Parasitic Helminths
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Clonorchis Sinensis (oriental liver fluke)
Definitive and Intermediate host?
How does the infection happen in humans?
How do we diagnosis the infection?
Is there any identifying characteristics for the egg, larvae or adult of each organism?
Name the diseases caused by the above organisms.
Symptoms
Definitive host: human
Intermediate host: freshwater fish and snail
How does the infection happen in humans?
Eating raw or undercooked fish that has been infected
How do we diagnosis the infection?
Presence of eggs in the stool
Is there any identifying characteristics for the egg, larvae or adult of each organism?
Egg: operculum
Adult: testes and uterus in one
Name the diseases caused by the above organisms
Clonorchiasis (liver disease)
Symptoms
Abdominal pain
Inflamed bile ducts
Liver damage
Bile duct cancer (extreme cases)
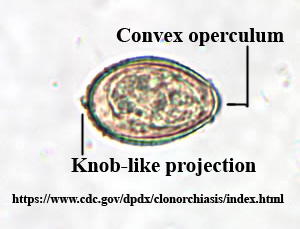
Chlonorchis sinensis egg
Operculum + small knob
Reminds me of an urn
Clonor sounds like urn
Schistosoma mansoni
Definitive and intermediate host?
How does the infection happen in humans?
How do we diagnosis the infection?
Is there any identifying characteristics for the egg, larvae or adult of each organism?
Name the diseases caused by the above organisms.
Symptoms
definitive host: humans
Intermediate host: freshwater snail
How does the infection happen in humans?
Infected human urinates/poops in the water
Uninfected human enters water that has been contaminated with infected urine and feces.
Larvae penetrates unbroken skin, traveling into the mesenteric veins (gut) or urinary tract (in some species)
How do we diagnosis the infection?
Presence of eggs in the feces or urine (some species only)
Is there any identifying characteristics for the egg, larvae or adult of each organism?
Egg: distinct lateral spine
Adult female: thinner, fits into male groove
Adult male: shorter, wider, groove where female can lie inside of
Name the diseases caused by the above organisms.
Schistosomiasis
Symptoms
Bloody urine
Painful/difficulty urinating
Abdominal pain
Diarrhea
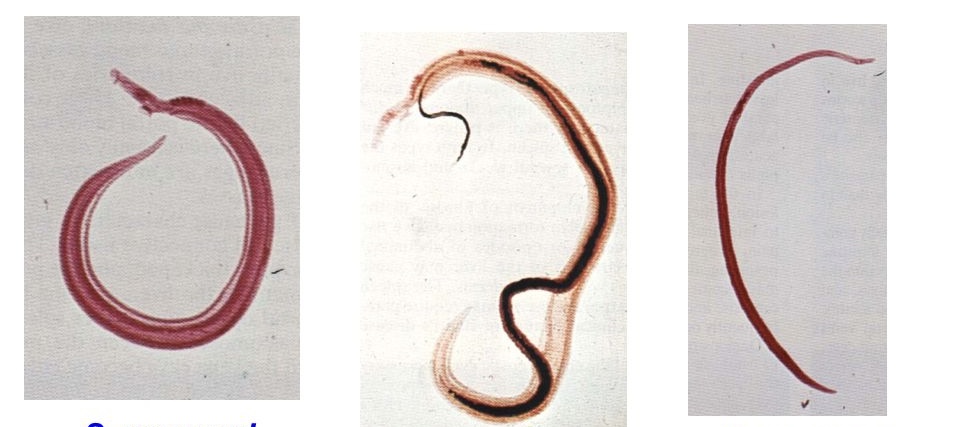
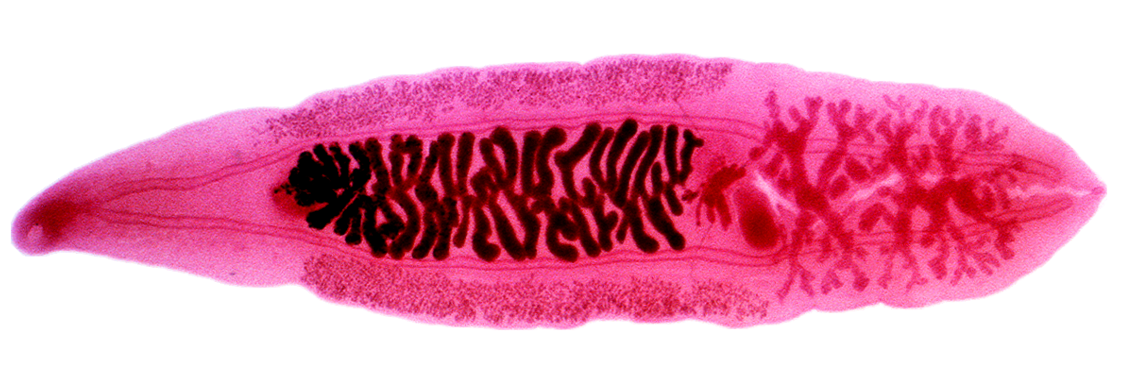
Schistosoma mansoni female and male adult
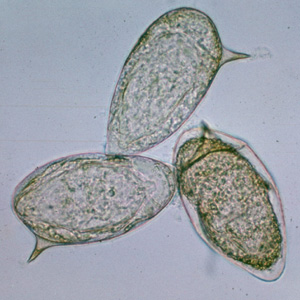
Schistosoma mansoni egg
Lateral spine
Mnemonic: S in Schistosoma = Spine
dipylidium caninum
Definitive and intermediate host?
How does the infection happen in humans?
How do we diagnosis the infection?
Is there any identifying characteristics for the egg, larvae or adult of each organism?
Name the diseases caused by the above organisms.
Symptoms
Definitive host
Dog or cat
Humans (children usually)
Intermediate host?
Cat or dog flea
How does the infection happen in humans?
Accidental ingestion of flea contaminated with the larval stage of the parasitic helminth
How do we diagnosis the infection?
Presence of proglottids or egg packets in the stool
Is there any identifying characteristics for the egg, larvae or adult of each organism?
Eggs: clusters of eggs (egg packets)
Name the diseases caused by the above organisms.
Dipylidiasis
Symptoms
Abdominal pain
Indigestion
Loss of appetite
Rmbr: its a dog tapeworm and tapeworms have segments (proglottids) containing egg packets
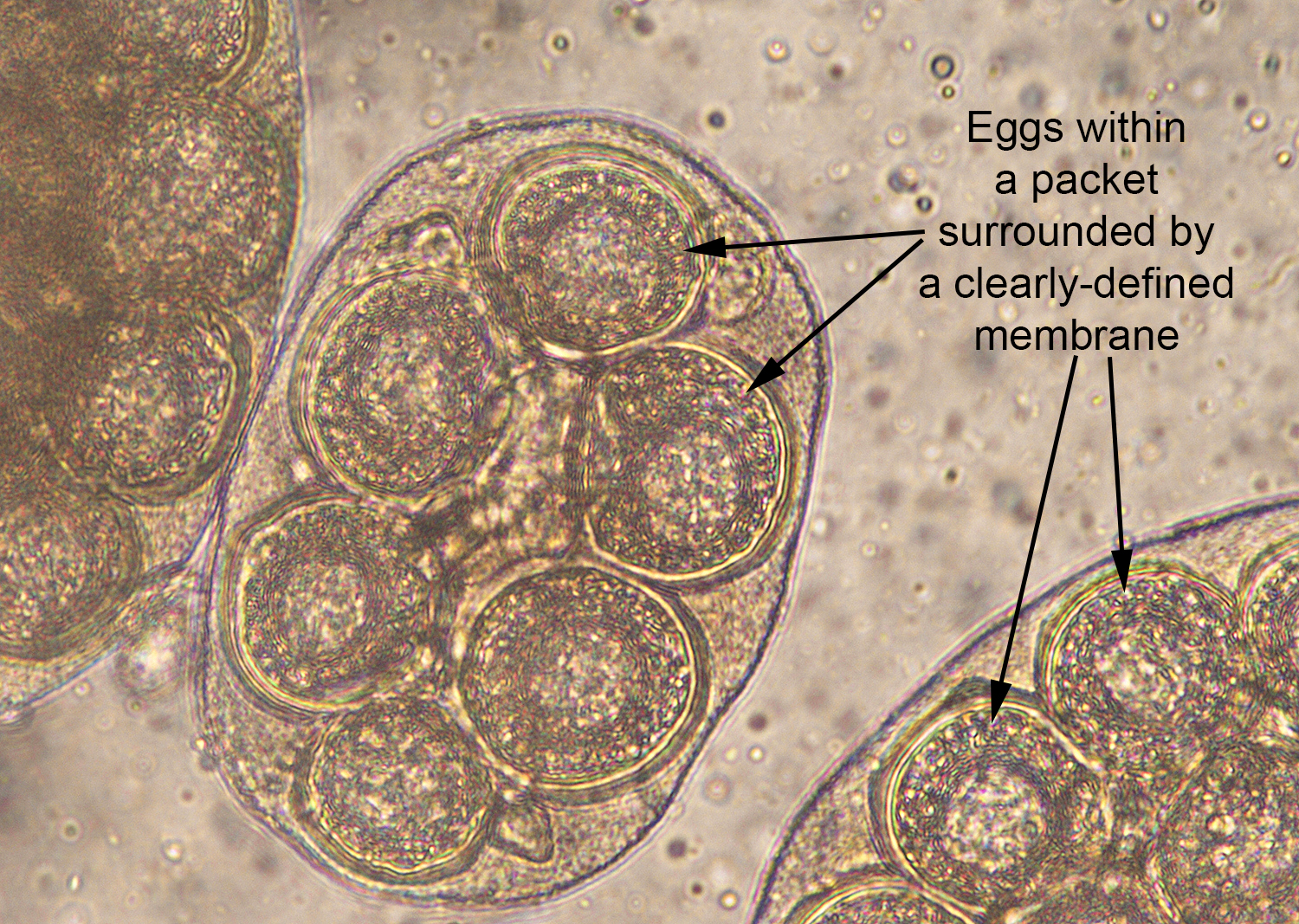
Dipylidium caninum egg packets
Echinococcus granulosus
Definitive and intermediate host?
How does the infection happen in humans?
How do we diagnosis the infection?
Is there any identifying characteristics for the egg, larvae or adult of each organism?
Name the diseases caused by the above organisms.
Symptoms
Definitive host?
Domestic and wild carnivores (eg: wolves, dogs, dingos)
intermediate host?
Herbivorous mammals (Eg: sheep, elk)
Humans (accidental, dead end intermediate hosts)
How does the infection happen in humans?
Fecal oral route (accidentally ingesting food contaminated with eggs or fingers contaminated with eggs, which come from the feces of wild/domestic carnivores)
How do we diagnosis the infection?
Imaging techniques (MRI, CT Scan) to detect hydatid cysts
Is there any identifying characteristics for the egg, larvae or adult of each organism?
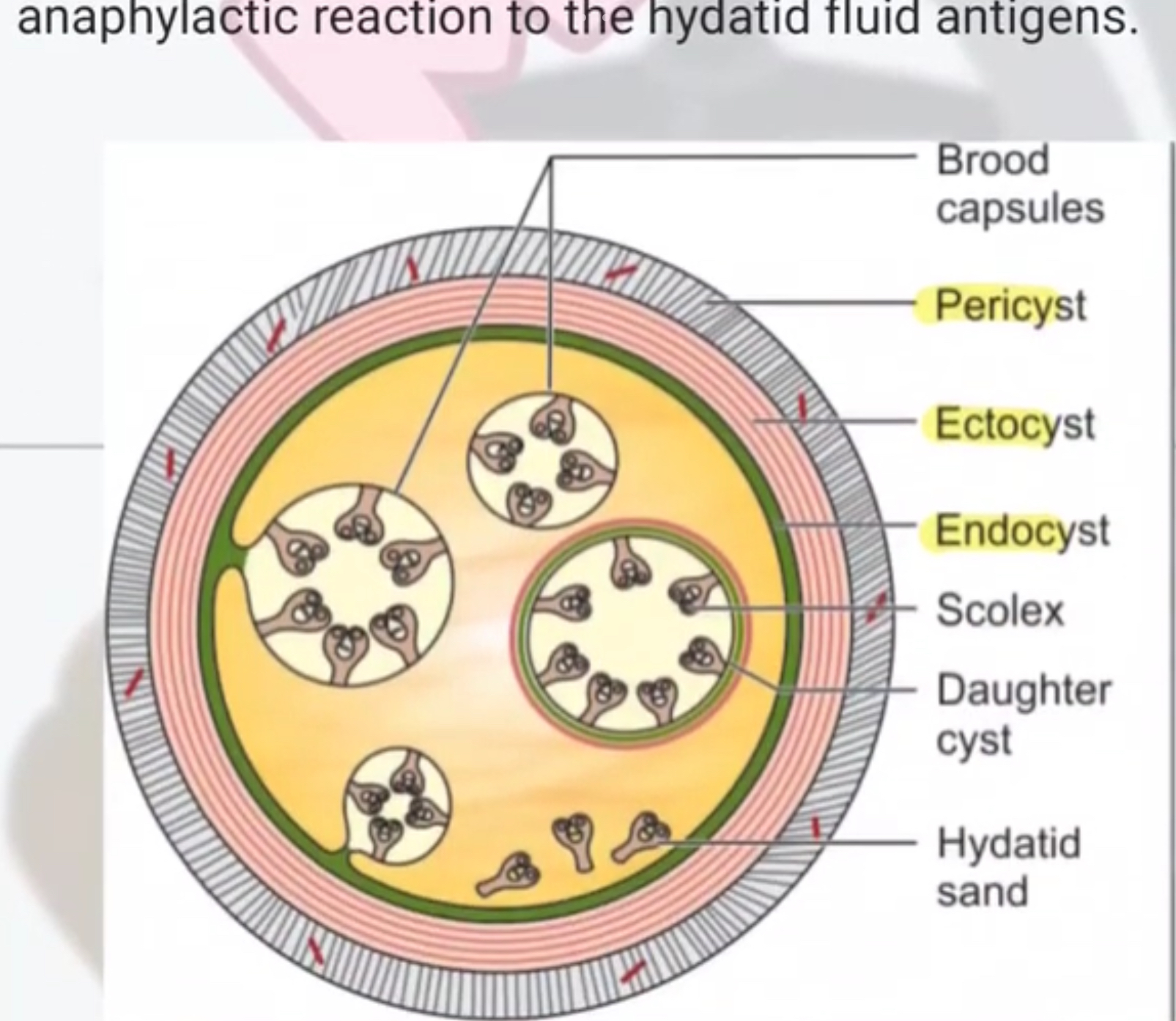
Hydatid cyst
Name the diseases caused by the above organisms.
Hydatid disease
Symptoms
Cysts form in liver + lungs
Cough
Shortness of breath
Chest pain
Abdominal pain
Pressure in liver/lungs
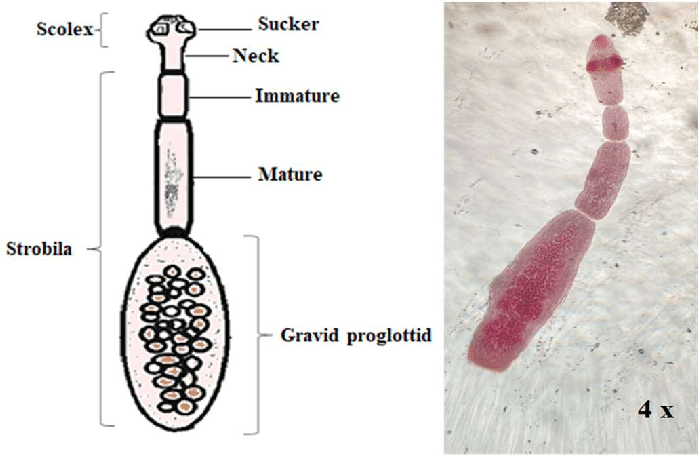
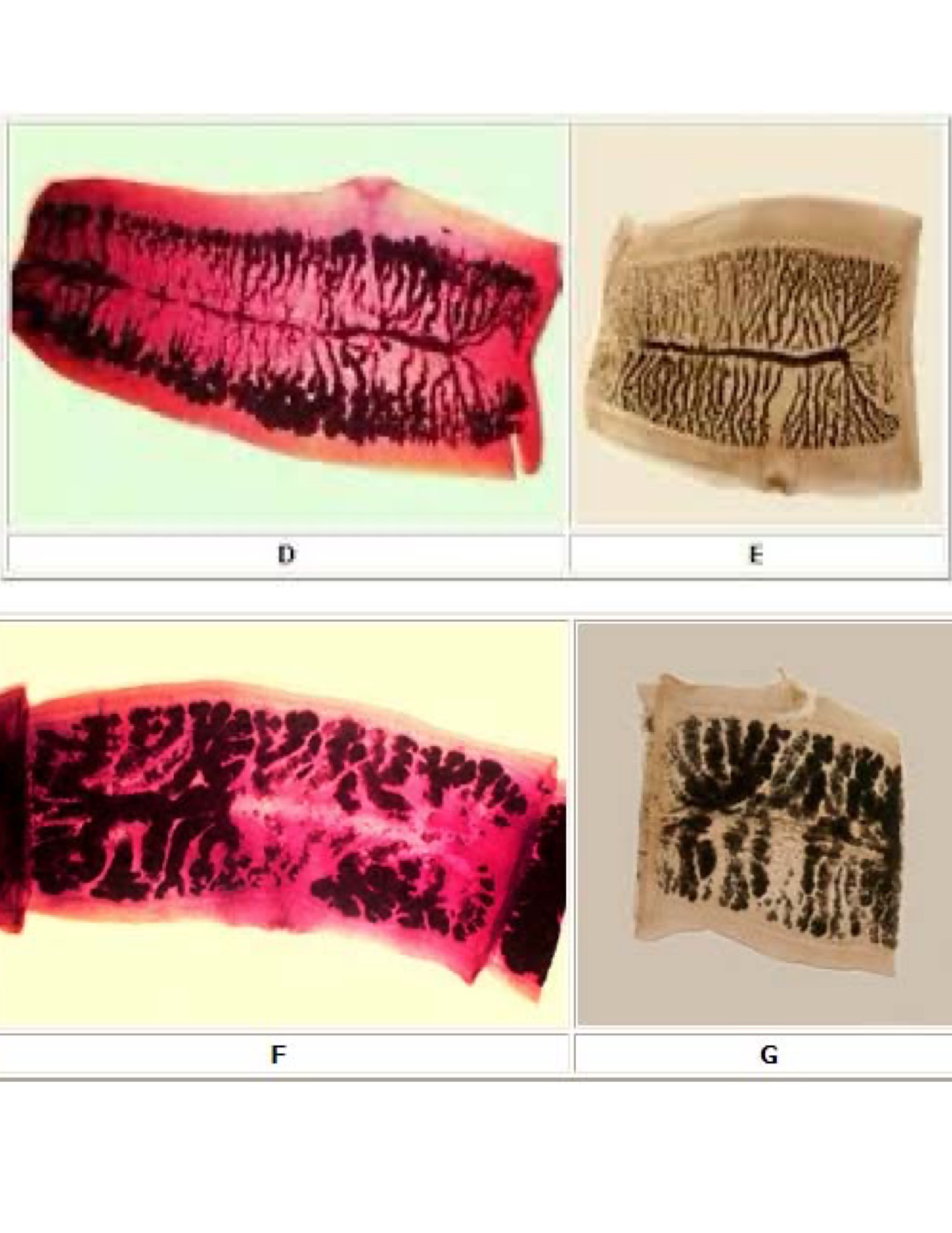
Echinococcus granulosus adult
Looks like a c*ck
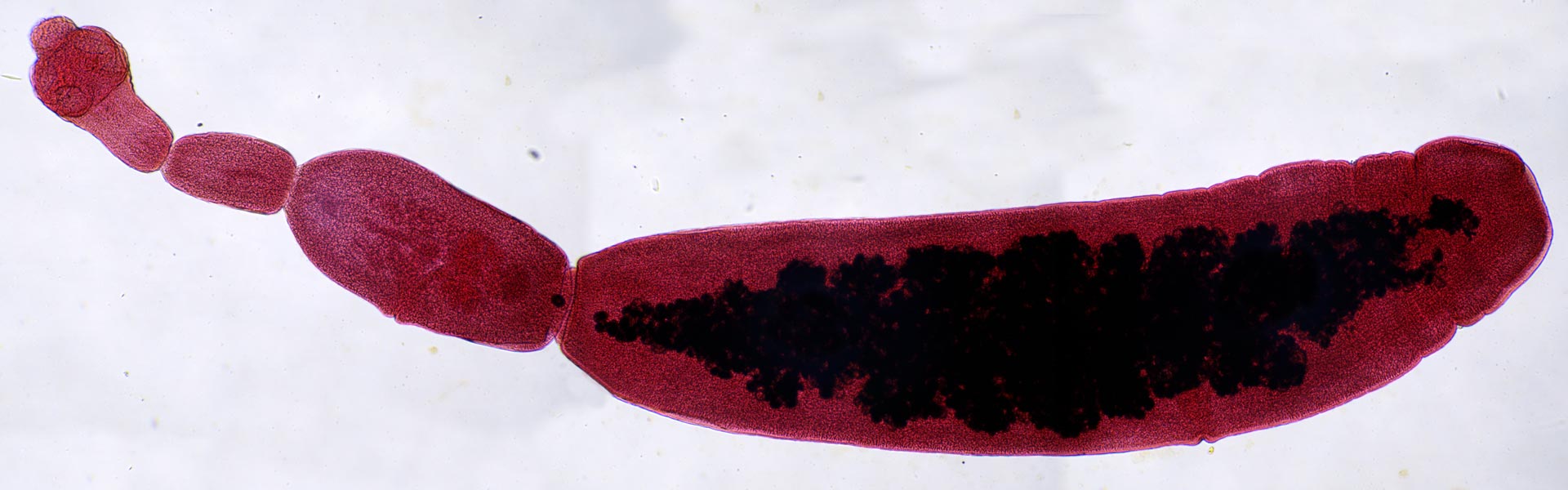
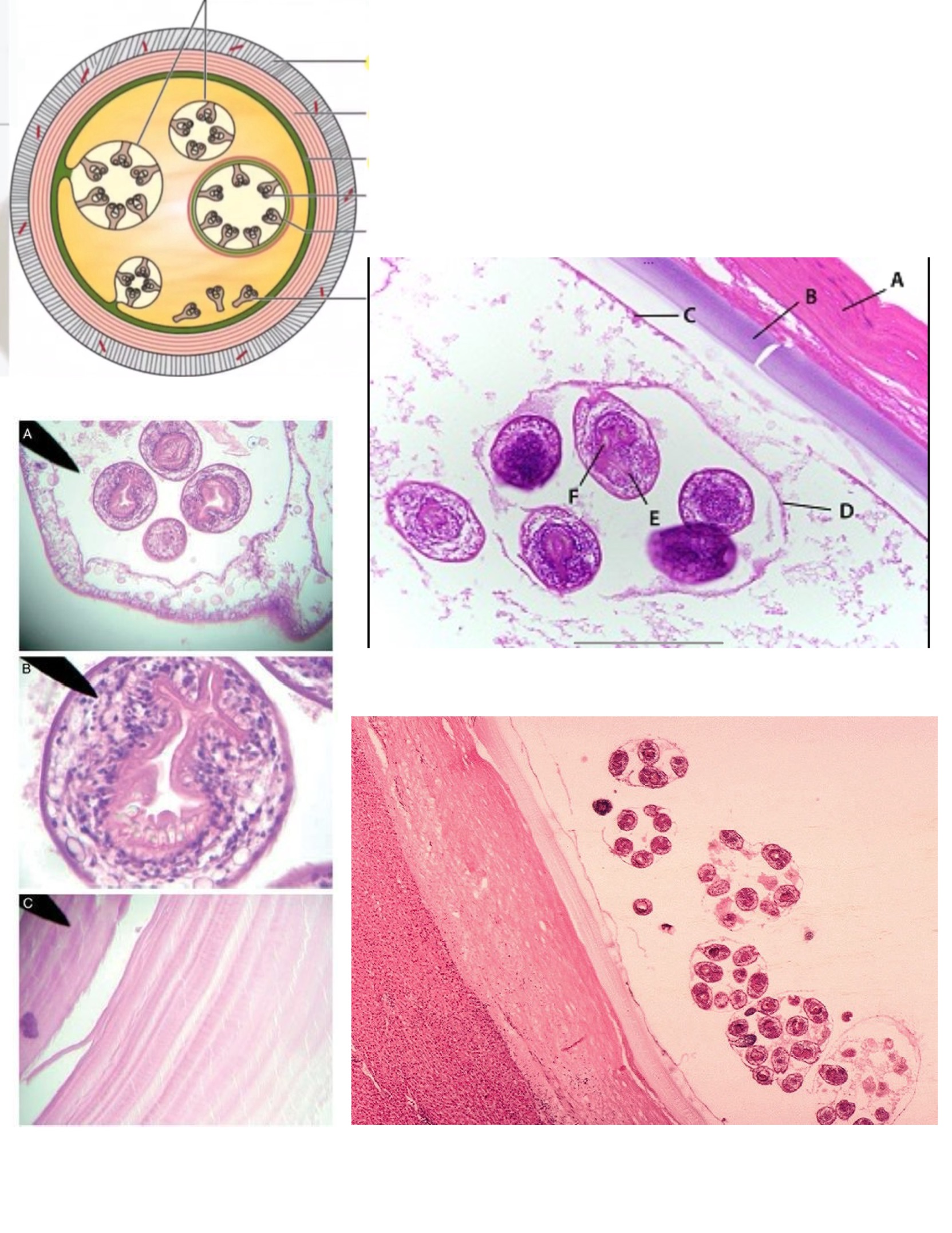
Echinococcus granulosus hydatid cyst w protoscolices
Taenia spp.
Definitive and intermediate host?
How does the infection happen in humans?
How do we diagnosis the infection?
Is there any identifying characteristics for the egg, larvae or adult of each organism?
Name the diseases caused by the above organisms.
Symptoms
Definitive host?
Humans
intermediate host?
Pork or cattle
How does the infection happen in humans?
Eating raw or undercooked pork or cattle that has been infected
How do we diagnosis the infection?
Presence of eggs or proglottids in the stool (bc rmbr its a tapeworm)
Is there any identifying characteristics for the egg, larvae or adult of each organism?
Scolex
Suckers
Hooklets
Proglottids
Eggs
Striated outer shell
Name the diseases caused by the above organisms.
Taeniasis
Cysticercosis
Infection with the larval stage of the worm in the brain, eyes, and muscles. Direct ingestion of Taenia solium eggs
Symptoms
Abdominal pain
Weight loss (hooks onto duodenum of small intestine, where most digestion occurs. Rmbr: tapeworm diet)
Cysticercosis: seizures, muscle/eye damage, mimics brain tumor symptoms
Pork tapeworm;
Taenia solium
Beef tapeworm:
Taenia saginata
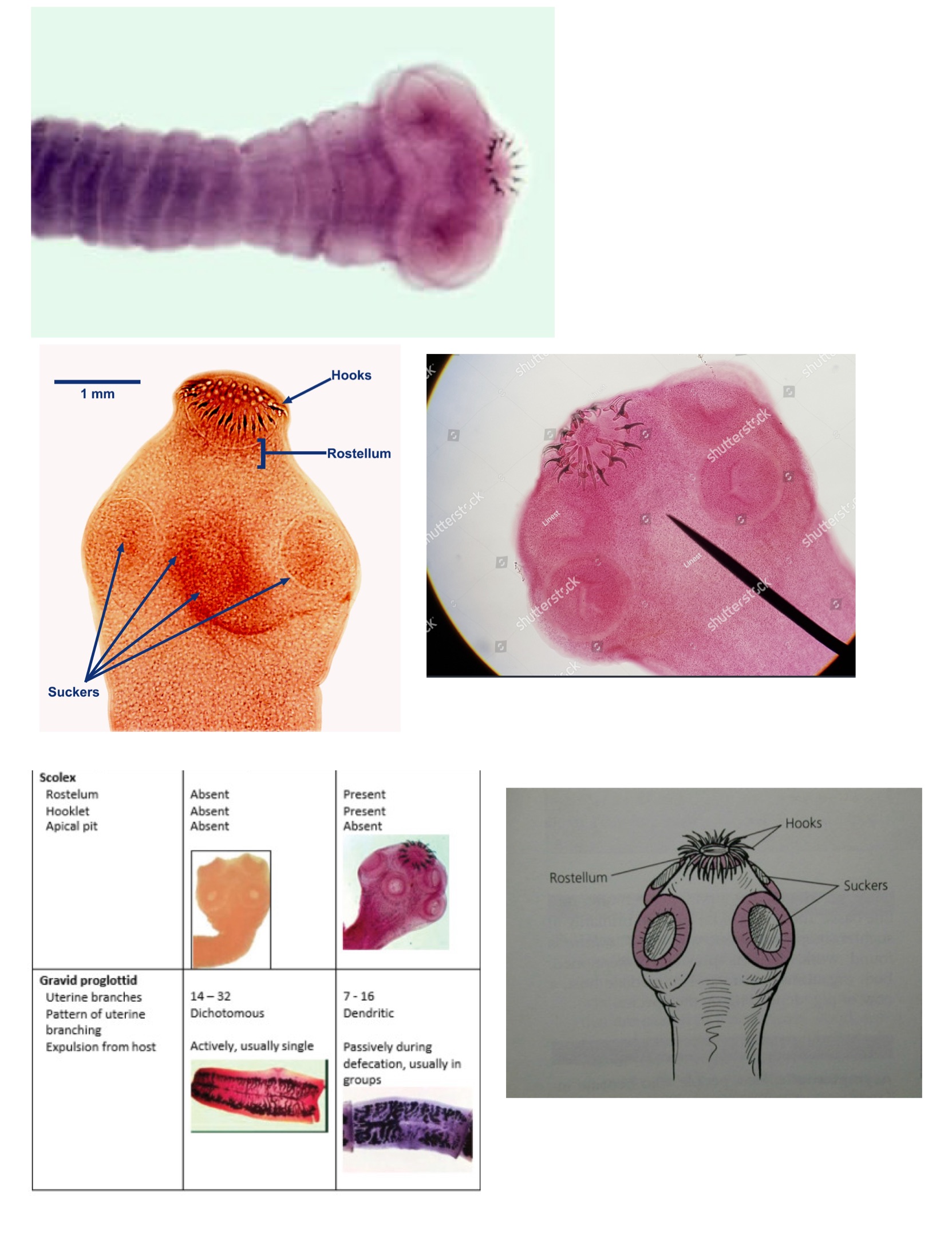
Taenia solium scolex
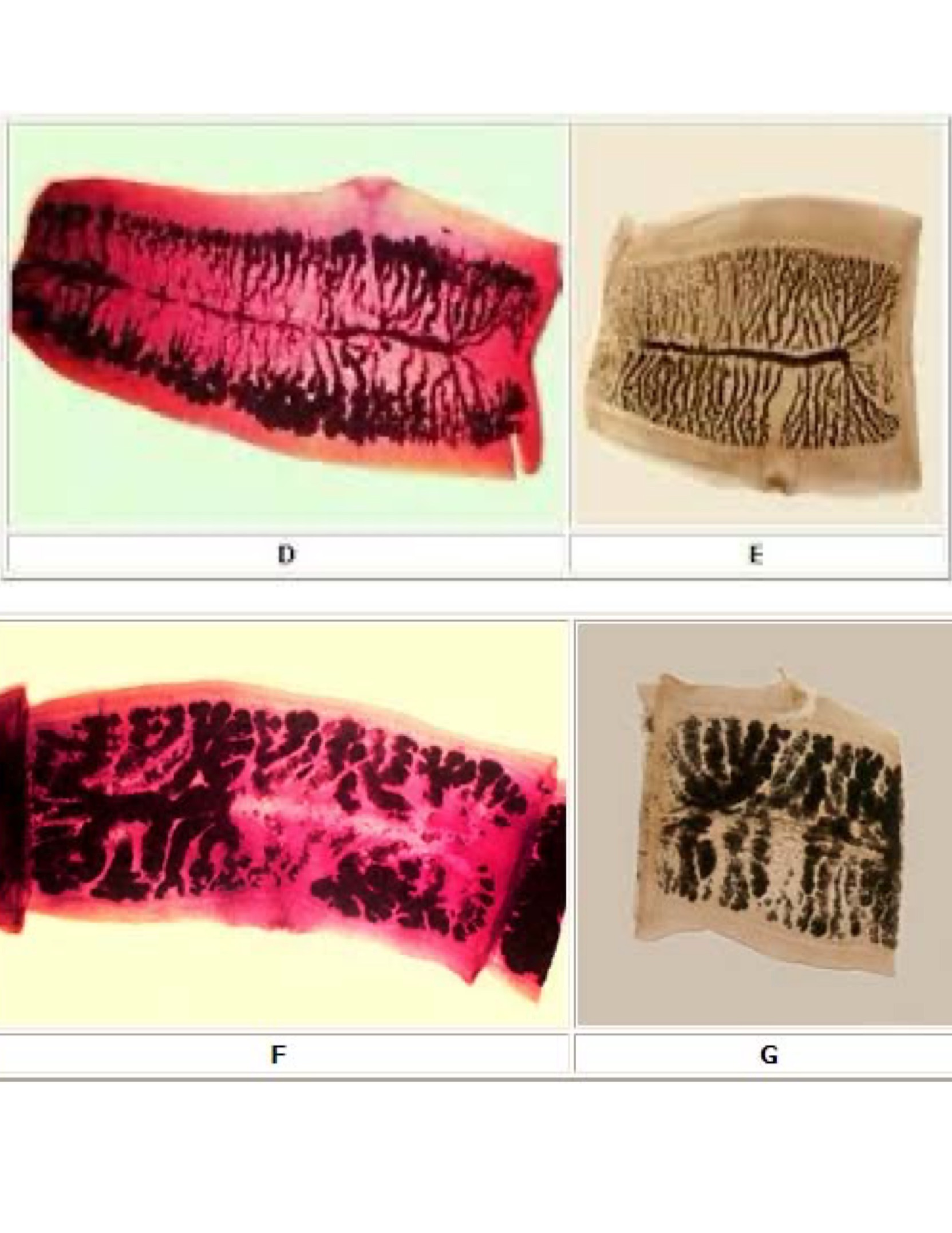
Taenia solium proglottids
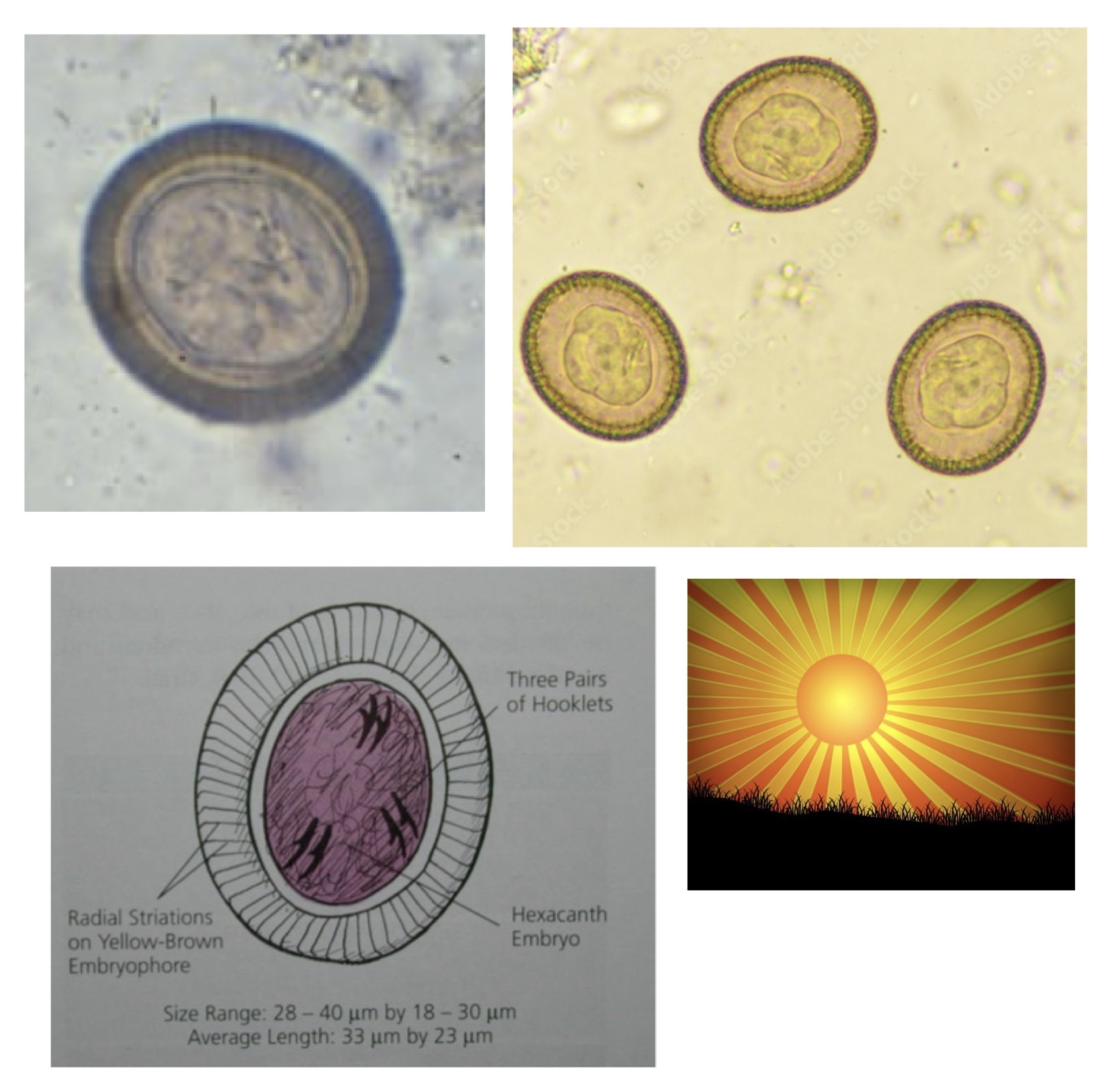
Taenia solium eggs
SOL= looks like sun rays aka striations
Ascaris lumbricoides
Definitive and intermediate host?
How does the infection happen in humans?
How do we diagnosis the infection?
Is there any identifying characteristics for the egg, larvae or adult of each organism?
Name the diseases caused by the above organisms.
Symptoms
Definitive host
Humans
intermediate host?
None
How does the infection happen in humans?
Ingestion of contaminated food or soil (contaminated w/human feces)
Eg: consuming unwashed/unpeeled fruits/veggies, hands/fingers w/dirt into mouth
Pathway: mouth, intestines, bronchial tree (lungs), throat, swallow, intestines, poop.
How do we diagnosis the infection?
Presence of eggs in the stool
Is there any identifying characteristics for the egg, larvae or adult of each organism?
Eggs: mammillations (Edge of the egg has scalloped/wavy edges)
Name the diseases caused by the above organisms.
Ascariasis and ascaris pneumonia
Symptoms
Cough
Abdominal discomfort
rmbr: its a human roundworm (Roundworms r found in soil)
Mnemonic: ASpoonful of soil. Lumb sounds like lung so it infects the lungs
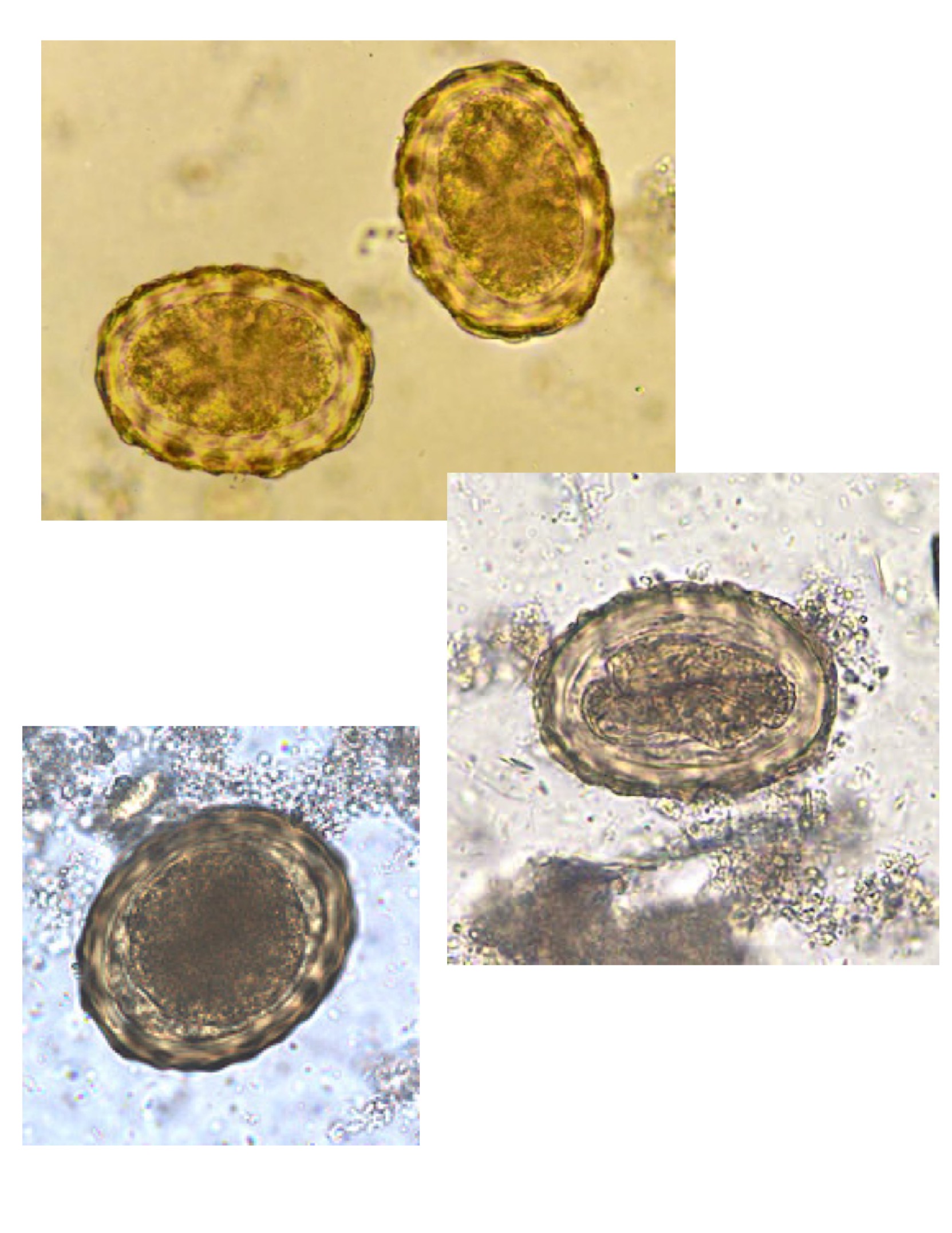
Ascaris lumbricoides egg
Mnemonic: ASC = A SCalloped edge
Enterobius vermicularis
Definitive and intermediate host?
How does the infection happen in humans?
How do we diagnosis the infection?
Is there any identifying characteristics for the egg, larvae or adult of each organism?
Name the diseases caused by the above organisms.
Symptoms
Definitive host:
Humans
intermediate host?
None
How does the infection happen in humans?
Ingestion of eggs (from self-contamination or contaminated clothing, bedding, fingers, etc.)
How do we diagnosis the infection?
Presence of eggs collected from the perianal region using cellophane tape
Is there any identifying characteristics for the egg, larvae or adult of each organism?
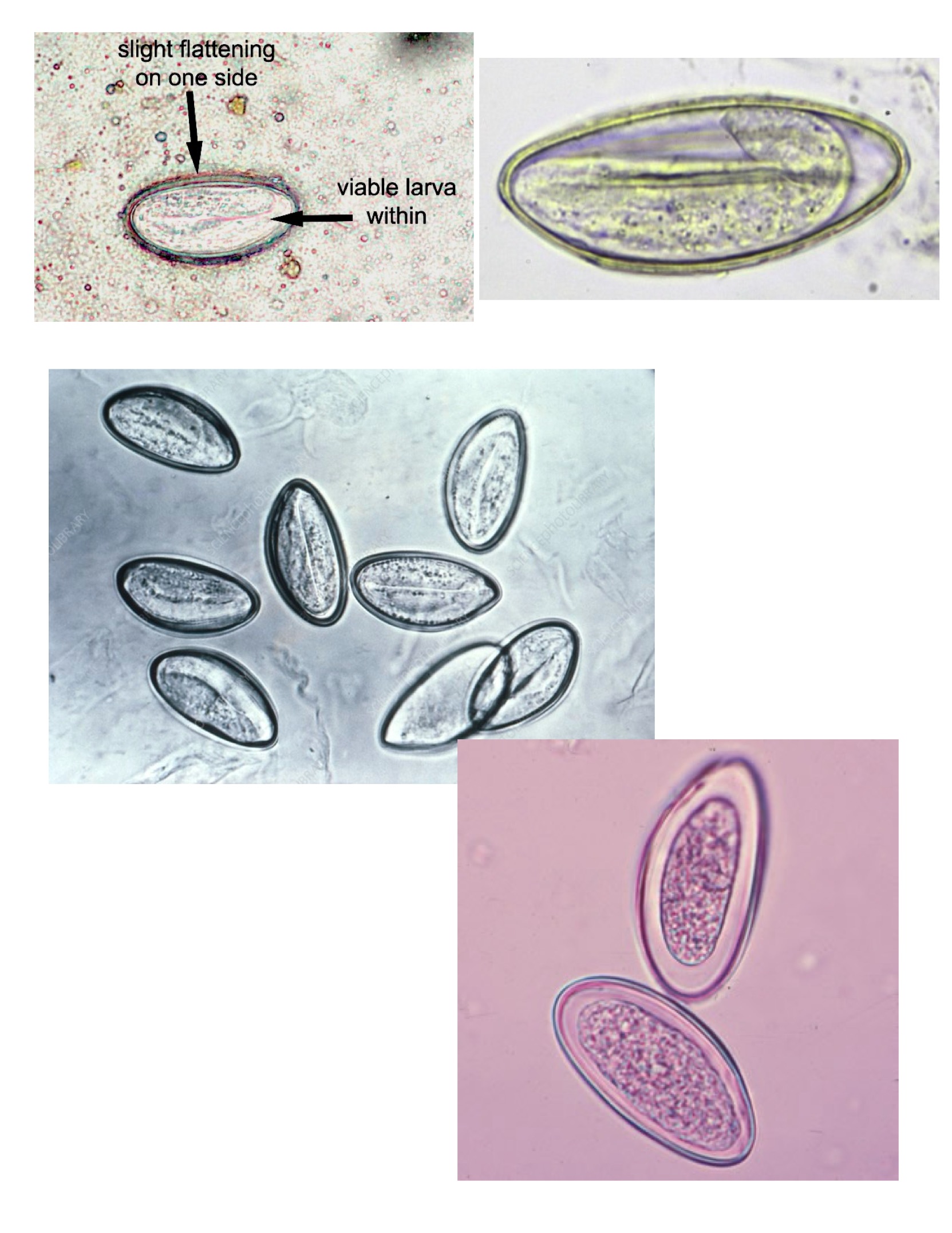
Egg: oval shaped with one flattened side and one rounded side.
Adult female: straight, pointed tail (that’s why they’re called pinworm)
Name the diseases caused by the above organisms.
Enterobiasis (pinworm infection)
Symptoms
Itchy rectum (Worm lays eggs on perianal region)
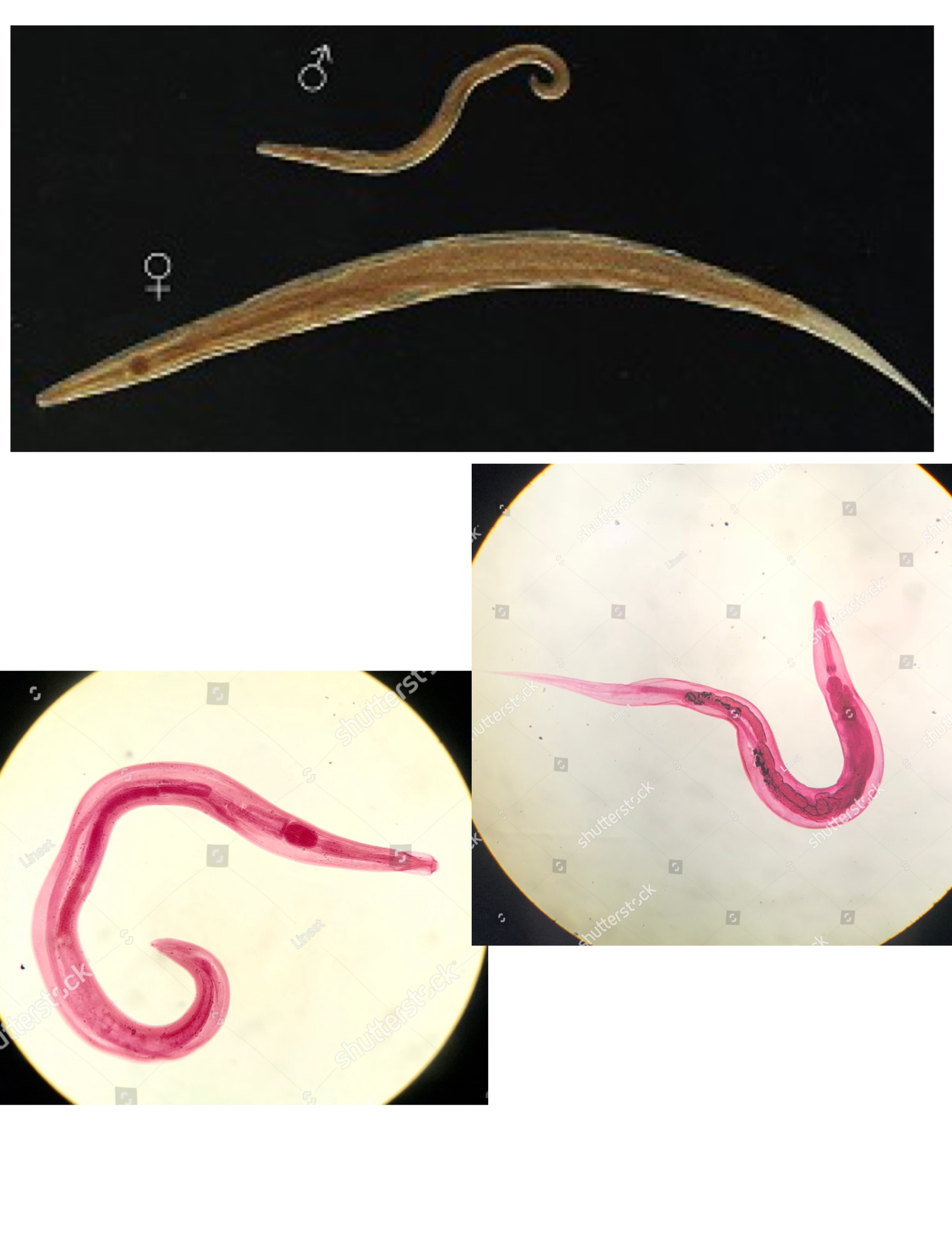
Enterobius vermicularis adult
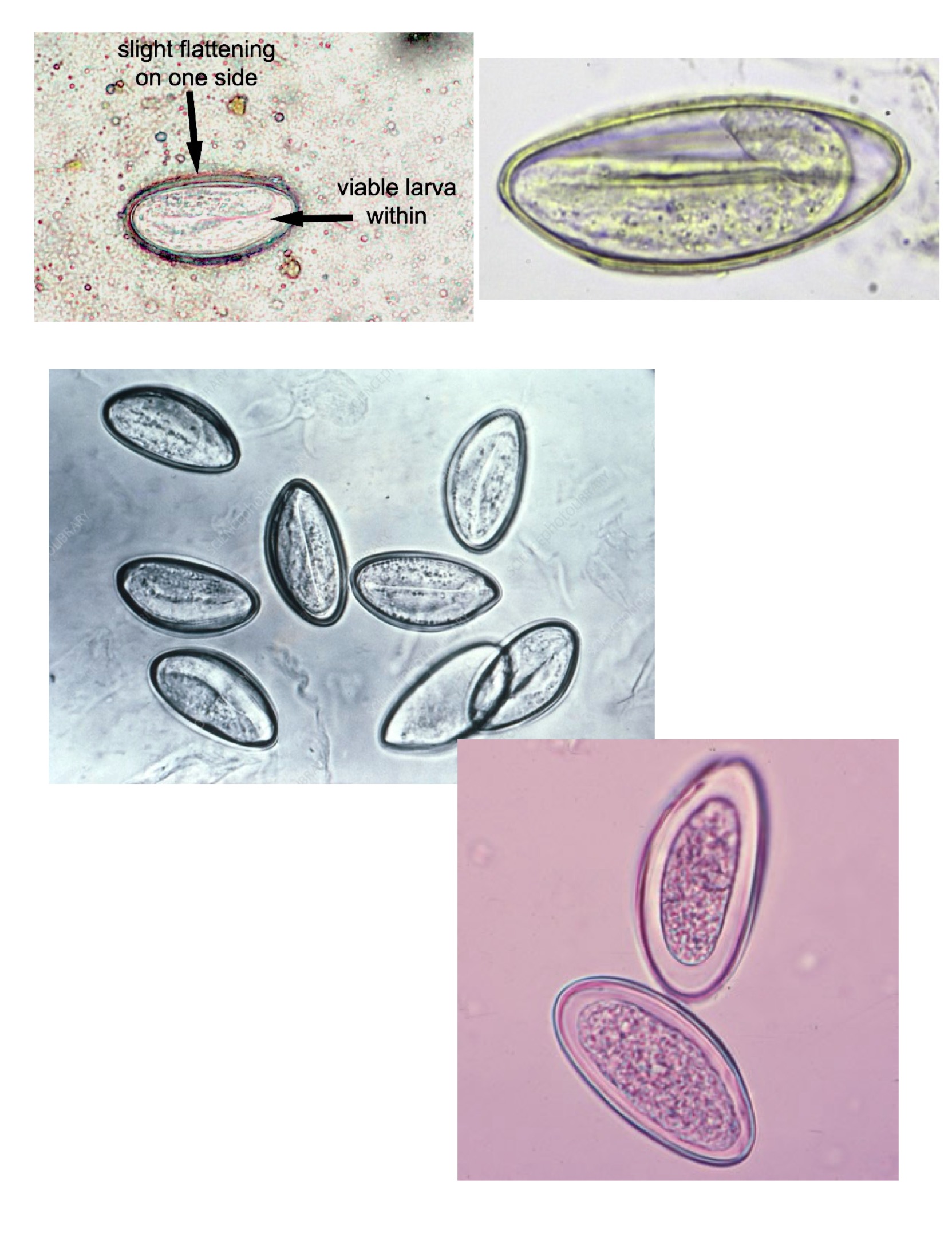
Enterobius vermicularis eggs
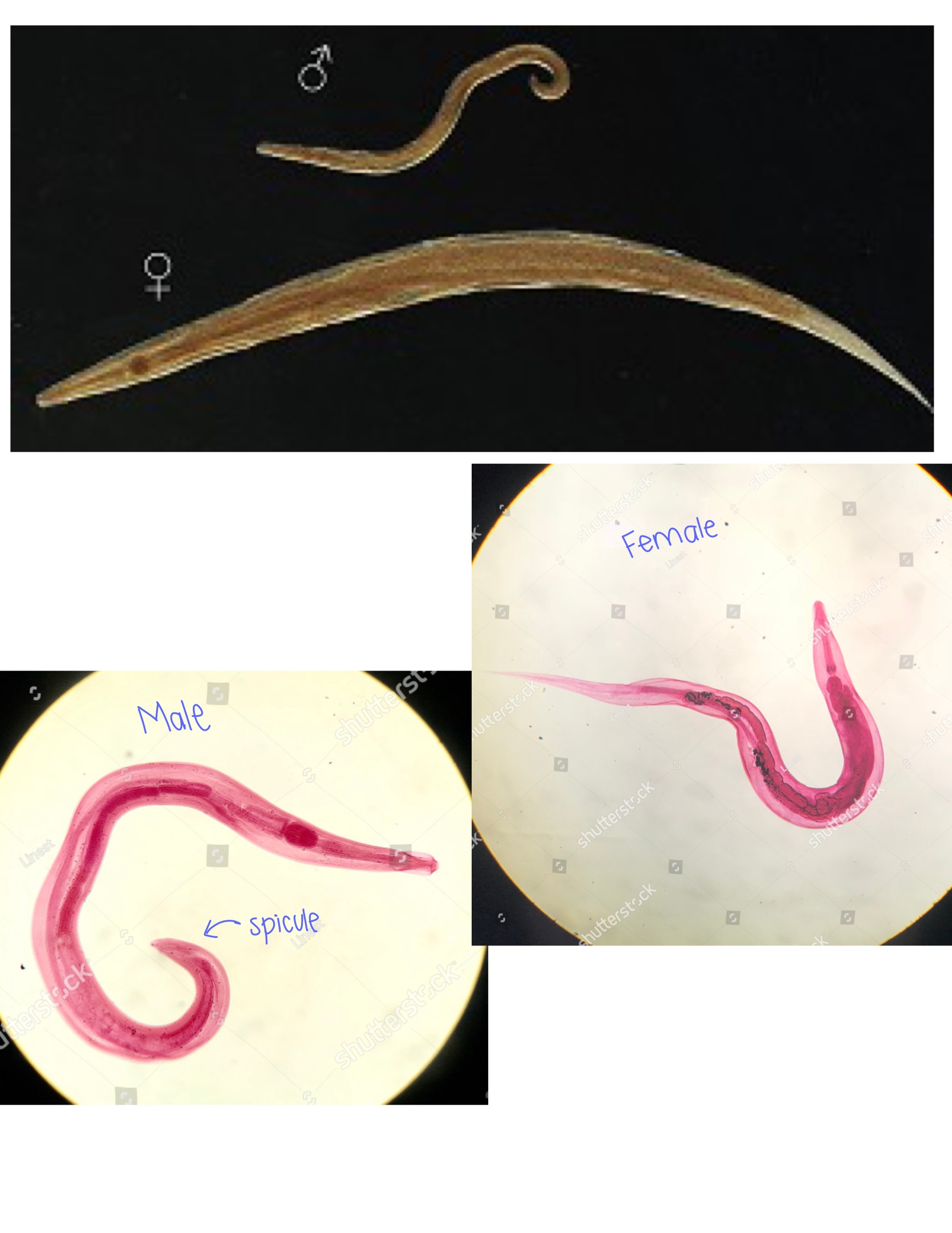
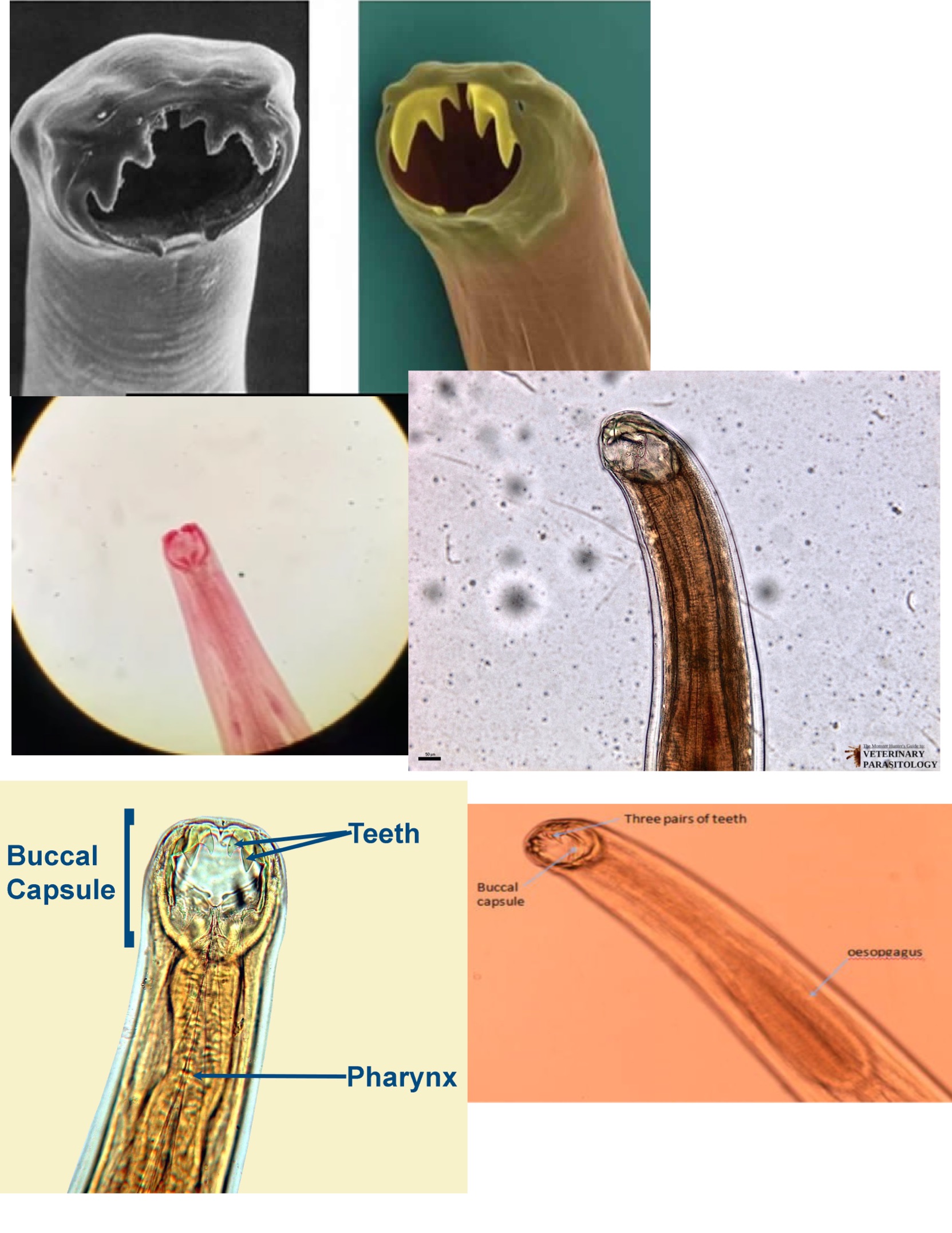
Ancylostoma duodenale (Necator americanus)
Definitive and intermediate host?
How does the infection happen in humans?
How do we diagnosis the infection?
Is there any identifying characteristics for the egg, larvae or adult of each organism?
Name the diseases caused by the above organisms.
Symptoms
Definitive host?
Humans
intermediate host?
None
How does the infection happen in humans?
Humans become infected by walking barefoot on contaminated soil, where infectious larvae are present
Larvae penetrate skin, enter circulation, travel to lungs, bronchial tree, throat, intestines (hook onto intestines)
How do we diagnosis the infection?
Presence of eggs in the stool sample
Is there any identifying characteristics for the egg, larvae or adult of each organism?
Adult: small hooks
Name the diseases caused by the above organisms.
Hookworm disease
Symptoms
Iron-deficiency Anemia
Fatigue
Anorexia
Mnemonic: duo = do not walk barefoot
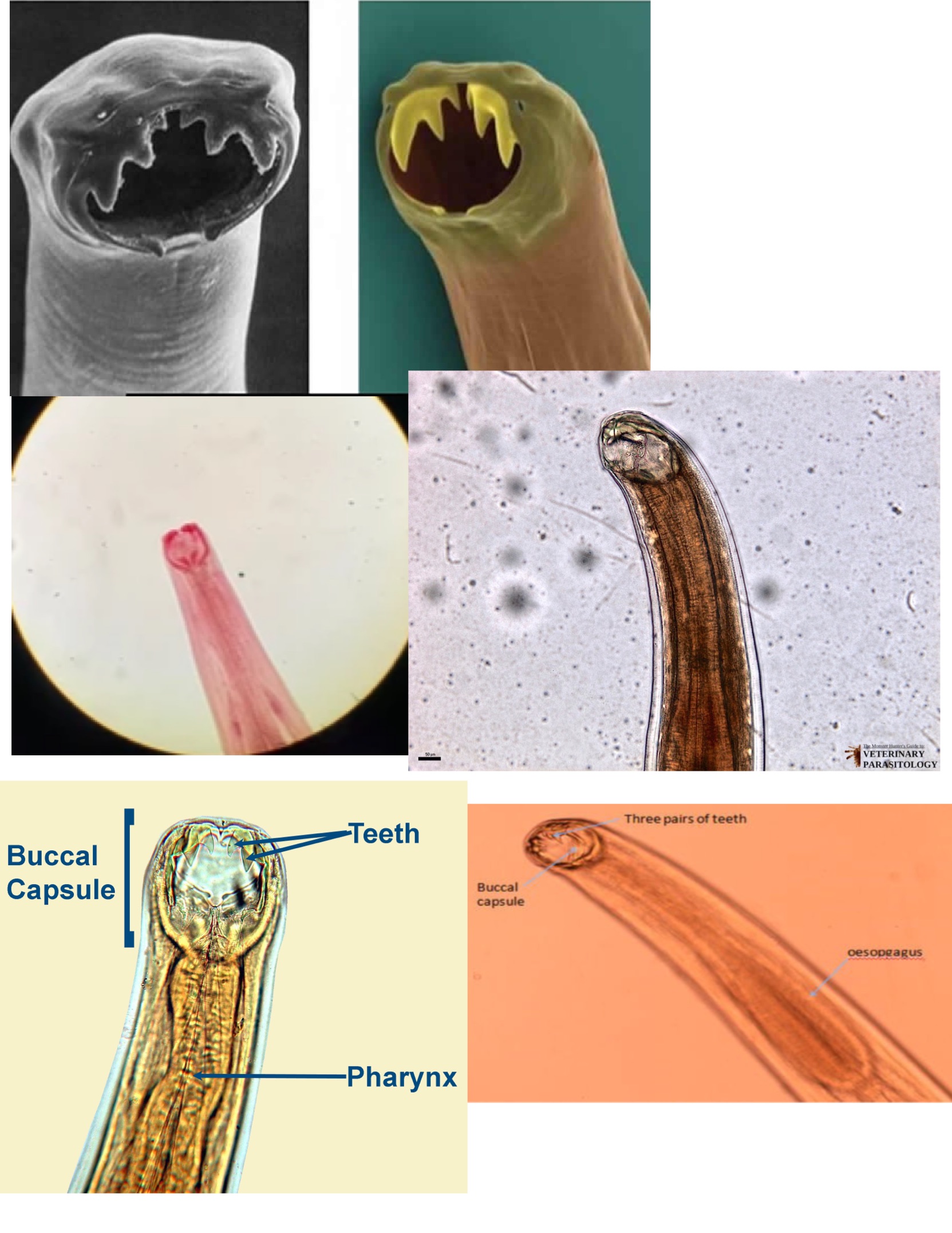
Ancylostoma duodenale
No scolex
Small hooks that look like fangs
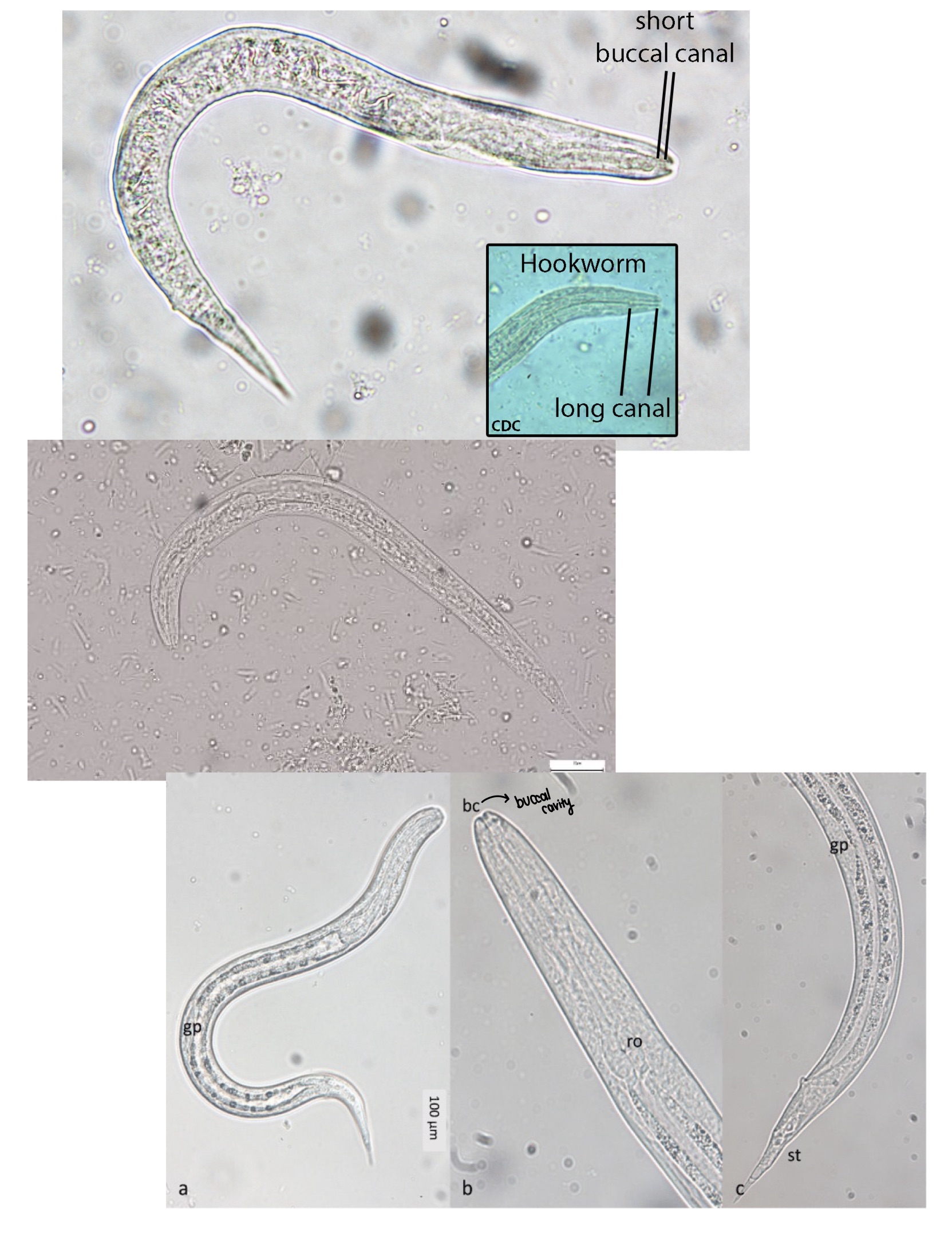
Strongyloides stercoralis
Definitive and intermediate host?
How does the infection happen in humans?
How do we diagnosis the infection?
Is there any identifying characteristics for the egg, larvae or adult of each organism?
Name the diseases caused by the above organisms.
Symptoms
Definitive host?
Humans
intermediate host?
None
How does the infection happen in humans?
Also walking barefoot in contaminated soil
Infective filariform larvae penetrate skin —> blood—> lungs —> swallowed —> intestines
Worms mature into adults in intestines and prod eggs that hatch to make rhabditiform larvae
The larvae are either
passed through feces or
can cause auto infection (stay in body and become filariform larvae - infectious)
How do we diagnosis the infection?
Presence of rhabditiform larvae in the stool, duodenal fluid, or biopsy specimens.
Not eggs bc eggs hatch in intestines —> rhabditiform
Is there any identifying characteristics for the egg, larvae or adult of each organism?
Rhabditiform larvae
Name the diseases caused by the above organisms.
Strongylodiasis
Symptoms
Itchy rash at site of entry (often feet)
Lung- shortness of breath, cough
Intestines - abdominal pain
Mnemonic : RALIS Strong
RhAbditiform Larvae IS Strong
STE= STEp in soil
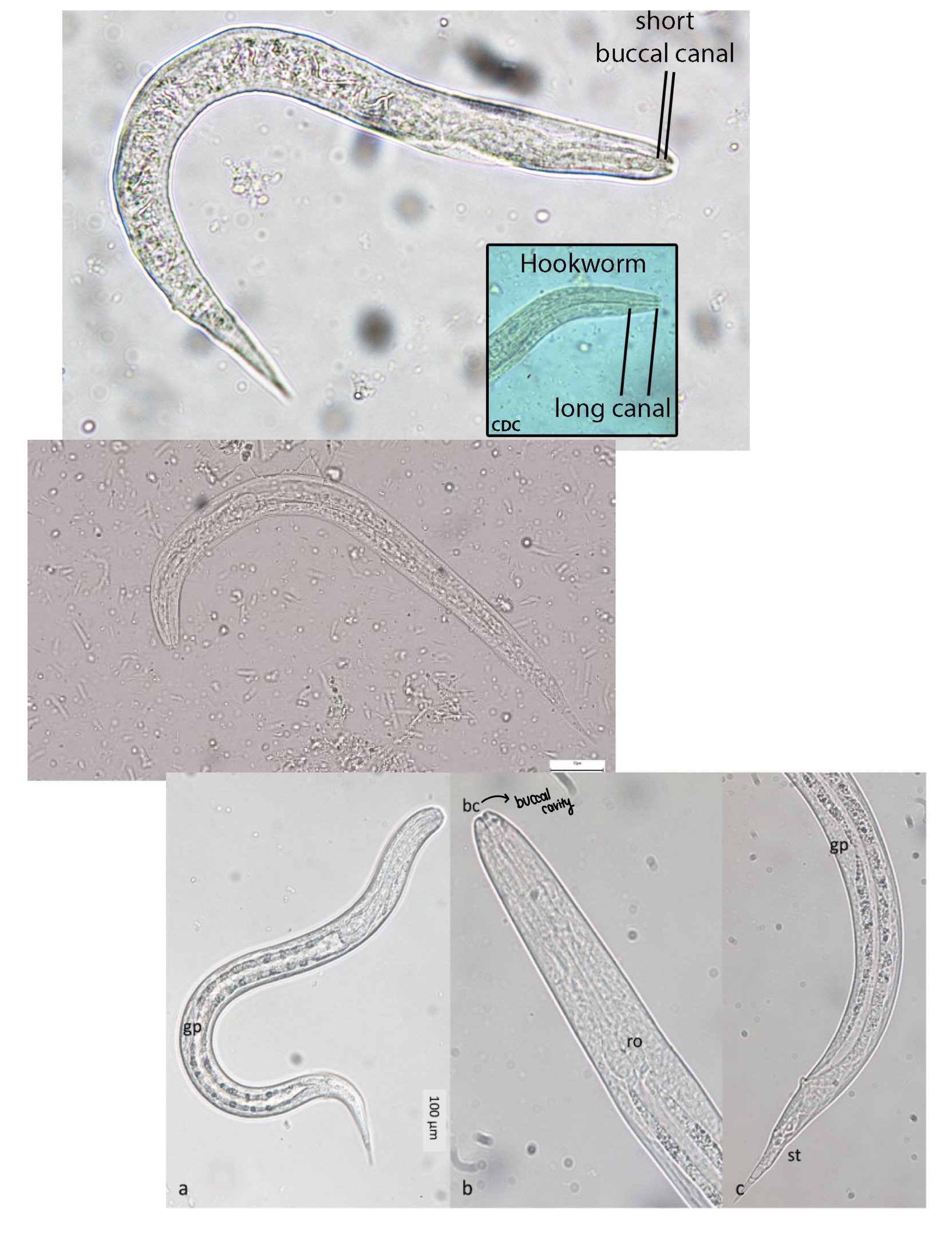
Strongyloides stercoralis rhabditiform larvae
Wuchereria bancrofti
Definitive and intermediate host?
How does the infection happen in humans?
How do we diagnosis the infection?
Is there any identifying characteristics for the egg, larvae or adult of each organism?
Name the diseases caused by the above organisms.
Symptoms
Definitive host
Humans
intermediate host?
Mosquitoes
How does the infection happen in humans?
Mosquito bites an infected human and ingests microfilariae.
Inside the mosquito, microfilariae develop into infective larvae.
Infective larvae enter a new human host via mosquito bite.
Larvae migrate to lymphatic vessels, mature into adult worms, and reproduce, releasing microfilariae into the bloodstream to continue the cycle.
Adults cause blockage of lymph vessels, leading to lymphatic filariasis (elephantiasis).
Summary: getting bit by a mosquito infected with larval stage of parasitic worm
How do we diagnosis the infection?
Blood tests to detect microfilariae in peripheral blood — best collected at night when microfilariae circulate.
Clinical symptoms (swelling, elephantiasis).
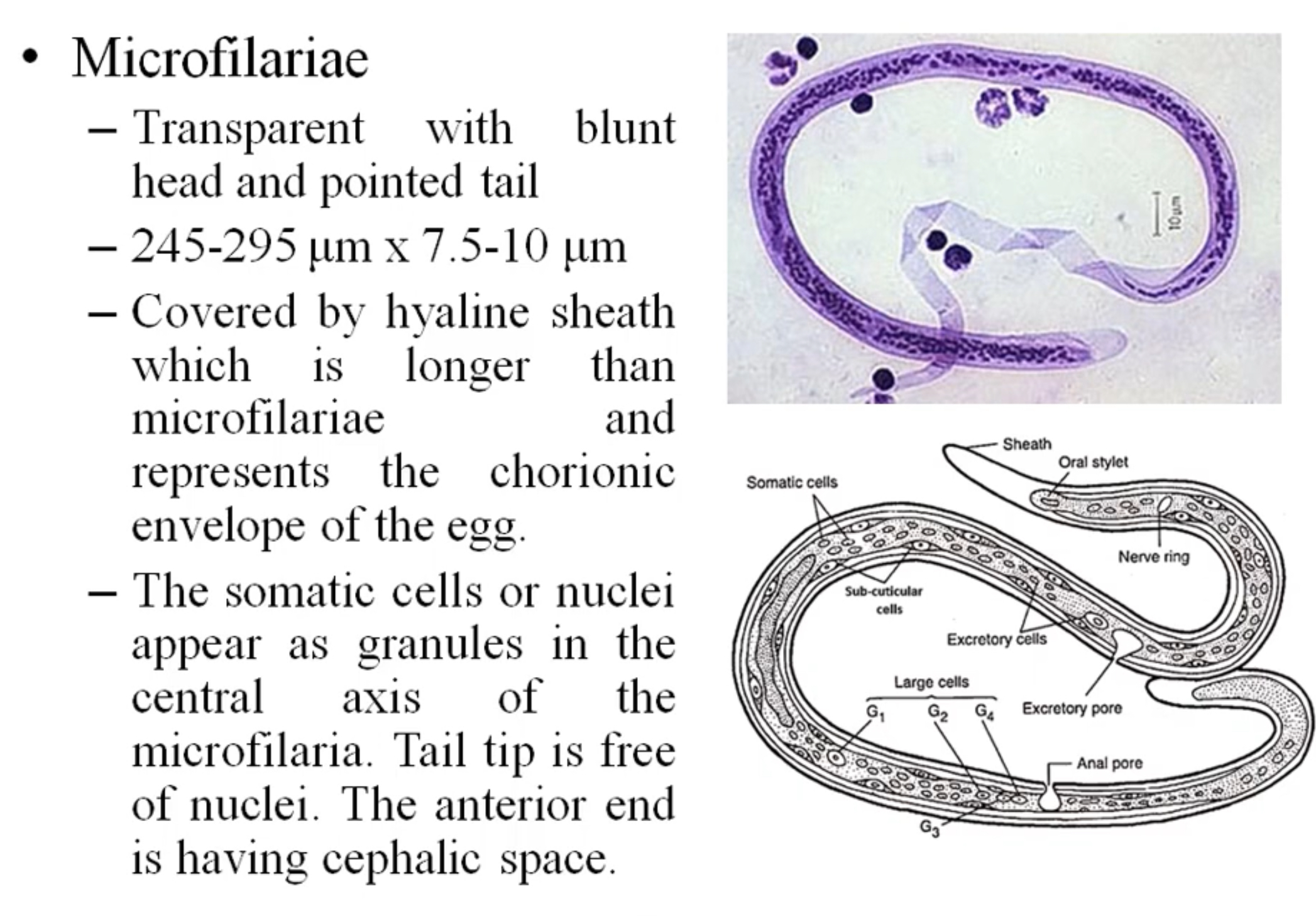
Is there any identifying characteristics for the egg, larvae or adult of each organism?
Microfilariae
Name the diseases caused by the above organisms.
Lymphatic filariasis- causes blockages of lymph vessels, leading to elephantiasis
Symptoms
Elephantiasis (swelling of limbs, genitalia)
Lymph node swelling
Mnemonic: we WUSCH mosquitos away
RIA= microfilaRIAe
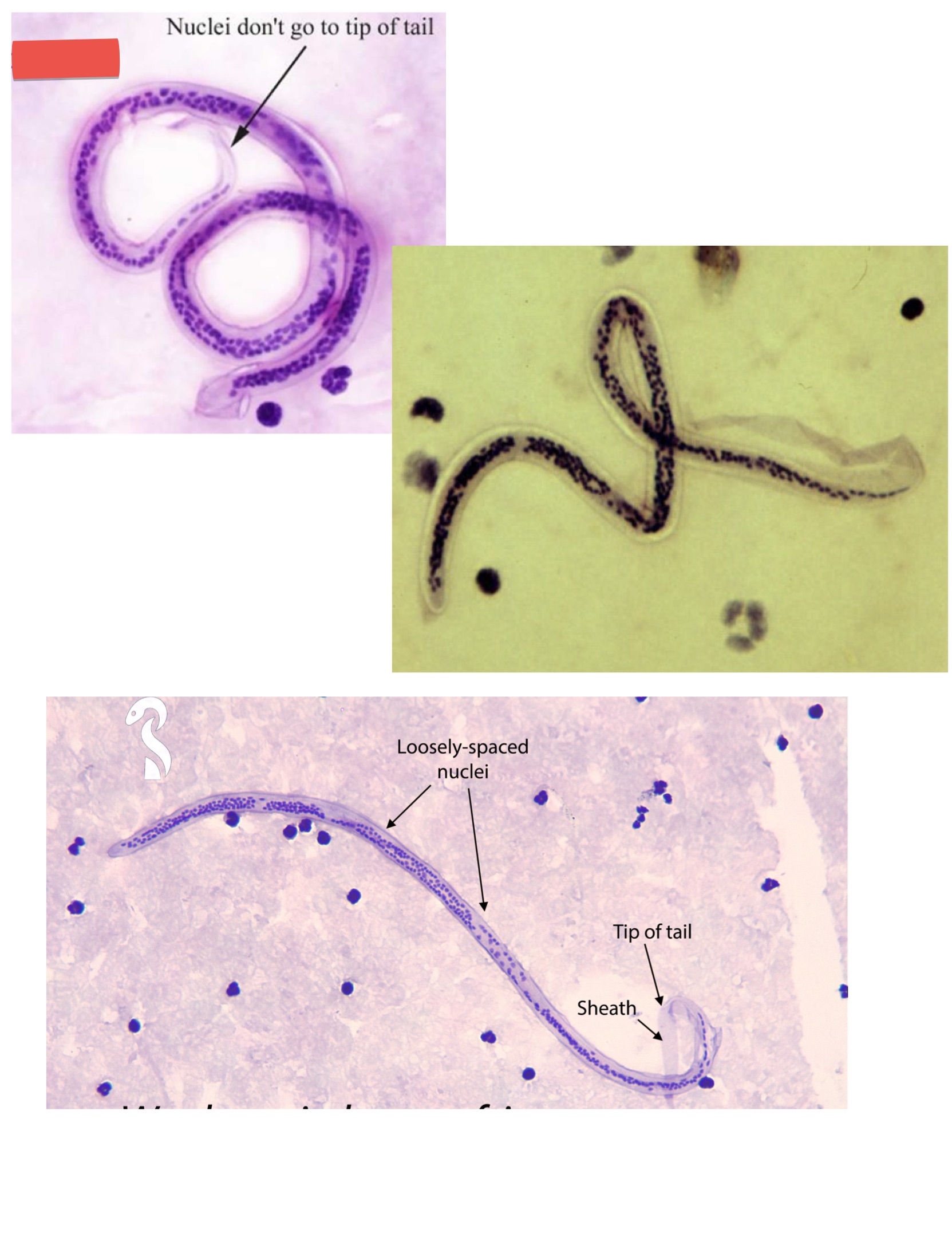
Wuchereria bancrofti microfilaria