14. Membrane Permeability
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Explain what is meant by permeability:
The ease of movement of a substance through a material
Explain why a substance is more permeable if it is porous
The gaps enable molecules to move through the membrane
What factors affect membrane permeability?
Temperature
pH
Alcohol
Detergents
Describe the effect of increasing temperature on the arrangement of particles.
Particles move faster
Particles move further apart
Bonds are broken
What happens to membrane permeability as temperature increases?
Membrane permeability also increases
Identify any other parts of the cell membrane which might be affected by increasing the temperature:
Temperature affects the 3D shape of proteins; at high temperatures membrane proteins denature, increasing the permeability of the membrane
→ Increasing temperature, increase membrane permeability
Explain the effect of an increase in temperature on the permeability of the phospholipid bilayer:
- Phospholipids gain kinetic energy and so move around more.
-This causes the phospholipids to be less tightly packed together
- Which causes an increase in membrane permeability
-The increase in temperature also causes hydrogen bonds in proteins to break more.
-This leads to proteins changing shape (denature) so the membrane becomes more permeable
What does beetroot contain?
A red pigment
→ This pigment is contained within the vacuole
Describe how permeability of the membranes in a beetroot cell effects the coloration of the solution surrounding it:
- increase permeability increases gaps in vacuole membrane/ disrupts vacuole membrane
- more pigment can diffuse out of vacuole (through tonoplast/ vacuole membrane)
- more intense coloration of solution

Describe the effect of increasing temperature on the permeability of beetroot cell membranes:
As temperature increases the permeability increases
More pigment leaves the cell
More intense colour of solution at higher temperatures

Explain this change in permeability (increasing temp):
Proteins denatures (change shape)
phospholipids move more as they have more kinetic energy
The hydrogen bonds break
more pigment leaks out, more permeable
increase permeability increases gaps in vacuole membrane/ disrupts vacuole membrane
more pigment can diffuse out of vacuole (through tonoplast/ vacuole membrane)
more intense coloration of solution
What happens when phospholipids are placed in alcohol?
They dissolve
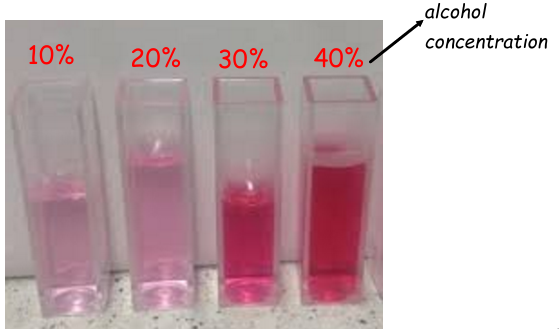
Describe the effect increasing alcohol has on the cell membrane:
Alcohol disrupts the cell membrane → cell membrane becomes more permeable → phospholipids dissolve in the ethanol (alcohol).
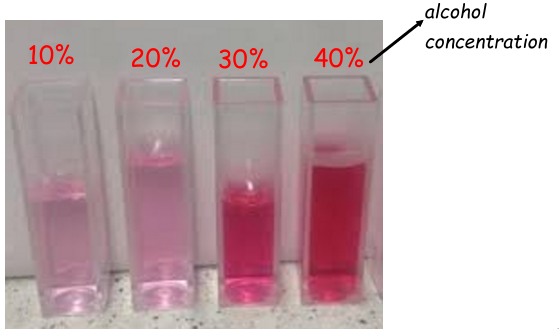
Suggest the effect increasing alcohol has on the proteins in the cell membranes:
Proteins are denatured
Explain why more pigment is able to leave the beetroot cell when increasing alchohol:
The membrane of the vacuole is also disrupted → so more betalain can escape from the vacuole
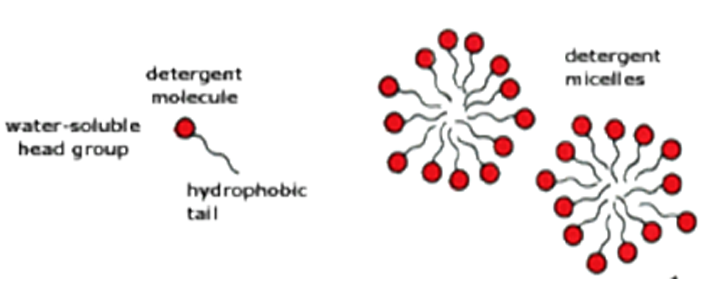
Explain why detergent molecules form micelle structures when placed in aqueous solutions:
- hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
- hydrophilic heads orientate outwards towards water
- hydrophobic tails orientate inwards away from water
Explain the effect detergent molecules has on membrane permeability:
Detergents increases membrane permeability membranes will get disrupted
→ more gaps in the membranes