1.1 airway remodelling + development + triggers
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
airway remodelling is the result of chronic biochemical pro inflammatory processes in the air ways
that results in a chronic thickening of the airway walls and restriction of airflow, which will progressively become harder to treat

Changes occur in airways following:
chronic and repeat exposure to triggers display increased blood flow due to novel vascularisation (angiogenesis),
an altered epithelial barrier presenting with a greater chance of shedding
and increased mucus producing cells (goblet cell hyperplasia)
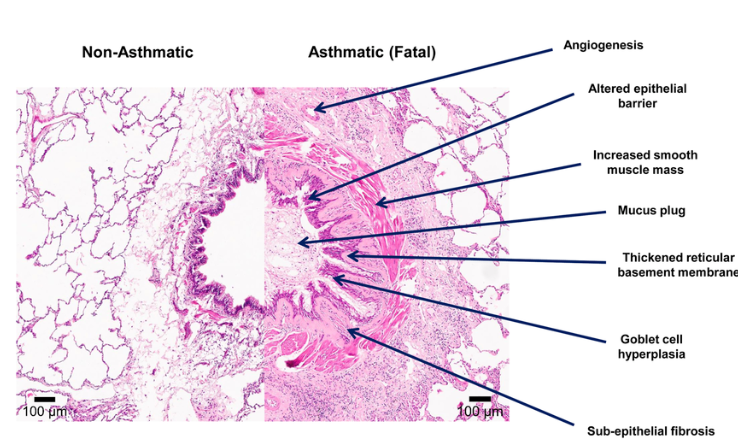
Frequent inflammatory episodes also thicken the basement membrane
narrowing the airway and reduce airway flexibility through fibrosis.
Airway remodelling occurs when bronchial epithelial cells transition into mesenchymal
increasing the smooth muscle content
Epithelial cells lose their cell adhesion
and functional polarity with tight junctions.
Additionally, eosinophils can further exacerbate airway remodelling
due to their release of TGF-B and cytokines by interactions with mast cells.
These mechanisms of airway remodelling may worsen inflammation
and aggravate asthma over time if not treated and managed correctly.
Asthma is a multi factorial disease which involves both a genetic and environmental component.
Both components inform each other
This complex inter-relationship translates into the many sub-types of asthma we observe in clinic
Briefly, some known causes for asthma include
Briefly, some known causes for asthma include
genetics
living environment
exposure
events in early life
physical factors
Genetics -
Family history of atopic disease, i.e. asthma, allergic rhinitis (hayfever), allergic dermatitis (eczema).
Your living environment
, such as urbanisation,
diet,
work stress etc,
the hygiene hypothesis .
Exposure to air-borne environmental irritants
, e.g. house dust mites,
mould,
pollen,
and ingested allergens, e.g. aspirin.
Events in early life
, e.g. low birth weight,
exposure to smoke,
prematurity,
viral infections
Physical factors
- those who are overweight or obese are at greater risk of asthma.
asthma triggers
viral
environment
pharmacuteics/cosmetics
indorr pollutants
animal
Viral -
Rhinovirus,
Respiratory Syncytial Virus
, Adenovirus.
asthmatics appear to be less vulnerable to COVID-19 infections.
Environment -
Changes in the weather (cold air),
humidity
Pharmaceutics/Cosmetics -
Aspirin,
Perfume,
Body sprays/deodorants
Indoor pollutants -
Cigarette/Cigar smoke,
Vaping,
Wood smoke,
House Dust Mite,
Cleaning materials
Animals -
animal fur/dander,
feathers