EQ1 - Hydrological Cycle
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What type of system is the hydrological ?
Closed system . driven by solar and gravitational potential energy . No external input / output
What are the 4 stores of water
Hydrosphere
Atmosphere
Cryosphere
Lithosphere
What percentage of water stored in the hydrosphere ?
96.5%
What percentage of water is stored in atmosphere ?
0.001%
What percentage does the lithosphere and cryosphere store ?
1.7%
Define water budget
balance of water stored , entering and exiting a certain area . Assess the availability of water
Define flux
rate of flow between stores
e.g. precipitation , evapotranspiration , surface run off
Define residence time
amount of time water is typically stored
What is an oceans residence time
3500 years
What is the cryosphere’s residence time
15,000 years
What percentage of fresh water is accessible
2.5%
What percentage of water is accessible
1%
What is the main input in the cycle
precipitation ( rain/ sleet /hail '/snow )
What is the main output of the cycle
Evaporation , transpiration , discharge/channel flow
What are the 3 types of rainfall
Relief
Convectional
Frontal
Relief rainfall
Occurs because of landscape shape / topography
Happens due to change in air temperature
CCC
Convectional rainfall
Warmth in the air rises
Cools in atmosphere
forms cloud
Rainfall occur
Frontal rainfall
Warm air fronts meet cooler air fronts
warm air rise cool air dense false
two airs mix to form rainfall
HEAVY rainfall
7 flows of the hydrological cycle
Interception , plant intercepts water
Infiltration , soaked / absorbed
percolation transfer of water deep in soil / bed rock
Throughflow , lateral movement down slope
Groundwaters flow , SLOW transfer of percolated water into bedrock
Surface runoff , movement of water overland
River/channel flow , water enter channel of river
How does climate effect the drainage basin
Wet climate lots In drainage lots come out
Drier climate les IN / OUT
Change amount/type of precipitation/evaporation
Define drainage basin
area surrounding a river
How does soil effect the drainage basin
Affects different flows - surface run off
Soil absorbent affect flow
Determines infiltration rates
How does geology effect the drainage basin
Surface run off
Impacts percolation / groundwater flow rates
Impermeable rock not absorb water easily and permeable rock
Affects soil formation
How does relief effect the drainage basin
surface run off
steep slope occur quicker
amount of precipitation relief rainfall/convectional rainfall
How does vegetation effect the drainage basin
surface run off
vegetation allow to be infiltrated interception
important
How can river management disrupt the drainage basin cycle
Construction of reservoirs
Use for domestic supply
Irrigation , agriculture
How can deforestation disrupt the drainage basin cycle
Reduces evapotranspiration/transpiration
Less water into atmosphere
Increase infiltration rates , surface run off due to water log nature of soil , surplus water
How can changing land use disrupt the drainage basin cyle
Arable to pastoral farming : soil compact increase surface run off
Pastoral to arable : ploughing increases infiltration
How can urbanisation disrupt the drainage basin cycle
Impermeable surfaces
Increase surface run off
Flooding
What are the 5 components affected by human factors
Evaporation
Evapotranspiration
Surface run off
Infiltration ground water
Interception
Named example of humans disrupting drainage basin
Amazonia
Lower humidity
Less precipitation
Compact surface / soil more surface run off infiltration
Soil erosion / silt into rivers
More evaporation less transpiration
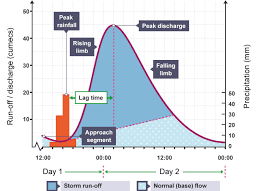
Explain a flashy hydrograph
Discharge line exponentially increase long rate of high peak discharge
Rising limb steep an falling limb
Lag time is short
Shows storm event , high rainfall , water logged
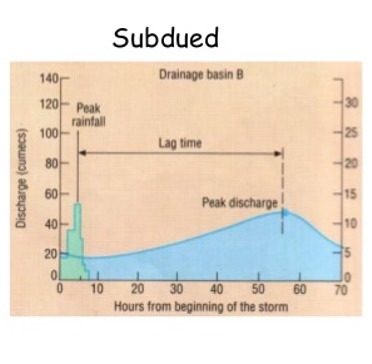
Explain a subdued hydrograph
Occur in area of less rainfall / slope
Rising limb shallow falling limb steeper
Lag time longer
Less water
Manageable drainage basin / changeable
Factors that affect shape of a flash hydrograph
intense storm exceed infiltration low evaporation
impermeable soil clay , slopes steep
Small basin , circular , streams flowing to main river
Vegetation minimal low density
Prior soil saturated
Urbanisation / concrete /deforestation
Factors that affect shape of a subdued hydrograph
steady rainfall
permeable rock
slopes gentle/flat
large drainage basin elongated few streams
high density vegetation
dry basin / water table low
rural low population , afforestation
Define water budget
Annual balance between inputs and outputs
What equation is used to calculate a water budget
P = E + R +/- S
Precipitation = evaporation runoff + / - storage
Defien river reigme
The annual variation of discharge in a river
what affects affect a river regime
size of river
seasons/amount of rainfall
temp
evaporation rates
geology
soil
vegetation
human activity
Amazon an example of river regime
High flow Dec-May wet season
June- Nov dry season
Human impact urbanisation / deforestation increase
Alaska example of a river regime
High flow April - August / snow melt
Low flow Sep- march / ice form
Large flow variability
Limited human impact