Memorizing
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
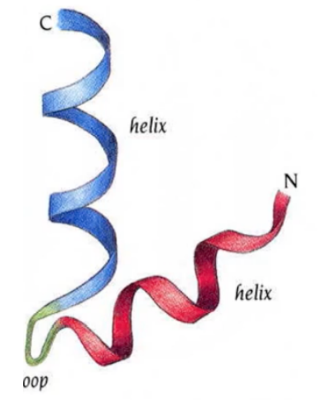
what motif?
helix-turn-helix, all alpha, active site is C alpha

what motif? what active site?
4 helix bundle, all alpha, top is active site
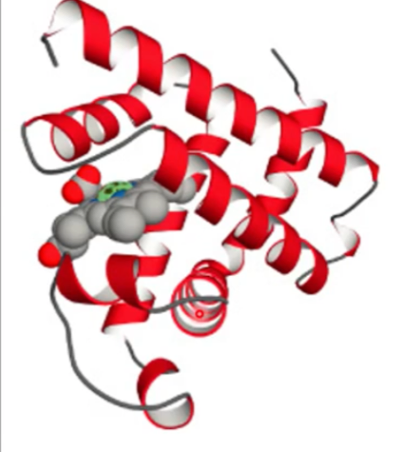
what motif? what active site?
globin fold, all alpha, active site at globin

what motif? what active site?
hairpin; antiparallel beta; active site at the curve
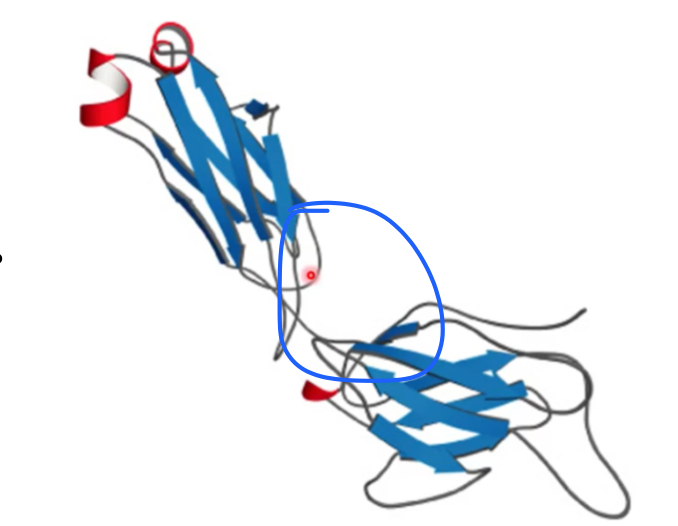
what motif? what active site?
up and down; antiparallel beta; active site at the top
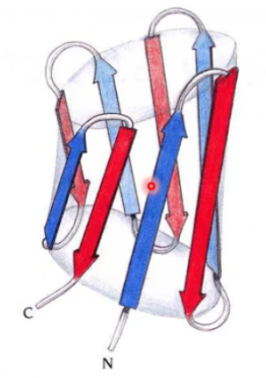
what motif? what active site?
plain barrel; antiparallel beta; active site in the center of barrel
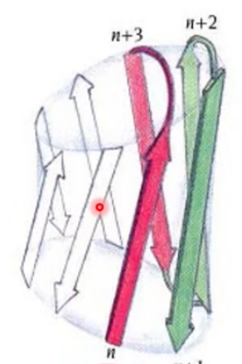
what motif? what active site?
Greek key motif; antiparallel beta; active site at the top
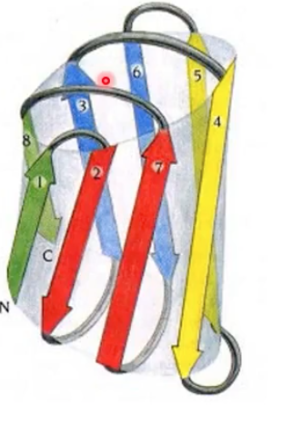
what motif? what active site?
jelly roll, antiparallel beta, active site at the top
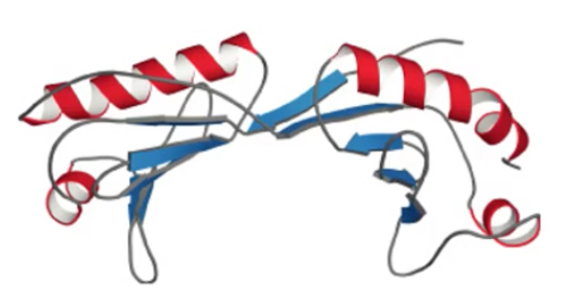
what motif? what active site?
saddle, antiparallel alpha and beta, active site on the alpha

what motif? what active site?
zinc motif, antiparallel alpha and beta, active site on the zinc ion
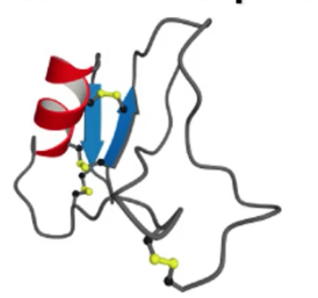
what motif? what active site?
disulfide crosslinked, antiparallel alpha and beta, active site on the disulfide (?)
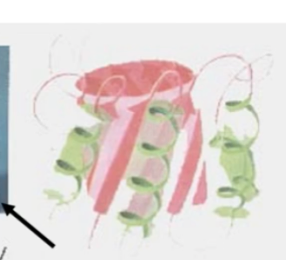
what motif? what active site?
TIM barrel, parallel alpha beta, active site at the top

what motif? what active site?
Beta twist, parallel alpha and beta, active site at the top

right or left
thumb points to the left, curves on bottom, it is left
what motif binds to the minor groove?
saddle
what motif binds to the major groove?
helix turn helix and zinc finger
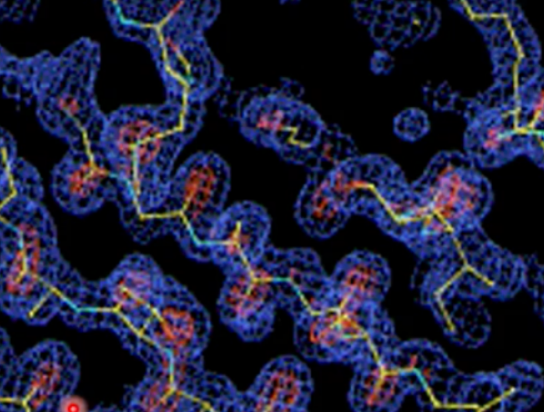
secondary structure that fits into electron density
beta
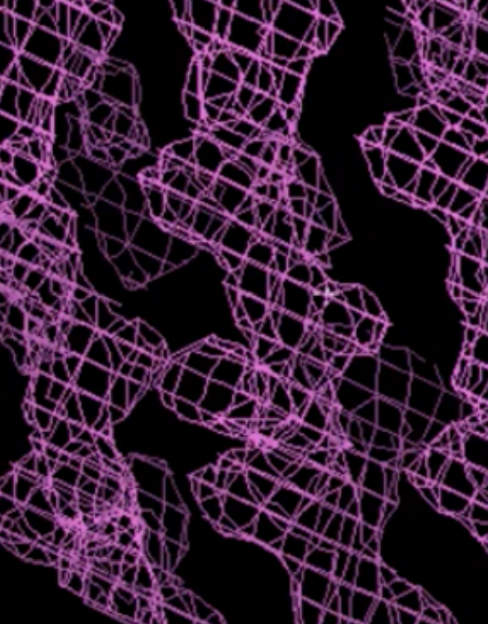
secondary structure that fits into electron density
beta
Crystal structure #’s
Resolution - better than 3A
R merge - less than 10% overall AND less than 50% for the highest resolution shell (# in parenthesis)
R free - less than 25% error
Ramanchadran plot - 0% error
Entropy goes ____ when nonpolar groups are internally buried. So that makes -T∆S more ____
∆G more ____, so protein more likely to ______.
Entropy goes UP when nonpolar groups are internally buried. So that makes -T∆S more NEGATIVE
∆G more NEGATIVE, so protein more likely to FOLD.
Entropy goes ____ when nonpolar groups are exposed to water. So that makes -T∆S more ____
∆G more ____, so protein more likely to ______.
Entropy goes DOWN when nonpolar groups are internally buried. So that makes -T∆S more POSTIVE
∆G more NEGATIVE, so protein more likely to UNFOLD.
reduced resolution in higher temperature for crystallography
due to radiation damage, so freeze crystal
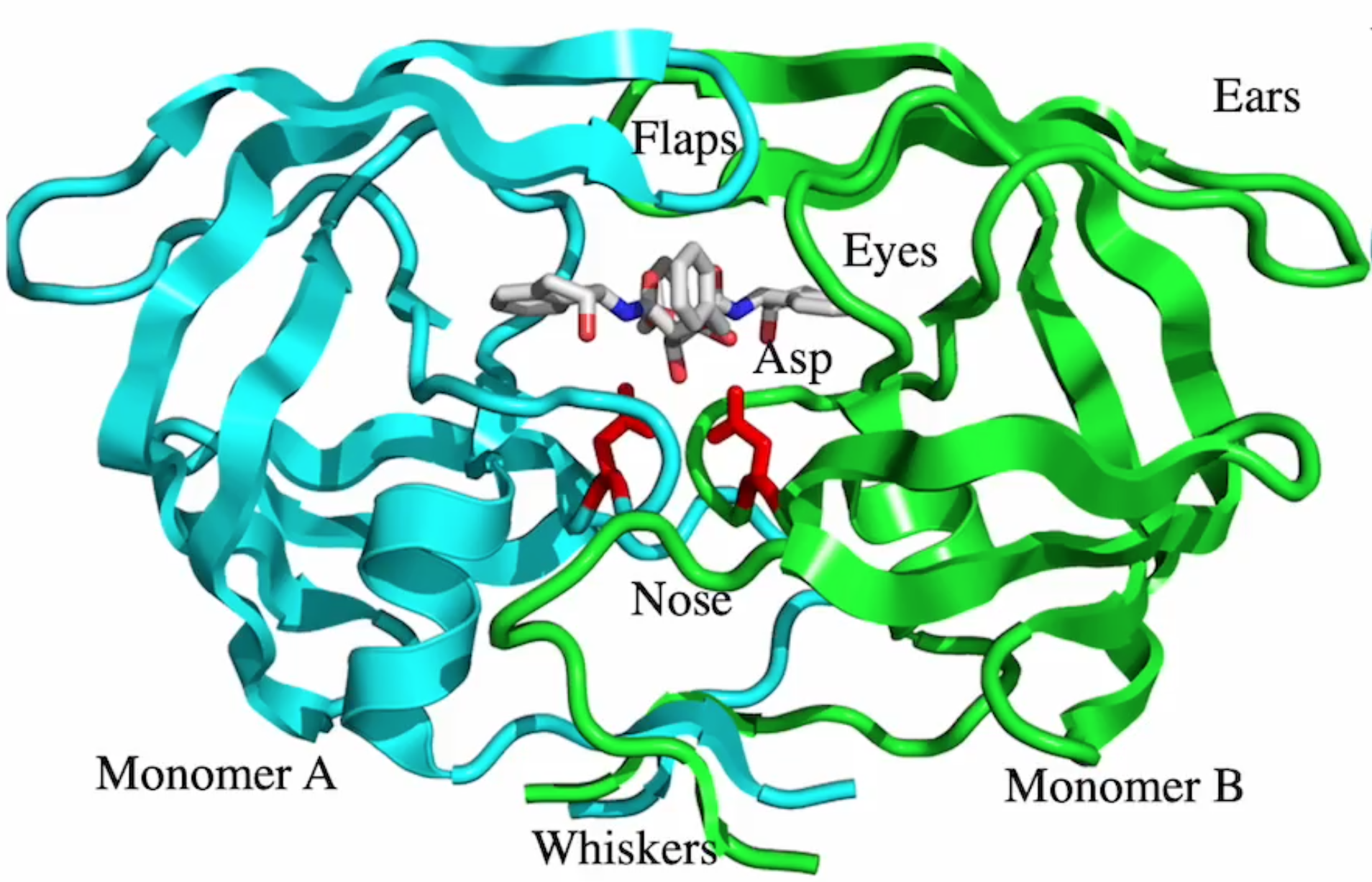
drug binding site?
blue
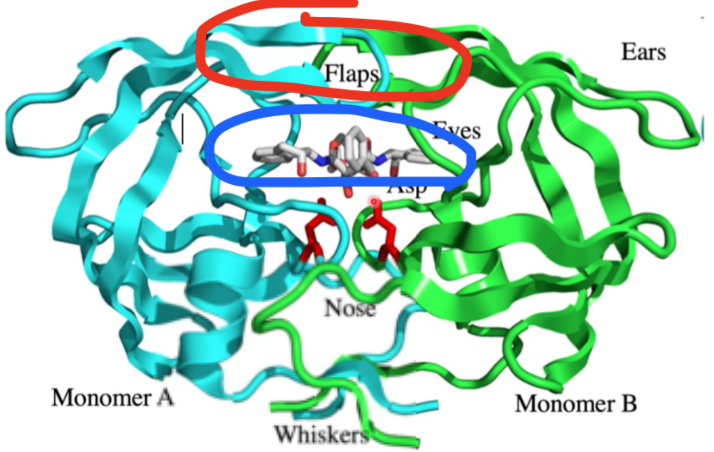
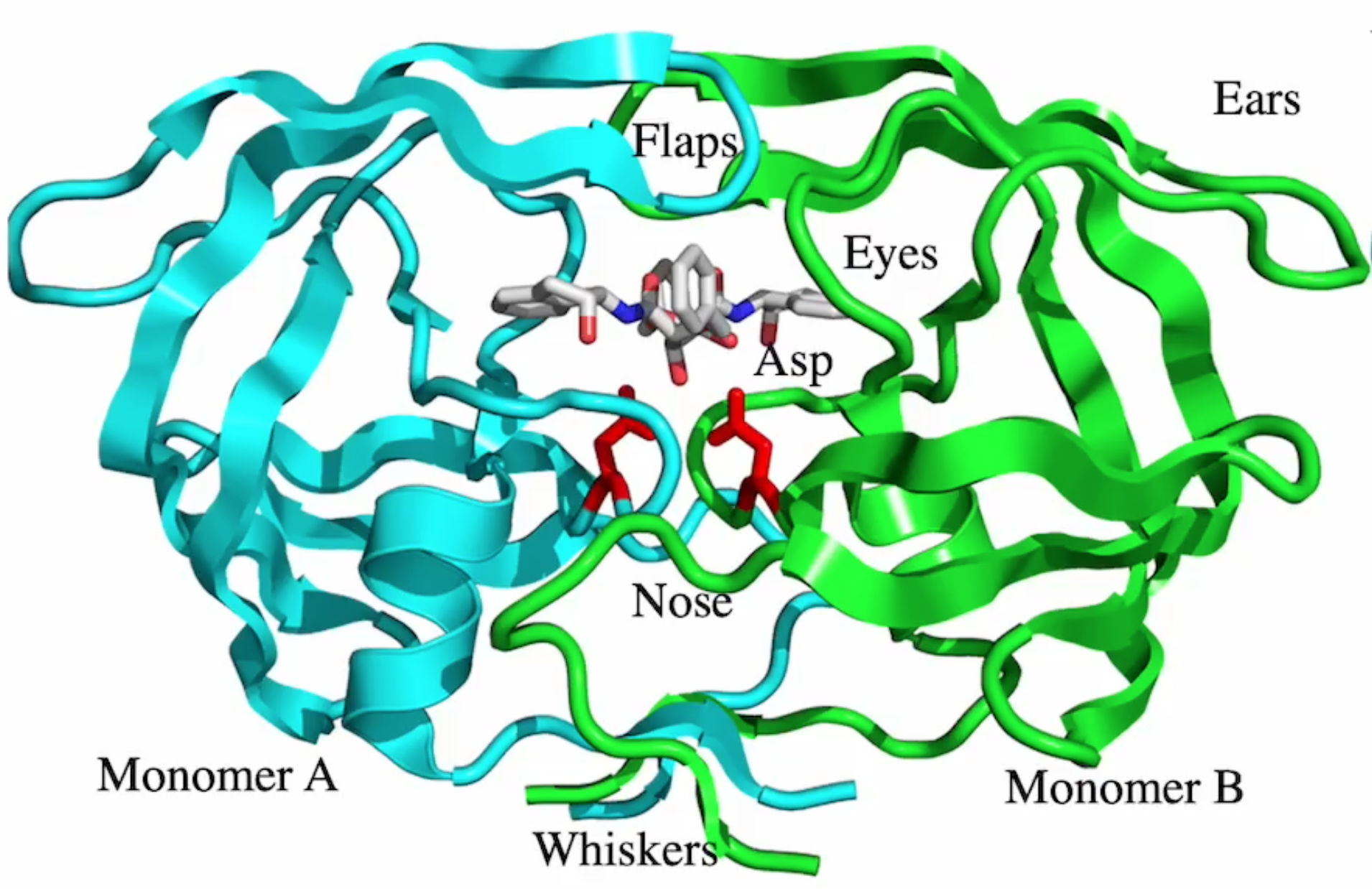
where does conformational change happen? what motif?
red, beta hairpin
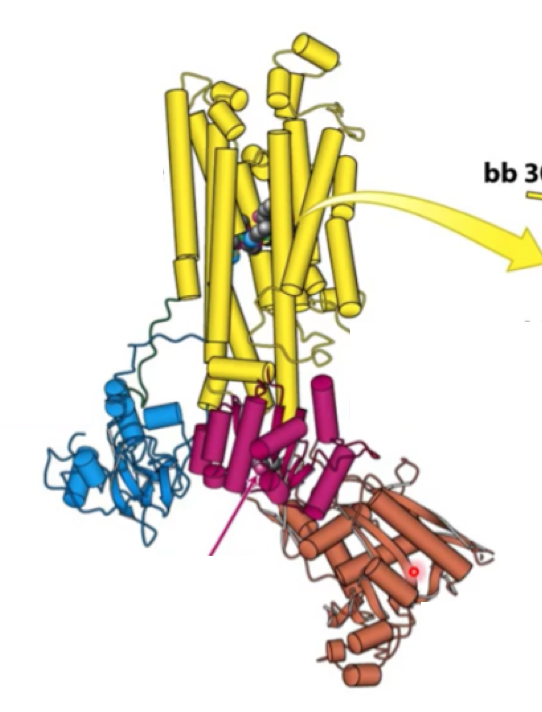
Where is transmembrane protein? where is N domain? where is adaptor domain? where is P domain?
Transmembrane domain - yellow
A domain - blue
P domain - magenta
N domain - brown
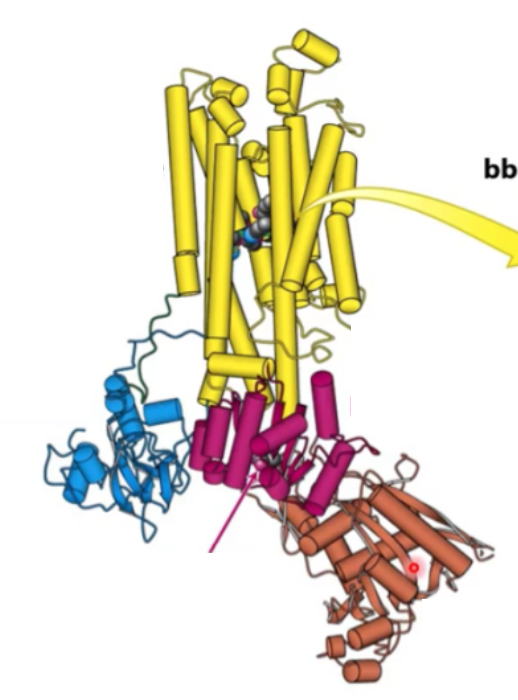
Where will digitalis bind?
Transmembrane domain (yellow)
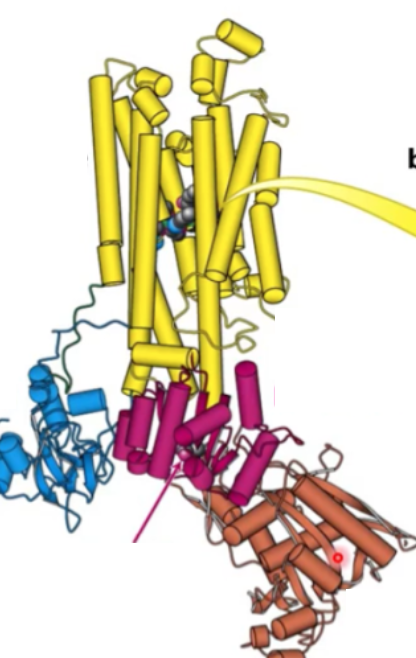
Where is Asp active site?
P domain
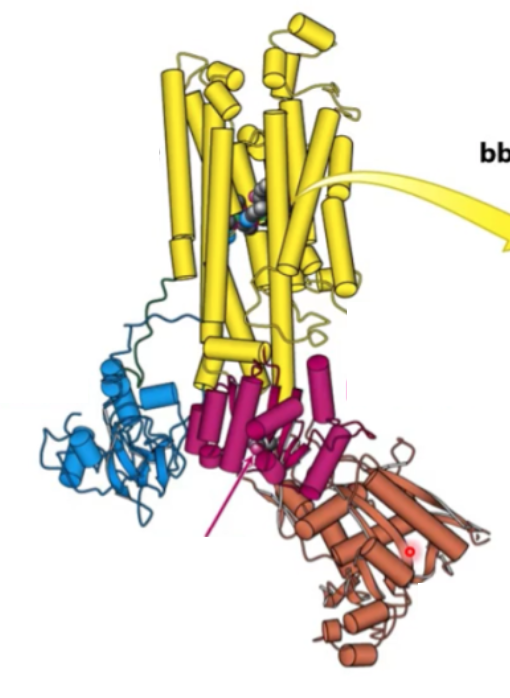
Where is phosphorylated?
P domain
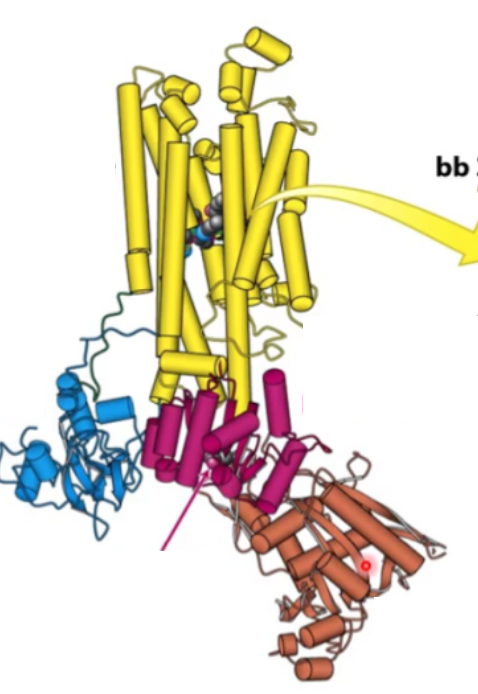
Where will ATP domain be hydrolyzed
N domain
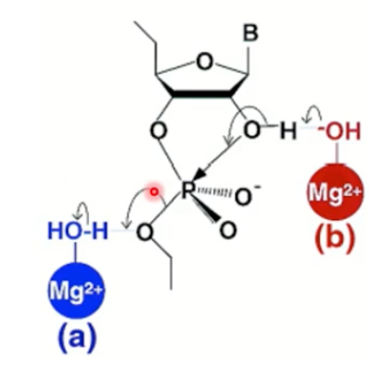
Which metal ion catalysis is this?
If Mg connected to 2' OH then it is general acid base
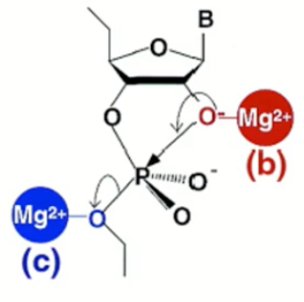
Which metal ion catalysis is this?
If Mg connected to the 2' O then it is Lewis acid
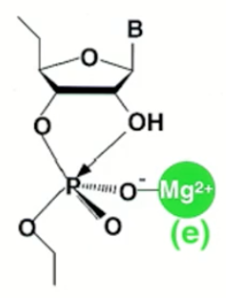
Which metal ion catalysis is this?
If Mg connected to the phosphate oxygen, then it is electrophilic catalysis