Substitution & Elimination
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Sn1, Sn2, E1, E2 (basics & tips)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Benyzl > allyl
Carbocation stability:
Benzyl vs Allyl
> or < ?
HBr, HCl, HI, H2SO4, H3PO4
Weak base
Tertiary > Secondary > Primary >Methyl
Carbocation stability:
Methyl, Primary, Secondary, Tertiary
Rank from most to least
SN2
If you have a methyl carbocation, which rxn(s) might occur?
SN2, E2
If you have a primary carbocation, which rxn(s) might occur?
SN1, E1, E2
If you have a tertiary carbocation, which rxn(s) might occur?
SN1,E1
If you have a tertiary carbocation and you have a weak Nu/B then which rxn(s) might occur?
E2
If you have a tertiary carbocation and you have a strong B then which rxn(s) might occur?
polar protic
H-bonding solvent type
(H on N,O,F)
polar aprotic
No H for H-bonding
SN2
Polar aprotic favors which rxn?
I > Br > Cl > F
Protic solvent nucleophilic strength in order starting from strongest to weakest
F > Cl > Br > I
Aprotic solvent nucleophilic strength in order from strongest to weakest
strong
When a (-) charge is present, it means _________ nucleophile.
stronger
The stronger the base, the ________ the nucleophile.
stays the same
Whatever doesn’t leave in stereochemistry does what?
Proton transfer
When H leaves, what mechanism?
SN1
SN1 or SN2?
3° > 2° > 1°
WEAK nucleophile
Polar PROTIC solvent
Racemic stereochemistry
SN2
SN1 or SN2?
1° > 2° > 3°
STRONG nucleophile
Polar APROTIC solvent
Inversion stereochemistry
double bond
In ALL elimination rxns, you ALWAYS form a what?
more
the more alkyl groups attatched to pi bonds, the ______ hyperconjugation exists.
Elimination
Which?
Elimination or Substitution?
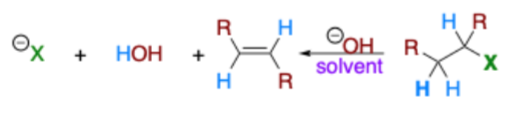
Substitution
Which?
Elimination or Substitution?
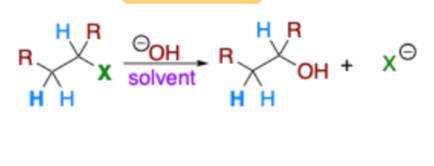
Right; left
within the periodic table, nucleophilicity increases from _______ to ______ across the periods and down a family.
Weak bases
Examples of what?
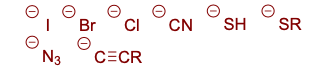
I–, Br–, SCN–, N3–, CH3CO2– , RS–, CN–, Amines, etc.
Aprotic
Acetone is polar _______.
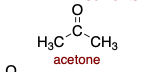
aprotic
DMF (dimethylformamide) is polar ________.
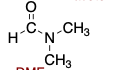
protic
H2O is polar _______.
aprotic
Acetonitrile is polar ________.
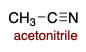
aprotic
DMSO (dimethylsulfoxide) is polar ________.
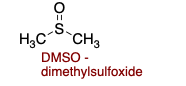
aprotic
HMPA (hexamethylphosphortriamide) is polar ________.
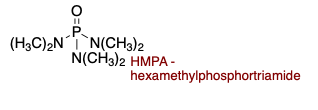
protic
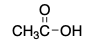
CH3 - OH is polar _______.
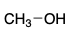
protic
CH3CH2 - OH is polar _______.
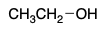
protic
This is polar _______.
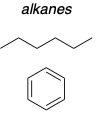
Non-polar solvents
These are examples of ?
strong bases
These are examples of:
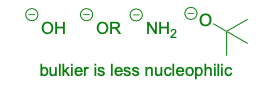
Good nucleophiles
These are examples of:
SN2
If 1° and has a good nucleophile then it is ______.
SN1
Which mechanism?
C+ (carbocation intermediate), solvent replaces L.G.
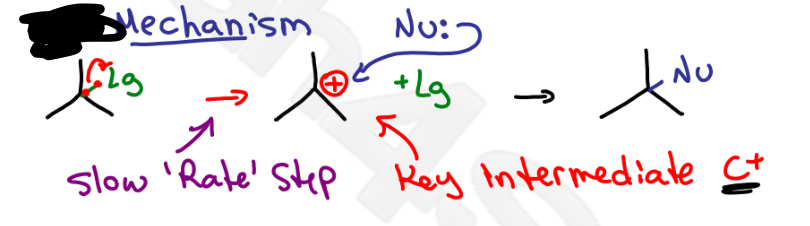
SN1
Which substitution rxn favors 3°?
SN2
Which mechanism?
occurs in 1 step
No C+ (carbocation intermediate), no replaced L.G.

E1
which mechanism?
C+ (carbocation intermediate), pi bonds between alpha and beta
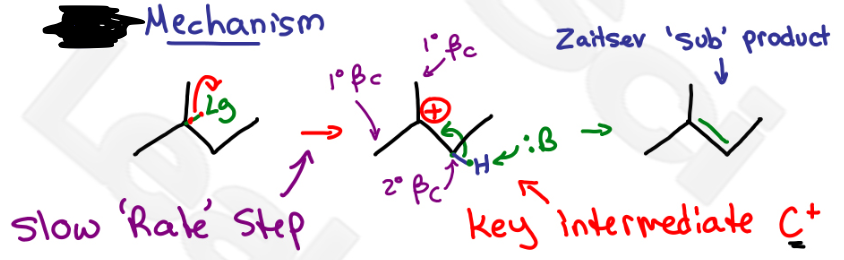
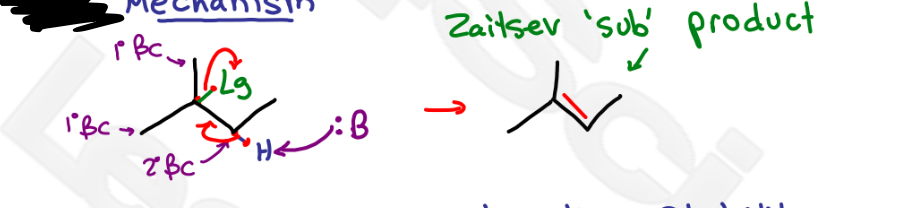
E2
Which mechanism?
no C+ (carbocation intermediate), pi bond between alpha and more substituted beta carbon
k[alkyl]
Rate for SN1
k[alkyl][Nu]
Rate for SN2
k[alkyl]
Rate for E1
k[alkyl][B]
rate for E2