EXAM 2 REVIEW
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/167
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MOORES REVIEW
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
168 Terms
1
New cards
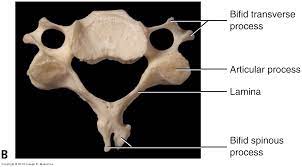
what does the bifid spinous process look like?
bony landmark that makes two centers for ossification
2
New cards
what is hydroxyapatite and what is it made up of?
crystalized mineral salts made up of calcium and phosphate
3
New cards
what makes up of 50% of the bone?
hydroxyapatite
4
New cards
what makes up the hardness of the bone?
hydroxyapatite
5
New cards
what makes up 25% of the bone?
collagen
6
New cards
what makes the bone strong
collagen (strong)
7
New cards
what percentage of water makes up of the bone
25%
8
New cards
what is the end part of the bone called?
epiphysis and the articular cartilage (hyaline type)
9
New cards
what is a metaphysis?
a growth plate that becomes a epiphyseal line
10
New cards
what is the epiphyseal growth plate from the metaphysis closed by?
estrogen
11
New cards
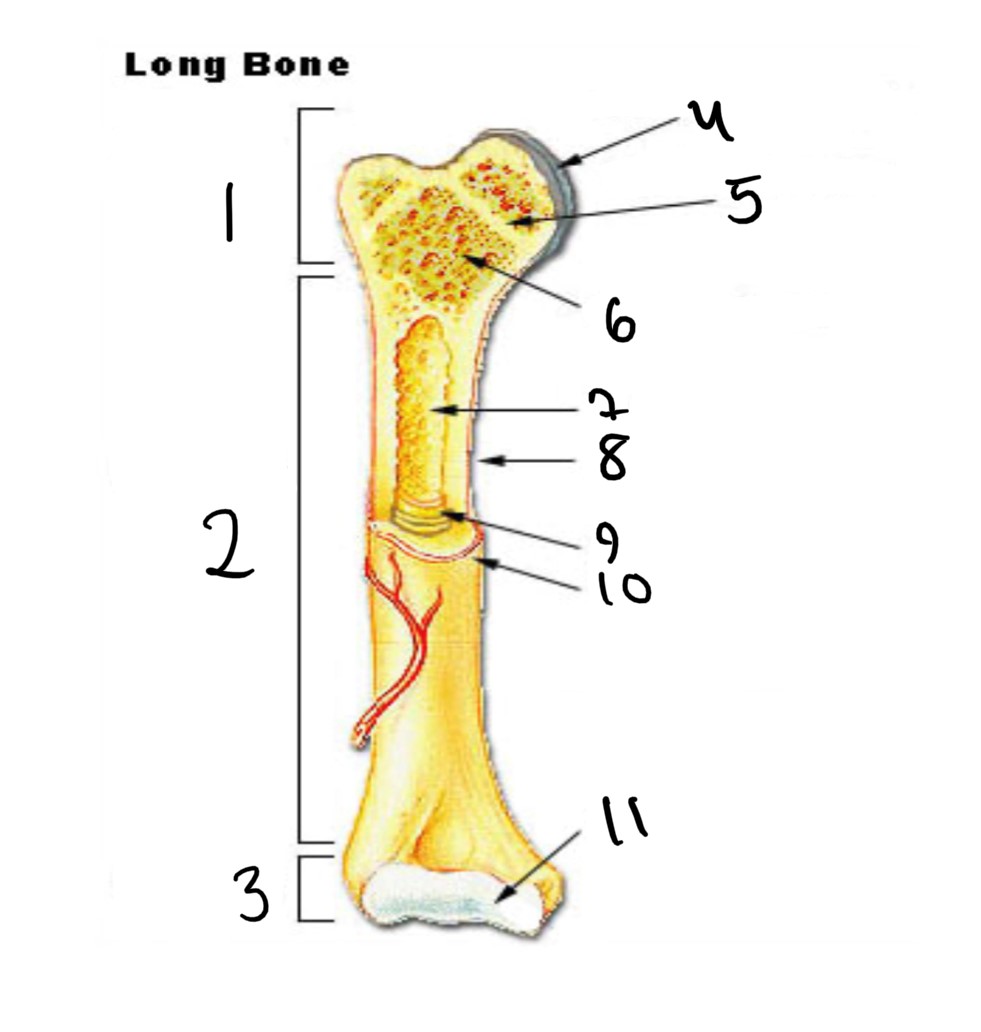
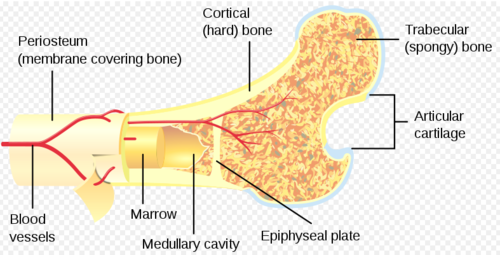
1
epiphysis
12
New cards
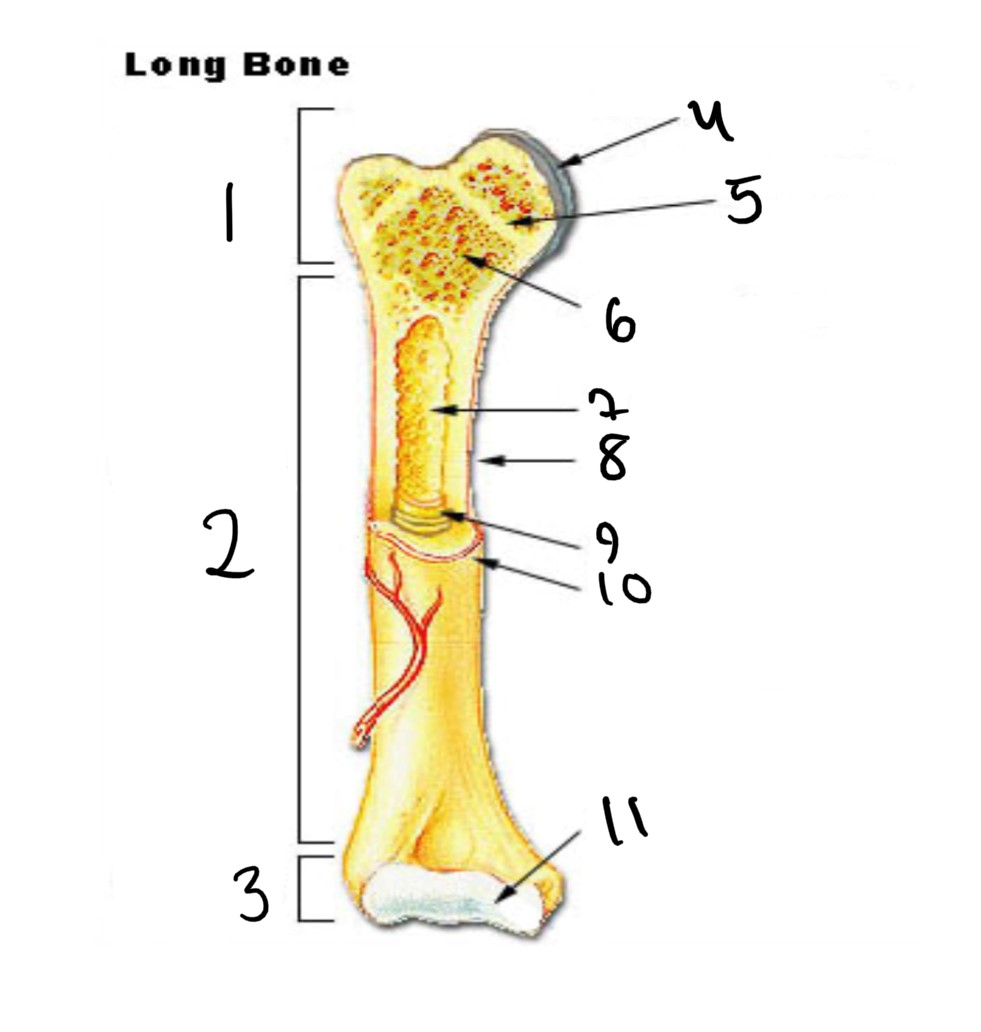
2
diaphysis
13
New cards
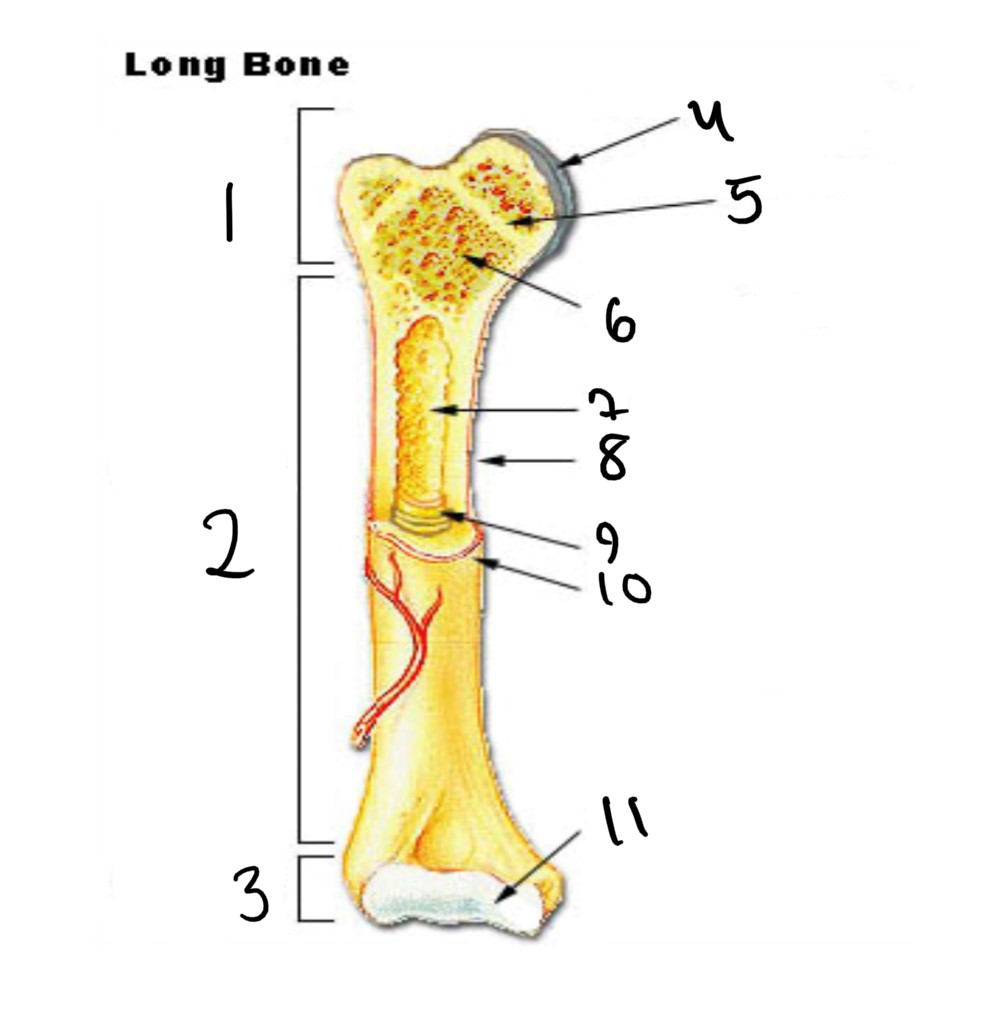
3
epiphysis
14
New cards
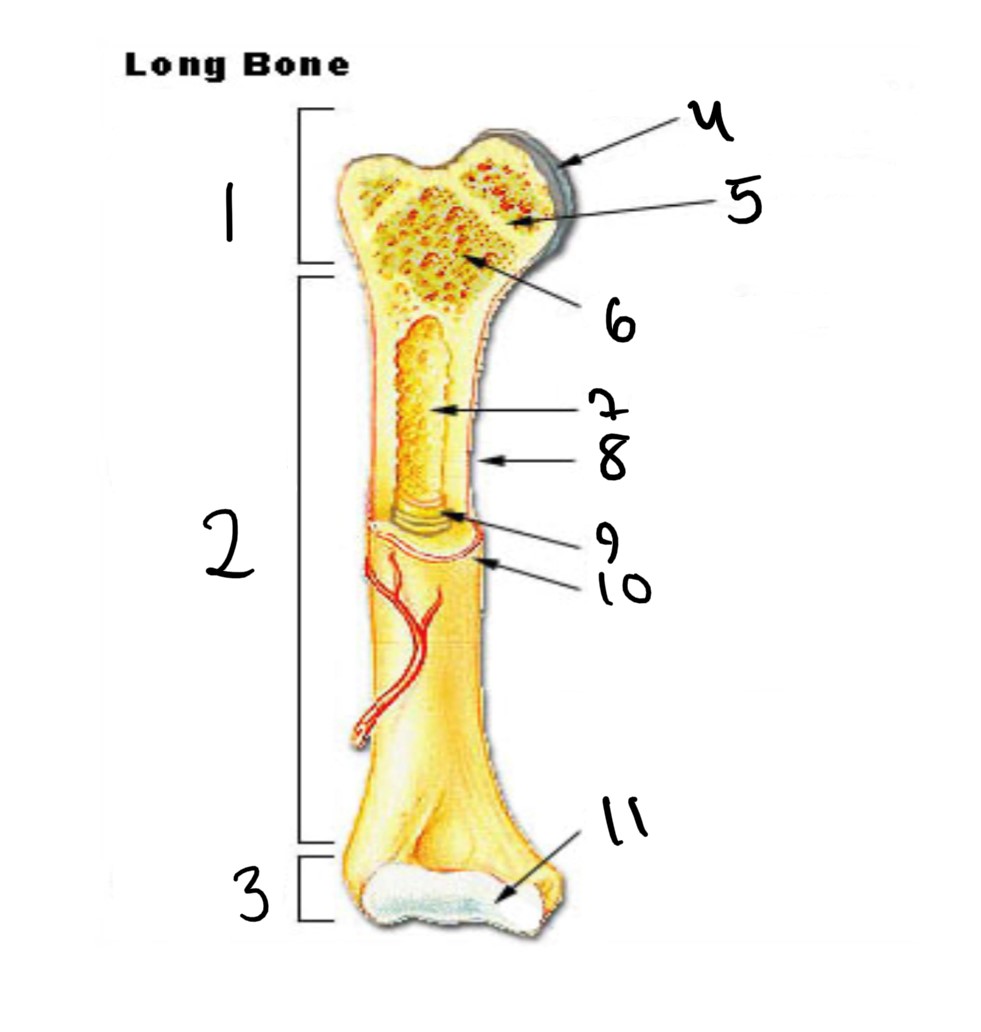
4
articular cartilage
15
New cards
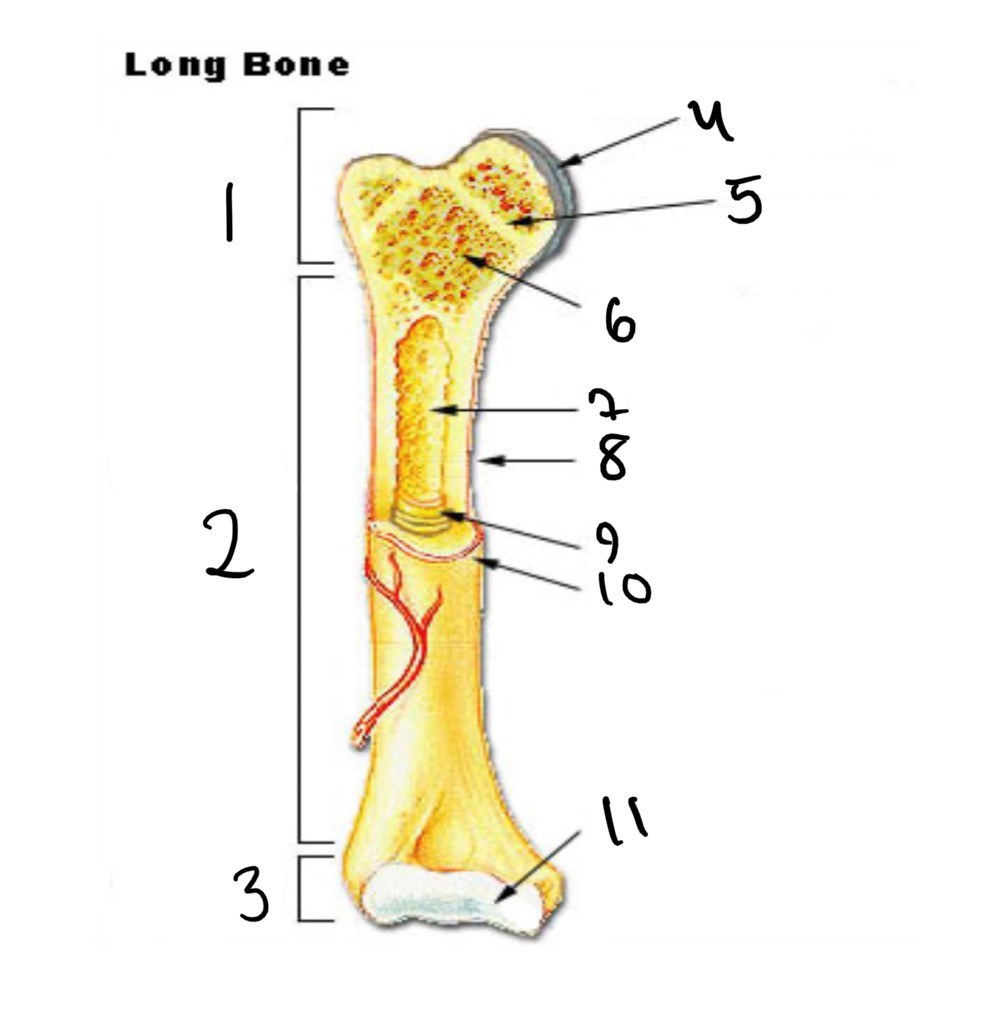
5
epiphyseal line
16
New cards
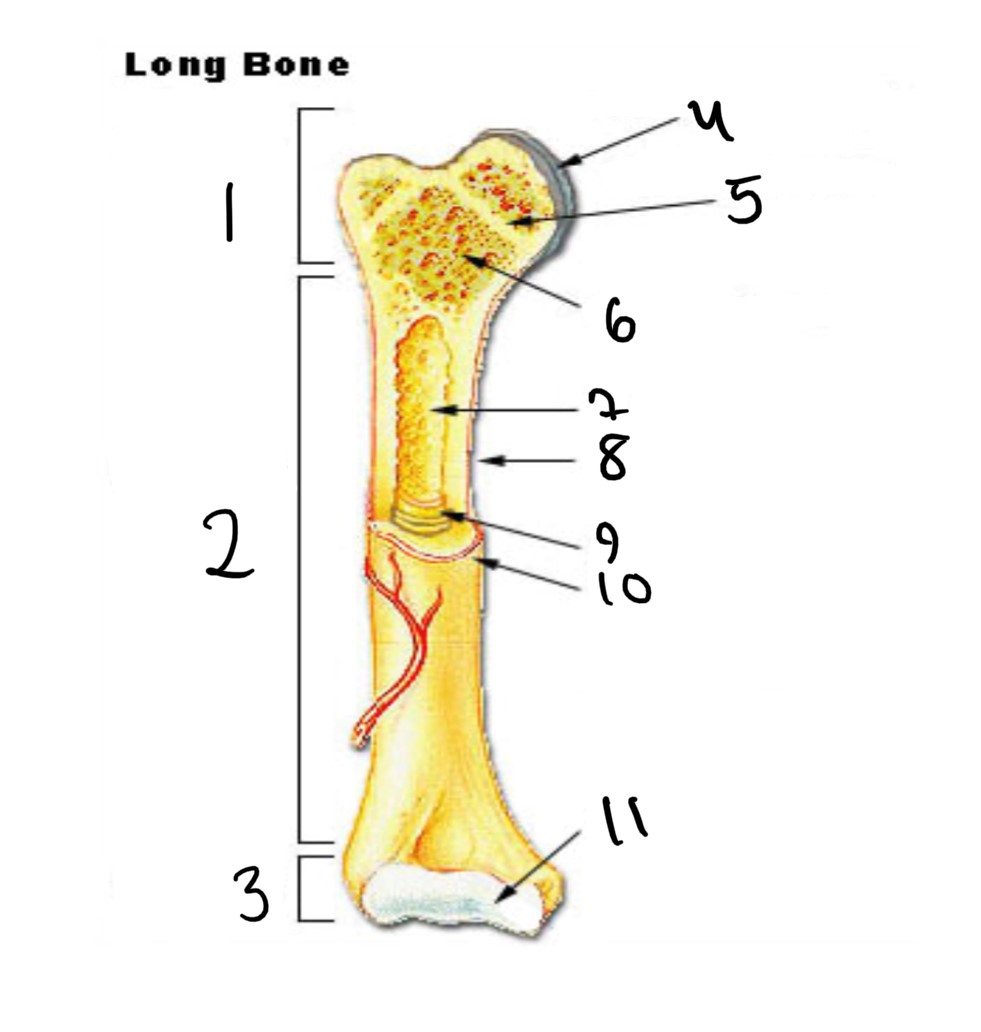
6
spongy bone
17
New cards
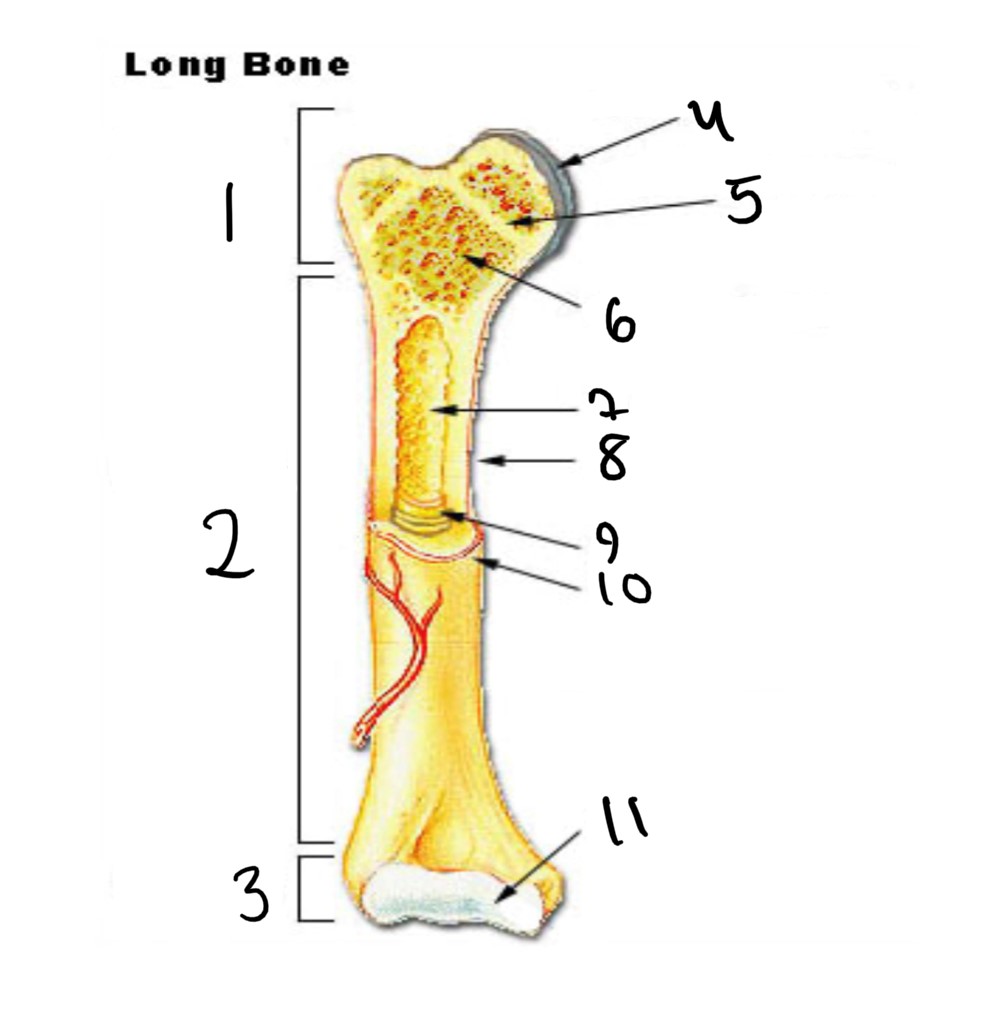
7
medullary cavity
18
New cards
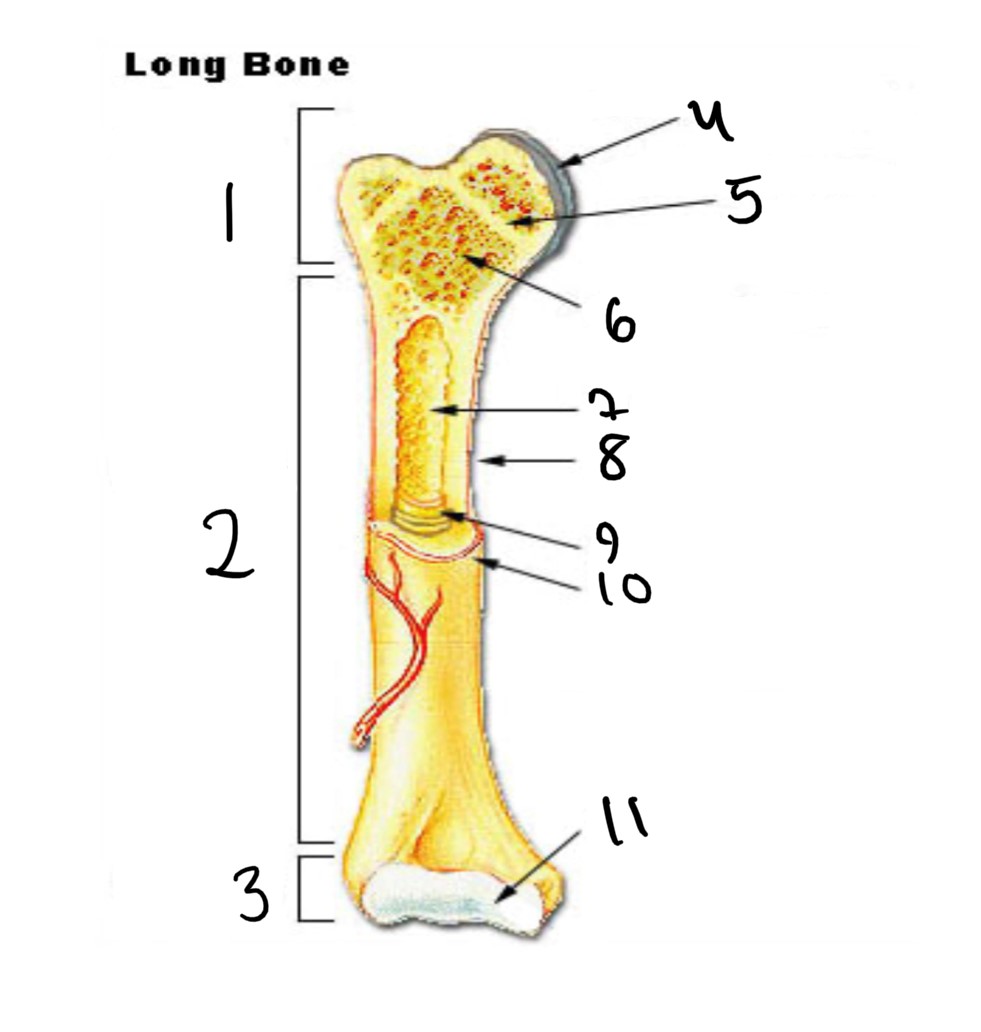
8
nutrient foramen (tube of the side)
19
New cards
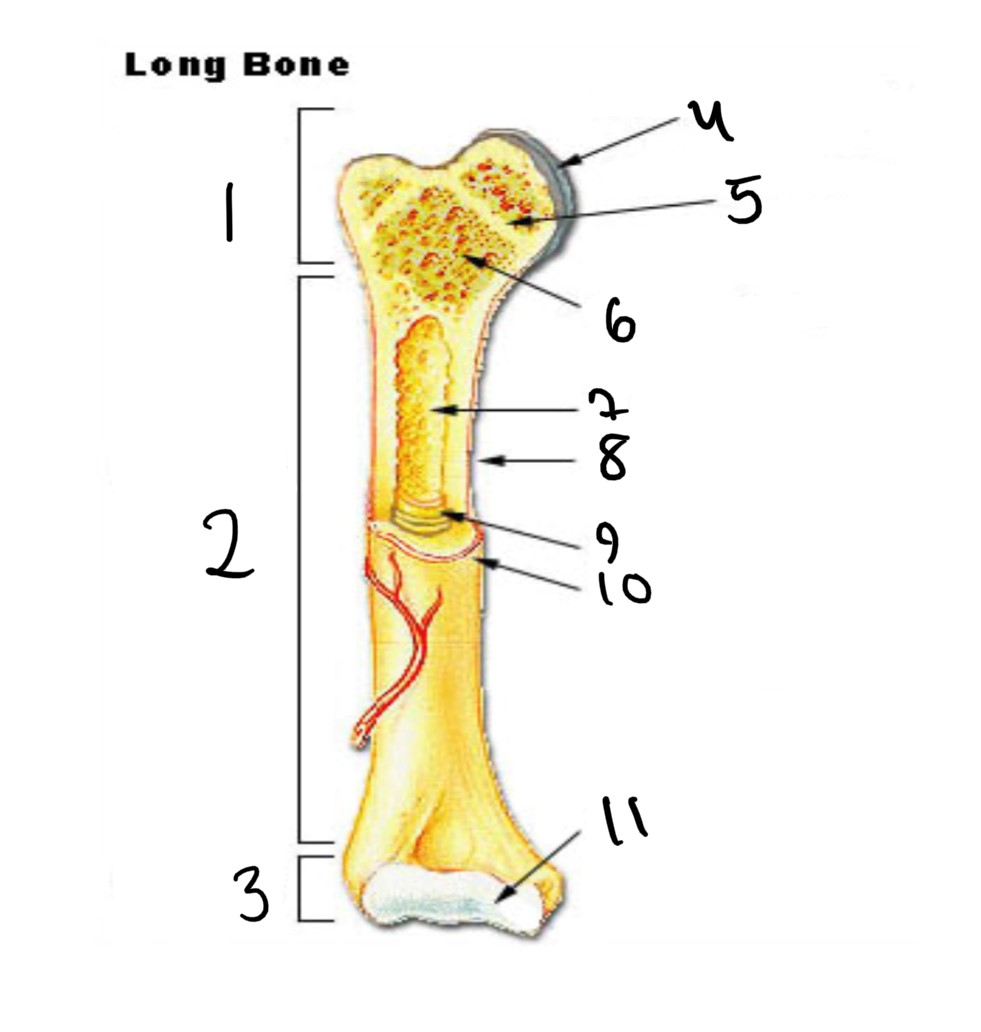
9
endosteum
20
New cards
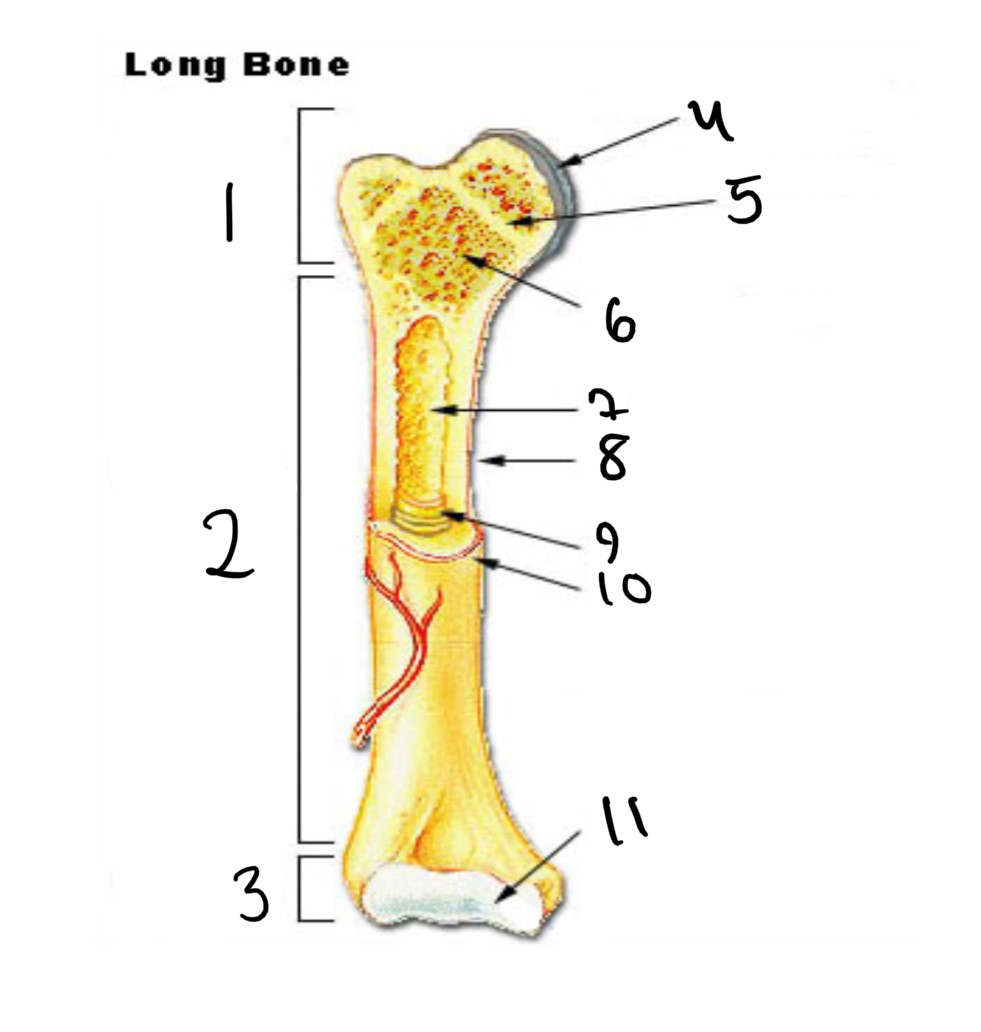
10
periosteum
21
New cards
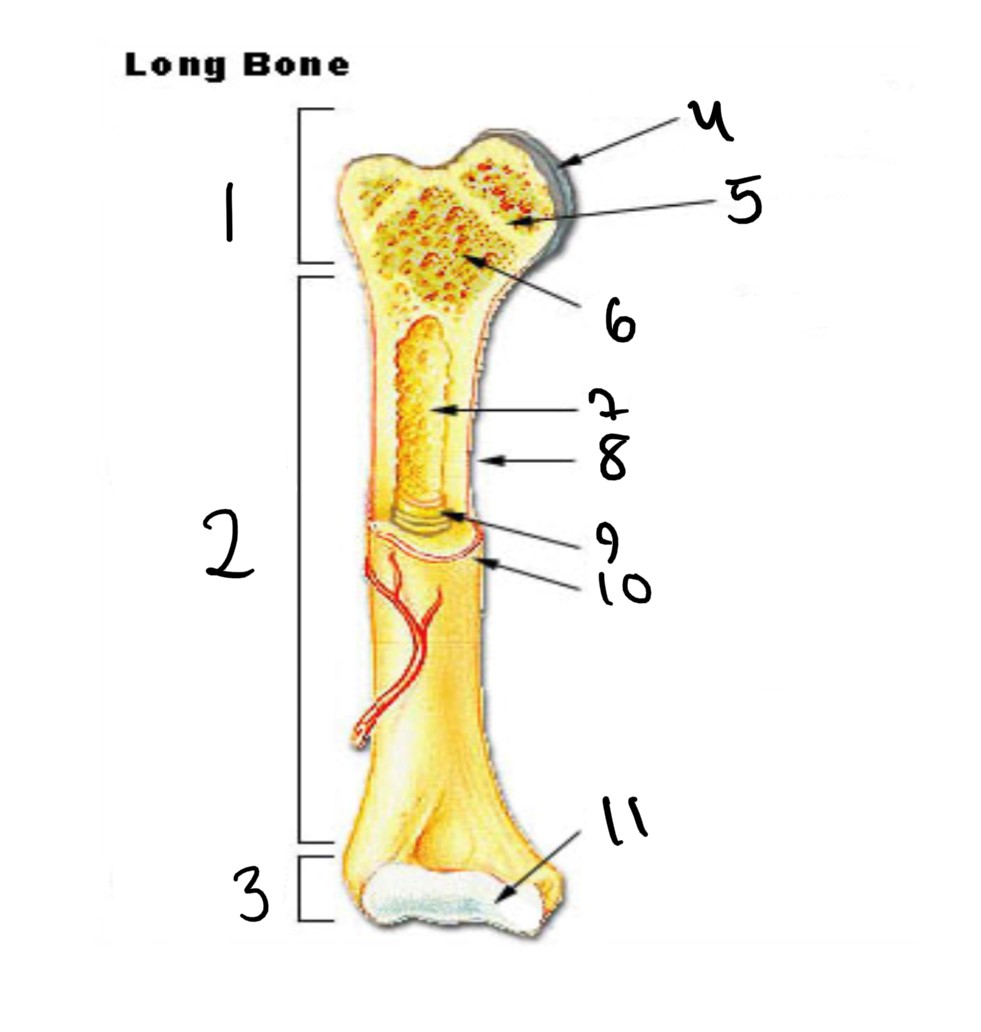
11
articular cartilage
22
New cards
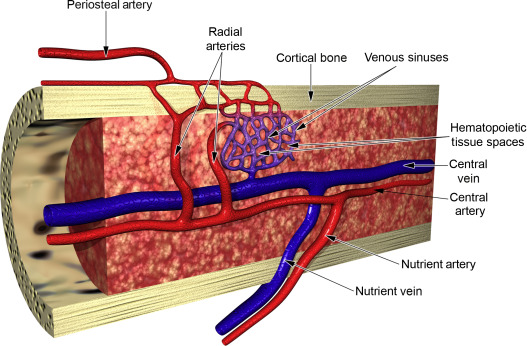
what is the nutrient artery?
two veins that sends branches upward and downward to the bone marrow
23
New cards
what is the function of a nutrient artery?
ramifies in the medullary membrane and give twigs to the adjoining canals
24
New cards
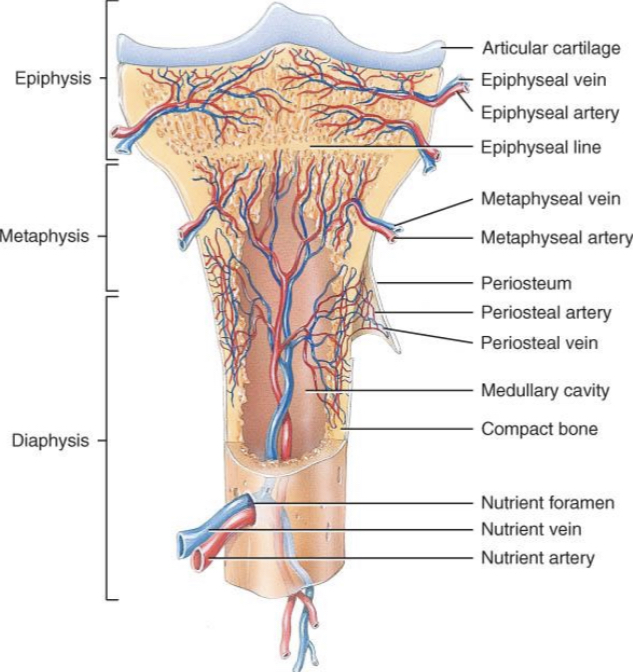
where does the nutrient arteries passes through within the compact bone?
the nutrient foramen
25
New cards
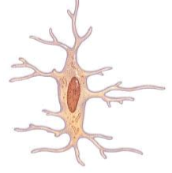
what are osteocytes?
mature bone cells and are the main cells in bone tissue
26
New cards
what is the function of osteocytes
maintains the bone’s bone tissue and daily metabolism such as the exchange of nutrients and waste in the blood
27
New cards
osteocytes do not undergo
cell division
28
New cards
before turning into an osteocytes, osteocytes start outs as
osteoblasts
29
New cards
what are osteoblasts
bone building cells
30
New cards
what is the function of osteoblasts
synthesize and secrete collagen and other organic components needed to build the bone matrix and also initiated calcification
31
New cards
what are osteoblasts responsible for?
bone deposition, or forming new bones, and forms the bone matrix
32
New cards
regarding calcium, what happens during bone deposition?
calcium is deposited into the bones. Ca+2 from blood to bone (osteoclasts)
33
New cards
what are osteoclasts?
big cells from monocytes (white blood cells)
34
New cards
where are the osteoclasts located in
THE endosteum
35
New cards
what are the functions of the osteoclasts
bone resorption or breaking down of bones
36
New cards
regarding calcium, what happens during bone resorption?
osteoclasts breaks down bone minerals releasing calcium into the blood. Ca+2 bone to blood
37
New cards
what are bone scans?
diagnostic procedures from a radioactive tracer
38
New cards
how are bone scans performed?
a radioactive tracer is absorbed by the bone from an injection though the veins
39
New cards
bone scans are used to measure
bone density
40
New cards
what is intramembranous ossification
where the bone forms from mesenchyme
41
New cards
how does intramembranous ossification produce bones?
mesenchymal tissue is converted into bone which creates flat bones
42
New cards
what is the first step of intramembranous ossification (O)
development of ossification center
43
New cards
what is the second step of intramembranous ossification (C)
Calcification
44
New cards
what is calcification?
where mineral salts makes the bone hard while collagen fibers making the bone strong
45
New cards
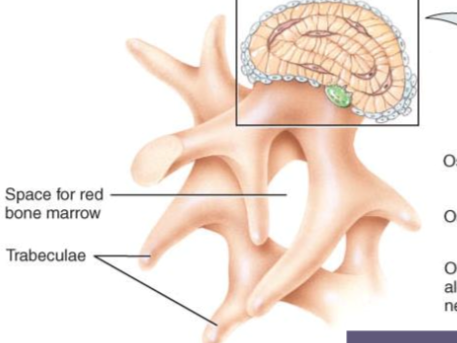
what is the third step of intramembranous ossification (T)
formation of the trabeculae
46
New cards
what is the fourth step of intramembranous ossification (P)
development of the periosteum
47
New cards
what is ossification?
process of bone formation
48
New cards
what is endochondral ossification
the development of long bones
49
New cards
what happens during endochondral ossification?
cartilage is replaced with bone making the bone stretch out like a bread stick which is why the bone is long
50
New cards
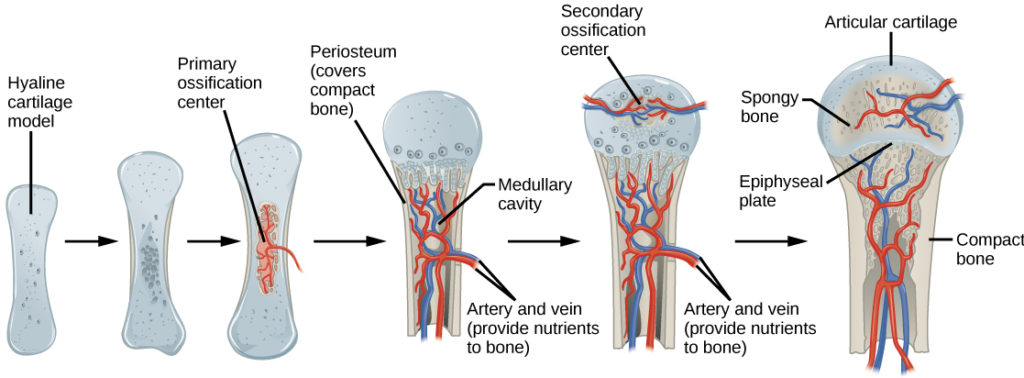
what is the first step of endochondral ossification? (D)
development of cartilage
51
New cards
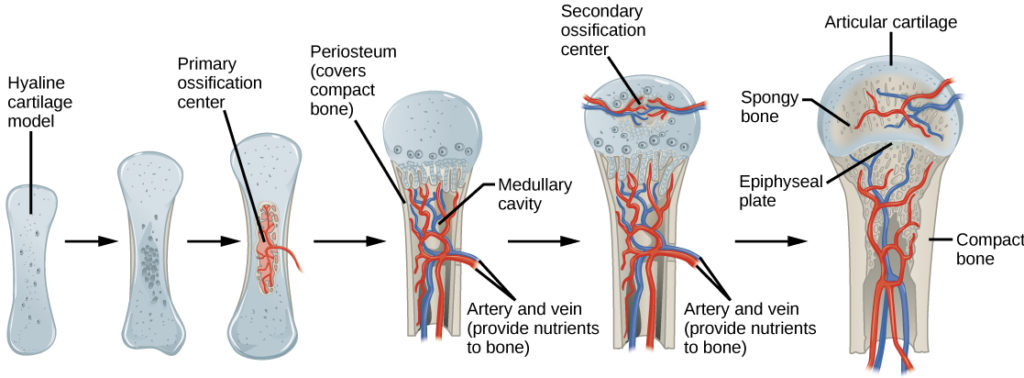
what is the second step of endochondral ossification? (G)
growth of cartilage
52
New cards
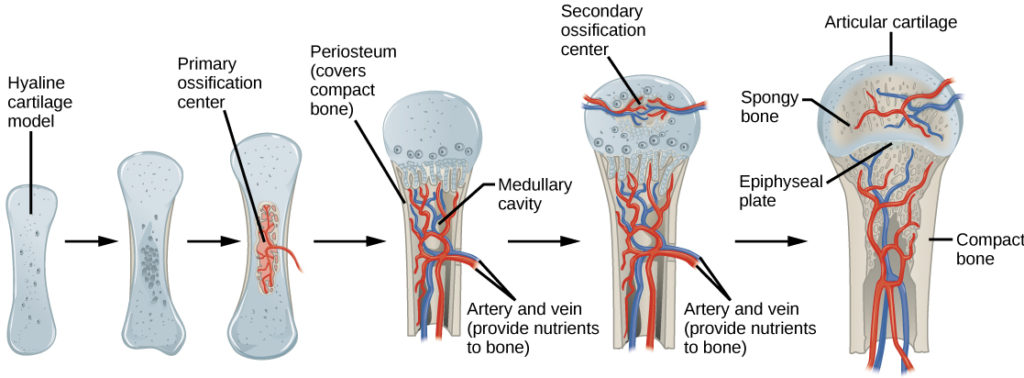
what is the third step of endochondral ossification? (P)
development of the primary ossification center
53
New cards
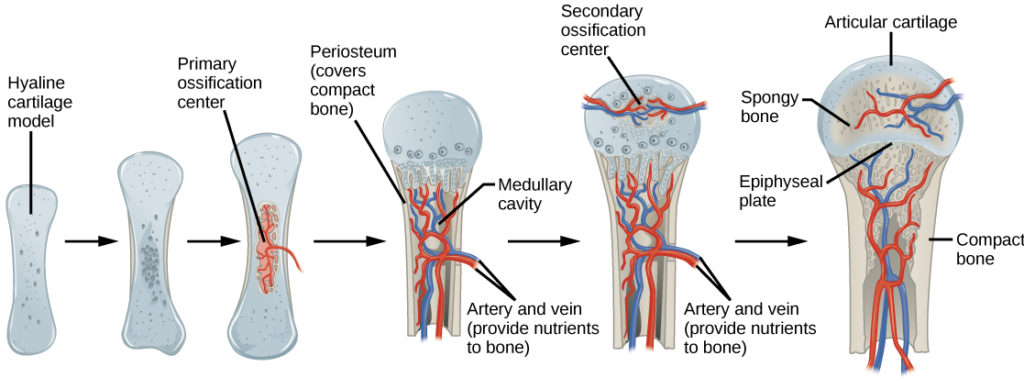
what is the fourth step of endochondral ossification? (S)
development of the secondary ossification
54
New cards
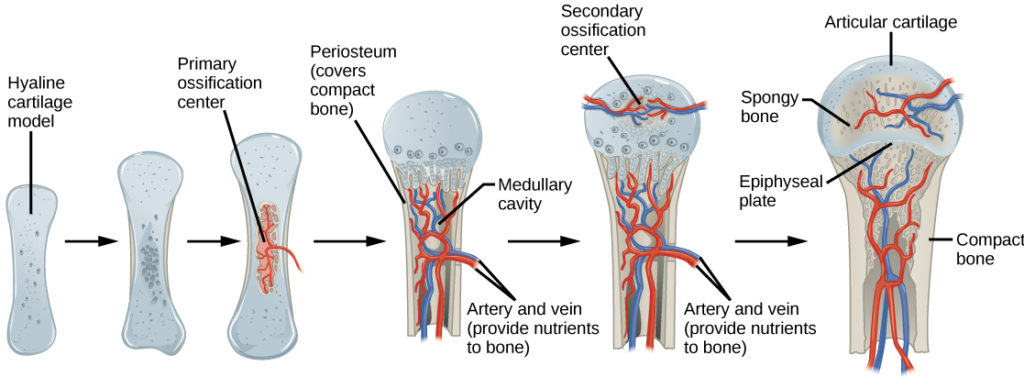
what is the fifth step of endochondral ossification? (A)
formation of articular cartilage and the epiphyseal plate
55
New cards
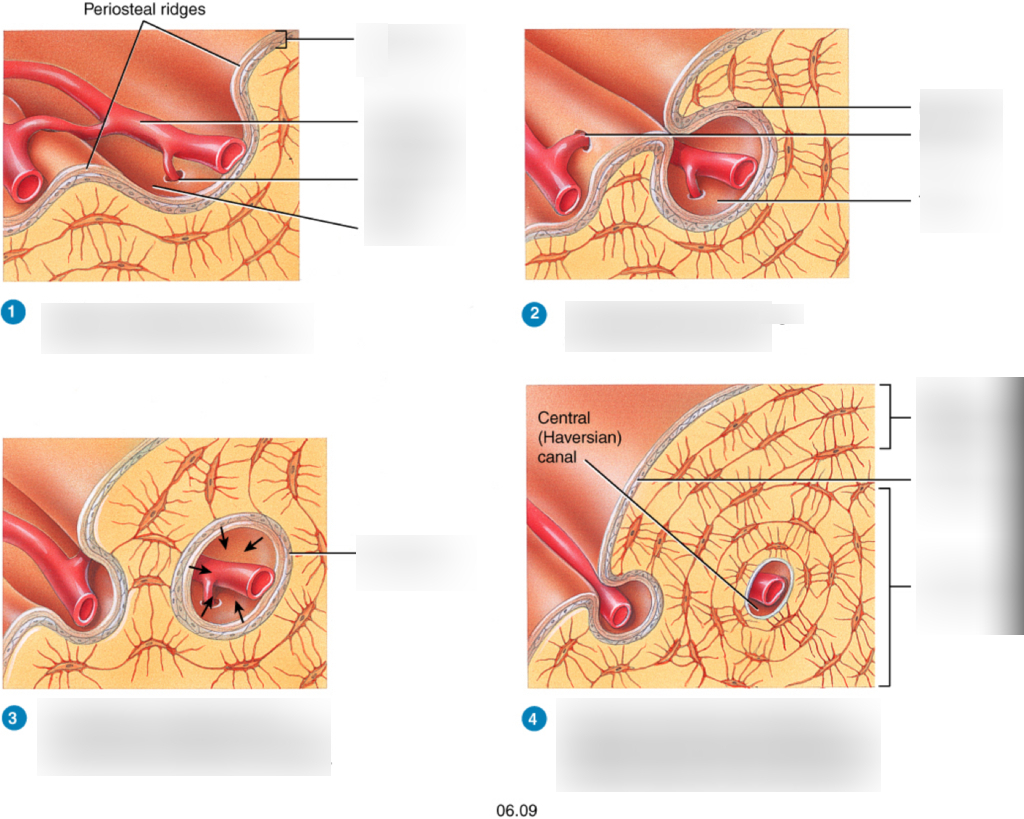
what is appositional growth?
where the bone grows wider or thicker in diameter
56
New cards
what is the first step in appositional growth
differentiate periosteal cells into osteoblast
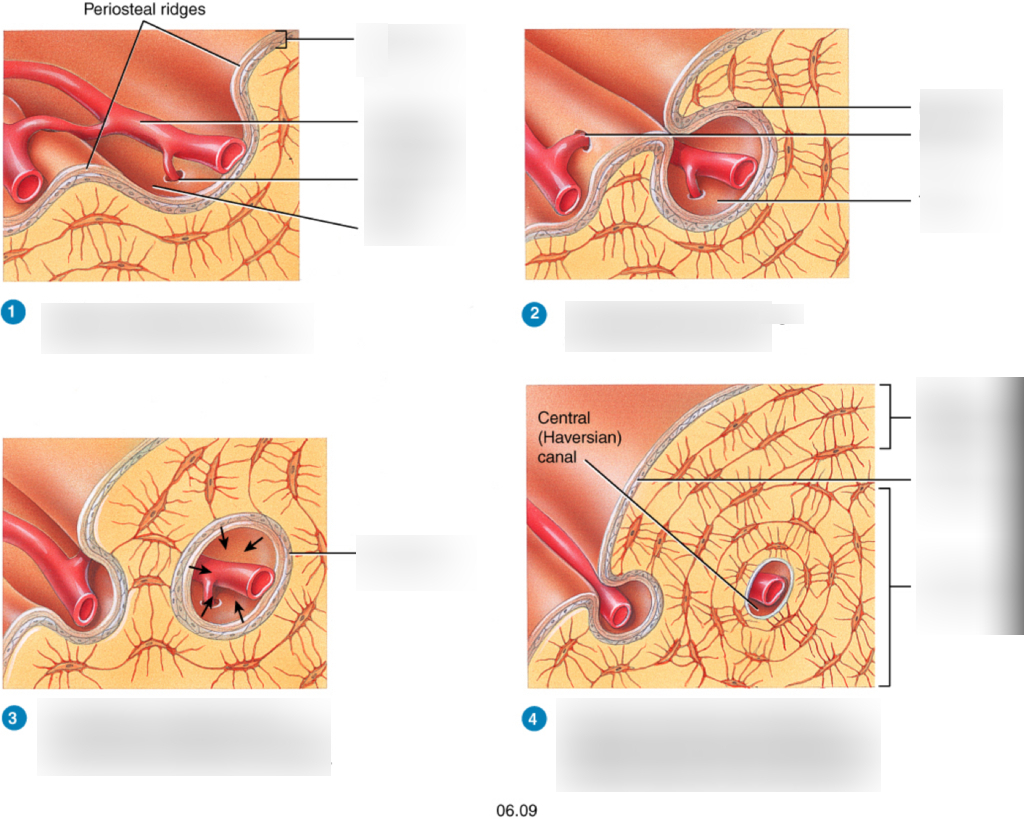
57
New cards
what is the second step in appositional growth
periosteal ridges fuse forming an endosteum or lined tunnel
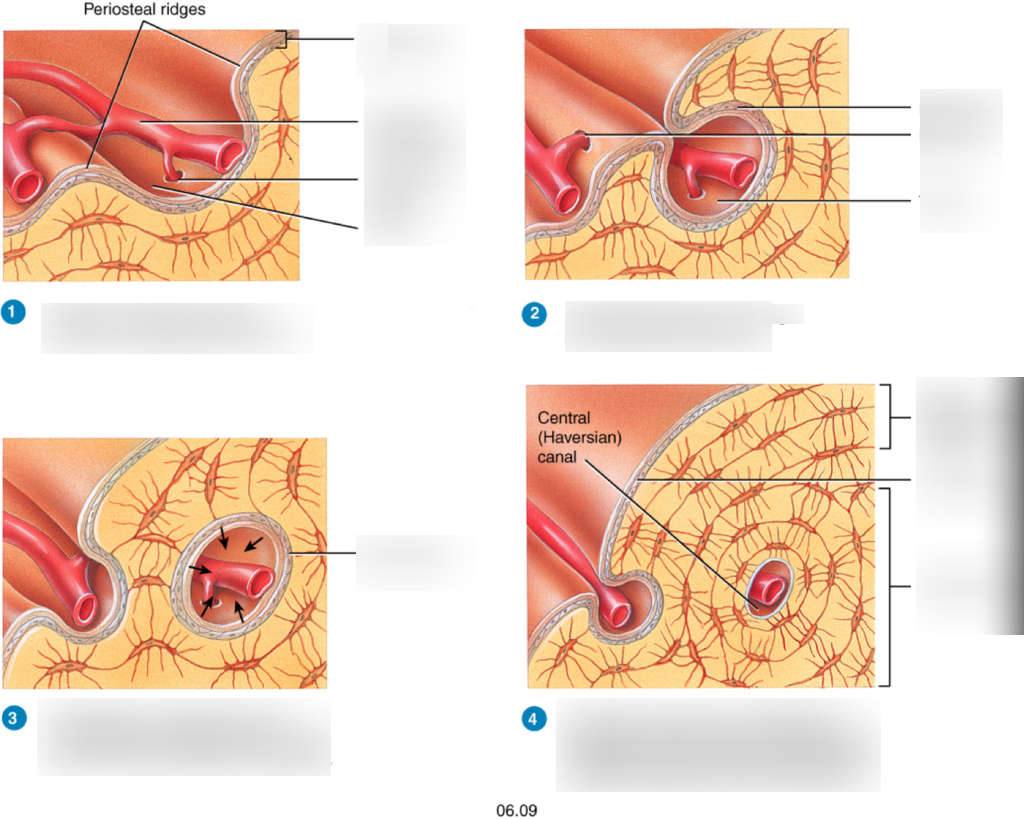
58
New cards
what is the third step in appositional growth
osteoblasts in the endosteum build new concentric lamellae inward toward the center of the tunnel forming a osteon
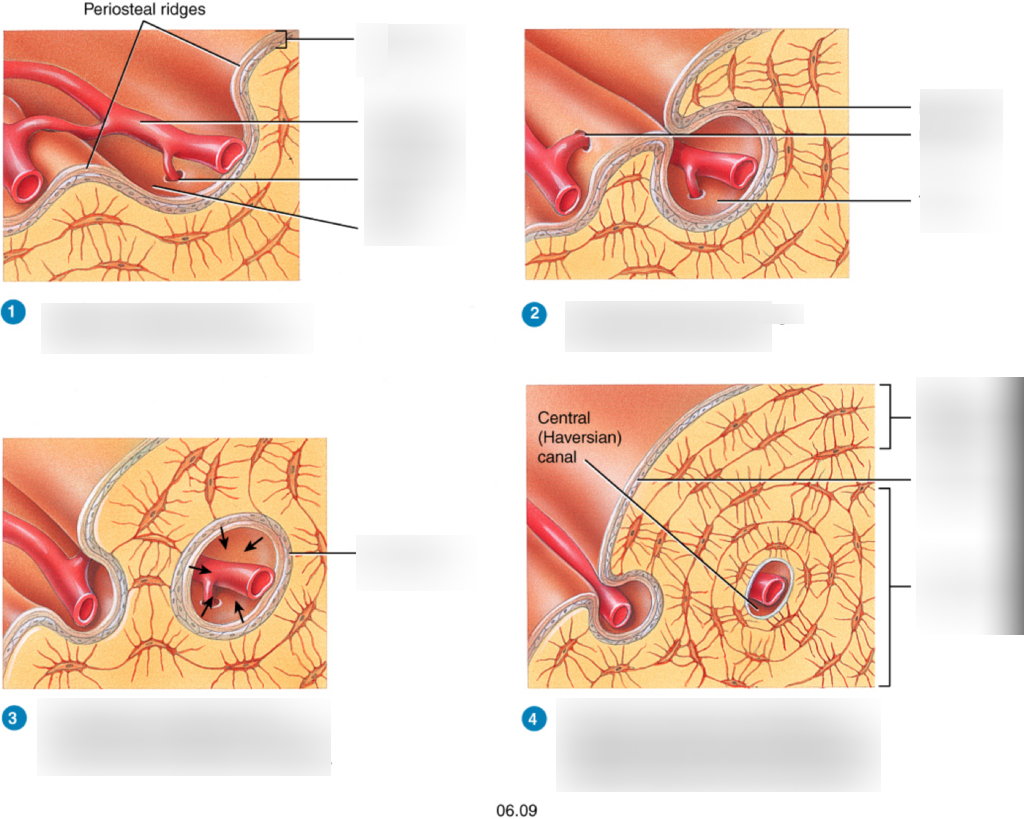
59
New cards
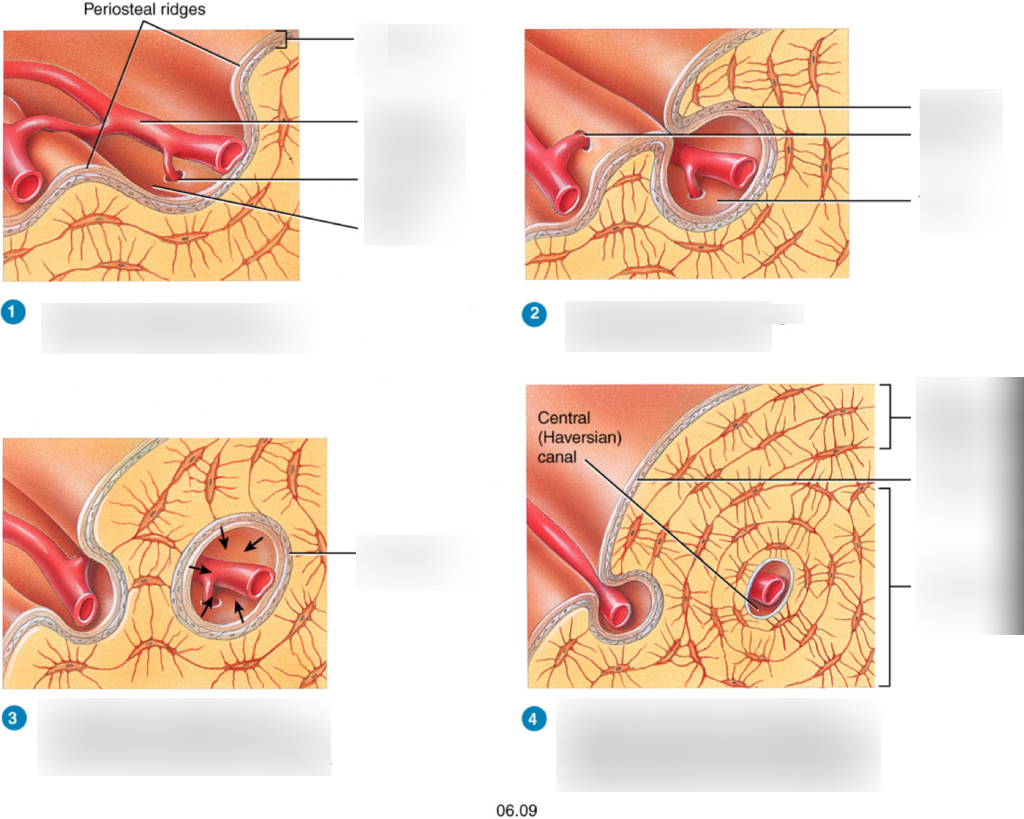
what is the fourth step in appositional growth
bone grows outwards as osteoblasts build new lamellae then more osteons forms as new periosteal ridges fold over blood vessels
60
New cards
what is interstitial growth?
the bone growing longer
61
New cards
first major event in interstitial growth
cartilage grows on the epiphyseal side of the epiphyseal plate
62
New cards
second major event in the interstitial growth
bone replaces cartilage on the diaphyseal side of the epiphyseal plate by endochondral ossification
63
New cards
what is the epiphyseal plate?
located in the metaphysis and a layer of hyaline cartilage of a growing bone by endochondral ossification
64
New cards
how many zones does the epiphyseal plate have?
4 zones
65
New cards
what is zone one of the epiphyseal plate
zone of resting cartilage
66
New cards
what is zone two of the epiphyseal plate
zone of proliferation (GROWTH) cartilage
67
New cards
what is zone three of the epiphyseal plate
zone of hypertrophic cartilage (accumulates glycogen)
68
New cards
what is zone four of the epiphyseal plate
zone of calcified cartilage
69
New cards
what minerals are needed for bone growth
calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, fluoride, and manganese
70
New cards
what vitamins are needed for bone growth
A,B,D,K, and B12
71
New cards
what hormones are needed for bone growth
IGF (insulin for growth), hGH (human growth hormone), thyroid hormones (T3 and T4), estrogen and testosterone
72
New cards
what proteins are needed for bone growth
intrinsic factor (IF) where vitamin B12 is absorbed in the bones or RBC (red blood cells)
73
New cards
what kind of bone is the intrinsic factor?
a glycoprotein
74
New cards
how are intrinsic factors produced?
the parietal cells of the gastric mucosa synthesizes and secretes glycoproteins
75
New cards
what happens in the intrinsic factor?
vitamin b12 is absorbed in the small intestines
76
New cards
what happens if we don’t have the intrinsic factor?
vitamin b12 cannot be aborded in which bone growth or RBC (red blood cell) production cannot occur
77
New cards
how many steps are there in fracture repair?
4
78
New cards
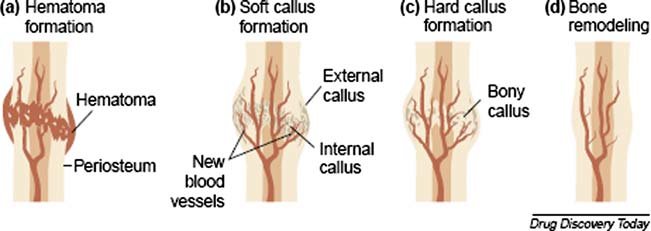
what is the first step in fracture repair
the formation of fracture hematoma (bruising)
79
New cards
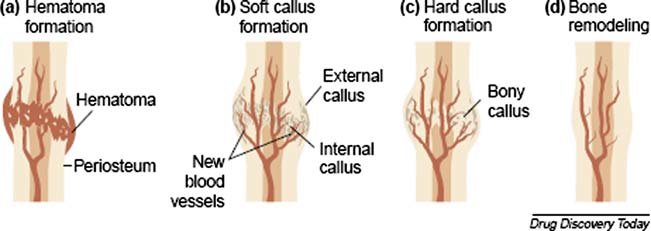
what is the second step of fracture repair?
fibrocartilaginous callus formation (soft bone))
80
New cards
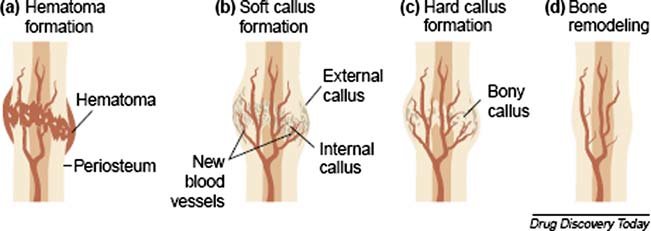
what is the third step in fracture repair
boney callus formation (hard bone)
81
New cards
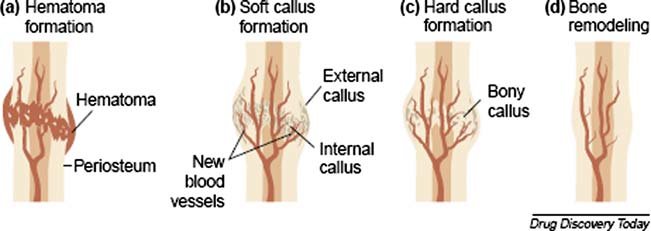
what is the fourth step in fracture repair?
bone remodeling
82
New cards
what is bone remodeling?
the final phase of a fracture repair
83
New cards
what happens during bone remodeling?
dead parts of the broken bone are reabsorbed by osteoclasts and then the compact bone replaces the spongy bone around the periphery of the fracture
84
New cards
what is bone resorption (osteo)?
breakdown of the bone matrix by the osteoClasts
85
New cards
in detail how the osteoclasts break down the matrix?
it removes bone tissue by removing the matrix and breaking up the organic bone
86
New cards
what does the parathyroid hormone (PTH) do?
regulated the Ca2+ in our blood usually when the calcium level is low
87
New cards
the regulation of calcium in the blood should be
9-11 mg
88
New cards
what happens when there is extra calcium in the blood?
it is deposited into the bones like a safe
89
New cards
regarding osteoclasts, what happens when the body needs calcium?
the calcium stored in the bones is removed by the osteoclasts
90
New cards
when the blood has a calcium level of 9-11 mg where does the excess calcium go?
the bones. it is stored in the bones like a safe (911)
91
New cards
what is calcium needed for in the body (homeostasis)?
muscle contraction, nerve impulses, and causes blood clotting (DOES NOT PREVENT IT)
92
New cards
how is homeostasis maintain when the calcium level is not between 9-11 mg?
the calcium stored in the bones is removed and placed into the blood to raise the calcium level in the blood.
93
New cards
what regulated the calcium levels in the blood and make sure it reaches the right levels?
the parathyroid hormone which increases calcium level in the blood
94
New cards
the parathyroids stops releasing calcium when
the negative feedback loops signals from the increased calcium levels
95
New cards
what is the parathyroid hormone?
a hormone secreted by the parathyroid gland and allows calcium to leave the blood in and out through the blood IF the calcium in the blood is not at the right level.
96
New cards
what is bone density
the amount of matter per cubic centimeter of bones
97
New cards
what is calcitonin?
inhibits activity of osteoclasts and secreted by the thyroid gland (because its a hormone)
98
New cards
what happens during calcitonin?
it speed blood Ca+ uptake by the bone and accelerates Ca+ deposition in the bone, decreases blood levels of calcium by putting calcium into bone or removes calcium from the blood and put it into bone
99
New cards
what happens when bone deposition exceeds bone resorption
the bone increases in mass and density
100
New cards
what is osteoporosis?
decrease in bone mass and makes the bones porous