U3
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
software requirement
establishing the needs of stakeholders that are to be solved by software
requirement
a condition or capability needed by the user to solve a problem
requirement
software capability that must be met or possessed by a system
functional requirement
specify something that the application or system should do
functional requirement
a behavior of the system that takes input and provides output
performance requirement
software requirements can also be a non-functional, it can be a
non-functional requirements
define the quality attributes of a software system, describe how the system should be
non-functional requirements
ensure the performance, maintainability, usability, and effectiveness of the entire system
Business Requirements
Architectural and Design Requirements
System and Integration Requirements
3 types of requirements
business requirements
known as stakeholder requirements specifications
business requirements
describe the characteristics of the proposed system
architectural and design requirements
more detailed and determines the overall design required to implement the business requirements.
system and integration requirements
break-down the steps needed to meet the business requirements
detailed description of each and every requirement
requirement analysis
analyzing customers’ needs to obtain a definition of the software requirements
requirement analysis
helps organizations to determine the actual needs of stakeholders and enables the development team to communicate with the stakeholders
requirement analysis
is the process of defining user expectations for a new software being built or modified
requirement engineering
requirement analysis is also known as
Eliciting requirements
Analyzing requirements
Requirements modeling
Review and retrospective
the requirements analysis process involves the following steps
eliciting requirements
communicating with the customers to determine what their requirements are
requirements gathering
eliciting requirements is sometimes also called
analyzing requirements
determine the quality of the requirements
requirements modeling
requirements are usually documented in different formats such as use cases, user stories, natural-language documents, or process specifications.
review and retrospective
conducted to reflect on the previous iterations of requirements gathering in a bid to make improvements in the process going forward
review and retrospective
team members reflect on what happened in the iteration and identify actions for improvement going forward
stakeholder issues
engineer/developer issues
2 requirement analysis issues
requirement analysis techniques
used to map the business workflow
business process modeling notation (BPMN)
is similar to creating process flowcharts to simplify understanding the business process
business process modeling notation (BPMN)
widely popular as a process improvement methodology
UML (Unified Modeling Language)
consists of an integrated set of diagrams that document the artifacts of a software system
UML (Unified Modeling Language)
useful technique while creating object-oriented software
UML (Unified Modeling Language)
validating the architectural design
flowchart technique
sequential flow and control logic of a set of activities that are related.
flowchart
are in different formats such as linear, cross-functional, and top-down used to representdata flows, system interactions
advantage of using flowchart
easy to read and write for both the technical and non-technical team members
show the parallel process by function, critical attributes of a process
data flow diagram
visually represent systems and processes that are complex and difficult to describe in text
data flow diagram
represent the flow of information through a process or a system and sub process through which the data moves
data flow diagram
describes various entities and their relationships with the help of standardized notations and symbols
role activity diagrams (RAD)
is a role-oriented process model that represents role-activity diagrams
role activity diagrams (RAD)
are a high-level view that captures the dynamics and role structure of an organization
roles
are used to grouping together activities into units of responsibilities
activities
are the basic parts of a role
activity
may be either carried out in isolation or it may require coordination with other activities within the role
gantt charts
visual representation of tasks that are scheduled along with the timelines
gantt charts
help to know what is scheduled to be completed by which date. The start and end dates of all the tasks in the project can be seen in a single view.
IDEF (integrated definition for function modeling)
child and parent systems with the help of a box
IDEF (integrated definition for function modeling)
provides a blueprint to gain an understanding of an organization’s system
workflow technique
visual diagram that represent one or more business processes
workflow technique
used by BA for taking notes during requirements elicitation
Information Gathering
Workflow Modeling
Business process Modeling
Implementation, Verification & Execution
workflow technique process comprises of four stages:
object oriented methods
uses object oriented paradigm and modeling language for designing a system
object oriented methods
emphasis on finding and describing the object in the problem domain
object oriented methods
method is applicable to the system which has dynamic requirements. It is a process of deriving use cases, activity flow, and events flow for the system
object oriented analysis
can be done through textual needs, communication with system stakeholder and vision document
So, when the object receives a message, state changes through behavior
The object has a state, and state changes are represented by behavior
gap analysis
is a technique that helps to analyze the gaps in the performance of a software application to determine whether the business requirements are met or not
gap
denotes the difference between the present state and the target state
need analysis, need assessment, or need-gap analysis
gap analysis is also known as
Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN)
UML (Unified Modeling Language)
Flowchart Technique
Data Flow Diagram
Role Activity Diagrams (RAD)
Gantt Charts
IDEF (Integrated Definition for Function Modeling)
Workflow Technique
Object Oriented Methods
Gap Analysis
10 requirement analysis techniques that can be used for software development process
Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN)
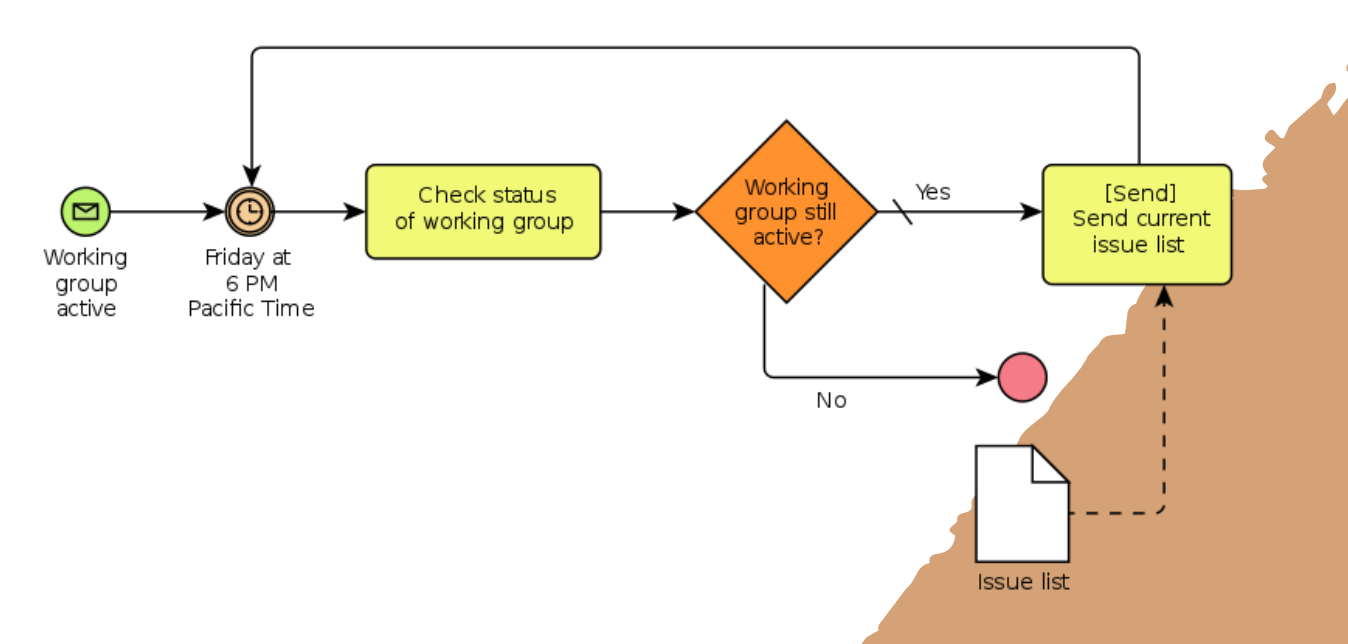
UML (Unified Modeling Language)
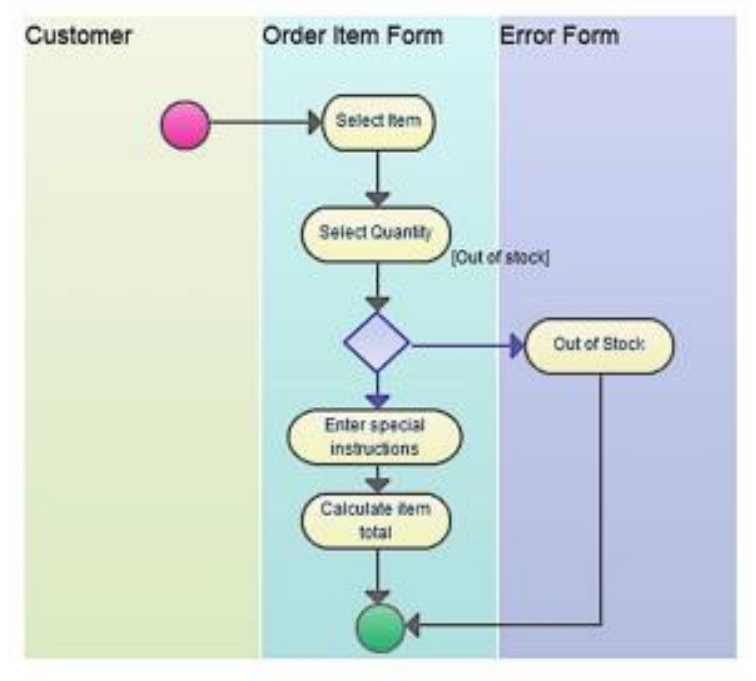
Flowchart Technique
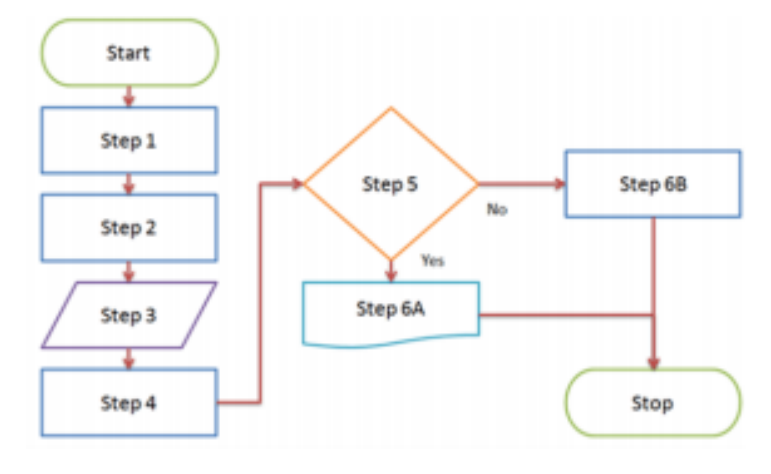
Data Flow Diagram
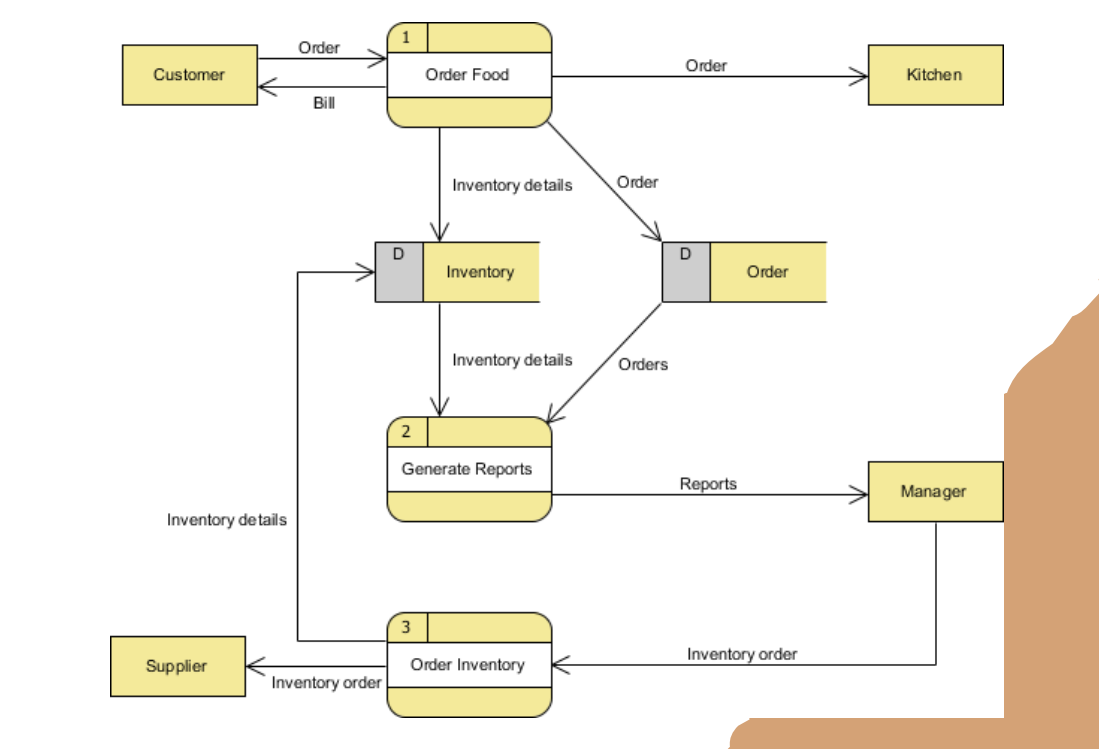
Role Activity Diagrams (RAD)
Gantt Charts
IDEF (Integrated Definition for Function Modeling)
Workflow Technique
Object Oriented Methods
Gap Analysis
analysis model
Software engineers perform analysis modeling and create an _________________ to provide information of 'what' software should do instead of 'how' to fulfill the requirements in software
analysis model
functions that software should perform, behavior it should exhibit, and constraints that are applied on the software
analysis model
determines the relationship of one component with other components. The clear and complete requirements specified in the __________ help the software development team to develop the software according to those requirements
analysis model
operates as a link between the 'system description' and the 'design model'
system description
provides information about the entire functionality of the system, which is achieved by implementing the software, hardware and data
Scenario based element
Class based elements
Behavioral elements
Flow oriented elements
analysis model is organized into four elements namely:
scenario based element
represents the system user point of view
scenario based element
use case diagram, user stories are
class based elements
the object of this type of element manipulated by the system. It defines the object, attributes and relationship
class based elements
class diagram, collaboration diagram are
behavioral elements
represent state of the system and how it is changed by the external events
behavioral elements
sequenced diagram, state diagram are
flow oriented elements
an information flows through a computer-based system it gets transformed
flow oriented elements
data flow diagram, control flow diagram are
structured analysis
top-down approach, which focuses on refining the problem with the help of functions performed in the problem domain
DFD (Data-Flow Diagram)
also known as bubble chart and work flow diagram
DFD (Data-Flow Diagram)
depicts data sources, data sinks, data storage and processes performed on data as nodes and logical flow of data as links between the nodes
data dictionary
is a repository that stores description of data objects to be used by the software
data dictionary
stores an organized collection of information about data and their relationships, data-flows, data types, data stores, processes and so on
data dictionary
comprises the source of data, which are data objects and entities
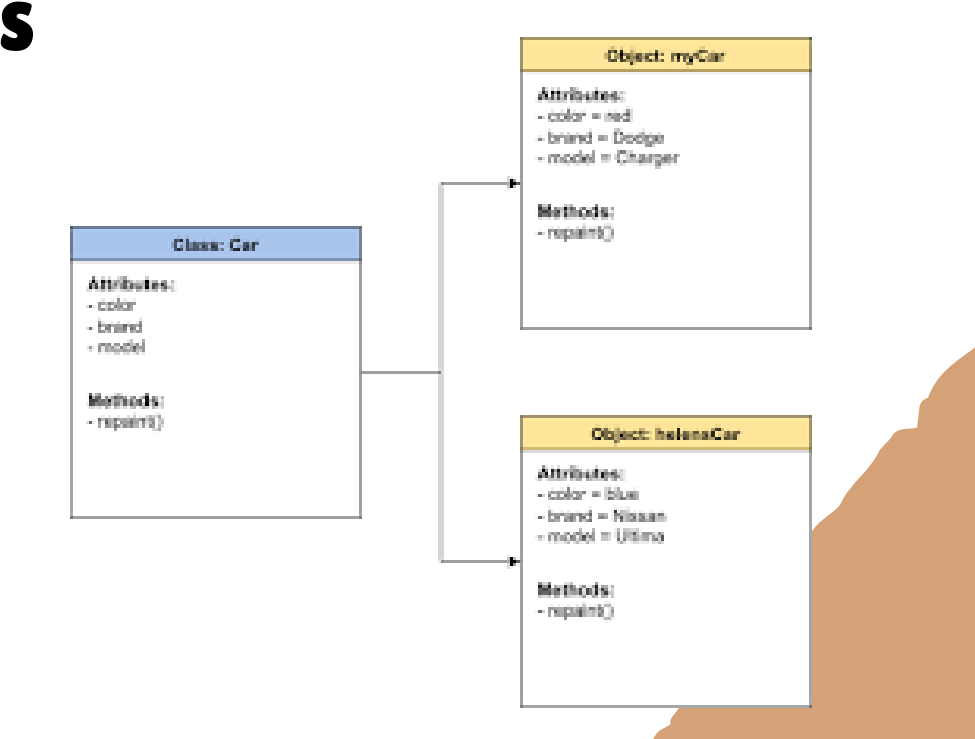
object-oriented modeling
used to describe system requirements using prototypes
object-oriented modeling
analyzes the problem domain and then partitions the problem with the help of objects
object-oriented modeling
defines a system as a set of objects, which interact with each other by the services they provide
object modelling
develops the static structure of the software system in terms of objects
dynamic modelling
a way of describing how an individual object responds to events
functional modelling
is the final component of object-oriented analysis
functional model
shows the processes that are performed within an object and how the data changes as it moves between methods
Structured Analysis/Structured Design (SASD) approach
is the traditional approach of software development based upon the waterfall model.
Unified Modeling Language (UML)
is a representation of a software in terms of it's structure, behavior and interactions, before the actual coding process begins
use-cases
are represented with the help of a use-case diagram, which depicts the relationships among actors and use cases within a system
use case
is the primary form of system/software requirements for a new software program underdeveloped. It specify the expected behavior (what), and not the exact method of making it happen (how)