Edexcel iGCSE ICT Unit1 (Types of Digital Devices)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Mainframe computer
A large, multi-user computer commonly used in large businesses and government agencies; more powerful than a minicomputer.

Embedded processor
A processor designed and programmed to perform only the tasks intended to be done by the device the processor is implanted within.
Device Convergence / Multi-functional
the tendency for functions once served by separate devices or machines to be merged into a single device

System software
software responsible for the general operation of a computer system, including the operation of hardware, running application software, and file management

Application Software
Software that performs some useful task such as word processing or playing a game for a user.

Operating System
The software that supports a computer's basic functions, such as scheduling tasks, executing applications, and controlling peripherals.

Open source software
Program code made publicly available for free; it can be copied, distributed, or changed without the stringent copyright protections of proprietary software products.

Software updates
Corrections to installed software that usually remove security flaws or add new features.
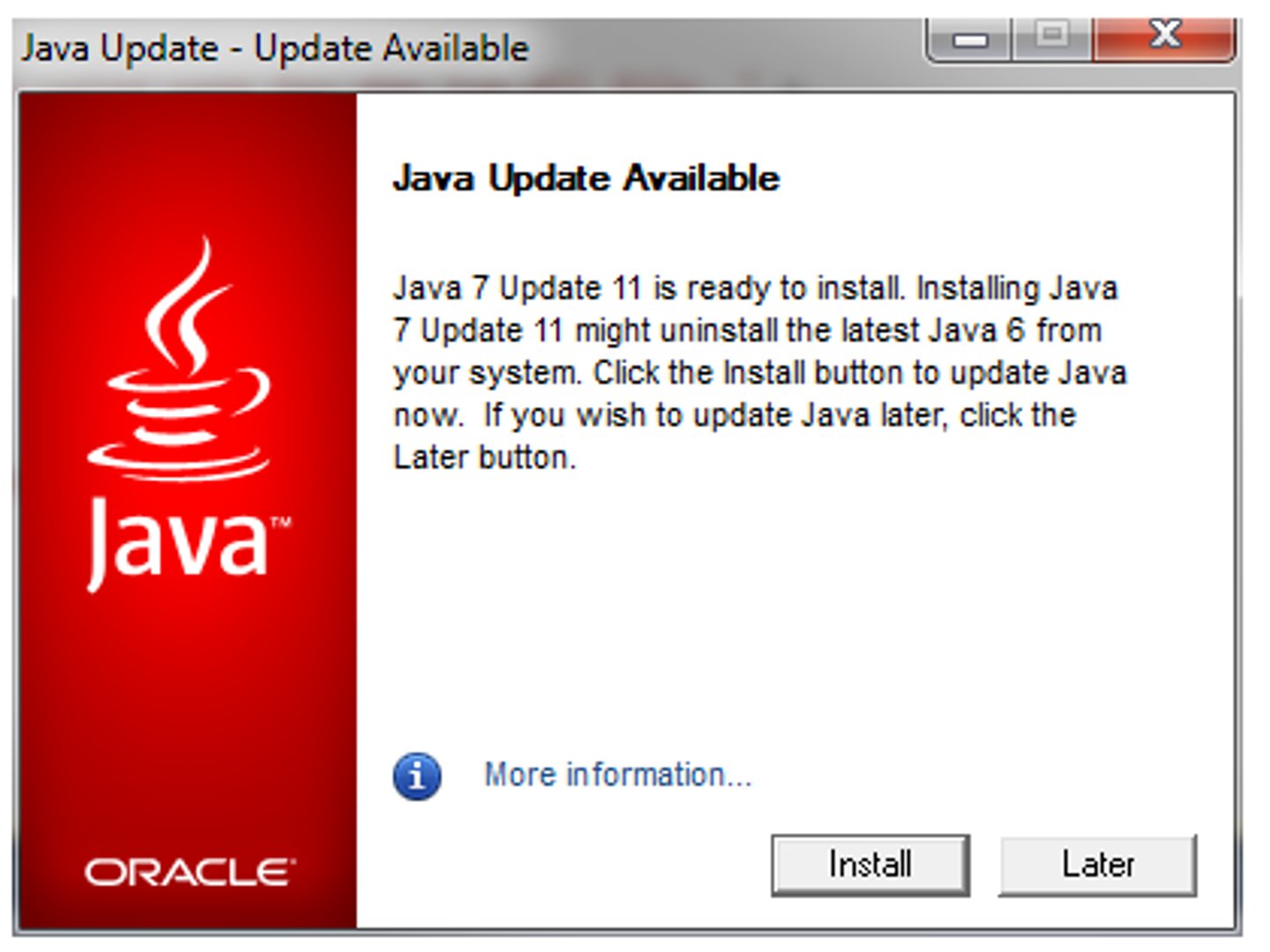
OCR (Optical Character Recognition)
the branch of computer science that involves reading text from paper and translating the images into a form that the computer can manipulate
OMR (Optical Mark Recognition)
Reader that detects marks on a piece of paper. Shaded areas are detected and the computer understands the information. (lottery ticket)

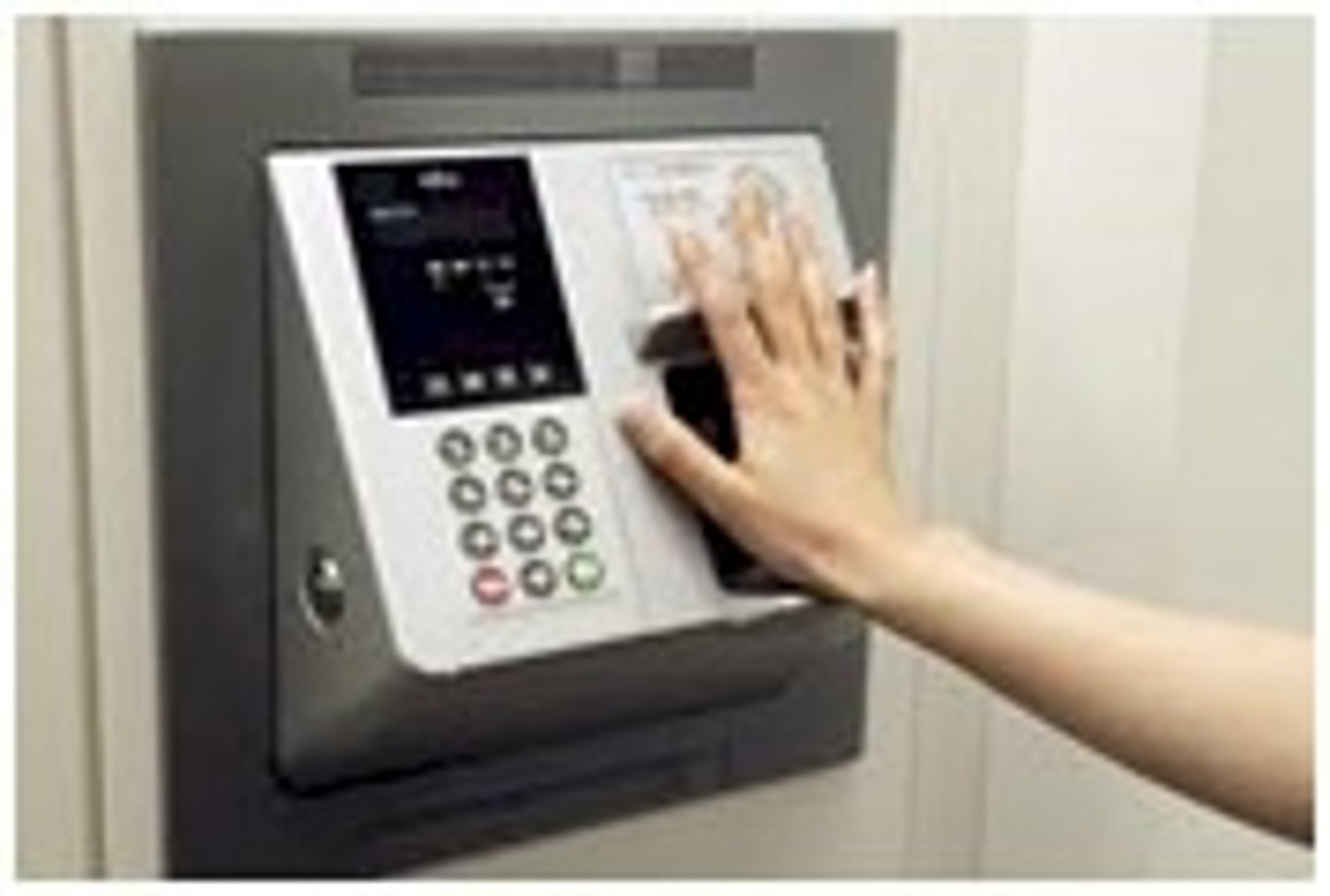
Biometrics
the identification of a user based on a physical characteristic, such as a fingerprint, iris, face, voice, or handwriting

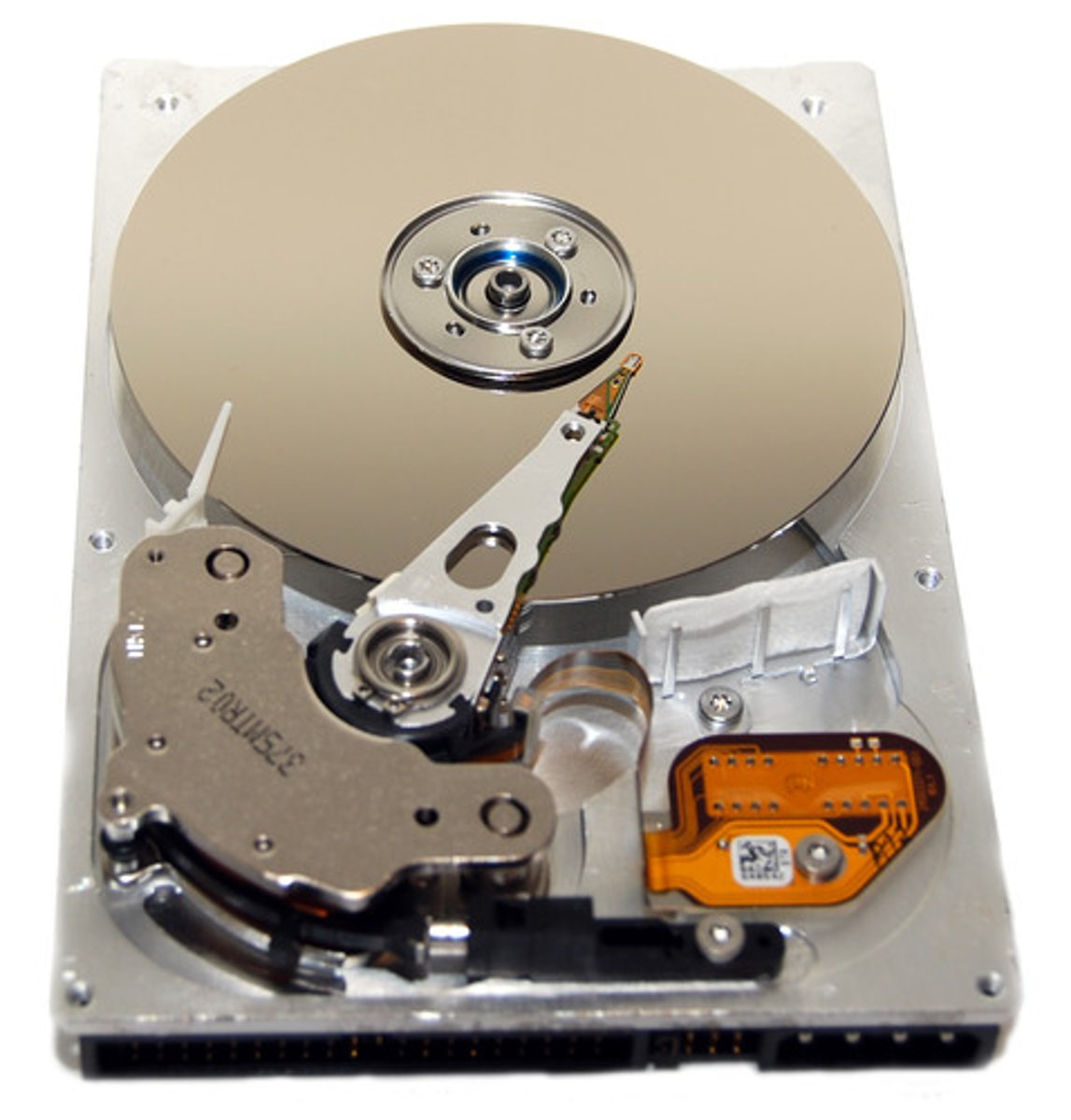
Magnetic Hard Drive
A hard drive consisting of one or more metal magnetic disks permanently sealed, with an access mechanism and read/write heads, inside its drive. Slow but cheap.

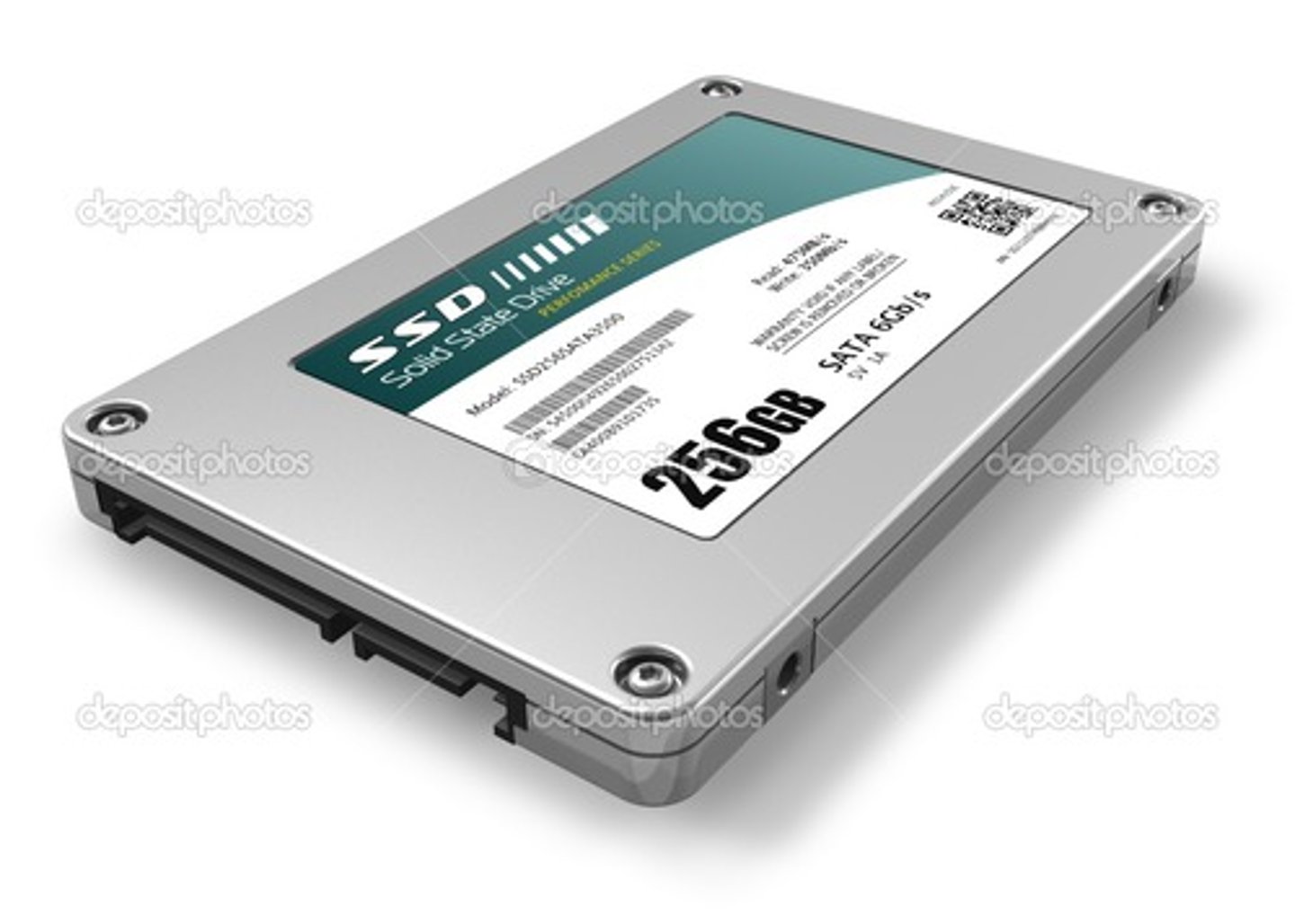
Solid State Drive
a storage device that typically uses flash memory to store data, instructions, and information. Fast but very expensive per GB

CD-R
Optical disc on which users can write once, but not erase, their file

CD-RW
A CD that allows data to be erased and written again several times.

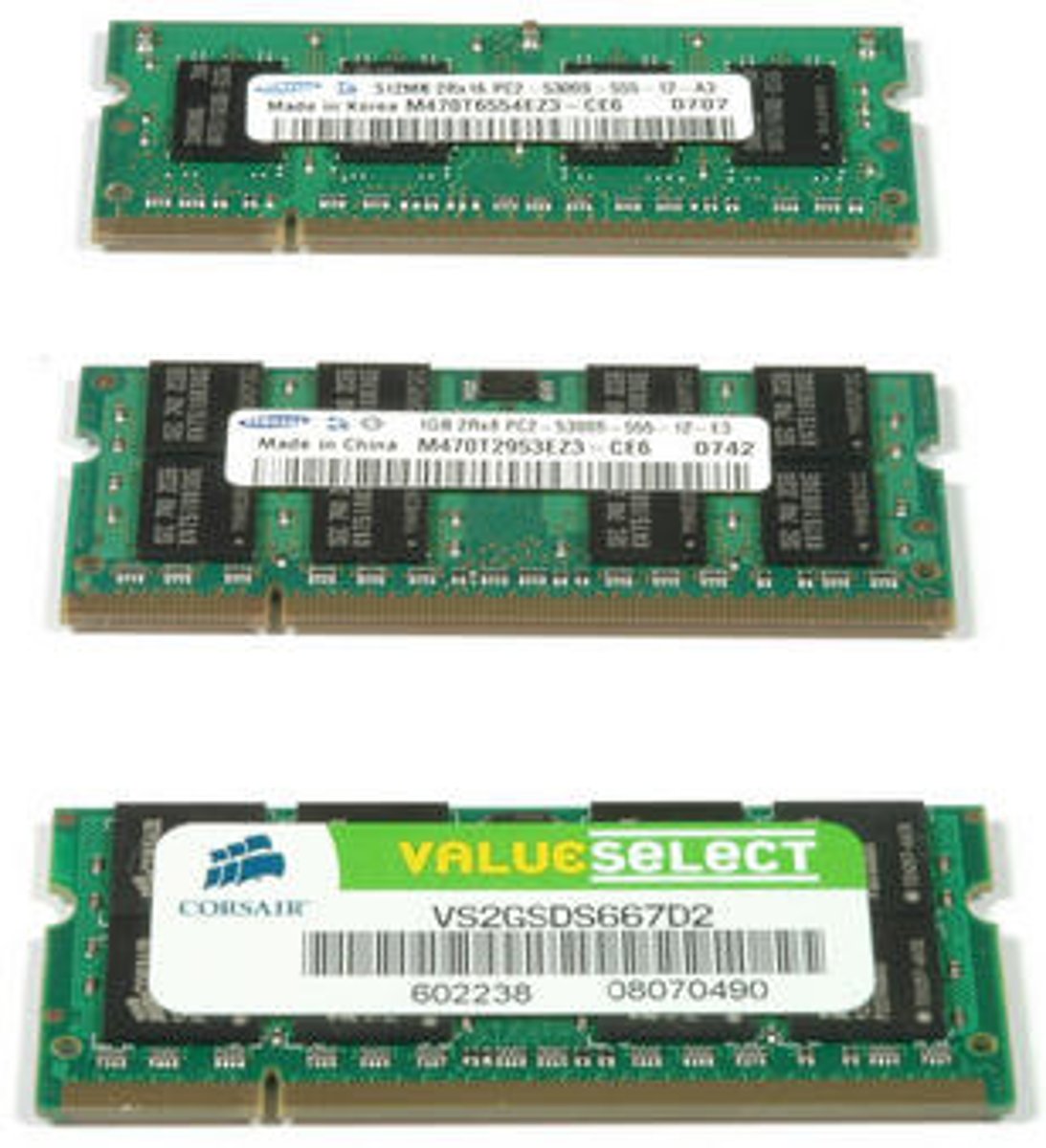
Random access memory
RAM, electronic circuits in a computer that can store code and data of running programs. Volatile, loses data when powered off.

Read Only Memory
Permanent storage; instructions are burned onto chips by the manufacturer. Start up instructions

CPU (Central Processing Unit)
The key component of a computer system, which contains the circuitry necessary to interpret and execute program instructions
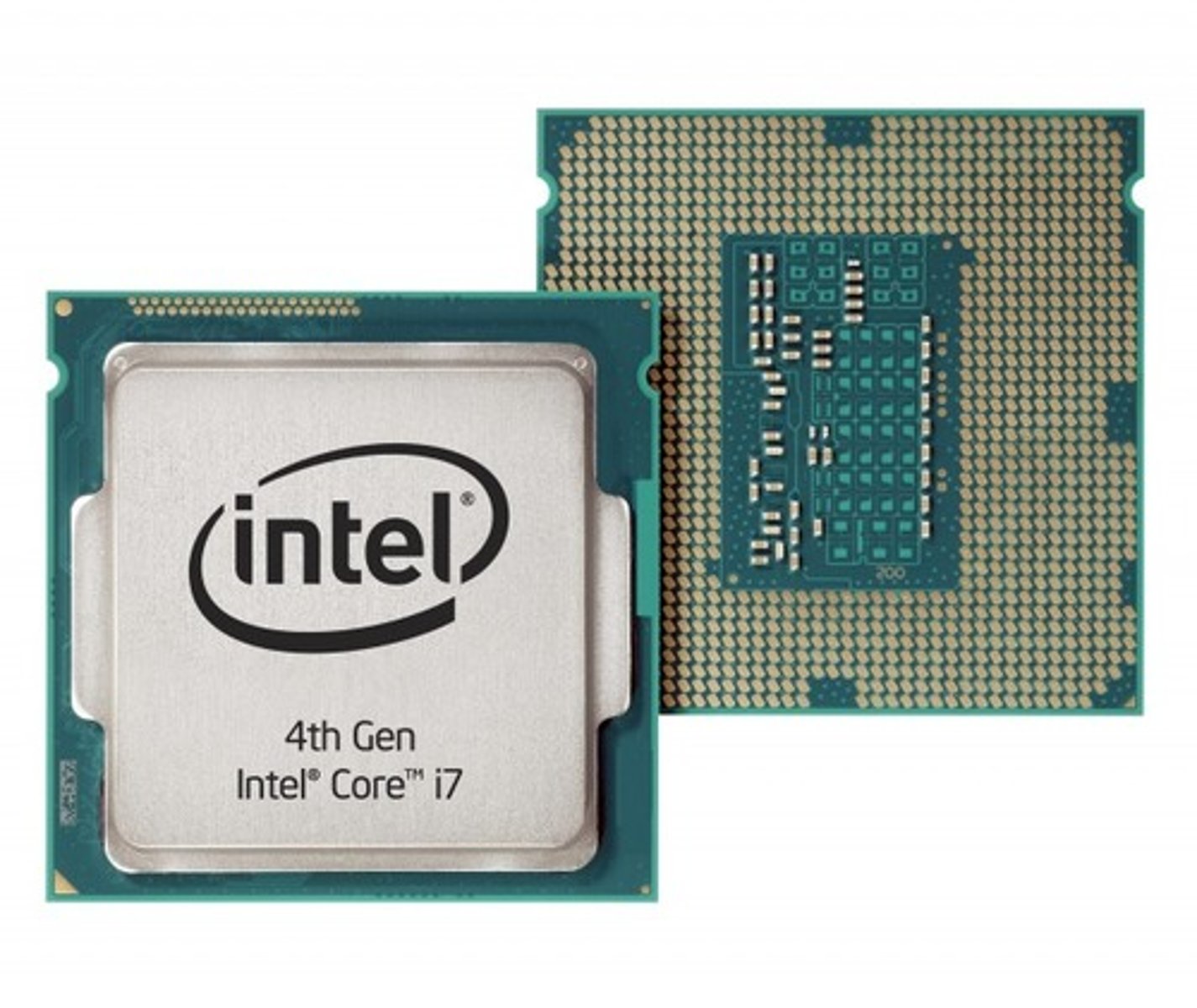

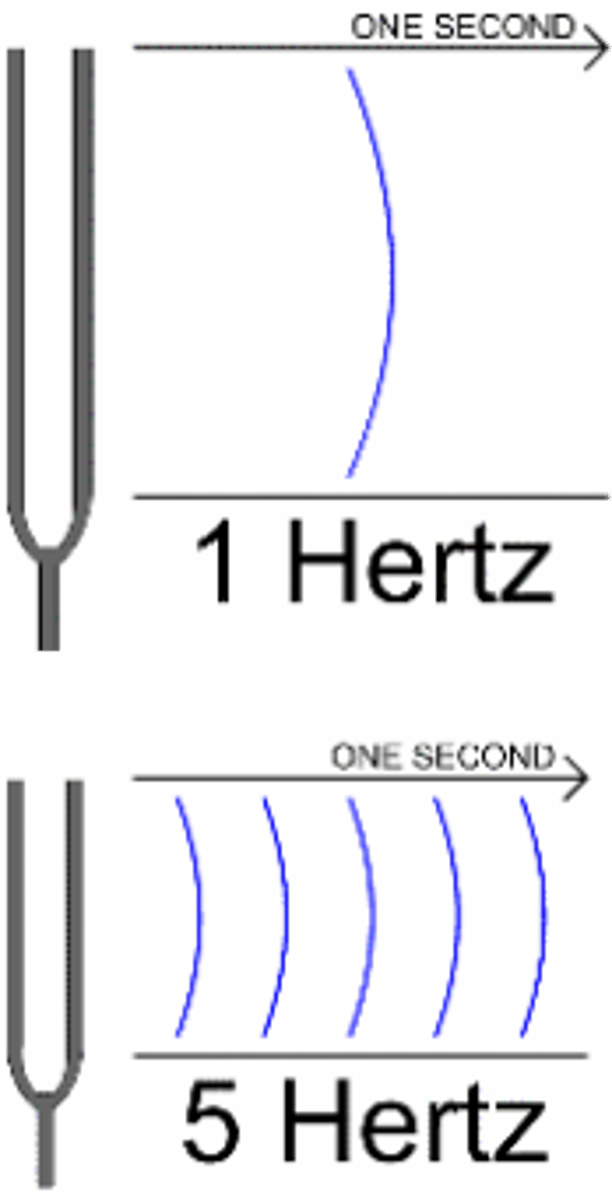
Hertz
The unit of frequency, equal to one cycle per second. Used to measure the speed of a CPU
Accessibility
The ability for people with various disabilities to use a piece of hardware.

Closed Source / Proprietary Software
The software whose source code is not freely available from the original author; Windows 7, for example.

Gigahertz
One billion ticks of the system clock per second.
Smartphone
A device that integrates a cell phone with the features of a PC, such as the ability to store information, receive email, and install programs.

Specialist Phone
phones that are designed for a specific market - e.g. elderly and partially sighted or challenging environments

Desktop
a personal computer designed to be in a stationary location, where all of its components fit on or under a desk or table

Laptop
A portable computer small enough to use on your lap. Has integrated components like a track-pad & screen

SIM Card
a small card used in mobile devices to authenticate the device to service providers and to store some user data

Tablet
a thin, lighter-weight mobile computer that has a touch screen

Micro SD
The smallest version of SD flash card memory used in cameras and digital recorders.

Memory management
The act of keeping track of how and where programs are loaded in main memory

Print Spooling
Windows printing is dependent upon the____ service that is a software process that captures print jobs from applications, places them in the print queue, and then sends each print job to the print device.
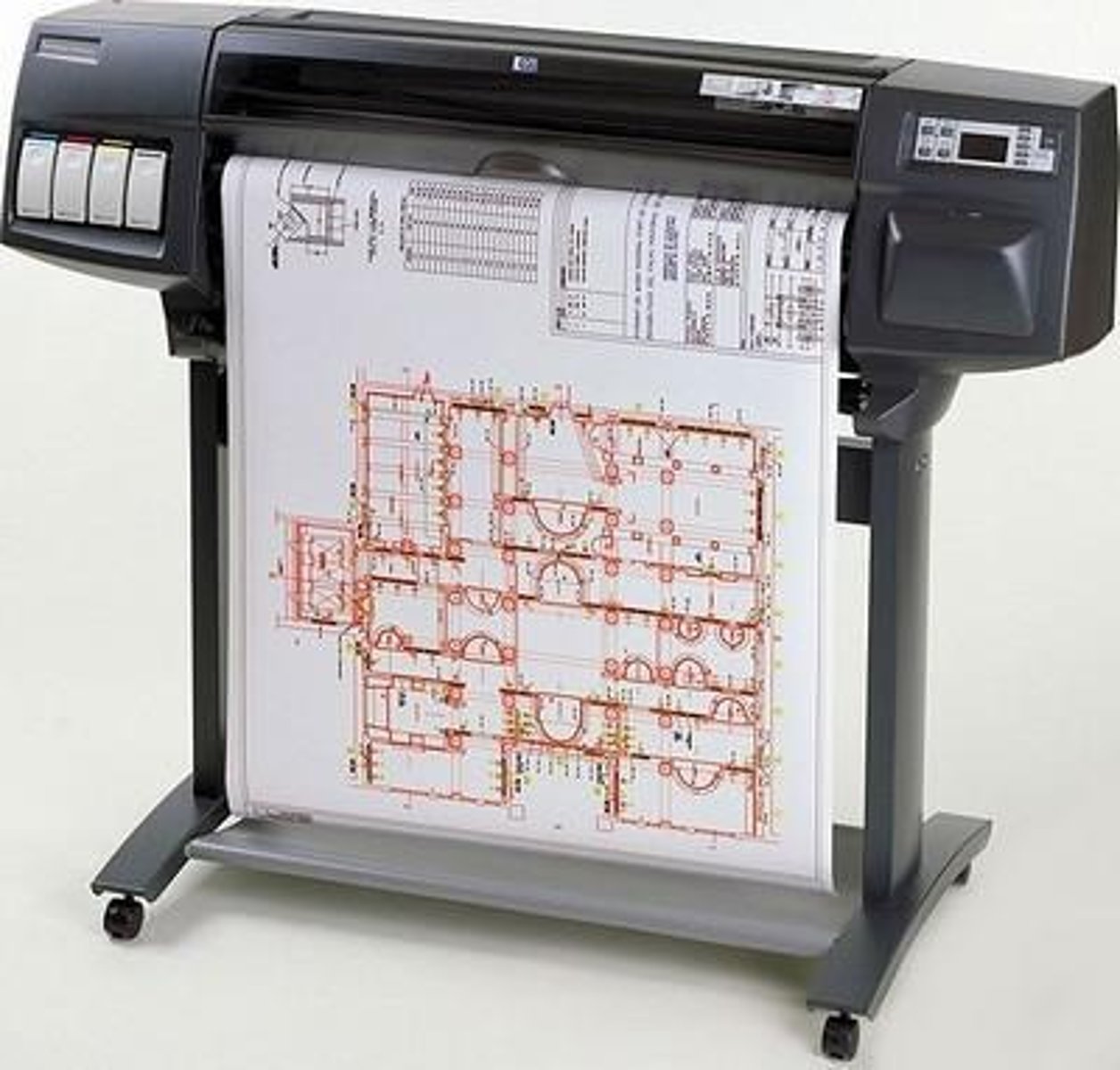
Plotter
An output device that uses robotic arms to produce large images such as blueprints or engineering drawings.

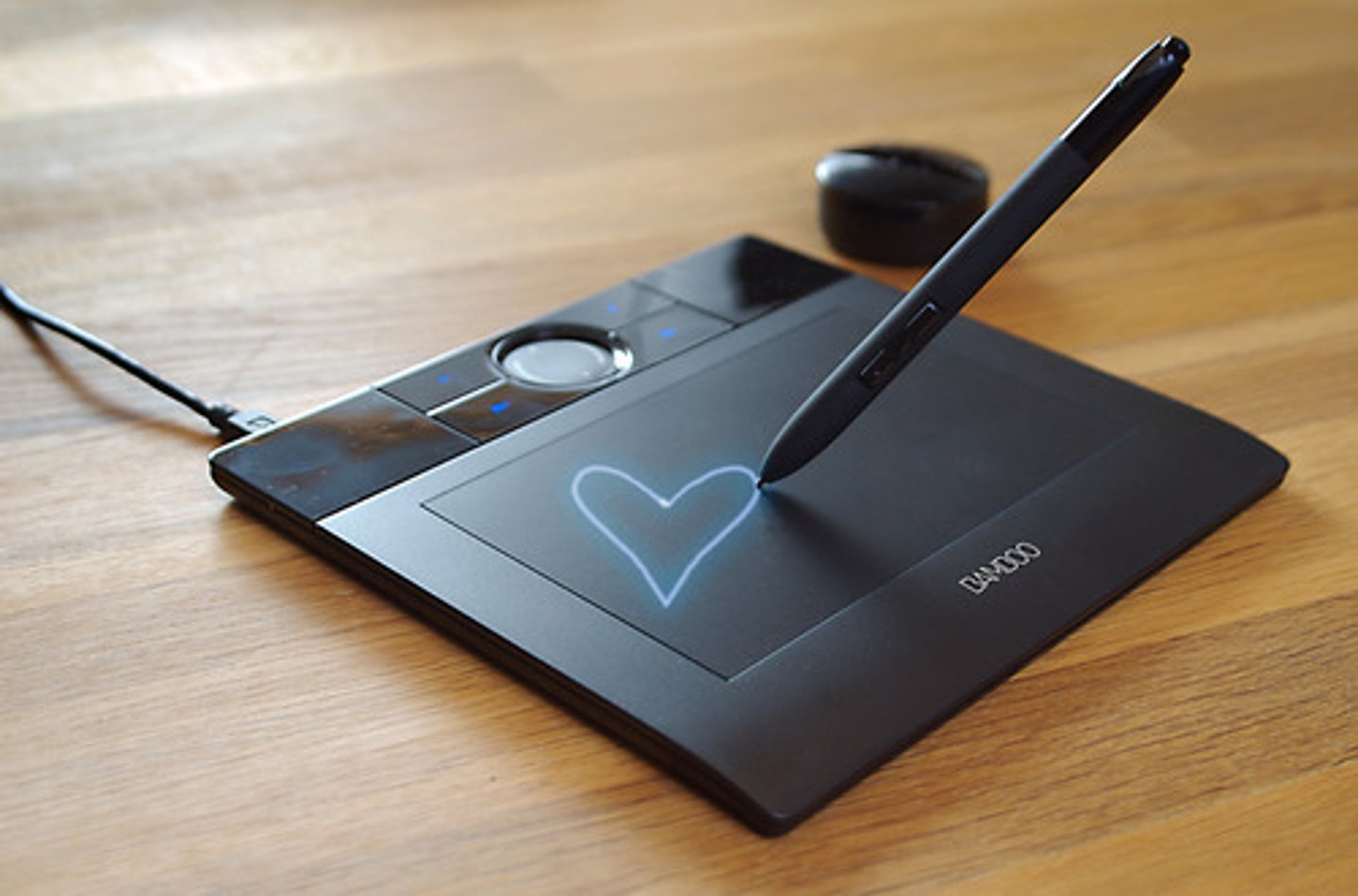
Graphics Tablet
A pressure-sensitive touch tablet used as a pointing device. The user presses on the tablet with a stylus.

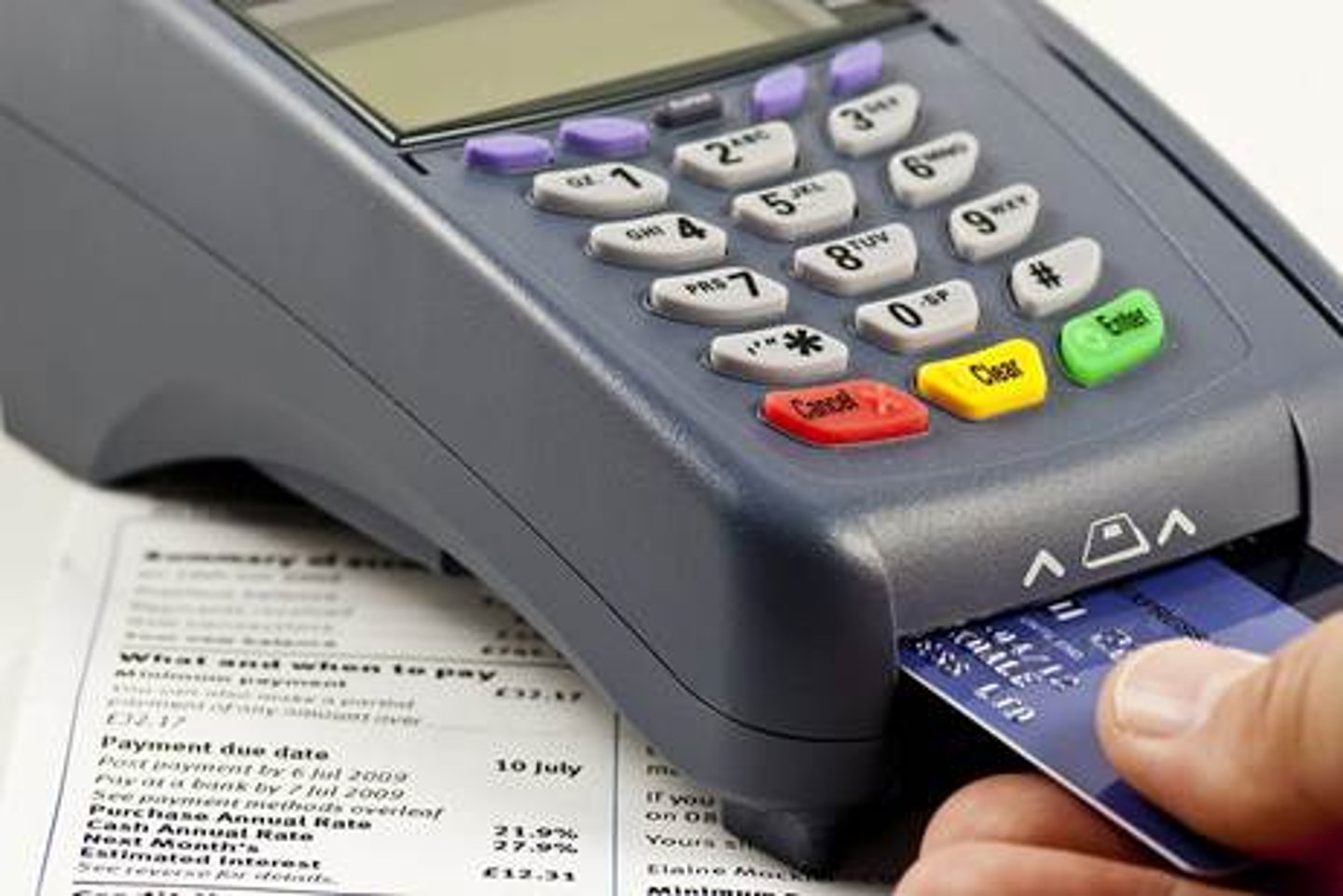
Chip & PIN
Systems designed to reduce credit card fraud by requiring the user to authenticate themselves at the point of sale.

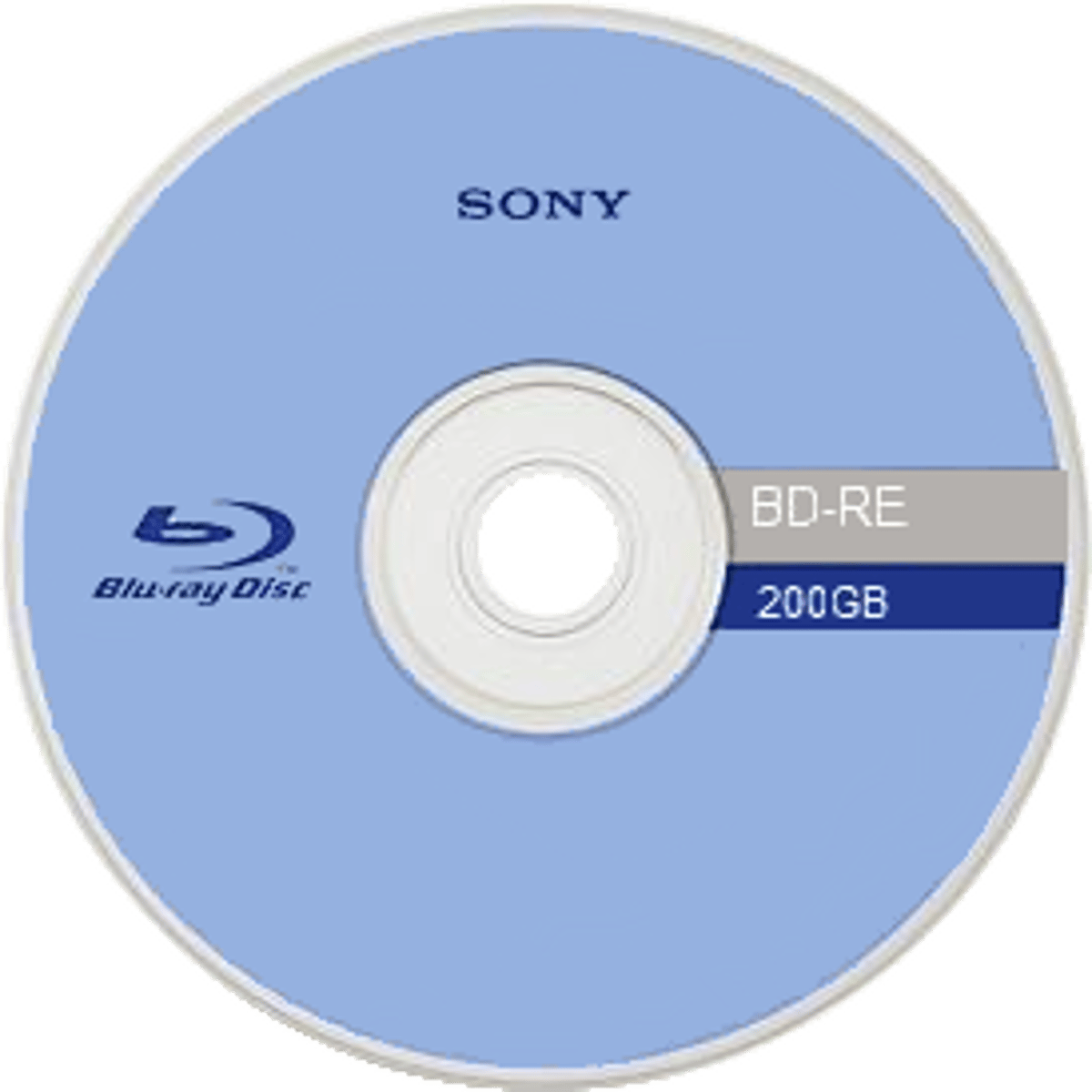
Blue-Ray
uses a blue lazer to put information onto a disk, allows for much more information than DVD or CD

Contrast Settings
An accessibility feature that allows people to choose high contrast to be able to see things better on screen
Screen Reader
Accessibility feature for users with eyesight problems, which reads text aloud.

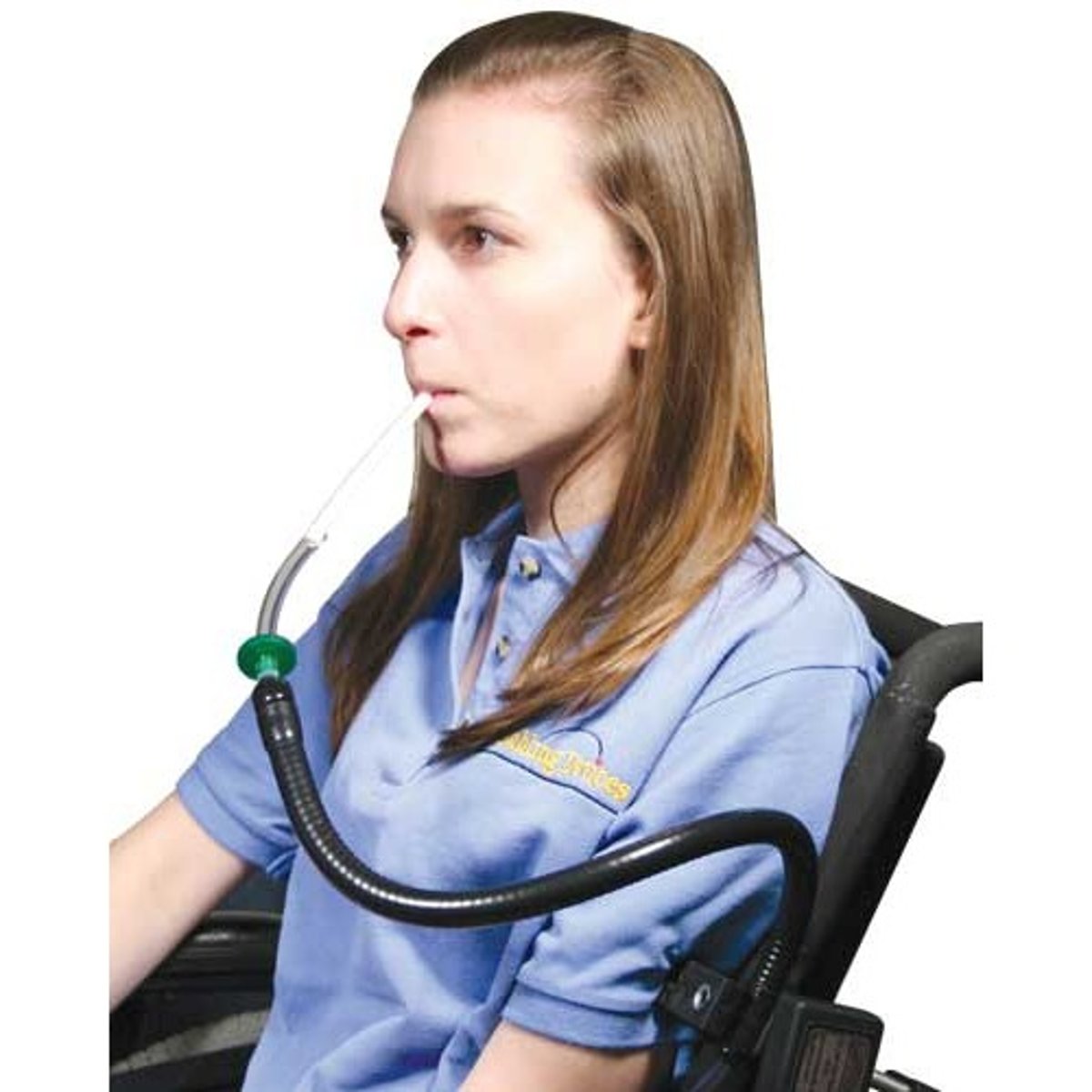
Puff-sip switch
An accessibility feature that allows a user to interact with a computer by using their mouth muscles & breathing

Screen Resolution
indicates the number of pixels that the computer uses to display the letters, numbers, graphics, and background you see on the screen
Processor Core
defined as a processing unit within a CPU. Allows for multitasking
Expandable Storage
A memory card you can add to your device. E.g. Micro SD

Interface
The way a human interacts with a computer through the input and output

Megapixels
A measurement of digital photo quality. One is made up of one million.

Laser printer
uses a toner cartridge filled with fine powder and a heated fuser
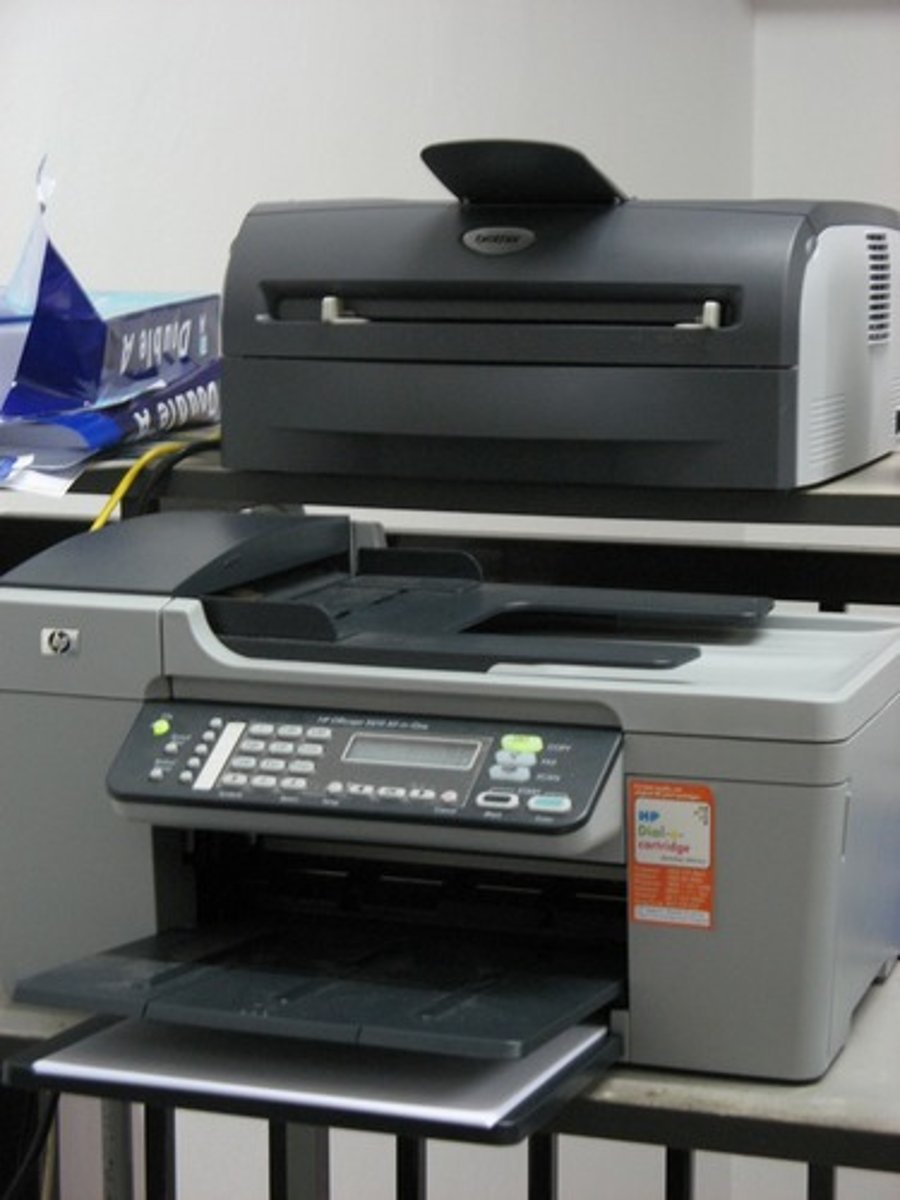

Ink jet printer
uses liquid ink sprayed through tiny nozzles onto paper
