Protein folding and purification
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Hydrophobic effect
hydrophobic regions cluster together to minimise interactions with water - entropic effect
water molecules for H bonds only with themselves, not with hydrophobic molecules
adapted to reduce the size of the hydrophobic-water interface so fold into structures with nonpolar cores
Hydrogen bonding
electrostatic attraction between lone pair of electrons on elec. neg. atom and H bonded to elec. neg. atom
drive formation of 2* structure with NH and CO backbone
drive formation of 3* structure with sidechains
Van der Waals interactions (ind. dip-dip)
random movement generates transient electric dipole
many weak interactions produce sig. cum. stability
facilitates dense packing of protein hydrophobic cores
Ionic interactions
oppositely charged a.a. sidechains held in proximity will form electrostatic interactions
Disulphide bonds
very strong covalent bond
not every sulphur forms disulphide bond, often many combinations but only one produces required structure
How can protein folding be aided?
once part of folded structure has formed, may increase likelihood of subsequent favourable interactions (cascade of lowest energy conformation)
chaperone proteins in cells increase likelihood of favourable interactions
leads to native (completely folded) structure
What are 3 properties of peptide bonds?
partial double bond character so planar with limited rotation
What is a residue?
Each amino acid unit in a polypeptide chain, sometimes what is left after a condensation reaction
What are the two terminus’ called in a polypeptide?
N (amino) and C (carboxyl)
From which terminus is the polypeptide named?
N to C
What is the charge of the N-terminus?
+ve
What is the charge of the C-terminus?
-ve
On average, how many amino acid residues are in each polypeptide chain?
50-2000 (any less it is just a peptide)
What is the average mass of an amino acid?
110 Da (gmol-1)
Which regions of the polypeptide are charged?
Ends, the backbone has no charge.
What is a Da?
1 Dalton → 1 g/mol
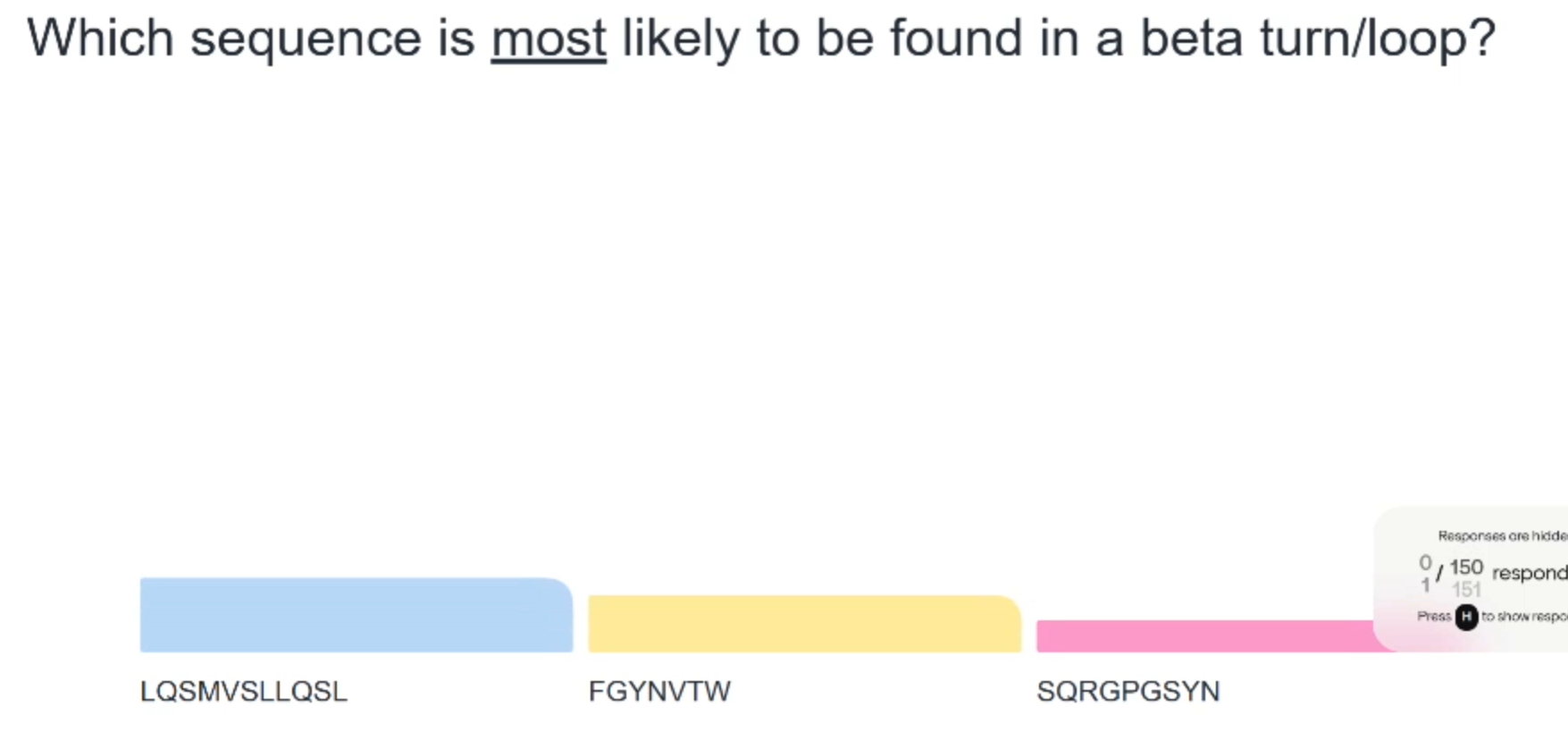
Pink as presence of glycine and proline makes beta turn more likely
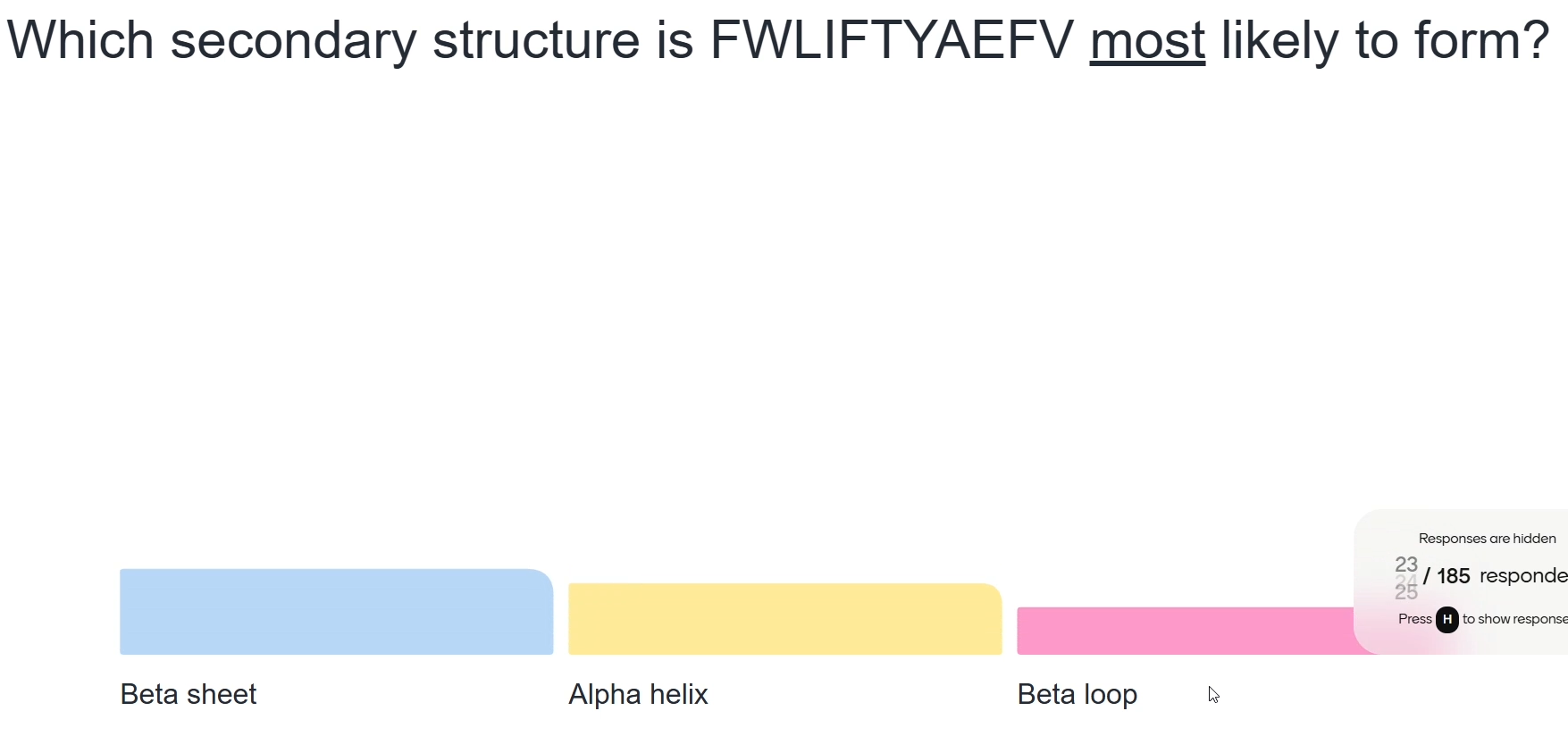
Beta sheet as amino acid present have large R groups (amino acids such as W,F,Y)
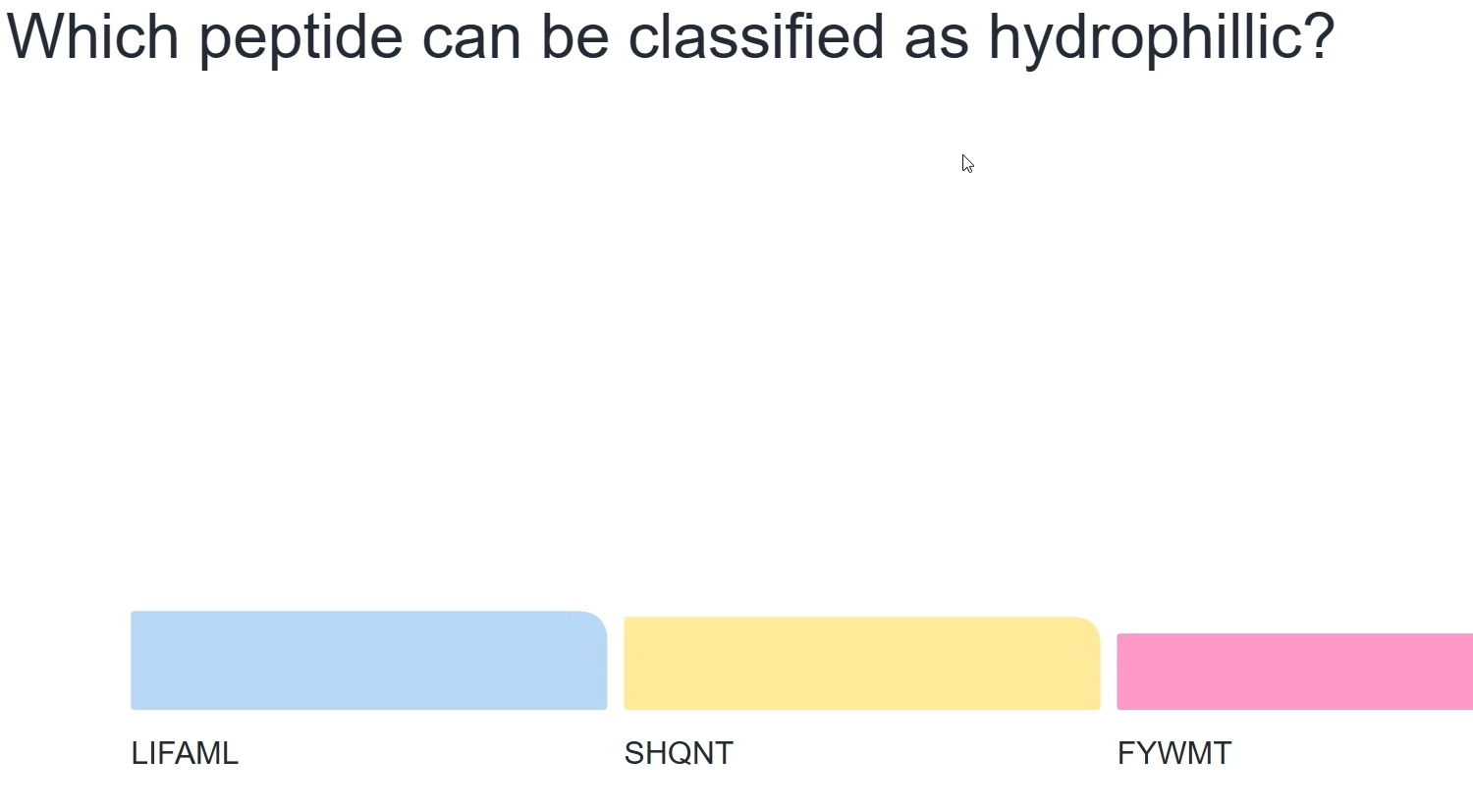
Yellow as these amino acids have polar sidechains (other two are mostly hydrophobic)
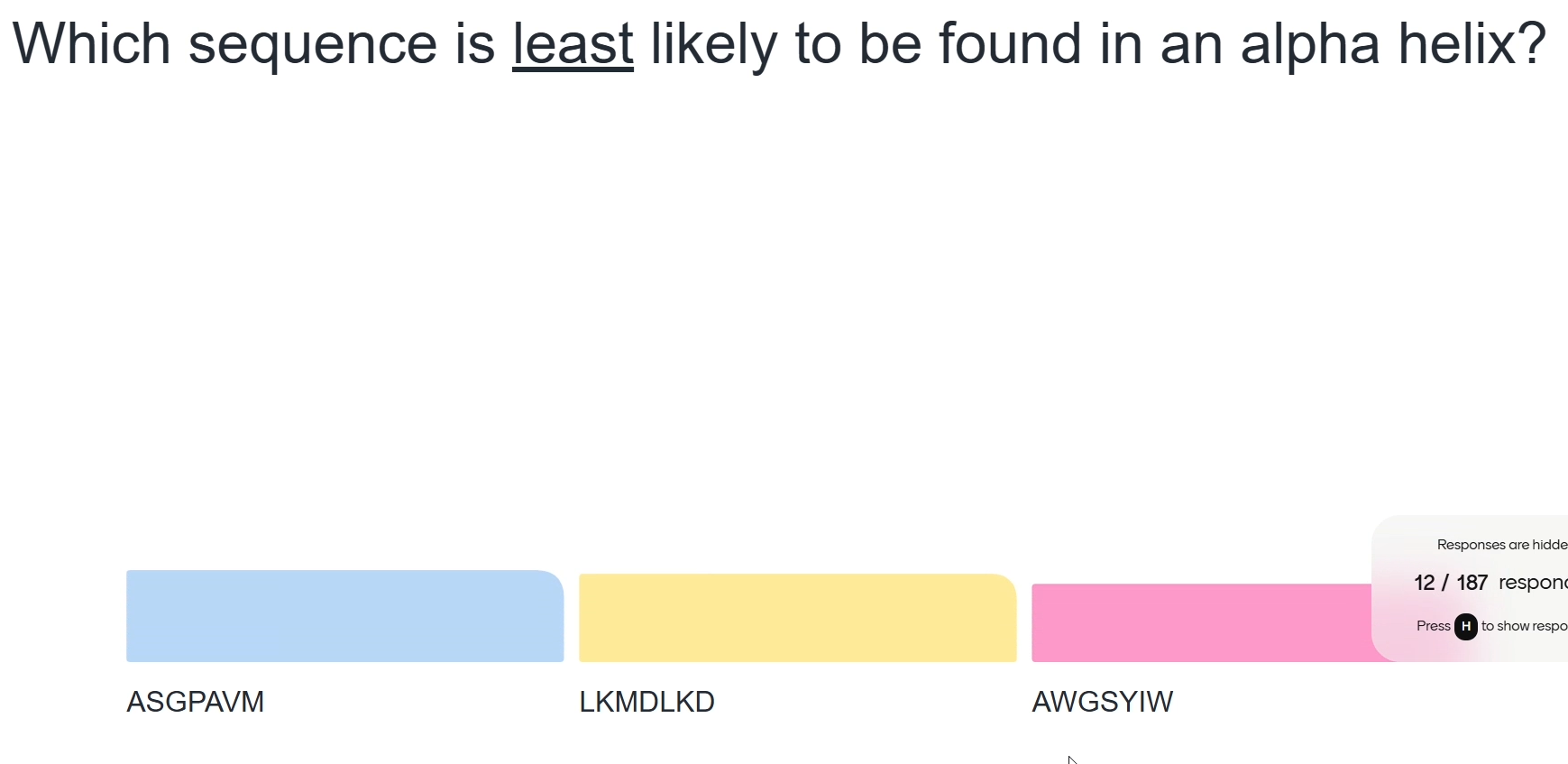
Blue as both glycine and proline residues are present (they cannot both be incorporated into an alpha helix, especially proline)
What amino acid will not be found in an aplha helix?
Proline (will break them)
Name 6 sidechain interactions that produce teriary structures
1) Hydrophobic (entrpic effect)
2) Hydrogen bonding
3) Induced dip dip
4) Ionic
5) Disulphide
6) Aromatic stacking
What determines a native tertiary structure?
The primary sequence and a cumulative effect of all interactions
What can be added to a ribonuclease to denature it and determine its tertiary structure?
8M Urea and beta-mercaptoethanol
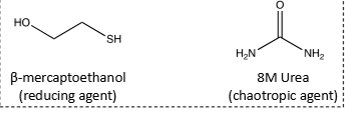
What happens as a denatured sequence becomes active (folded)?
Decrease in entropy (free energy)
What makes the quaternary structure of alpha keratin strong?
Many intertwined alpha helices, stabilised by disulphide bonds
What is the purpose of posttranslational modifications?
Tune activity of protein to be more specific to its purpose
Which amino acid lacks a chiral centre?
Glycine
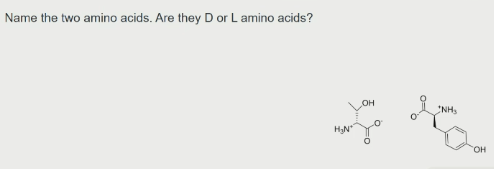
D-Thr, L-Tyr
In a folded protein, charged amino acids tend to be on the…
Exposed on the outside of the protein
What type of interaction would be observed from glutamic acid and lysine sidechain?
Ionic interaction
Which interaction do we use beta-mercaptoethanol to disrupt?
Disulphide bonds
Name 3 types of column chromatograpy?
Size exclusion chromatography (based upon molecular size e.g. agarose gel)
Ion exchange (based on molecular charge think)
Affinity chromatography (based on specific binding interaction)
What is the step called in which you separate your protein of interest from unwanted bacterial proteins in the lysate?
Protein purification
How can protein purity be checked?
Gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
How can activity of proteins be assessed?
An assay (e.g. monitor activity of lactate dehydrogenase using light absorbtion)

Met → Phe or Val → Lys
Val → Lys as length, branching and charge are altered.
Met→ Phe is more likely to be incorporated as have similar hydrophobicity