everything so far
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
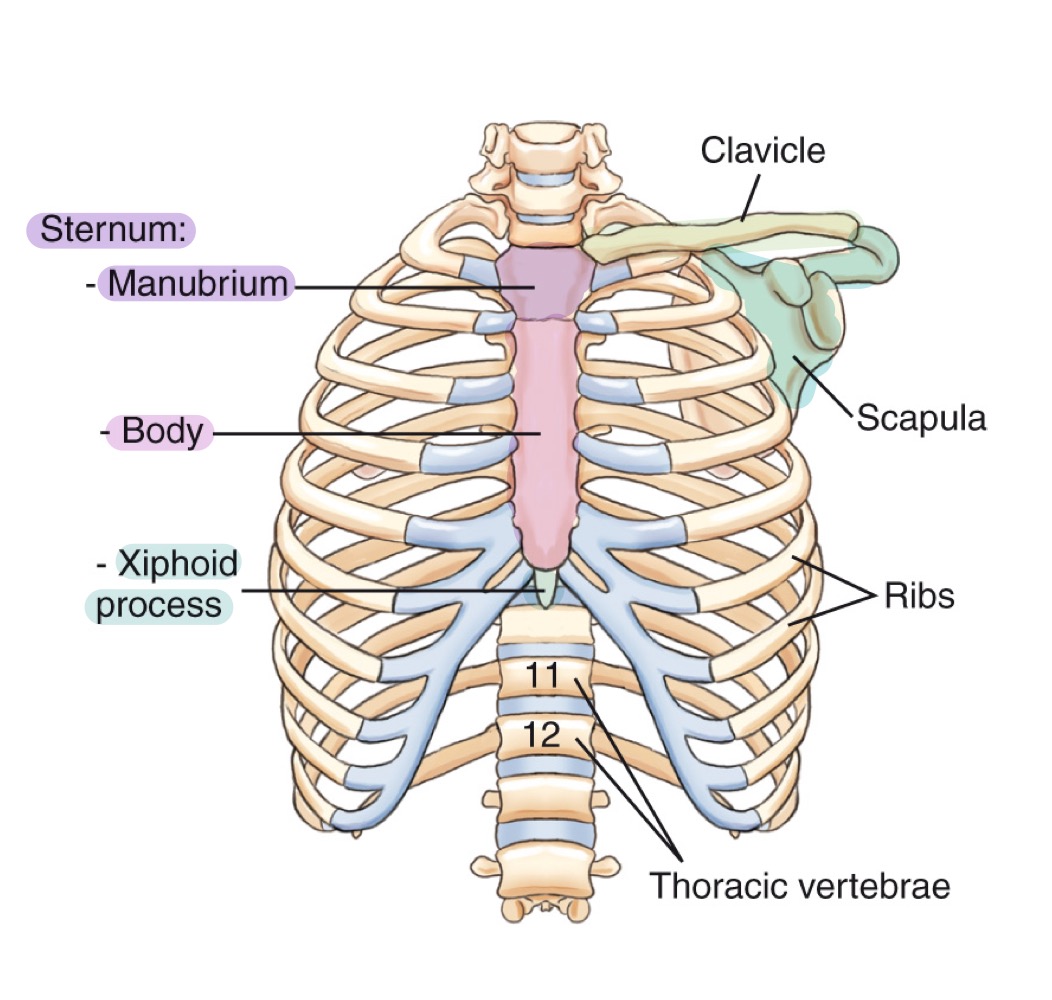
Bony thorax
Protective framework of the thoracic cage: sternum, clavicles, scapulae, 12 pairs of ribs, and 12 thoracic vertebrae.
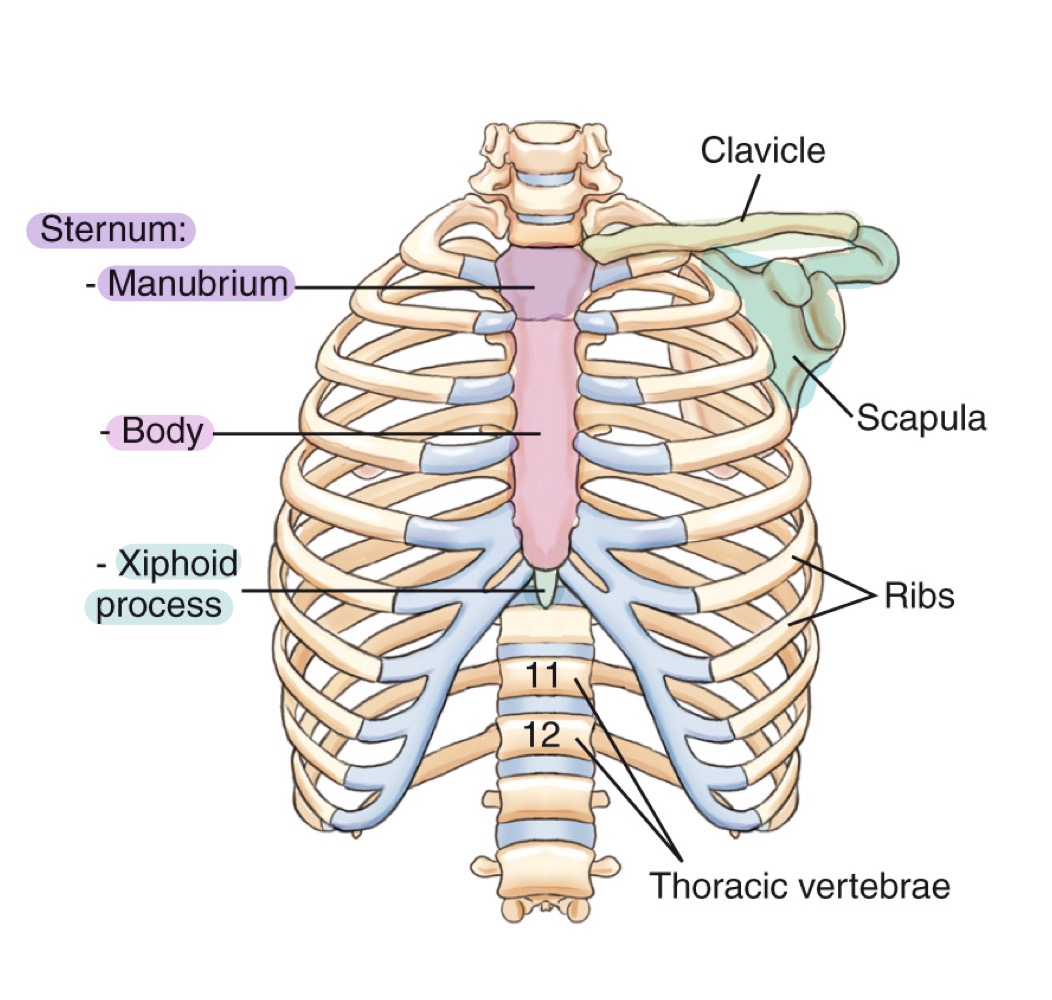
Sternum
Flat bone in the center of the chest; parts include manubrium, body, and xiphoid process.
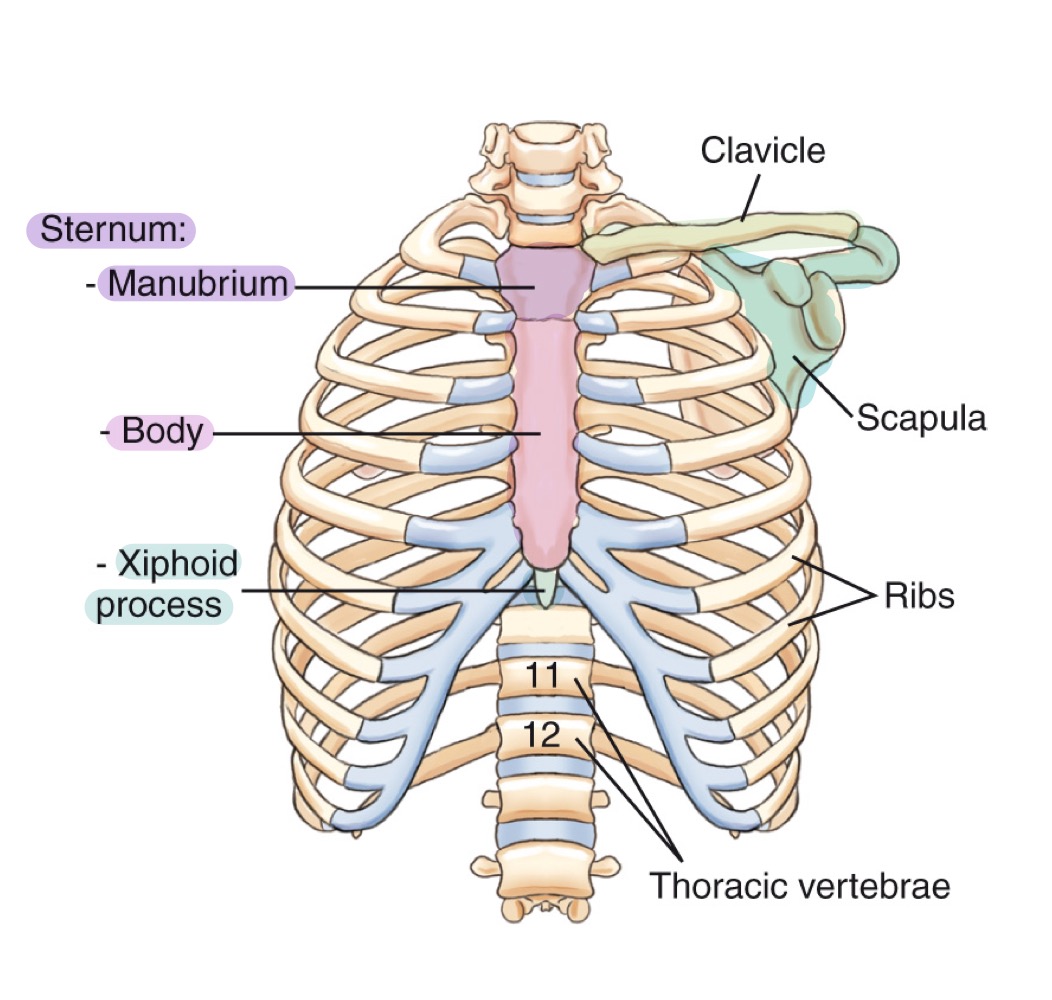
Manubrium
Upper part of the sternum, articulating with clavicles and first pair of ribs.
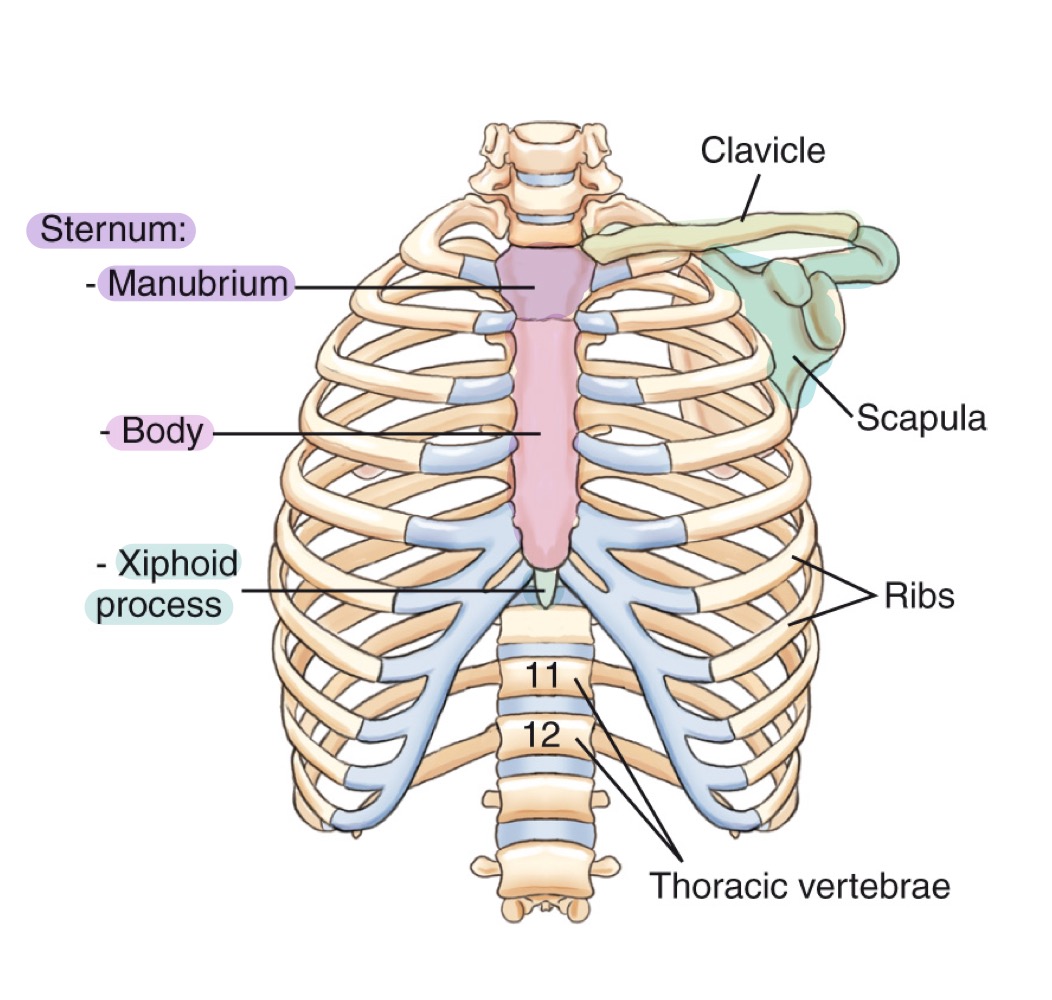
Body (of sternum)
Central portion of the sternum, between manubrium and xiphoid process.
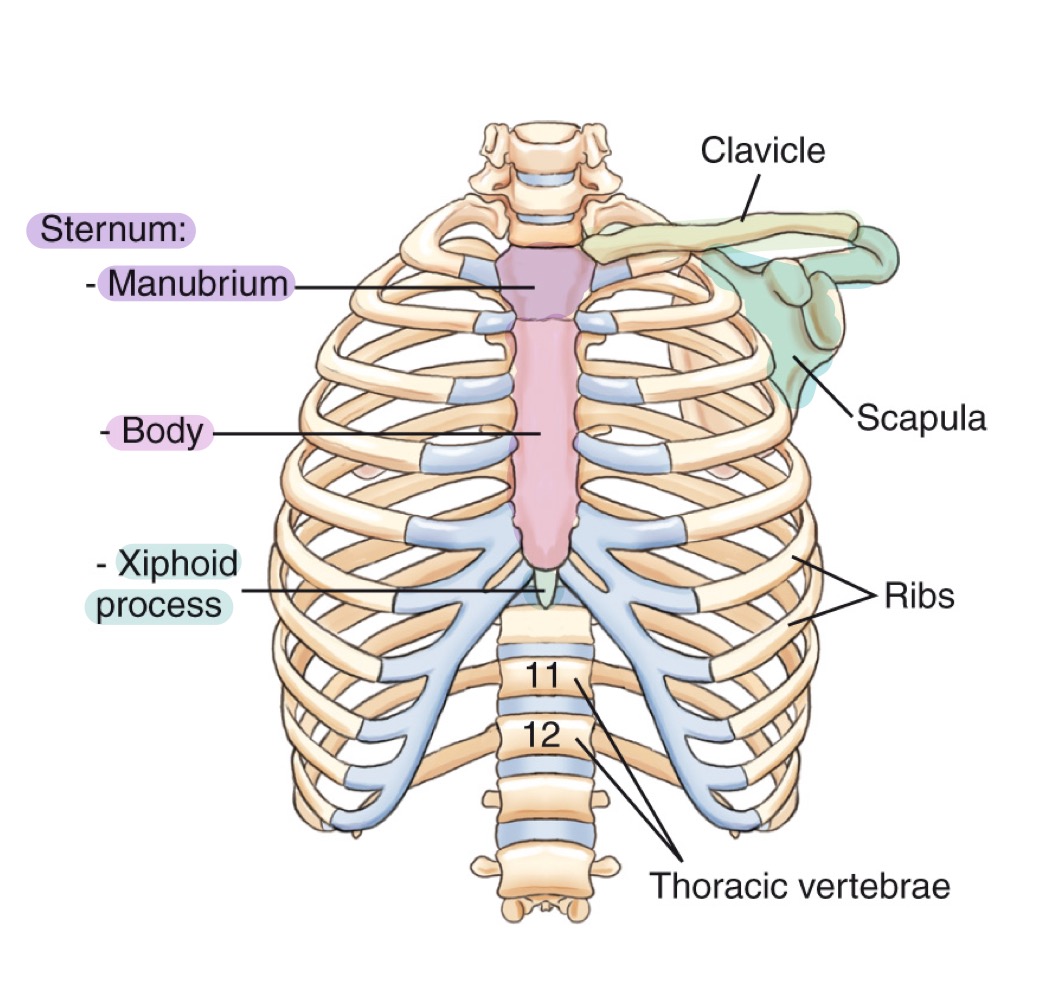
Xiphoid process
Small, inferior projection at the end of the sternum.
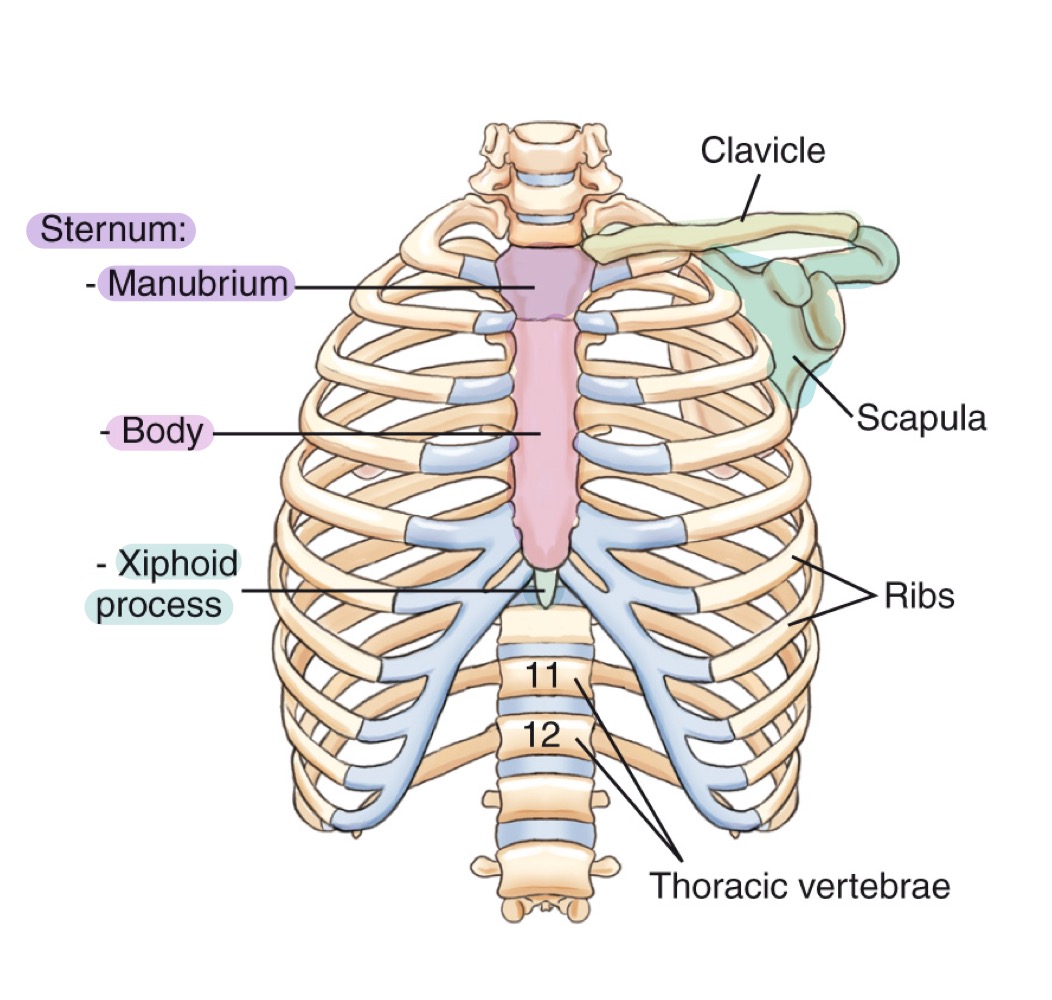
Clavicle
Collarbone; long bone articulating with sternum and scapula, forming the anterior thoracic cage.
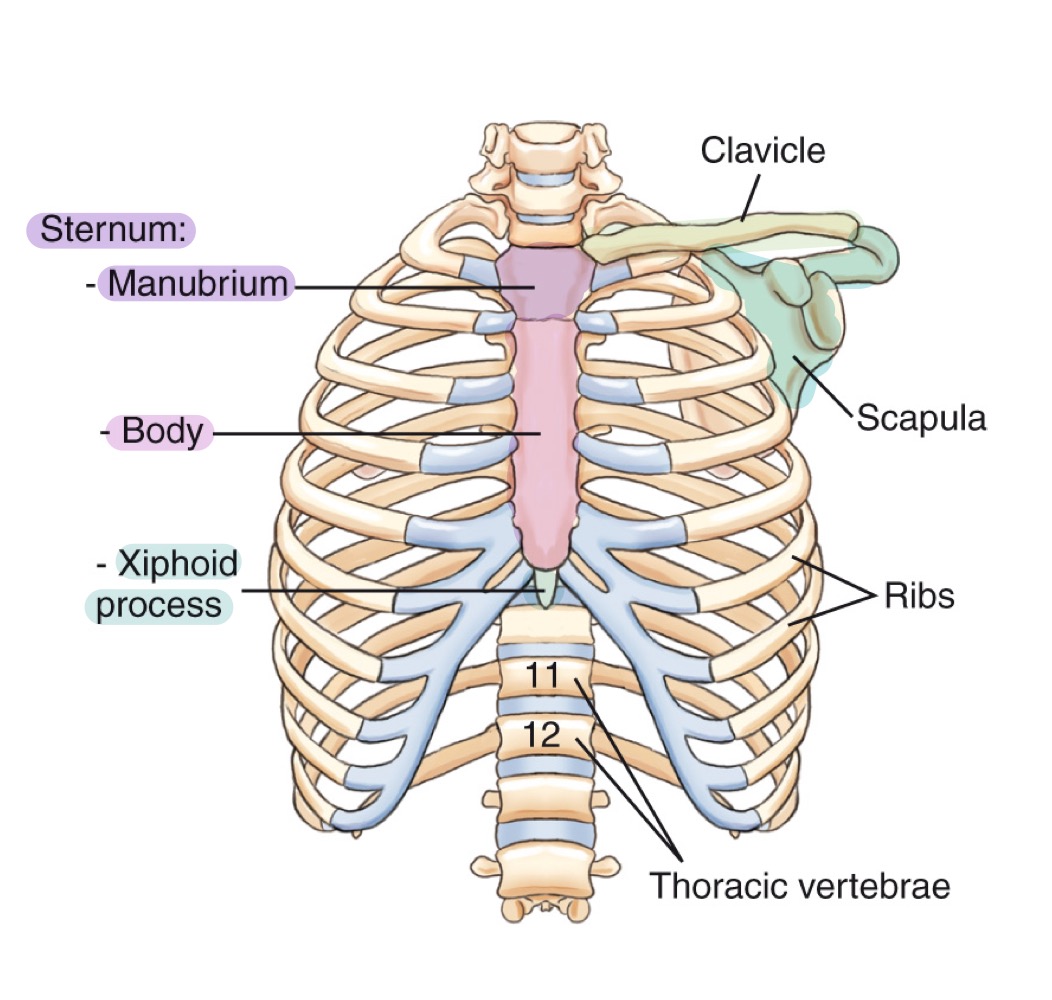
Scapula
Shoulder blade; flat bone on the posterior thorax providing muscle attachment points.
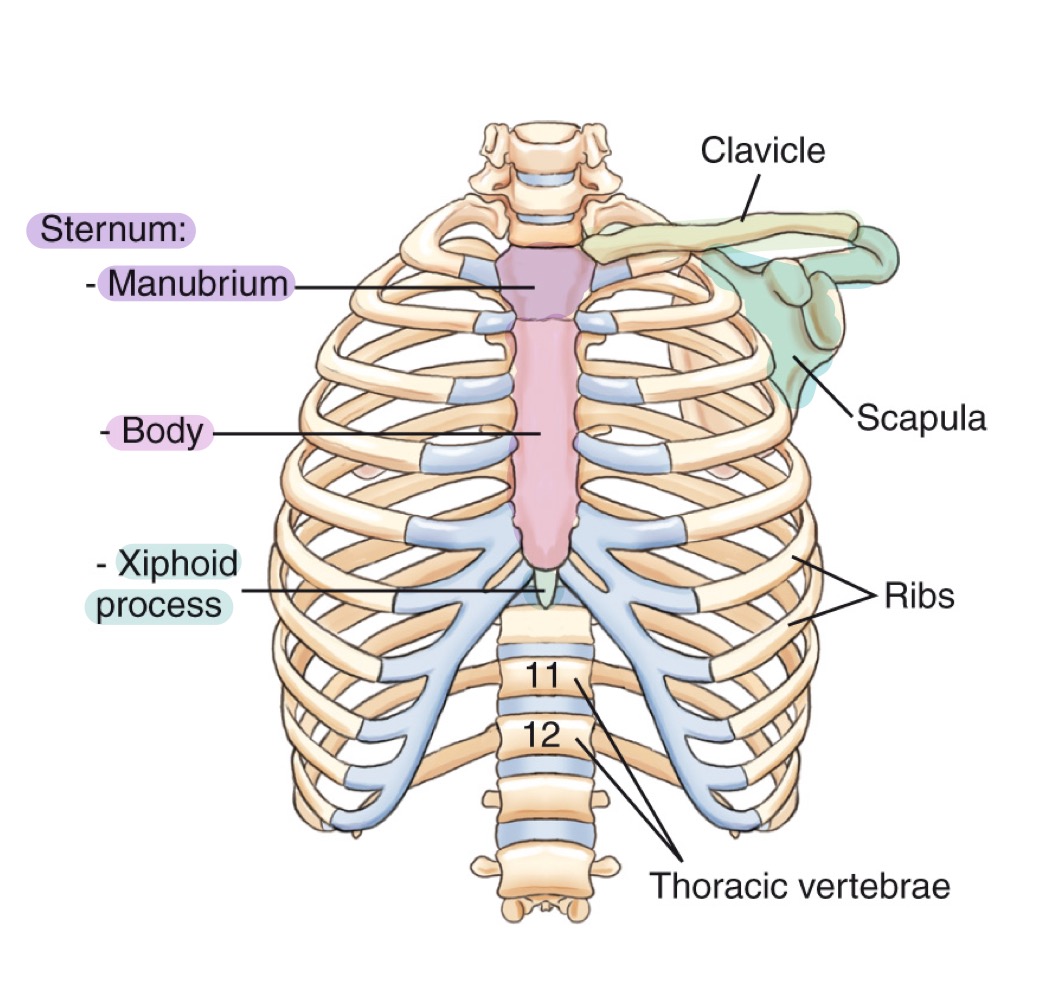
Ribs
Twelve pairs of curved bones forming the protective cage around lungs and heart.
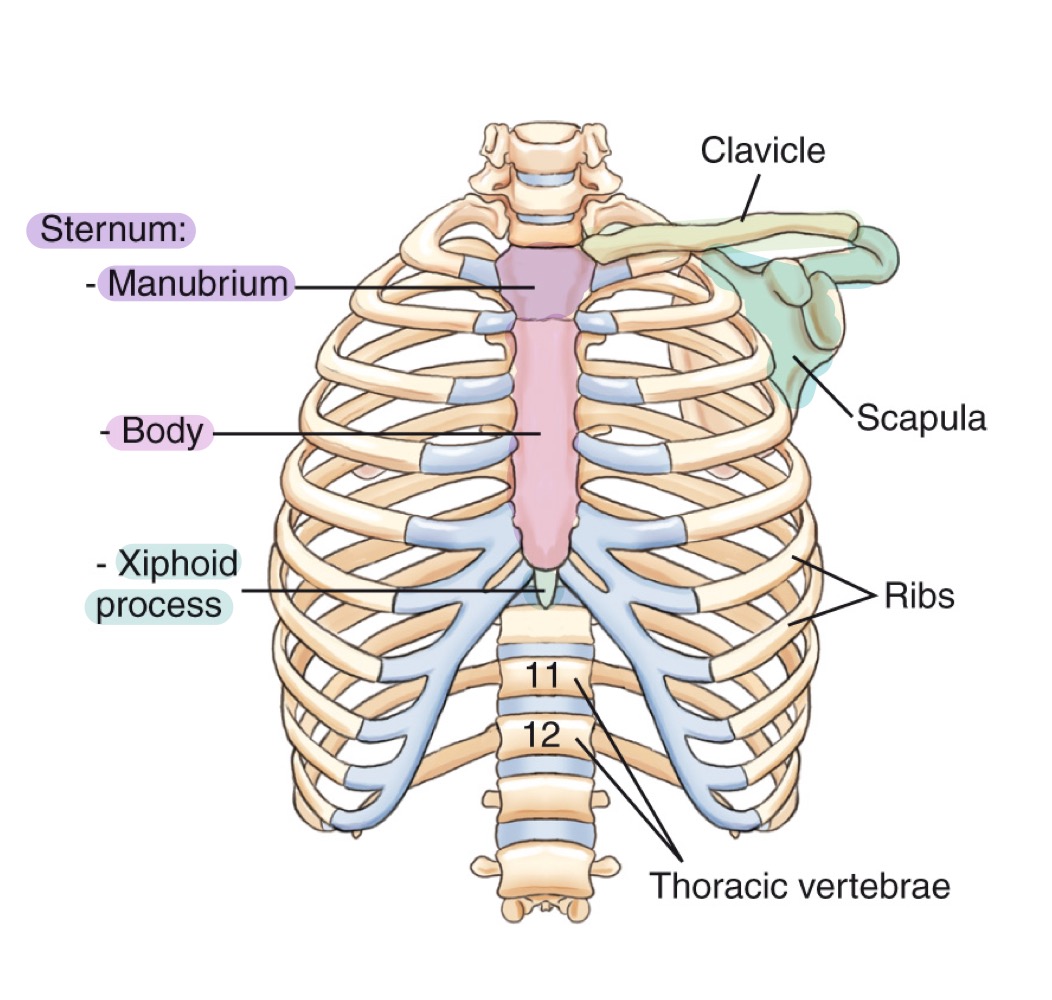
Thoracic vertebrae
The twelve vertebrae (T1–T12) forming the posterior thoracic skeleton and attaching to the ribs.
Respiratory system
System for gas exchange between air and blood; consists of pharynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs.
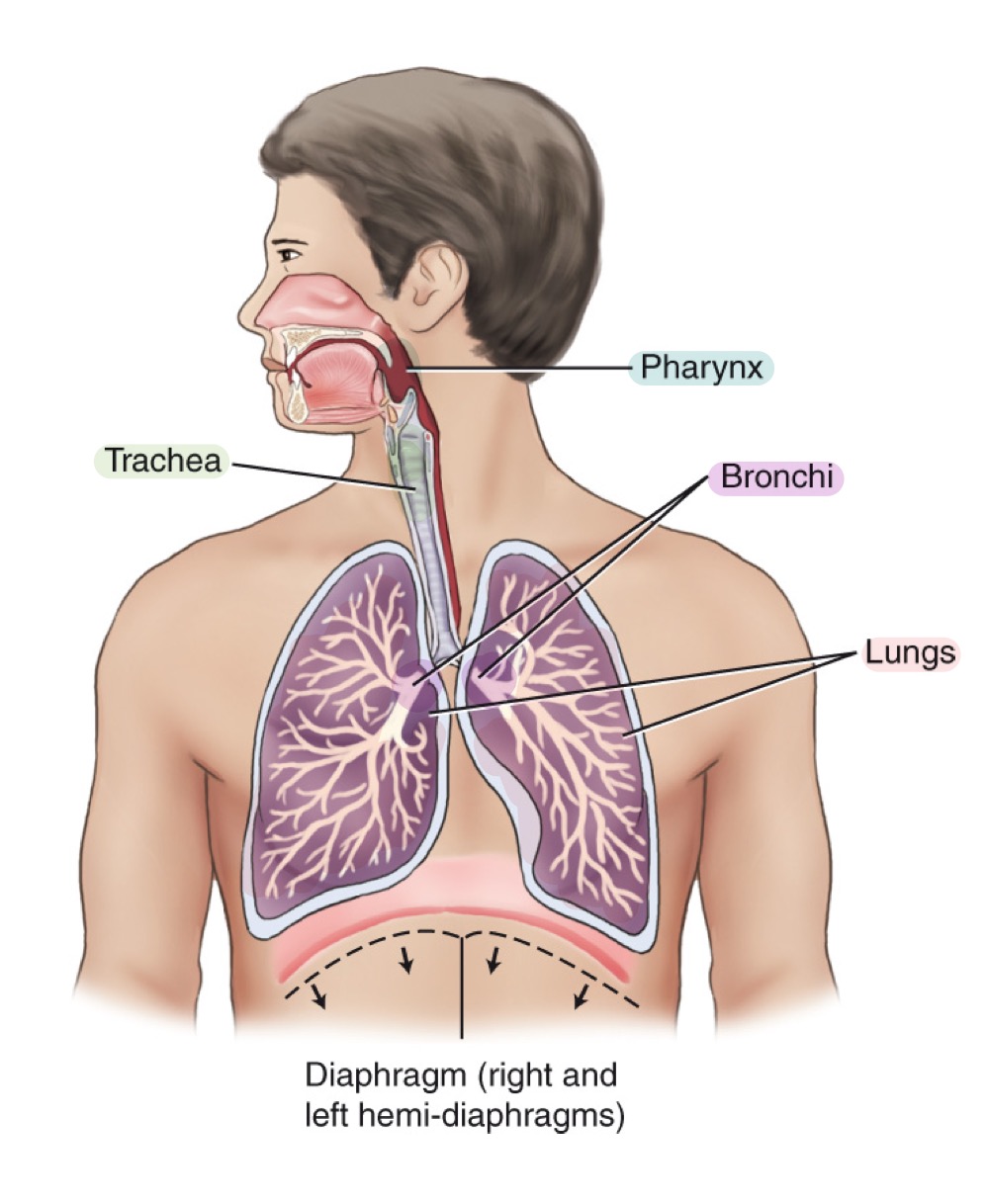
what structures are included in the respiratory system?
pharynx
trachea
bronchi
lungs
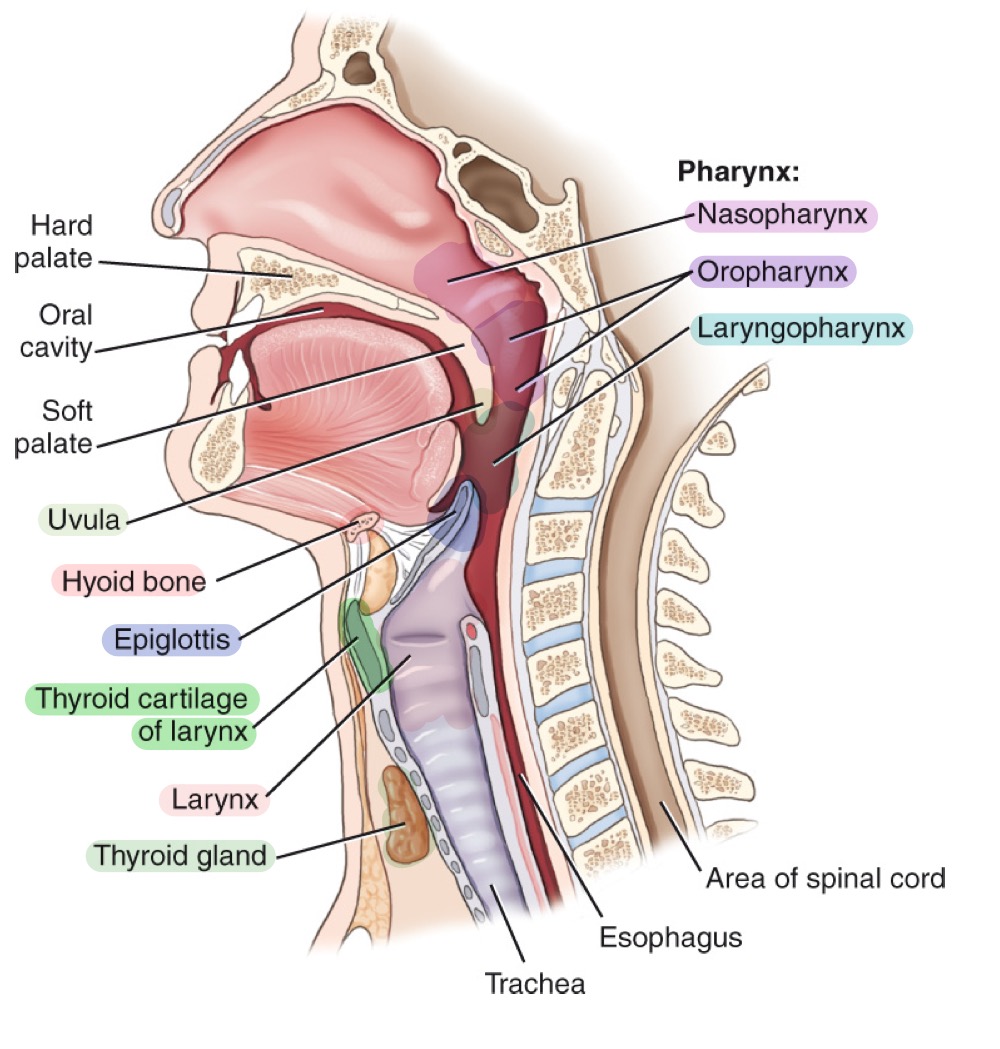
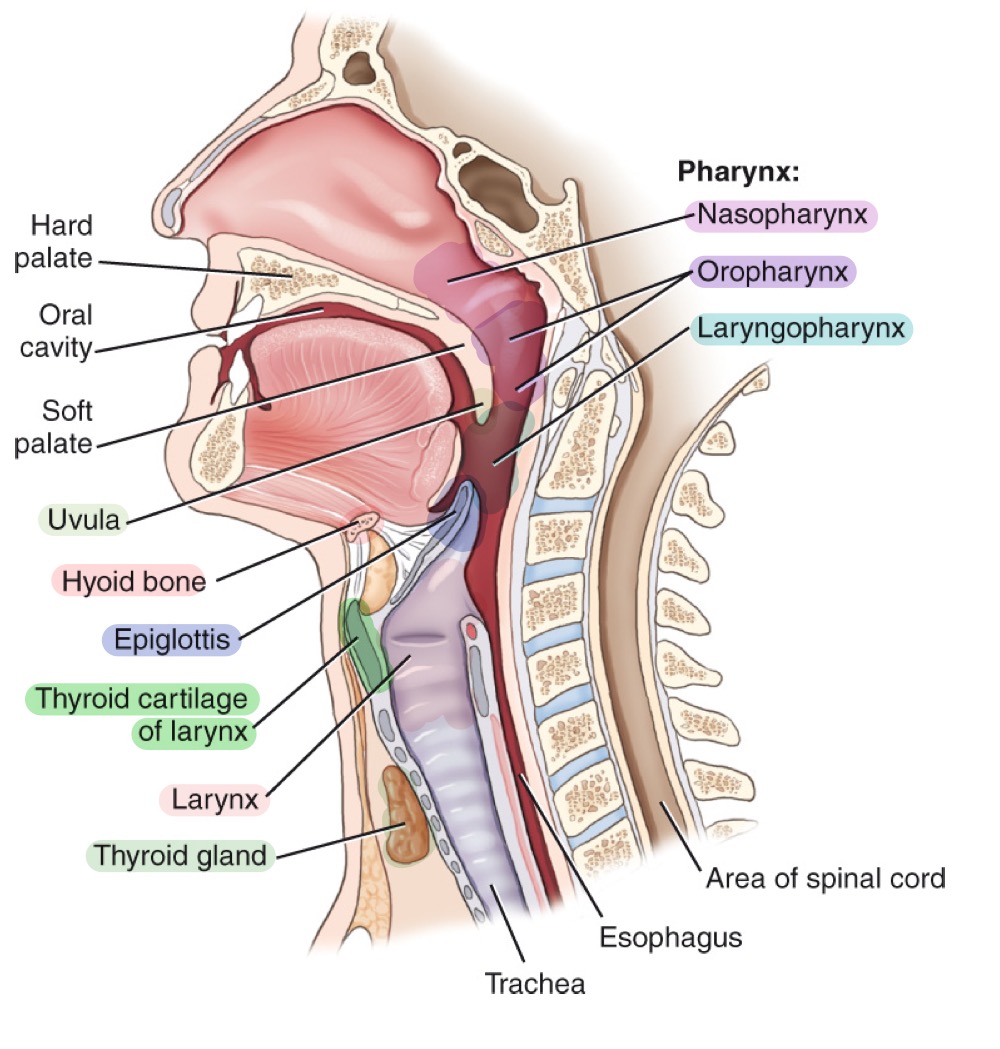
Pharynx
Muscular tube for air and food; divisions: nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx.
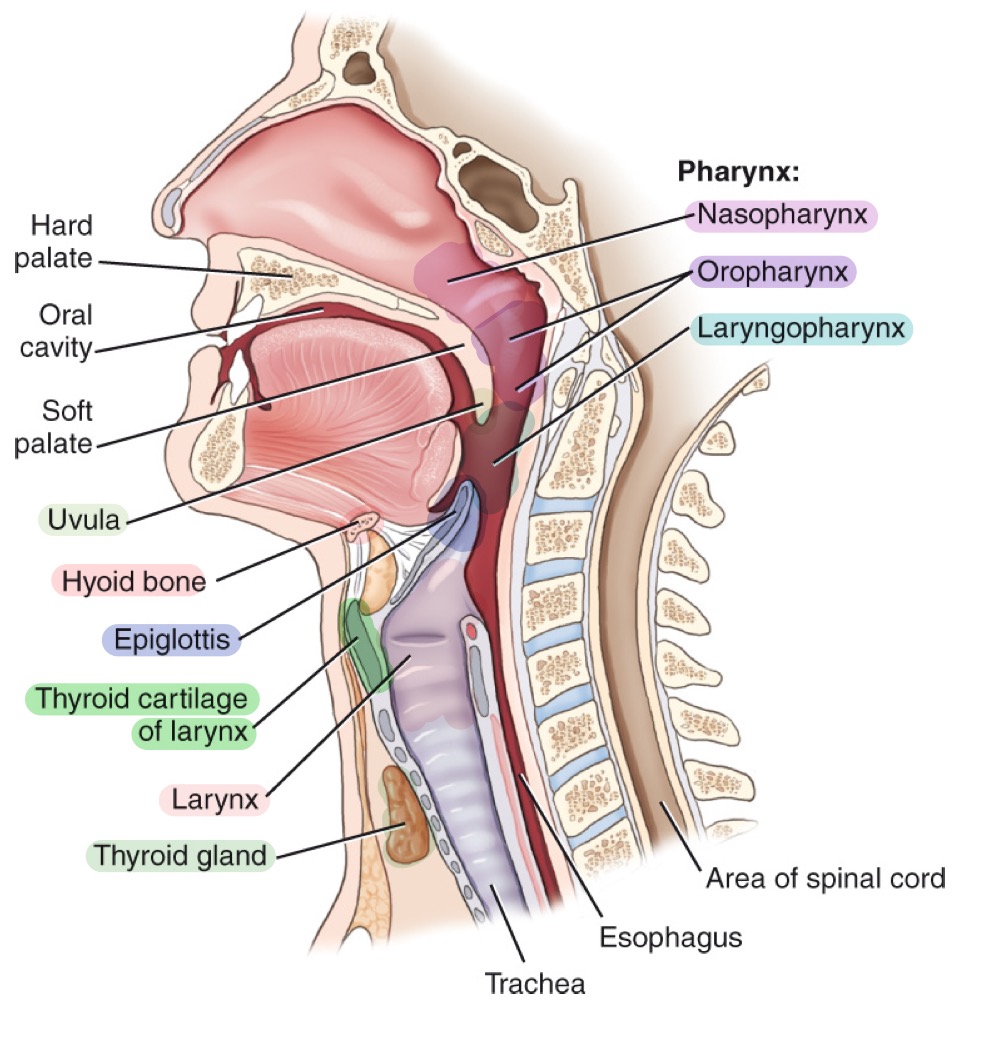
Nasopharynx
Upper part of the pharynx, behind the nasal cavity.
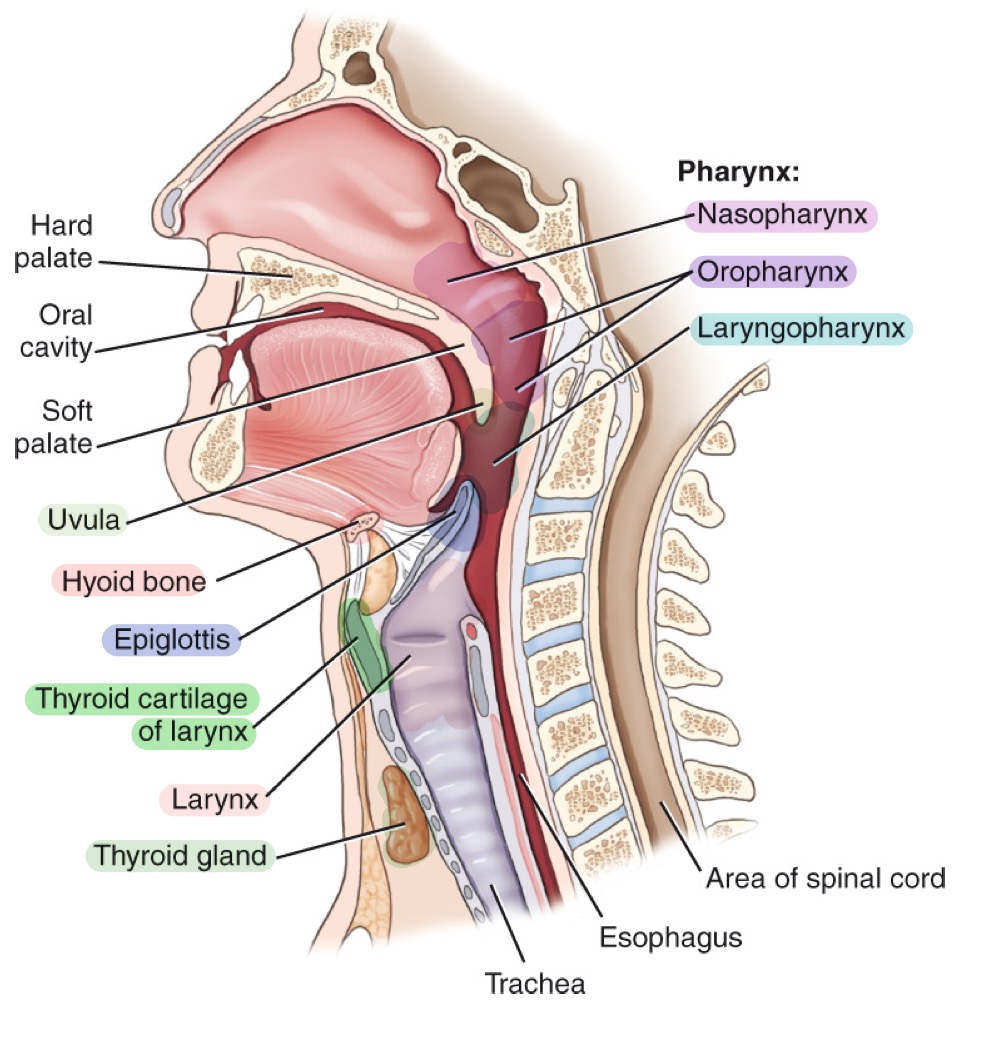
Oropharynx
Middle part of the pharynx, behind the oral cavity.
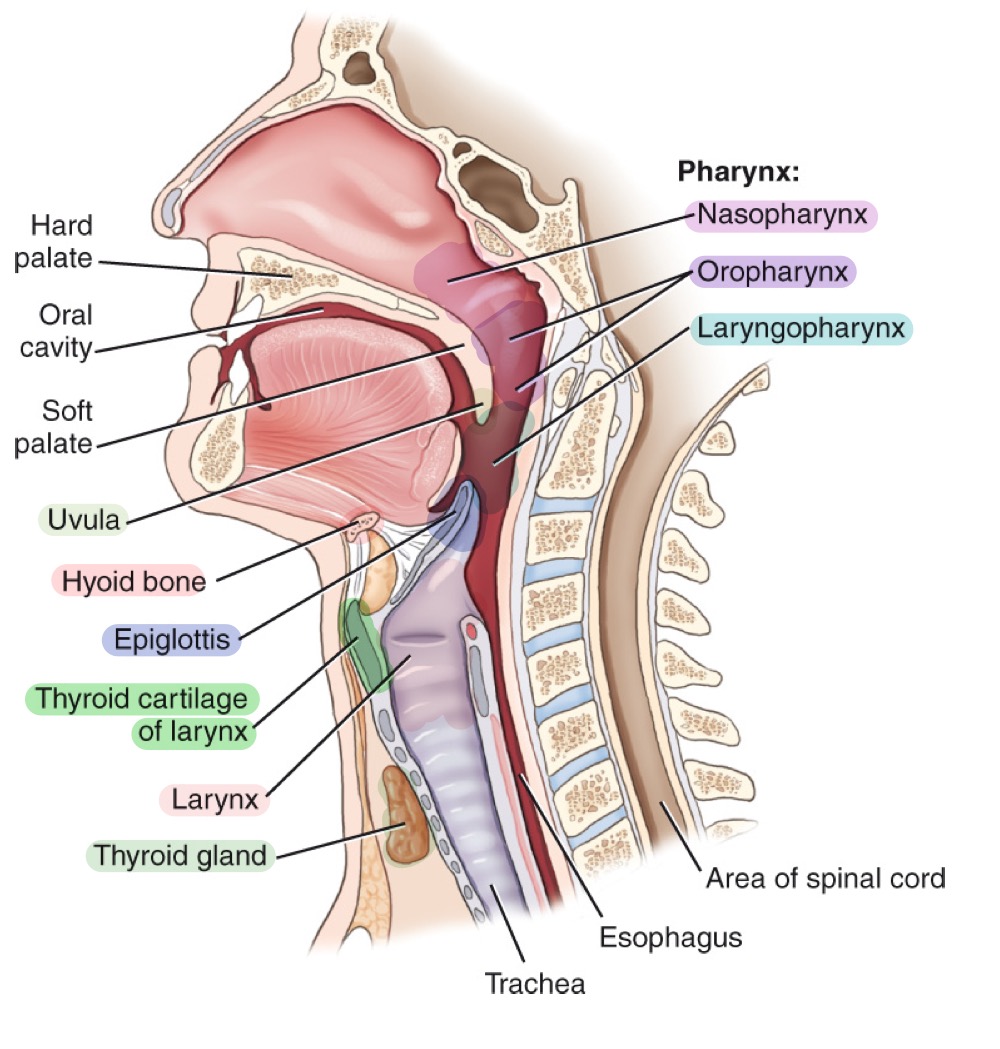
Laryngopharynx
Lower part of the pharynx, directing air to larynx and food to esophagus.
Trachea
Windpipe; airway conducting air to bronchi; reinforced by C-shaped cartilaginous rings.
Carina
Cartilaginous ridge at the tracheal bifurcation into right and left main bronchi (around T5).
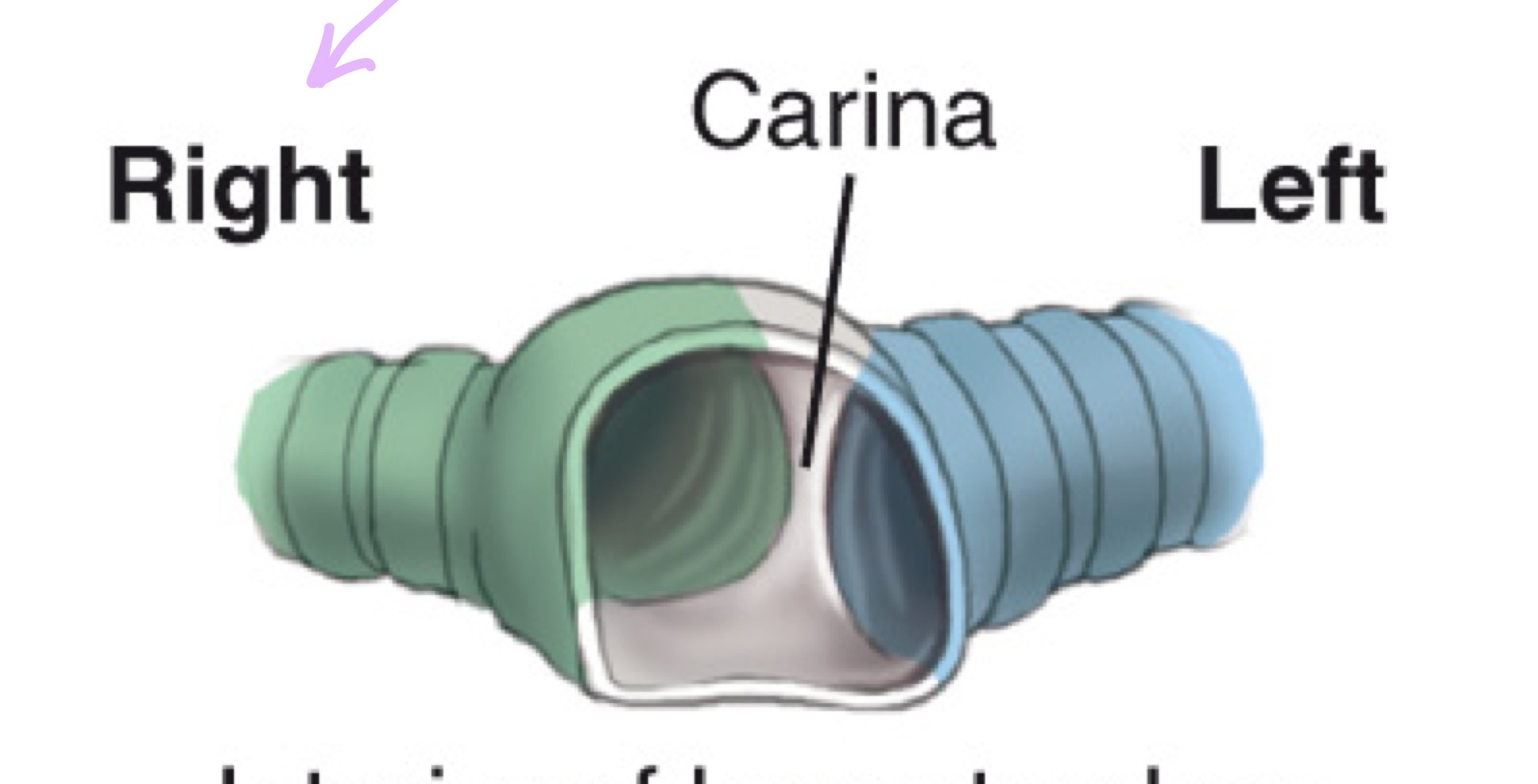
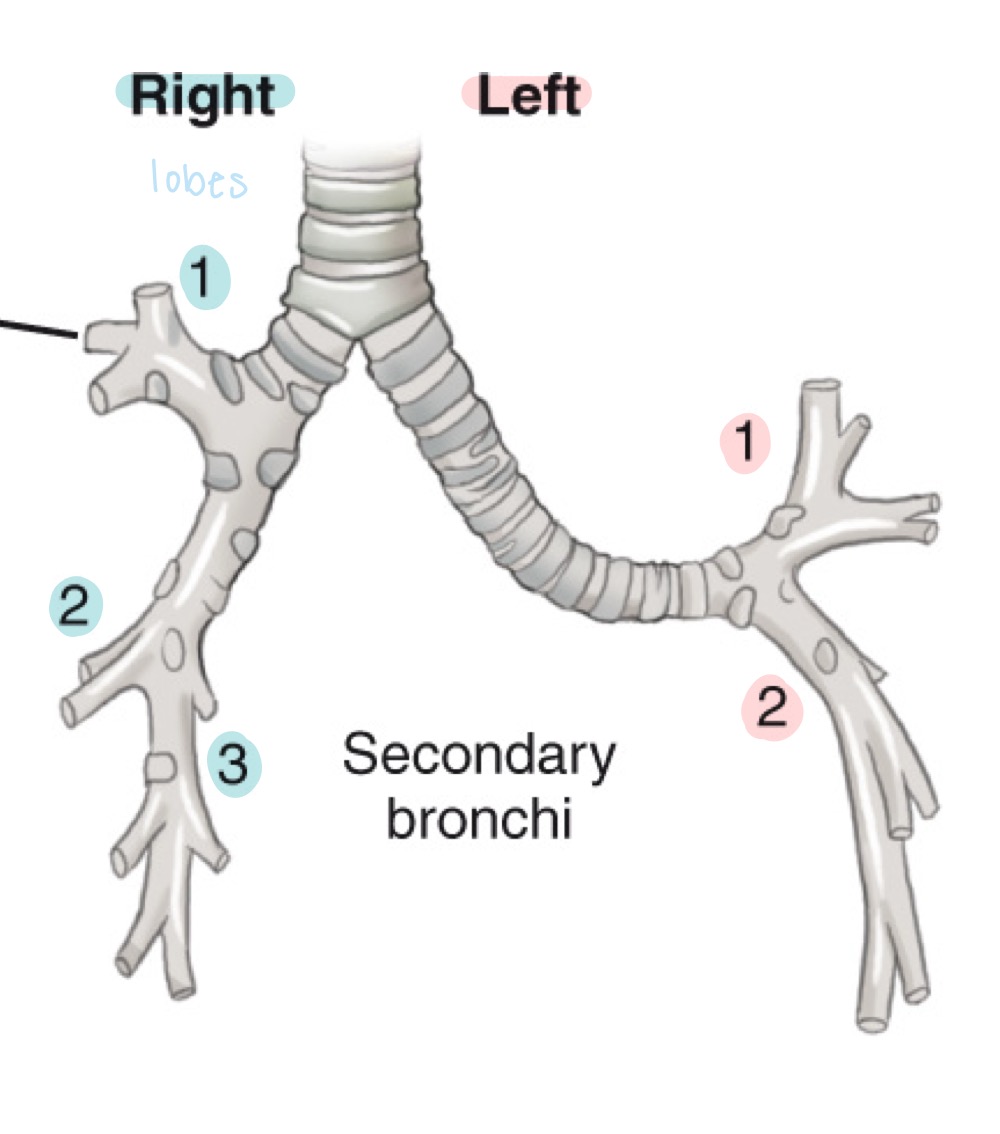
Bronchi
Main airways branching from the trachea into the lungs; include right and left primary bronchi.
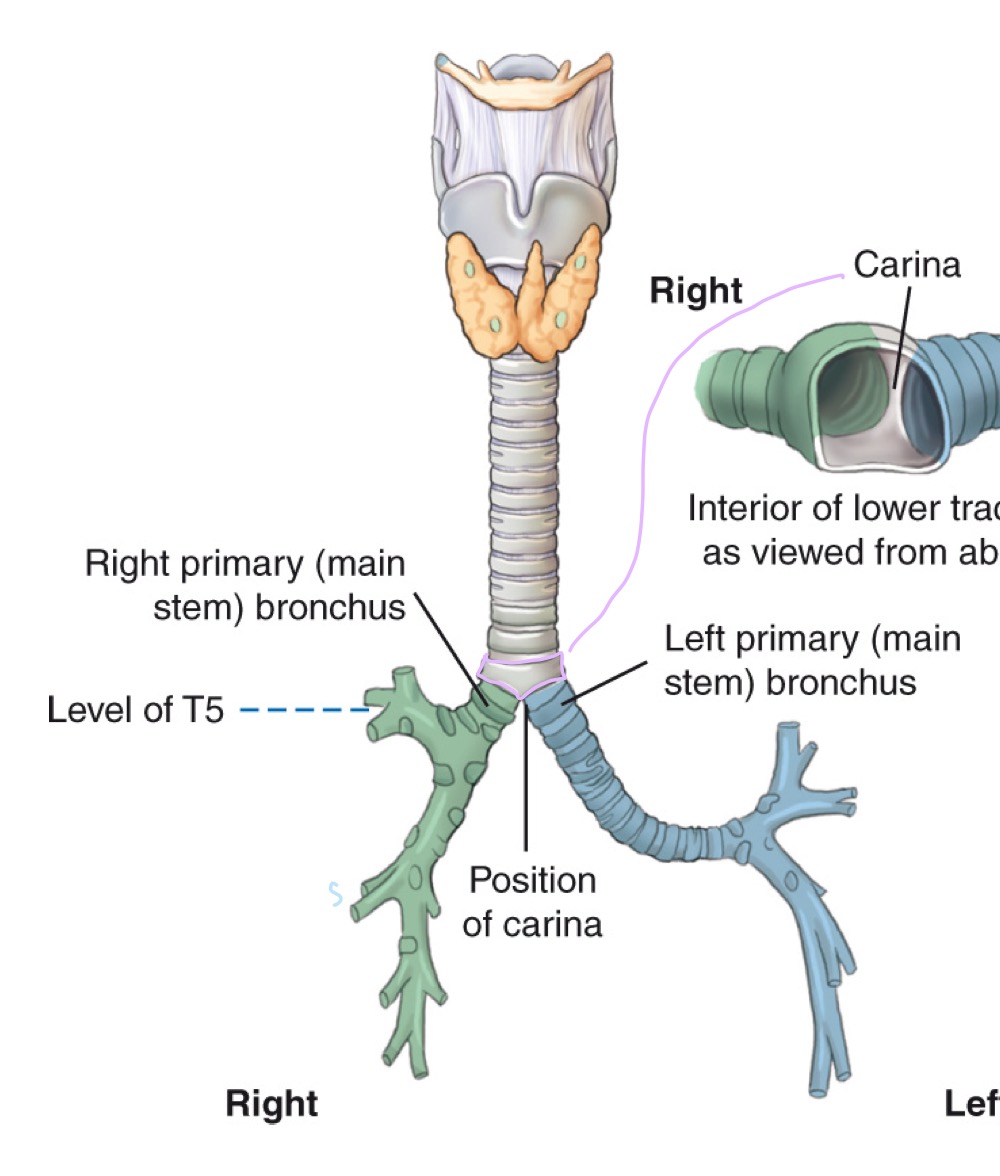
Right primary bronchus
Shorter, more vertical main bronchus supplying the right lung.
Left primary bronchus
Longer, more horizontal main bronchus supplying the left lung.
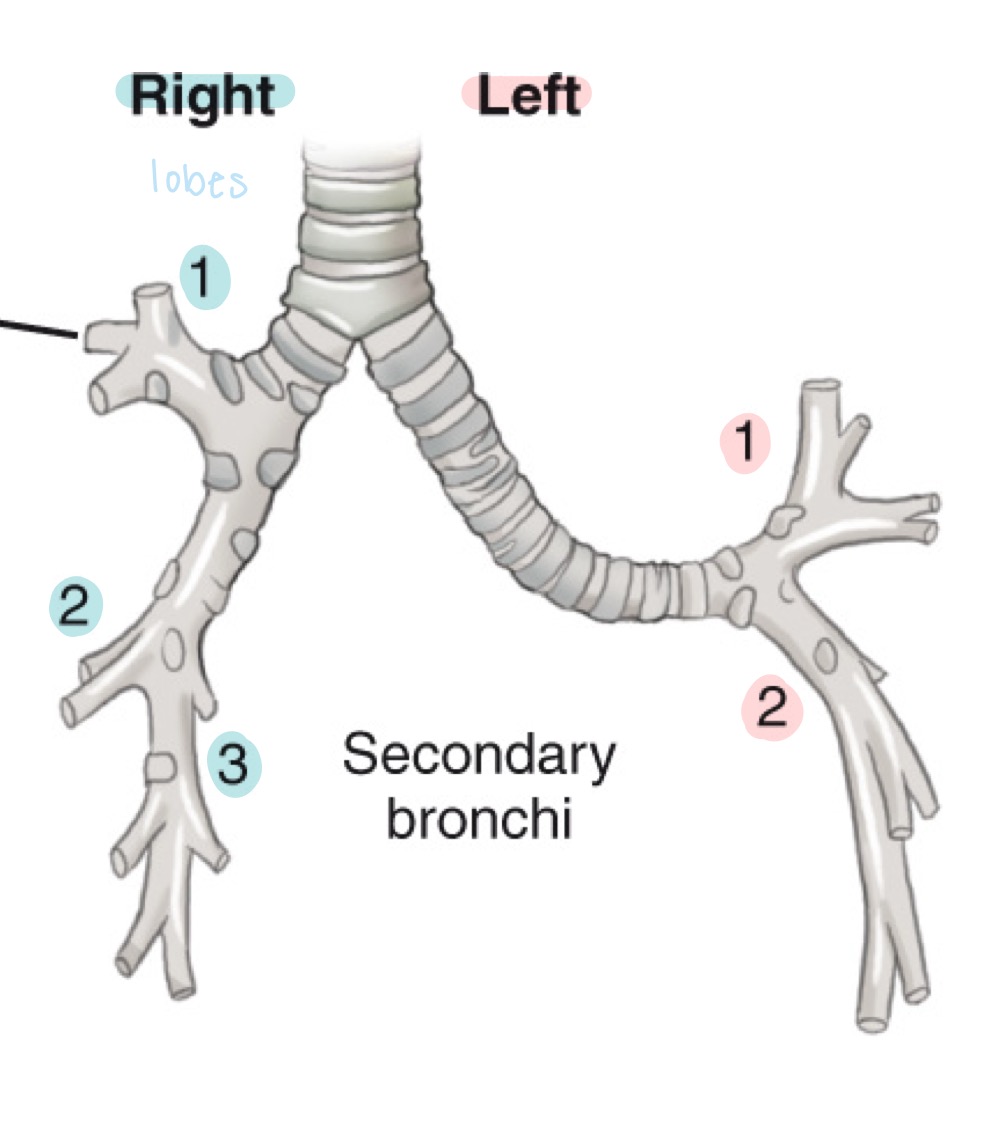
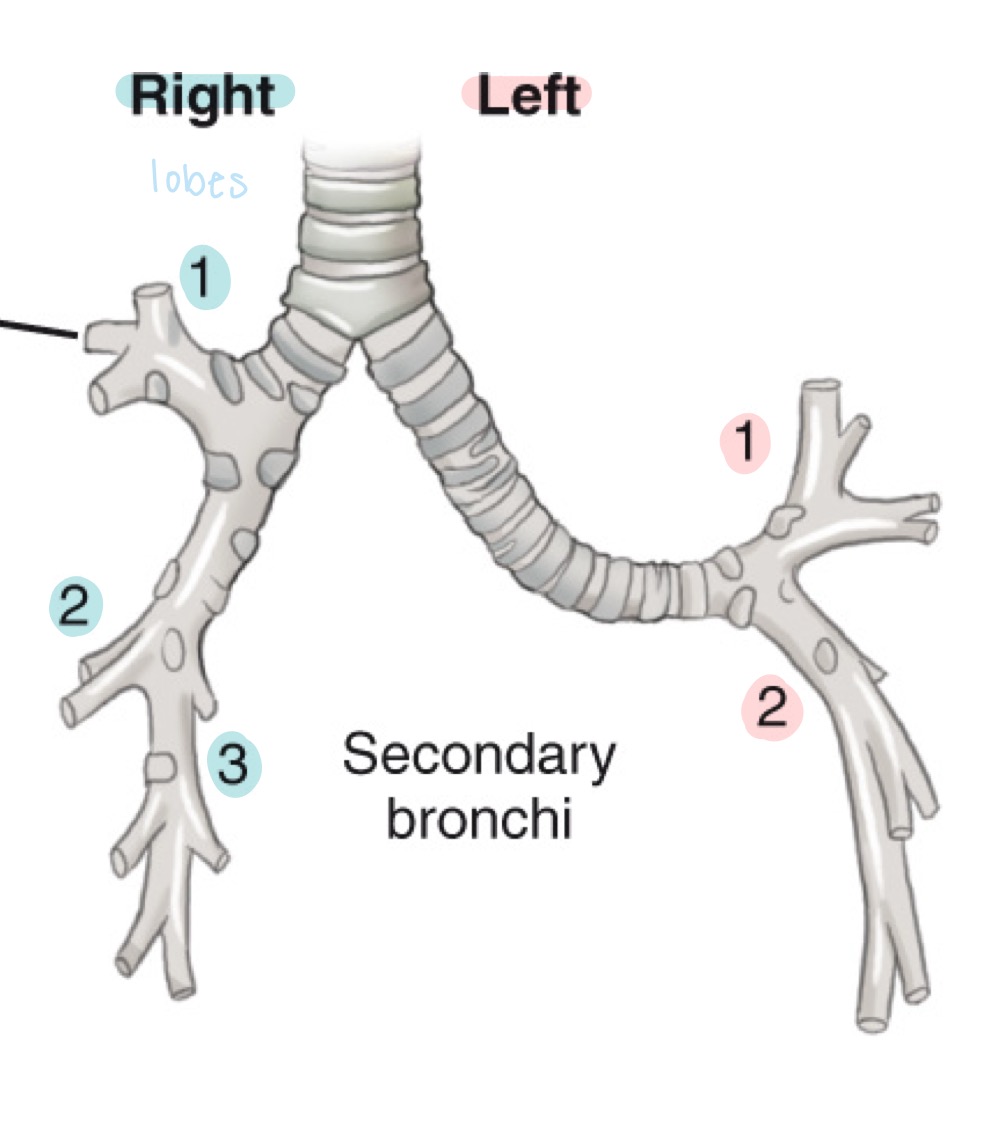
Secondary bronchi
Lobar bronchi; airways branching from primary bronchi to each lung lobe.
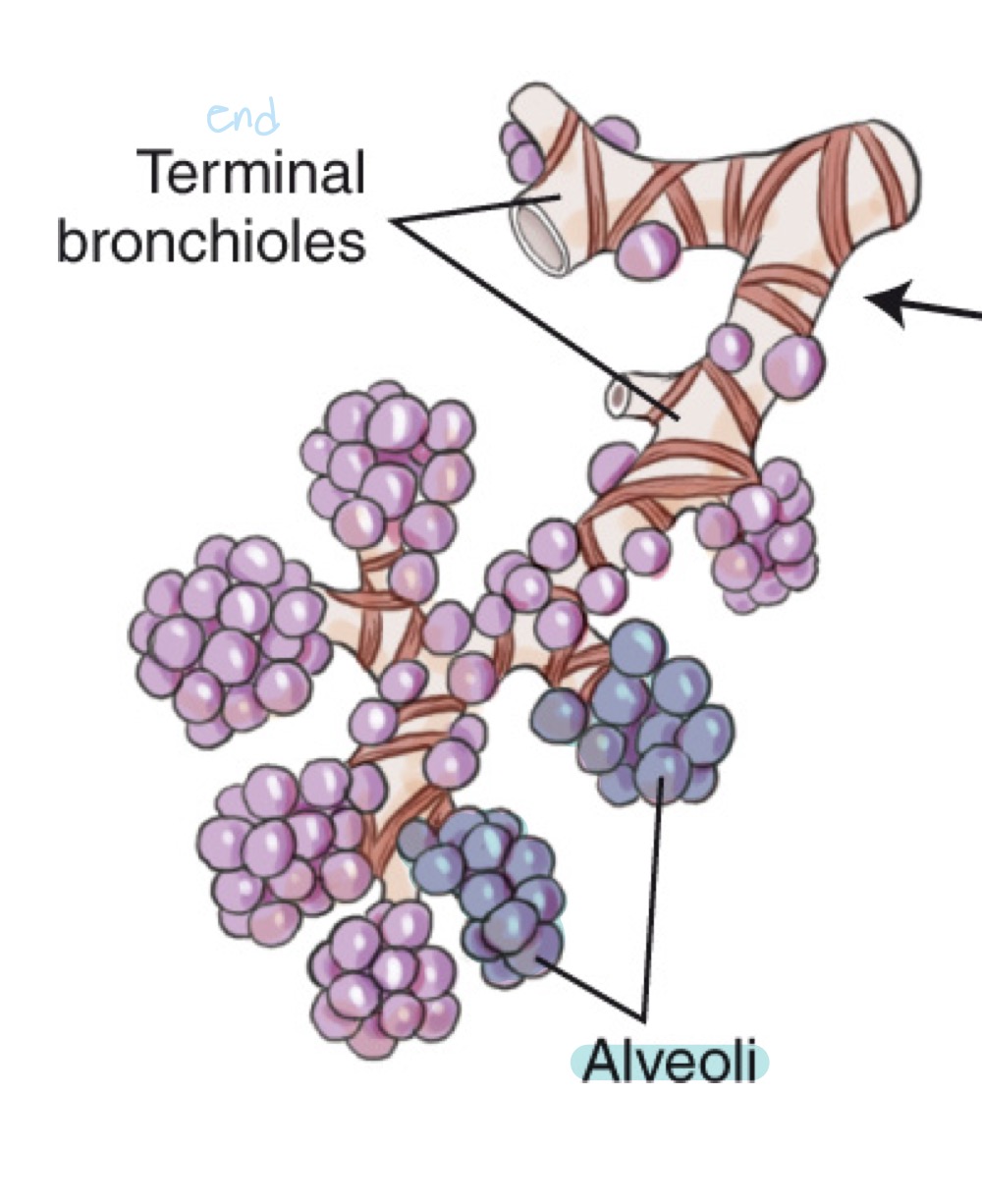
Alveoli
Tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs.
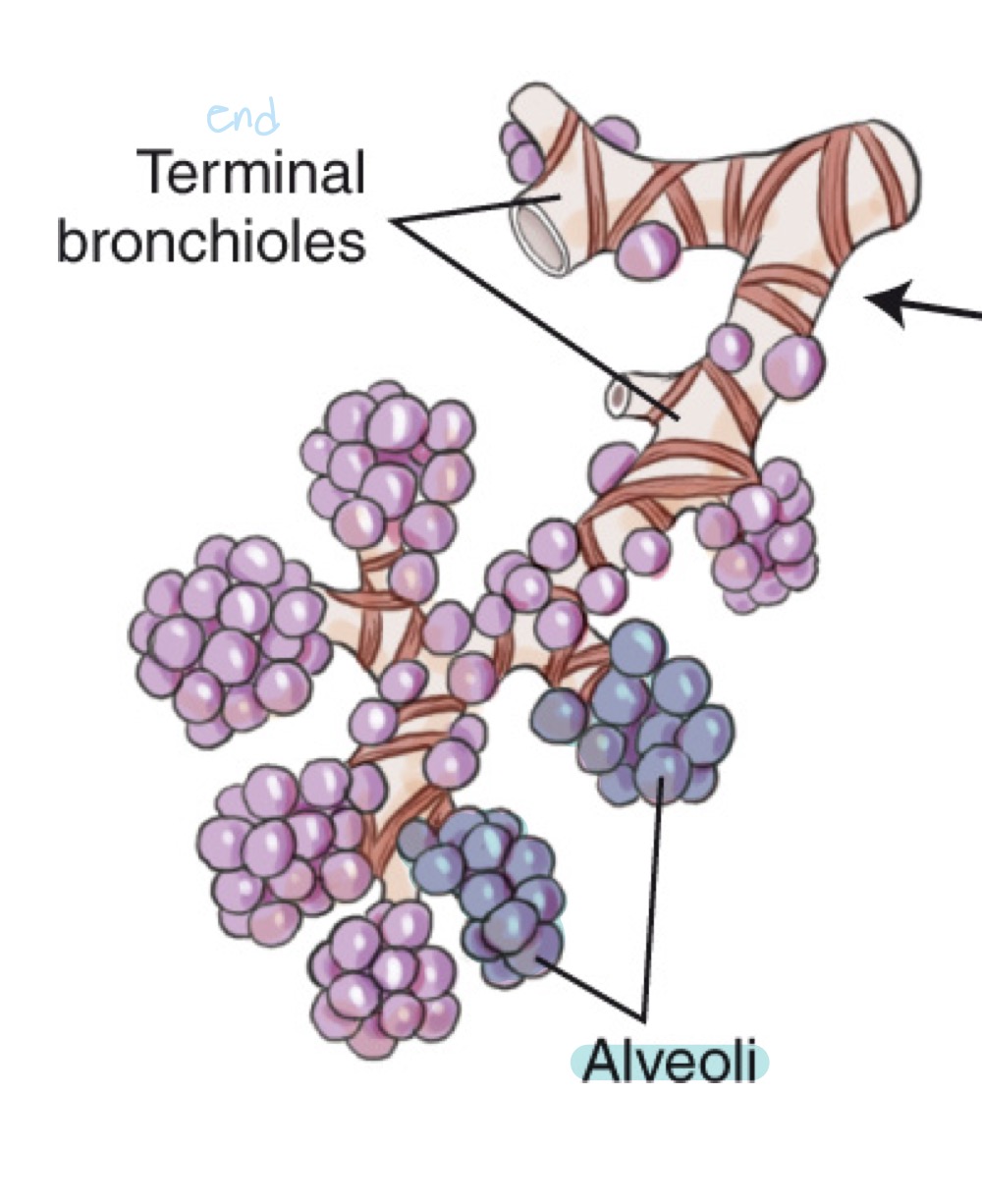
Terminal bronchioles
Final sterile branches of the bronchial tree leading to alveolar sacs.
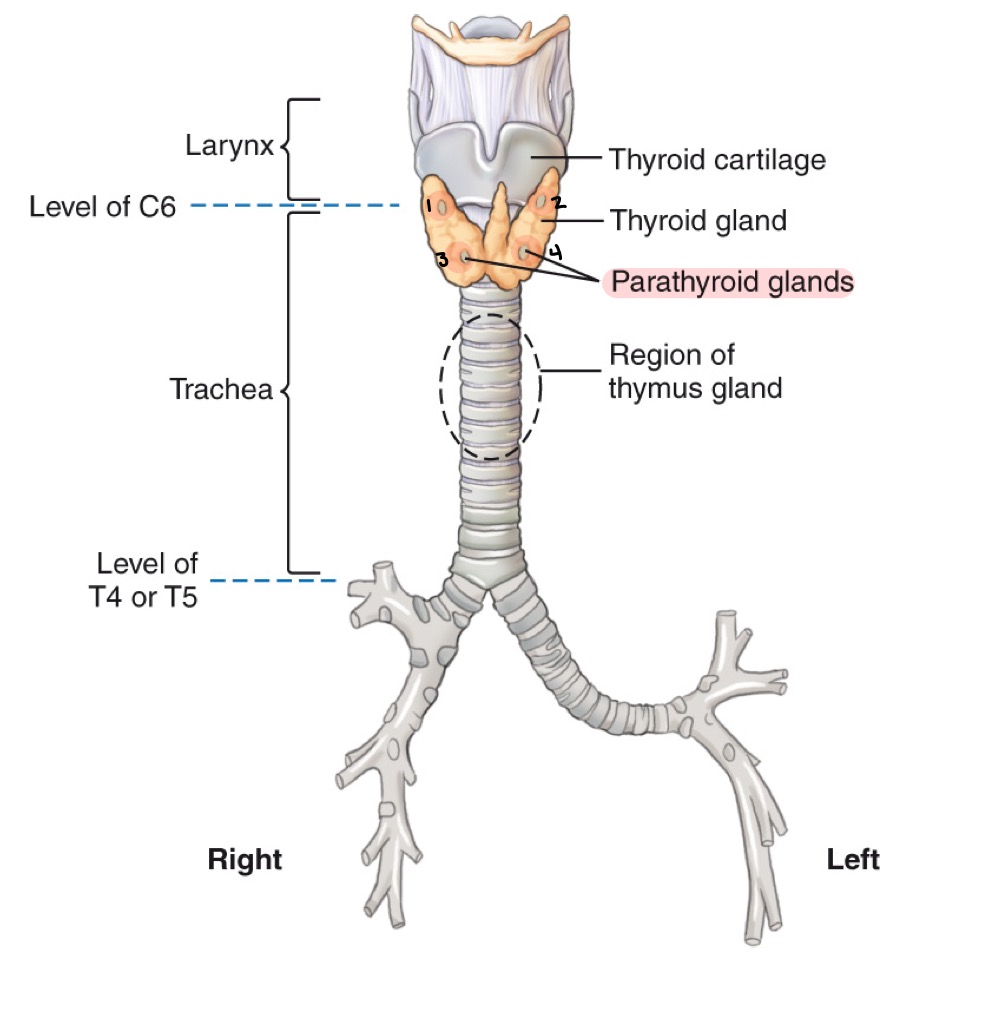
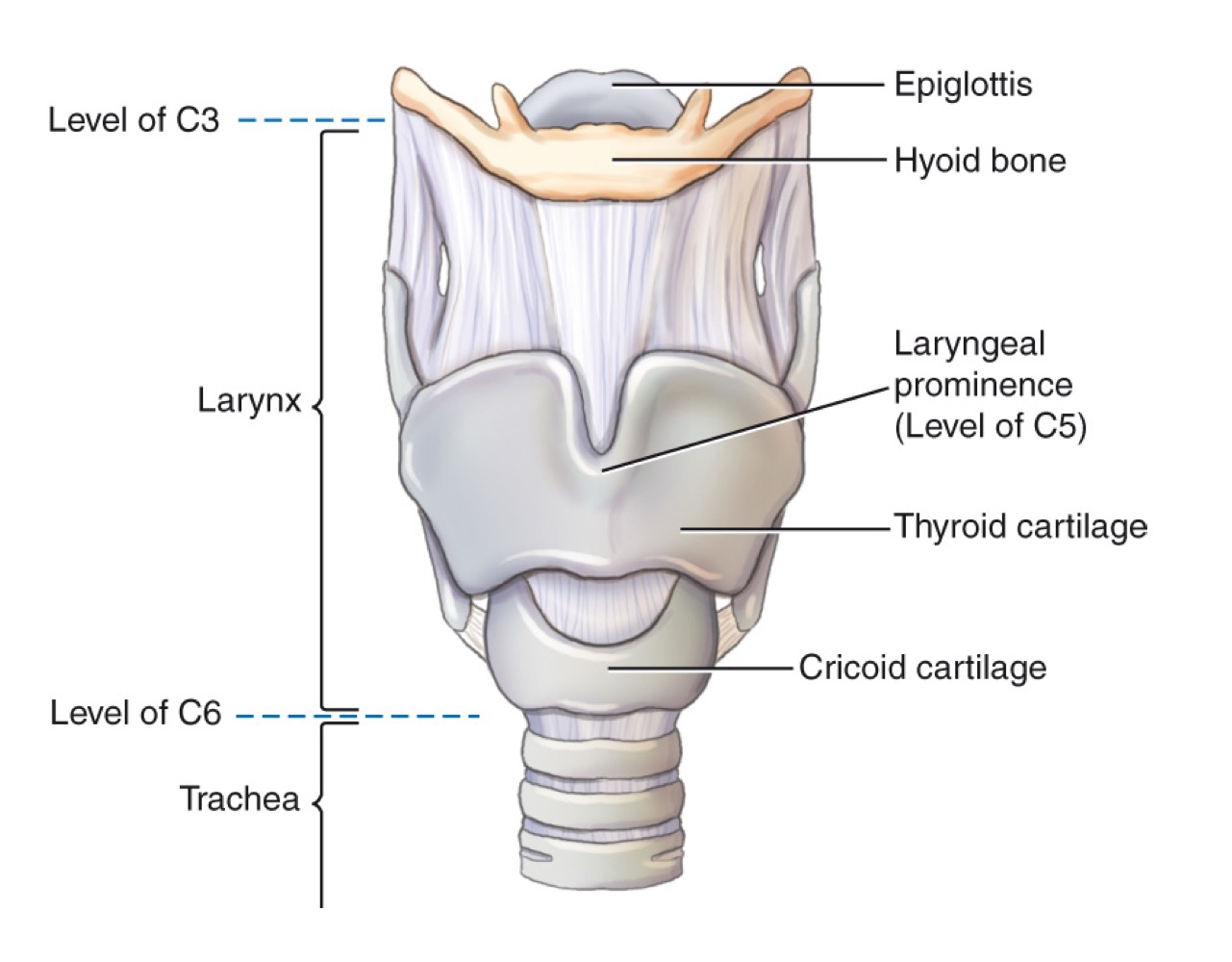
Larynx
Voice box; airway containing vocal cords, pivotal in breathing, swallowing, and speaking.
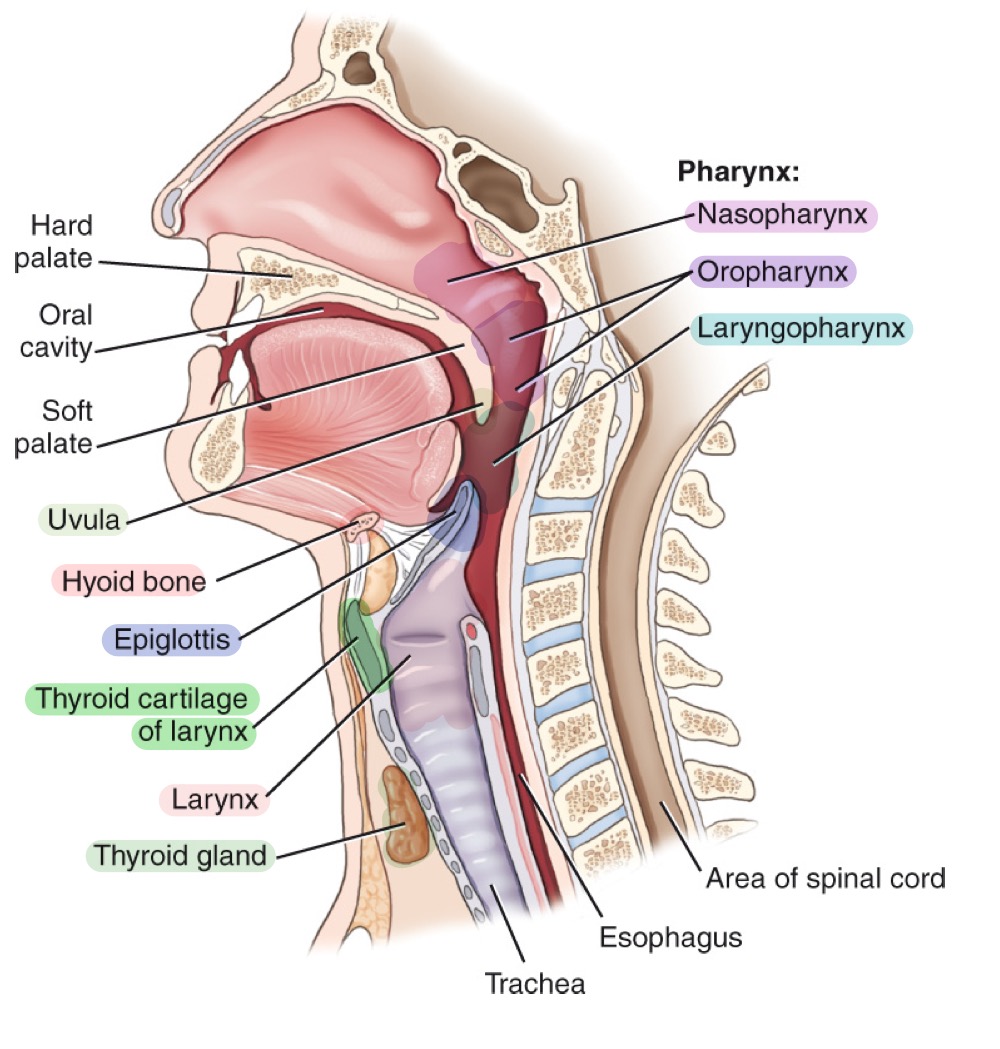
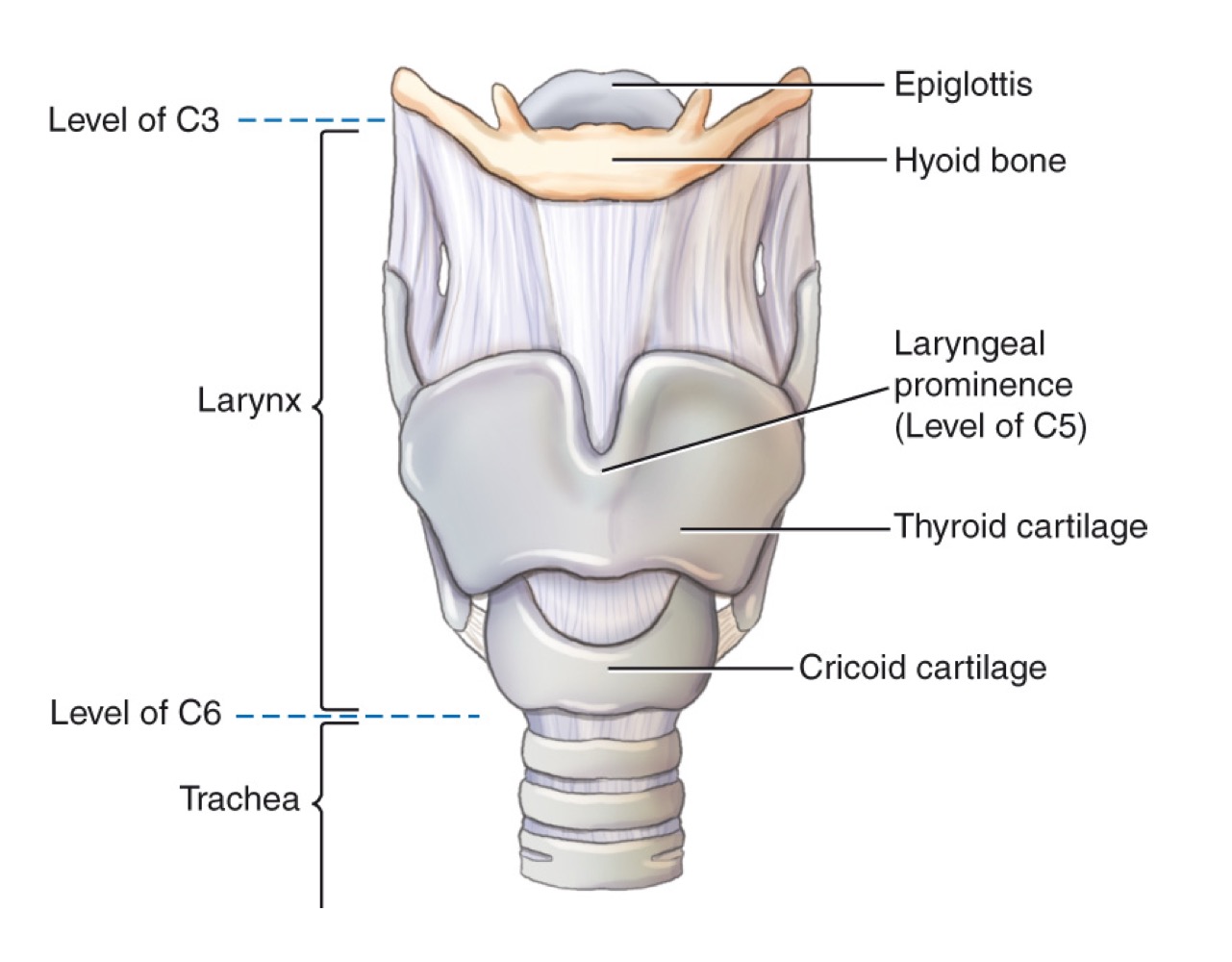
Epiglottis
Leaf-shaped flap covering the laryngeal inlet during swallowing to prevent food entry.
Thyroid cartilage
Adam’s apple; ring-shaped cartilage forming the bulk of the laryngeal skeleton.
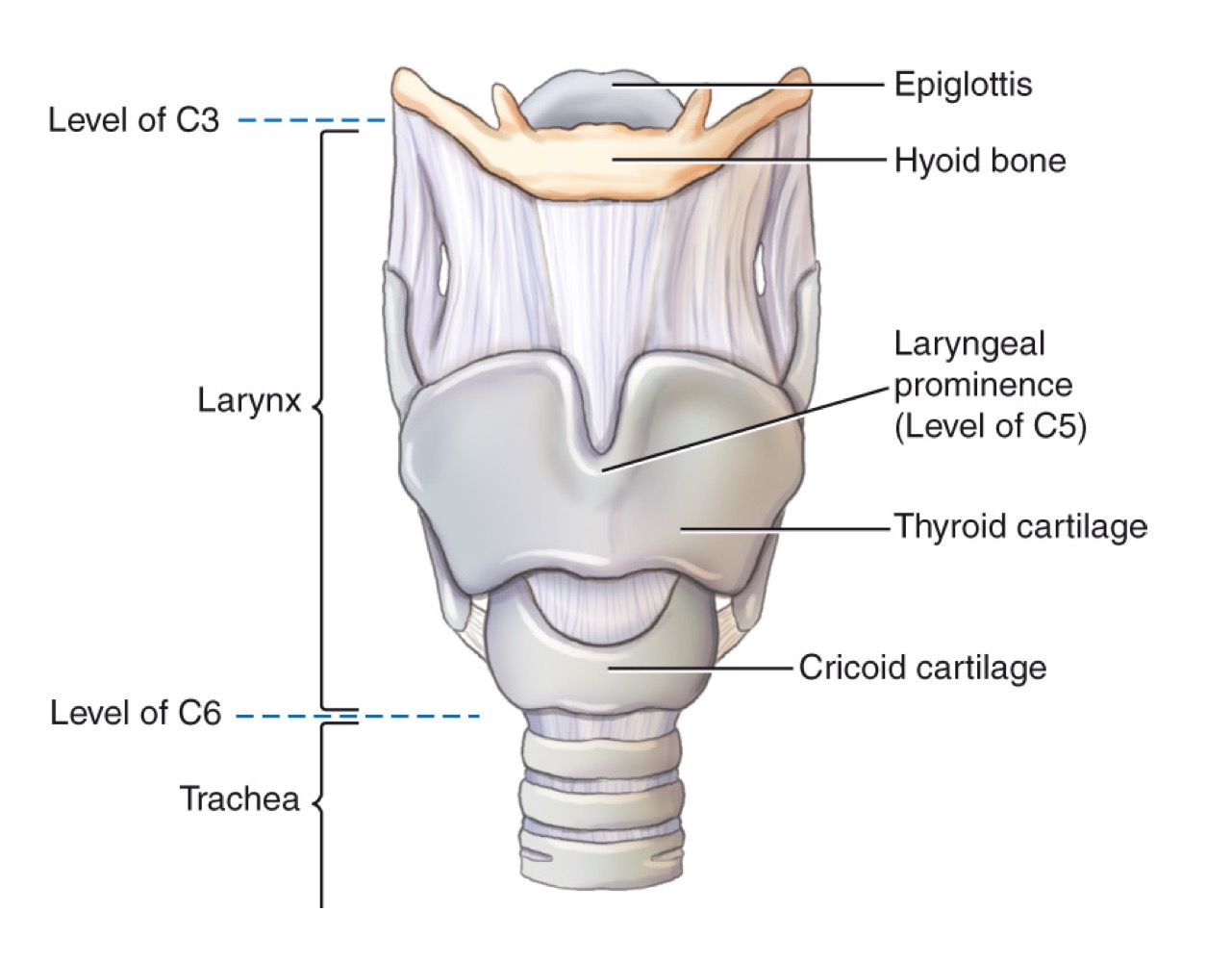
Cricoid cartilage
Ring-shaped cartilage below the thyroid cartilage, completing the laryngeal skeleton.
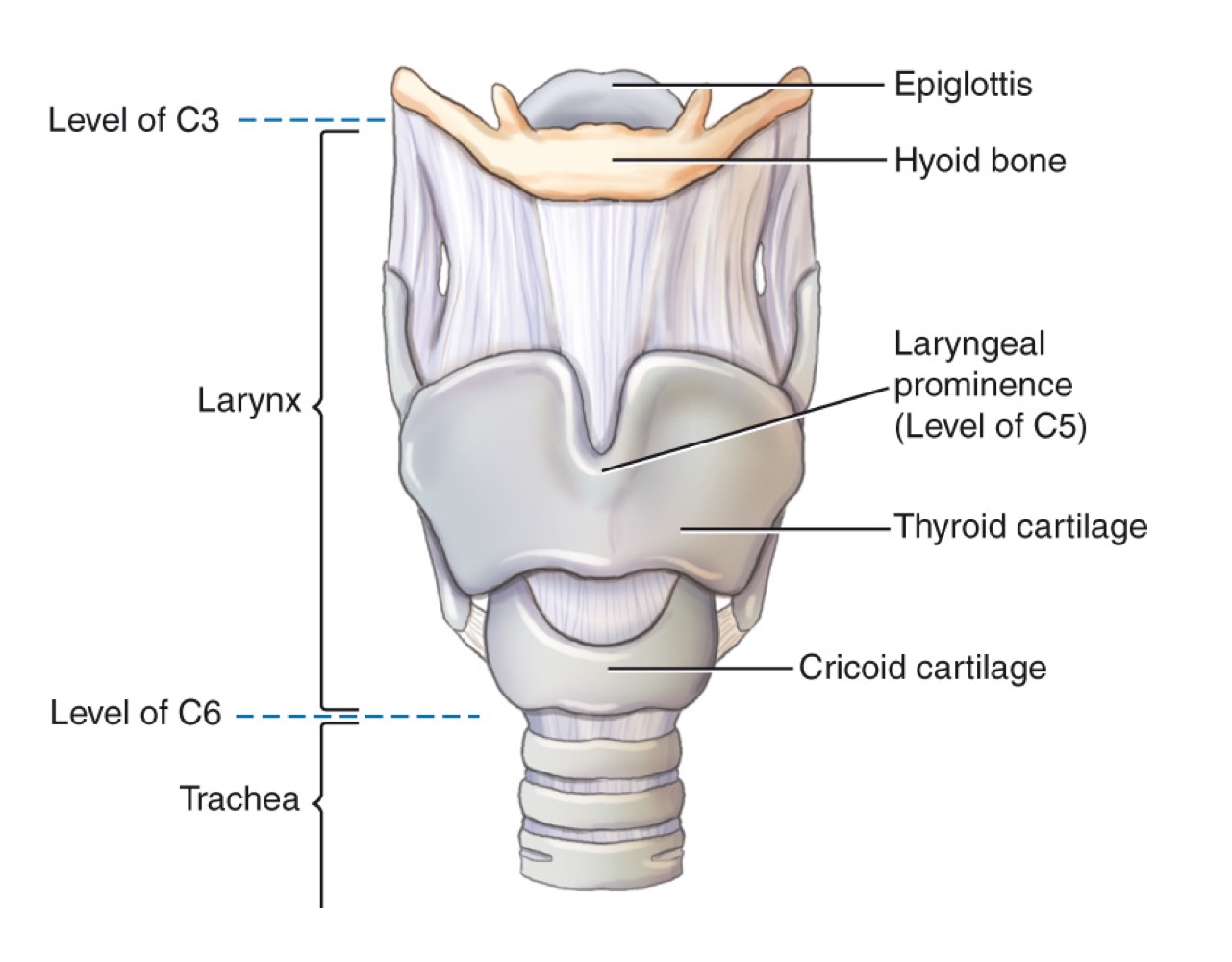
Hyoid bone
U-shaped bone in the neck; provides attachment for tongue and neck muscles; free-floating.
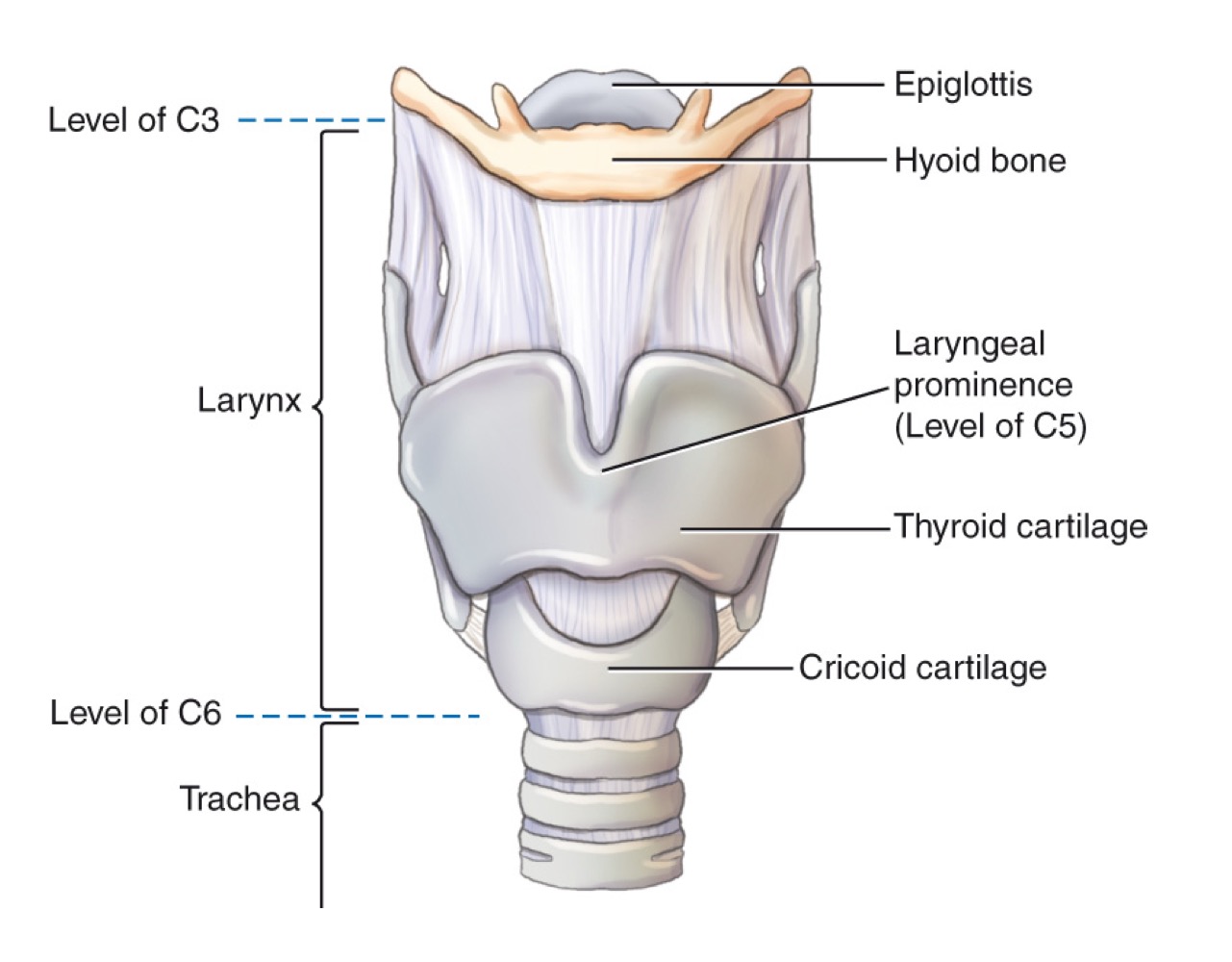
Larynx (voice box)
Cartilaginous structure housing vocal cords; located above the trachea.
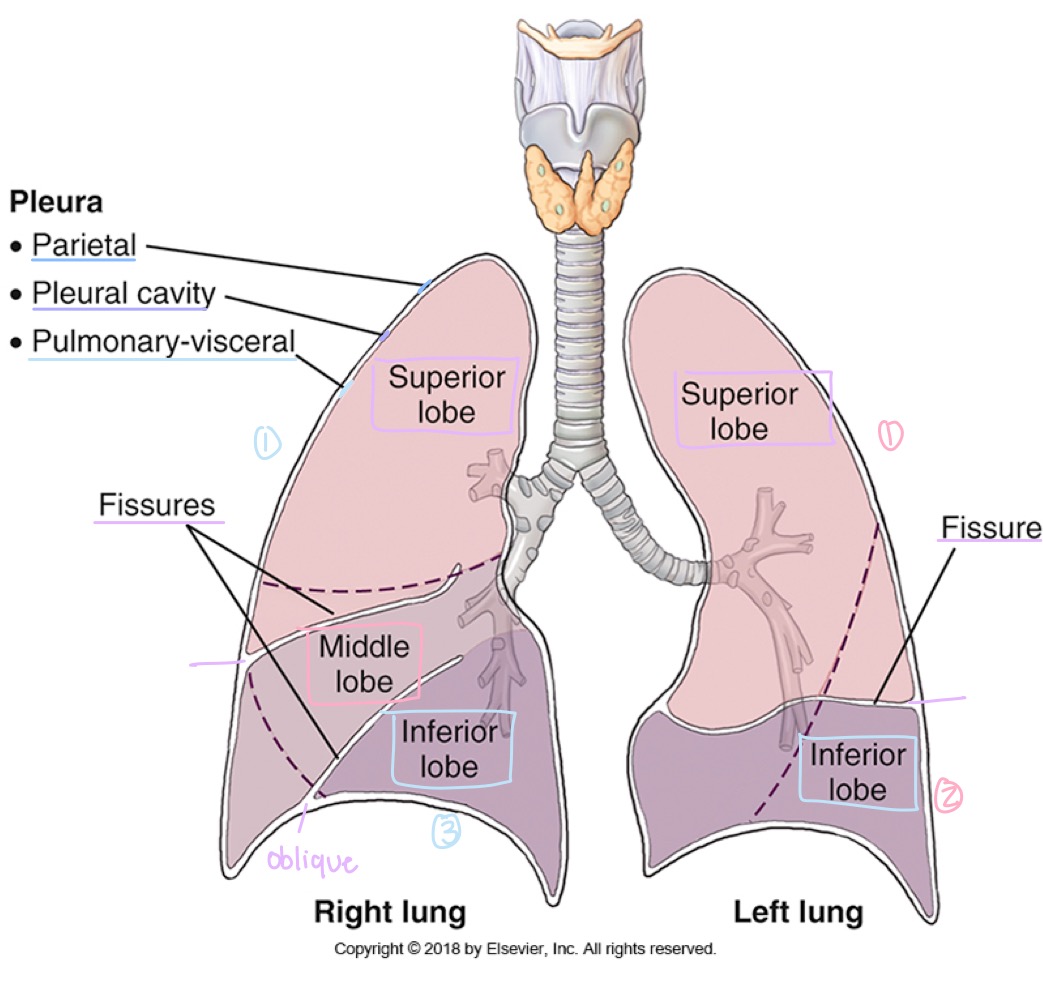
Pulmonary/visceral pleura
Innermost layer of the pleura, covering the lungs themselves.
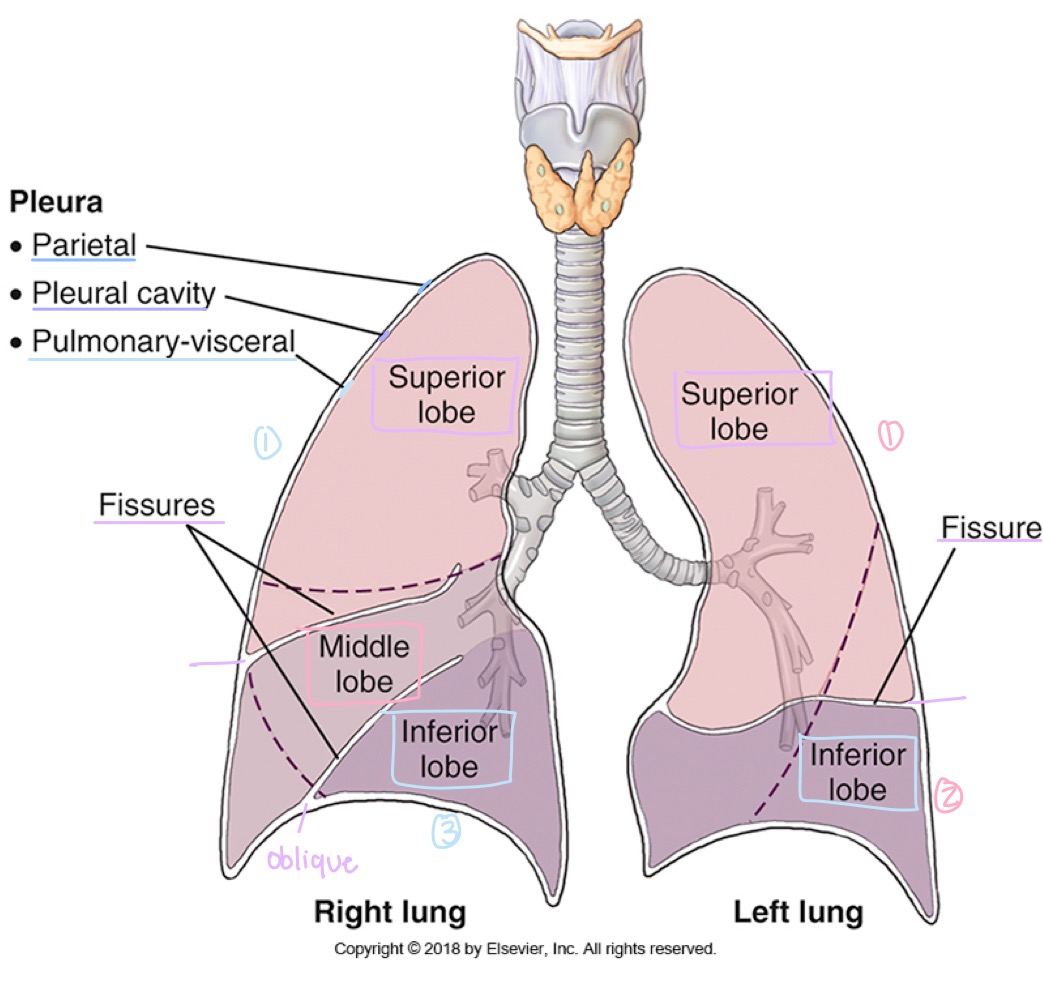
Parietal pleura
Outer layer of the pleura, lining the chest wall, diaphragm, and mediastinum.
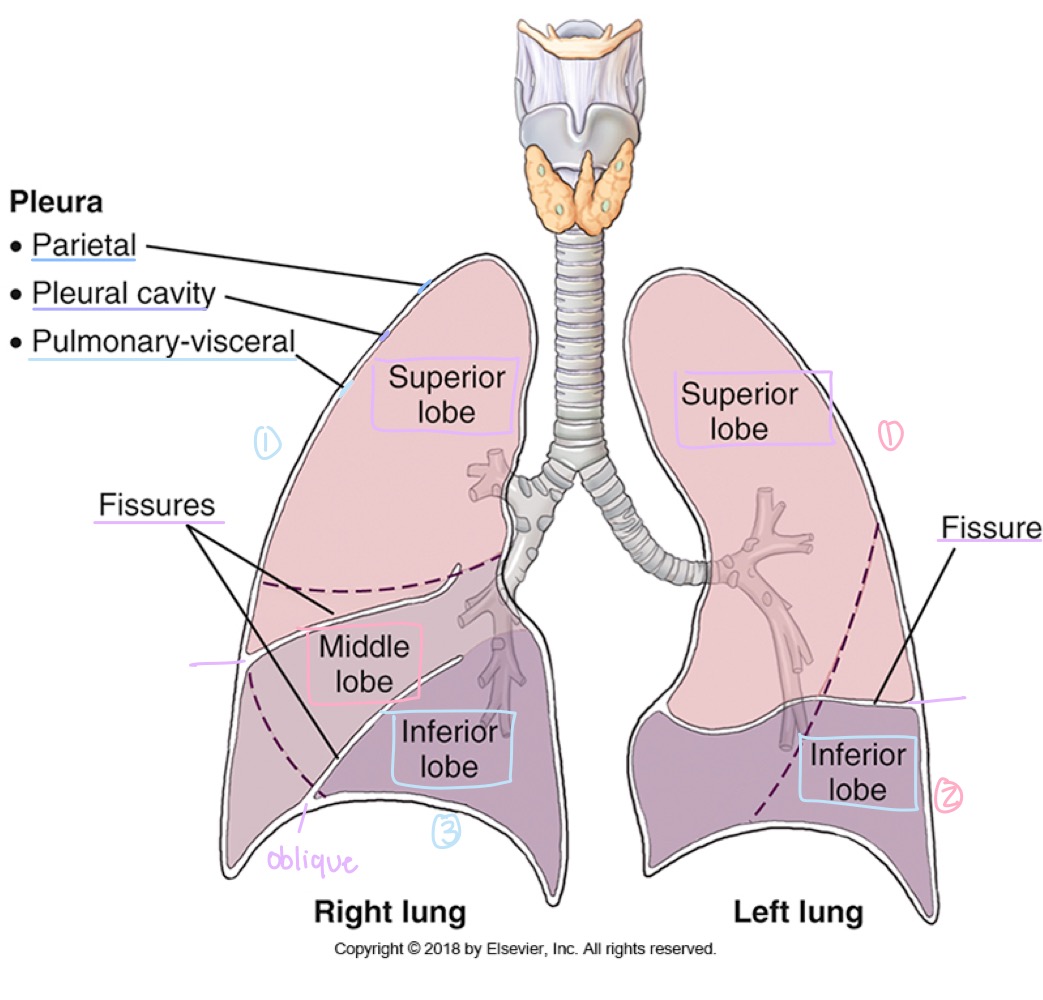
Pleural cavity
Potential space between visceral and parietal pleura, containing lubricating fluid.
Pneumothorax
Air in the pleural cavity causing lung collapse.
Hemothorax
Accumulation of blood in the pleural cavity.
Pleurisy
Inflammation of the pleura, often causing sharp chest pain during breathing.
Mediastinum
Central compartment of the thoracic cavity between the lungs; contains trachea, esophagus, thymus, heart, and great vessels.
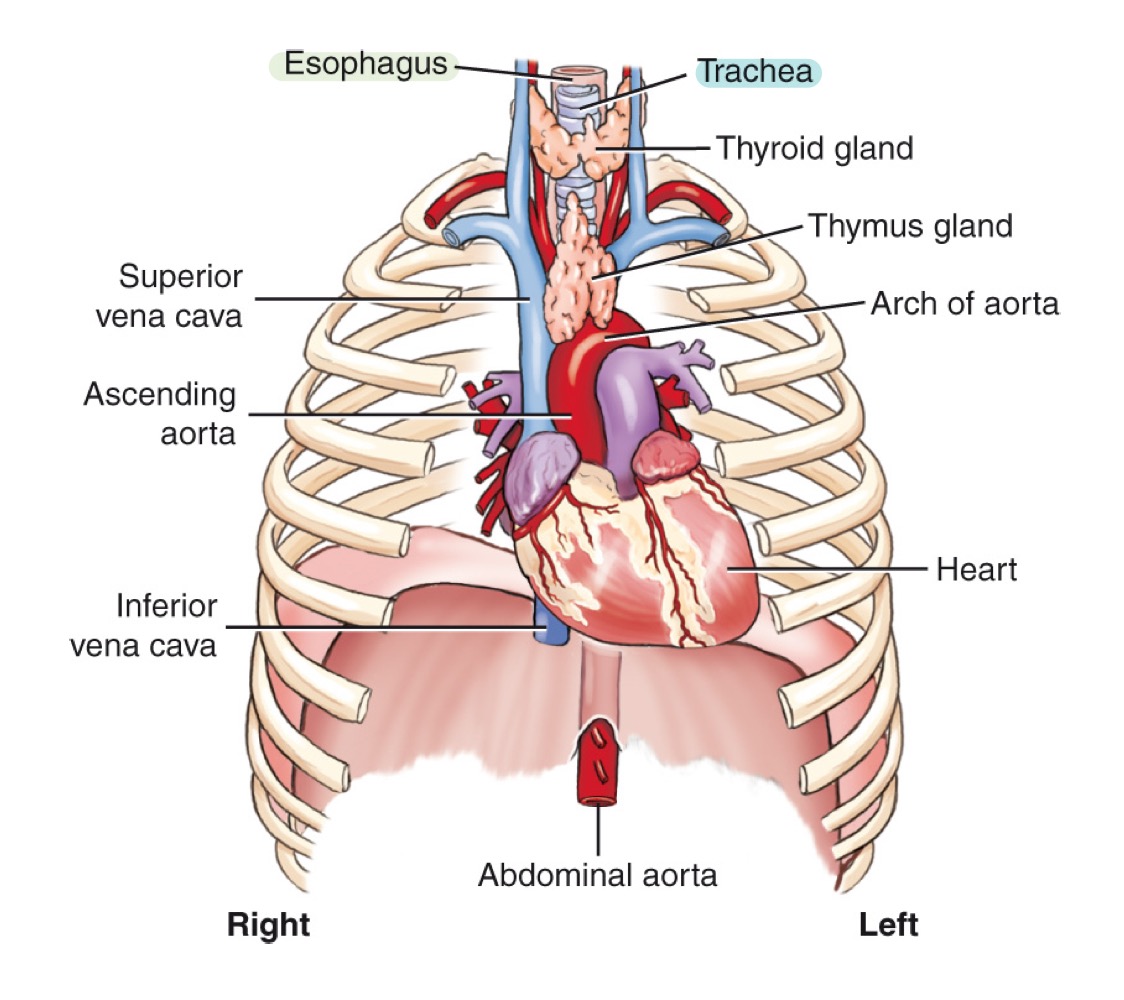
what organs are included in the mediastinum?
trachea
esophagus
thymus
heart
great vessels
Thymus gland
Lymphoid organ in the mediastinum, important in immune development; prominent in children.
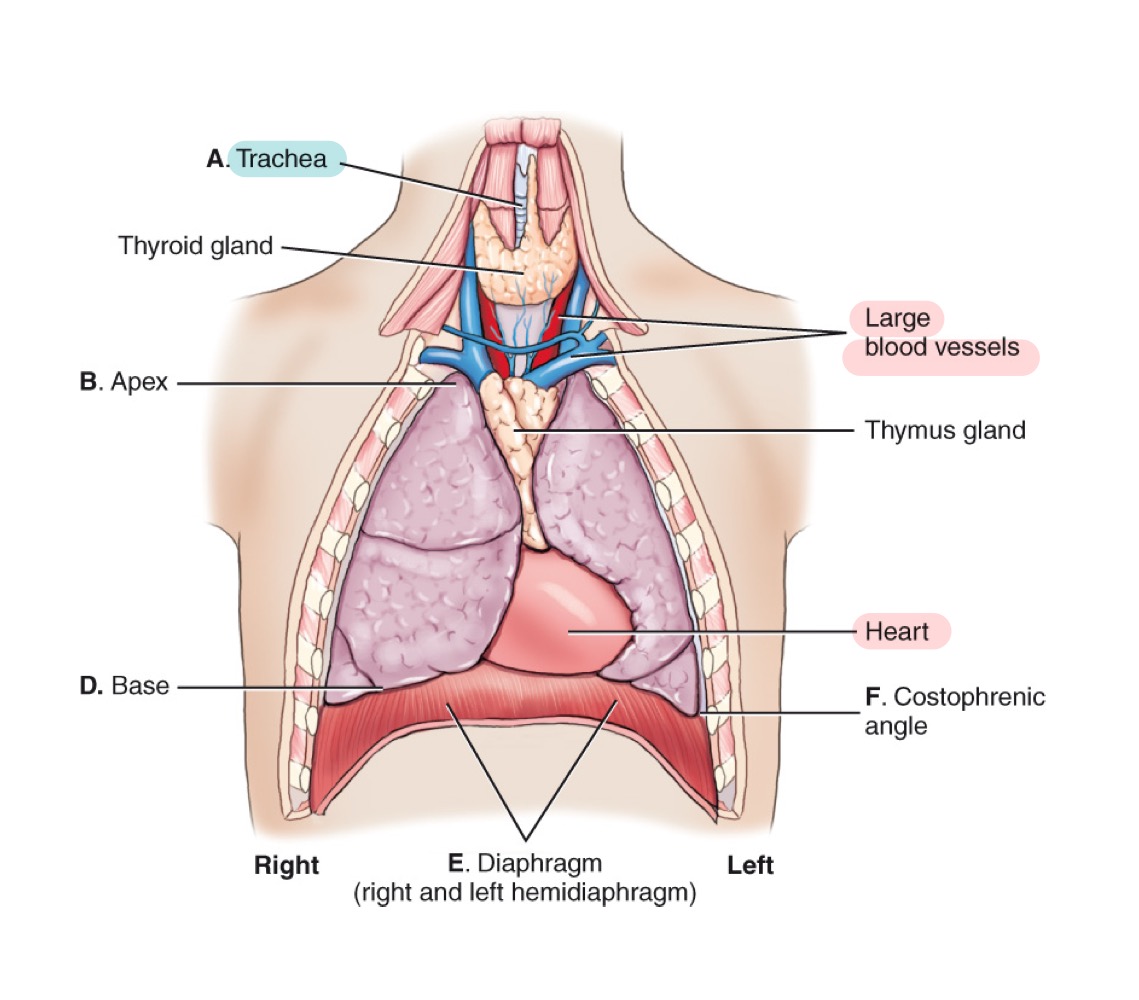
Heart
Muscular organ pumping blood through the body; located in the mediastinum.
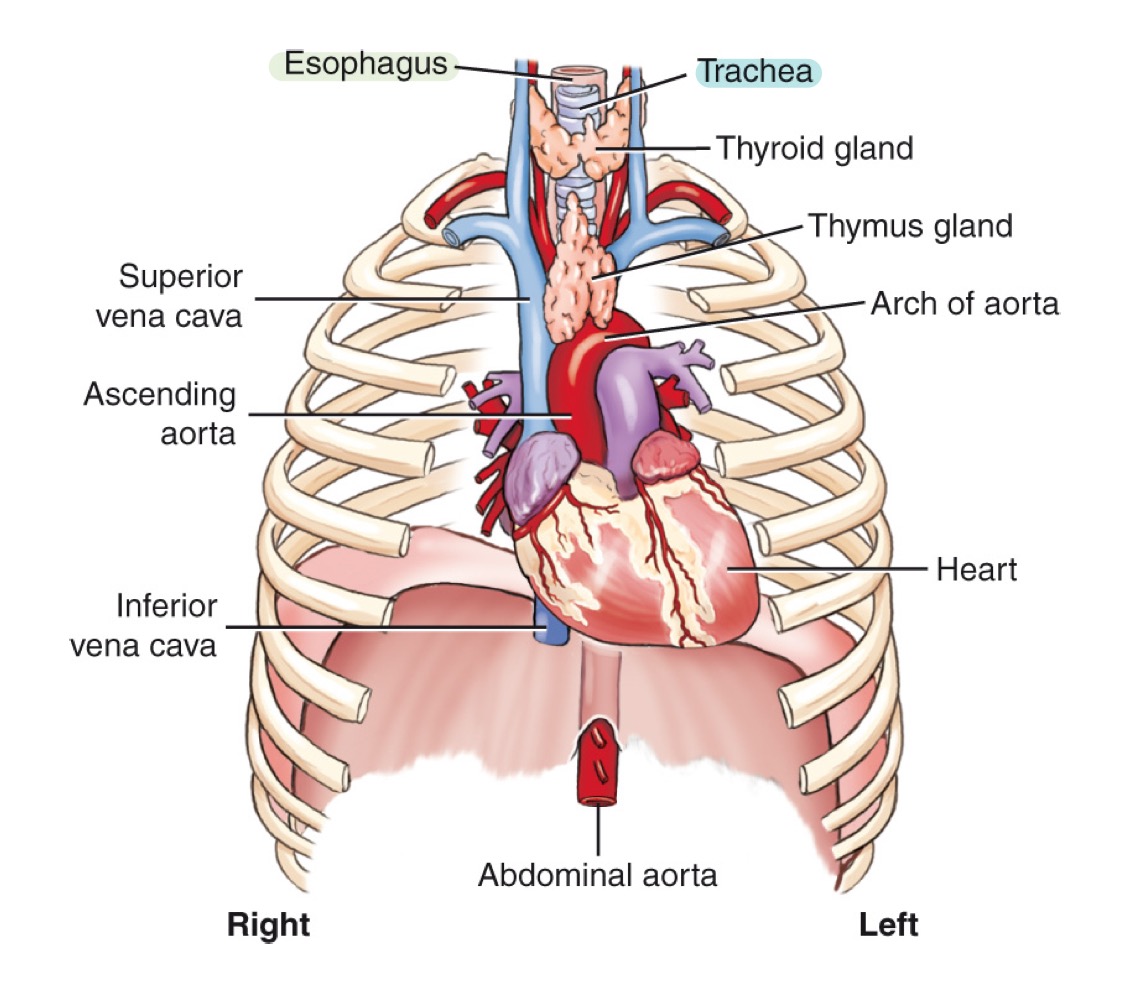
Great vessels
Major arteries and veins entering/leaving the heart (e.g., aorta and venae cavae).
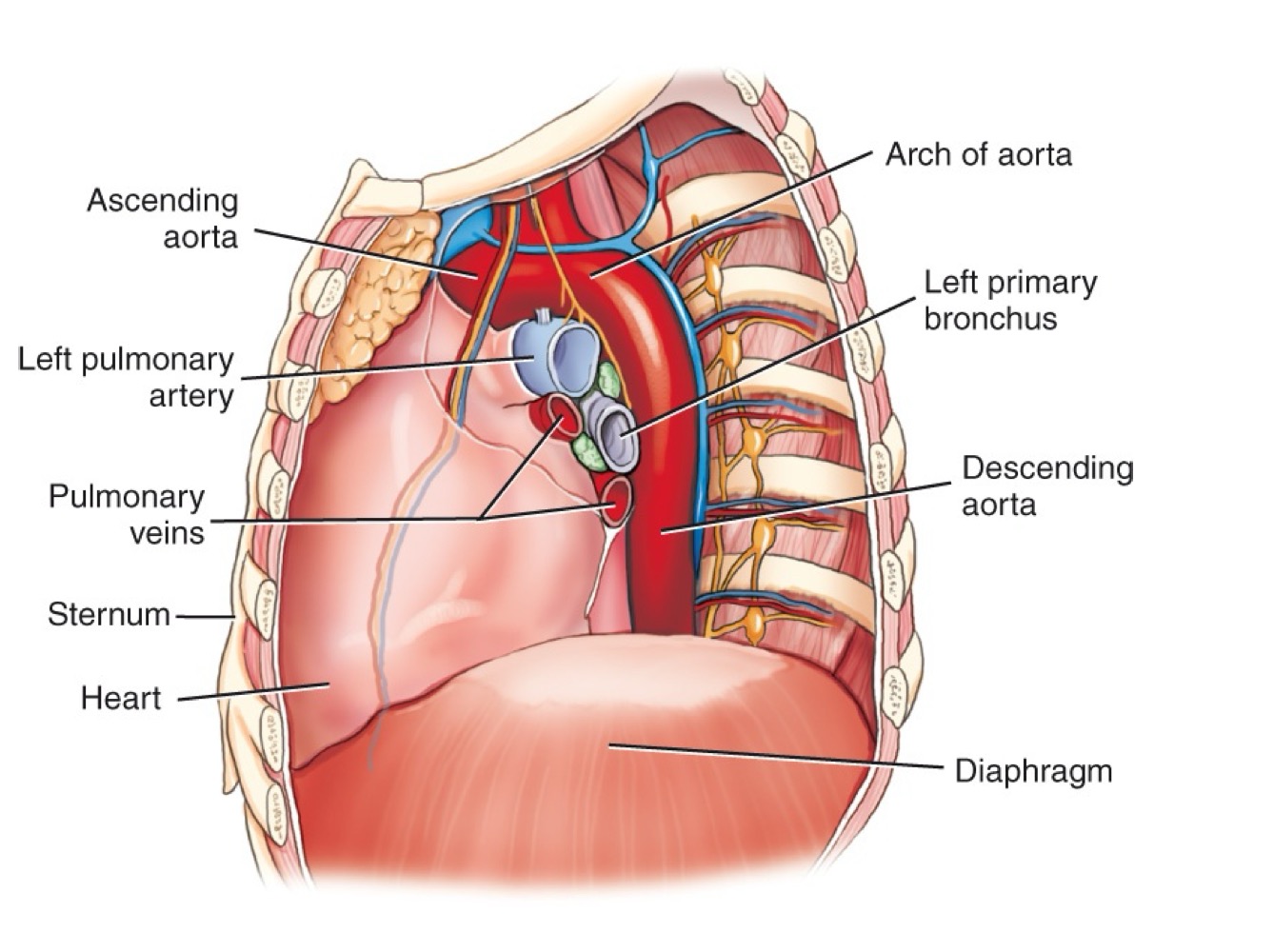
Arch of the aorta
Curved portion of the aorta over the heart, giving off major branches.
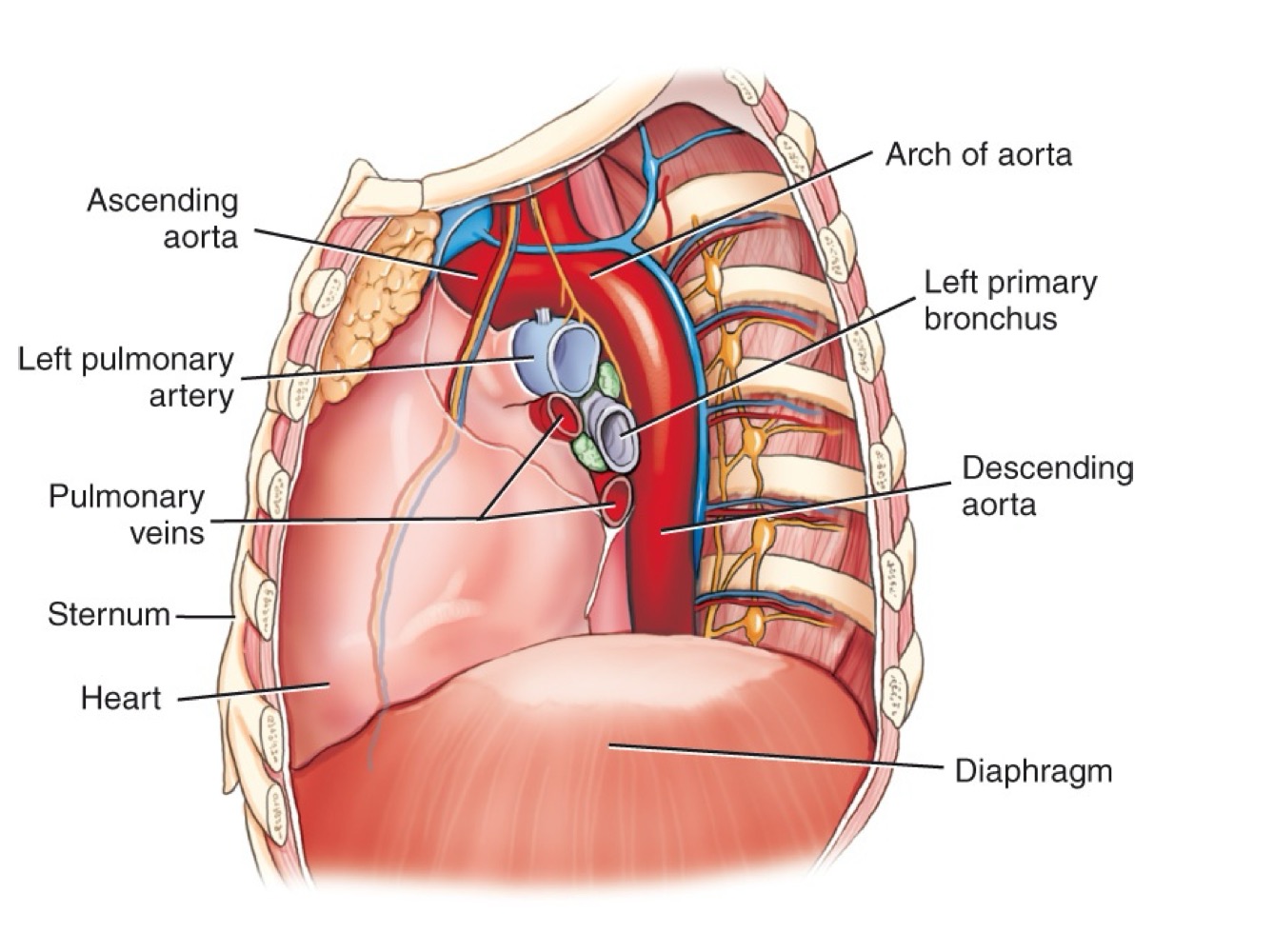
Ascending aorta
Section of the aorta rising from the heart before it arches backward.
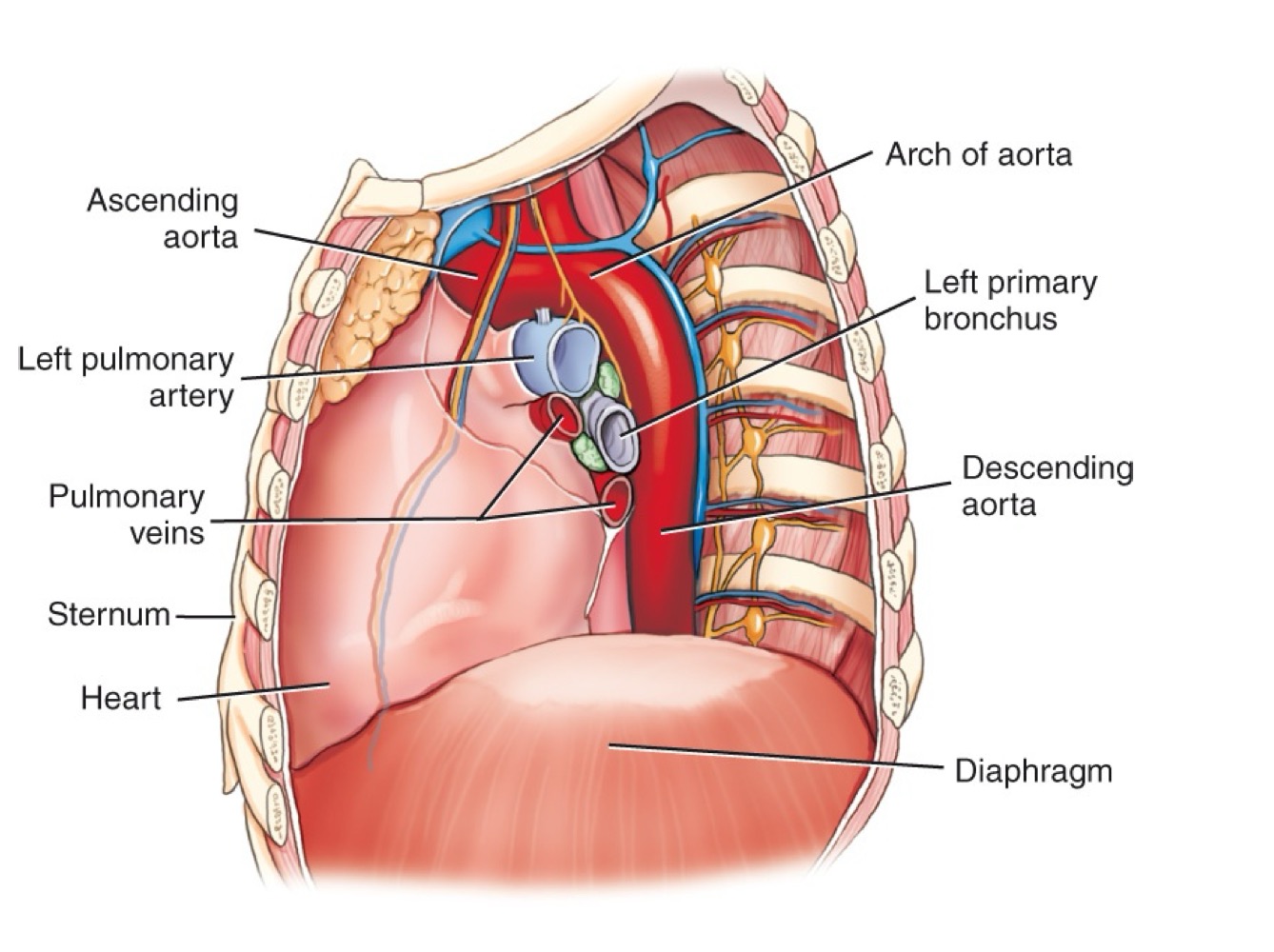
Descending aorta
Section of the aorta continuing downward through the thorax.
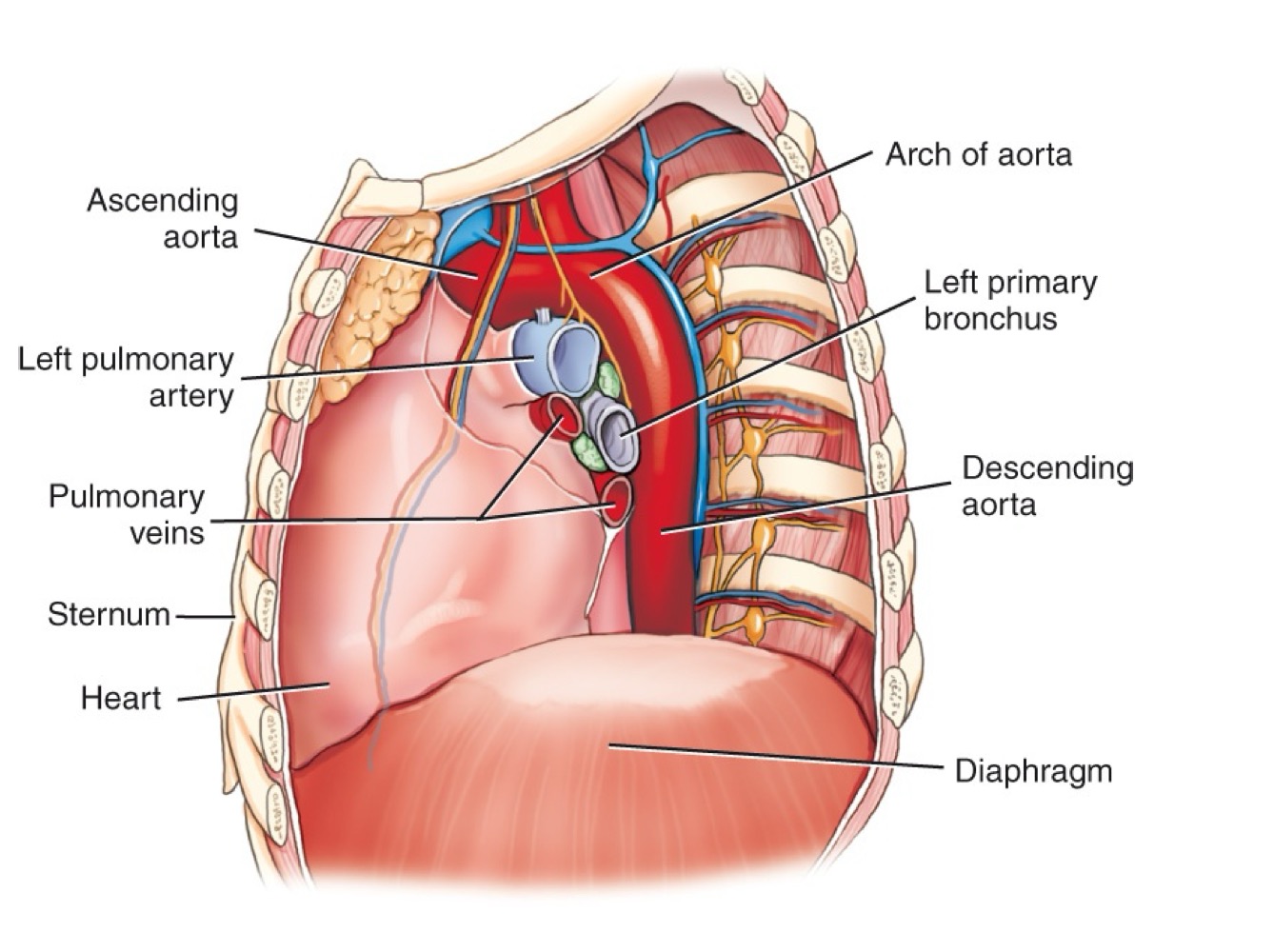
Abdominal aorta
Continuation of the aorta after passing through the diaphragm into the abdomen.
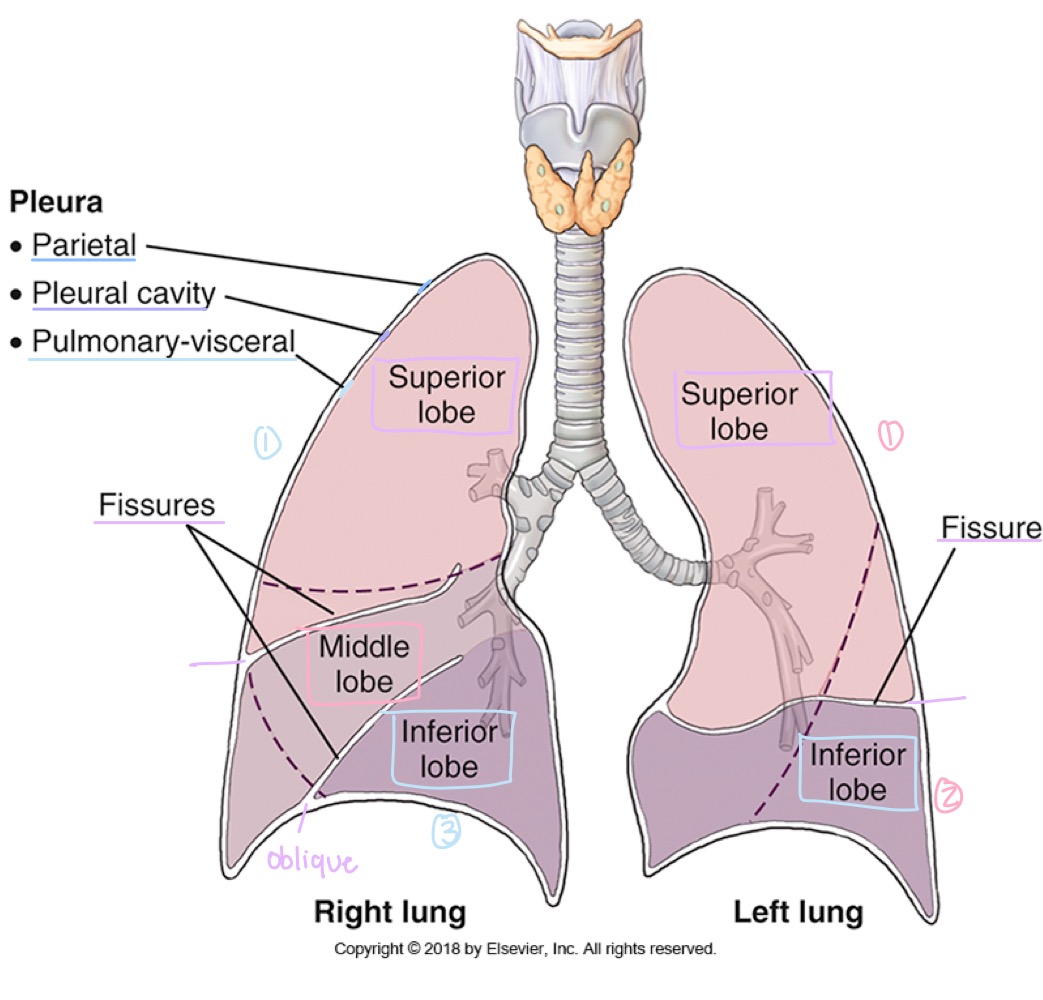
Lung lobes
Right lung has three lobes (upper, middle, lower); left lung has two lobes (upper and lower).
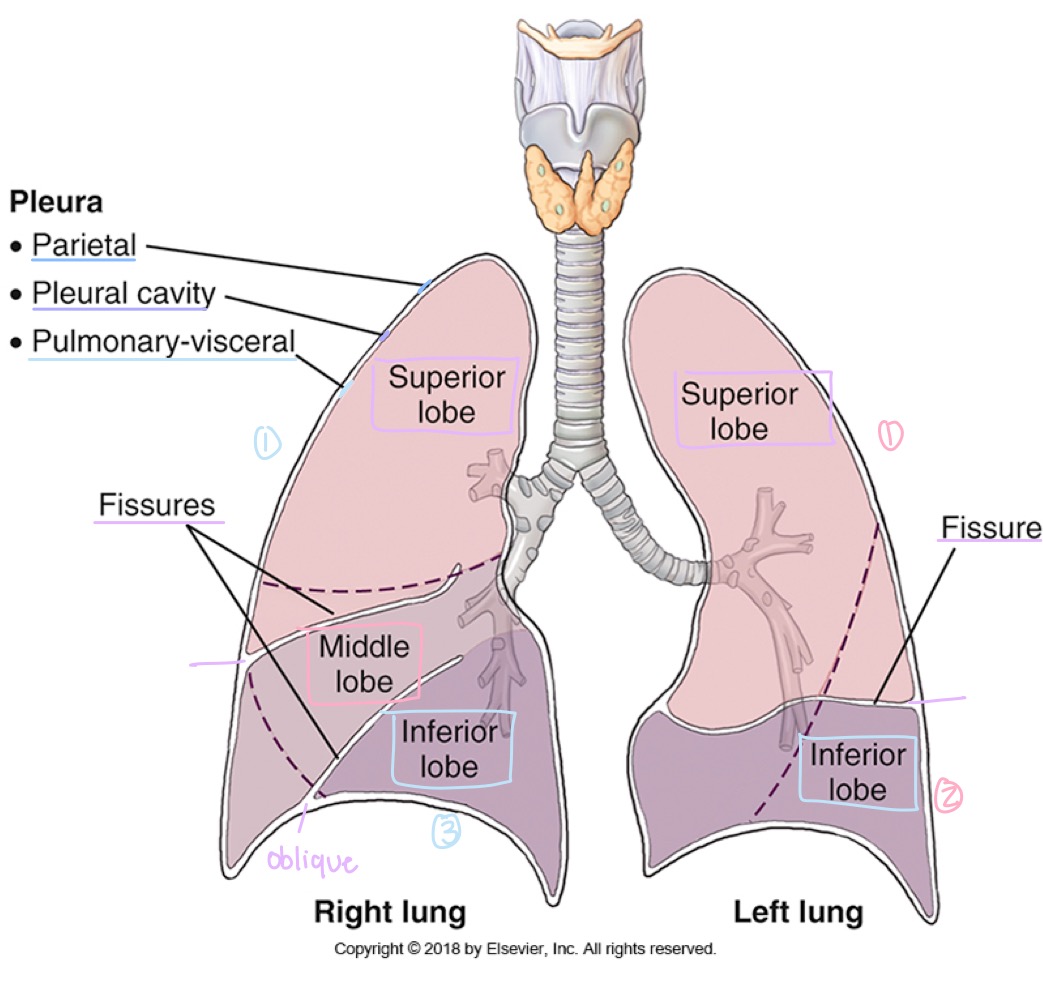
how many lobes does the right lung have?
three: upper , middle , lower
how many lobes does the left lung have?
two: upper and lower
Fissures (lung separations)
Oblique fissure and, in the right lung, horizontal fissure dividing the lungs into lobes.
Vertebra prominens (C7)
Prominent spinous process at the seventh cervical vertebra, used as a radiographic landmark.
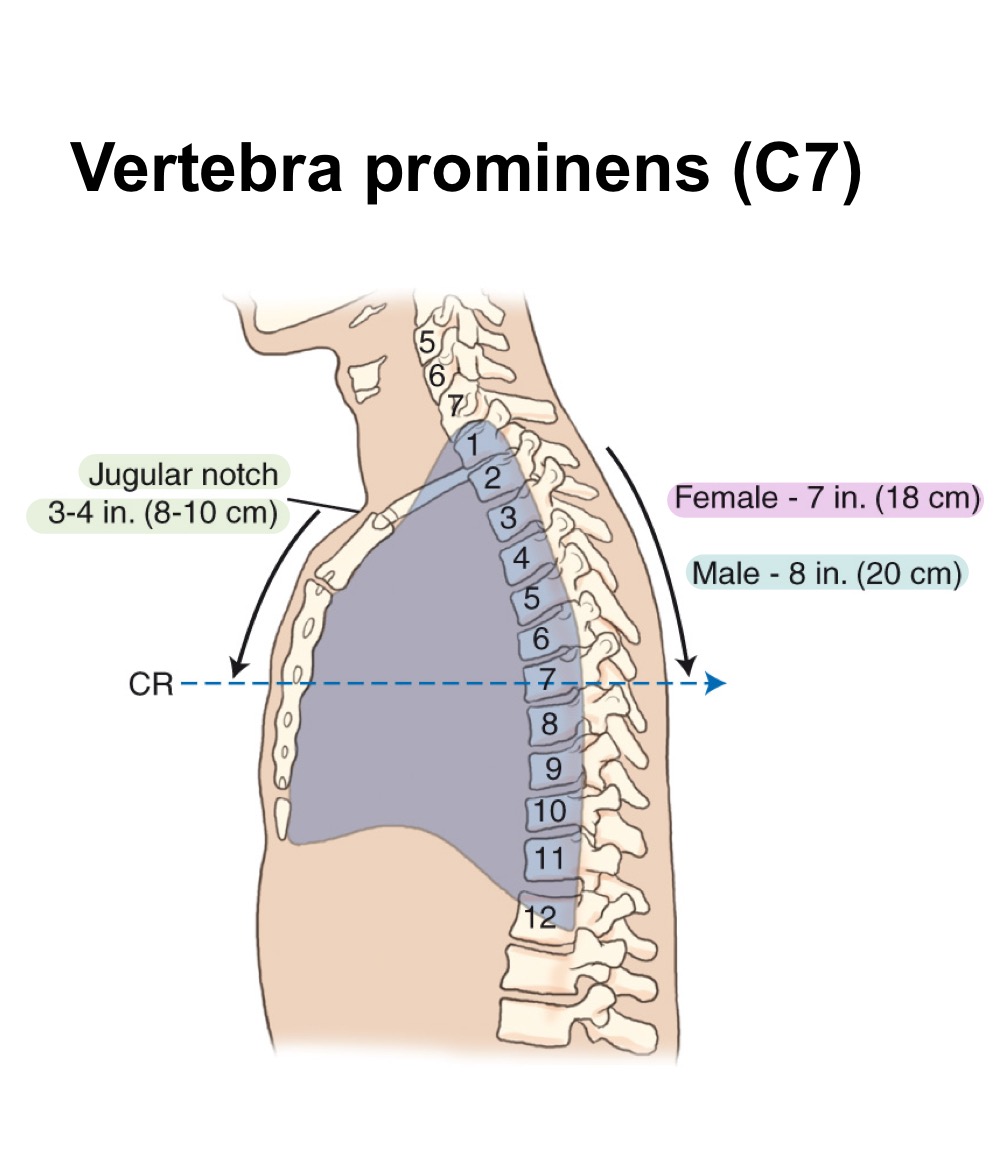
Jugular notch (suprasternal notch)
Palpable notch at the superior border of the manubrium; useful chest landmark.
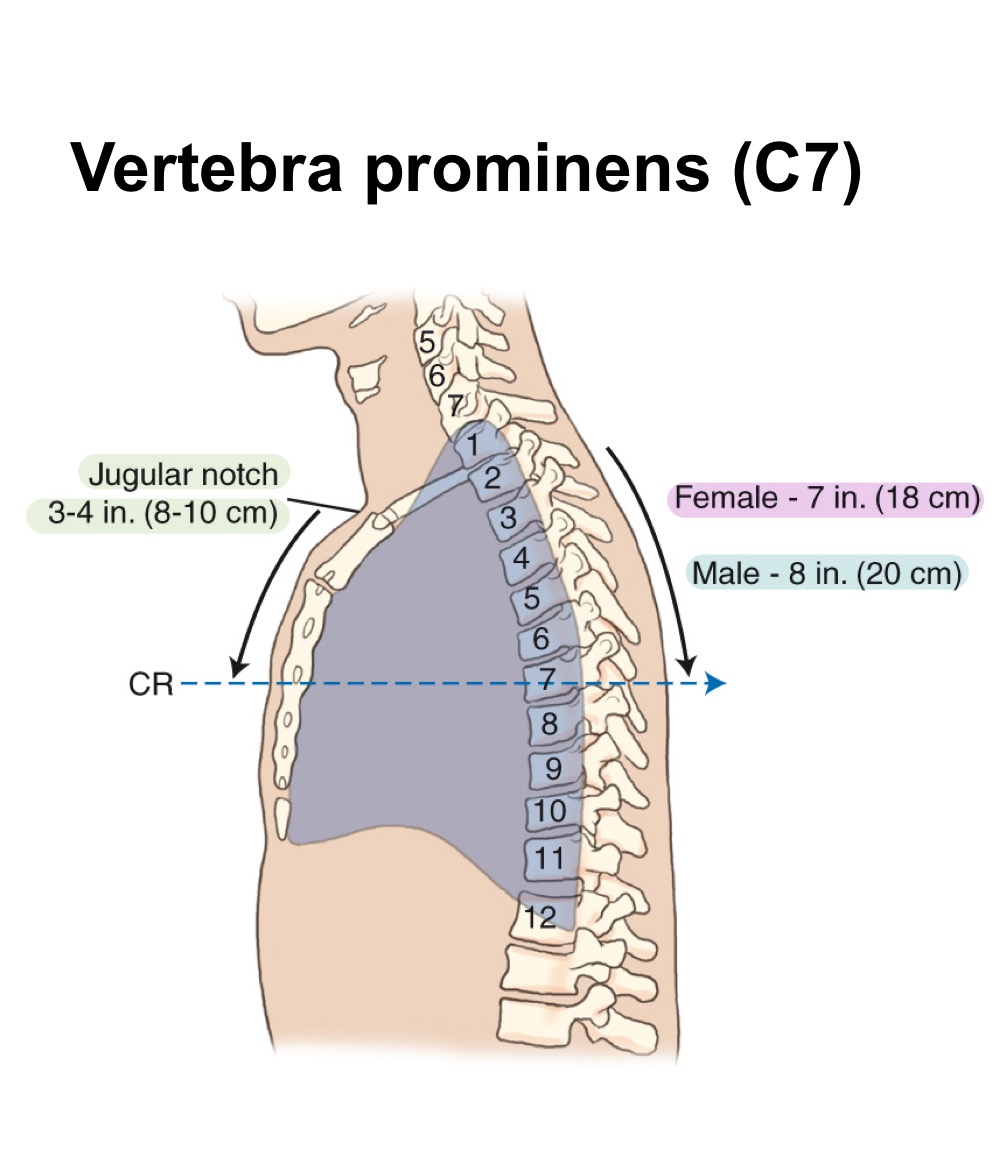
Topographic landmarks
External reference points (e.g., C7, jugular notch) used to position chest radiographs.
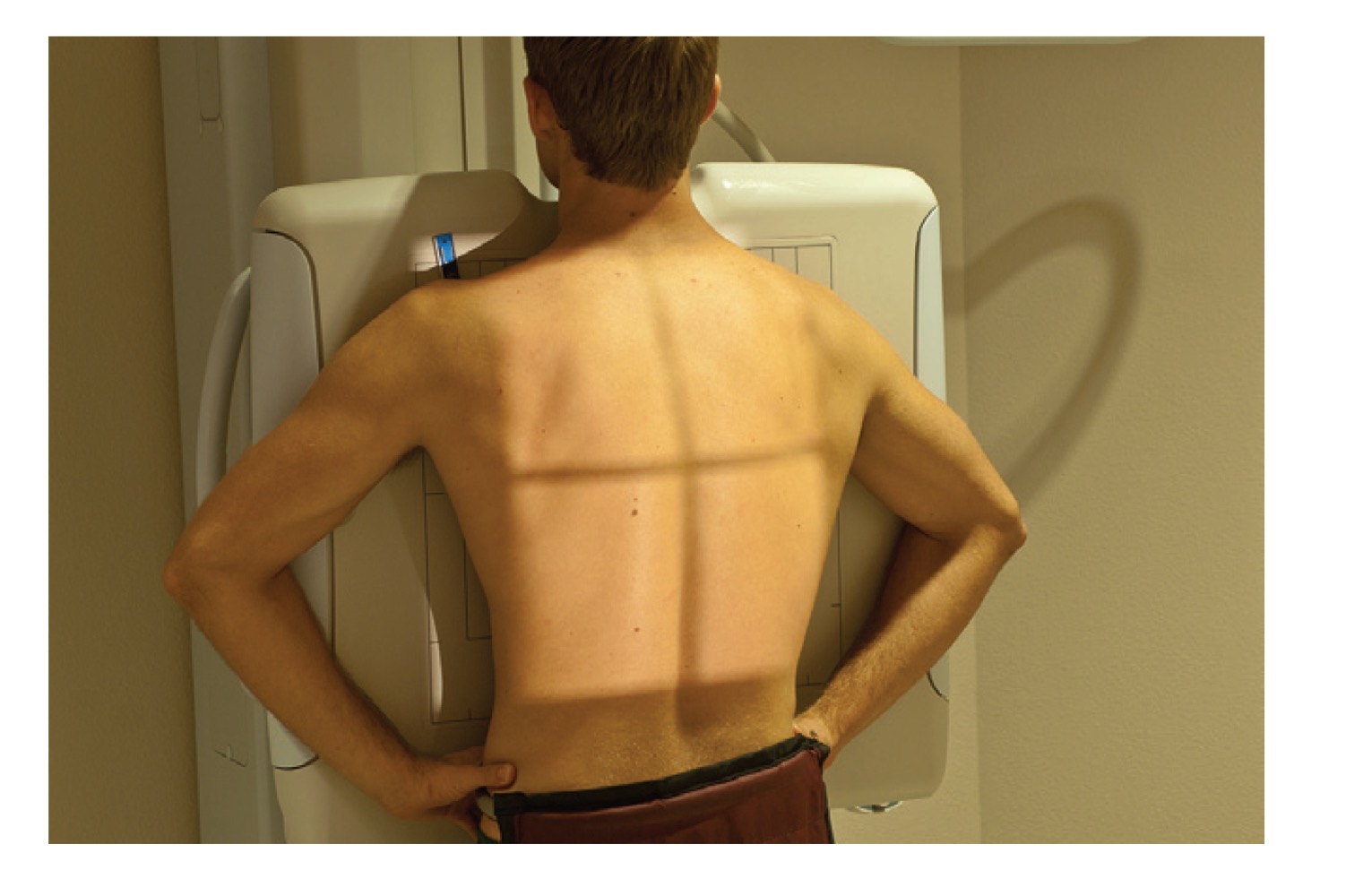
PA chest projection
Posteroanterior radiographic view of the chest; heart and mediastinal structures appear smaller.
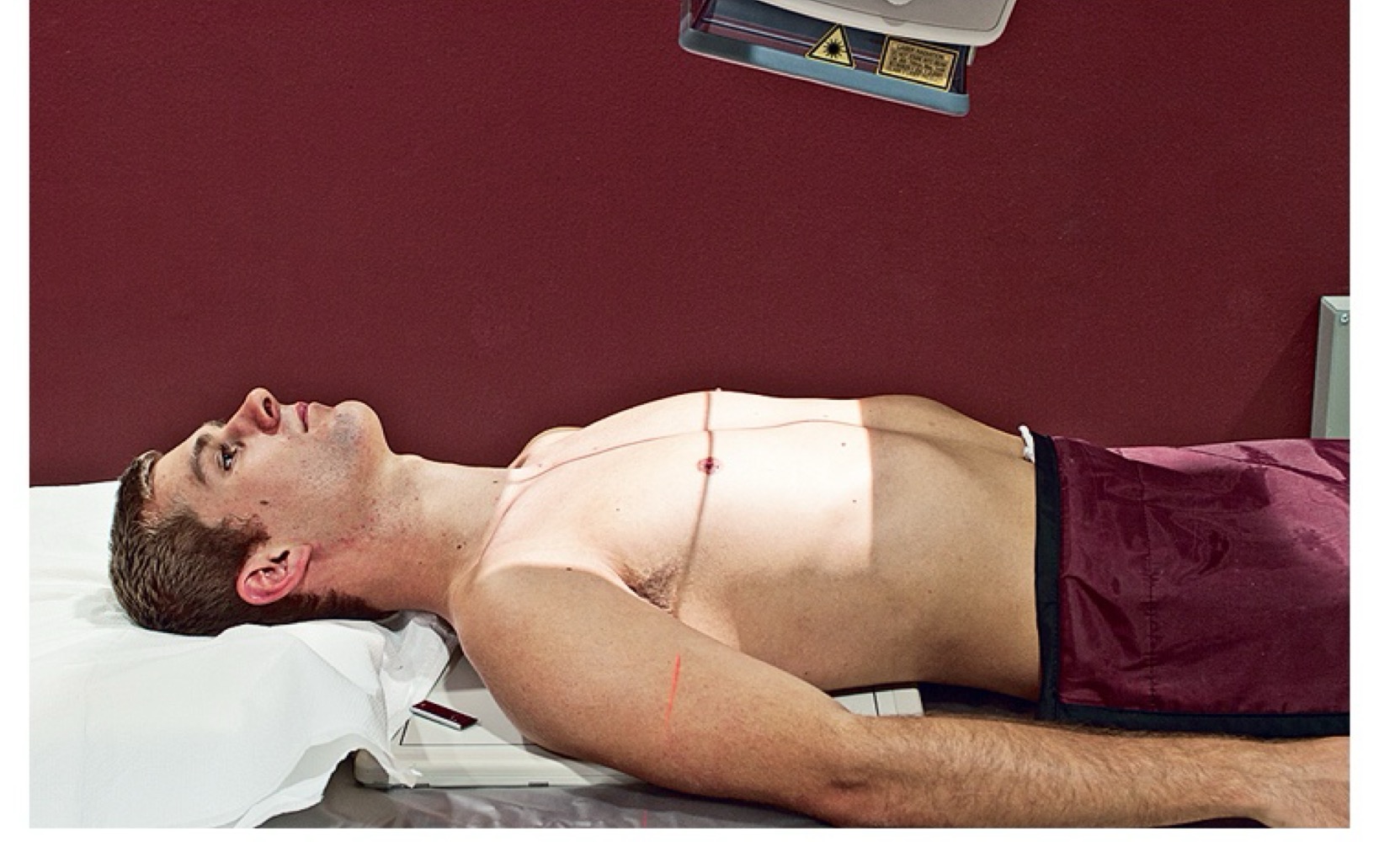
AP chest projection
Anteroposterior chest radiograph; may enlarge cardiac silhouette compared with PA view.
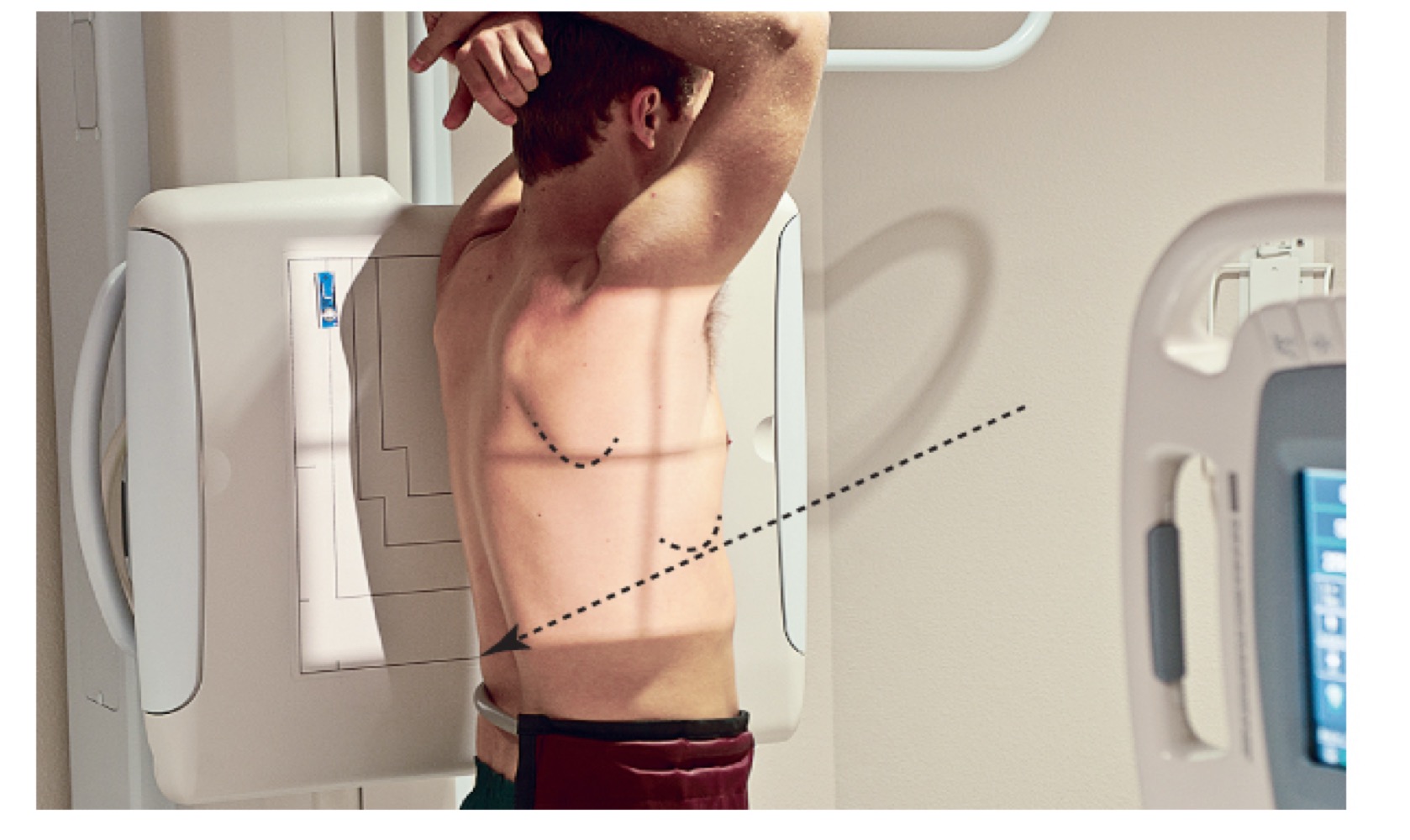
Lateral chest projection
Radiographic view from the side; shows true spatial relationships and posterior aspects of lungs/heart.
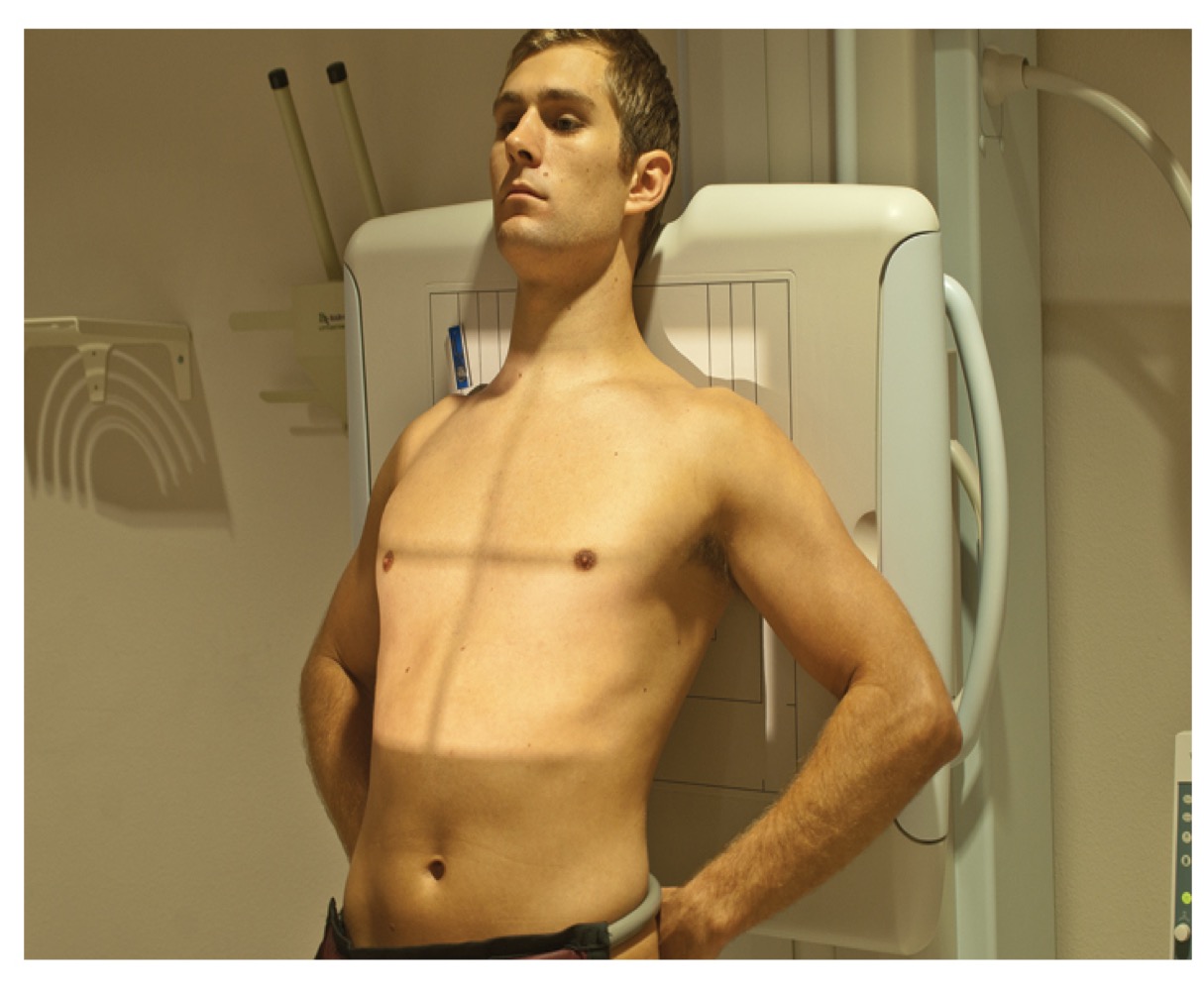
AP lordotic projection
AP chest view with patient leaning back to project clavicles above lungs; assesses apical regions.
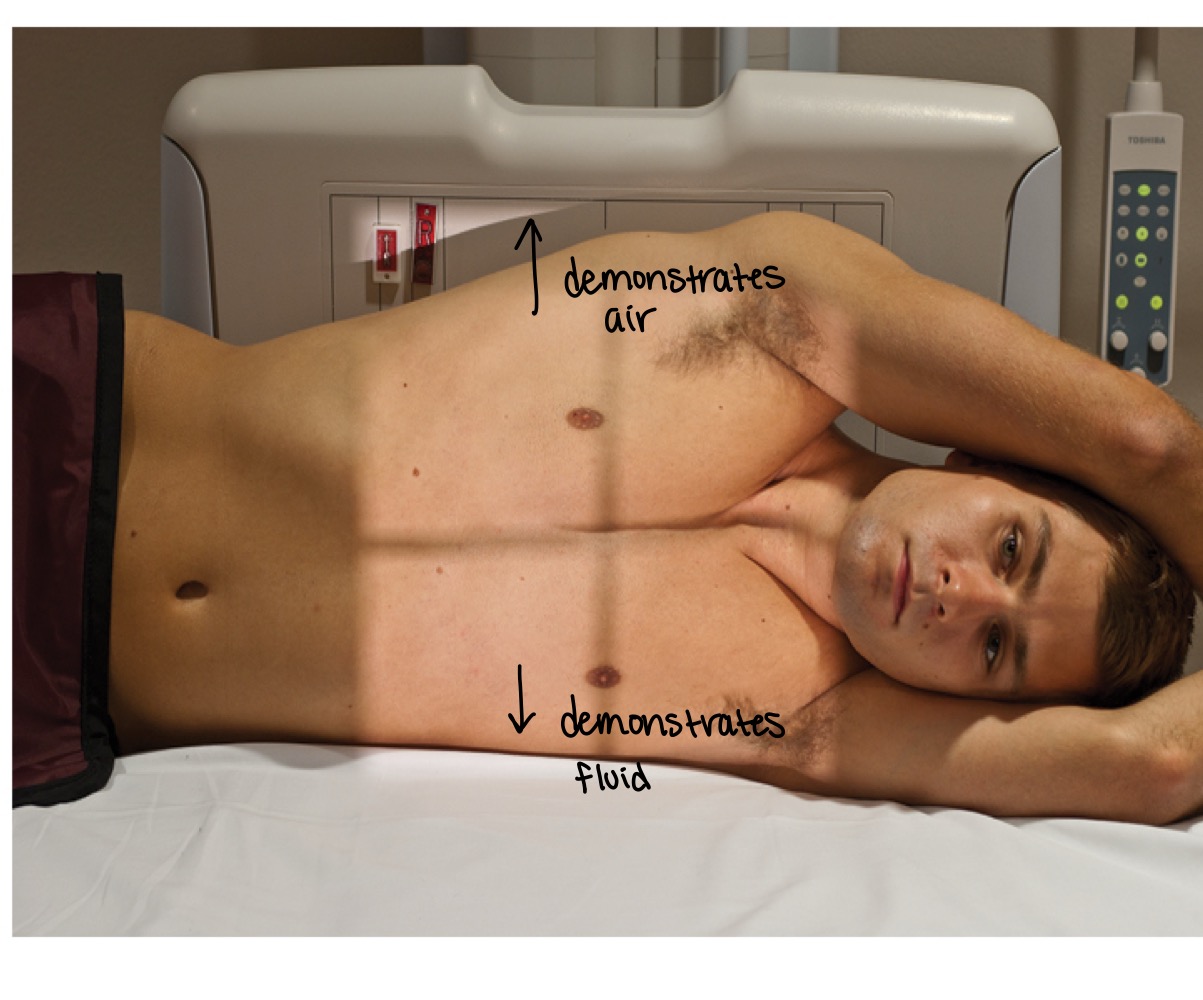
Decubitus positions
Chest radiographs taken with patient lying on one side to show air or fluid levels.
Chin extension
Positioning cue in PA chest radiographs to reduce chin interference and obscure airway shadows.
Collimation
Restriction of the X-ray beam to the area of interest to minimize exposure and improve image quality.
Lead shielding/backscatter protection
Use of shields to protect organs from unnecessary radiation and minimize backscatter exposure.
Exposure factors
Technical settings (kVp, mA, exposure time) to optimize image quality; chest often uses high kVp.
kVp (kilovoltage peak)
Voltage controlling X-ray beam energy; higher kVp improves penetration for chest radiographs.
mA (milliampere)
Current controlling the number of X-ray photons produced; affects image brightness.
SID (source-to-image distance)
Distance from X-ray source to image receptor; standard chest exams often use 72 inches.
Situs inversus
Condition where major visceral organs are mirrored from normal positions; relevant for labeling.
Topographic land marks for PA chest
vertebra prominens & jugular notch
Breathing instructions
big breath in, blow it all the way out, another big breath in and hold it, you can breath
Inspiration vs. expiration
Inspiration enlarges thoracic cavity and lungs; expiration reduces lung volume and changes diaphragmatic position.
Evaluation criteria (image quality)
full inspiration, no rotation, scapulae removed, proper collimation.
Pigg-O-Stat
Immobilization device for pediatric chest radiographs to minimize movement.
Aperture projections and special views
Additional chest positions (AP supine, AP lordotic, lateral decubitus) for specific clinical indications.
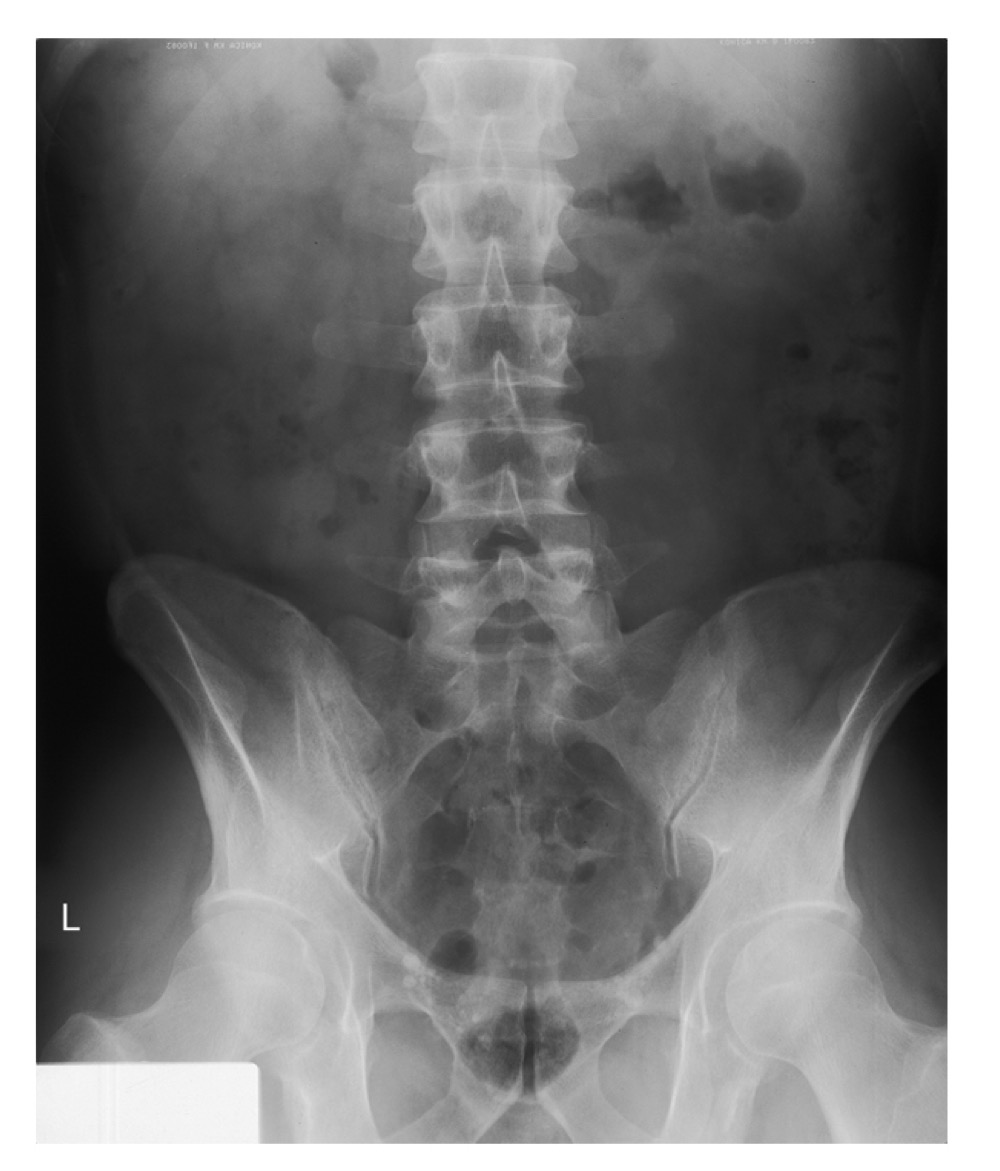
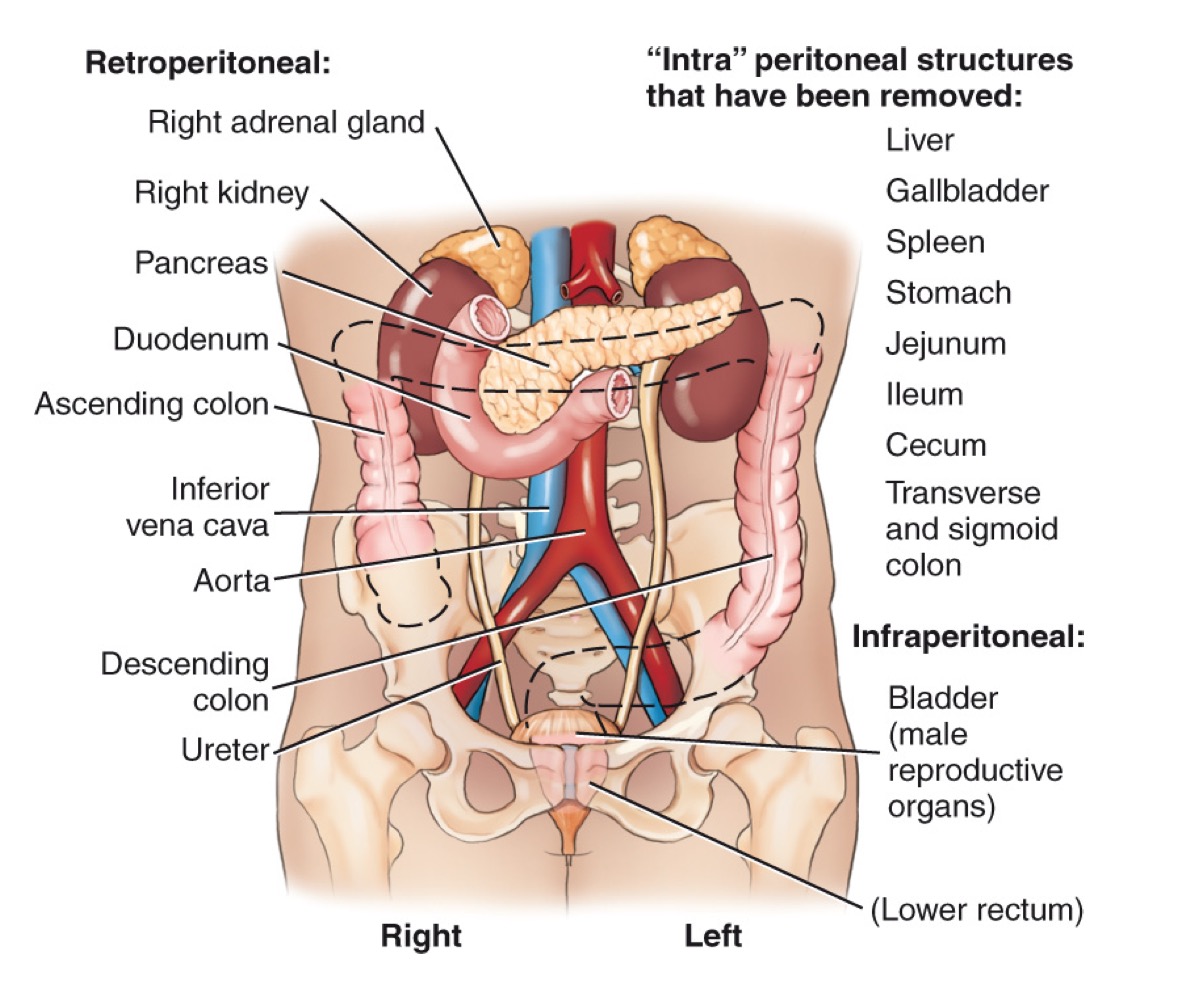
KUB (Kidney-Ureter-Bladder)
A radiographic view of the abdomen used to evaluate abdominal and urinary structures; may not show all structures, but helps visualize soft tissues and can indicate exposure quality (e.g., borders of psoas major muscles).
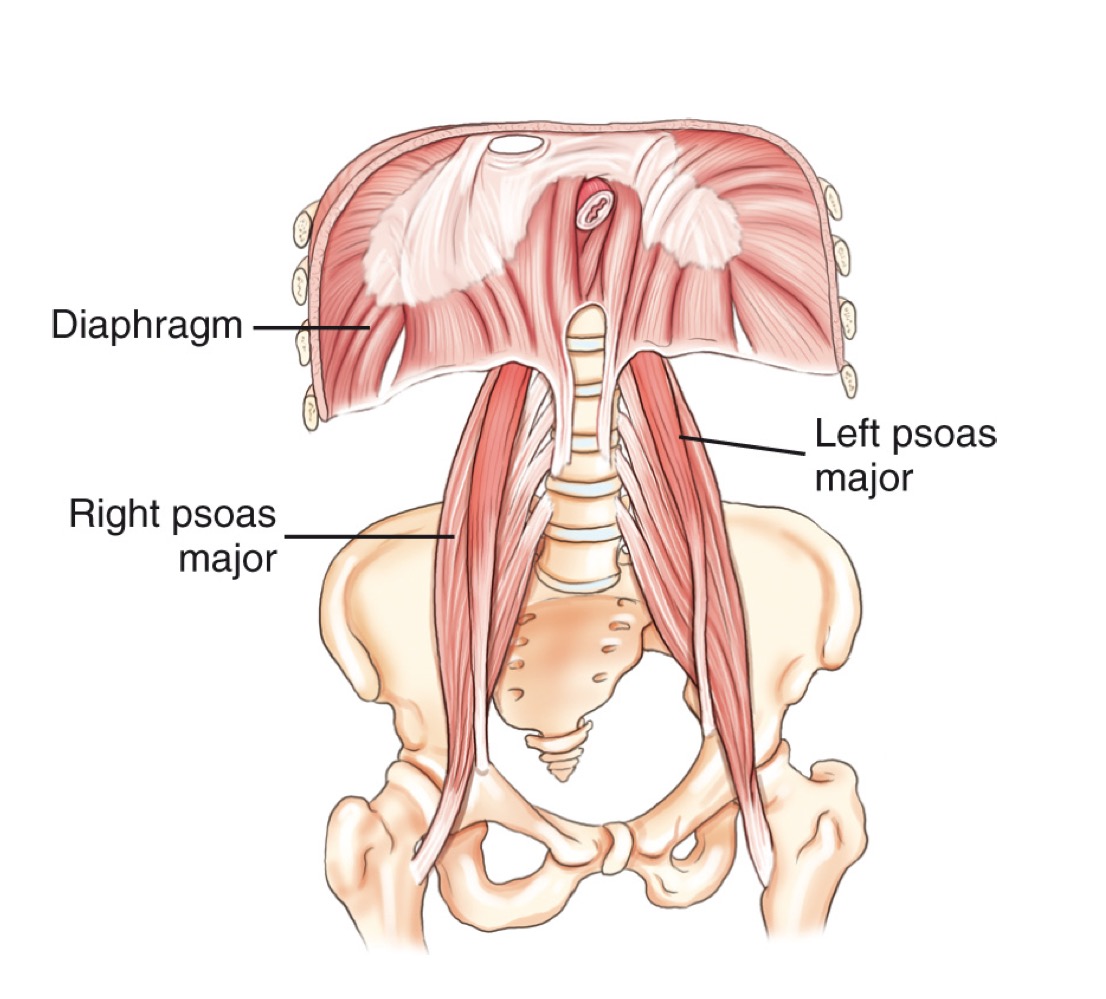
Psoas major
A large muscle of the posterior abdominal wall; its borders are visible on a properly exposed KUB and serve as a radiographic exposure indicator.
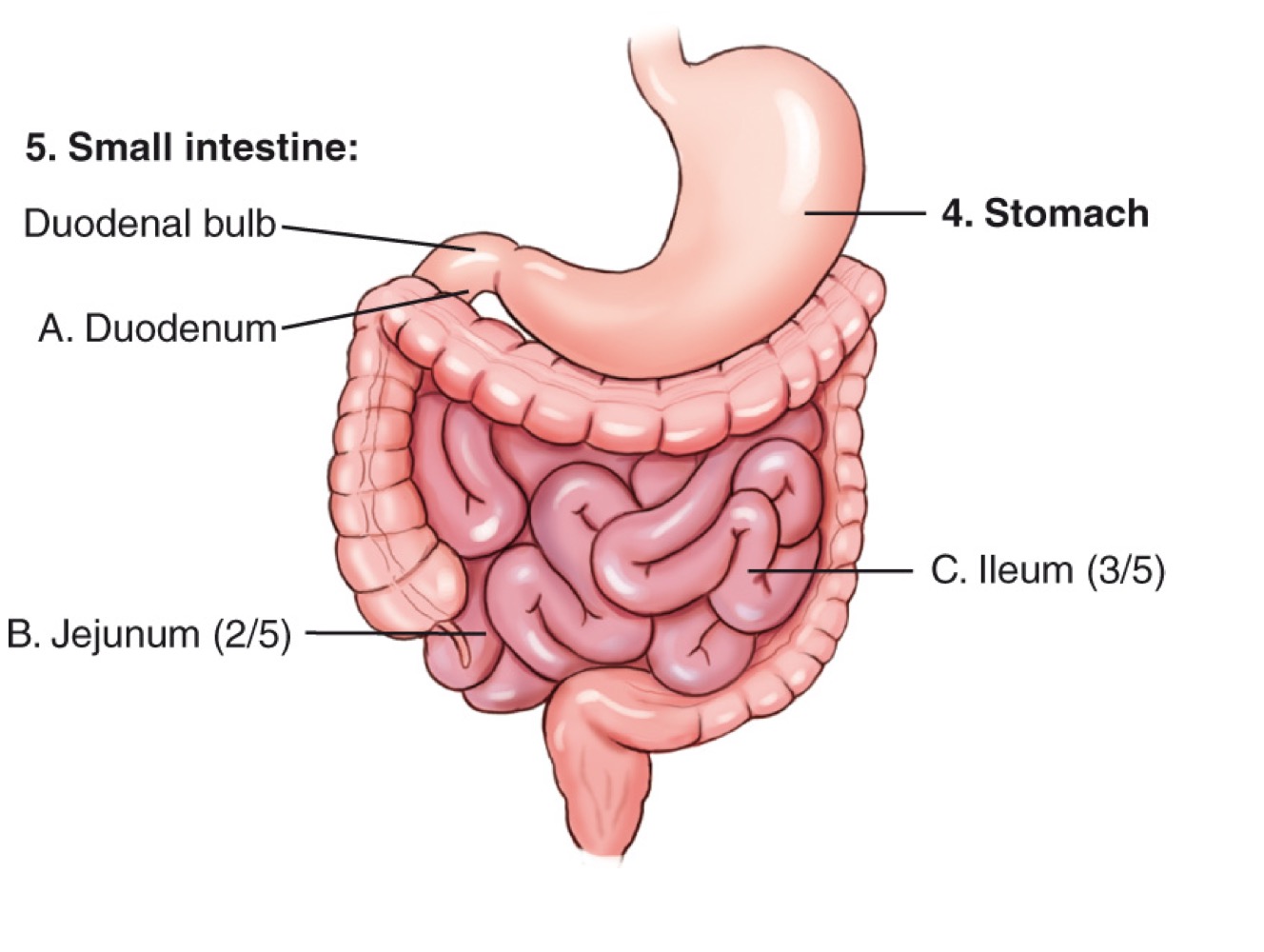
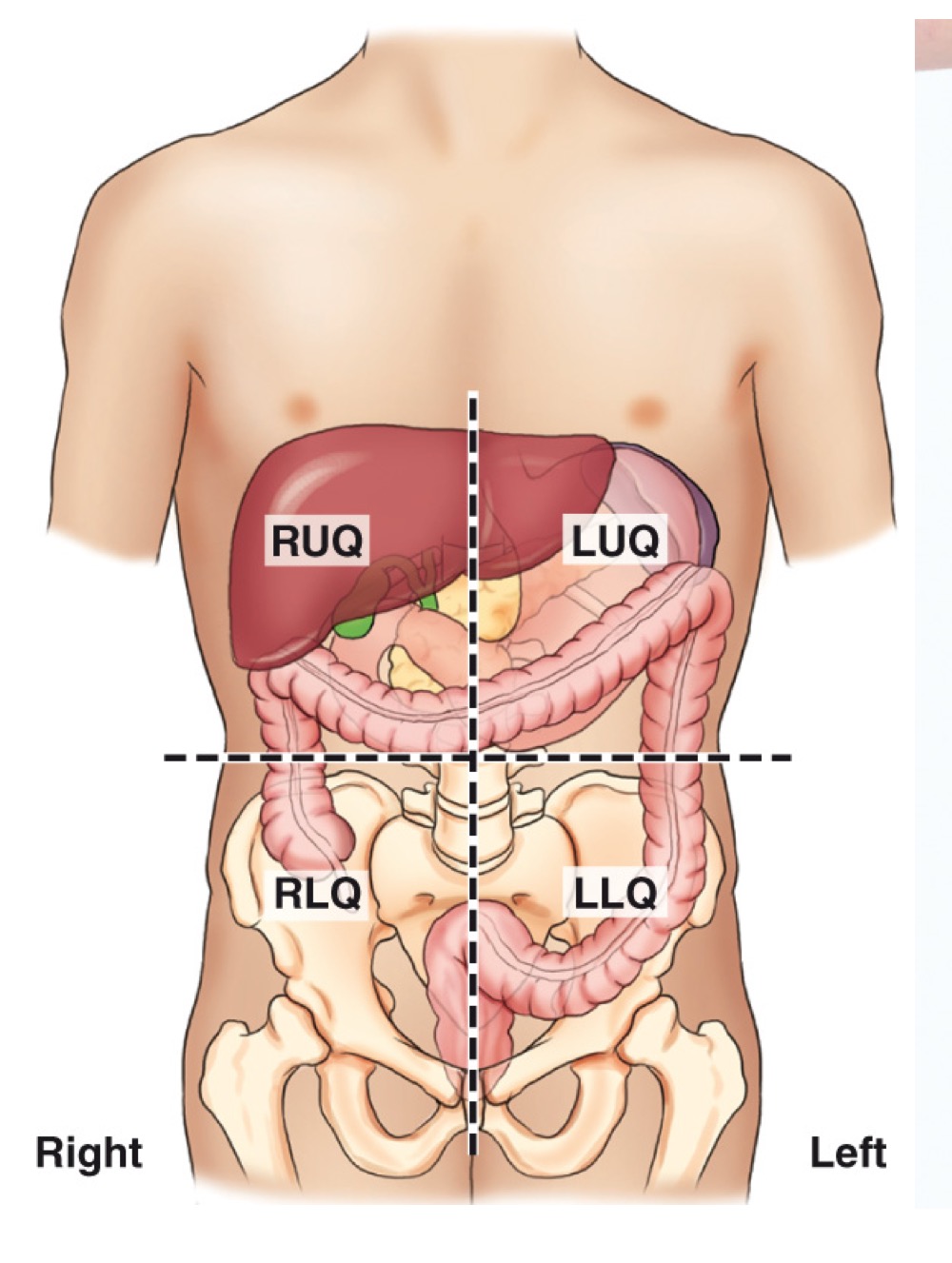
Stomach
An organ of the digestive tract located in the left upper quadrant (LUQ).
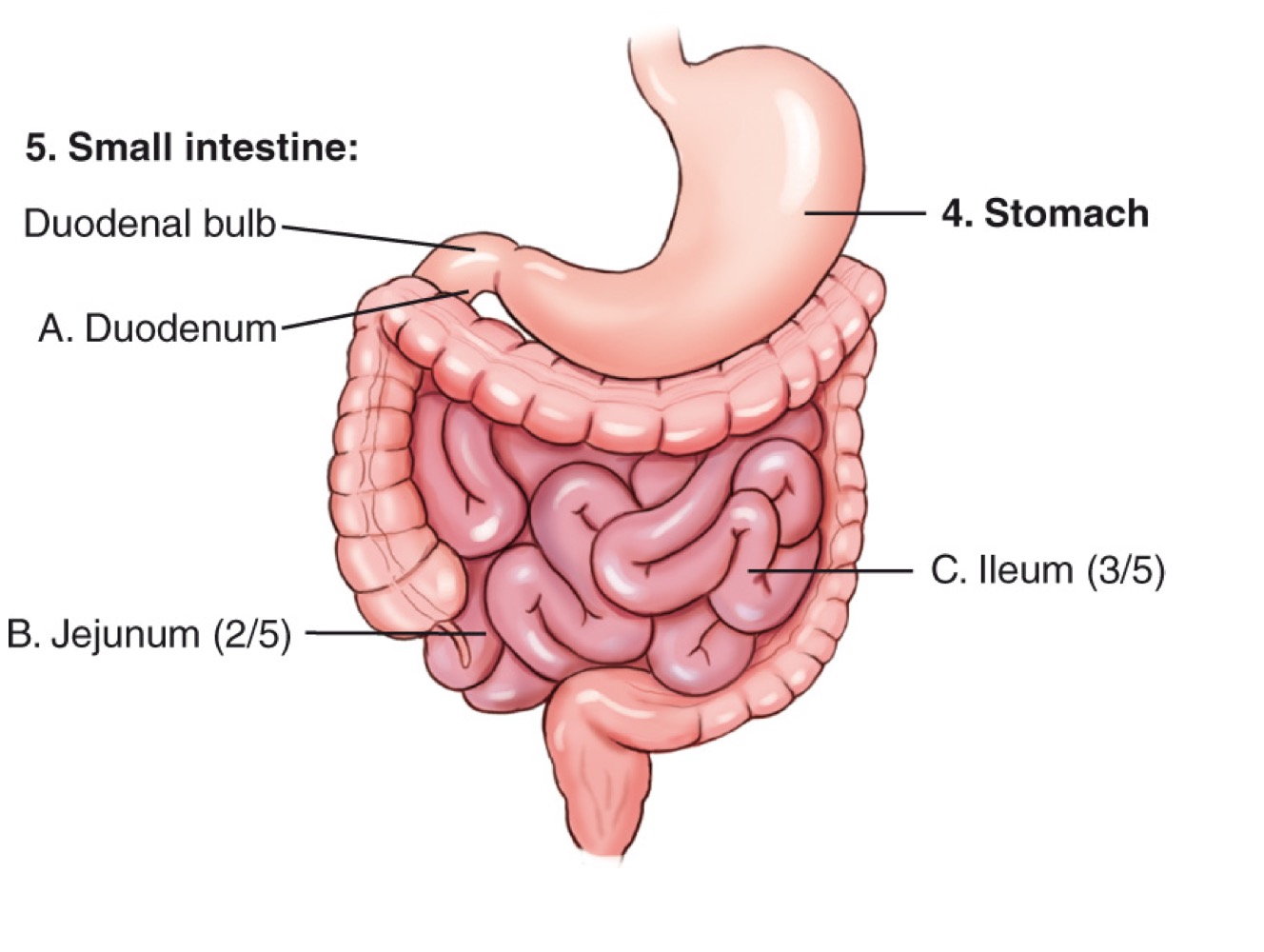
Duodenum
The first and shortest portion of the small intestine; about 10 inches long and the widest part, receiving bile and pancreatic ducts.
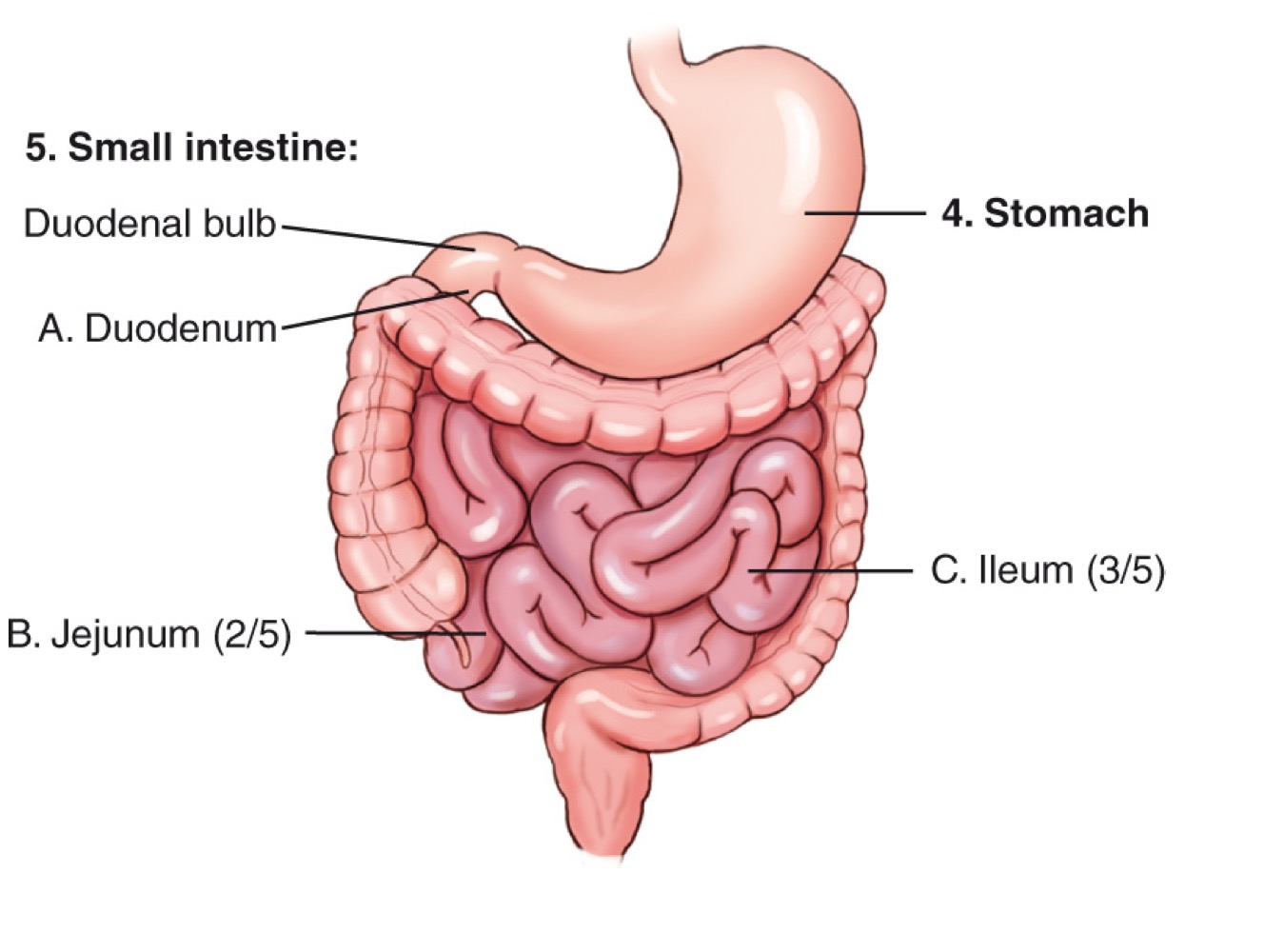
Jejunum
The middle portion of the small intestine; makes up about two-fifths of the small intestine and is a major site of nutrient absorption.
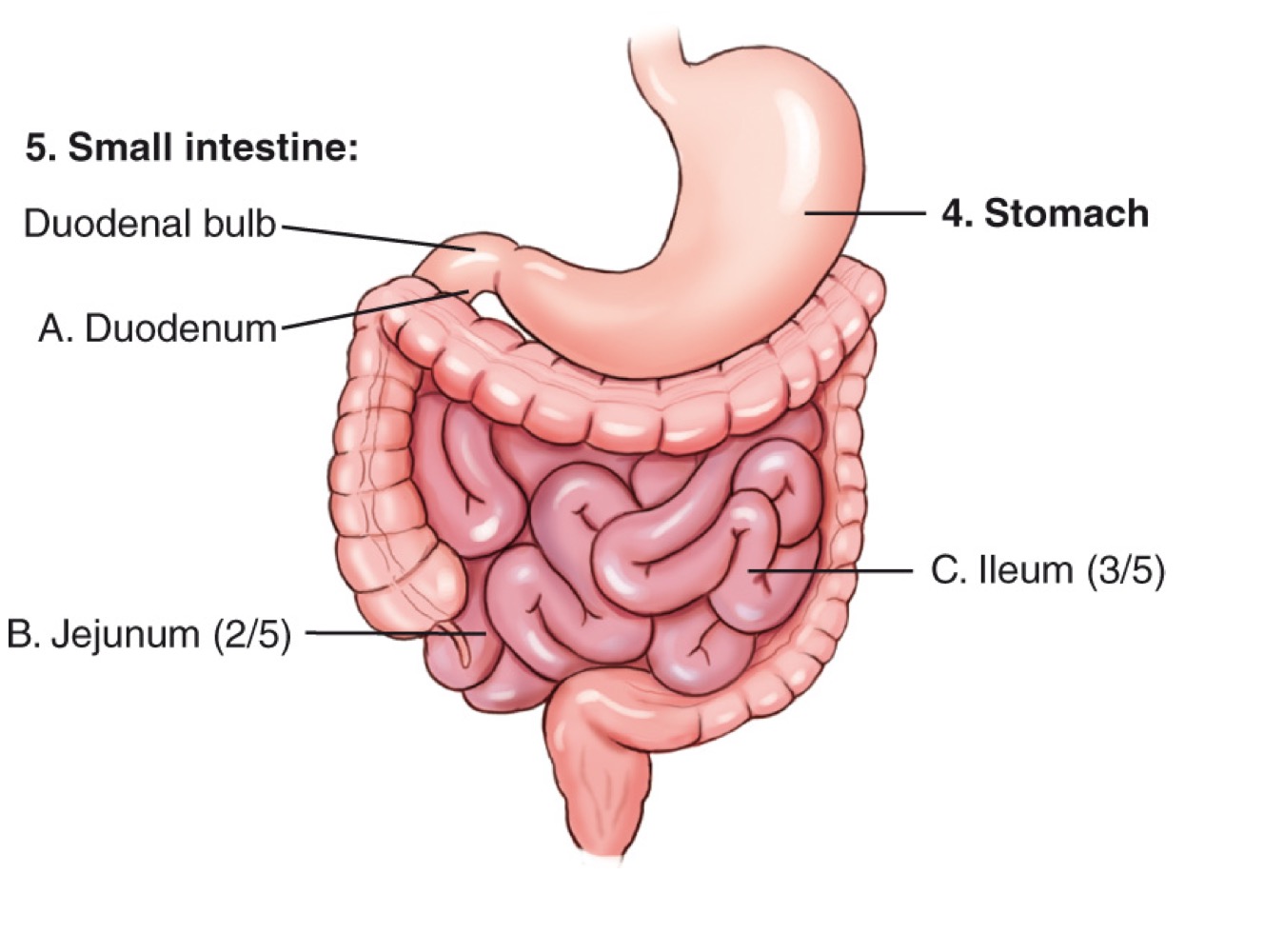
Ileum
The final portion of the small intestine; makes up about three-fifths of the small intestine and ends at the ileocecal valve.
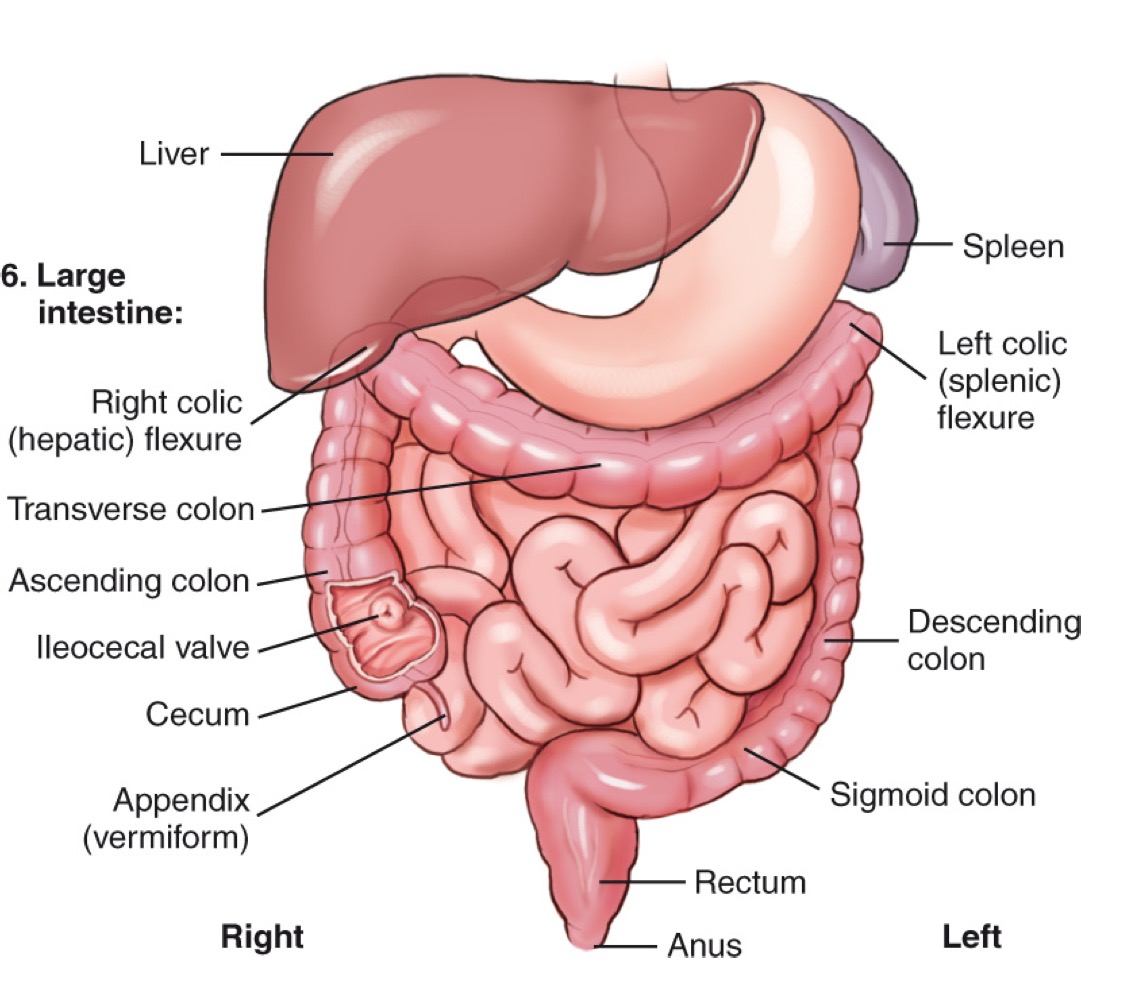
Ileocecal valve
The valve between the ileum and the cecum that regulates the flow of intestinal contents into the large intestine.
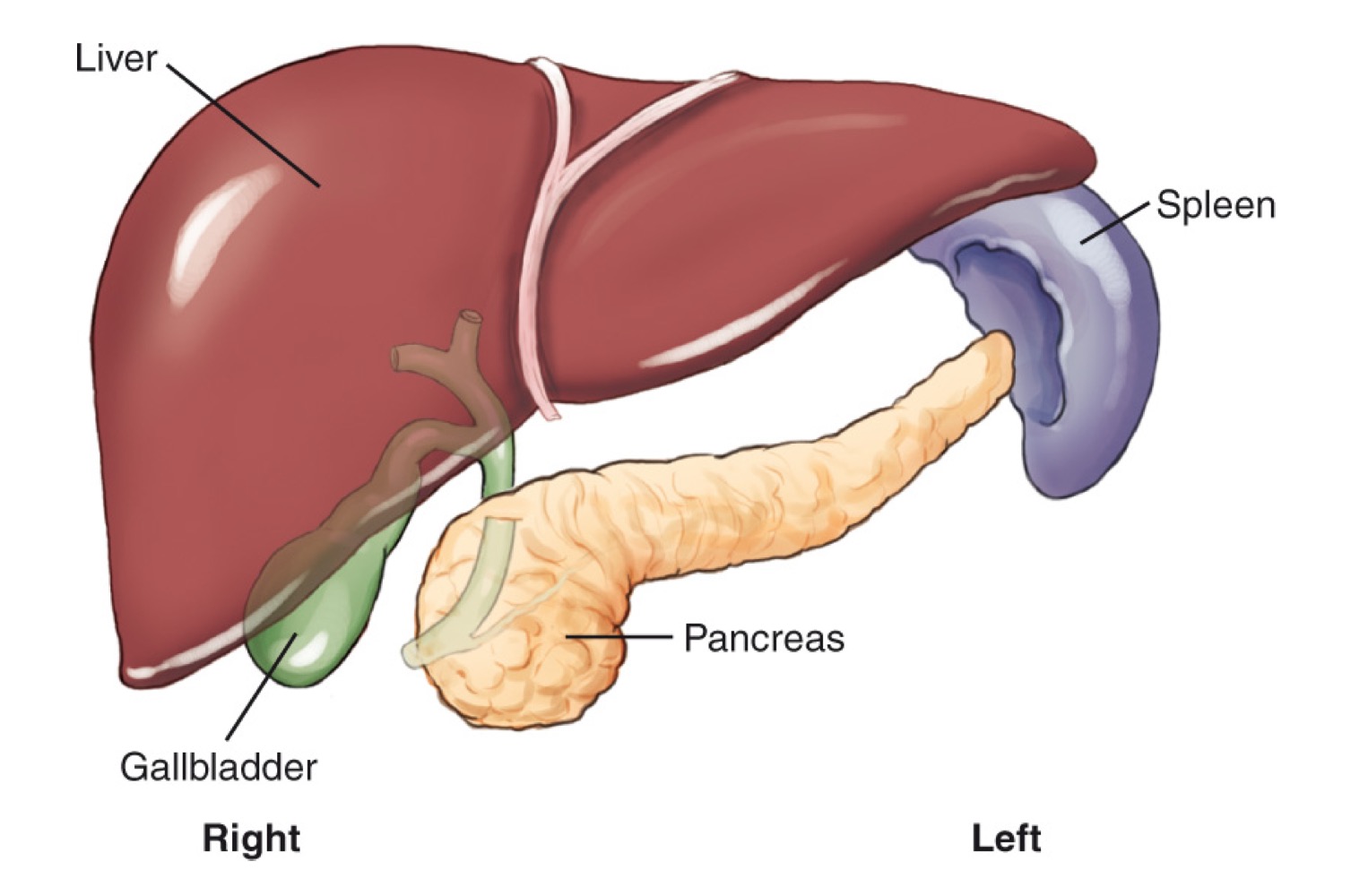
Liver
A large organ in the right upper quadrant (RUQ) that produces bile.
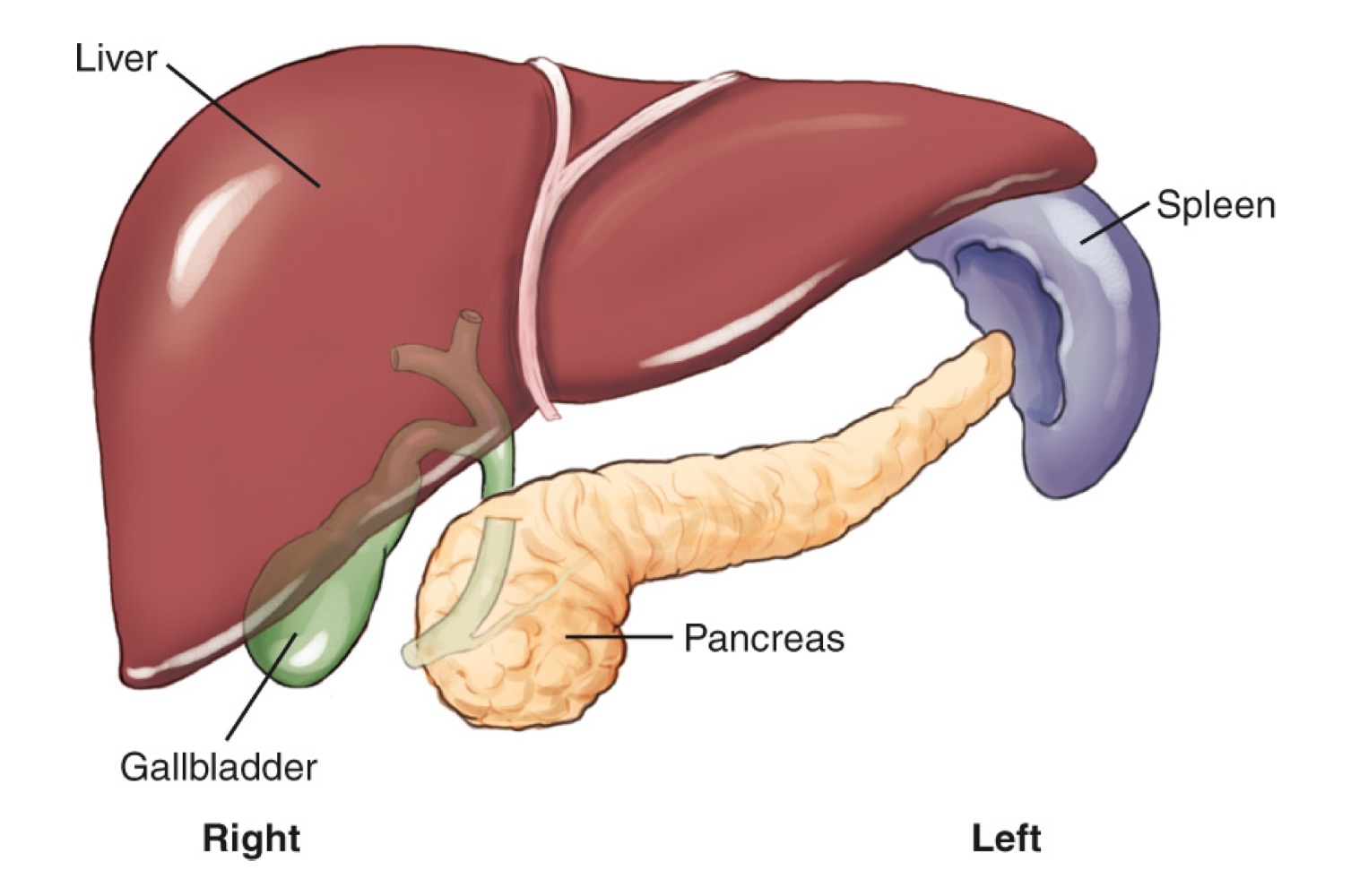
Gallbladder
A small organ located inferior to the liver that stores and concentrates bile and releases it as needed.
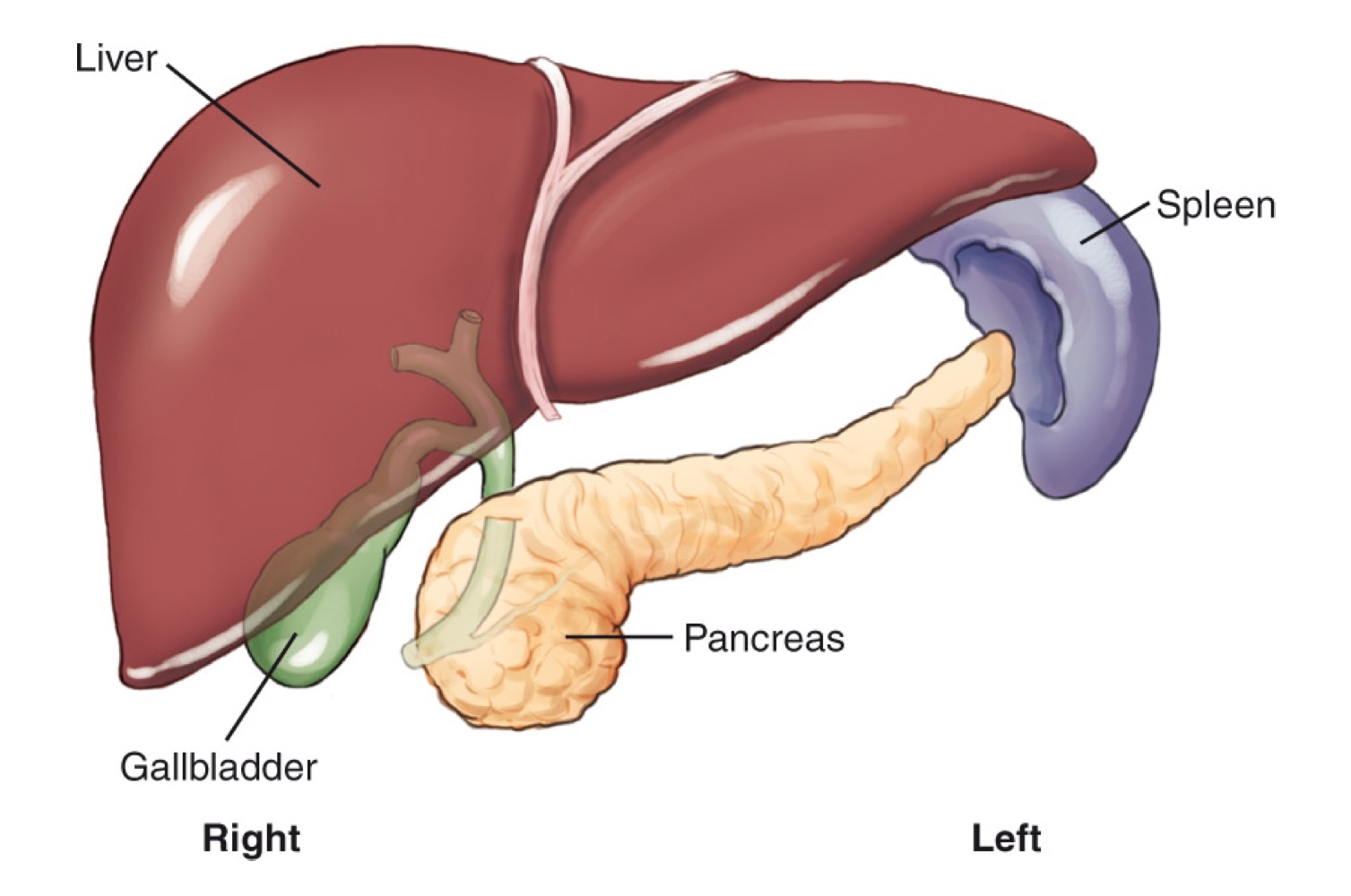
Pancreas
A retroperitoneal gland located posterior to the stomach; produces pancreatic juices and insulin.
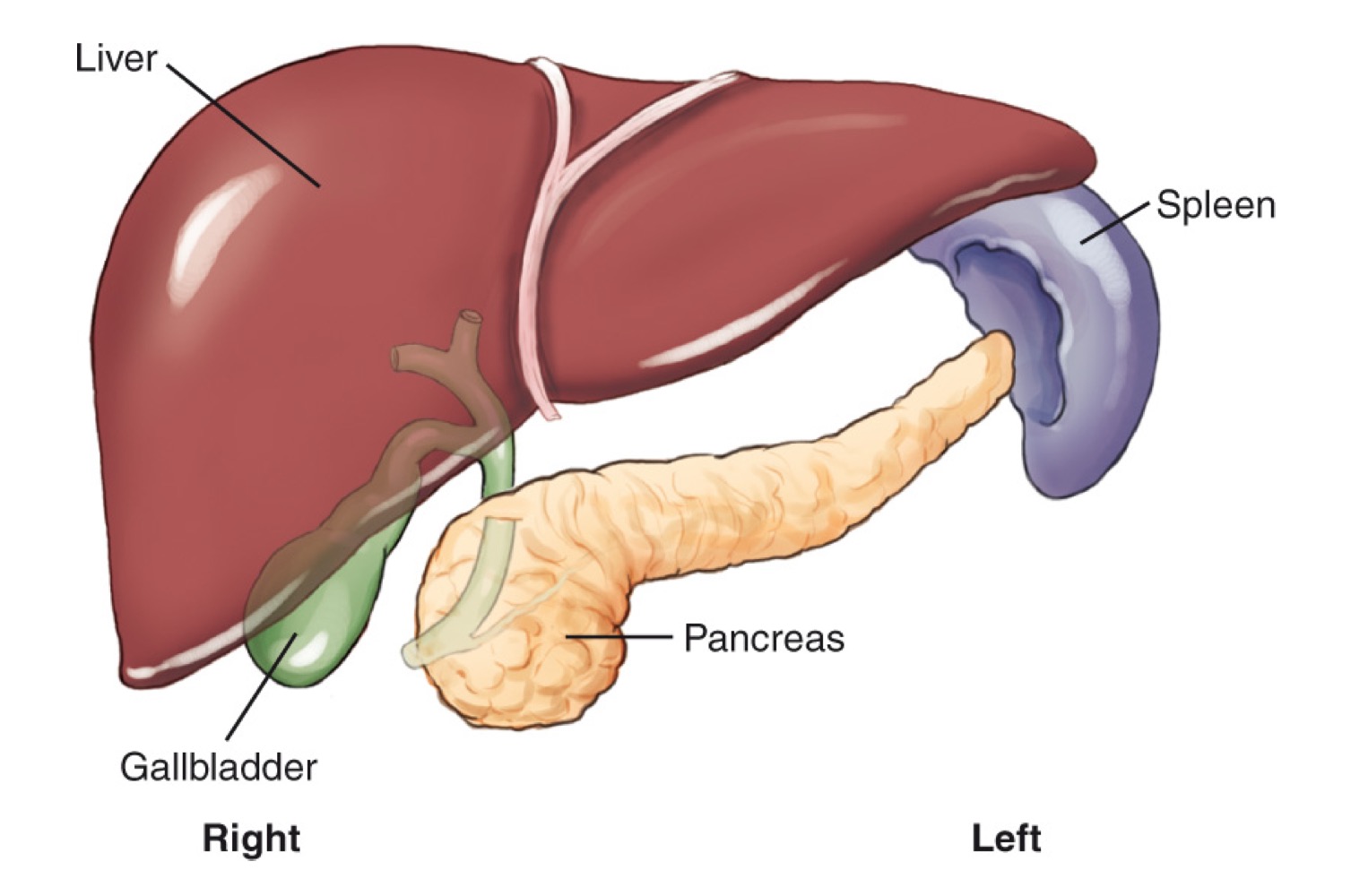
Spleen
A lymphatic-system organ located in the LUQ, posterior to the stomach.
Appendix (vermiform)
A narrow tube extending from the cecum; its exact function is not clearly known.
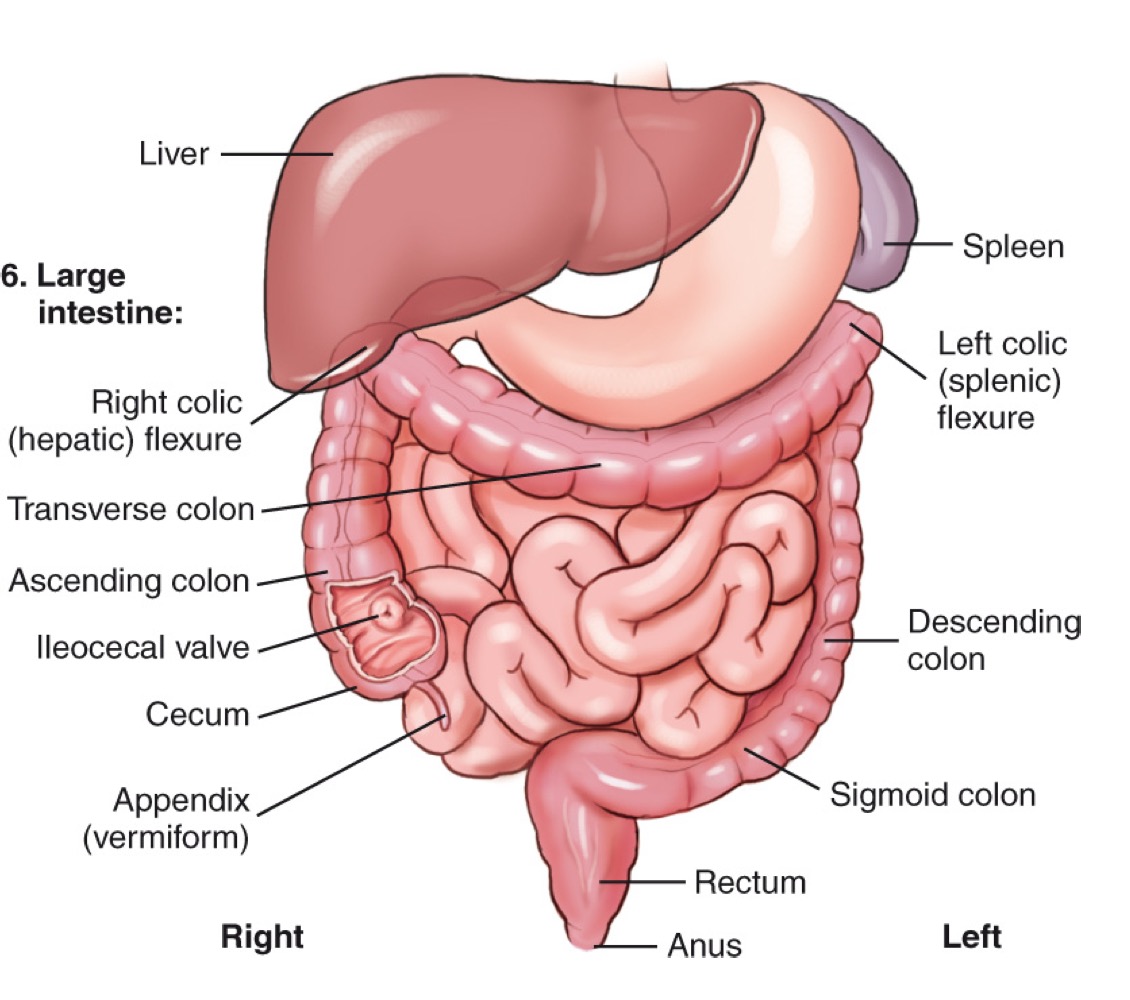
Cecum
The beginning section of the large intestine that connects to the ileum.
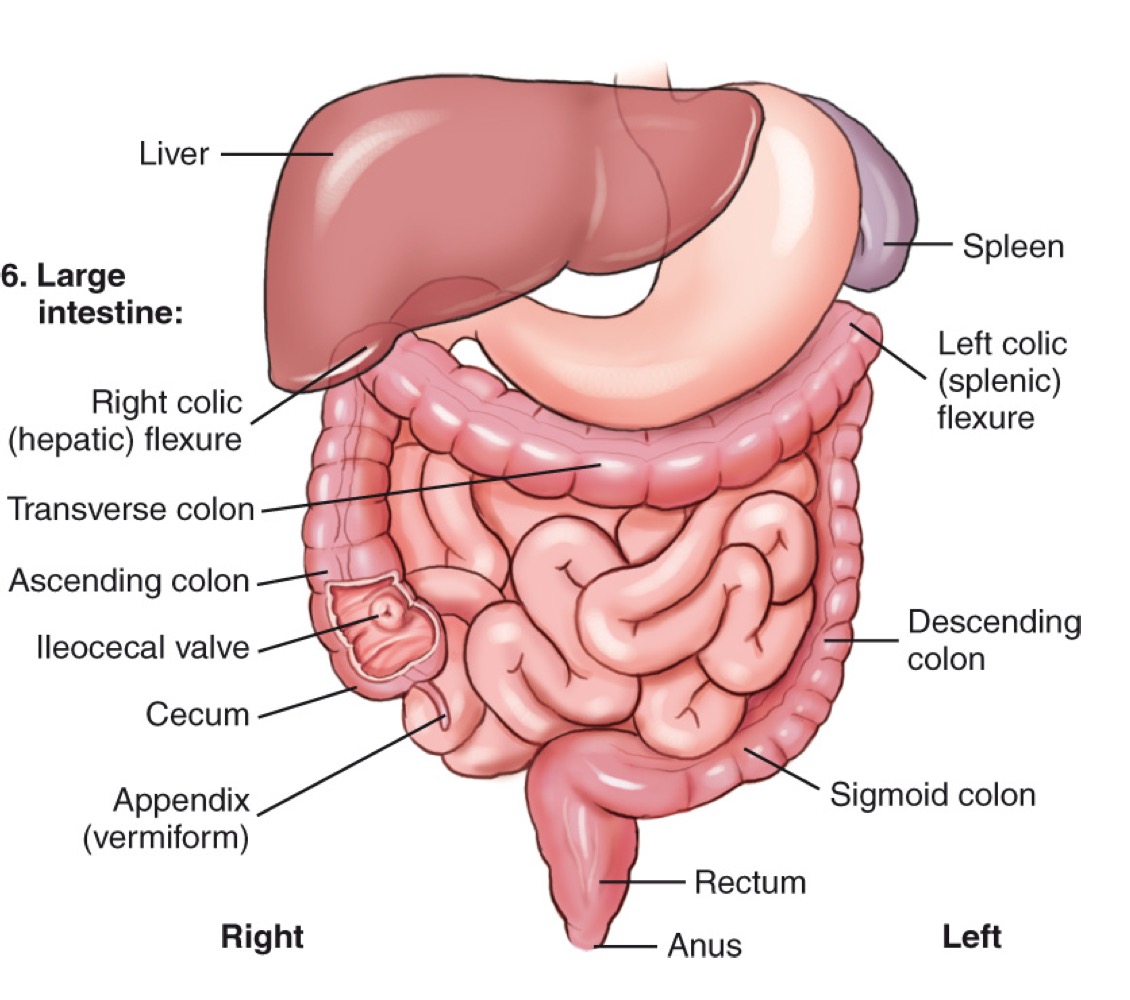
Ascending colon
The portion of the large intestine that travels upward on the right side of the abdomen.
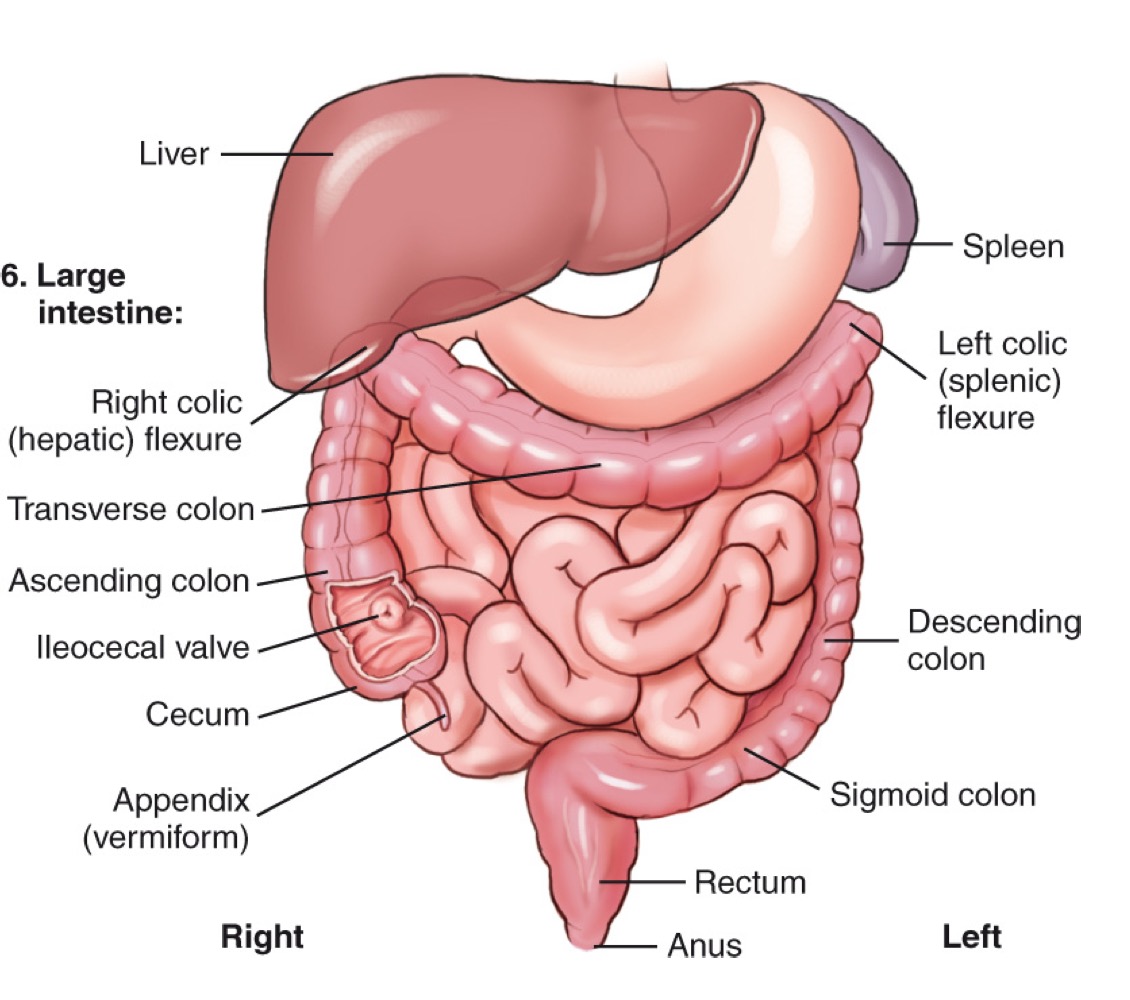
Transverse colon
The section of the large intestine that extends horizontally across the abdomen.
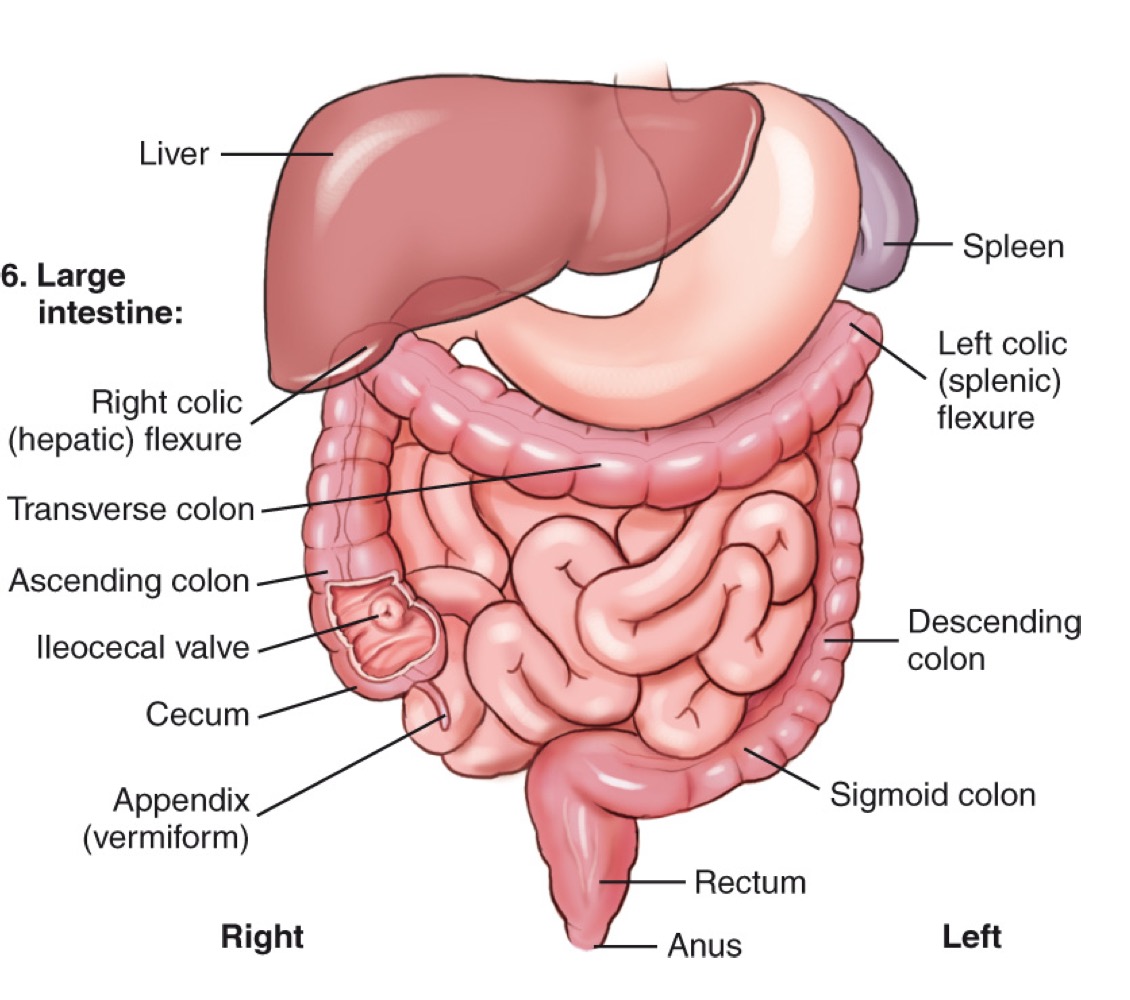
Descending colon
The portion of the large intestine that travels downward on the left side.
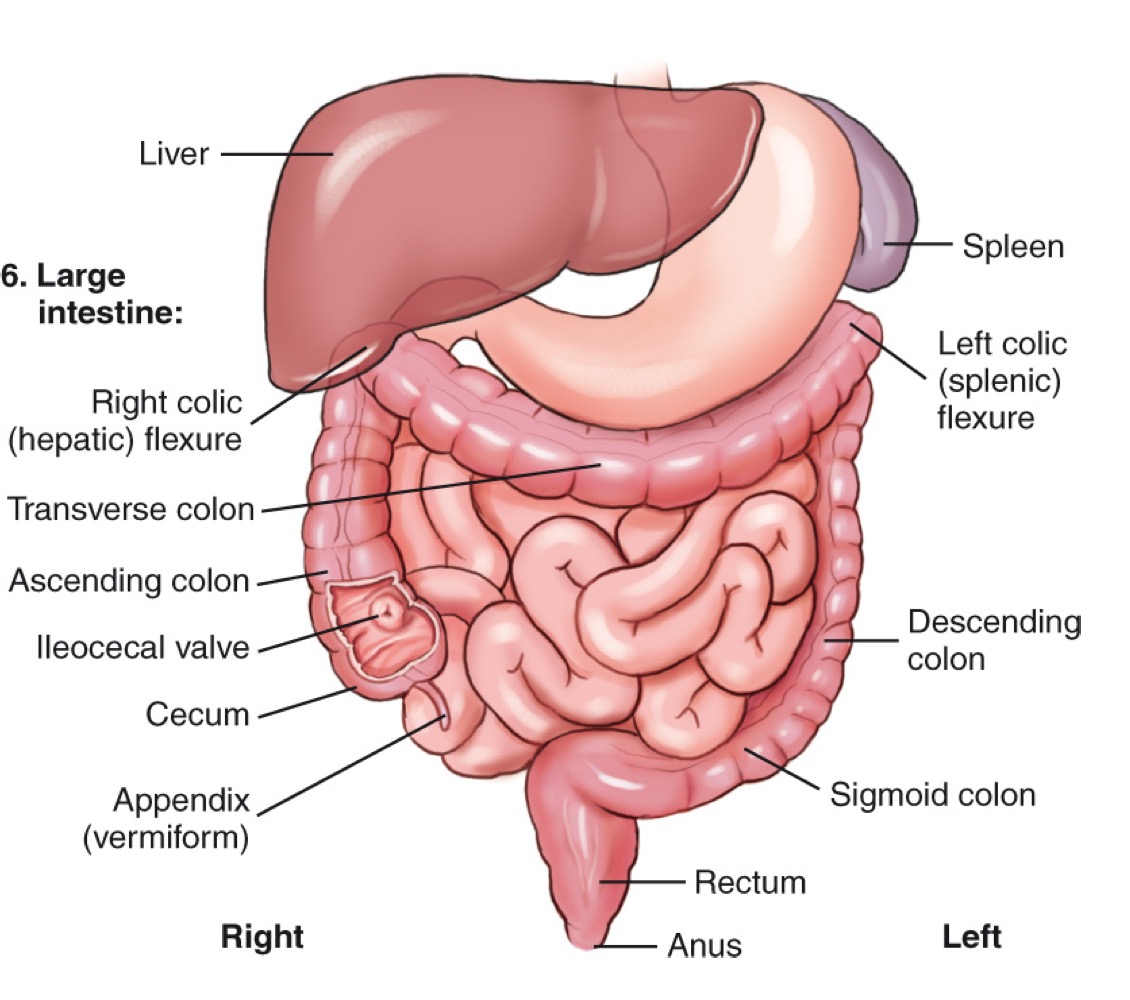
Sigmoid colon
The S-shaped part of the large intestine leading to the rectum.
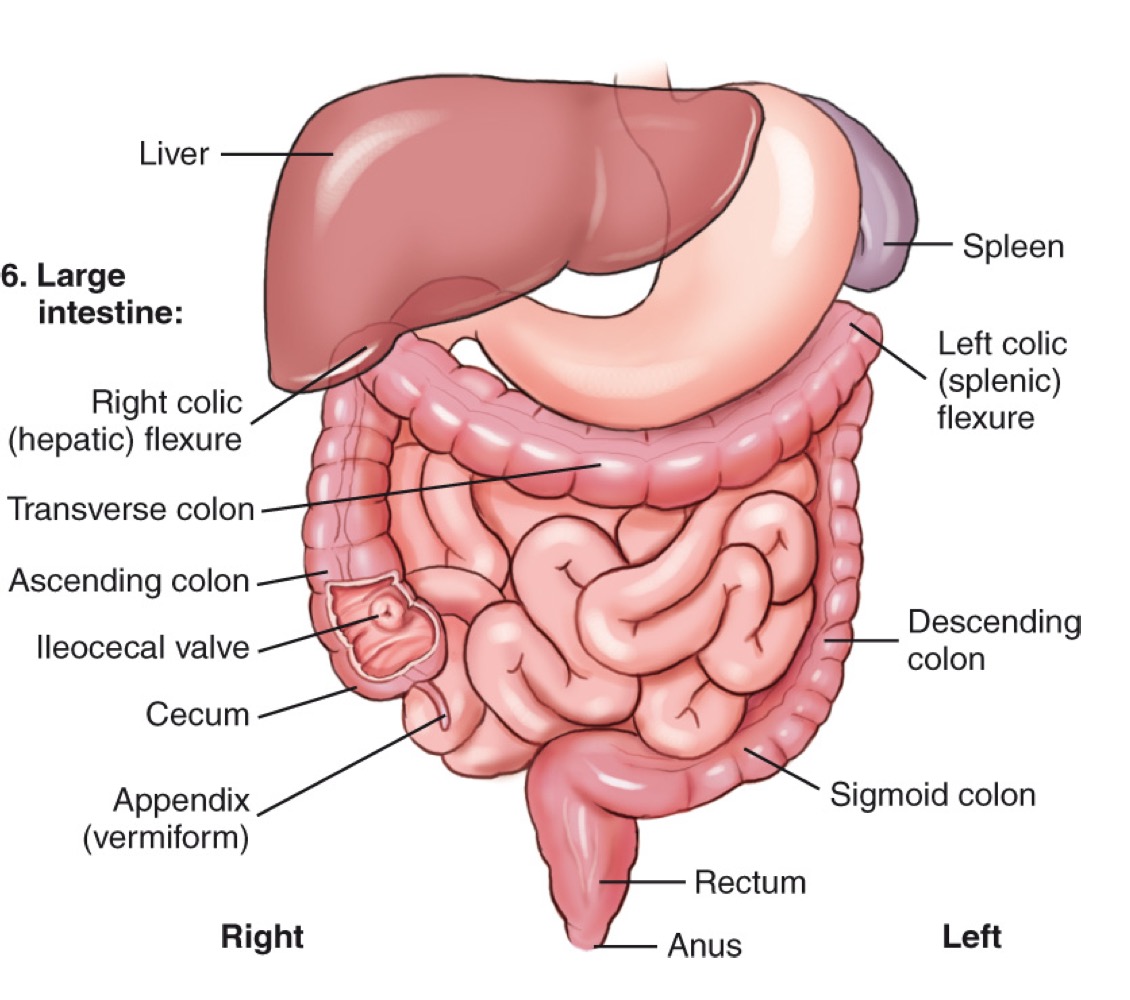
Rectum
The final section of the large intestine that ends at the anal canal.
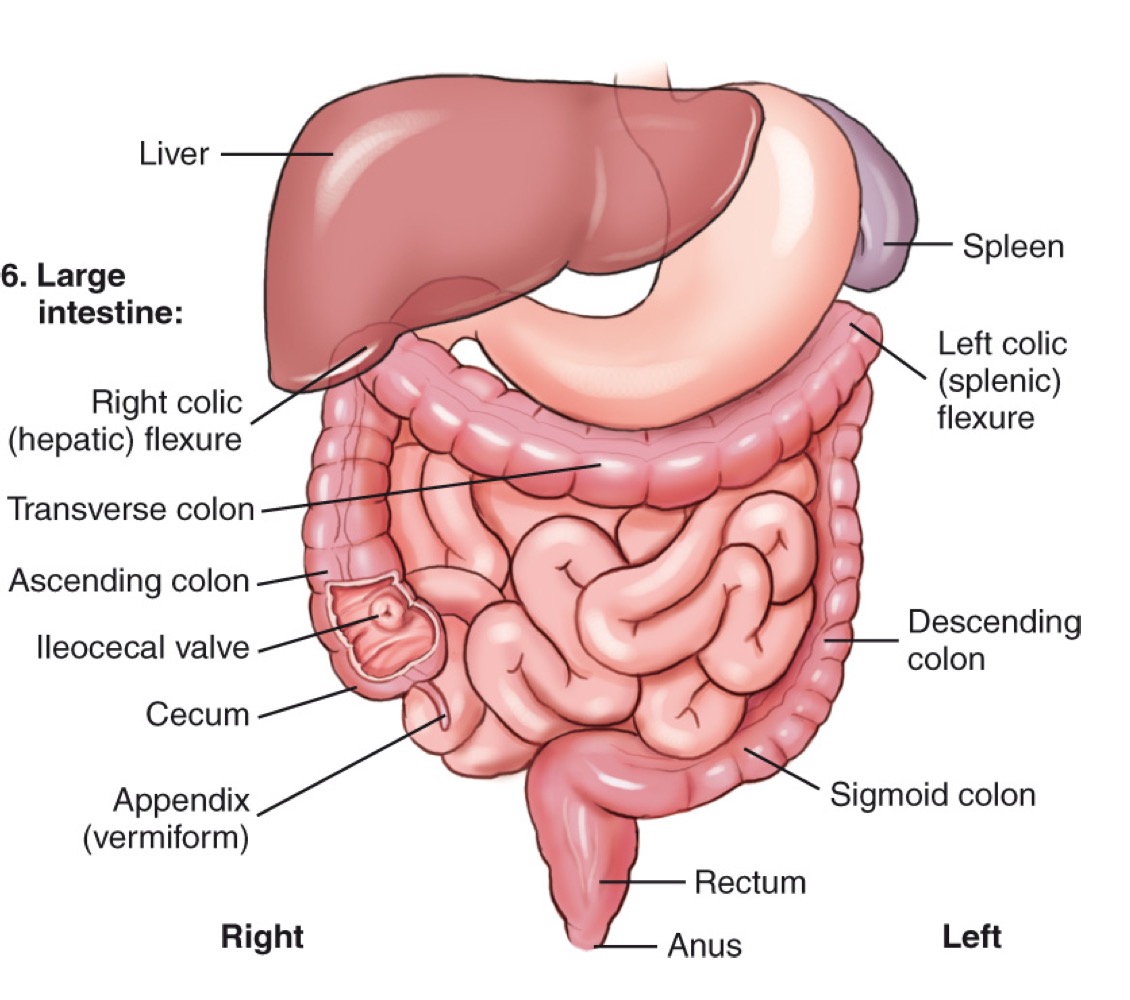
Right colic (hepatic) flexure
The bend where the ascending colon meets the transverse colon on the right side.
Left colic (splenic) flexure
The bend where the transverse colon meets the descending colon near the spleen.
Abdominal quadrants
Four regions (RUQ, LUQ, RLQ, LLQ) used to localize organs and pathology within the abdomen.
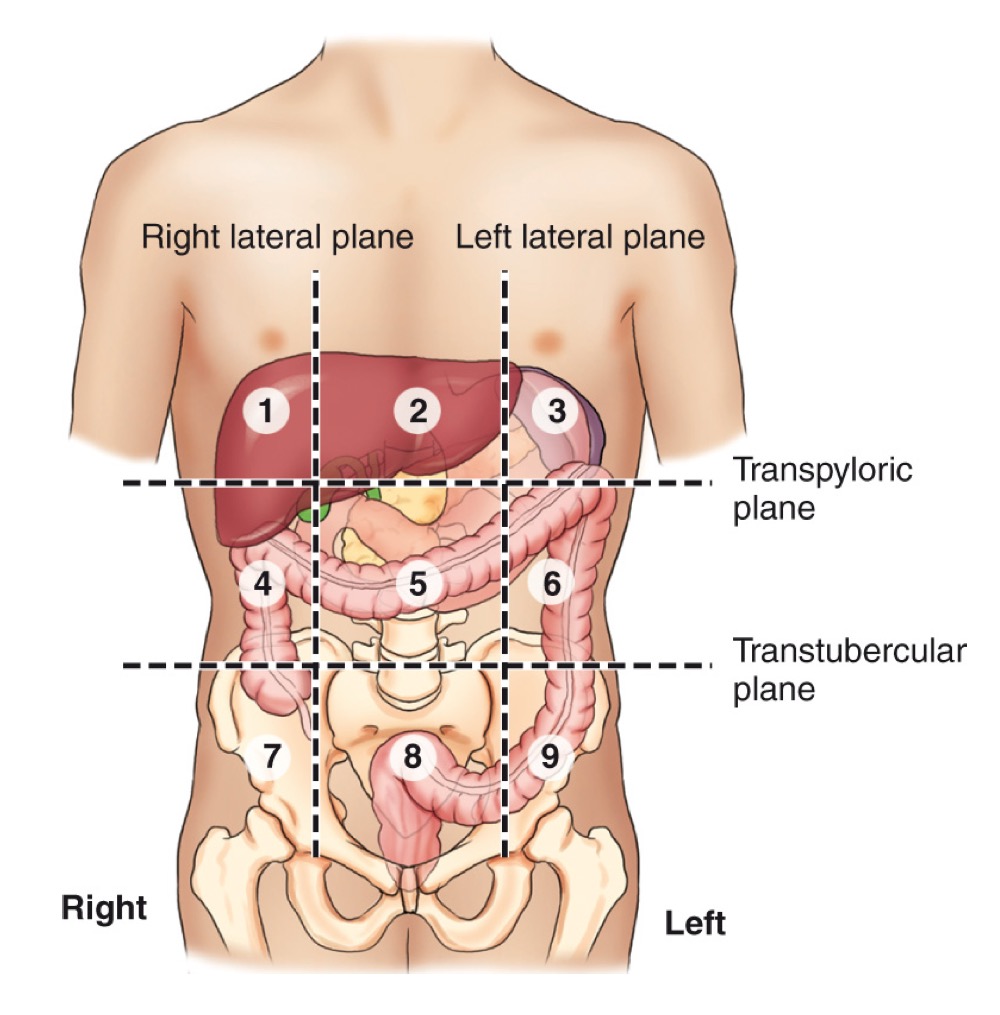
Nine abdominal regions
A grid of regions: Right hypochondriac, Epigastric, Left hypochondriac, Right lumbar, Umbilical, Left lumbar, Right iliac (inguinal), Hypogastric, Left iliac (inguinal).
Xiphoid process
The lower end of the sternum; approximately at the T9–T10 level.
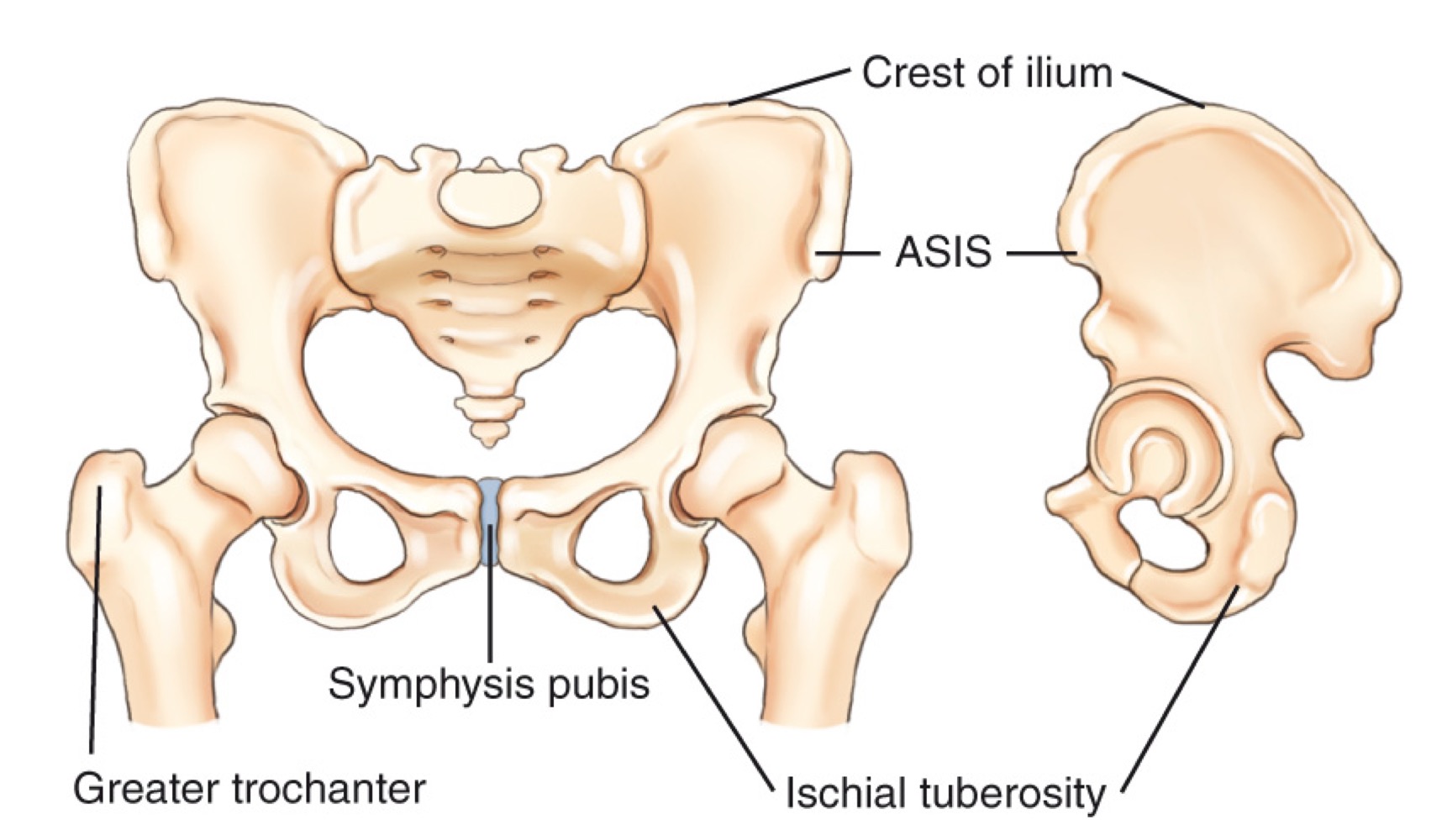
ASIS (anterior superior iliac spine)
A prominent bony landmark on the front of the pelvis used for imaging positioning and anatomy references.
Greater trochanter
A large prominence on the upper femur; a key bony landmark for imaging and level determination.
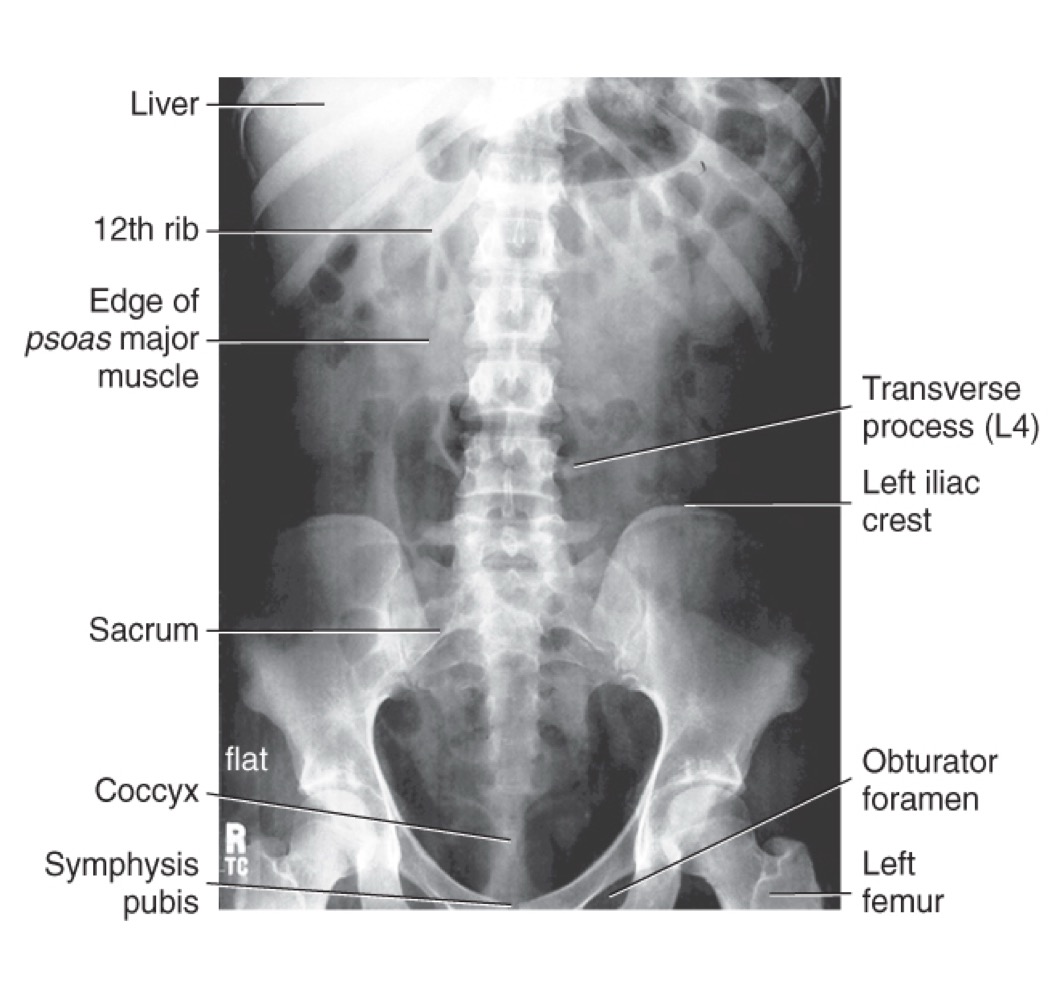
Inferior costal margin
The lower edge of the rib cage, typically around the 12th rib.
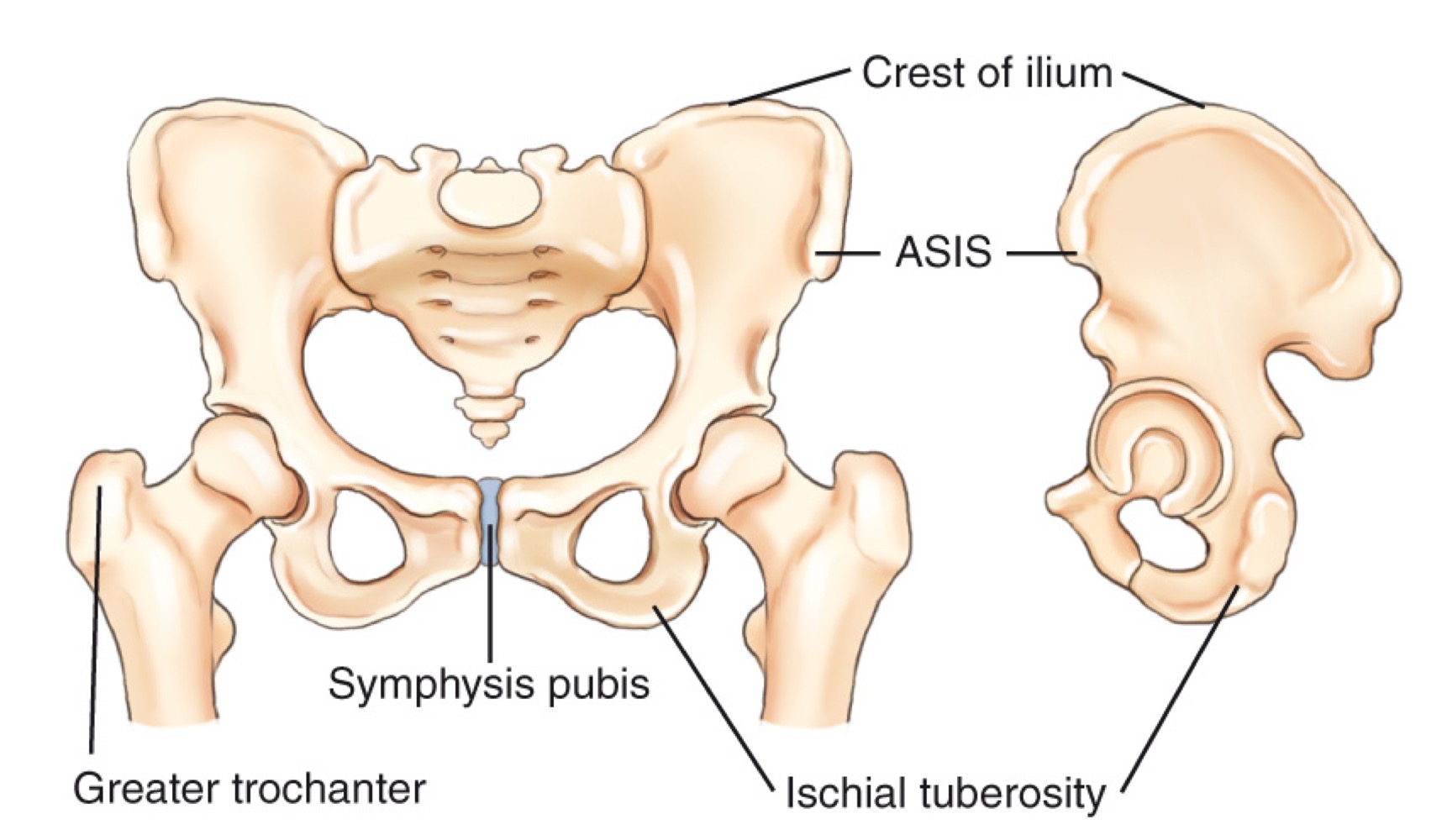
Symphysis pubis
The cartilaginous joint at the front of the pelvis where the two pubic bones meet.
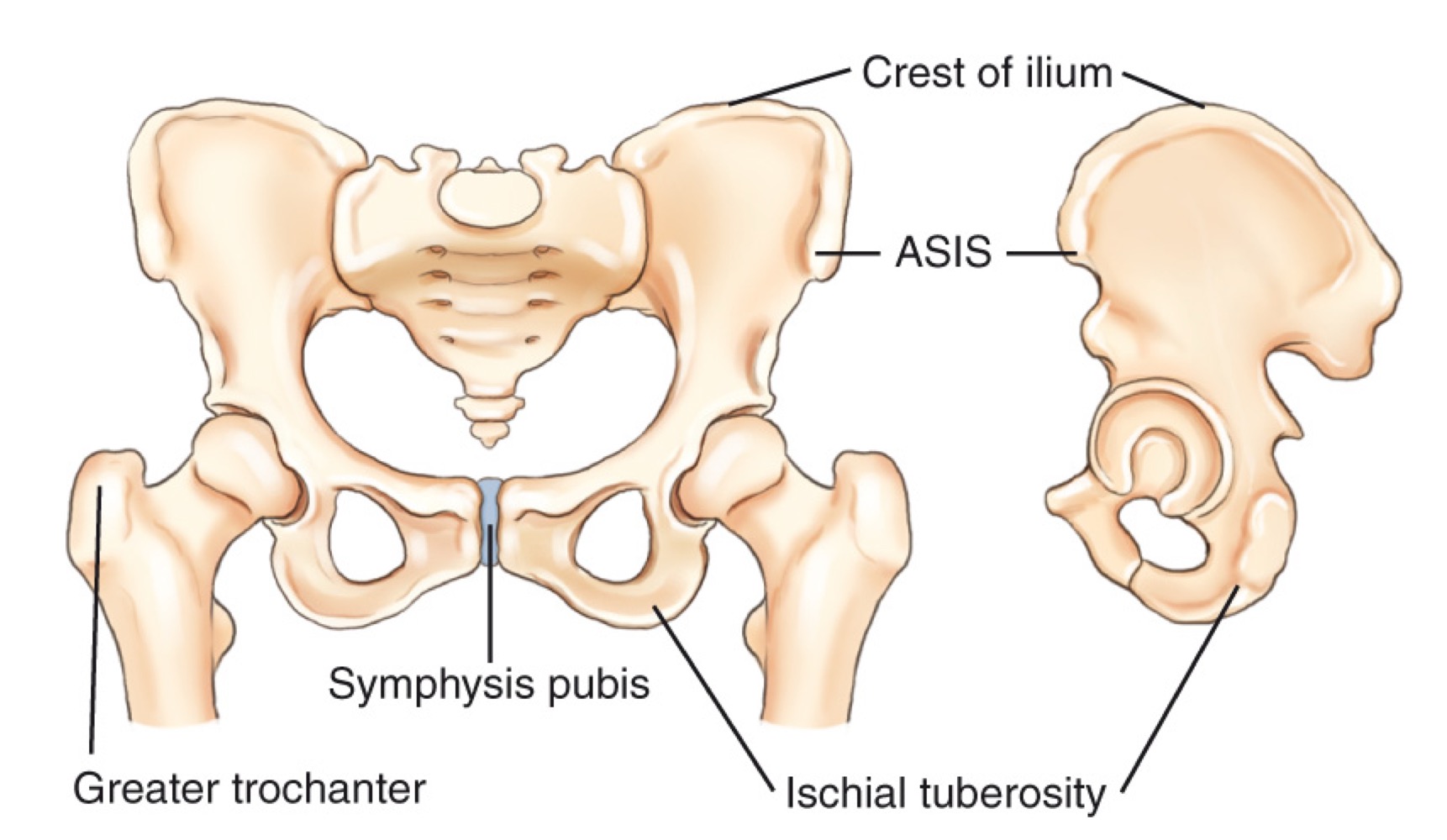
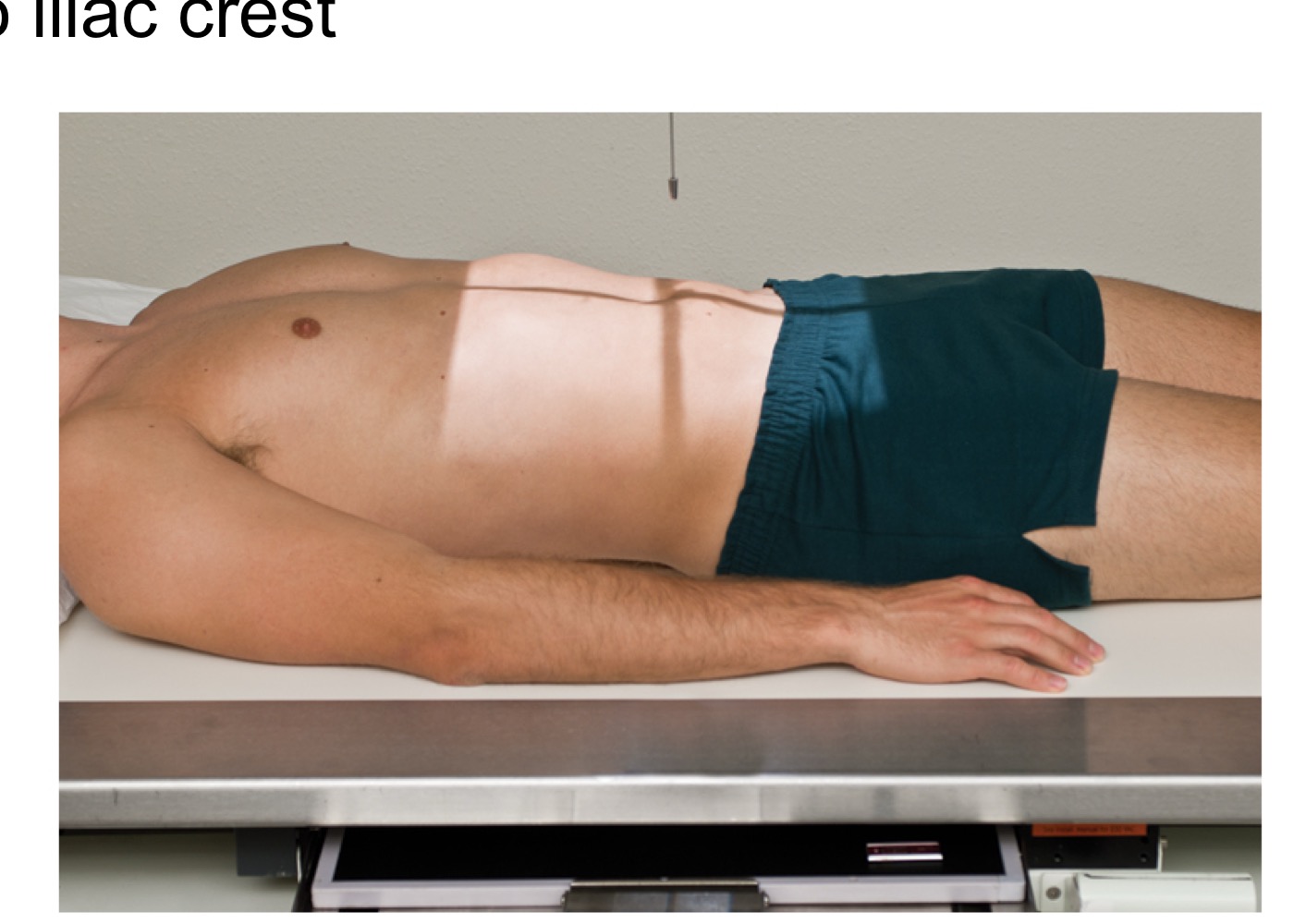
Iliac crest
The superior border of the pelvis; a landmark used to estimate imaging levels (e.g., around L4–L5).
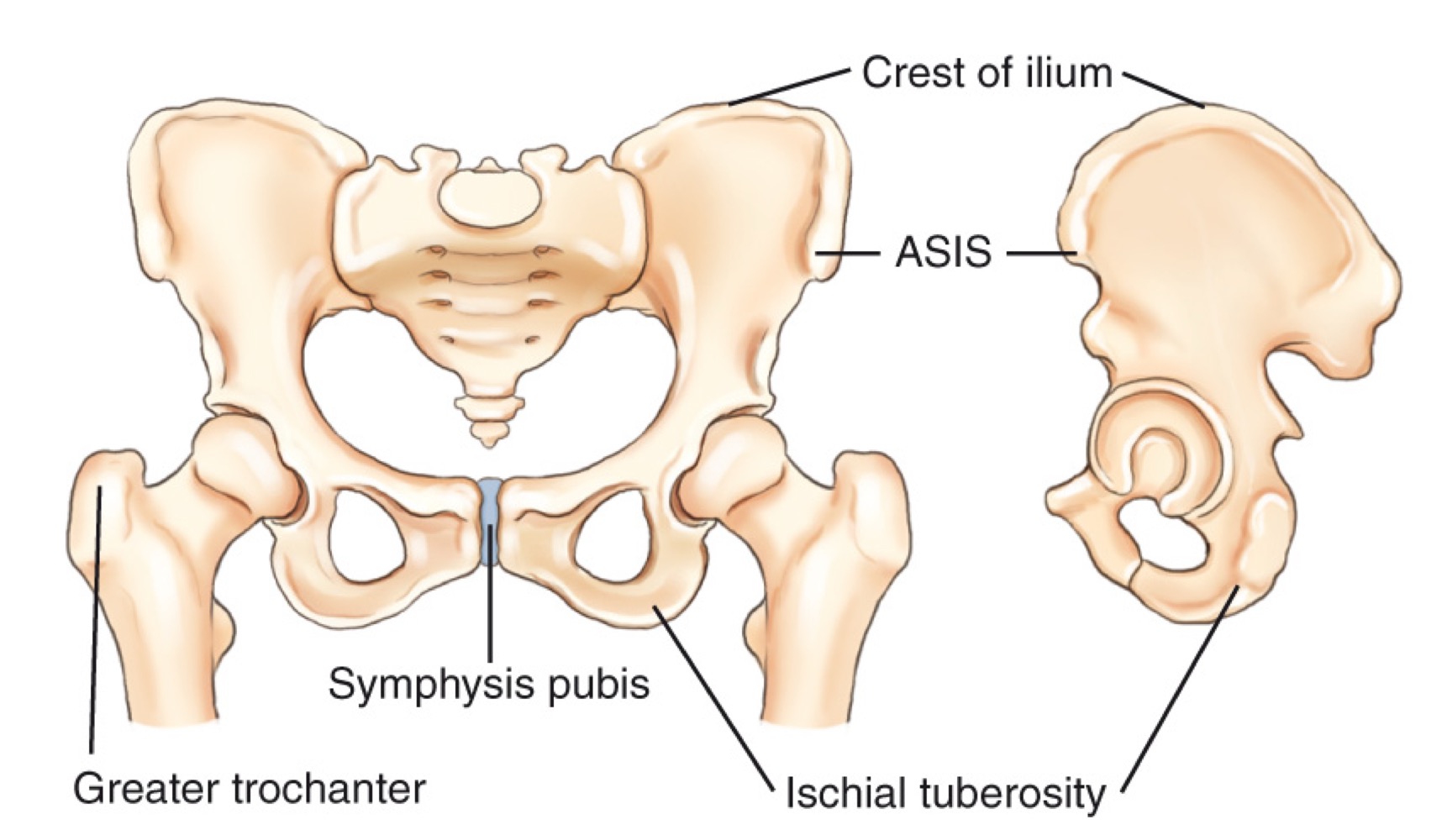
Ischial tuberosity
The sit bones at the lower, posterior aspect of the pelvis.
AP supine abdomen (KUB)
Anteroposterior view of the abdomen with the patient lying on their back; used in routine abdominal imaging.