Biochemistry Exam 1
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
weaker
the higher the dielectric constant, the (stronger/weaker) the interaction between charges
stronger
alcohol causes dehydration, which leads to (stronger/weaker) charges in the body
cooling
high heat capacity of water has what affect on the body?
high heat of vaporization
what property of water helps prevent dehydration?
high
does water have a high or low dielectric constant?
clathrate
molecules of one component are physically trapped within the crystal structure of another (ex. water molecules surrounding a non-polar solute)
40%
what percentage of body weight does the ICF account for?
20%
what percentage of body weight does the ECF account for?
Na+ and Cl-
what ions are most abundant in the ECF?
K+ and PO4
what ions/molecules are more abundant in the ICF?
confusion, drowsiness, muscle weakness, seizures, coma
what can hypo and hypernatremia lead to?
abnormal hear rhythm
what can hypo and hyperkalemia lead to?
hypo - weakness, numbness in hands and feet
hyper - nausea, vomiting, confusion, coma
what can hypo and hypercalcemia lead to?
85%
how much hemoglobin saturation does the brain require for proper functioning?
metabolic acidosis
exercise causes the release of lactic acid, resulting in _________
metabolic alkalosis
biochemical reactions and protein degradation lead to build up of ammonia, resulting in _________
respiratory acidosis
conditions, such as COPD or pneumonia, may not allow the body to eliminate CO2 from the blood, resulting in _________
respiratory alkalosis
hyperventilation results in elimination of CO2, resulting in _________
weak acid and its conjugate base or weak base and its conjugate acid
buffers consist of a _____________________
second
dihydrogen phosphate loses 3H+, but the ________ proton is the most suitable buffer for physiological pH
we can increase the salt concentration to neutralize externally added acid
how can we increase the buffering range of the bicarbonate anion in the body, since it is out of range (pKa=6.1)?
20
in order to maintain a pH of 7.4, we need ____ times more HCO3- than CO2
kidneys
the concentration of HCO3- is regulated by the __________
lungs
the concentration of CO2 is regulated by the _________
amino, carboxylic acid, and R group
an amino acid contains three groups: ________, ________, ________
longer
the (longer/shorter) the R side chain, the more hydrophobic
greater
when pH is (greater/less) than the pKa of an ionizable group, it is deprotonated
less
when pH is (greater/less) than the pKa of an ionizable group, it is protonated
greater
when determining the secondary most predominant form of an amino acid - the form at the lower pH will be secondary when the average pKa is (greater/less) than the pH
less
when determining the secondary most predominant form of an amino acid - the form at the higher pH will be secondary when the average pKa is (greater/less) than the pH
melatonin
tryptophan can be converted into serotonin, which can then be converted into ________
sopnification
hydrolyzing fats with alkalis is considered __________ (breaks down fats into soap and glycerol)
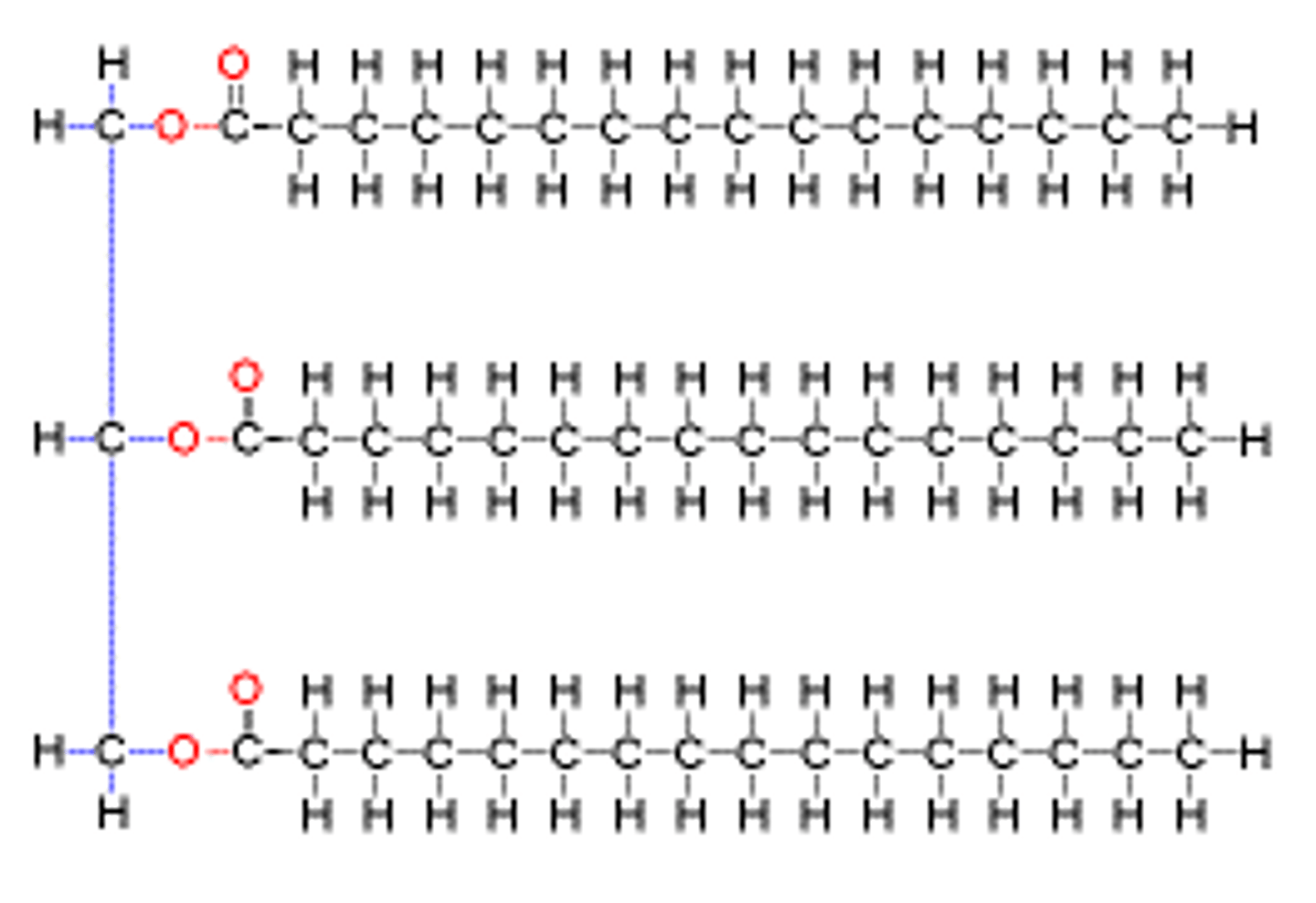
triacyglycerols
storage molecule in the fat that gives us maximal energy upon oxidation
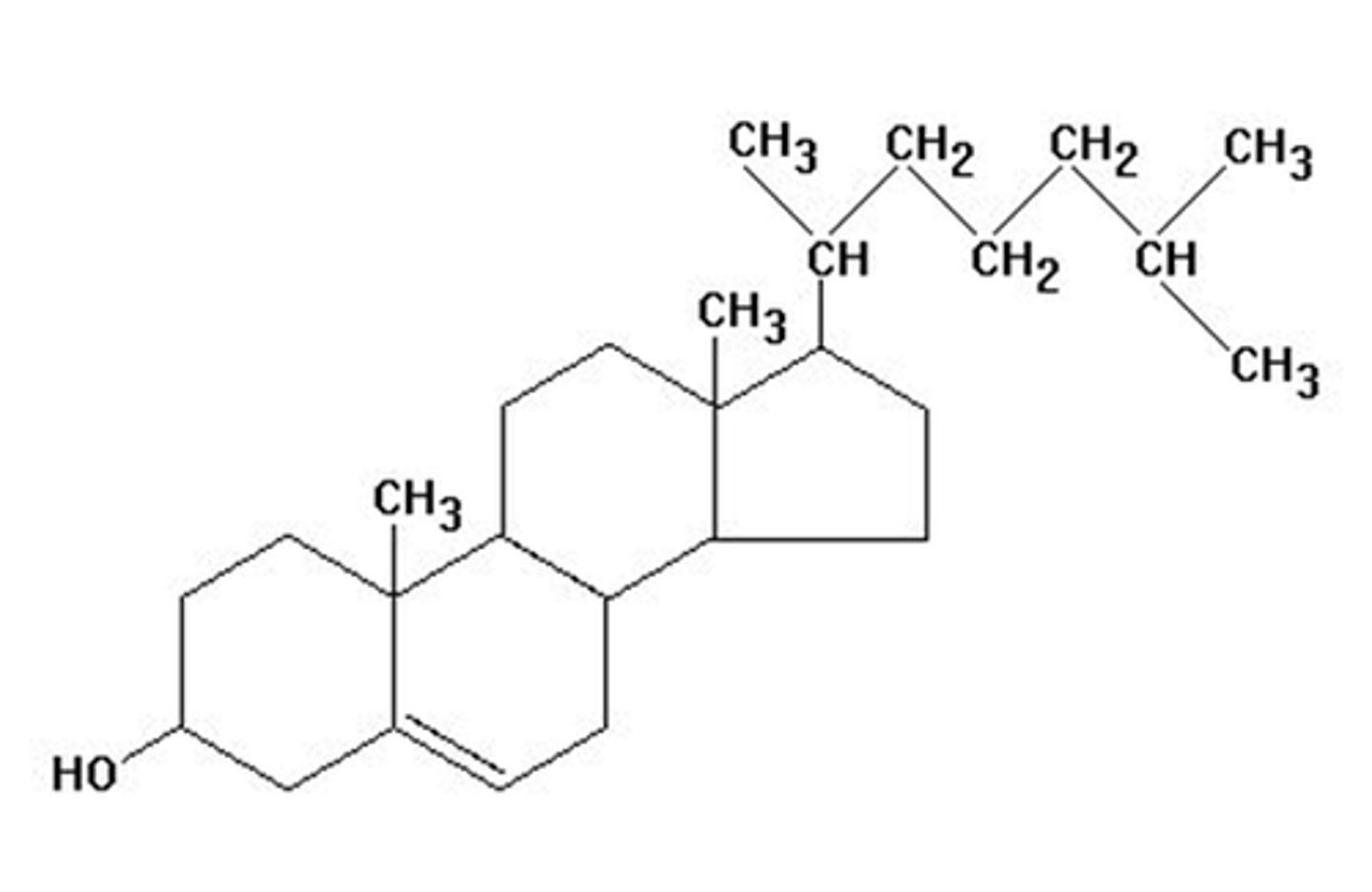
cholesterol
made up of four rings and is a hormone precursor
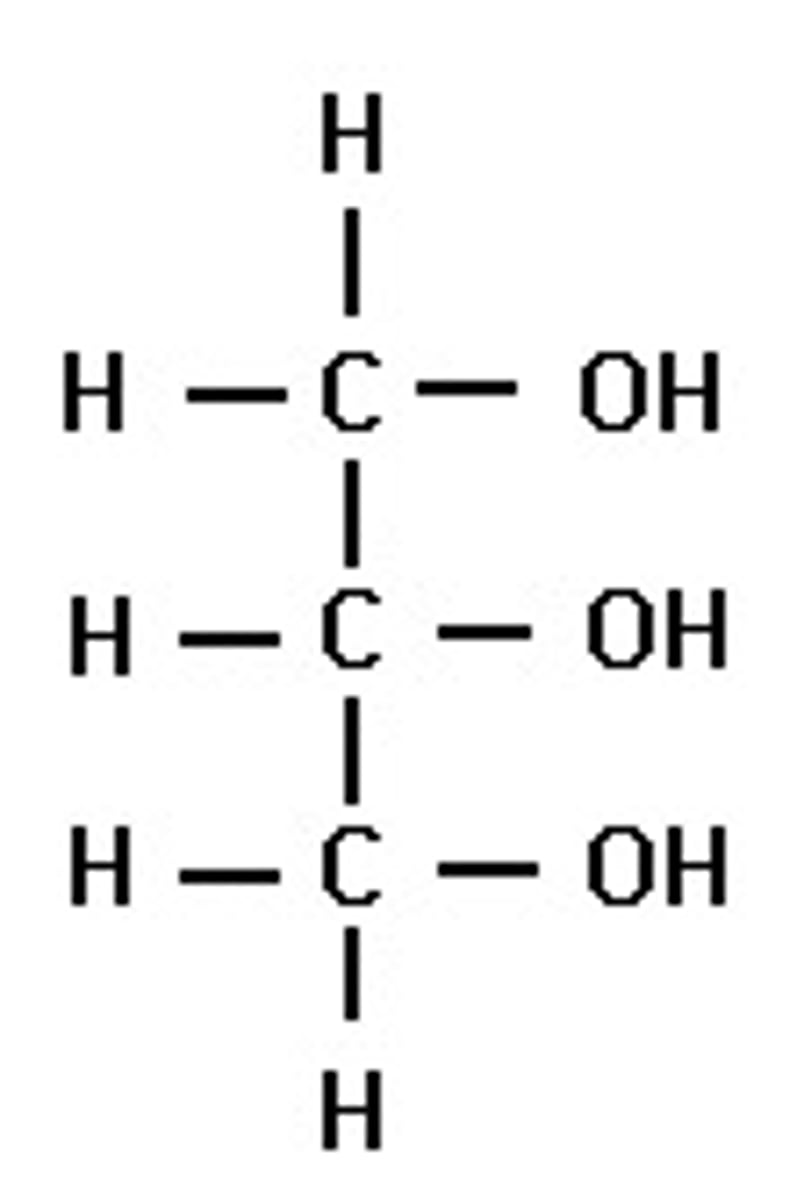
glycerol
a three-carbon alcohol with a hydroxyl group attached to each carbon
hydrophilic
R1 and R2 on a glycerol are from fatty acids, but R3 is a ___________ group
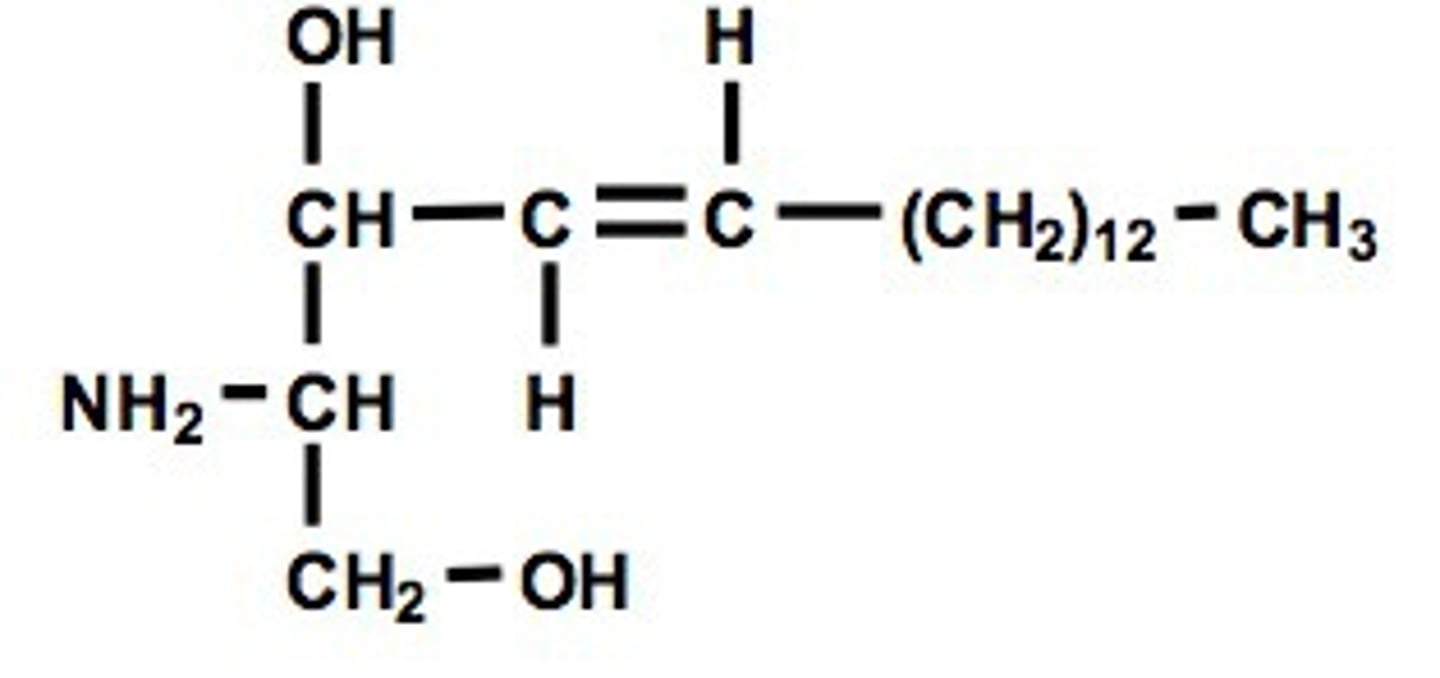
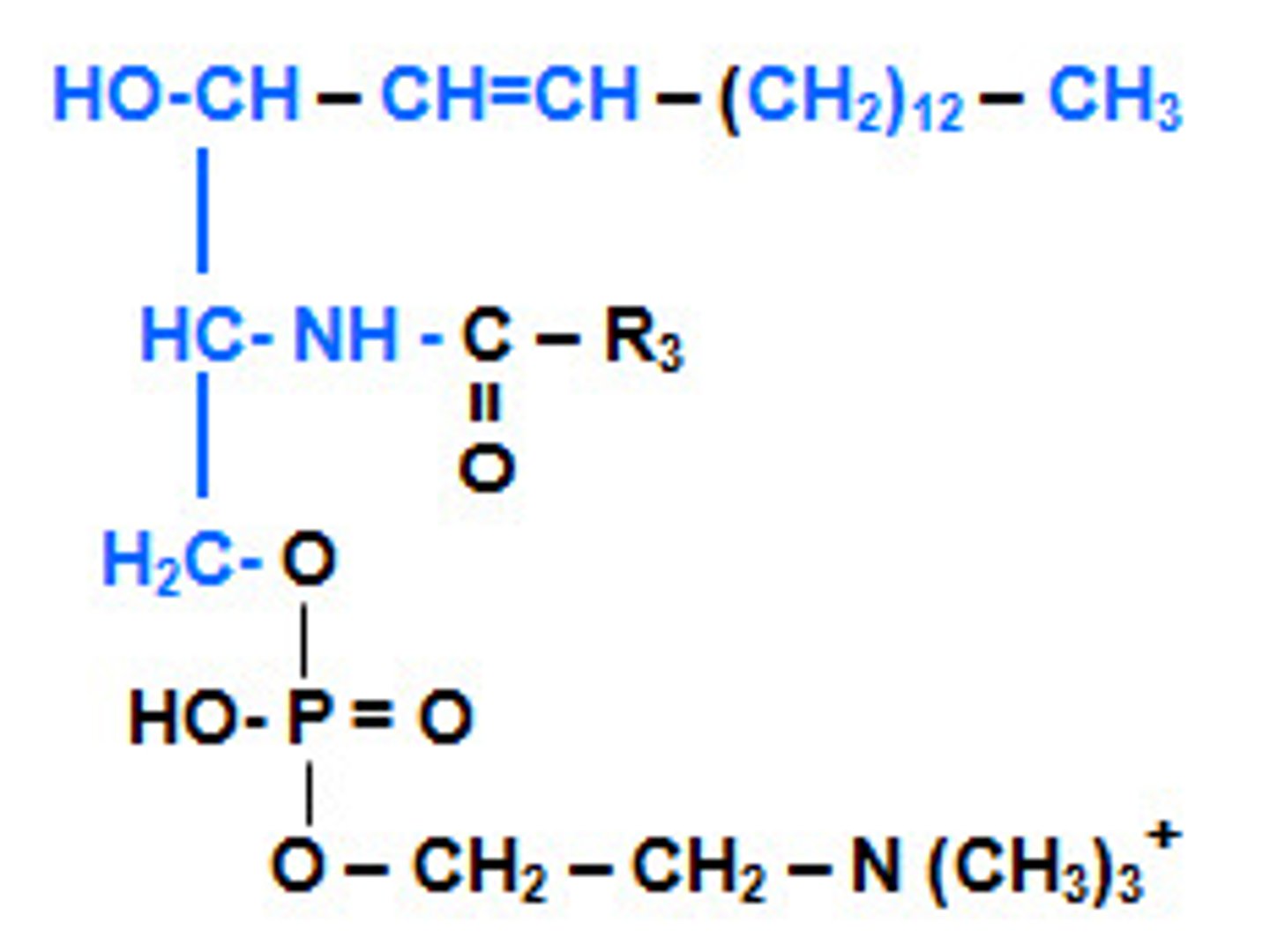
sphingolipid
lipid containing sphingosine rather than glycerol
ceramide
made from adding an amide to a sphingolipid
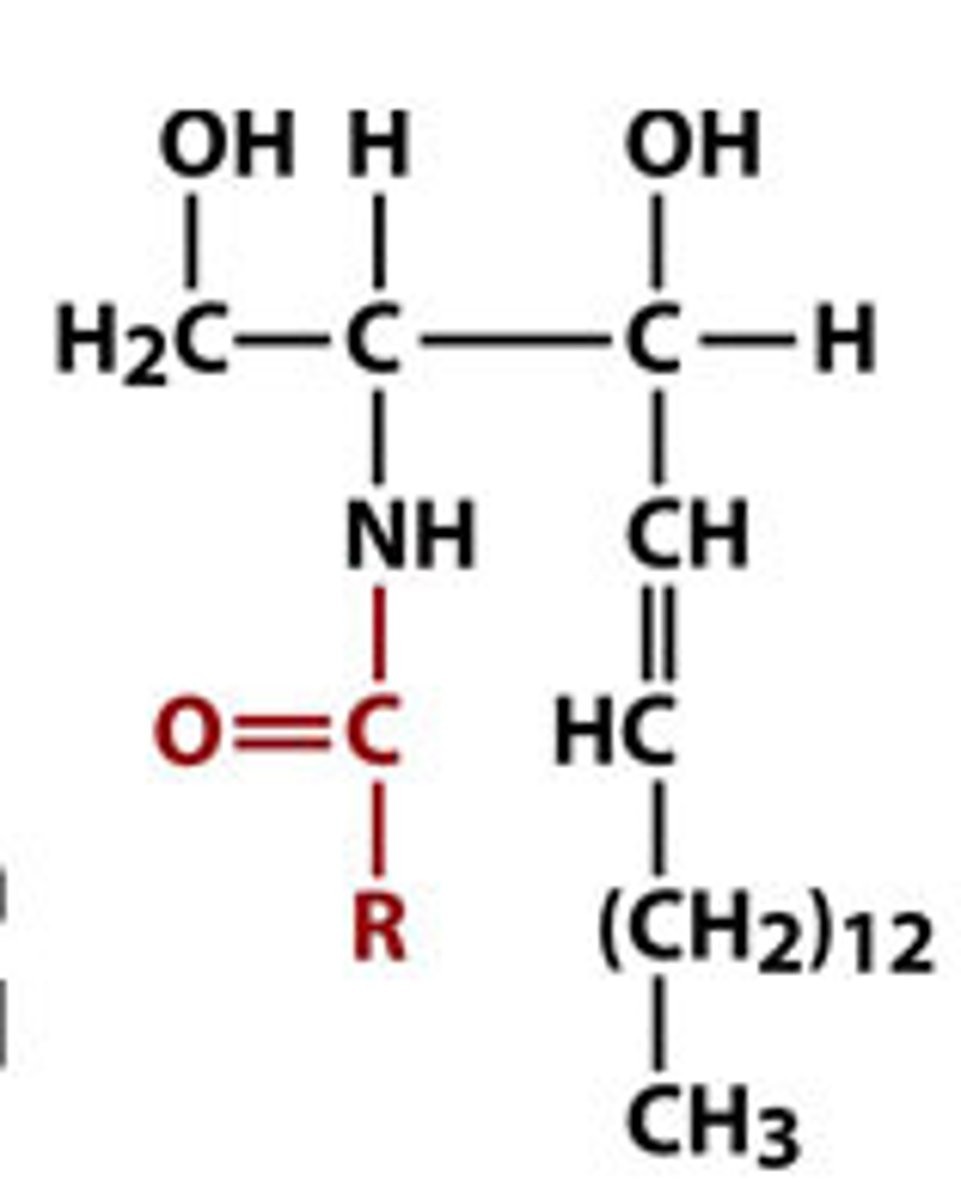
sphingomyelin
made from adding phosphocholine to a ceramide
a lipid with a saccharide
what is a glycolipid?
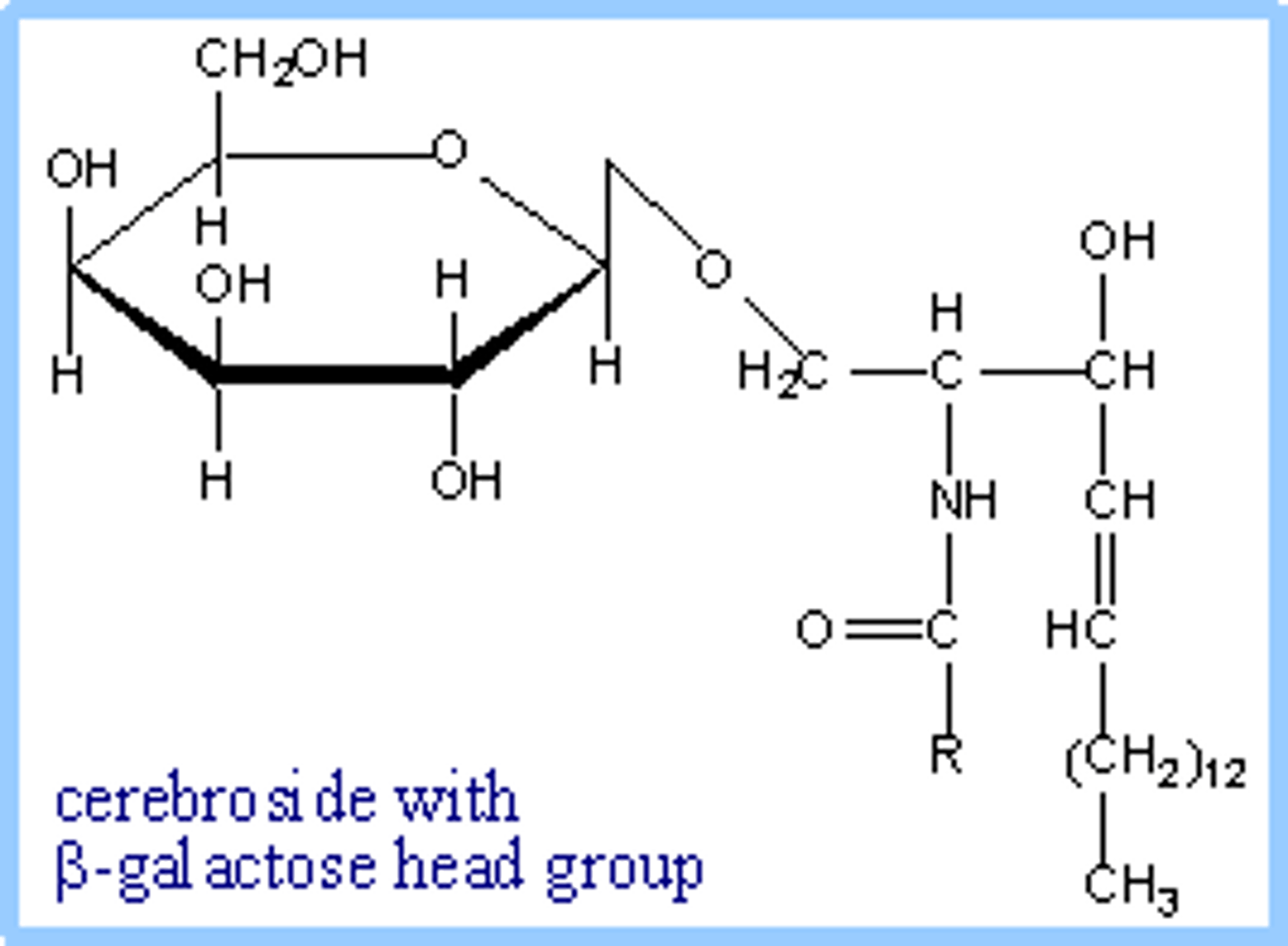
glycosphingolipid
a sphingolipid with a head group composed of sugars, including cerebrosides and globosides
glycoglycerolipids
glycerol based glycolipids that are more commnoly found in plants and bacteria
membrane lipids
the following are functions of __________:
1. separation of cellular processes
2. signaling and transport
3. regulation of what enters and leaves the cell
4. stability and integrity
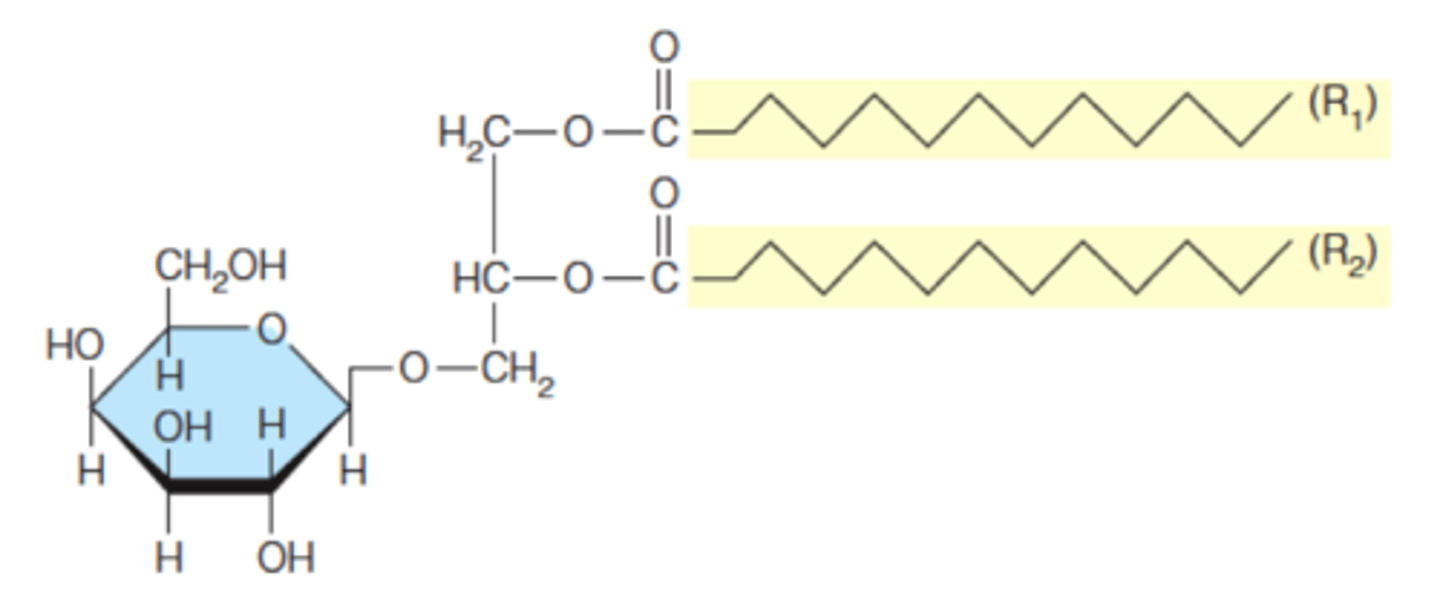
glycerophospholipid
a lipid containing a glycerol, phosphate, and two fatty acids
phosphotidylinositol (PI)
glycerophospholipid that is a major source of signaling metabolites
ex: arachiadonic acid >> prostaglandins OR diacylglycerol >> protein kinases
IP3
second messenger that signal the release of Ca2+
phosphotidylethanolamine (PE)
glycerophospholipid that moves from the cytosol to the membrane to increase H-bonding potential
phophotidylcholine (PC)
glycerophospholipid that is important for signaling
ex: Ach precursor
phophotidylserine (PS)
glycerophospholipid that flips lipids from inner to outer membrane and vice versa, which triggers non-inflammatory phagocytes during apoptosis
glycosyl phosphotidylinositol (GPI) anchoring
reversible method for anchoring proteins to a cell membrane (can be cut at the phosphate group to remove)
lipid raft
lipid-protein complexes that freely move laterally and regulate signaling
separation
what can be done to a lipid raft when we don't want them working all of the time?
pathogens
when a lipid raft comes together, it forms a binding site that allows ________ to enter
cholesterol and sphingomyelin
_______ and _______ are essential for raft formation
glycolipids
lipids that are important for cell communication, such as antigen recognition of blood types
increases
decreasing permeability (increases/decreases) rigidity
cardiovascular health and diabetes
fish oils are good for what health conditions? (counteracts cholesterol-induced rigidity and increases insulin receptor activity)
enter
binding of insulin to receptors, triggers glucose to (enter/exit) a cell
carbon 1
carbon 6
onic acids have a carboxylic acid on carbon ___ whereas uronic acids have a carboxylic acid on carbon ___
oxidized sugars
toxic products can be linked to ____________ to increase solubility and excretion (ex: bilirubin in the liver)
polyols
when carbonyls are converted to alcohols, they are considered _______ (ex: glyceraldehyde >> glycerol)
amino
cell surface oligosaccharides used for cell identification are made by ______ sugars
cartilage
what structure in the body is made from amino sugars?
sialic acid
which monosaccharide derivative is considered an N-acetyl-mannosamine
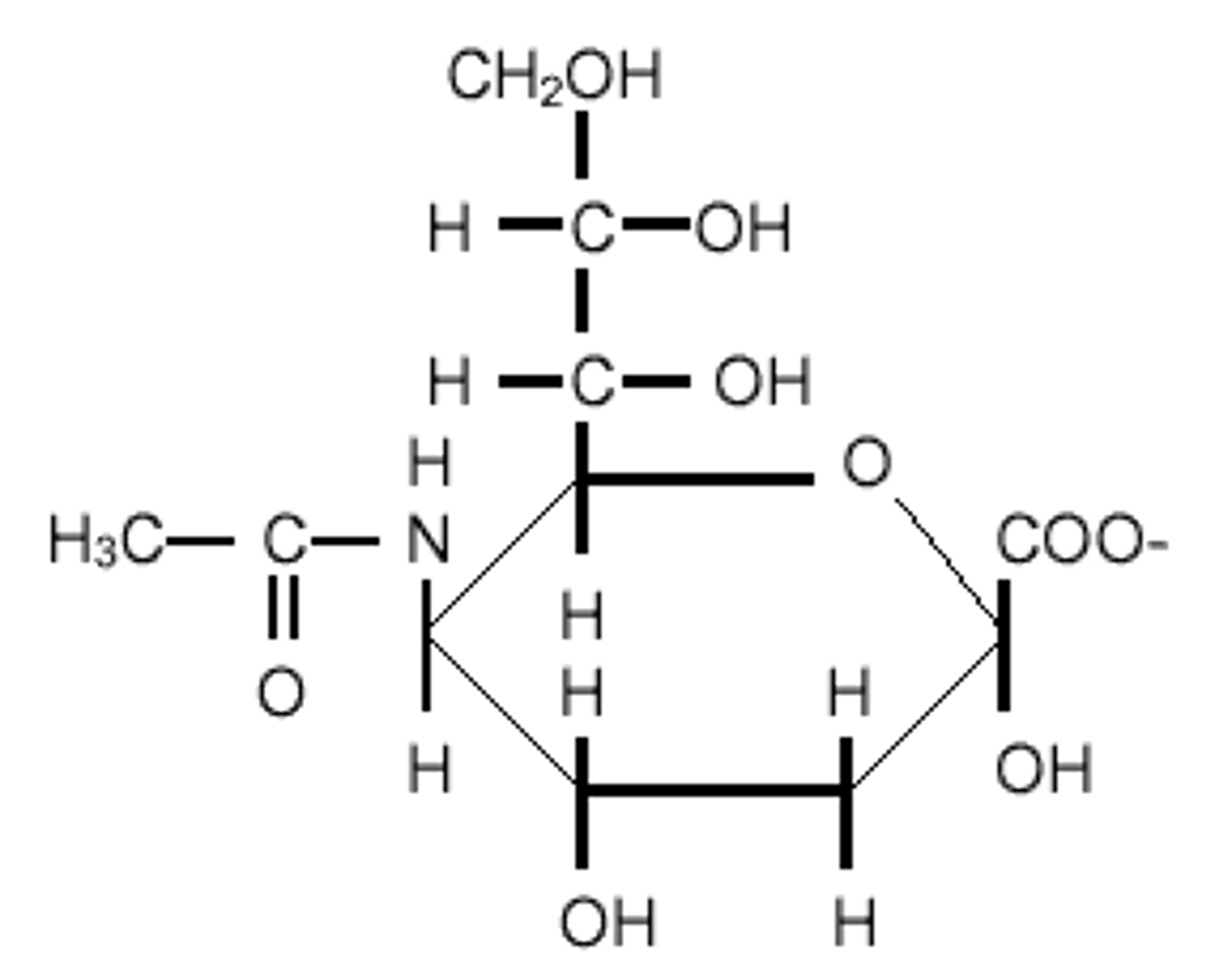
glycosidic
an ether bond through the anomeric carbon is considered a ________ link
enzyme
to make food lactose free, we can add an _______, such as beta-galactosidase aka lactase
starch
energy reserve in plants
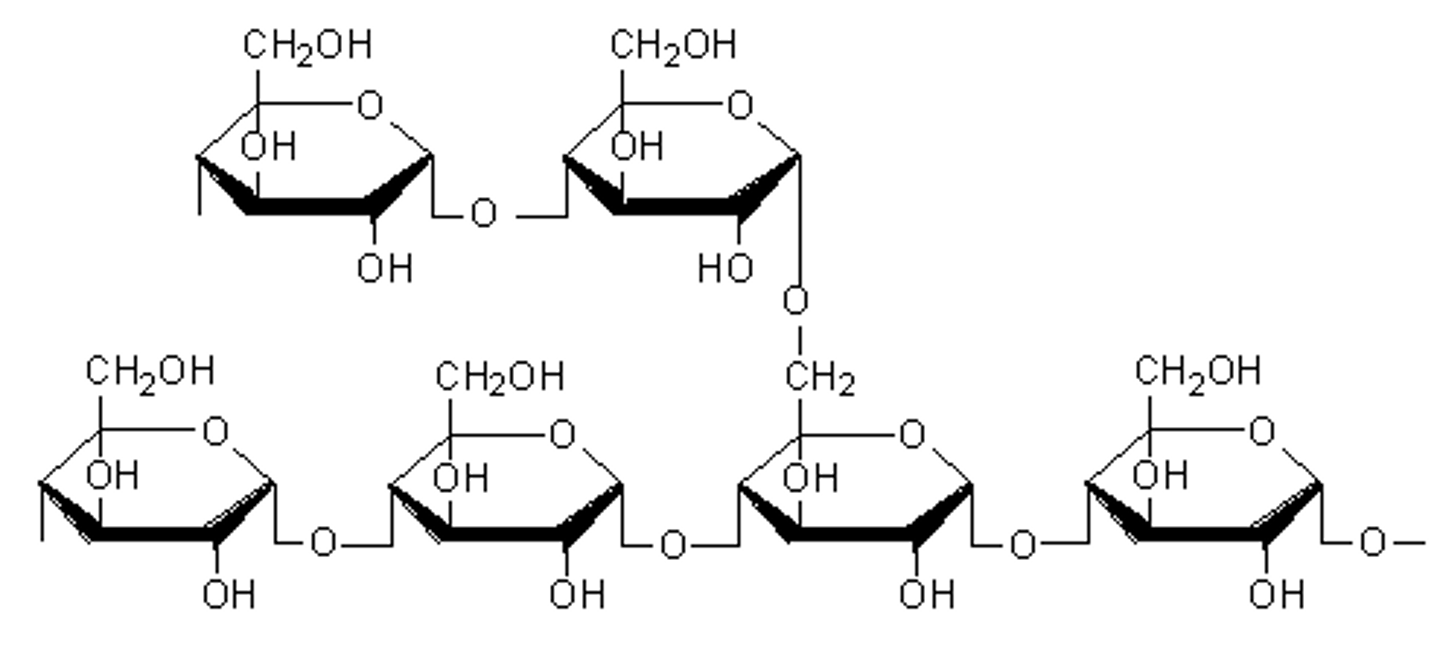
amylopectin
insoluble starch with branching at (1 -> 6) that can absorb water, but will not dissolve
saliva
pancreatic amylase
_____ begins digestion of starches in the mouth, and ______ breaks it down further in the pancreas
intestine
starches are broken down by the pancreas into dextrins, maltotriose, and maltose. dextrins are further broken down in the __________
glycogen
storage form of sugar in animals
cellulose
plant fiber that absorbs water and swells to make us feel full - helps maintain body weight
true
the human body cannot digest cellulose - true or false
chitin
indigestible polysaccharide that promotes wound healing and is biodegradable (ex: stitches)
chondroitins
structural component of cartilage that resists compression
heparin
highly charged polysaccharid that solubilizes blood clots to improve blood blow
carbohydrates
cancer cells lack ________, making them easier to move throughout the body
glycosylated proteins
protein backbones with carbohydrate side chains
peptidoglycans and proteoglycans
carbohydrate backbones with polypeptide side chains (two answers)
bursting
peptidoglycans protect cells from _______
lysozymes
enzymes that attack the peptidoglycan layer
peptidoglycans
penicillins and vancomycins interfere with biosynthesis of _________ on bacteria so that they easily undergo lysis
proteoglycans
protein chain on carbohydrate that offers resilience and cell adherence
nucleic acids
_________ are made up of an aromatic nitrogen base, carbohydrate, and phosphate group
nucleosides
nucleotides lacking a phosphate group are called ________
two
one
purines have ______ ring(s), while pyrimidines have _____
anomeric carbon
in DNA and RNA, bases always attached to the ____________ through an N-glycosidic link
3' and 5'
which carbons do phosphates connect to on cyclic nucleotides
purine di and triphosphates
what nucleotide is the highest in energy
cyclic
(cyclic/linear) nucleotides act as intracellular messengers to activate pathways
adenine = adenylic acid
guanine = guanylic acid
how are purines named when in nucleotide form?
cytosine = cytidylic acid
uracil = uridylic acid
thymine = deoxythymidylic acid (only found in DNA)
how are pyrimidines named when in nucleotide form?
purines - end in "sine" (adenosine)
pyrimidines - end in "dine" (thymidine)
how are nucleosides named (different for purines and pyrimidines)?
nucleoside name + monophosphate (adenosine monophosphate) OR replace "ine" with "ylic acid" (dexoythymidylic acid)
how are nucleotides with one phosphate named?
nucleoside name + di/triphosphate (adenosine triphosphate aka ATP)
how are nucleotides with two or three phosphates named?
cofactors
non-proteins required for enzymes to function
NAD and FAD
examples of cofactors that easily lose and gain electrons and are used in oxidation/reduction reactions
ATP
cofactor that acts as a source of phosphate for kinases and hydrolyzes to release energy for cells
phosphodiester
nucleotides attach through ____________ bonds at C3' and C5', which forms the primary structure of nucleic acids
G - C
A - T (DNA)
A - U (RNA)
what are the nucleotide base pairings for DNA and RNA