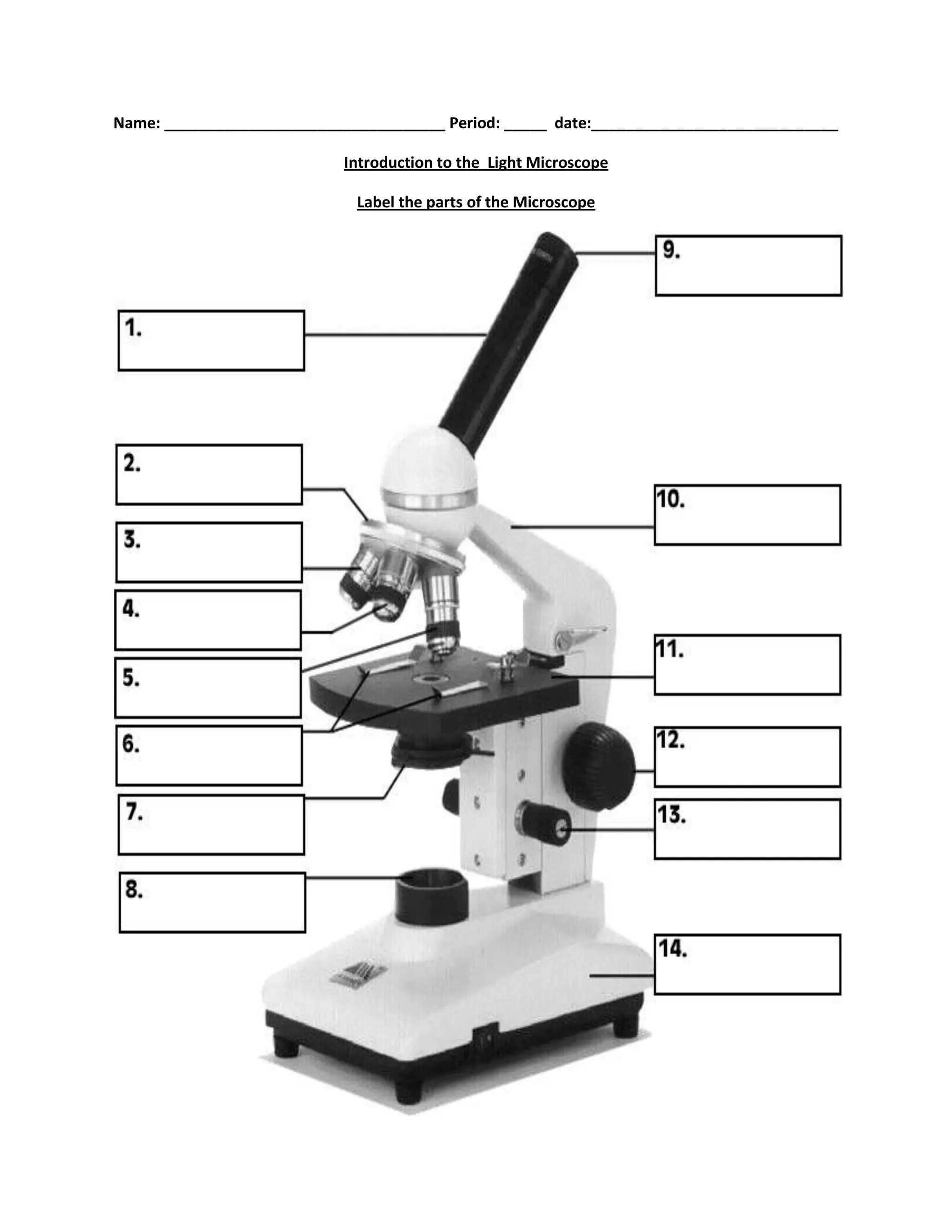
#1
body tube
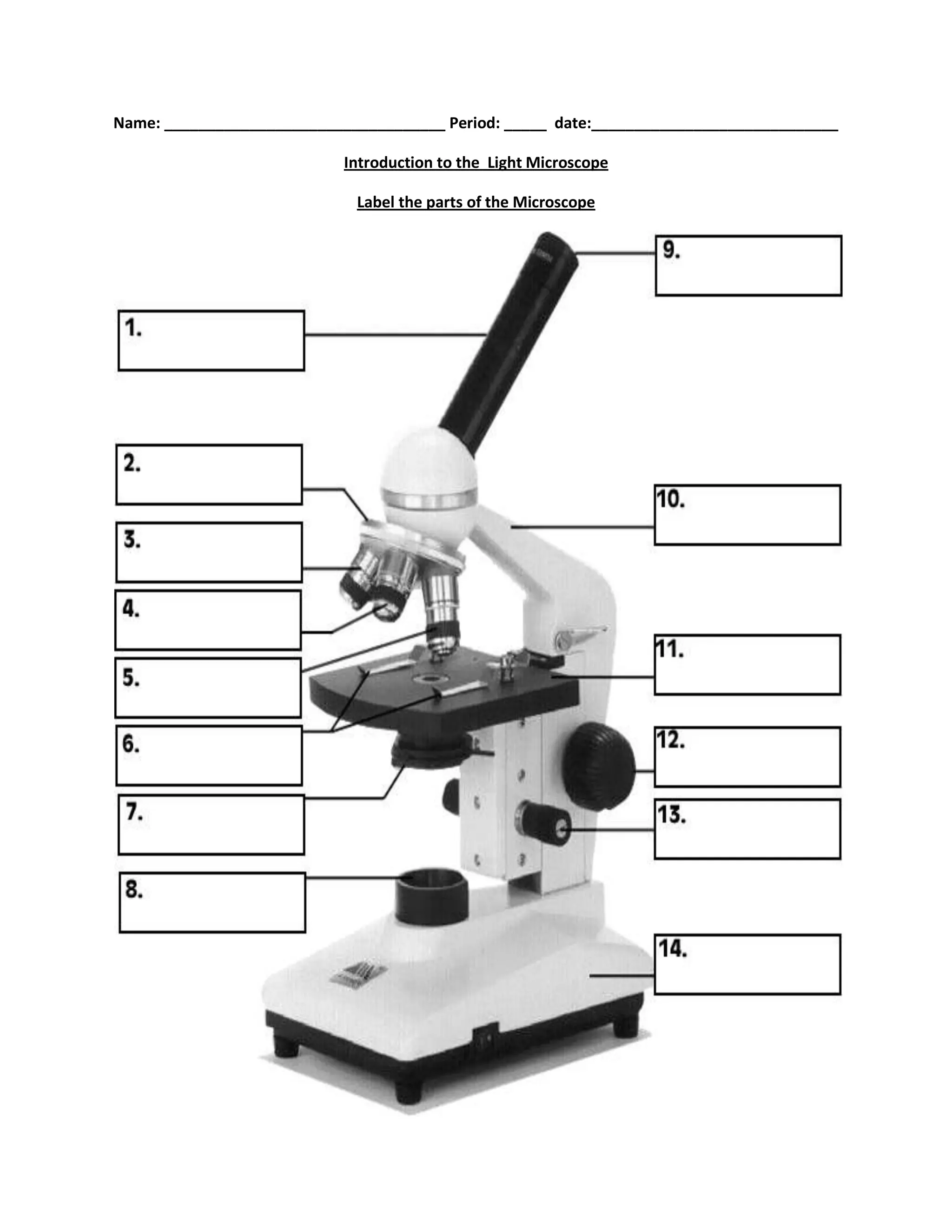
#2
nosepiece
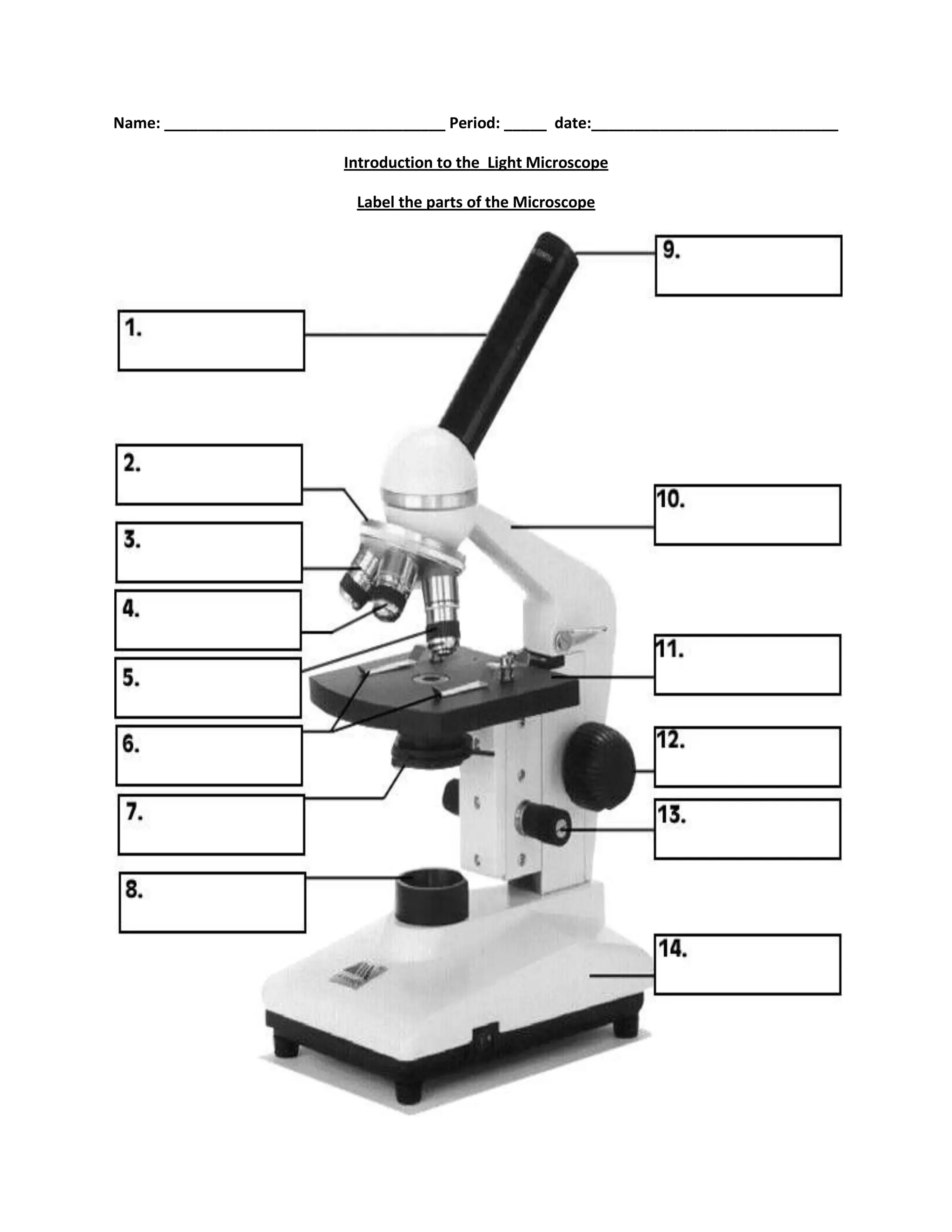
#6
stage clips
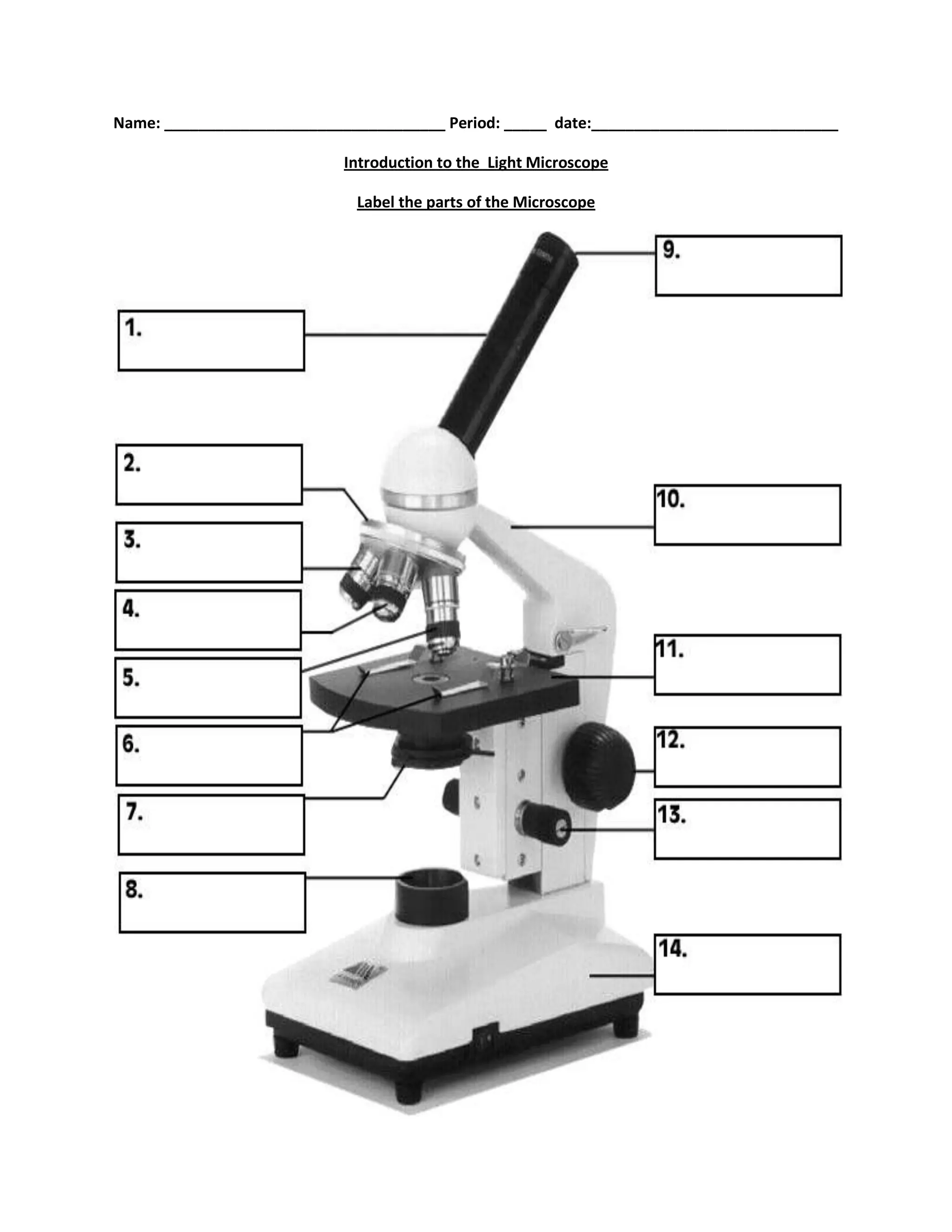
#7
diaphragm
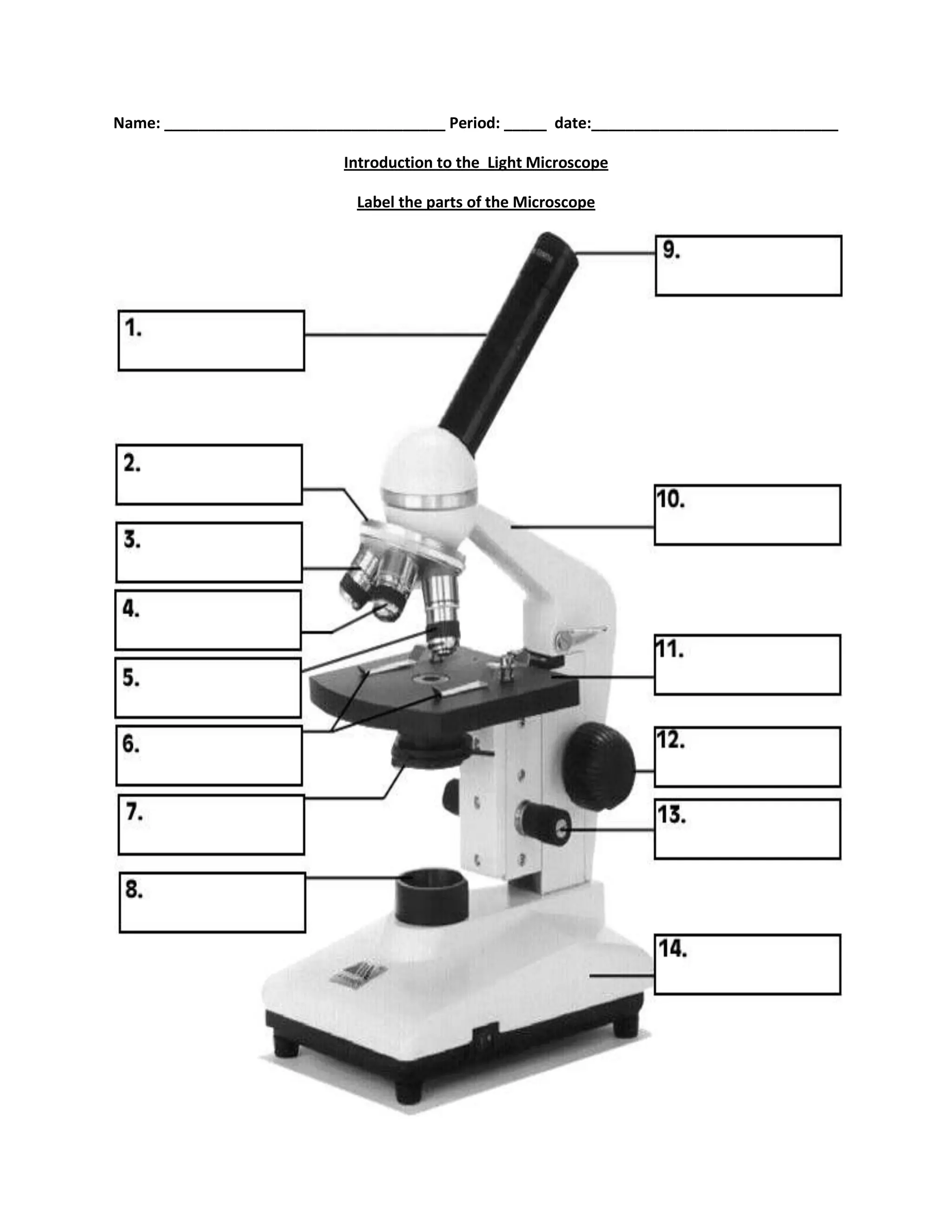
#8
light source
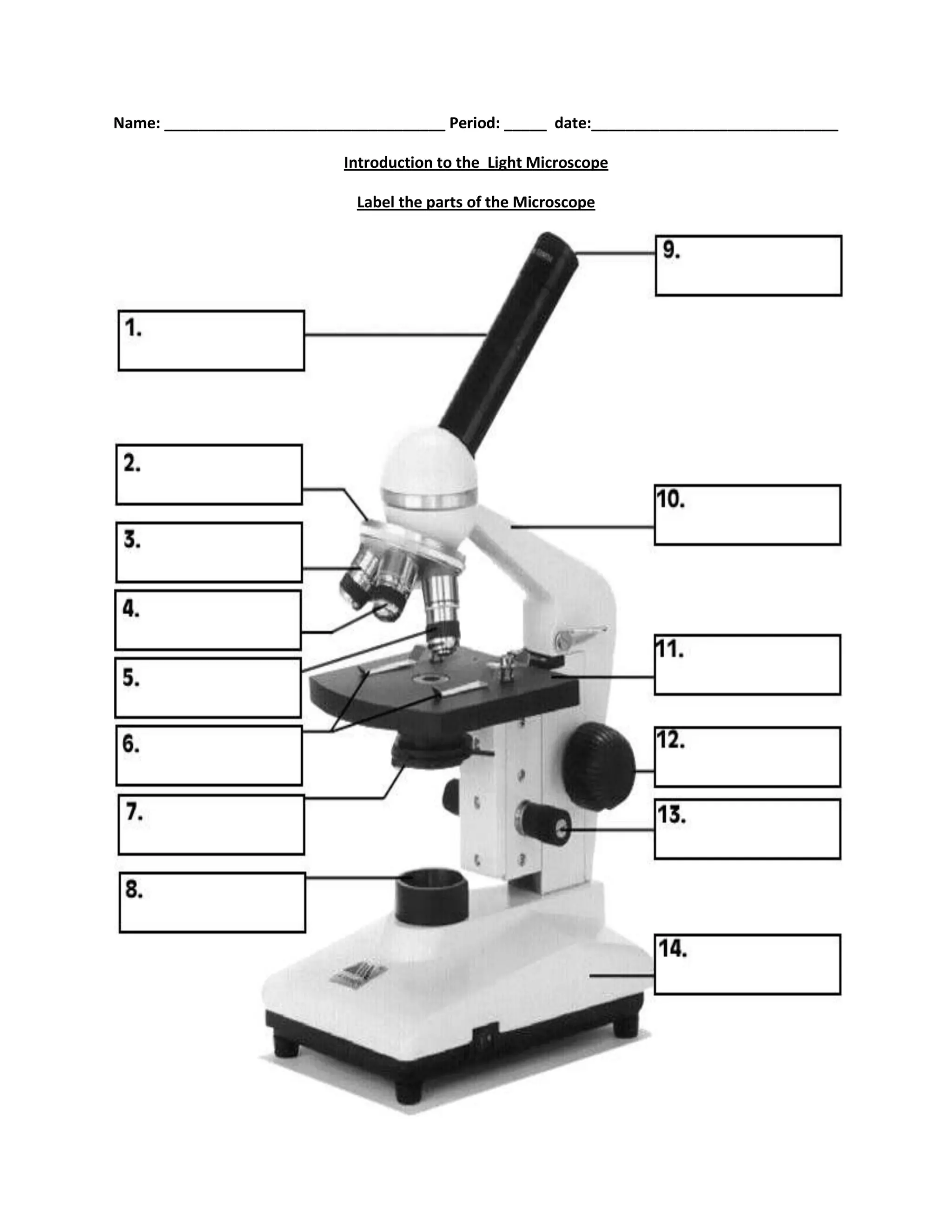
#9
eyepiece
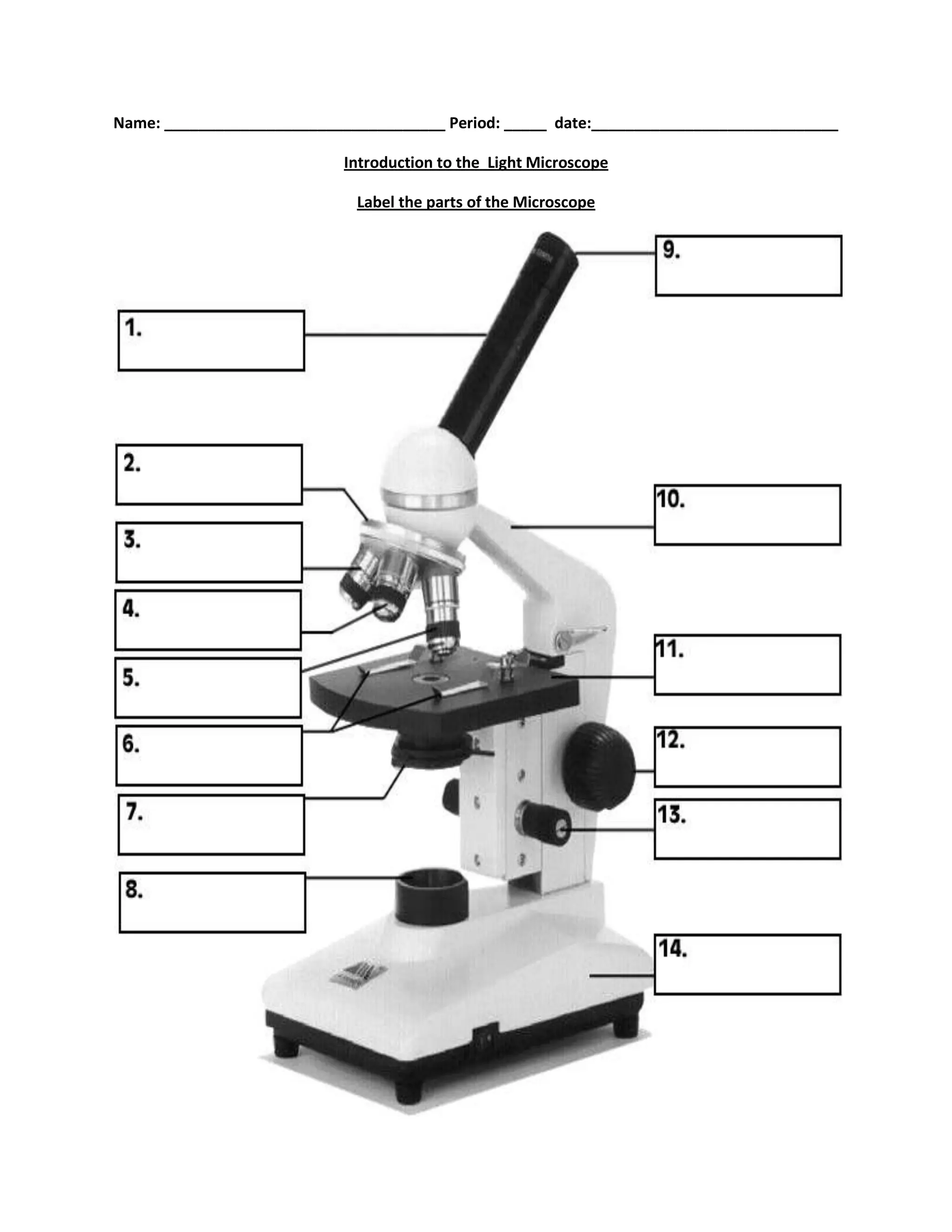
#10
arm
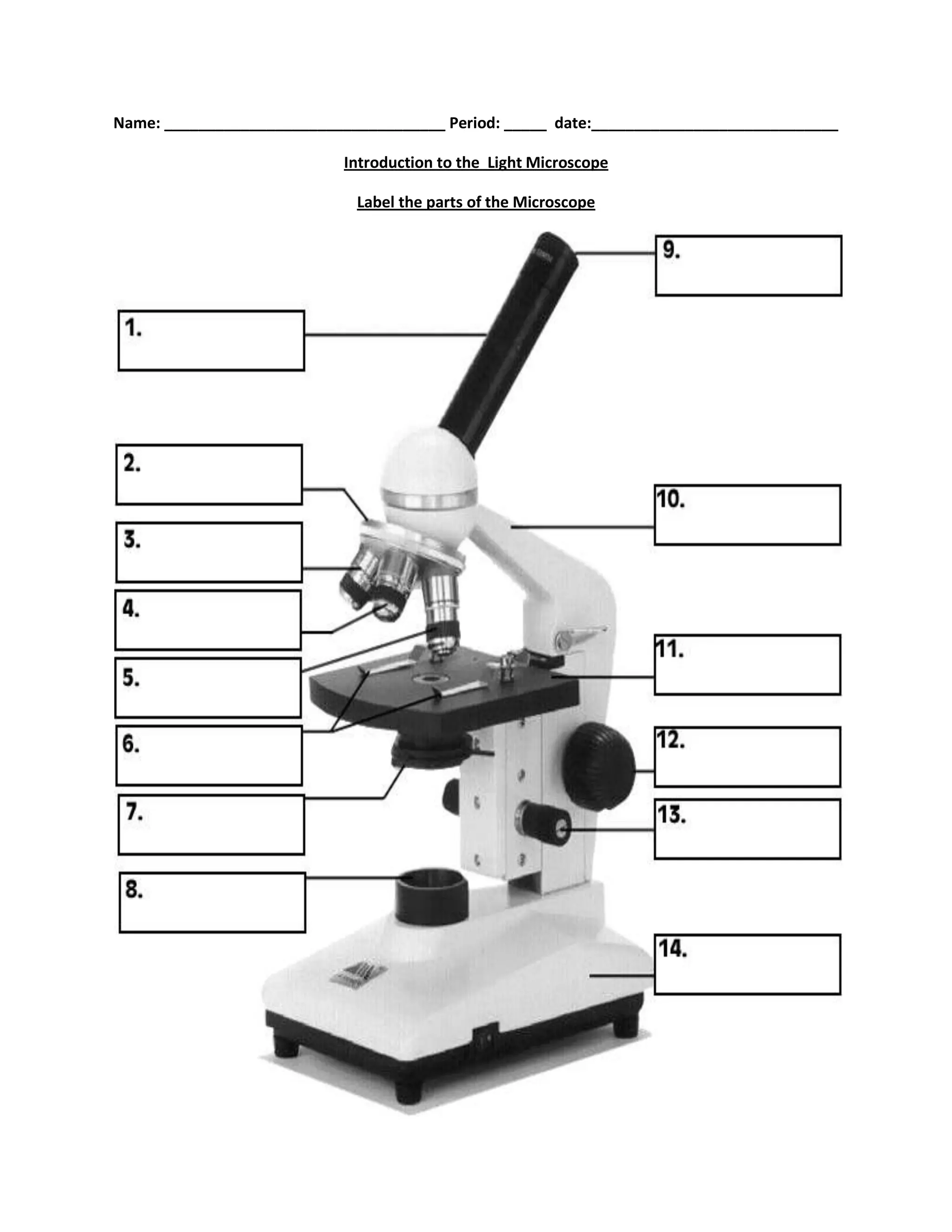
#11
stage
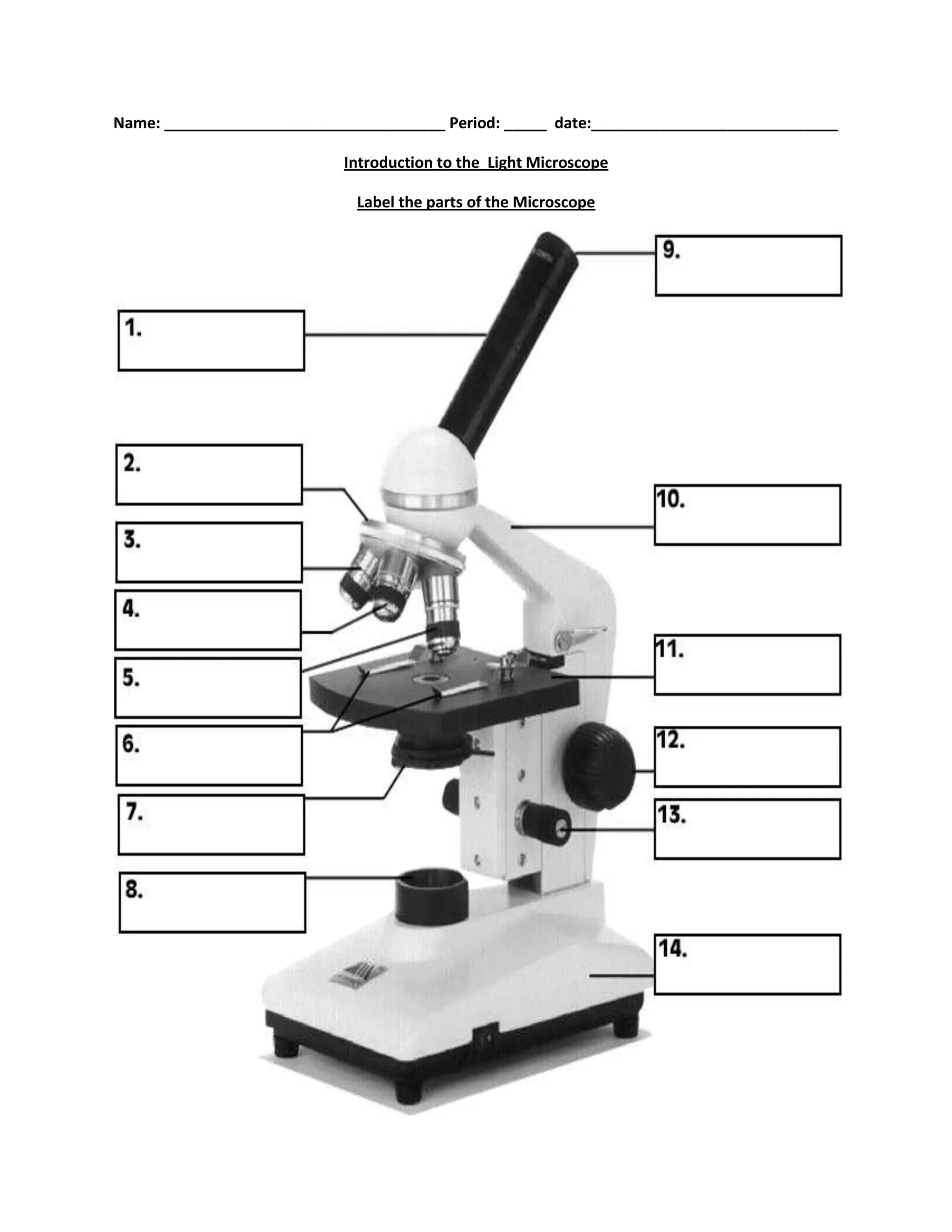
#12
course focus
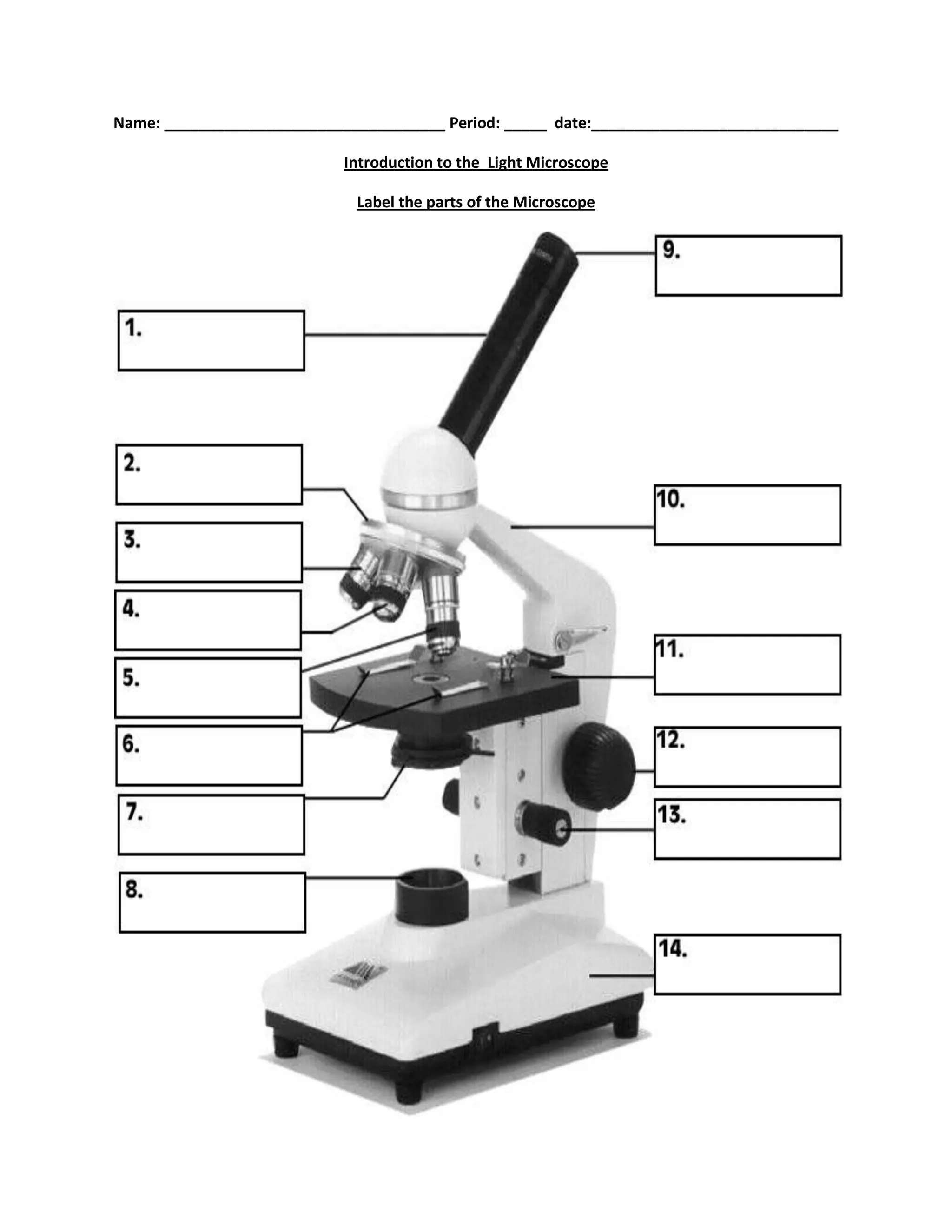
#13
fine focus
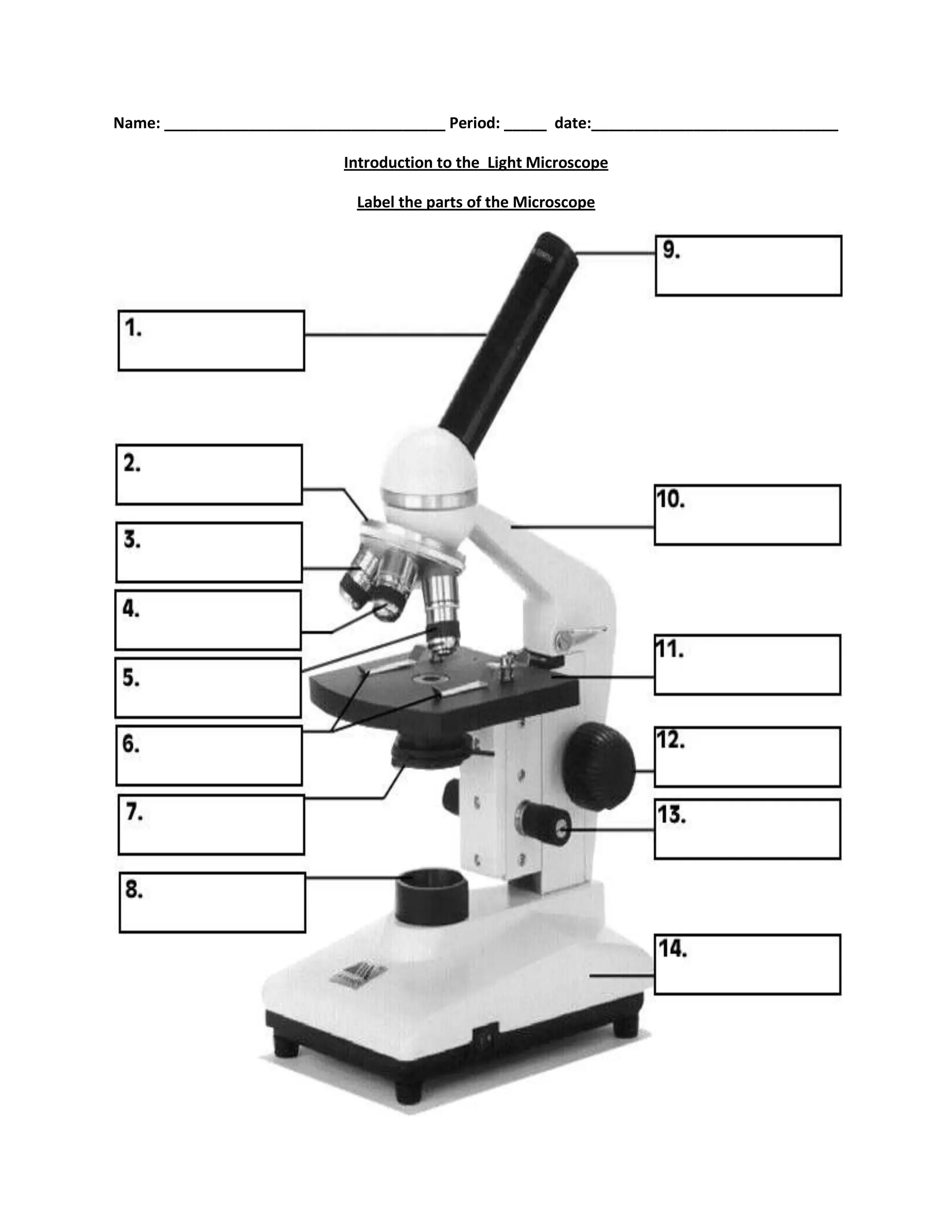
#14
base
the lens that is within the eyepiece of the light microscope is called the:
ocular lens
the wheel under the stage that adjusts the amount of light is called the:
diaphragm
to focus a specimen, it is best to start with the ____ objective
scanning objective
when using the high power objective, you should not adjust the:
coarse focus
who discovered that all animals are made up of cells?
Schwann
who developed cell theory?
Virchow
who created the 1st microscope and looked at water?
Van Leewenhoek
who saw cork under the microscope and coined the term “cells”?
Hooke
who discovered all plants are made up of cells?
Schleiden
what level of organization is the smallest unit of life that is capable of carrying out all the functions of living things?
cellular level
what level of organization is a group of cells that performs a specific function in an organism?
tissue level
what level of organization are several different types of tissue that function together for a specific purpose?
organ level
what level of organization are several organs working together?
organ system level
cell walls cannot be found in which cells?
animal
what is cell theory?
-all living things are made up of cells
-cells are the basic unit of organization (structure and function) in living things
-all cells come from pre-existing cells
the nucleus includes everything except :
cytoplasm
one difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes:
euk cells have membrane bound organelles and a nucleus while pro doesnt.
how can you tell a cell is not bacteria?
if it has organelles
what organelle involves lipid synthesis and detoxification?
smooth ER
what organelle is a rigid sugar containing structure outside the cell membrane providing external support and protection for the cell?
cell wall
what organelle is a lipid bilayer boundary outside of the cell for protection and controls entry/exit of substances and maintains homeostasis?
cell membrane
what organelle is a small structure within the nucleus that makes ribosomes?
nucleolus
what organelle is a network of fine protein tubes and threads that provide the cell with shape and internal structural support/movement?
cytoskeleton
what organelle makes proteins?
ribosomes
what organelle is a gel-like substance that fills intracellular space and contains/holds the organelles. (everything except the nucleus)
cytoplasm