Semester 1 review
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/115
Last updated 5:54 PM on 12/11/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
1
New cards
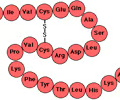
Polypeptide
amino acid chain
2
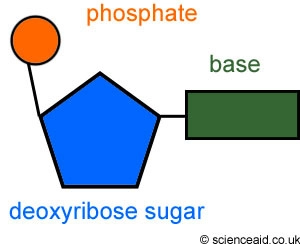
New cards
nucleotide
The definition is the picture->->->->->->->->
3
New cards
Cell Division
Drugs that are used to treat diseases like cancer usually target what cellular process?
4
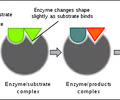
New cards
Enzyme
protein that speeds up chemical reactions
5
New cards
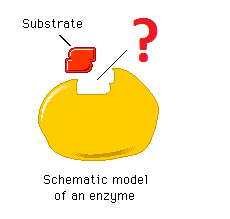
Active Site
enzymes are specific so only the correct substrate will fit into the enzyme's ___________ site
6
New cards
substrate
molecule that the enzyme works on to build-up or break-down into the resulting product.
7
New cards
Factors that effect how enzymes work
temperature, pH, concentration
8
New cards
catalyst
lowers activation energy for chemical reactions to proceed. Enzymes act as catalyst in biological reactions.
9
New cards
Photosynthetic Equation
6H20 + 6CO2 --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
10
New cards
Chloroplast
organelle found in cells of plants and some other organisms that captures the energy from sunlight and converts it into chemical energy
11
New cards
Reactants of Photosynthesis
6H20 + 6CO2
12
New cards
Products of Photosynthesis
C6H12O6 + 6O2
13
New cards
Photosynthetic Pigments
Chemicals like chlorophyll (in chloroplasts) that absorb light energy and use it to carry out photosynthesis.
14
New cards
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
Chemical energy source created in cellular respiration that cells use for most of their work.
15
New cards
Autotrophic
An organism capable of synthesizing its own food from inorganic substances, using light or chemical energy. Green plants, algae, and certain bacteria are autotrophs.
16
New cards
Chloroplasts
Organelle that absorbs sunlight and uses it to drive the synthesis of organic compounds from carbon dioxide and water.
17
New cards
Photosynthesis
The process that converts light energy into chemical energy that is stored in glucose or other organic compounds; occurs in plants, algae, and certain prokaryotes.
18
New cards
Chlorophyll
Green pigment located in membranes within the chloroplasts of plants and algae and in the membranes of certain prokaryotes.
19
New cards
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
What is the balanced equation for photosynthesis?
20
New cards
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
What provides the carbon atoms that are incorporated into sugar molecules in photosynthesis?
21
New cards
Cancer
What disease is characterized by repeated cell divisions caused by disruptions to the cell cycle
22
New cards
Tumor
Uncontrolled cell division
23
New cards
What might cause a disruption to the cell cycle?
Mutations to a gene that controls the cell cycle
24
New cards
Checkpoints (in G1, G2, and M phase)
What happens throughout the cell cycle that helps the cell to PREVENT disruptions to the cell cycle?
25
New cards
tumor
What do we call the abnormal growth of tissue caused by a disruption to the cell cycle?
26
New cards
malignant cancer
rapidly dividing tumor cells which metastasize
27
New cards
transcription
the process whereby the DNA sequence in a gene is copied into mRNA
28
New cards
translation
the process whereby genetic information coded in mRNA directs the formation of a specific protein at a ribosome
29
New cards
mRNA
messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome
30
New cards
tRNA
transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome
31
New cards
rRNA
ribosomal RNA; is a component in the structure of a ribosome
32
New cards
codon
a specific sequence of three adjacent bases on a strand of mRNA that provides genetic code information for a particular amino acid
33
New cards
anticodon
group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon
34
New cards
complementary base pairing
Hydrogen bonding between particular bases.
35
New cards
In DNA, T pairs with A; G pairs with C;
36
New cards
RNA, U pairs with A and G pairs with C
37
New cards
RNA polymerase
An enzyme that links together the growing chain of RNA nucleotides during transcription using a DNA strand as a template.
38
New cards
cytoplasm
the organelles and jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
39
New cards
ribosome
organelles at which proteins are synthesized.
40
New cards
nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA in eukaryotic cells
41
New cards
thymine ... cytosine
In a DNA double helix an adenine of one strand always pairs with a(n) _____ of the complementary strand, and a guanine of one strand always pairs with a(n) _____ of the complementary strand.
42
New cards
After DNA replication is completed, strands produced are "semi-conservative"
each new DNA double helix consists of one old DNA strand and one new DNA strand
43
New cards
anti-parallel
one strand of the DNA double helix runs 3' to 5', the complementary strand runs 5' to 3'
44
New cards
sister chromatids
After replication is complete, the new DNAs, called _________, are identical to each other and joined together at the centromere
45
New cards
passive transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell
46
New cards
diffusion
movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
47
New cards
concentration gradient
the difference in the concentration of molecules across a distance.
48
New cards
equilibrium
the concentration of molecules will be the same throughout the space the molecules occupy.
49
New cards
osmosis
the process by which water molecules diffuse across a cell membrane.
50
New cards
cytolysis
the bursting of a cell
51
New cards
facilitated diffusion
the transport of substances through a cell membrane along a concentration gradient with the aid of carrier proteins.
52
New cards
carrier protein
a protein that transports substances across a cell membrane.
53
New cards
active transport
the movement of chemical substances, usually across the cell membrane, against a concentration gradient; requires cells to use energy.
54
New cards
endocytosis
the process by which a cell membrane surrounds a particle and encloses the particle in a vesicle to bring the particle into the cell.
55
New cards
exocytosis
the process by which a substance is released from the cell through a vesicle that transports the substance to the cell surface and then fuses with the membrane to let the substance out.
56
New cards
selectively permeable
some materials can pass through while others can not
57
New cards
diffusion
molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
58
New cards
osmosis
diffusion of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane
59
New cards
passive transport
the movement of materials across a cell membrane without using energy
60
New cards
active transport
the cell must use energy to transport materials across the cell membrane
61
New cards
solute
a substance ex. (sugar or salt) that is dissolved in another substance
62
New cards
solvent
usually a liquid that dissolves another substance ex. water
63
New cards
Gene mutation
Mutations in the sequencing of the DNA. Affects one gene and typically one protein.
64
New cards
Chromosomal mutation
Mutations in part or the whole chromosome. Affects many genes and many proteins.
65
New cards
Point mutation
The change in ONE nitrogen base in the DNA sequencing. Ex: A changes to C
66
New cards
Substitution
Same as point mutation. One base changed to another.
67
New cards
Frame Shift Mutation
An INSERTION or DELETION gene mutation. (Changes the "reading frame" base sequencing by shifting the codon grouping of 3.)
68
New cards
Base deletion
Mutation where one nitrogen base of the DNA is lost and shifts the reading frame. Many amino acids are incorrect.
69
New cards
Base insertion
Mutation where one nitrogen base of the DNA is added and shifts the reading frame. Many amino acids are incorrect.
70
New cards
chromosome deletion mutation
Mutation where a segment of the chromosome (containing one or more genes) is lost. Affects many proteins and genes.
71
New cards
Base Insertion Mutation
Mutation where one or more nucleotides is added to the genetic sequence, often drastically altering the proteins made.
72
New cards
Base Deletion Mutation
frame-shift mutation where a nucleotide is deleted from the genetic material
73
New cards
Substitution Mutation
74
New cards
substitution (point mutation)
What type of gene mutation is show in this image?
75
New cards
insertion (framshift mutation)
What type of gene mutation is show in this image?
76
New cards
deletion (frameshift mutation)
What type of gene mutation is show in this image?
77
New cards
substitution (point mutation)
What type of gene mutation is show in this image?
78
New cards
point mutation (substitution)
What type of gene mutation is show in this image?
79
New cards
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid
80
New cards
double helix
2 complimentary strands of DNA joined by hydrogen bonds in a twist
81
New cards
A, T, C, G
four nitrogenous bases of DNA
82
New cards
thymine
Adenine (A) pairs with ____
83
New cards
cytosine
Guanine (G) pairs with _____
84
New cards
DNA replication
synthesis of DNA strands which are identical to each other and to the original DNA molecule
85
New cards
DNA polymerase
enzyme that bonds the complementary nucleotides to an open DNA strand. Can also proofread and fix errors in incorrect base pairing.
86
New cards
nucleus
place where DNA storage & replication occurs
87
New cards
RNA
ribonucleic acid
88
New cards
uracil
base that replaces Thymine (T) in RNA
89
New cards
protein
nutrient that carries out MOST of the functions of the cell
90
New cards
e.g. enzymes, hormones, antibodies, cell membrane proteins, haemoglobin, muscle, clotting, collagen ...
91
New cards
nucleotide
one unit of a sugar + phosphate + base
92
New cards
chromatin
long strands of DNA
93
New cards
(when cell NOT replicating)
94
New cards
gene expression
DNA codes for proteins which create the expressed traits of the organism
95
New cards
histone
protein that DNA coils aroound
96
New cards
triplet/codon
3 bases on DNA that code for an amino acid
97
New cards
(or base triplet)
98
New cards
amino acid
subunit that makes up a protein
99
New cards
(20 amino acids - 10 nonessential
100
New cards
i.e. made by human body)